

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 169-184.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023381
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
顾明明( ), 姜幸慧, 马志毅, 邱水玲, 刘浩宇, 张洺瑞, 卢佳宁, 丘宇俊, 王本治, 甘乾福(
), 姜幸慧, 马志毅, 邱水玲, 刘浩宇, 张洺瑞, 卢佳宁, 丘宇俊, 王本治, 甘乾福( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-11
修回日期:2023-11-27
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-06-20
通讯作者:
甘乾福
作者简介:E-mail: ganning707@163.com基金资助:
Ming-ming GU( ), Xing-hui JIANG, Zhi-yi MA, Shui-ling QIU, Hao-yu LIU, Ming-rui ZHANG, Jia-ning LU, Yu-jun QIU, Ben-zhi WANG, Qian-fu GAN(
), Xing-hui JIANG, Zhi-yi MA, Shui-ling QIU, Hao-yu LIU, Ming-rui ZHANG, Jia-ning LU, Yu-jun QIU, Ben-zhi WANG, Qian-fu GAN( )
)
Received:2023-10-11
Revised:2023-11-27
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-06-20
Contact:
Qian-fu GAN
摘要:
本试验旨在研究甘薯和芋头在闽东山羊瘤胃中的降解特性及表面附着微生物群落动态变化。选用4头14月龄健康装有永久瘤胃瘘管的闽东公山羊[平均体重(26.60±2.35) kg],采用尼龙袋法分别在2、4、8、16、24、36和48 h测定甘薯和芋头的营养成分的动态降解率及降解过程中表面附着微生物变化。结果表明:1)甘薯和芋头的瘤胃降解率随滞留时间的延长均逐渐升高。干物质(DM)有效降解率分别为66.48%和62.88%,粗蛋白(CP)有效降解率分别为34.28%和32.62%,淀粉有效降解率分别为53.44%和43.60%,其中甘薯淀粉有效降解率显著高于芋头(P<0.05)。2)alpha及beta多样性结果表明,甘薯和芋头在不同滞留时间点对瘤胃细菌的丰富度、多样性和组成无显著影响(P>0.05)。门水平上,两组间优势菌均为拟杆菌门和厚壁菌门。属水平上,两组间优势菌属均为普雷沃氏菌属。Mantel检验进一步表明,假丁酸弧菌属与甘薯和芋头瘤胃降解率均呈显著正相关(r>0,P<0.05)。3)功能预测分析表明,甘薯和芋头通过磷酸戊糖途径、乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢以及丙酸代谢调控瘤胃微生物相互作用利用淀粉的功能。综上所述,甘薯和芋头具有较好的瘤胃降解性能,其中甘薯DM和淀粉降解率更佳。在降解过程中,两种饲料均不会破坏瘤胃微生物的动态平衡,因此甘薯和芋头是具有潜力的精饲料资源。
顾明明, 姜幸慧, 马志毅, 邱水玲, 刘浩宇, 张洺瑞, 卢佳宁, 丘宇俊, 王本治, 甘乾福. 甘薯和芋头在闽东山羊瘤胃中的降解特性及表面附着微生物群落变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 169-184.
Ming-ming GU, Xing-hui JIANG, Zhi-yi MA, Shui-ling QIU, Hao-yu LIU, Ming-rui ZHANG, Jia-ning LU, Yu-jun QIU, Ben-zhi WANG, Qian-fu GAN. Degradation characteristics of sweet potato and taro in the rumen of Mindong goats and changes in microbial community attached to the surface[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 169-184.
| 项目Items | 含量Content (%) | 营养水平Nutrient levels2) | 含量Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 羊草Leymus chinensis | 55.00 | 干物质Dry matter (DM, %) | 88.69 |
| 玉米Corn | 31.00 | 代谢能Metabolic energy (ME, MJ·kg-1) | 11.67 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 12.20 | 粗蛋白质Crude protein (CP, %) | 10.94 |
| 食盐Salt | 0.50 | 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, %) | 48.66 |
| 石粉Limestone | 0.10 | 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 24.83 |
| 碳酸氢钙Ca(HCO3)2 | 0.20 | 粗脂肪Ether extract (EE, %) | 2.36 |
| 预混料Premix1) | 1.00 | 钙Calcium (Ca, %) | 0.62 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 磷Phosphorus (P, %) | 0.35 |
表1 饲粮组成及营养成分(干物质基础)
Table 1 Dietary composition and nutrient composition (dry matter basis)
| 项目Items | 含量Content (%) | 营养水平Nutrient levels2) | 含量Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 羊草Leymus chinensis | 55.00 | 干物质Dry matter (DM, %) | 88.69 |
| 玉米Corn | 31.00 | 代谢能Metabolic energy (ME, MJ·kg-1) | 11.67 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 12.20 | 粗蛋白质Crude protein (CP, %) | 10.94 |
| 食盐Salt | 0.50 | 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, %) | 48.66 |
| 石粉Limestone | 0.10 | 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 24.83 |
| 碳酸氢钙Ca(HCO3)2 | 0.20 | 粗脂肪Ether extract (EE, %) | 2.36 |
| 预混料Premix1) | 1.00 | 钙Calcium (Ca, %) | 0.62 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 磷Phosphorus (P, %) | 0.35 |
组别 Groups | 干物质 Dry matter | 粗蛋白 Crude protein | 淀粉 Starch |
|---|---|---|---|
| 甘薯SP | 92.28±0.21a | 12.41±0.44a | 40.58±0.17b |
| 芋头TR | 94.39±0.39a | 10.09±0.21a | 62.47±0.22a |
表2 甘薯和芋头的营养成分
Table 2 Nutrient content of sweet potato and taro (DM,%)
组别 Groups | 干物质 Dry matter | 粗蛋白 Crude protein | 淀粉 Starch |
|---|---|---|---|
| 甘薯SP | 92.28±0.21a | 12.41±0.44a | 40.58±0.17b |
| 芋头TR | 94.39±0.39a | 10.09±0.21a | 62.47±0.22a |
项目 Items | 干物质瘤胃降解率 Rumen degradation rate of dry matter (%) | 粗蛋白瘤胃降解率 Rumen degradation rate of crude protein (%) | 淀粉瘤胃降解率 Rumen degradation rate of strach (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘薯SP | 芋头TR | 甘薯SP | 芋头TR | 甘薯SP | 芋头TR | |
| 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||||
| 2 | 37.66±2.83Ae | 33.97±3.84Ae | 13.36±4.48Ae | 10.56±0.98Ae | 24.05±2.63Ae | 16.22±1.38Be |
| 4 | 54.79±2.28Ad | 46.52±6.45Ad | 23.84±3.45Ad | 25.91±3.19Ad | 38.91±4.10Ad | 24.83±3.33Bd |
| 8 | 59.35±1.02Ad | 54.87±6.67Ac | 31.42±1.75Ac | 28.09±2.39Acd | 51.84±3.39Ac | 39.39±2.05Bc |
| 12 | 69.16±0.63Ac | 68.77±2.11Ab | 35.82±2.53Ac | 31.89±1.84Ac | 55.22±3.20Ac | 42.40±1.30Bc |
| 24 | 84.54±7.46Ab | 82.45±2.69Aa | 45.52±1.48Ab | 44.44±0.96Ab | 70.27±1.81Ab | 58.10±1.14Bb |
| 36 | 88.79±1.06Aab | 84.87±1.60Ba | 49.07±1.00Aab | 47.55±0.87Aab | 73.47±1.43Aab | 69.85±1.32Ba |
| 48 | 91.43±1.08Aa | 88.31±1.32Ba | 52.22±1.63Aa | 50.43±1.10Aa | 77.41±1.89Aa | 72.56±2.77Ba |
| 时间Time | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| 样品Sample | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
时间×样品 Time×sample | 0.69 | 0.35 | <0.05 | |||
| 瘤胃降解参数Rumen degradation parameters | ||||||
| a (%) | 31.72±2.78A | 23.90±2.99B | 8.21±1.96A | 8.54±2.68A | 15.34±2.64A | 10.50±1.70B |
| b (%) | 60.39±2.61B | 64.54±2.81A | 43.19±1.84A | 42.09±2.55A | 60.58±2.49B | 65.64±1.87A |
| c (%·h-1) | 0.08±0.01A | 0.09±0.01A | 0.09±0.01A | 0.08±0.02A | 0.10±0.01A | 0.06±0.01A |
| ED (%) | 66.48±4.28A | 62.88±6.41A | 34.28±4.22A | 32.62±6.75A | 53.44±5.62A | 43.60±5.39B |
表3 甘薯和芋头瘤胃降解特性
Table 3 Rumen degradation properties of sweet potato and taro
项目 Items | 干物质瘤胃降解率 Rumen degradation rate of dry matter (%) | 粗蛋白瘤胃降解率 Rumen degradation rate of crude protein (%) | 淀粉瘤胃降解率 Rumen degradation rate of strach (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘薯SP | 芋头TR | 甘薯SP | 芋头TR | 甘薯SP | 芋头TR | |
| 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||||
| 2 | 37.66±2.83Ae | 33.97±3.84Ae | 13.36±4.48Ae | 10.56±0.98Ae | 24.05±2.63Ae | 16.22±1.38Be |
| 4 | 54.79±2.28Ad | 46.52±6.45Ad | 23.84±3.45Ad | 25.91±3.19Ad | 38.91±4.10Ad | 24.83±3.33Bd |
| 8 | 59.35±1.02Ad | 54.87±6.67Ac | 31.42±1.75Ac | 28.09±2.39Acd | 51.84±3.39Ac | 39.39±2.05Bc |
| 12 | 69.16±0.63Ac | 68.77±2.11Ab | 35.82±2.53Ac | 31.89±1.84Ac | 55.22±3.20Ac | 42.40±1.30Bc |
| 24 | 84.54±7.46Ab | 82.45±2.69Aa | 45.52±1.48Ab | 44.44±0.96Ab | 70.27±1.81Ab | 58.10±1.14Bb |
| 36 | 88.79±1.06Aab | 84.87±1.60Ba | 49.07±1.00Aab | 47.55±0.87Aab | 73.47±1.43Aab | 69.85±1.32Ba |
| 48 | 91.43±1.08Aa | 88.31±1.32Ba | 52.22±1.63Aa | 50.43±1.10Aa | 77.41±1.89Aa | 72.56±2.77Ba |
| 时间Time | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| 样品Sample | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
时间×样品 Time×sample | 0.69 | 0.35 | <0.05 | |||
| 瘤胃降解参数Rumen degradation parameters | ||||||
| a (%) | 31.72±2.78A | 23.90±2.99B | 8.21±1.96A | 8.54±2.68A | 15.34±2.64A | 10.50±1.70B |
| b (%) | 60.39±2.61B | 64.54±2.81A | 43.19±1.84A | 42.09±2.55A | 60.58±2.49B | 65.64±1.87A |
| c (%·h-1) | 0.08±0.01A | 0.09±0.01A | 0.09±0.01A | 0.08±0.02A | 0.10±0.01A | 0.06±0.01A |
| ED (%) | 66.48±4.28A | 62.88±6.41A | 34.28±4.22A | 32.62±6.75A | 53.44±5.62A | 43.60±5.39B |
指数 Index | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
| Chao1指数Chao1 index | 甘薯SP | 356.94±8.69 | 335.38±69.87 | 369.21±65.11 | 372.93±47.01 | 397.67±61.40 |
| 芋头TR | 347.52±140.01 | 336.43±77.29 | 391.02±64.27 | 418.41±53.97 | 393.52±80.38 | |
| ACE指数ACE index | 甘薯SP | 351.87±8.02 | 335.86±68.88 | 369.74±65.84 | 370.46±46.49 | 395.04±62.42 |
| 芋头TR | 345.70±69.38 | 333.29±39.05 | 390.62±33.39 | 421.65±21.66 | 390.22±26.45 | |
| Shannon指数Shannon index | 甘薯SP | 5.67±0.32 | 5.71±0.32 | 5.70±0.62 | 5.38±0.81 | 5.30±1.04 |
| 芋头TR | 5.77±0.43 | 5.60±0.37 | 6.05±0.32 | 6.30±0.17 | 5.34±0.17 | |
| Simpson指数Simpson index | 甘薯SP | 0.94±0.02 | 0.94±0.01 | 0.92±0.03 | 0.89±0.09 | 0.87±0.11 |
| 芋头TR | 0.94±0.02 | 0.94±0.02 | 0.95±0.01 | 0.96±0.01 | 0.87±0.05 | |
表4 甘薯和芋头表面附着瘤胃菌群alpha多样性指数的动态变化
Table 4 Dynamic change of alpha diversity index of rumen bacteria attached to the surface of sweet potato and taro
指数 Index | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
| Chao1指数Chao1 index | 甘薯SP | 356.94±8.69 | 335.38±69.87 | 369.21±65.11 | 372.93±47.01 | 397.67±61.40 |
| 芋头TR | 347.52±140.01 | 336.43±77.29 | 391.02±64.27 | 418.41±53.97 | 393.52±80.38 | |
| ACE指数ACE index | 甘薯SP | 351.87±8.02 | 335.86±68.88 | 369.74±65.84 | 370.46±46.49 | 395.04±62.42 |
| 芋头TR | 345.70±69.38 | 333.29±39.05 | 390.62±33.39 | 421.65±21.66 | 390.22±26.45 | |
| Shannon指数Shannon index | 甘薯SP | 5.67±0.32 | 5.71±0.32 | 5.70±0.62 | 5.38±0.81 | 5.30±1.04 |
| 芋头TR | 5.77±0.43 | 5.60±0.37 | 6.05±0.32 | 6.30±0.17 | 5.34±0.17 | |
| Simpson指数Simpson index | 甘薯SP | 0.94±0.02 | 0.94±0.01 | 0.92±0.03 | 0.89±0.09 | 0.87±0.11 |
| 芋头TR | 0.94±0.02 | 0.94±0.02 | 0.95±0.01 | 0.96±0.01 | 0.87±0.05 | |
项目 Items | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
拟杆菌门 Bacteroidota | 甘薯SP | 52.44±12.75ab | 53.62±6.33ab | 43.94±7.61b | 51.48±11.76ab | 62.63±13.12a |
| 芋头TR | 55.07±16.13 | 57.60±15.25 | 59.46±13.68 | 46.76±8.43 | 59.01±11.03 | |
变形菌门 Proteobacteria | 甘薯SP | 27.76±13.40 | 26.39±13.07 | 24.61±15.85 | 23.14±10.57 | 11.88±3.12 |
| 芋头TR | 27.45±24.17 | 27.22±21.22 | 21.31±18.30 | 26.25±12.19 | 12.74±8.67 | |
厚壁菌门 Firmicutes | 甘薯SP | 15.32±3.68 | 17.37±7.20 | 28.09±11.16 | 20.98±7.76 | 20.78±9.30 |
| 芋头TR | 16.20±8.03 | 13.07±6.37 | 14.62±4.87 | 23.09±4.72 | 22.70±5.77 | |
螺旋体门 Spirochaetes | 甘薯SP | 1.31±0.80 | 1.22±0.59 | 2.28±2.18 | 2.56±1.12 | 2.07±0.63 |
| 芋头TR | 0.35±0.17 | 0.81±0.67 | 2.07±1.24 | 2.56±1.21 | 3.76±2.08 | |
纤维杆菌门 Fibrobacterota | 甘薯SP | 2.89±2.76a | 1.15±1.05ab | 0.62±0.28ab | 1.02±0.76ab | 0.39±0.27b |
| 芋头TR | 0.61±0.06 | 0.91±0.45 | 0.89±0.49 | 0.39±0.20 | 0.74±0.56 | |
放线菌门 Actinobacteria | 甘薯SP | 0.90±0.51b | 0.11±0.08b | 0.28±0.16b | 0.60±0.33b | 2.09±1.95a |
| 芋头TR | 0.08±0.07b | 0.13±0.10b | 0.17±0.14b | 0.66±0.41a | 0.92±0.57a | |
脱硫杆菌门 Desulfobacterota | 甘薯SP | 0.11±0.01 | 0.10±0.05 | 0.14±0.12 | 0.13±0.11 | 0.13±0.02 |
| 芋头TR | 0.15±0.02 | 0.17±0.11 | 0.16±0.08 | 0.18±0.05 | 0.10±0.01 | |
迷踪菌门 Elusimicrobia | 甘薯SP | 0.42±0.03 | 0.00±0.01 | 0.03±0.01 | 0.04±0.03 | 0.01±0.00 |
| 芋头TR | 0.05±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.02±0.00 | |
其他菌门 Others | 甘薯SP | 0.02±0.01 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.03±0.01 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 芋头TR | 0.00±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.02±0.01 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | |
疣微菌门 Verrucomicrobiota | 甘薯SP | 0.01±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 芋头TR | 0.02±0.00 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.03±0.02 | 0.00±0.00 | |
表5 甘薯和芋头表面附着主要菌门相对丰度的动态变化
Table 5 Dynamic changes of relative abundance of main bacteria phyla attached to the surface of sweet potato and taro (%)
项目 Items | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
拟杆菌门 Bacteroidota | 甘薯SP | 52.44±12.75ab | 53.62±6.33ab | 43.94±7.61b | 51.48±11.76ab | 62.63±13.12a |
| 芋头TR | 55.07±16.13 | 57.60±15.25 | 59.46±13.68 | 46.76±8.43 | 59.01±11.03 | |
变形菌门 Proteobacteria | 甘薯SP | 27.76±13.40 | 26.39±13.07 | 24.61±15.85 | 23.14±10.57 | 11.88±3.12 |
| 芋头TR | 27.45±24.17 | 27.22±21.22 | 21.31±18.30 | 26.25±12.19 | 12.74±8.67 | |
厚壁菌门 Firmicutes | 甘薯SP | 15.32±3.68 | 17.37±7.20 | 28.09±11.16 | 20.98±7.76 | 20.78±9.30 |
| 芋头TR | 16.20±8.03 | 13.07±6.37 | 14.62±4.87 | 23.09±4.72 | 22.70±5.77 | |
螺旋体门 Spirochaetes | 甘薯SP | 1.31±0.80 | 1.22±0.59 | 2.28±2.18 | 2.56±1.12 | 2.07±0.63 |
| 芋头TR | 0.35±0.17 | 0.81±0.67 | 2.07±1.24 | 2.56±1.21 | 3.76±2.08 | |
纤维杆菌门 Fibrobacterota | 甘薯SP | 2.89±2.76a | 1.15±1.05ab | 0.62±0.28ab | 1.02±0.76ab | 0.39±0.27b |
| 芋头TR | 0.61±0.06 | 0.91±0.45 | 0.89±0.49 | 0.39±0.20 | 0.74±0.56 | |
放线菌门 Actinobacteria | 甘薯SP | 0.90±0.51b | 0.11±0.08b | 0.28±0.16b | 0.60±0.33b | 2.09±1.95a |
| 芋头TR | 0.08±0.07b | 0.13±0.10b | 0.17±0.14b | 0.66±0.41a | 0.92±0.57a | |
脱硫杆菌门 Desulfobacterota | 甘薯SP | 0.11±0.01 | 0.10±0.05 | 0.14±0.12 | 0.13±0.11 | 0.13±0.02 |
| 芋头TR | 0.15±0.02 | 0.17±0.11 | 0.16±0.08 | 0.18±0.05 | 0.10±0.01 | |
迷踪菌门 Elusimicrobia | 甘薯SP | 0.42±0.03 | 0.00±0.01 | 0.03±0.01 | 0.04±0.03 | 0.01±0.00 |
| 芋头TR | 0.05±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.02±0.00 | |
其他菌门 Others | 甘薯SP | 0.02±0.01 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.03±0.01 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 芋头TR | 0.00±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.02±0.01 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | |
疣微菌门 Verrucomicrobiota | 甘薯SP | 0.01±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 芋头TR | 0.02±0.00 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.03±0.02 | 0.00±0.00 | |
项目 Items | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
| 普雷沃氏菌属Prevotella | 甘薯SP | 39.82±10.97 | 41.56±6.61 | 36.48±8.89 | 35.30±10.92 | 50.76±14.63 |
| 芋头TR | 36.52±9.87 | 40.94±9.35 | 41.79±9.08 | 29.89±5.76 | 46.83±17.85 | |
| 琥珀酸弧菌属Succinivibrio | 甘薯SP | 17.46±11.89a | 10.53±6.51ab | 12.48±8.78ab | 6.39±3.51ab | 3.67±2.64b |
| 芋头TR | 16.81±14.03 | 20.21±15.87 | 13.47±13.13 | 14.92±9.45 | 3.92±2.96 | |
| 瘤胃杆菌属Ruminobacter | 甘薯SP | 9.83±7.77 | 13.54±9.52 | 10.92±6.32 | 17.46±7.54 | 9.39±5.39 |
| 芋头TR | 10.34±5.17 | 6.65±4.68 | 7.45±6.92 | 10.82±6.31 | 8.52±7.47 | |
| 月形单胞菌属Selenomonas | 甘薯SP | 5.02±3.92 | 6.27±4.99 | 5.48±4.61 | 1.44±0.74 | 0.33±0.20 |
| 芋头TR | 1.72±0.99 | 0.90±0.48 | 0.62±0.55 | 1.15±0.63 | 0.45±0.05 | |
| 其他Others | 甘薯SP | 3.15±2.32 | 4.26±2.50 | 3.36±2.04 | 4.70±2.55 | 5.18±4.57 |
| 芋头TR | 1.05±0.50c | 0.95±0.38c | 1.90±0.83bc | 5.27±2.53ab | 8.21±5.08a | |
| 瘤胃球菌属Ruminococcus | 甘薯SP | 1.64±1.20 | 2.23±1.77 | 2.82±2.02 | 1.85±0.55 | 1.29±0.51 |
| 芋头TR | 1.90±0.21 | 1.37±1.26 | 2.17±2.06 | 6.59±5.63 | 5.14±3.60 | |
| 理研菌科_RC9肠群Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group | 甘薯SP | 2.27±0.74 | 2.05±0.63 | 2.00±0.72 | 3.07±1.87 | 2.31±2.00 |
| 芋头TR | 5.66±4.41 | 4.57±3.75 | 4.79±3.97 | 3.35±1.80 | 1.97±0.62 | |
| F082 | 甘薯SP | 1.79±1.26 | 1.72±1.57 | 2.20±1.87 | 2.88±2.75 | 1.15±0.47 |
| 芋头TR | 4.19±2.48 | 4.24±3.45 | 3.33±3.22 | 1.98±1.47 | 0.90±0.21 | |
| Muri菌属Muribaculaceae | 甘薯SP | 1.55±0.49 | 1.60±0.65 | 1.51±0.87 | 1.35±0.56 | 1.61±0.68 |
| 芋头TR | 1.65±0.93 | 1.64±0.16 | 2.06±0.76 | 2.69±1.13 | 3.33±2.02 | |
| 密螺旋体属Treponema | 甘薯SP | 1.30±0.80 | 1.22±0.72 | 1.62±0.20 | 2.54±1.11 | 2.51±1.03 |
| 芋头TR | 0.34±0.16 | 0.79±0.66 | 2.06±0.72 | 2.54±1.20 | 3.76±2.49 | |
| 乳杆菌属Lactobacillus | 甘薯SP | 0.36±0.19 | 0.49±0.07 | 8.01±7.49 | 0.67±0.53 | 0.47±0.40 |
| 芋头TR | 0.21±0.01 | 0.22±0.16 | 0.19±0.06 | 0.10±0.01 | 0.21±0.11 | |
| 沙特尔沃思氏菌属Shuttleworthia | 甘薯SP | 0.32±0.05 | 0.50±0.06 | 0.59±0.06 | 5.35±3.95 | 3.18±2.40 |
| 芋头TR | 0.02±0.01b | 0.03±0.01b | 0.11±0.10b | 0.74±0.37a | 0.71±0.57a | |
| 假丁酸弧菌属Pseudobutyrivibrio | 甘薯SP | 0.79±0.59Aa | 0.50±0.20Bab | 0.40±0.25Bab | 0.27±0.11Aab | 0.08±0.05Ab |
| 芋头TR | 1.15±0.27Aa | 1.45±0.56Aa | 1.51±0.42Aa | 0.51±0.30Ab | 0.16±0.09Ab | |
| 丝状杆菌属Fibrobacter | 甘薯SP | 2.89±1.28 | 1.14±1.09 | 0.53±0.30 | 1.01±0.76 | 0.48±0.28 |
| 芋头TR | 0.61±0.06 | 0.91±0.15 | 2.09±1.39 | 0.39±0.20 | 0.74±0.10 | |
| 普氏菌科UCG-003属Prevotellaceae_UCG-003 | 甘薯SP | 0.91±0.44 | 0.92±0.79 | 0.68±0.30 | 1.01±0.59 | 0.38±0.11 |
| 芋头TR | 2.47±1.55 | 1.86±0.47 | 2.04±0.97 | 1.63±0.89 | 1.05±0.77 | |
表6 甘薯和芋头表面附着主要菌属相对丰度的动态变化
Table 6 Dynamic changes of relative abundance of main bacteria genera attached to the surface of sweet potato and taro (%)
项目 Items | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
| 普雷沃氏菌属Prevotella | 甘薯SP | 39.82±10.97 | 41.56±6.61 | 36.48±8.89 | 35.30±10.92 | 50.76±14.63 |
| 芋头TR | 36.52±9.87 | 40.94±9.35 | 41.79±9.08 | 29.89±5.76 | 46.83±17.85 | |
| 琥珀酸弧菌属Succinivibrio | 甘薯SP | 17.46±11.89a | 10.53±6.51ab | 12.48±8.78ab | 6.39±3.51ab | 3.67±2.64b |
| 芋头TR | 16.81±14.03 | 20.21±15.87 | 13.47±13.13 | 14.92±9.45 | 3.92±2.96 | |
| 瘤胃杆菌属Ruminobacter | 甘薯SP | 9.83±7.77 | 13.54±9.52 | 10.92±6.32 | 17.46±7.54 | 9.39±5.39 |
| 芋头TR | 10.34±5.17 | 6.65±4.68 | 7.45±6.92 | 10.82±6.31 | 8.52±7.47 | |
| 月形单胞菌属Selenomonas | 甘薯SP | 5.02±3.92 | 6.27±4.99 | 5.48±4.61 | 1.44±0.74 | 0.33±0.20 |
| 芋头TR | 1.72±0.99 | 0.90±0.48 | 0.62±0.55 | 1.15±0.63 | 0.45±0.05 | |
| 其他Others | 甘薯SP | 3.15±2.32 | 4.26±2.50 | 3.36±2.04 | 4.70±2.55 | 5.18±4.57 |
| 芋头TR | 1.05±0.50c | 0.95±0.38c | 1.90±0.83bc | 5.27±2.53ab | 8.21±5.08a | |
| 瘤胃球菌属Ruminococcus | 甘薯SP | 1.64±1.20 | 2.23±1.77 | 2.82±2.02 | 1.85±0.55 | 1.29±0.51 |
| 芋头TR | 1.90±0.21 | 1.37±1.26 | 2.17±2.06 | 6.59±5.63 | 5.14±3.60 | |
| 理研菌科_RC9肠群Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group | 甘薯SP | 2.27±0.74 | 2.05±0.63 | 2.00±0.72 | 3.07±1.87 | 2.31±2.00 |
| 芋头TR | 5.66±4.41 | 4.57±3.75 | 4.79±3.97 | 3.35±1.80 | 1.97±0.62 | |
| F082 | 甘薯SP | 1.79±1.26 | 1.72±1.57 | 2.20±1.87 | 2.88±2.75 | 1.15±0.47 |
| 芋头TR | 4.19±2.48 | 4.24±3.45 | 3.33±3.22 | 1.98±1.47 | 0.90±0.21 | |
| Muri菌属Muribaculaceae | 甘薯SP | 1.55±0.49 | 1.60±0.65 | 1.51±0.87 | 1.35±0.56 | 1.61±0.68 |
| 芋头TR | 1.65±0.93 | 1.64±0.16 | 2.06±0.76 | 2.69±1.13 | 3.33±2.02 | |
| 密螺旋体属Treponema | 甘薯SP | 1.30±0.80 | 1.22±0.72 | 1.62±0.20 | 2.54±1.11 | 2.51±1.03 |
| 芋头TR | 0.34±0.16 | 0.79±0.66 | 2.06±0.72 | 2.54±1.20 | 3.76±2.49 | |
| 乳杆菌属Lactobacillus | 甘薯SP | 0.36±0.19 | 0.49±0.07 | 8.01±7.49 | 0.67±0.53 | 0.47±0.40 |
| 芋头TR | 0.21±0.01 | 0.22±0.16 | 0.19±0.06 | 0.10±0.01 | 0.21±0.11 | |
| 沙特尔沃思氏菌属Shuttleworthia | 甘薯SP | 0.32±0.05 | 0.50±0.06 | 0.59±0.06 | 5.35±3.95 | 3.18±2.40 |
| 芋头TR | 0.02±0.01b | 0.03±0.01b | 0.11±0.10b | 0.74±0.37a | 0.71±0.57a | |
| 假丁酸弧菌属Pseudobutyrivibrio | 甘薯SP | 0.79±0.59Aa | 0.50±0.20Bab | 0.40±0.25Bab | 0.27±0.11Aab | 0.08±0.05Ab |
| 芋头TR | 1.15±0.27Aa | 1.45±0.56Aa | 1.51±0.42Aa | 0.51±0.30Ab | 0.16±0.09Ab | |
| 丝状杆菌属Fibrobacter | 甘薯SP | 2.89±1.28 | 1.14±1.09 | 0.53±0.30 | 1.01±0.76 | 0.48±0.28 |
| 芋头TR | 0.61±0.06 | 0.91±0.15 | 2.09±1.39 | 0.39±0.20 | 0.74±0.10 | |
| 普氏菌科UCG-003属Prevotellaceae_UCG-003 | 甘薯SP | 0.91±0.44 | 0.92±0.79 | 0.68±0.30 | 1.01±0.59 | 0.38±0.11 |
| 芋头TR | 2.47±1.55 | 1.86±0.47 | 2.04±0.97 | 1.63±0.89 | 1.05±0.77 | |

图4 甘薯和芋头营养物质降解率与菌属相关性分析1:普雷沃氏菌属Prevotella;2:琥珀酸弧菌属Succinivibrio;3:瘤胃杆菌属Ruminobacter;4:月形单胞菌属Selenomonas;5:其他Others;6:瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus;7:理研菌科_RC9肠群Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group;8:F082;9:Muri菌属Muribaculaceae;10:密螺旋体属Treponema;11:乳杆菌属Lactobacillus;12:沙特尔沃思氏菌属Shuttleworthia;13:假丁酸弧菌属Pseudobutyrivibrio;14:丝状杆菌属Fibrobacter;15:普氏菌科UCG-003属 Prevotellaceae_UCG-003.甘薯SP_DM: 甘薯的干物质Dry matter of sweet potato; 甘薯SP_CP: 甘薯的粗蛋白Crude protein of sweet potato; 甘薯SP_淀粉: 甘薯的淀粉Starch of sweet potato; 芋头SP_DM: 芋头的干物质Dry matter of taro; 芋头SP_CP: 芋头的粗蛋白Crude protein of taro; 芋头SP_淀粉: 芋头的淀粉Starch of taro. 根据Pearson相关系数对单元格进行着色,红色表示正相关,蓝色表示负相关。r表示解释变量和被解释变量之间的线性相关程度;P表示相关性显著水平。Cells were colored based on Pearson correlation coefficient, red color and blue color indicated positive and negative correlation, respectively. r represent the degree of linear correlation between the explanatory variable and the explained variable; P represents a significant level of correlation. 下同The same bleow.
Fig.4 Correlation analysis between nutrient degradation rate of sweet potato and taro and bacteria genus
项目 Items | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
| 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 甘薯SP | 1.31±0.07 | 1.32±0.09 | 1.32±0.13 | 1.27±0.07 | 1.28±0.03 |
| 芋头TR | 1.29±0.05 | 1.31±0.01 | 1.32±0.04 | 1.27±0.04 | 1.26±0.02 | |
| 丙酮酸代谢Pyruvate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.92±0.05 | 0.93±0.08 | 0.96±0.05 | 0.96±0.03 | 0.93±0.03 |
| 芋头TR | 0.95±0.03 | 0.93±0.01 | 0.92±0.03 | 0.96±0.04 | 0.93±0.04 | |
| 淀粉和蔗糖代谢Starch and sucrose metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.98±0.11 | 1.03±0.16 | 1.09±0.27 | 1.02±0.08 | 1.09±0.04 |
| 芋头TR | 0.95±0.08b | 0.95±0.04b | 0.99±0.05b | 1.00±0.03ab | 1.08±0.07a | |
| 磷酸戊糖途径Pentose phosphate pathway | 甘薯SP | 0.68±0.02b | 0.68±0.01b | 0.71±0.03b | 0.70±0.01b | 0.74±0.01a |
| 芋头TR | 0.69±0.01b | 0.69±0.01b | 0.69±0.01b | 0.70±0.01ab | 0.72±0.02a | |
| 乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.74±0.03a | 0.75±0.03a | 0.72±0.03a | 0.72±0.03a | 0.64±0.02b |
| 芋头TR | 0.74±0.04a | 0.74±0.04a | 0.75±0.04a | 0.72±0.02ab | 0.66±0.05b | |
| 果糖和甘露糖代谢Fructose and mannose metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.71±0.09 | 0.73±0.14 | 0.74±0.15 | 0.67±0.08 | 0.74±0.05 |
| 芋头TR | 0.68±0.11 | 0.69±0.08 | 0.72±0.08 | 0.66±0.06 | 0.72±0.06 | |
| 丁酸代谢Butanoate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.59±0.02 | 0.59±0.04 | 0.59±0.03 | 0.57±0.01 | 0.57±0.01 |
| 芋头TR | 0.58±0.02 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.57±0.02 | |
| 半乳糖代谢Galactose metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.71±0.07 | 0.74±0.10 | 0.74±0.11 | 0.72±0.06 | 0.73±0.02 |
| 芋头TR | 0.70±0.06 | 0.72±0.04 | 0.73±0.05 | 0.70±0.03 | 0.74±0.03 | |
| 丙酸代谢Propanoate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.45±0.03ab | 0.46±0.03ab | 0.46±0.04ab | 0.48±0.03a | 0.40±0.06b |
| 芋头TR | 0.48±0.04ab | 0.46±0.03ab | 0.45±0.04ab | 0.49±0.02a | 0.41±0.05b | |
| C5-支链二元酸代谢C5-branched dibasic acid metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.26±0.02 | 0.26±0.01 | 0.24±0.05 | 0.26±0.02 | 0.21±0.03 |
| 芋头TR | 0.26±0.05 | 0.26±0.05 | 0.26±0.04 | 0.28±0.03 | 0.23±0.04 | |
表7 KEGG3级中碳水化合物代谢途径丰度变化
Table 7 Changes in carbohydrate metabolic pathway abundance at KEGG3 level (%)
项目 Items | 组别 Groups | 瘤胃滞留时间Rumen retention time (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 24 | 48 | ||
| 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 甘薯SP | 1.31±0.07 | 1.32±0.09 | 1.32±0.13 | 1.27±0.07 | 1.28±0.03 |
| 芋头TR | 1.29±0.05 | 1.31±0.01 | 1.32±0.04 | 1.27±0.04 | 1.26±0.02 | |
| 丙酮酸代谢Pyruvate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.92±0.05 | 0.93±0.08 | 0.96±0.05 | 0.96±0.03 | 0.93±0.03 |
| 芋头TR | 0.95±0.03 | 0.93±0.01 | 0.92±0.03 | 0.96±0.04 | 0.93±0.04 | |
| 淀粉和蔗糖代谢Starch and sucrose metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.98±0.11 | 1.03±0.16 | 1.09±0.27 | 1.02±0.08 | 1.09±0.04 |
| 芋头TR | 0.95±0.08b | 0.95±0.04b | 0.99±0.05b | 1.00±0.03ab | 1.08±0.07a | |
| 磷酸戊糖途径Pentose phosphate pathway | 甘薯SP | 0.68±0.02b | 0.68±0.01b | 0.71±0.03b | 0.70±0.01b | 0.74±0.01a |
| 芋头TR | 0.69±0.01b | 0.69±0.01b | 0.69±0.01b | 0.70±0.01ab | 0.72±0.02a | |
| 乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.74±0.03a | 0.75±0.03a | 0.72±0.03a | 0.72±0.03a | 0.64±0.02b |
| 芋头TR | 0.74±0.04a | 0.74±0.04a | 0.75±0.04a | 0.72±0.02ab | 0.66±0.05b | |
| 果糖和甘露糖代谢Fructose and mannose metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.71±0.09 | 0.73±0.14 | 0.74±0.15 | 0.67±0.08 | 0.74±0.05 |
| 芋头TR | 0.68±0.11 | 0.69±0.08 | 0.72±0.08 | 0.66±0.06 | 0.72±0.06 | |
| 丁酸代谢Butanoate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.59±0.02 | 0.59±0.04 | 0.59±0.03 | 0.57±0.01 | 0.57±0.01 |
| 芋头TR | 0.58±0.02 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.58±0.02 | 0.57±0.02 | |
| 半乳糖代谢Galactose metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.71±0.07 | 0.74±0.10 | 0.74±0.11 | 0.72±0.06 | 0.73±0.02 |
| 芋头TR | 0.70±0.06 | 0.72±0.04 | 0.73±0.05 | 0.70±0.03 | 0.74±0.03 | |
| 丙酸代谢Propanoate metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.45±0.03ab | 0.46±0.03ab | 0.46±0.04ab | 0.48±0.03a | 0.40±0.06b |
| 芋头TR | 0.48±0.04ab | 0.46±0.03ab | 0.45±0.04ab | 0.49±0.02a | 0.41±0.05b | |
| C5-支链二元酸代谢C5-branched dibasic acid metabolism | 甘薯SP | 0.26±0.02 | 0.26±0.01 | 0.24±0.05 | 0.26±0.02 | 0.21±0.03 |
| 芋头TR | 0.26±0.05 | 0.26±0.05 | 0.26±0.04 | 0.28±0.03 | 0.23±0.04 | |
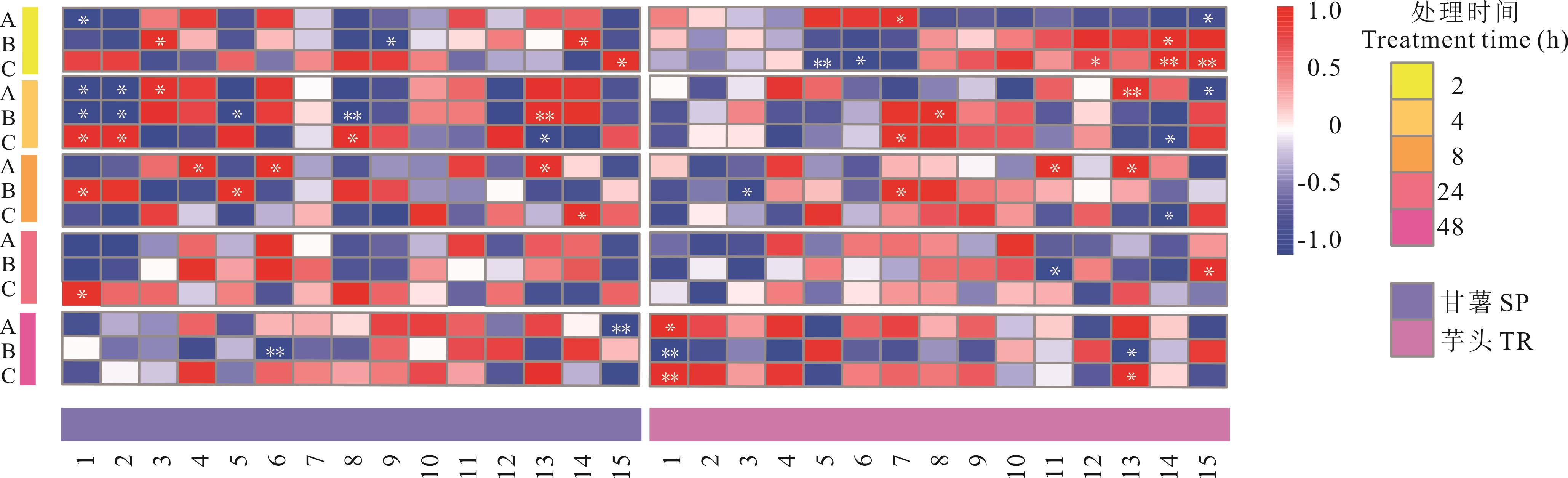
图5 瘤胃微生物菌属与改变的碳水化合物代谢途径之间的相关性分析A:丙酸代谢Propanoate metabolism;B:磷酸戊糖途径Pentose phosphate pathway;C:乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. *表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。* means significant correlation (P<0.05), and ** means extremely significant correlation (P<0.01).
Fig.5 Correlation analysis between rumen microbial genera and altered carbohydrate metabolic pathways
| 1 | Chen Y X, Li X N. Effects of sweet potato replacing corn on growth performance, digestive performance and serum indexes of piglets. China Feed, 2022(10): 117-120. |
| 陈亚新, 李小娜. 用红薯替代玉米对仔猪生长性能、消化性能及血清指标的影响. 中国饲料, 2022(10): 117-120. | |
| 2 | Zhou Z X. The nutritional value and health function of sweet potatoes. Food and Drug, 2006, 8(8): 75-76. |
| 周增学. 红薯的营养价值与保健功能. 食品与药品, 2006, 8(8): 75-76. | |
| 3 | Wei X, Ji J Q, Chen X F, et al. Effect of lysine supplementation level on in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics in high-concentrate diet. Feed Industry, 2023, 44(7): 68-73. |
| 韦肖, 计接权, 陈新锋, 等. 赖氨酸添加水平对高精料日粮体外瘤胃发酵特性的影响. 饲料工业, 2023, 44(7): 68-73. | |
| 4 | Zhou J H, Lu D, Jiang X X, et al. Effect of sweet potato residue fermented by probiotics on growth performance and apparent nutrient digestibility of beef cattle. China Feed, 2021(1): 131-134. |
| 周剑辉, 陆丹, 蒋小霞, 等. 益生菌发酵红薯渣对肉牛生长性能、养分表观消化率的影响. 中国饲料, 2021(1): 131-134. | |
| 5 | Yu J Y, Tian Z G, Xu M J, et al. The plant distribution and feeding situation of taro corm. Contemporary Animal Husbandry, 2018(11): 22-26. |
| 于继英, 田子罡, 徐美娟, 等. 我国芋头资源分布和饲用情况. 当代畜牧, 2018(11): 22-26. | |
| 6 | Sukhija S, Singh S, Rira C S. Isolation of starches from different tubers and study of their physicochemical, thermal, rheological and morphological characteristics. Starch-starke, 2016, 68(1/2): 160-168. |
| 7 | Singla D, Singh A, Dhull S B, et al. Taro starch: Isolation, morphology, modification and novel applications concern-A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 163: 1283-1290. |
| 8 | Ribeiro P P, Bertozzi D A M, Nitzsche T F, et al. Anticancer and immunomodulatory benefits of taro (Colocasia esculenta) corms, an underexploited tuber crop. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(1): 265. |
| 9 | López Y B, Pinos R J, Murillo P, et al. Effects of replacing corn by cocoyam-corm (Colocasia esculenta) on in vitro degradation of diets and grouth performance of finishing pelibuey lambs. Agrociencia, 2018, 52: 97-105. |
| 10 | Liang Y S, Li F D, Li F. Analysis of rumen adaptive mechanism under the condition of higher concentrate diets. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2016, 28(1): 20-26. |
| 梁玉生, 李发弟, 李飞. 高精料饲粮条件下反刍动物瘤胃适应机制的解析. 动物营养学报, 2016, 28(1): 20-26. | |
| 11 | Mcallister T A, Bae H D, Jones G A, et al. Microbial attachment and feed digestion in the rumen. Journal of Animal Science, 1994, 72(11): 3004-3018. |
| 12 | Gupta A K, Singh S, Kundu S, et al. Evaluation of tropical feedstuffs for carbohydrate and protein fractions by CNCP system. Indian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2011, 81(11): 1154. |
| 13 | Wang X L, Zhao H B, Huang D J, et al. Effect of protein and carbohydrate supplements on changes of the detergent fibers and the ruminal metabolites in the rumen of heifers. Feed Industry, 2010(S2): 64-67, 120. |
| 王星凌, 赵红波, 黄德建, 等. 不同蛋白质和碳水化合物饲料来源对牛瘤胃洗涤纤维降解和瘤胃液产物的定量研究. 饲料工业, 2010(S2): 64-67, 120. | |
| 14 | Ling W Q, Zhang L, Li J, et al. Effects of Lentilactobacillus buchneri combined with different sugars on nutrient composition, fermentation quality, rumen degradation rate, and aerobic stability of alfalfa silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 等. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. | |
| 15 | Zhang L Y. Feed analysis and feed quality testing technology. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2007. |
| 张丽英. 饲料分析及饲料质量检测技术. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2007. | |
| 16 | Lu G Q, Shi Z R. Discussion on the determination method and standardization of sweet potato starch. Horticulture & Seed, 1997(6): 39-44. |
| 陆国权, 施志仁. 甘薯淀粉的测定方法及其标准化探讨. 园艺与种苗, 1997(6): 39-44. | |
| 17 | Ørskov E R, Mcdonald I. The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighted according to rate of passage. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1979, 92(2): 499-503. |
| 18 | Li Q, Zhang J X, Ma T, et al. Rumen degradation and small intestine digestion characteristics of different types of concentrate feeds. Feed Industry, 2023, 44(4): 71-79. |
| 李琴, 张建新, 马涛, 等. 不同类型精饲料的瘤胃降解与小肠消化特征. 饲料工业, 2023, 44(4): 71-79. | |
| 19 | Wang C, Zou Y Y, Fan Q P, et al. Effects of adding whole-plant maize silage to the diet on the growth performance and rumen degradation rate of mutton sheep. Animals Breeding and Feed, 2023, 22(6): 13-16. |
| 王诚, 邹颖颖, 范秋苹, 等. 日粮中添加全株玉米青贮对肉羊生长性能及瘤胃降解率的影响. 养殖与饲料, 2023, 22(6): 13-16. | |
| 20 | Fu L X, Ma T, Diao Q Y, et al. Correlation analysis of ruminal degradation characteristics and in vitro small intestinal digestibility of rumen undegraded protein of common concentrates for mutton sheep. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(7): 2641-2651. |
| 富丽霞, 马涛, 刁其玉, 等. 肉用绵羊常用精饲料的瘤胃降解特性与瘤胃非降解蛋白质体外小肠消化率的相关分析. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(7): 2641-2651. | |
| 21 | Diao Q Y. Studies on ruminal degredation and intestinal digestion of feed constituents in beef cattle. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2000. |
| 刁其玉. 饲料营养成分在瘤胃和小肠降解规律的研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2000. | |
| 22 | Li R L, Liu J X. The degradation in the rumen of different cereal feed. Feed Industry, 2006(15): 22-24. |
| 李瑞丽, 刘建新. 不同淀粉源饲料的瘤胃降解特性研究初探. 饲料工业, 2006(15): 22-24. | |
| 23 | Jiang J. Study on kinetics of starch degradability of common used feed for ruminants. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 姜豇. 反刍动物常用精饲料淀粉降解动力学研究. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2005. | |
| 24 | Zhu Y J, Yu Z Y, Yuan C L, et al. Research about ruminal and small intestinal digestibility of Shandong province mainly concentrates for sheep. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(17): 1-6. |
| 朱亚骏, 于子洋, 袁翠林, 等. 山东省羊主要精饲料瘤胃降解率和小肠消化率的研究. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(17): 1-6. | |
| 25 | Li Y, Zhang Y J. Research progress in sheep protein nutrition. China Herbivore Science, 2014(S1): 23-26. |
| 李芸, 张英杰. 羊蛋白质营养研究进展. 中国草食动物科学, 2014(S1): 23-26. | |
| 26 | Yang Y W, Ma J F, Yu Y, et al. Comparison on degradation rule of three kinds of potato vines fodder in rumen of beef cattle. Feed Industry, 2020, 41(11): 11-18. |
| 杨宇为, 马吉锋, 于洋, 等. 三种马铃薯秧饲料在肉牛瘤胃中降解规律的比较. 饲料工业, 2020, 41(11): 11-18. | |
| 27 | Liu J, Diao Q Y, Zhao Y G, et al. Effects of dietary NFC/NDF ratios on rumen pH, NH3-N and VFA of meat sheep. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2012, 24(6): 1069-1077. |
| 刘洁, 刁其玉, 赵一广, 等. 饲粮不同NFC/NDF对肉用绵羊瘤胃pH、氨态氮和挥发性脂肪酸的影响. 动物营养学报, 2012, 24(6): 1069-1077. | |
| 28 | Li J G, Feng Y L. Degradation of feed protein in ruminant rumen and its influencing factors. China Feed, 1998(15): 15-16. |
| 李建国, 冯仰廉. 饲料蛋白质在反刍动物瘤胃的降解及其影响因素. 中国饲料, 1998(15): 15-16. | |
| 29 | Zhang L L, Xu X F, Jin S G. Comparative study on the degradation patterns of soybean meal protein and corn protein powder protein in the rumen of sheep. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2010(7): 97-98. |
| 张力莉, 徐晓锋, 金曙光. 豆粕蛋白质和玉米蛋白粉蛋白质在绵羊瘤胃内降解规律的比较研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2010(7): 97-98. | |
| 30 | Yu Y. Study on determination of the digestibility of amino acid in grain and by-products based on simulating the protein digestion process in roosters. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. |
| 于耀. 基于模拟鸡体内蛋白质消化过程估测谷物及副产物氨基酸消化率的研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. | |
| 31 | Zhang C Y, Yang J H, Gao X, et al. Evaluation of the nutritional value of five commonly used forages in southern China and their degradation characteristics in the rumen of buffalo. China Feed, 2023(17): 15-21. |
| 张村宇, 杨嘉骅, 高鑫, 等. 南方地区五种常用粗饲料营养价值评估及其在水牛瘤胃中的降解特性研究. 中国饲料, 2023(17): 15-21. | |
| 32 | Wang H C, Wang S C, Mu C L, et al. The research progress of starch in ruminants production. Feed Review, 2018(10): 22-25. |
| 王洪超, 王思春, 穆春玲, 等. 淀粉在反刍动物生产中的应用研究进展. 饲料博览, 2018(10): 22-25. | |
| 33 | Dong C X, Dai D W, Xu X F, et al. Research progress on effects of subacute ruminal acidosis on gastrointestinal health of dairy cows. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(8): 4767-4776. |
| 董春晓, 戴东文, 徐晓锋, 等. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒对奶牛胃肠道健康影响的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(8): 4767-4776. | |
| 34 | Behzad K, Parisa K, Qendrim Z, et al. Variations in fecal pH and fecal particle size due to changes in dietary starch: Their potential as an on-farm tool for assessing the risk of ruminal acidosis in dairy cattle. Research in Veterinary Science, 2022, 152: 678-686. |
| 35 | Krieg J, Seifried N, Steingass H, et al. In situ and in vitro ruminal starch degradation of grains from different rye, triticale and barley genotypes. Animal, 2017, 11(10): 1745-1753. |
| 36 | Henderson G, Cox F, Ganesh S, et al. Rumen microbial community composition varies with diet and host, but a core microbiome is found across a wide geographical range. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 14567. |
| 37 | Hu J J, Li Y H, Lu J Z, et al. Effect of jasmine slag supplementation on apparent digestibility of nutrients, ruminal fermentation and rumen flora of goat. Feed Research, 2023, 46(2): 1-6. |
| 胡俊杰, 李叶红, 陆俊致, 等. 日粮中添加茉莉花渣对山羊营养物质表观消化率、瘤胃发酵及瘤胃菌群的影响. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(2): 1-6. | |
| 38 | Cremonesi P, Conte G, Severgnini M, et al. Evaluation of the effects of different diets on microbiome diversity and fatty acid composition of rumen liquor in dairy goat. Animal, 2018, 12(9): 1856-1866. |
| 39 | Canaes T S, Zanferari F, Maganhe B L, et al. Increasing dietary levels of citral oil on nutrient total tract digestibility, ruminal fermentation, and milk composition in Saanen goats. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2017, 229: 47-56. |
| 40 | Zhang D Q. Effect of alfalfa meal on digestion, antioxidation and rumen microbial community in Boer goats. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 张冬强. 苜蓿草粉对波尔山羊消化、抗氧化及瘤胃微生物区系的影响. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016. | |
| 41 | Servin J A, Herbold C W, Skophammer R G, et al. Evidence excluding the root of the tree of life from the Actinobacteria. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2007, 25(1): 1-4. |
| 42 | Zhan J S, Yang Q, Hu Y, et al. Effects of dietary concentration: roughage ratio on rumen fermentation and flora population structure in Hu sheep. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(7): 122-130. |
| 占今舜, 杨群, 胡耀, 等. 日粮精粗比对湖羊瘤胃发酵和菌群结构的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 122-130. | |
| 43 | Wang S X, Dai D W, Yang Y K, et al. Effects of concentrate supplementation on growth performance, rumen fermentation and microbial community structure of grazing yaks in cold season. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(11): 6266-6276. |
| 王书祥, 戴东文, 杨英魁, 等. 补饲精料对冷季放牧牦牛生长性能、瘤胃发酵及菌群结构的影响. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(11): 6266-6276. | |
| 44 | Mohanmmadzadhe H, Yáñezruiz D R, Martínez F G, et al. Molecular comparative assessment of the microbial ecosystem in rumen and faeces of goats fed alfalfa hay alone or combined with oats. Anaerobe, 2014, 29: 52-58. |
| 45 | Liu J, Li W, Li X, et al. Comparative studies on developmental patterns of gastrointestinal microbiota of different breed lambs. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(10): 6475-6496. |
| 刘洁, 李伟, 李鑫, 等. 不同品种羔羊胃肠道微生物发育规律的比较研究. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(10): 6475-6496. | |
| 46 | Yang X Y, Niu Z L, Wu Q, et al. Effects of lamb milk replacer on growth performance, apparent nutrient digestibility, rumen fermentation parameters, microflora structure and health status of Leizhou goats. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(3): 1758-1770. |
| 杨讯业, 牛志力, 吴琼, 等. 羔羊代乳料对雷州山羊生长性能、养分表观消化率、瘤胃发酵参数和菌群结构及健康状况的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(3): 1758-1770. | |
| 47 | Zhang H Q, Wang P S, Li X, et al. Effects of fermented hybrid Broussonetia papyrifera on growth performance, meat quality, digestive enzyme activity and intestinal flora structure of Hu sheep. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50(5): 1876-1887. |
| 张华强, 王品胜, 李晓, 等. 发酵杂交构树对湖羊生长性能、肉品质、消化酶活力及肠道菌群结构的影响. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50(5): 1876-1887. | |
| 48 | Neubauer V, Petri R, Humer E, et al. High-grain diets supplemented with phytogenic compounds or autolyzed yeast modulate ruminal bacterial community and fermentation in dry cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(3): 2335-2349. |
| 49 | Li J C, Lian H X, Zheng A R, et al. Effects of different roughages on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, ruminal fermentation, and microbial community in weaned Holstein calves. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2022, 9: 864320. |
| 50 | Palevich N, Maclean P H, Kelly W J, et al. Complete genome sequence of the polysaccharide-degrading rumen bacterium Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans MA3014 reveals an incomplete glycolytic pathway. Genome Biology and Evolution, 2020, 12(9): 1566-1572. |
| 51 | Li R W, Connor E E, Li C, et al. Characterization of the rumen microbiota of pre-ruminant calves using metagenomic tools. Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 14(1): 129-139. |
| 52 | Lareau A J, Suen G. The Ruminococci: key symbionts of the gut ecosystem. Journal of Microbiology, 2018, 56(3): 199-208. |
| 53 | Granja-salcedo Y T, Fernandes R M, de Araujo R C, et al. Long-term encapsulated nitrate supplementation modulates rumen microbial diversity and rumen fermentation to reduce methane emission in grazing steers. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 1732. |
| 54 | Haliemariam S, Zhao S G, Wang J Q. Complete genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis of nitrogen metabolism of Succinivibrio dextrinosolvens strain Z6 isolated from dairy cow rumen. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1826. |
| 55 | Auddert M D, Stewart R D, Dewhurst R J, et al. Identification of microbial genetic capacities and potential mechanisms within the rumen microbiome explaining differences in beef cattle feed efficiency. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1229. |
| 56 | Chen H, Wang C, Huasai S, et al. Effects of dietary forage to concentrate ratio on nutrient digestibility, ruminal fermentation and rumen bacterial composition in Angus cows. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 17023. |
| 57 | Liu C, Wu H, Liu S, et al. Dynamic alterations in yak rumen bacteria community and metabolome characteristics in response to feed type. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01116. |
| 58 | Rosmalia A, Permana I G, Despal D. Synchronization of rumen degradable protein with non-fiber carbohydrate on microbial protein synthesis and dairy ration digestibility. Veterinary World, 2022, 15(2): 252-261. |
| 59 | Javad G, Mohammad F V, Ding X Z, et al. Temporal changes in microbial communities attached to forages with different lignocellulosic compositions in cattle rumen. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2020, 96(6): fiaa069. |
| 60 | Zhao F F, Zhang X Z, Zhang Y, et al. Tannic acid-steeped corn grain modulates in vitro ruminal fermentation pattern and microbial metabolic pathways. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2021, 8: 698108. |
| 61 | Li C, Chen N, Zhang X X, et al. Mixed silage with Chinese cabbage waste enhances antioxidant ability by increasing ascorbate and aldarate metabolism through rumen Prevotellaceae UCG-004 in Hu sheep. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13(9): 516. |
| [1] | 申迪, 曾子铭, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 廖扬, 王迅, 黄伟华, 刘书杰, 杨英魁, 王书祥. 低精料日粮和高精料日粮对牦牛生长性能和瘤胃菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 155-165. |
| [2] | 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 冯启贤, 李妍, 周燚, 刘一佳, 阳伏林, 周晶. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| [3] | 覃娟清, 党浩千, 金华云, 郭宇康, 张富, 刘庆华. 不同添加剂处理笋壳对其发酵品质及湖羊瘤胃微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 155-167. |
| [4] | 周迪, 杨帅, 张欣欣, 袁婧, 高艳霞, 李建国, 汪波, 周广生, 傅廷栋, 叶俊, 杨利国, 滑国华. 添加剂种类和组合对晾晒后全株油菜青贮效果的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 124-135. |
| [5] | 周承福, 汪水平, 张佰忠, 张秀敏, 王荣, 马志远, 王敏. 水热处理对黄豆秸秆体外发酵、甲烷生成及微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 171-181. |
| [6] | 王挺, 宋磊, 王旭哲, 马春晖, 杜保军, 张凡凡. 复合乳酸菌对番茄皮渣与苜蓿混合青贮发酵品质及瘤胃降解率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 167-177. |
| [7] | 郭艳霞, 李孟伟, 唐振华, 彭丽娟, 彭开屏, 谢芳, 谢华德, 杨承剑. 添加亚油酸条件下不同剂量硝酸钠对水牛瘤胃体外发酵脂肪酸组成及相关微生物数量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 159-167. |
| [8] | 郑娟善, 丁考仁青, 李新圃, 梁泽毅, 张剑搏, 杜梅, 丁学智. 瘤胃微生物在木质纤维素价值化利用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 182-192. |
| [9] | 李宏, 宋淑珍, 高良霜, 郎侠, 刘立山, 宫旭胤, 魏玉兵, 吴建平. 饲养水平对阿勒泰羊胃肠道发育、瘤胃发酵参数及瘤胃微生物区系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 180-190. |
| [10] | 李蒋伟, 王志有, 侯生珍, 雷云, 贾建磊, 周力, 桂林生. 日粮精粗比对育肥藏羊瘤胃组织形态及微生物菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 100-109. |
| [11] | 张剑搏, 丁考仁青, 梁泽毅, Anum-aliAhmad, 杜梅, 郑娟善, 丁学智. 早期营养干预对幼龄反刍动物瘤胃微生物区系发育的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 199-211. |
| [12] | 马晓文, 李发弟, 李飞, 郭龙. 饲粮大麦粉碎粒度对湖羊瘤胃微生物组成及肌肉脂肪酸的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 202-211. |
| [13] | 付东青, 贾春英, 连晓春, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 玉米秸秆与番茄皮渣裹包混贮发酵品质及瘤胃降解特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 147-158. |
| [14] | 赵娜, 杨雪海, 魏金涛, 郭万正, 陈芳, 周广生, 傅廷栋. 饲用油菜的营养成分分析及其在山羊瘤胃降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 50-57. |
| [15] | 孔凡林, 刁其玉, 渠建江, 屠焰. 构树在肉牛瘤胃中降解特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 179-189. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||