

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 1-12.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024319
• 研究论文 •
安玉霞1( ), 王文强1, 余殿3, 梁咏亮2, 杨君珑1, 李小伟1(
), 王文强1, 余殿3, 梁咏亮2, 杨君珑1, 李小伟1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-26
修回日期:2024-09-18
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-05-12
通讯作者:
李小伟
作者简介:E-mail: lxwbq@126.com基金资助:
Yu-xia AN1( ), Wen-qiang WANG1, Dian YU3, Yong-liang LIANG2, Jun-long YANG1, Xiao-wei LI1(
), Wen-qiang WANG1, Dian YU3, Yong-liang LIANG2, Jun-long YANG1, Xiao-wei LI1( )
)
Received:2024-08-26
Revised:2024-09-18
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-05-12
Contact:
Xiao-wei LI
摘要:
锁阳系国家二级保护植物,其药用价值极高,生长在生态脆弱的荒漠地区。近年来,由于气候变化,对锁阳的地理分布构成了严重的威胁。为了明确影响锁阳在中国分布的主要环境因子以及潜在适生区的分布对合理保护和管理具有重要意义。基于166条有效分布记录和39个自然环境变量,运用最大熵模型(maximum entropy model, MaxEnt)对锁阳当前和未来两个时期(2050和2070年)的代表性路径(SSP126和SSP585)潜在的地理分布进行模拟,探讨影响其地理分布最关键的环境因素,并预测适生区在气候变化影响下的空间分布格局。采用刀切法评估环境变量对模型的贡献率,确定影响锁阳分布的主要环境变量。模型预测结果显示,当前模拟的锁阳潜在分布区与实际分布基本吻合,受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC值)为0.900,预测结果良好。最湿月的降水量和最冷季的平均气温是决定锁阳栖息地的重要变量,其次为基本饱和度和海拔以及最暖月的最高温度。未来气候的变化会使锁阳的栖息地范围缩小且向东迁移。本研究通过对锁阳潜在适生区的预测可以为锁阳的保护和管理提供参考和指导意义。
安玉霞, 王文强, 余殿, 梁咏亮, 杨君珑, 李小伟. 基于优化MaxEnt模型的锁阳分布研究:现状评估与未来预测[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 1-12.
Yu-xia AN, Wen-qiang WANG, Dian YU, Yong-liang LIANG, Jun-long YANG, Xiao-wei LI. A study of the distribution of the parasitic herb Cynomorium songaricum based on the optimized MaxEnt model: Current status assessment and future predictions[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(7): 1-12.
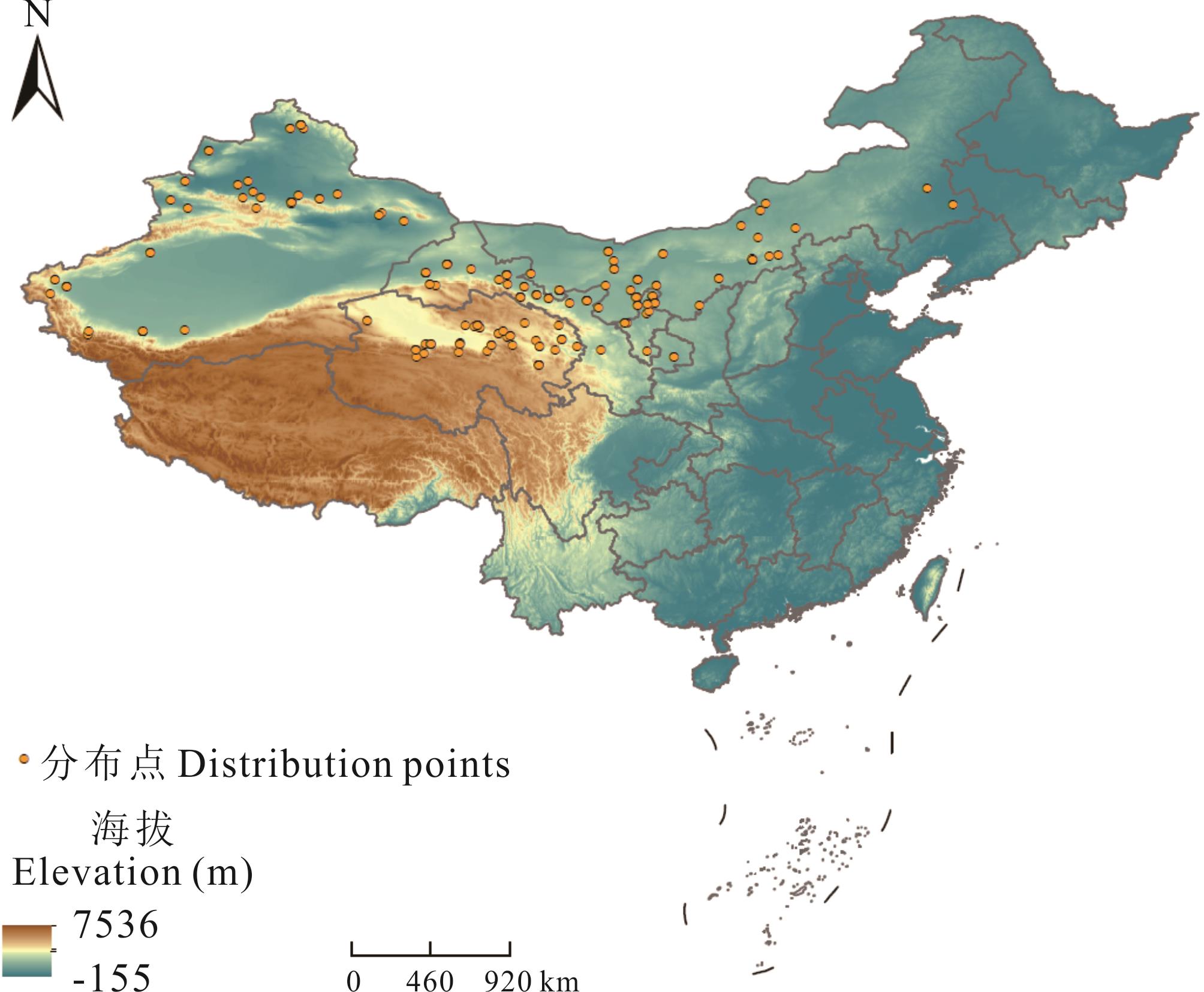
图1 锁阳物种分布点基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2767 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 Distribution points of C. songaricum species
| 分布概率Distribution probability (P) | 评价等级Evaluation level |
|---|---|
| P<0.2382 | 非适生区Non-suitable areas |
| 0.2382≤P<0.4000 | 低适生区Low suitable area |
| 0.4≤P<0.6 | 中适生区Medium suitable area |
| 0.6≤P≤1.0 | 高适生区Highly suitable area |
表1 适生区划分
Table 1 Division of potential distribution
| 分布概率Distribution probability (P) | 评价等级Evaluation level |
|---|---|
| P<0.2382 | 非适生区Non-suitable areas |
| 0.2382≤P<0.4000 | 低适生区Low suitable area |
| 0.4≤P<0.6 | 中适生区Medium suitable area |
| 0.6≤P≤1.0 | 高适生区Highly suitable area |
| 代码Code | 环境因子Environmental factor | 贡献率Contribution percent | 置换重要性Permutation importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| bio13 | 最湿月的降水量Precipitation in the wettest month | 48.9 | 54.1 |
| bio11 | 最冷季的平均气温The average temperature of the coldest season | 11.8 | 21.1 |
| t_bs | 基本饱和度Basic saturation | 9.1 | 2.3 |
| elev | 海拔Elevation | 7.5 | 3.6 |
| bio05 | 最暖月的最高温度The highest temperature of the warmest month | 7.4 | 6.2 |
| bio17 | 最干燥季的降水量Precipitation in the driest season | 5.6 | 3.3 |
| t_caco3 | 碳酸盐或石灰含量Carbonate or lime content | 2.9 | 0.9 |
| awc_class | 土壤有效水含量Soil available water content | 2.7 | 4.6 |
| slope | 坡度Gradient | 2.3 | 1.2 |
| t_oc | 有机碳含量Organic carbon content | 1.9 | 2.7 |
表2 锁阳分布模拟的10个环境变量
Table 2 Ten environmental variables simulated by C. songaricum distribution (%)
| 代码Code | 环境因子Environmental factor | 贡献率Contribution percent | 置换重要性Permutation importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| bio13 | 最湿月的降水量Precipitation in the wettest month | 48.9 | 54.1 |
| bio11 | 最冷季的平均气温The average temperature of the coldest season | 11.8 | 21.1 |
| t_bs | 基本饱和度Basic saturation | 9.1 | 2.3 |
| elev | 海拔Elevation | 7.5 | 3.6 |
| bio05 | 最暖月的最高温度The highest temperature of the warmest month | 7.4 | 6.2 |
| bio17 | 最干燥季的降水量Precipitation in the driest season | 5.6 | 3.3 |
| t_caco3 | 碳酸盐或石灰含量Carbonate or lime content | 2.9 | 0.9 |
| awc_class | 土壤有效水含量Soil available water content | 2.7 | 4.6 |
| slope | 坡度Gradient | 2.3 | 1.2 |
| t_oc | 有机碳含量Organic carbon content | 1.9 | 2.7 |

图6 当前气候下锁阳的潜在适宜区基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2767 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.6 Potential suitable area of C. songaricum under current climate

图7 未来气候变化下锁阳的适生区分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2767 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.7 The distribution of suitable areas of C. songaricum under future climate change

图8 锁阳潜在适生区质心变化基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2767 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.8 C. songaricum potential suitable area centroid change
| 1 | Chai W W, Jia X, Zhao Y H, et al. Spatio-temporal correlation between human activity intensity and vegetation cover on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(15): 6708-6721. |
| 柴文雯, 贾夏, 赵永华, 等. 黄土高原人类活动强度与植被覆盖的时空关联性. 生态学报, 2024, 44(15): 6708-6721. | |
| 2 | Alberto F J, Aitken S N, Ricardo A, et al. Potential for evolutionary responses to climate change-evidence from tree populations. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(6): 1645-1661. |
| 3 | Mendoza-González G, Martínez M L, Rojas-Soto O R, et al. Ecological niche modeling of coastal dune plants and future potential distribution in response to climate change and sea level rise. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(8): 2524-2535. |
| 4 | Werners S E, Sparkes E, Totin E, et al. Advancing climate resilient development pathways since the IPCC’s fifth assessment report. Environmental Science and Policy, 2021, 126: 168-176.. |
| 5 | Tang A M, Hughes P N, Dijkstra T A, et al. Atmosphere-vegetation-soil interactions in a climate change context; impact of changing conditions on engineered transport infrastructure slopes in Europe. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 2018, 51(2): 156-168. |
| 6 | Rao J, Tang Q, Feng Y, et al. Habitat condition and vegetation restoration patterns in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 38(1): 310-318. |
| 饶洁, 唐强, 冯韫, 等. 三峡水库消落带生境特征与植被恢复模式. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(1): 310-318. | |
| 7 | Bo C, Cheng K B, Lin L Z, et al. Modeling habitat distribution of Cornus officinalis with MaxEnt modeling and fuzzy logics in China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 9(6): 742-751. |
| 8 | Jun H D, Huan J W, Quan S G. Multiple phenological responses to climate change among 42 plant species in Xi’an, China. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2013, 57(5): 749-758. |
| 9 | Qian Q Q, Xu D P, Liao W K, et al. Predicting the current and future suitable distribution range of Trilocha varians (Walker, 1855) (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) in China. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 2024, 114(3): 317-326. |
| 10 | Zhang L, Cao B, Bai C, et al. Predicting suitable cultivation regions of medicinal plants with MaxEnt modeling and fuzzy logics: a case study of Scutellaria baicalensis in China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(5): 361. |
| 11 | Sutherst R W, Maywald G F. A computerised system for matching climates in ecology. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 1985, 13(3): 281-299. |
| 12 | Phillips J S, Anderson P R, Schapire E R. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 2006, 190(3/4): 231-259. |
| 13 | Hirzel A, Guisan A. Which is the optimal sampling strategy for habitat suitability modelling. Ecological Modelling, 2002, 157(2): 331-341. |
| 14 | Borthakur S, Baruah S P, Deka K, et al. Habitat distribution modelling for improving conservation status of Brucea mollis Wall. Ex Kurz.-An endangered potential medicinal plant of Northeast India. Journal for Nature Conservation, 2018, 43: 104-110. |
| 15 | Yang X Q, Kushwaha S P S, Saran S, et al. MaxEnt modeling for predicting the potential distribution of medicinal plant, Justicia adhatoda L. in Lesser Himalayan foothills. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 51: 83-87. |
| 16 | Marini  M, Barbet-Massin M, Lopes E L, et al. Predicting the occurrence of rare Brazilian birds with species distribution models. Journal of Ornithology, 2010, 151(4): 857-866. |
| 17 | Pearson R G, Raxworthy C J, Nakamura M, et al. Predicting species distributions from small numbers of occurrence records: A test case using cryptic geckos in Madagascar. Journal of Biogeography, 2007, 34(1): 102-117. |
| 18 | Jin F. Studies on the plant diet culture in Mongolian Nation. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2004. |
| 金凤. 蒙古族植物饮食文化研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2004. | |
| 19 | Chen H Z. Nutriments analysis and methods establishment for determination of bioactive components in Cynomorium songaricum. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 陈汉哲. 锁阳营养品质分析及生物活性成分定量方法建立. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 20 | Tao R, Miao L, Yu X A, et al. Cynomorium songaricum Rupr demonstrates phytoestrogenic or phytoandrogenic like activities that attenuates benign prostatic hyperplasia via regulating steroid 5-α-reductase. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2019, 235: 65-74. |
| 21 | Xue H Y, Jiao C Y, Yao J. Research progress on pharmacology of Cynomorii herba. Drugs and Clinic, 2018, 33(3): 709-712. |
| 薛海燕, 焦婵媛, 姚军. 锁阳药理作用的研究进展. 现代药物与临床, 2018, 33(3): 709-712. | |
| 22 | Zhao P Y, Yang Y Q, Wang F F, et al. Content analysis and quality evaluation of main active components and mineral elements of Cynomorium songaricum in different habitats. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2023, 48(4): 908-920. |
| 赵鹏宇, 杨月琴, 王非凡, 等. 不同生境下锁阳主要活性成分和矿质元素含量的分析及其品质评价. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(4): 908-920. | |
| 23 | Zhang R, Gu Z R, Guo Y, et al. Content difference of effective components of cynomorii herba between different producing areas and its response to environmental factors. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2022, 28(7): 142-150. |
| 张锐, 顾志荣, 郭燕, 等. 锁阳有效成分含量的产地差异及对环境因子的响应规律. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(7): 142-150. | |
| 24 | Zhang M R, Guo M N, Sun L, et al. Study on the suitability regionalization of Polygonatum sibiricum Delar. ex Redoute in Shanxi Province based on optimized MaxEnt model. Journal of Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 24(2): 216-220. |
| 张孟容, 郭敏娜, 孙靓, 等. 基于优化MaxEnt模型的山西省黄精产地适宜性区划研究. 山西中医药大学学报, 2023, 24(2): 216-220. | |
| 25 | Phillips S J, Dudik M. Modeling of species distributions with MaxEnt: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography, 2008, 31(2): 161-175. |
| 26 | Cobos M E, Peterson A T, Barve N, et al. Kuenm: an R package for detailed development of ecological niche models using MaxEnt. PeerJ, 2019, 7. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.6281. |
| 27 | Warren D L, Seifert S N. Ecological niche modeling in MaxEnt: the importance of model complexity and the performance of model selection criteria. Ecological Applications, 2011, 21(2): 335-342. |
| 28 | Guo Y B, Mo K, Wang G R, et al. Analysis of prediction and spatial-temporal changes of suitable distribution of gastrodiae rhizoma under future climate conditions. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine Information, 2022, 29(7): 1-7. |
| 郭怡博, 莫可, 王桂荣, 等. 未来气候条件下天麻适生区预测及时空变化分析.中国中医药信息杂志, 2022, 29(7): 1-7. | |
| 29 | Zhang M Z, Ye X Z, Li J H, et al. Prediction of potential suitable area of Ulmus elongata in China under climate change scenarios. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(12): 3822-3835. |
| 张明珠, 叶兴状, 李佳慧, 等. 气候变化情景下长序榆在中国的潜在适生区预测. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(12): 3822-3835. | |
| 30 | Zhang Y B, Liu Y L, Qin H, et al. Prediction on spatial migration of suitable distribution of Elaeagnus mollis under climate change conditions in Shanxi Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(2): 496-502. |
| 张殷波, 刘彦岚, 秦浩, 等. 气候变化条件下山西翅果油树适宜分布区的空间迁移预测. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(2): 496-502. | |
| 31 | Eshetae T D S. Spatial characterization and distribution modelling of Ensete ventricosum (wild and cultivated) in Ethiopia. Geocarto International, 2021, 36(4): DOI: 10.1080/10106049.2019.1588392. |
| 32 | Warren D L, Wright A N, Seifert S N, et al. Incorporating model complexity and spatial sampling bias into ecological niche models of climate change risks faced by 90 California vertebrate species of concern. Diversity and Distributions, 2014, 20(3/4): 334-343. |
| 33 | Veloz S D. Spatially autocorrelated sampling falsely inflates measures of accuracy for presence-only niche models. Journal of Biogeography, 2009, 36(12): 2290-2299. |
| 34 | Zhao D M, Jiao Y M, Qiu Y M, et al. Assessment on landslide susceptibility of the core area of Hani race terraces heritage site Maximum Entropy model. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(4): 392-399, 407. |
| 赵冬梅, 角媛梅, 邱应美, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的哈尼梯田核心区滑坡易发性评价. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(4): 392-399, 407. | |
| 35 | Li Y, Lu L Y, Tian X H, et al. Prediction of the suitable habitat distribution of oriental white stork in Shandong Province. Acta Ecological Sinica, 2023, 43(6): 2194-2201. |
| 李雨, 卢柳妍, 田秀华, 等. 东方白鹳在山东省适宜栖息地的分布预测. 生态学报, 2023, 43(6): 2194-2201. | |
| 36 | Yang Z W, Han S Y, Li Y, et al. Impacts and assessment of climate change on the global distribution of potentially suitable habitats for Panthera uncia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(4): 1412-1425. |
| 杨子文, 韩姝伊, 李壹, 等. 气候变化对雪豹全球潜在适生区分布的影响与评估. 生态学报, 2023, 43(4): 1412-1425. | |
| 37 | Jiang R Y. Distribution of parasitic angiosperms and the parasite-host interactions in China. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2022. |
| 蒋若衍. 中国寄生被子植物的分布及其与寄主的关系. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2022. | |
| 38 | Yan B L, Wang Z W, Wang Y H, et al. Effect of short-term rainfall change on plant community characteristics in desert steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(5): 1004-1012. |
| 闫宝龙, 王占文, 王悦骅, 等. 短期降雨改变对荒漠草原植物群落特征的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(5): 1004-1012. | |
| 39 | Duan Y Z, Zhu G X, Du Z Y, et al. Simulation and analysis of the suitable environment for Nitraria L. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(2): 124-129. |
| 段义忠, 朱国旭, 杜忠毓, 等. 西北干旱区白刺属植物适生环境的模拟分析. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(2): 124-129. | |
| 40 | Madina·Halimujiang. Study on the geographical distribution patterns and potential suitable areas of four Nitraria species. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2022. |
| 玛地娜·哈力木江. 四种白刺属植物地理分布格局及其潜在适宜区研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2022. | |
| 41 | Deb J C, Phinn S, Butt N, et al. The impact of climate change on the distribution of two threatened dipterocarp trees. Ecology & Evolution, 2017, 7(7): 2238-2248. |
| 42 | Guo Y, Gu Z R, Qi M, et al. Multi-index comprehensive quality evaluation of Cynomorium songaricum from different producing areas based on Projection Pursuit model. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2022, 41(8): 14-21. |
| 郭燕, 顾志荣, 祁梅, 等. 基于投影寻踪模型的不同产地锁阳药材多指标综合质量评价. 中国野生植物资源, 2022, 41(8): 14-21. | |
| 43 | Sun X, Lin Y L, Li B L, et al. Analysis and function prediction of soil microbial communities of Cynomorium songaricum in two daodi-origins. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2020, 55(6): 1334-1344. |
| 孙晓, 林余霖, 李葆莉, 等. 干旱区沙生药用植物锁阳土壤微生物群落分析与功能预测. 药学学报, 2020, 55(6): 1334-1344. | |
| 44 | Gu Z R, Sun L P, Qian Q, et al. Study on HPLC fingerprints and content determination of water fraction of Cynomorii herba from different producing areas. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM, 2020, 27(11): 82-88. |
| 顾志荣, 孙岚萍, 钱倩, 等. 不同产地锁阳水溶性部位HPLC指纹图谱及含量测定研究. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2020, 27(11): 82-88. | |
| 45 | Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China. Beijing: Science Press, 1986. |
| 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志, 北京: 科学出版社, 1986. | |
| 46 | Xiang J W, Zhang L P, Deng Y, et al. Projection and evaluation of extreme temperature and precipitation in major regions of China by CMIP6 models. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2021, 54(1): 46-57, 81. |
| 向竣文, 张利平, 邓瑶, 等. 基于CMIP6的中国主要地区极端气温/降水模拟能力评估及未来情景预估. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2021, 54(1): 46-57, 81. | |
| 47 | Shi Y F, Shen Y P, Hu R J. Preliminary study on signal impact and foreground of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humidin Northwest China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology Permafrost, 2002, 24(3): 219-226. |
| 施雅风, 沈永平, 胡汝骥. 西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的信号、影响和前景初步探讨. 冰川冻土, 2002, 24(3): 219-226. | |
| 48 | Yao X Y, Zhang M J, Zhang Y, et al. New insights into climate transition in northwest China. Arid Land Geography, 2022, 45(3): 671-683. |
| 姚旭阳, 张明军, 张宇, 等. 中国西北地区气候转型的新认识.干旱区地理, 2022, 45(3): 671-683. | |
| 49 | Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B. Global warming and abrupt climate change. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(1): 114-120. |
| 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 全球变暖与气候突变. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(1): 114-120. | |
| 50 | Li Z S, Ma Y S, Li Y X, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of the potential habitat of Asterothamnus centraliasiaticus on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under climate change. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(6): 1566-1575. |
| 李政升, 马玉寿, 李有鑫, 等. 气候变化下青藏高原中亚紫菀木潜在适生区的时空动态变化. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(6): 1566-1575. | |
| 51 | Zhao J P, Wang Y L, Lu X L, et al. Climatic suitable area analysis and response to climate change of Actinidia arguta in China. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(10): 1523-1532. |
| 赵金鹏, 王闫利, 陆兴利, 等. 软枣猕猴桃在中国的适生区分析及对未来气候变化的响应. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(10): 1523-1532. | |
| 52 | Chen S S, Liu X, Tong X Y, et al. Prediction of Camellia edithae species distribution based on multi-model combination. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(2): 58-66. |
| 陈思斯, 刘想, 童鑫玥, 等. 基于多模型集合预测尖萼红山茶物种分布. 生态科学, 2020, 39(2): 58-66. | |
| 53 | Wan G Z, Luo Y H, Zhang D X, et al. Prediction of the potential habitat of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao in Gansu Province based on the Maximum Entropy model and analysis on its ecological characteristics. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM, 2024, 31(1): 1-5. |
| 万广珍, 罗永慧, 张鼎新, 等. 基于最大熵模型的甘肃省蒙古黄芪潜在适生区预测及生态特征分析. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2024, 31(1): 1-5. |
| [1] | 龚昕, 霍新茹, 李雯, 杨彦东, 刘超, 秦伟春, 沈艳, 王国会, 马红彬. 宁夏罗山山地草原植被群落特征及其空间分异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 1-15. |
| [2] | 于双, 李小伟, 王瑞霞, 杨君珑, 马龙. 灵武白芨滩不同年限柠条固沙林林下草本群落演替规律及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 13-23. |
| [3] | 王鹏, 金正, 余婷, 秦康强, 桑新亚, 陶建平, 罗唯学. 预测姜黄属植物在中国当前和未来气候情景下的潜在分布区变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 14-27. |
| [4] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [5] | 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| [6] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| [7] | 杨鑫, 曹文侠, 鱼小军, 汪海斌, 郝媛媛. 基于近20年MODIS NDVI日数据的青海省草地资源动态监测及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 1-14. |
| [8] | 张敏, NIPAPAN Kanjana, 李铷, 傅杨, 汤东生. 环境因子对云南扁穗雀麦种子萌发和出苗的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 143-151. |
| [9] | 孙思思, 吴战平, 肖启涛, 于飞, 古书鸿, 方荻, 李浪, 赵兴炳. 云贵高原草地生态系统CO2通量变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 184-191. |
| [10] | 孙丽坤, 刘光琇, 张宝贵, 章高森. 环境因子对中国柽柳遗传变异的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 178-186. |
| [11] | 陆姣云,段兵红,杨梅,杨晗,杨惠敏. 植物叶片氮磷养分重吸收规律及其调控机制研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 178-188. |
| [12] | 范顺祥, 郑建伟, 魏士凯, 黄选瑞, 张志东. 河北省森林草原区主要草本植物功能群适宜分布预测[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 24-32. |
| [13] | 葛兆轩, 孙国龙, 袁业, 黄选瑞, 张志东. 河北省森林草原区草本植物物种多样性和功能多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 35-44. |
| [14] | 陶冶, 刘耀斌, 吴甘霖, 张元明. 准噶尔荒漠区域尺度浅层土壤化学计量特征及其空间分布格[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 13-23. |
| [15] | 李杰,蔡立群,张鸣,张仁陟. 不同耕作措施下旱作春小麦叶水势动态及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 75-81. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||