

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 53-64.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024415
陈俊玲2,3( ), 王莎莎2,3, 叶菁1,3, 林怡1,3, 王义祥1,3(
), 王莎莎2,3, 叶菁1,3, 林怡1,3, 王义祥1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-22
修回日期:2024-12-16
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-07-02
通讯作者:
王义祥
作者简介:E-mail: sd_wolong@163.com基金资助:
Jun-ling CHEN2,3( ), Sha-sha WANG2,3, Jing YE1,3, Yi LIN1,3, Yi-xiang WANG1,3(
), Sha-sha WANG2,3, Jing YE1,3, Yi LIN1,3, Yi-xiang WANG1,3( )
)
Received:2024-10-22
Revised:2024-12-16
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-07-02
Contact:
Yi-xiang WANG
摘要:
生草覆盖作为一种生态友好型果园管理方式引起关注,但不同生草覆盖对土壤碳矿化及其温度敏感性作用机制仍缺乏认识。本研究基于福建省尤溪县玉池村28年的长期定位试验,研究清耕、果园套种圆叶决明和平托花生3种地被管理方式下果园土壤矿化速率及其温度敏感性的变化,为亚热带地区气候变化背景下果园土壤固碳减排与科学管理提供理论依据。结果表明:相对清耕模式,果园生草覆盖处理28年后土壤有机碳含量增加了19.20%~30.04%。在不同生草覆盖模式下,土壤有机碳累积矿化量与培养时间和温度呈正相关关系。在35 ℃时,果园套种平托花生处理的有机碳累积矿化量最高,为633.41 mg·kg-1,套种圆叶决明处理次之,两者分别比清耕处理提高72.75%和61.27%,潜在矿化量分别提高2.98和1.14倍。高温条件下(>25 ℃),果园套种平托花生和圆叶决明处理土壤矿化温度敏感性系数(Q10)分别比清耕处理降低了35.20%和47.37%。综上,长期果园生草覆盖提高了土壤有机碳含量,随着温度变化(>25 ℃),果园土壤有机碳矿化的温度敏感性随之降低,土壤碳库应对温度变化的响应稳定。其中平托花生覆盖处理效果优于圆叶决明覆盖处理。
陈俊玲, 王莎莎, 叶菁, 林怡, 王义祥. 长期不同果园生草覆盖下土壤碳矿化及其温度敏感性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 53-64.
Jun-ling CHEN, Sha-sha WANG, Jing YE, Yi LIN, Yi-xiang WANG. Soil carbon mineralization in an orchard with and without interplanted ground cover species and its temperature sensitivity under long-term conditions[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(9): 53-64.
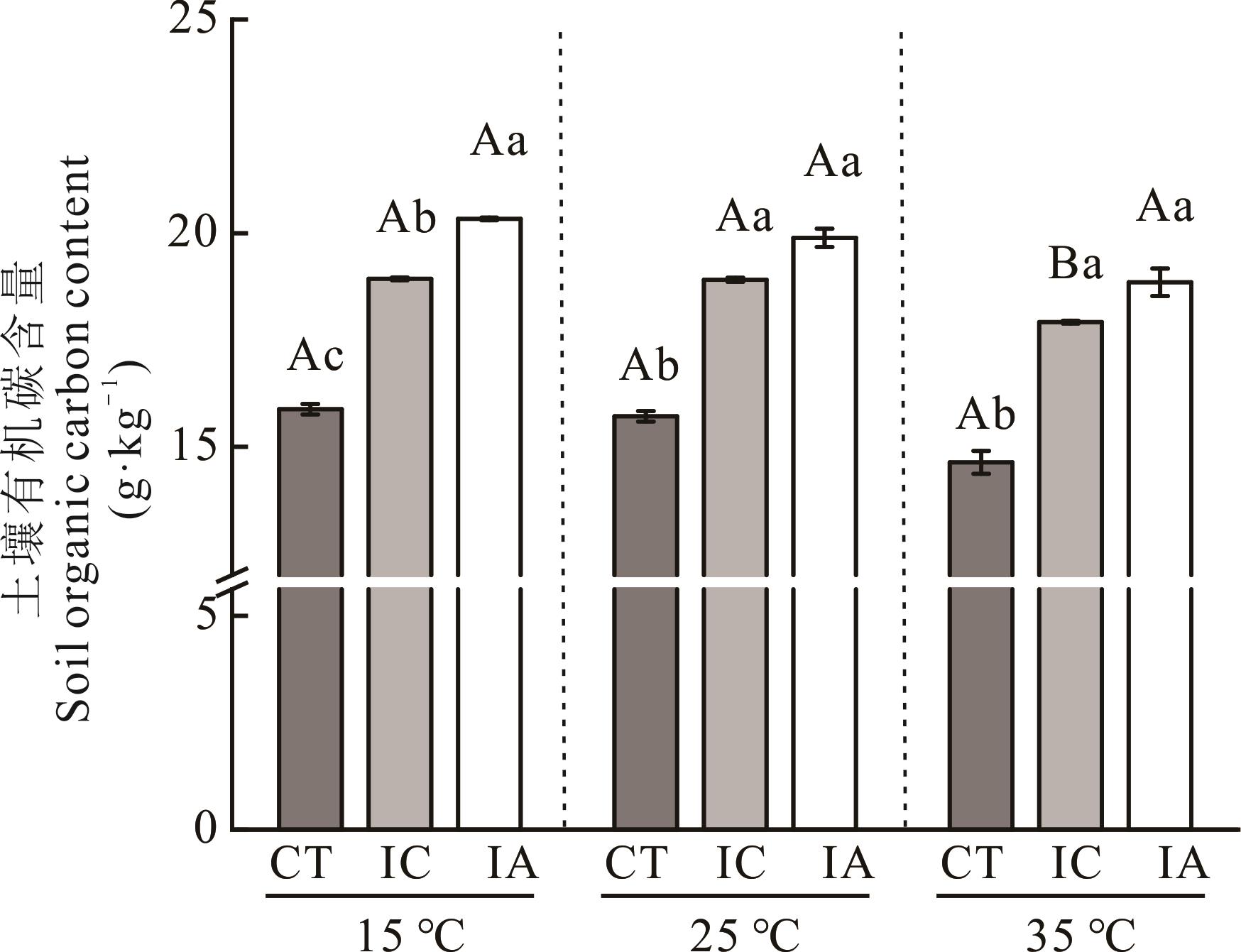
图2 不同培养温度下土壤有机碳含量不同大写字母表示同一处理不同温度间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示同一温度不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different capital letters indicate significant differences among different temperatures of the same treatment (P<0.05), different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at the same temperature (P<0.05). 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Soil organic carbon content at different culture temperatures
培养温度 Culture temperature (℃) | 指标 Index | 处理Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | IC | IA | ||
| 15 | C0 (mg·g-1) | 3.013±0.387c | 5.338±0.017b | 7.306±0.534a |
| k | 0.0007±0.0001a | 0.0005±0.0001b | 0.0004±0.0001b | |
| T1/2 (d) | 7.988±0.063c | 8.285±0.002b | 8.440±0.036a | |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.987 | 0.984 | |
| Sig | P<0.001 | P<0.018 | P<0.001 | |
| 25 | C0 (mg·g-1) | 9.158±0.963b | 10.235±0.676b | 18.902±1.323a |
| k | 0.0004±0.0001a | 0.0004±0.0001a | 0.0003±0.0001b | |
| T1/2 (d) | 8.551±0.055b | 8.611±0.032b | 8.920±0.034a | |
| R2 | 0.943 | 0.977 | 0.973 | |
| Sig | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | |
| 35 | C0 (mg·g-1) | 15.962±0.356b | 41.615±4.754a | 47.506±3.288a |
| k | 0.0003±0.0000a | 0.0002±0.0000b | 0.0002±0.0000b | |
| T1/2 (d) | 8.837±0.011b | 9.311±0.062a | 9.382±0.035a | |
| R2 | 0.953 | 0.929 | 0.975 | |
| Sig | P<0.001 | P<0.026 | P<0.001 | |
表1 不同温度条件下不同处理间土壤有机碳矿化拟合结果
Table 1 Fitting results of soil organic carbon mineralization under different temperature conditions and different treatments
培养温度 Culture temperature (℃) | 指标 Index | 处理Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | IC | IA | ||
| 15 | C0 (mg·g-1) | 3.013±0.387c | 5.338±0.017b | 7.306±0.534a |
| k | 0.0007±0.0001a | 0.0005±0.0001b | 0.0004±0.0001b | |
| T1/2 (d) | 7.988±0.063c | 8.285±0.002b | 8.440±0.036a | |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.987 | 0.984 | |
| Sig | P<0.001 | P<0.018 | P<0.001 | |
| 25 | C0 (mg·g-1) | 9.158±0.963b | 10.235±0.676b | 18.902±1.323a |
| k | 0.0004±0.0001a | 0.0004±0.0001a | 0.0003±0.0001b | |
| T1/2 (d) | 8.551±0.055b | 8.611±0.032b | 8.920±0.034a | |
| R2 | 0.943 | 0.977 | 0.973 | |
| Sig | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | |
| 35 | C0 (mg·g-1) | 15.962±0.356b | 41.615±4.754a | 47.506±3.288a |
| k | 0.0003±0.0000a | 0.0002±0.0000b | 0.0002±0.0000b | |
| T1/2 (d) | 8.837±0.011b | 9.311±0.062a | 9.382±0.035a | |
| R2 | 0.953 | 0.929 | 0.975 | |
| Sig | P<0.001 | P<0.026 | P<0.001 | |
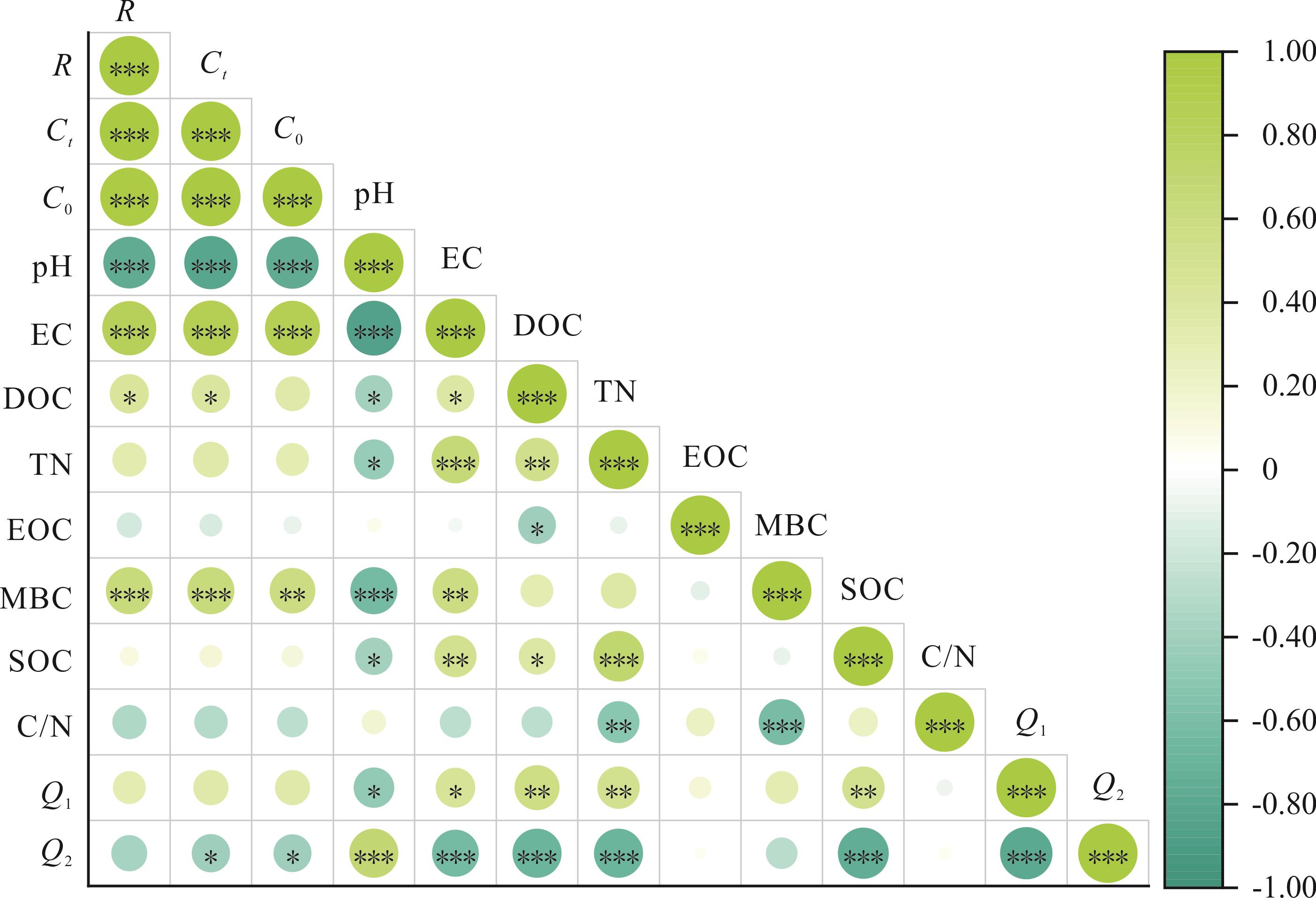
图7 各指标间的相关性分析*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001. R: 土壤有机碳矿化速率Soil organic carbon mineralization rate; Ct : 累积矿化量Cumulative mineralization; C0: 土壤潜在矿化碳库Soil potential mineralized carbon pool; EC:土壤电导率Electrical conductivity; DOC: 可溶性有机碳Soil soluble organic carbon; TN: 土壤总氮Soil total nitrogen; EOC: 易氧化有机碳Easily oxidized organic carbon; MBC: 微生物生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon; SOC: 土壤有机碳含量Soil total organic carbon content; C/N: 碳氮比The ratio of carbon to nitrogen; Q1: 15~25 ℃温度敏感性系数Temperature sensitivity coefficient at 15-25 ℃; Q2: 25~35 ℃温度敏感性系数Temperature sensitivity coefficient at 25-35 ℃. 下同The same below.
Fig.7 Correlation analysis among various indicators
| [1] | Batjes N H. Harmonized soil property values for broad-scale modelling (WISE30sec) with estimates of global soil carbon stocks. Geoderma, 2016, 269(1): 61-68. |
| [2] | Pan G X, Ding Y J, Chen S T, et al. Exploring the nature of soil organic matter from humic substances isolation to SOMics of molecular assemblage. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(5): 451-470. |
| 潘根兴, 丁元君, 陈硕桐, 等. 从土壤腐殖质分组到分子有机质组学认识土壤有机质本质. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(5): 451-470. | |
| [3] | Zhang S. Modelling the temperature sensitivity of global soil organic carbon mineralization. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2024. |
| 张帅. 全球土壤有机碳矿化温度敏感性模拟研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2024. | |
| [4] | Yang S. Temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon mineralization in temperate forests in Northeast China. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 杨山. 东北温带森林土壤有机碳矿化温度敏感性研究. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2021. | |
| [5] | Weng B Q, Ying Z Y, Huang Y B, et al. Study on construction and application of comprehensive utilization mode and ecological rehabilitation of empoldered red soil mountains in Northern Fujian. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 20(1): 147-150. |
| 翁伯琦, 应朝阳, 黄毅斌, 等. 闽北山区红壤丘陵开发地生态恢复与综合利用模式构建及其应用研究. 水土保持学报, 2006, 20(1): 147-150. | |
| [6] | Miñarro M, Dapena E. Effects of groundcover management on ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in an apple orchard. Applied Soil Ecology, 2003, 23(2): 111-117. |
| [7] | Weng B Q, Huang Y B, Ying Z Y, et al. The technology and efficient analysis of ecological orchard in red soil hills. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(12): 465-470. |
| 翁伯琦, 黄毅斌, 应朝阳, 等. 红壤山地生态果园开发及成效分析. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(12): 465-470. | |
| [8] | Huang J X, Xiong D C, Liu X F, et al. Effects of warming on soil organic carbon mineralization: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(1): 12-24. |
| 黄锦学, 熊德成, 刘小飞, 等. 增温对土壤有机碳矿化的影响研究综述. 生态学报, 2017, 37(1): 12-24. | |
| [9] | Lu W. Mineralization and kinetic characteristics of organic carbon in long-term fertilized yellow soil at different temperatures. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019. |
| 卢韦. 不同温度下长期施肥黄壤有机碳的矿化及动力学特征. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019. | |
| [10] | Wu J H, Pan J J, Ge X J, et al. Variations of soil organic carbon mineralization and temperature sensitivity under different land use types. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(3): 130-135. |
| 邬建红, 潘剑君, 葛序娟, 等. 不同土地利用方式下土壤有机碳矿化及其温度敏感性. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(3): 130-135. | |
| [11] | Zhu R H, Zheng Z C, Li T X, et al. Dynamics of soil organic carbon mineralization in tea plantations converted from farmland at Western Sichuan, China. PLoS One, 2017, 12(9): e0185271. |
| [12] | Chen Z X, Zhang C, Li Q, et al. Mechanism underlying temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon decomposition: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(9): 2575-2584. |
| 陈浈雄, 张超, 李全, 等. 土壤有机碳分解温度敏感性的影响机制研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(9): 2575-2584. | |
| [13] | Wang D, Lü Y L, Xu L, et al. Impact of changes in vegetation types on soil C mineralization and associated temperature sensitivity in the Changbai Mountain forests of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(19): 6373-6381. |
| 王丹, 吕瑜良, 徐丽, 等. 植被类型变化对长白山森林土壤碳矿化及其温度敏感性的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 6373-6381. | |
| [14] | Chen X F, Liu M, Jiang C Y, et al. Mineralization of soil organic carbon and its sensitivity to temperature in soil aggregates, relative to particle size in red paddy soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(5): 1118-1127. |
| 陈晓芬, 刘明, 江春玉, 等. 红壤性水稻土不同粒级团聚体有机碳矿化及其温度敏感性. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(5): 1118-1127. | |
| [15] | Wang D. Study on soil carbon mineralization and its temperature sensitivity in the forest vertical transect of Changbai Mountain. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2014. |
| 王丹. 长白山垂直样带森林土壤碳矿化及其温度敏感性研究. 重庆: 西南大学, 2014. | |
| [16] | Gao J L, Wang J J, Bai Y, et al. The influence of the grain for green project on climate change in Shaanxi Province and its driving mechanism. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2025, 32(2): 150-157. |
| 高建伦, 王晶晶, 白玥, 等. 退耕还林工程对陕西省气候的影响及其驱动机制. 水土保持研究, 2025, 32(2): 150-157. | |
| [17] | Cao Q, Shen Y Y, Wang Z K, et al. Effects of living mulch on soil physical and chemical properties in orchards: a review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(8): 180-188. |
| 曹铨, 沈禹颖, 王自奎, 等. 生草对果园土壤理化性状的影响研究进展. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 180-188. | |
| [18] | Wang Y X, Wang F, Weng B Q, et al. Effect of sod cultivation on mineralization of soil organic carbon in nectarine orchards. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(6): 86-92. |
| 王义祥, 王峰, 翁伯琦, 等. 生草栽培对油桃园土壤有机碳矿化的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 86-92. | |
| [19] | Bao S D. Agrochemical analysis of the soil (the third edition). Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| [20] | Li J, Du X R, Mo X L, et al. Characteristics of soil organic carbon mineralization and its influencing factors under different land use types in karst areas. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2025, 45(2): 730-742. |
| 黎俊, 杜馨如, 莫小亮, 等. 喀斯特不同土地利用方式土壤有机碳矿化特征及其影响因素. 生态学报, 2025, 45(2): 730-742. | |
| [21] | Li S J, Qiu L P, Zhang X C. Mineralization of soil organic and its relations with soil physical and chemical properties on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(5): 1217-1226. |
| 李顺姬, 邱莉萍, 张兴昌. 黄土高原土壤有机碳矿化及其与土壤理化性质的关系. 生态学报, 2010, 30(5): 1217-1226. | |
| [22] | Yang L, Li W Y, Luo J L, et al. Effects of plastic film mulching and natural grass growing on soil nutrients, pH, water content and temperature in peach orchard. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(12): 2719-2726. |
| 杨乐, 李文杨, 骆建莉, 等. 地膜覆盖和自然生草对桃园土壤养分、pH及水热的影响. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(12): 2719-2726. | |
| [23] | Xue T T, Cheng C Y, Yang F, et al. Effect of organic mulching practices on soil properties in vineyards: A review. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2024, 29(6): 206-218. |
| 薛婷婷, 程春颖, 杨帆, 等. 葡萄园有机覆盖措施对土壤特性的影响研究进展. 中国农业大学学报, 2024, 29(6): 206-218. | |
| [24] | Huang G H, Ning X Y, Lu Y P, et al. Research progress on carbon sequestration potential and its effects based on grass planting model in the orchard. Northern Horticulture, 2023(14): 146-153. |
| 黄国华, 宁心怡, 卢玉鹏, 等. 基于果园生草模式的固碳潜力及影响研究进展. 北方园艺, 2023(14): 146-153. | |
| [25] | Tai J C, Yang H S, Fan F, et al. Effects of manual sowing methods of Medicago sativa and Bromus inermis on the distribution and content of soil organic carbon and nitrogen. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(6): 41-45. |
| 邰继承, 杨恒山, 范富, 等. 播种方式对紫花苜蓿+无芒雀麦人工草地浅剖面土壤C、N分布及储量的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 41-45. | |
| [26] | Li H K, Zhang G J, Zhao Z Y, et al. Effects of interplanted herbage on soil properties of non-irrigated apple orchards in the Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2007, 16(2): 32-39. |
| 李会科, 张广军, 赵政阳, 等. 生草对黄土高原旱地苹果园土壤性状的影响. 草业学报, 2007, 16(2): 32-39. | |
| [27] | Haynes R J, Goh K M. Some effects of orchard soil management on sward composition, levels of available nutrients in the soil and leaf nutrient content of nature ‘Golden Delicious’ apple trees. Scientia Horticulturae, 1980, 13: 15-25. |
| [28] | Montanarella L, Pennock D J, Mckenzie N, et al. World’s soils are under threat. Soil Discussions, 2016, 2(2): 79-82. |
| [29] | Wang Y X. Characteristics of organic carbon stock and carbon fixation capacity in orchard soils by different managing measures. Fujian: Fuzhou Agriculture and Forestry University, 2011. |
| 王义祥. 不同经营措施下果园土壤有机碳库特性及固碳潜力研究. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2011. | |
| [30] | Luo X H, Zhan J, Wang Y X, et al. Soil & water conservation function and comprehensive benefits of intercropping forage in eroded fruit garden. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(5): 729-734. |
| 罗旭辉, 詹杰, 王义祥, 等. 侵蚀果园长期植草的生态效益分析. 草地学报, 2011, 19(5): 729-734. | |
| [31] | Cao Y X, Cheng M, Wen Y L. Effects of iron addition on soil organic carbon mineralization characteristics under different vegetation types in Mount Luya. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2024, 30(1): 18-25. |
| 曹亚鑫, 程曼, 文永莉. 芦芽山不同植被类型下土壤有机碳矿化特征及其对铁添加的响应. 应用与环境生物学报, 2024, 30(1): 18-25. | |
| [32] | Zheng Z D, Huang Y B, Weng B Q, et al. Studies on the comprehensive development of hilly land in Fujian——I. Effects of different planting manners on the orchard ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2003, 11(3): 155-157. |
| 郑仲登, 黄毅斌, 翁伯奇, 等. 福建山地综合开发中红壤保育研究——Ⅰ.不同垦殖方式对果园生态系统的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2003, 11(3): 155-157. | |
| [33] | Huang Y B, Ying C Y, Zheng Z D, et al. Studies on the ecological forages and its utilization in ecological orchard. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2001(3): 52-55. |
| 黄毅斌, 应朝阳, 郑仲登, 等. 生态牧草筛选及其在生态果园应用的研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2001(3): 52-55. | |
| [34] | Ma G H, Zeng M, Wang Y Y, et al. Research progress on orchard sod culture. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(7): 273-277. |
| 马国辉, 曾明, 王羽玥, 等. 果园生草制研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(7): 273-277. | |
| [35] | Jiao X Y. Study on the cultivation techniques and benefits of raw grass in orchards. Fruit Growers’ Friend, 2024(7): 70-73. |
| 焦秀颖. 果园生草栽培技术与效益研究. 果农之友, 2024(7): 70-73. | |
| [36] | Zhang X H, Xin H M. Nutrient and soil enzyme activities of pear orchard as affected by planting herbage. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 41(8): 85-88. |
| 张喜焕, 辛贺明. 生草栽培对梨园土壤养分及土壤酶活性的影响. 河南农业科学, 2012, 41(8): 85-88. | |
| [37] | Guan G, Guo F P, Guo D D, et al. Effects of raw grass cultivation on soil biological properties and root exudation of Gannan navel orange. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(5): 216-226. |
| 管冠, 郭富鹏, 郭等等, 等. 生草栽培对赣南脐橙土壤生物学性质及根系分泌物的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(5): 216-226. | |
| [38] | Hu F, Yang Y L, Ni Z J, et al. Effects of sod culture on fruit quality and soil in peach orchard. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science & Technology, 2020, 47(3): 31-37. |
| 胡枫, 杨熠路, 倪照君, 等. 生草对桃园土壤及桃果实品质的影响. 江苏林业科技, 2020, 47(3): 31-37. | |
| [39] | Liu Y H, Du X L, Huang J X, et al. Effect of environmental factors on mineral soil respiration: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(10): 2835-2844. |
| 刘源豪, 杜旭龙, 黄锦学, 等. 环境因子对矿质土壤呼吸影响的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(10): 2835-2844. | |
| [40] | Alster C J, Weller Z D, Vonfischer J C. A meta-analysis of temperature sensitivity as a microbial trait. Global Change Biology, 2018, 24(9): 4211-4224. |
| [41] | Song K C, Wang G H, Xu D M, et al. Soil organic carbon mineralization and its temperature sensitivity in desert steppe with different enclosure ages. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(3): 453-459. |
| 宋珂辰, 王国会, 许冬梅, 等. 不同封育年限荒漠草原土壤有机碳矿化及温度敏感性. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(3): 453-459. | |
| [42] | Mi J, Li J, Chen D, et al. Predominant control of moisture on soil organic carbon mineralization across a broad range of arid and semiarid ecosystems on the Mongolia plateau. Landscape Ecology, 2015, 30(9): 1683-1699. |
| [43] | Wang Q, He T, Liu J. Litter input decreased the response of soil organic matter decomposition to warming in two subtropical forest soils. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 33814. |
| [44] | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Eldridge D J, Ochoa V, et al. Soil microbial communities drive the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to global change in drylands across the globe. Ecology Letters, 2017, 20(10): 1295-1305. |
| [45] | Craine J, Spurr R, Mclauchlan K, et al. Landscape-level variation in temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon decomposition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(3): 373-375. |
| [1] | 冉健民, 宋小艳, 王丹, 王长庭. 退化高寒草甸土壤有机碳组分变化与增汇潜力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 38-52. |
| [2] | 王玉霞, 杜灵通, 易志远, 罗霄, 苏丽, 乔成龙, 薛斌. 宁夏贺兰山东麓葡萄产区土壤有机碳库空间变异及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 41-53. |
| [3] | 秦文利, 张静, 肖广敏, 崔素倩, 叶建勋, 智健飞, 张立锋, 谢楠, 冯伟, 刘振宇, 潘璇, 代云霞, 刘忠宽. 绿肥部分替代化肥氮对土壤物理性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 27-45. |
| [4] | 魏孔钦, 赵俊威, 张前兵. 施磷对紫花苜蓿土壤呼吸速率及活性有机碳组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 80-92. |
| [5] | 李思媛, 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤有机碳及土壤微生物生物量生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 58-70. |
| [6] | 郭鑫, 罗欢, 许雪梅, 马爱霞, 尚振艳, 韩天虎, 牛得草, 文海燕, 李旭东. 不同品质凋落物分解对黄土高原草地土壤有机碳及其稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 83-93. |
| [7] | 钱虹宇, 蒲玉琳, 郎山鑫, 李怡燃, 周南丁. 土壤有机磷矿化特征对高寒草甸退化及温度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 15-27. |
| [8] | 韩小雨, 郭宁, 李冬冬, 谢明阳, 焦峰. 氮添加对内蒙古不同草原生物量及土壤碳氮变化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 13-25. |
| [9] | 王星, 于双, 许冬梅, 宋珂辰. 不同恢复措施对退化荒漠草原土壤碳氮及其组分特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 26-35. |
| [10] | 刘慧霞, 董乙强, 崔雨萱, 刘星宏, 何盘星, 孙强, 孙宗玖. 新疆阿勒泰地区荒漠草地土壤有机碳特征及其环境影响因素分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 41-52. |
| [11] | 季波, 何建龙, 吴旭东, 王占军, 谢应忠, 蒋齐. 宁夏典型天然草地土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 24-35. |
| [12] | 王晓娇, 齐鹏, 蔡立群, 陈晓龙, 谢军红, 甘慧炯, 张仁陟. 培肥措施对旱地农田产量可持续性及土壤有机碳库稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 58-69. |
| [13] | 于双, 许冬梅, 许爱云, 刘金龙, 陶利波. 不同恢复措施对宁夏荒漠草原土壤碳氮储量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 12-19. |
| [14] | 张苗苗, 陈伟, 林丽, 张德罡, 吴玉鑫, 肖海龙. 青海省不同高寒草地土壤主要养分及可溶性有机碳特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 20-28. |
| [15] | 王旭洋, 李玉强, 连杰, 罗永清, 牛亚毅, 龚相文. CENTURY模型在不同生态系统的土壤有机碳动态预测研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 179-189. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||