

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 80-92.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023124
收稿日期:2023-04-17
修回日期:2023-05-16
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
张前兵
作者简介:E-mail: qbz102@163.com基金资助:
Kong-qin WEI( ), Jun-wei ZHAO, Qian-bing ZHANG(
), Jun-wei ZHAO, Qian-bing ZHANG( )
)
Received:2023-04-17
Revised:2023-05-16
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Qian-bing ZHANG
摘要:
探究施磷对紫花苜蓿土壤呼吸速率及活性有机碳组分含量的影响,明确不同施磷处理条件下苜蓿田土壤呼吸速率及土壤活性有机碳组分之间的关系,以期为人工草地土壤固碳和可持续发展提供数据支撑。本试验采用随机区组设计,设置0(P0)、50(P1)、100(P2)和150 kg·hm-2(P3)4种施磷水平,重复3次。研究不同施磷水平下紫花苜蓿0~60 cm土层的土壤有机碳(SOC)、微生物量碳(MBC)、溶解性有机碳(DOC)、颗粒有机碳(POC)、易氧化有机碳(EOC)含量、土壤温湿度及呼吸速率(RS)。结果表明,不同土层SOC、MBC、DOC、POC和EOC含量随施磷量增加而升高,在P3处理下达到最大,分别为15.77 g·kg-1、0.42 g·kg-1、0.34 g·kg-1、4.68 g·kg-1和2.06 g·kg-1,且显著大于P0处理(P<0.05)。SOC、MBC、DOC、POC及EOC在垂直分布上均以0~20 cm土层含量最高,分别占总含量的38.35%~41.58%、38.31%~39.49%、45.54%~46.65%、46.29%~47.35%和40.40%~44.17%。施磷处理使土壤RS提高了0.31%~14.90%,且刈割前后差异显著(P<0.05)。随施磷量增加,不同土层MBC、DOC、POC及EOC的敏感指数均呈上升趋势。施磷处理下0~30 cm土层微生物量碳敏感指数最高,30~60 cm土层易氧化有机碳敏感指数最高。建议用微生物量碳指示表层土壤有机碳的变化,而易氧化有机碳可指示深层土壤有机碳的变化。各活性有机碳组分有效率随施磷量增加变化规律不明显。结构方程结果表明,施磷可直接影响SOC含量,也可通过改变MBC、DOC、POC和EOC含量而间接影响SOC含量。综上,施磷提高了土壤RS,但持续磷输入整体增加了苜蓿田土层内SOC、MBC、DOC、POC和EOC含量,提高了固碳潜力及土壤质量,可为全球磷沉降背景下人工草地生态系统土壤有机碳动态变化及人工草地管理提供科学依据。
魏孔钦, 赵俊威, 张前兵. 施磷对紫花苜蓿土壤呼吸速率及活性有机碳组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 80-92.
Kong-qin WEI, Jun-wei ZHAO, Qian-bing ZHANG. Effects of phosphorus application on soil respiration rate and active organic carbon components of alfalfa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 80-92.
土层深度 Soil depth (cm) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | pH | 容重 Bulk weight (g·cm-3) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 21.56 | 7.59 | 1.54 | 1.18 | 0.53 | 145.47 | 19.30 | 119.8 |
表1 试验田耕层土壤理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of cultivated soil in the experimental field
土层深度 Soil depth (cm) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | pH | 容重 Bulk weight (g·cm-3) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 21.56 | 7.59 | 1.54 | 1.18 | 0.53 | 145.47 | 19.30 | 119.8 |
变异指标 Variation | 土壤有机碳SOC | 微生物量碳MBC | 溶解性有机碳DOC | 颗粒有机碳POC | 易氧化有机碳EOC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| P | 983.27 | ** | 1575.75 | ** | 835.88 | ** | 2034.25 | ** | 3354.33 | ** |
| D | 4109.20 | ** | 6705.61 | ** | 2324.46 | ** | 18778.21 | ** | 8570.09 | ** |
| S | 106.16 | ** | 1256.24 | ** | 14998.94 | ** | 156.56 | ** | 2607.10 | ** |
| P×D | 76.73 | ** | 18.79 | ** | 12.75 | ** | 68.34 | ** | 25.86 | ** |
| P×S | 18.14 | ** | 63.06 | ** | 41.66 | ** | 28.82 | ** | 176.18 | ** |
| D×S | 23.07 | ** | 274.55 | ** | 192.70 | ** | 89.71 | ** | 189.73 | ** |
| P×D×S | 7.55 | ** | 11.49 | ** | 11.19 | ** | 26018.00 | ** | 23.75 | ** |
表2 施磷水平、土层深度和茬次对各因子影响的方差分析
Table 2 Three-factor variance analysis of influence of phosphorus application level, soil depth and stubble times on each factor
变异指标 Variation | 土壤有机碳SOC | 微生物量碳MBC | 溶解性有机碳DOC | 颗粒有机碳POC | 易氧化有机碳EOC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| P | 983.27 | ** | 1575.75 | ** | 835.88 | ** | 2034.25 | ** | 3354.33 | ** |
| D | 4109.20 | ** | 6705.61 | ** | 2324.46 | ** | 18778.21 | ** | 8570.09 | ** |
| S | 106.16 | ** | 1256.24 | ** | 14998.94 | ** | 156.56 | ** | 2607.10 | ** |
| P×D | 76.73 | ** | 18.79 | ** | 12.75 | ** | 68.34 | ** | 25.86 | ** |
| P×S | 18.14 | ** | 63.06 | ** | 41.66 | ** | 28.82 | ** | 176.18 | ** |
| D×S | 23.07 | ** | 274.55 | ** | 192.70 | ** | 89.71 | ** | 189.73 | ** |
| P×D×S | 7.55 | ** | 11.49 | ** | 11.19 | ** | 26018.00 | ** | 23.75 | ** |
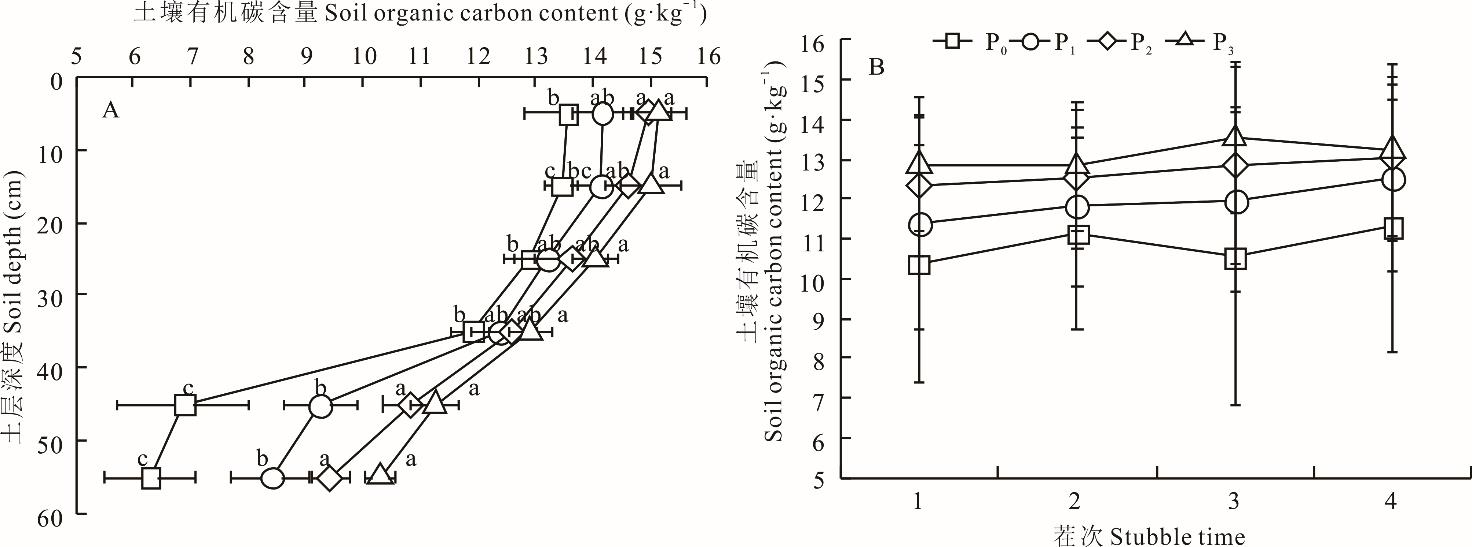
图1 不同施磷处理下土壤有机碳含量不同小写字母表示相同土层下不同施磷处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different phosphorus treatments under the same soil layer (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig. 1 Soil organic carbon content under different phosphorus treatments
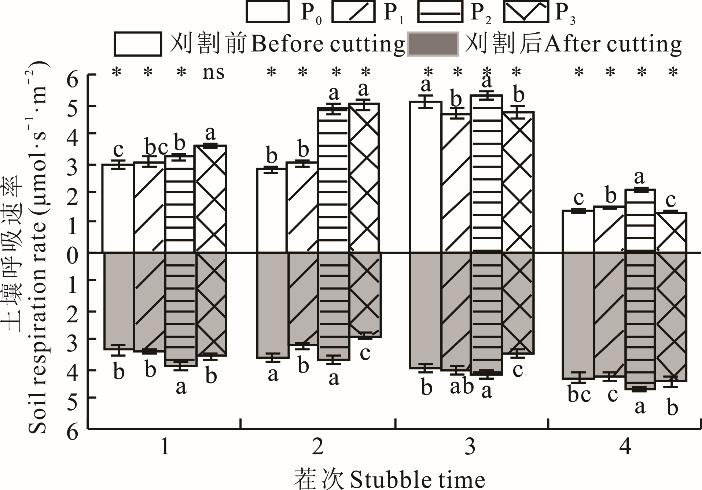
图7 不同施磷处理下土壤呼吸速率不同小写字母表示相同茬次不同施磷处理之间差异显著(P<0.05);*表示相同施磷处理刈割前后差异显著(P<0.05),ns表示无显著差异。Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference among different phosphorus application treatments under the same stubble (P<0.05). * indicates significant difference before and after cutting under the same phosphorus application treatment (P<0.05), ns indicate no significant difference.
Fig.7 Soil respiration rate under different phosphorus treatments
处理 Treatment | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | 拟合系数 Fitting coefficient (R2) | 温度敏感性系数 Temperature sensitivity coefficient (Q10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | RS=0.100e0.074T | 0.715* | 2.096 |
| P1 | RS=1.125e0.065T | 0.781* | 1.916 |
| P2 | RS=1.327e0.068T | 0.996** | 1.973 |
| P3 | RS=0.082e0.092T | 0.779* | 2.510 |
表3 土壤呼吸速率与温度的拟合方程及温度敏感性系数
Table 3 Fitting equation of soil respiration rate and temperature and temperature sensitivity coefficient
处理 Treatment | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | 拟合系数 Fitting coefficient (R2) | 温度敏感性系数 Temperature sensitivity coefficient (Q10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | RS=0.100e0.074T | 0.715* | 2.096 |
| P1 | RS=1.125e0.065T | 0.781* | 1.916 |
| P2 | RS=1.327e0.068T | 0.996** | 1.973 |
| P3 | RS=0.082e0.092T | 0.779* | 2.510 |
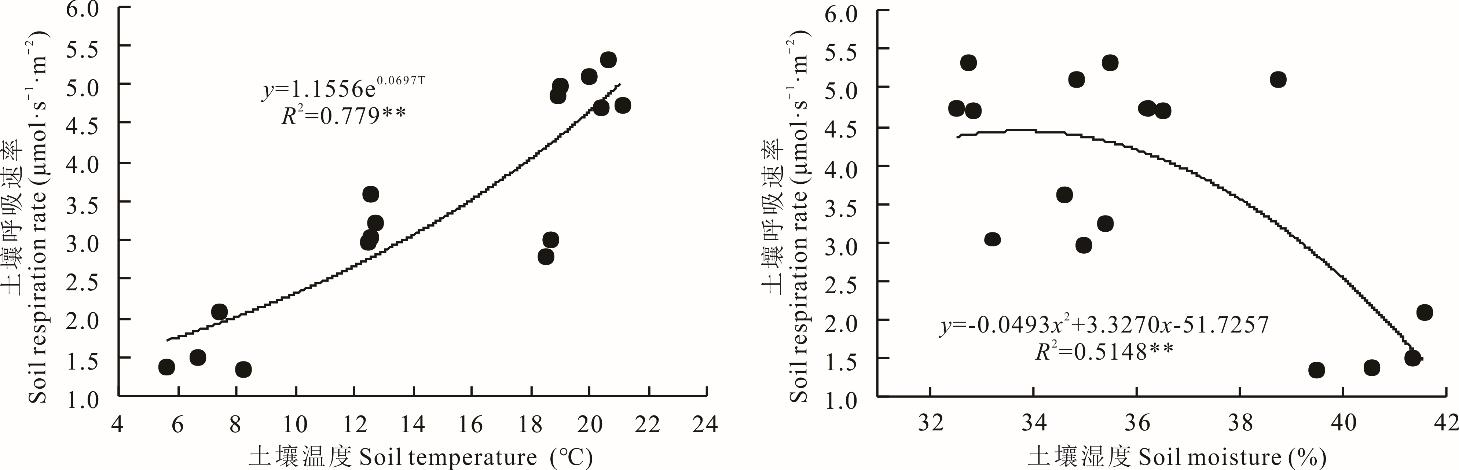
图8 土壤呼吸速率与土壤温湿度相关性分析**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。** means extremely significant correlation (P<0.01).
Fig. 8 Correlation analyse between soil respiration and soil temperature and moisture
处理 Treatment | 有机碳 SOC | 颗粒有机碳 POC | 溶解性有机碳 DOC | 易氧化有机碳 EOC | 微生物量碳 MBC | 土壤呼吸 RS | 温度 Temperature | 湿度 Moisture | 平均值 Average | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.026 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 4 |
| P1 | 0.478 | 0.373 | 0.333 | 0.295 | 0.343 | 0.000 | 0.356 | 0.702 | 0.360 | 3 |
| P2 | 0.807 | 0.642 | 0.867 | 0.636 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.731 | 0.327 | 0.751 | 2 |
| P3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.971 | 0.610 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.948 | 1 |
表4 测定指标隶属函数分析
Table 4 Analysis of membership function of measurement index
处理 Treatment | 有机碳 SOC | 颗粒有机碳 POC | 溶解性有机碳 DOC | 易氧化有机碳 EOC | 微生物量碳 MBC | 土壤呼吸 RS | 温度 Temperature | 湿度 Moisture | 平均值 Average | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.026 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 4 |
| P1 | 0.478 | 0.373 | 0.333 | 0.295 | 0.343 | 0.000 | 0.356 | 0.702 | 0.360 | 3 |
| P2 | 0.807 | 0.642 | 0.867 | 0.636 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.731 | 0.327 | 0.751 | 2 |
| P3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.971 | 0.610 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.948 | 1 |
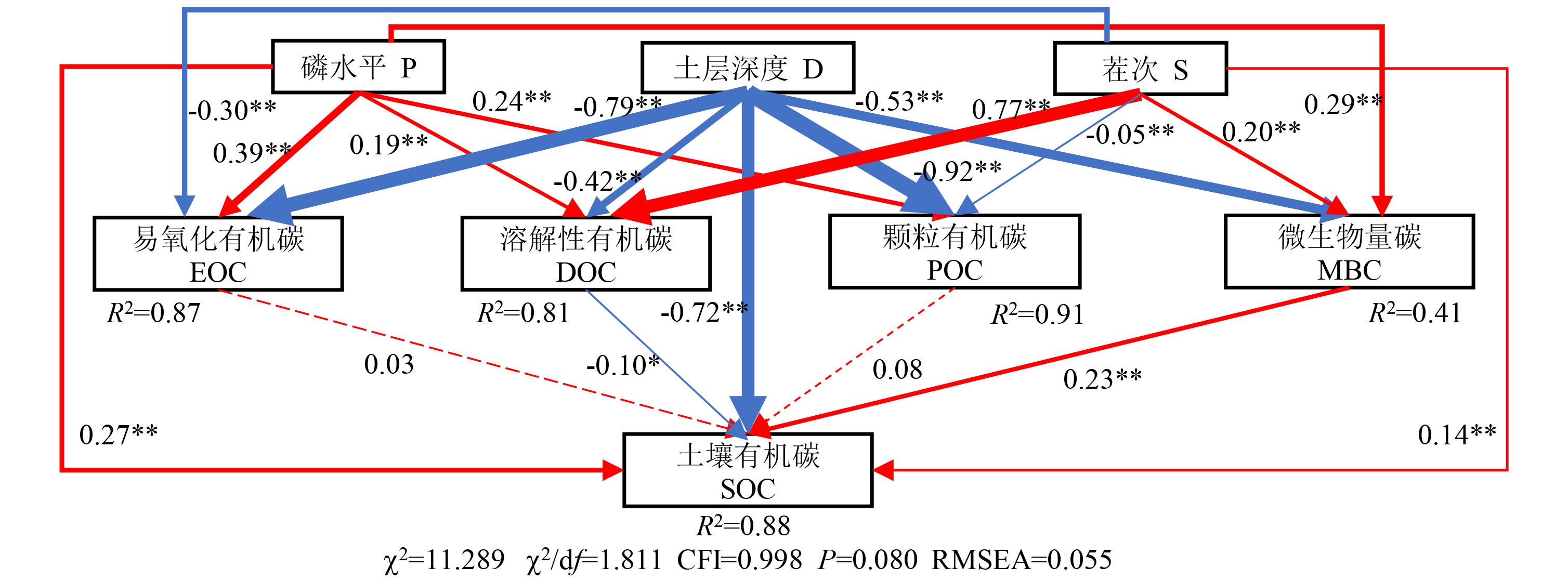
图9 土壤活性有机碳与土壤有机碳的结构方程模型P表示施磷水平,D表示土层深度,S表示茬次。红色表示正相关,蓝色表示负相关。虚线表示不显著,实线表示显著。线条粗细表示路径系数大小。*表示P<0.05;**表示P<0.01。P represents phosphorus application, D represents soil depth, S represents stubble times. Red shows a positive correlation and blue shows a negative correlation. The dotted line is not significant, the solid line is significant. The line thickness indicates the path coefficient. * indicates P<0.05; ** indicates P<0.01.
Fig. 9 Structural equation model of soil active organic carbon and soil organic carbon
| 1 | Kamran M, Yan Z, Jia Q, et al. Irrigation and nitrogen fertilization influence on alfalfa yield, nutritive value, and resource use efficiency in an arid environment. Field Crops Research, 2022, 284: 108587. |
| 2 | Xie H L, Yang Y P, Dong Y, et al. Analysis of the international development trend of alfalfa. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 740-750. |
| 谢华玲, 杨艳萍, 董瑜, 等. 苜蓿国际发展态势分析. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 740-750. | |
| 3 | Gu X D, Zhang F J, Wang T, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on growth and leaf nitrogen metabolism of alfalfa in alkaline soil in Yinchuan plain of Hetao basin. Peer Journal, 2022, 10(10): 13261. |
| 4 | Zhang J L, Nie J, Cao W D, et al. Long-term green manuring to substitute partial chemical fertilizer simultaneously improving crop productivity and soil quality in a double-rice cropping system. European Journal of Agronomy, 2023, 142: 126641. |
| 5 | Xu M G, Zhang X B, Sun N, et al. Advance in research of synergistic effects of soil carbon sequestration on crop yields improvement in croplands. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1441-1449. |
| 徐明岗, 张旭博, 孙楠, 等. 农田土壤固碳与增产协同效应研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1441-1449. | |
| 6 | Wang X, Yu D, Li C, et al. Characteristics of variations in the organic carbon fractions in paddy soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2016, 80(4): 983-991. |
| 7 | Zhang H, Niu L, Hu K, et al. Long-term effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated carbon and nitrogen in the North China Plain. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2021, 85(3): 732-745. |
| 8 | Li J H, Zhang R, Cheng B H, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on decomposition and accumulation of soil organic carbon in alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation and Development, 2020, 32(3): 1467-1477. |
| 9 | Wu C, Yan B, Jing H, et al. Application of organic and chemical fertilizers promoted the accumulation of soil organic carbon in farmland on the Loess Plateau. Plant and Soil, 2022, 483(1/2): 285-299. |
| 10 | Yao Y H, Zhang S B, Zhou J S, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on organic carbon mineralization and priming effect in a moso bamboo plantation soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 75(5): 1-15. |
| 姚易寒, 张少博, 周家树, 等. 氮磷添加对毛竹林土壤有机碳矿化及其激发效应的影响. 土壤学报, 2022, 75(5): 1-15. | |
| 11 | Ye L F, Liu H Y, Deng H D, et al. Effects of decadal nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on microbial taxonomic and functional attributes associated with soil organic carbon decomposition and concentration in an alpine meadow. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 46: 109790. |
| 12 | Hu A, Huang R, Liu G, et al. Effects of green manure combined with phosphate fertilizer on movement of soil organic carbon fractions in tropical sown pasture. Agronomy, 2022, 12(5): 1101. |
| 13 | Li J H, Cheng B H, Zhang R, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus additions accelerate decomposition of slow carbon pool and lower total soil organic carbon pool in alpine meadows. Land Degradation and Development, 2021, 32(4): 1761-1772. |
| 14 | Liu Q, Liang X, Dong P L, et al. Effects of different fertilization methods on farmland soil active organic carbon and carbon pool management indicators in loess hilly area. Soils, 2023, 55(2): 446-452. |
| 刘强, 梁鑫, 董佩丽, 等. 不同施肥措施对黄土丘陵区农田土壤有机碳组分和碳库管理指数的影响. 土壤, 2023, 55(2): 446-452. | |
| 15 | Liu H, Zhou G, Bai S H, et al. Differential response of soil respiration to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in a highly phosphorus-limited subtropical forest, China. Forest Ecology and Management, 2019, 448: 499-508. |
| 16 | Jiang Y, Gan X L, Cao F F, et al. Effects of short-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil respiration components in a subalpine grassland of Qilian Mountains. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(4): 2283-2292. |
| 江原, 甘小玲, 曹丰丰, 等. 短期氮磷添加对祁连山亚高山草地土壤呼吸组分的影响. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4): 2283-2292. | |
| 17 | Zhou J J, Chen Z F, Yang Q, et al. Response of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in farming-withdrawn grassland in the semiarid loess hilly-gully region. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 479-488. |
| 周俊杰, 陈志飞, 杨全, 等. 黄土丘陵区退耕草地土壤呼吸及其组分对氮磷添加的响应. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 479-488. | |
| 18 | Shen J, He Z M, Dong Q, et al. Effects of environmental factors on seasonal dynamics of soil respiration in coastal protection forests. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2022, 42(6): 640-647. |
| 沈健, 何宗明, 董强, 等. 环境因子对沿海防护林土壤呼吸季节动态的影响. 森林与环境学报, 2022, 42(6): 640-647. | |
| 19 | Lu X, Wen L, Sun H, et al. Responses of soil respiration to phosphorus addition in global grasslands: A meta-analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 349: 131413. |
| 20 | Shi J, Gong J, Baoyin T, et al. Short-term phosphorus addition increases soil respiration by promoting gross ecosystem production and litter decomposition in a typical temperate grassland in northern China. Catena, 2021, 197: 104952. |
| 21 | Zhang Q B, Yang L, Wang J, et al. Effects of different irrigation methods and fertilization measures on soil respiration and its component contributions in cotton field in arid region. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(12): 2420-2430. |
| 张前兵, 杨玲, 王进, 等. 干旱区不同灌溉方式及施肥措施对棉田土壤呼吸及各组分贡献的影响. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(12): 2420-2430. | |
| 22 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 23 | Chen S, Xu C, Yan J, et al. The influence of the type of crop residue on soil organic carbon fractions: An 11-year field study of rice-based cropping systems in southeast China. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 2016, 223: 261-269. |
| 24 | Zhang Y R, An H, Liu B R, et al. Effects of short-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil labile organic carbon in desert grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 12-24. |
| 张雅柔, 安慧, 刘秉儒, 等. 短期氮磷添加对荒漠草原土壤活性有机碳的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 12-24. | |
| 25 | Wu Z D, Ma S F, Lu J Y, et al. Responses of soil organic carbon components to long-term nitrogen addition in the Stipa baicalensis meadow steppe. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(2): 1-12. |
| 武振丹, 马尚飞, 卢俊艳, 等. 贝加尔针茅草甸草原土壤有机碳组分对长期氮素添加的响应. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(2): 1-12. | |
| 26 | Liu H, Hao Z, Yuan Y, et al. Application of mineral phosphorus fertilizer influences rhizosphere chemical and biological characteristics. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2023, 69(5): 771-784. |
| 27 | Zhao X Y, Guan M R, Sun M Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on litterfall production and nutrient dynamics in evergreen broad-leaved forests. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 44(6): 55-62. |
| 赵晓雅, 关梦冉, 孙孟瑶, 等. 氮磷添加对亚热带常绿阔叶林凋落物产量及其养分含量的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6): 55-62. | |
| 28 | Wei Y, Xiong X, Ryo M, et al. Repeated litter inputs promoted stable soil organic carbon formation by increasing fungal dominance and carbon use efficiency. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2022, 58(6): 619-631. |
| 29 | Yue X J, Huang P, Li Y H, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil microorganisms in arid and semi-arid areas of China and its influencing factors. World Forestry Research, 2022, 35(4): 64-69. |
| 岳雪娇, 黄沛, 李永华, 等. 中国干旱半干旱区土壤微生物分布特征及其影响因素. 世界林业研究, 2022, 35(4): 64-69. | |
| 30 | Sun Y L, Wei K Q, Liu X S, et al. Diurnal changes in photosynthesis and photosynthetic product partitioning in alfalfa in response to phosphorus application. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 85-94. |
| 孙延亮, 魏孔钦, 刘选帅, 等. 紫花苜蓿光合日进程及光合产物分配对施磷的响应. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 85-94. | |
| 31 | Wang G C, Xiao L J, Lin Z Q, et al. A global quantitative study of the contribution of plant root carbon inputs to non-root soil carbon pools. Science China Earth Sciences, 2023, 53(5): 1067-1082. |
| 王国成, 肖浏骏, 林子祺, 等. 植物根系碳输入对非根际土壤碳库贡献的全球定量研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2023, 53(5): 1067-1082. | |
| 32 | Shi J, Gong J, Li X, et al. Plant-microbial linkages regulate soil organic carbon dynamics under phosphorus application in a typical temperate grassland in northern China. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2022, 335: 108006. |
| 33 | Zhang W L, Kolbe H, Zhang R L. Research progress of SOC functions and transformation mechanisms. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(2): 317-331. |
| 张维理, Kolbe H, 张认连. 土壤有机碳作用及转化机制研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(2): 317-331. | |
| 34 | Luo R, Fan J, Wang W, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment accelerates soil organic carbon loss in alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 303-312. |
| 35 | Zhang Y R, An H, Wang B, et al. Effects of short-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition on unprotected soil organic carbon in desert grassland. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(1): 95-103. |
| 张雅柔, 安慧, 王波, 等. 短期氮磷添加对荒漠草原土壤非保护性有机碳的影响. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(1): 95-103. | |
| 36 | Patoine G, Eisenhauer N, Cesarz S, et al. Drivers and trends of global soil microbial carbon over two decades. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 4195. |
| 37 | Zhao J W, Li S Y, Sun Y L, et al. Fine root turnover of alfalfa in different soil horizons under different nitrogen and phosphorus levels. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 118-128. |
| 赵俊威, 李生仪, 孙延亮, 等. 不同氮磷水平下不同土层中紫花苜蓿细根周转特征. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 118-128. | |
| 38 | Wang B, Liang C, Yao H, et al. The accumulation of microbial necromass carbon from litter to mineral soil and its contribution to soil organic carbon sequestration. Catena, 2021, 207: 105622. |
| 39 | Wang B, An S, Liang C, et al. Microbial necromass as the source of soil organic carbon in global ecosystems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2021, 62: 108422. |
| 40 | Yuan Y, Li Y, Mou Z, et al. Phosphorus addition decreases microbial residual contribution to soil organic carbon pool in a tropical coastal forest. Global Change Biology, 2021, 27(2): 454-466. |
| 41 | Qu X, Wang X, Wu J, et al. Both carbon sequestration and yield are related to particulate organic carbon stability affected by organic amendment origins in mollisol. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2021, 21(9): 3044-3056. |
| 42 | Gao X, Zhao X S, Zhao F Y, et al. Effect of organic fertilizer on soil fertility and active organic carbon pool in monocultured peanut fields. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2023, 54(1): 67-76. |
| 高欣, 赵雪淞, 赵凤艳, 等. 有机培肥对连作花生土壤肥力及活性有机碳库的影响. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(1): 67-76. | |
| 43 | Zeng W, Zhang J, Wang W. Strong root respiration response to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in nitrogen-limited temperate forests. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642: 646-655. |
| [1] | 罗原骏, 蒲玉琳, 袁大刚, 李亚丽, 钱虹宇. 基于31P 核磁共振探究退化高寒湿地土壤磷素演变特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 1-12. |
| [2] | 唐璎, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 董霖. 甘肃不同区域青贮紫花苜蓿乳酸菌群落特征及其驱动因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 112-124. |
| [3] | 曲艳, 赵坤, 韩子晨, 吕世海, 沃强, 戎郁萍. 短期氮磷添加对呼伦贝尔辉河流域草地土壤温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 68-79. |
| [4] | 周建玲, 梁巧兰, 魏列新, 周其宇, 田龙, 陈应娥, 王存颖, 张国印. 不同症状类型苜蓿病毒病AMV病原检测及其寄主范围测定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 126-137. |
| [5] | 张鑫苗, 伍国强, 魏明. MAPK在植物响应逆境胁迫中的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 182-197. |
| [6] | 白旭琴, 贾春云, 李文栓, 李亚敏, 刘长风, 韩秀云, 褚美函, 巩宗强, 李晓军. 叶面喷施硒肥对紫花苜蓿富硒降镉效果的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 50-60. |
| [7] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷耦合下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量及磷素空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 104-115. |
| [8] | 徐蕊, 王峥, 王仪明, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿对轮作水稻产量和蔗糖代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 129-140. |
| [9] | 王宝强, 马文静, 王贤, 朱晓林, 赵颖, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [10] | 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 冯启贤, 李妍, 周燚, 刘一佳, 阳伏林, 周晶. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| [11] | 廖小琴, 王长庭, 刘丹, 唐国, 毛军. 氮磷配施对高寒草甸植物根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 160-174. |
| [12] | 王少鹏, 刘佳, 洪军, 林积圳, 张义, 史昆, 王赞. 紫花苜蓿MsPPR1基因的克隆及抗旱功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 49-60. |
| [13] | 李思媛, 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤有机碳及土壤微生物生物量生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 58-70. |
| [14] | 安晓霞, 张盈盈, 马春晖, 李曼, 张前兵. 施磷与接种丛枝菌根真菌对苜蓿产量和磷素利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 71-84. |
| [15] | 叶婷, 吴晓娟, 芦奕晓, 刘生娟, 姜卓慧, 杨惠敏. 混播比例对两种苜蓿混播草地产量和种群密度稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||