

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 26-42.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025107
刘娜1( ), 吴明玥1, 纪旭1, 胡舒萍1, 张芙宁1, 贾昕1,2,3(
), 吴明玥1, 纪旭1, 胡舒萍1, 张芙宁1, 贾昕1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-26
修回日期:2025-06-09
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
贾昕
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: xinjia@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Na LIU1( ), Ming-yue WU1, Xu JI1, Shu-ping HU1, Fu-ning ZHANG1, Xin JIA1,2,3(
), Ming-yue WU1, Xu JI1, Shu-ping HU1, Fu-ning ZHANG1, Xin JIA1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-26
Revised:2025-06-09
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Xin JIA
摘要:
以塔里木河流域的牧草植物为研究对象,旨在掌握该流域牧草植物资源的分布格局及其影响因子,为牧草资源的科、属、种层次开发利用提供理论支撑,同时基于将营养成分相似性的牧草划分整理,为塔里木河流域潜在高营养价值牧草品种的筛选与替代提供了理论依据。通过整合历史文献、野外调查及在线平台数据,更新了塔里木河流域牧草植物名录并分析了其科属种的组成及分布格局;利用冗余分析(RDA)探讨了人为、气候和土壤因子对不同牧草类群和生活型植物分布的影响;基于主成分分析(PCA)对营养价值相似的牧草植物进行了聚类分析。结果表明:1)塔里木河流域牧草植物共计41科153属269种,呈沿塔里木盆地边缘分布的特点,主要集中于北部和静县、西部乌恰县、西南部叶城县、和田县、东部若羌县及中部阿克苏市;2)年均温(MAT)与地方生产总值(GDP)是影响牧草类群区域分布的主要因子,贡献率达66.8%,年均温是影响牧草植物不同生活型区域分布差异的主要因子,其贡献率达62.2%,pH、速效钾(AK)为次要因子,贡献率分别为13.1%和10.8%,土壤有机质(SOM)仅对牧草类群植物分布有影响;3)牧草植物间的养分相似性独立于其系统发育关系及牧草等级划分。
刘娜, 吴明玥, 纪旭, 胡舒萍, 张芙宁, 贾昕. 塔里木河流域牧草植物分布格局与养分分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 26-42.
Na LIU, Ming-yue WU, Xu JI, Shu-ping HU, Fu-ning ZHANG, Xin JIA. Analysis of the distribution pattern and nutrition profiles of forage plants in the Tarim River Basin[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 26-42.
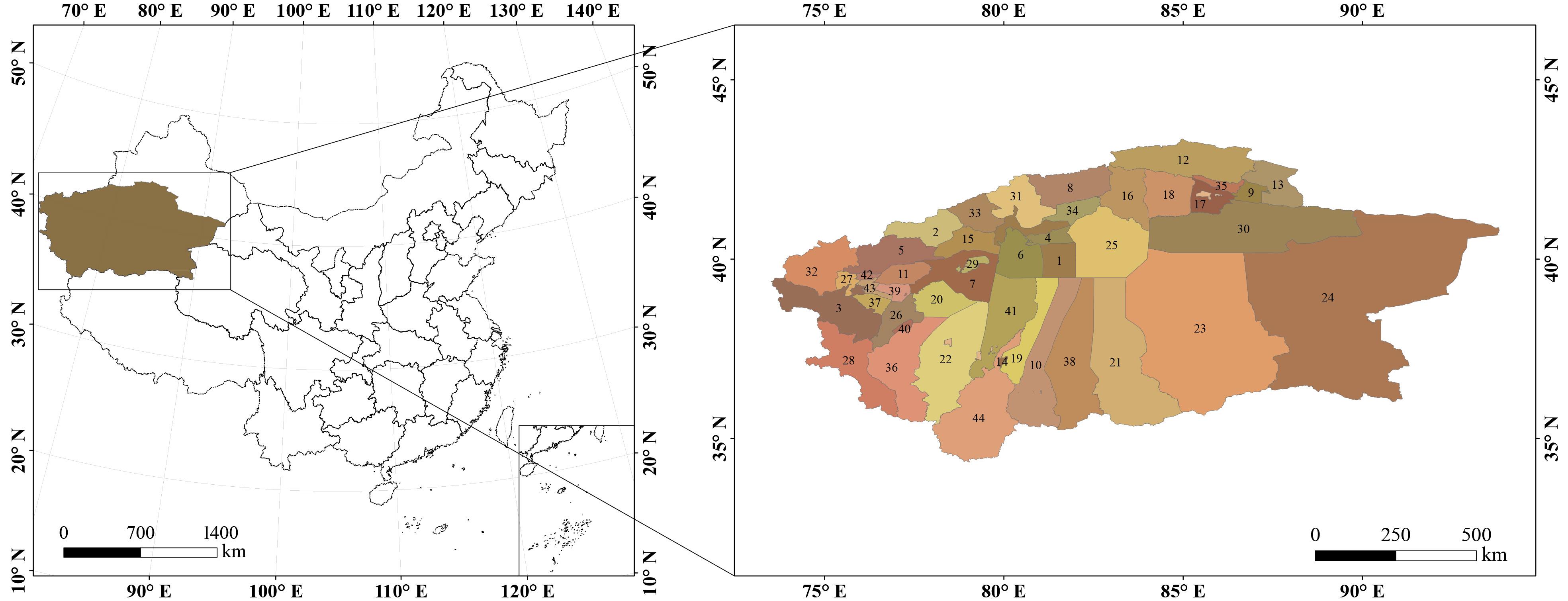
图1 塔里木河流域县域行政区划概况1: 阿克苏市Aksu City; 2: 阿合奇县Akqi County; 3: 阿克陶县Akto County; 4: 阿拉尔市Alar City; 5: 阿图什市Artux City; 6: 阿瓦提县Awat County; 7: 巴楚县Bachu County; 8:拜城县Bai County; 9: 博湖县Bohu County; 10: 策勒县Qira County; 11: 伽师县Jiashi County; 12: 和静县Hejing County; 13: 和硕县Hoxud County; 14: 和田市Hotan City; 15: 柯坪县Keping County; 16: 库车市Kucha City; 17: 库尔勒市Korla City; 18: 轮台县Luntai County; 19: 洛浦县Lop County; 20: 麦盖提县Makit County; 21: 民丰县Minfeng County; 22: 皮山县Pishan County; 23: 且末县Qiemo County; 24: 若羌县Ruoqiang County; 25: 沙雅县Shaya County; 26: 莎车县Yarkant County; 27: 疏附县Shufu County; 28: 塔什库尔干塔吉克自治县Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County; 29: 图木舒克市Tumushuke City; 30: 尉犁县Yuli County; 31: 温宿县Wensu County; 32: 乌恰县Wuqia County; 33: 乌什县Uqturpan County; 34: 新和县Xinhe County; 35: 焉耆回族自治县Yanqi Hui Autonomous County; 36: 叶城县Yecheng County; 37: 英吉沙县Yingjisha County; 38: 于田县Yutian County; 39: 岳普湖县Yopurga County; 40: 泽普县Zepu County; 41: 墨玉县Moyu County; 42: 喀什市Kashgar City; 43: 疏勒县Shule County; 44: 和田县Hotan County. 下同The same below. 基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2762号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2762 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 Overview of county-level administrative divisions in the Tarim River Basin
科名(科内物种数) Family name (Number of species in the family) | 属名(属内物种数) Genus name (Number of species in the genus) | |
|---|---|---|
| 刺柏属Juniperus (1) | ||
| 麻黄属Ephedra (1) | ||
| 杨属Populus (3) | ||
| 榆属Ulmus (1) | ||
| 荨麻属Urtica (1) | ||
| 木蓼属Atraphaxis (3);沙拐枣属Calligonum (8);蓼属Persicaria (3);拳参属Bistorta (1);酸模属Rumex (1) | ||
| 裸果木属Gymnocarpos (1) | ||
| 沙蓬属Agriophyllum (1);假木贼属Anabasis (2);滨藜属Atriplex (4);樟味藜属Camphorosma (1);角果藜属Ceratocarpus (1);藜属Chenopodium (2);红叶藜属Oxybasis (1);虫实属Corispermum (1);盐节木属Halocnemum (1);盐生草属Halogeton (2);盐穗木属Halostachys (1);梭梭属Haloxylon (2);戈壁藜属Iliamna (1);盐爪爪属Kalidium (5);驼绒藜属Krascheninnikovia (3);盐角草属Salicornia (2);山猪毛菜属Oreosalsola (2);碱猪毛菜属Soda (4);猪毛菜属Salsola (2);合头藜属Sympegma (1);苋属Amaranthus (1);腺毛藜属Dysphania (1);麻叶藜属Chenopodium (1);沙冰藜属Bassia (1);雾冰藜属Grubovia (1) | ||
| 铁线莲属Clematis (4) | ||
| 山柑属Capparis (1) | ||
| 独行菜属Lepidium (2);涩芥属Strigosella (1);念珠芥属Neotorularia (1);四齿芥属Tetracme (1) | ||
| 委陵菜属Potentilla (4);毛莓草属Sibbaldia (2);金露梅属Dasiphora (1);蕨麻属Argentina (1);蔷薇属Rosa (1);悬钩子属Rubus (1);地榆属Sanguisorba (1);羽衣草属Alchemilla (1) | ||
| 骆驼刺属Alhagi (1);紫穗槐属Amorpha (1);黄芪属Astragalus (3);锦鸡儿属Caragana (5);甘草属Glycyrrhiza (4);百脉根属Lotus (1);苜蓿属Medicago (3);草木樨属Melilotus (2);棘豆属Oxytropis (1);车轴草属Trifolium (4);刺槐属Robinia (1);野豌豆属Vicia (2) | ||
| 牻牛儿苗属Erodium (1);老鹳草属Geranium (1) | ||
| 白刺属Nitraria (4);骆驼蓬属Peganum (3);驼蹄瓣属Zygophyllum (2) | ||
| 远志属Polygala (1) | ||
| 木槿属Hibiscus (1);锦葵属Malva (1) | ||
| 胡颓子属Elaeagnus (1);沙棘属Hippophae (1) | ||
| 红砂属Reaumuria (2);柽柳属Tamarix (5);水柏枝属Myricaria (1) | ||
| 柳兰属Chamerion (1) | ||
| 锁阳属Cynomorium (1) | ||
| 珍珠菜属Lysimachia (1) | ||
| 补血草属Limonium (1) | ||
| 旋花属Convolvulus (2) | ||
| 青兰属Dracocephalum (1) | ||
| 车前属Plantago (1) | ||
| 亚菊属Ajania (1);蒿属Artemisia (11);紫菀木属Asterothamnus (1);蓝刺头属Echinops (1);旋覆花属Inula (1);花花柴属Karelinia (1);栉叶蒿属Neopallasia (1);鸦葱属Takhtajaniantha (2);苦苣菜属Sonchus (2);苦荬菜属Ixeris (1);绢蒿属Seriphidium (2);莴苣属Lactuca (2);蓟属Cirsium (1);紫菀属Aster (2);紫菀木属Asterothamnus (1)火绒草属Leontopodium (1);漏芦属Rhaponticum (1);飞蓬属Erigeron (1) | ||
| 水麦冬属Triglochin (1) | ||
| 芨芨草属Neotrinia (2);獐毛属Aeluropus (2);冰草属Agropyron (1);三芒草属Aristida (1);雀麦属Bromus (1);拂子茅属Calamagrostis (3);隐子草属Cleistogenes (1);披碱草属Elymus (6);九顶草属Enneapogon (1);旱麦草属Eremopyrum (1);洽草属Koeleria (1);狼尾草属Pennisetum (1);芦苇属Phragmites (1);狗尾草属Setaria (1);针茅属Stipa (7);稗属Echinochloa (1);甘蔗属Saccharum (1);狗牙根属Cynodon (1);虎尾草属Chloris (1);黄花茅属Anthoxanthum (1);剪股颖属Agrostis (1);碱茅属Puccinellia (1);孔颖草属Bothriochloa (1);赖草属Leymus (2);马唐属Digitaria (1);新麦草属Psathyrostachys (1);鸭茅属Dactylis (1);偃麦草属Elytrigia (1);燕麦属Avena (1);虉草属Phalaris (1);早熟禾属Poa (2);大麦属Hordeum (1);羊茅属Festuca (8);棒头草属Polypogon (1);画眉草属Eragrostis (1);荩草属Arthraxon (1);细柄茅属Ptilagrostis (1);异燕麦属Helictotrichon (1) | ||
| 榕属Ficus (1) | ||
| 扁穗草属Blysmus (2);薹草属Carex (7) | ||
| 泽泻属Alisma (1) | ||
| 葱属Allium (2) | ||
| 卫矛属Euonymus (1) | ||
| 香蒲属Typha (2) | ||
| 拉拉藤属Galium (1) | ||
| 牛舌草属Anchusa (1) | ||
| 灯芯草属Juncus (2) | ||
| 马齿苋属Portulaca (1) | ||
表1 塔里木河流域牧草植物科属物种数
Table 1 List of the number of species in each family and genus
科名(科内物种数) Family name (Number of species in the family) | 属名(属内物种数) Genus name (Number of species in the genus) | |
|---|---|---|
| 刺柏属Juniperus (1) | ||
| 麻黄属Ephedra (1) | ||
| 杨属Populus (3) | ||
| 榆属Ulmus (1) | ||
| 荨麻属Urtica (1) | ||
| 木蓼属Atraphaxis (3);沙拐枣属Calligonum (8);蓼属Persicaria (3);拳参属Bistorta (1);酸模属Rumex (1) | ||
| 裸果木属Gymnocarpos (1) | ||
| 沙蓬属Agriophyllum (1);假木贼属Anabasis (2);滨藜属Atriplex (4);樟味藜属Camphorosma (1);角果藜属Ceratocarpus (1);藜属Chenopodium (2);红叶藜属Oxybasis (1);虫实属Corispermum (1);盐节木属Halocnemum (1);盐生草属Halogeton (2);盐穗木属Halostachys (1);梭梭属Haloxylon (2);戈壁藜属Iliamna (1);盐爪爪属Kalidium (5);驼绒藜属Krascheninnikovia (3);盐角草属Salicornia (2);山猪毛菜属Oreosalsola (2);碱猪毛菜属Soda (4);猪毛菜属Salsola (2);合头藜属Sympegma (1);苋属Amaranthus (1);腺毛藜属Dysphania (1);麻叶藜属Chenopodium (1);沙冰藜属Bassia (1);雾冰藜属Grubovia (1) | ||
| 铁线莲属Clematis (4) | ||
| 山柑属Capparis (1) | ||
| 独行菜属Lepidium (2);涩芥属Strigosella (1);念珠芥属Neotorularia (1);四齿芥属Tetracme (1) | ||
| 委陵菜属Potentilla (4);毛莓草属Sibbaldia (2);金露梅属Dasiphora (1);蕨麻属Argentina (1);蔷薇属Rosa (1);悬钩子属Rubus (1);地榆属Sanguisorba (1);羽衣草属Alchemilla (1) | ||
| 骆驼刺属Alhagi (1);紫穗槐属Amorpha (1);黄芪属Astragalus (3);锦鸡儿属Caragana (5);甘草属Glycyrrhiza (4);百脉根属Lotus (1);苜蓿属Medicago (3);草木樨属Melilotus (2);棘豆属Oxytropis (1);车轴草属Trifolium (4);刺槐属Robinia (1);野豌豆属Vicia (2) | ||
| 牻牛儿苗属Erodium (1);老鹳草属Geranium (1) | ||
| 白刺属Nitraria (4);骆驼蓬属Peganum (3);驼蹄瓣属Zygophyllum (2) | ||
| 远志属Polygala (1) | ||
| 木槿属Hibiscus (1);锦葵属Malva (1) | ||
| 胡颓子属Elaeagnus (1);沙棘属Hippophae (1) | ||
| 红砂属Reaumuria (2);柽柳属Tamarix (5);水柏枝属Myricaria (1) | ||
| 柳兰属Chamerion (1) | ||
| 锁阳属Cynomorium (1) | ||
| 珍珠菜属Lysimachia (1) | ||
| 补血草属Limonium (1) | ||
| 旋花属Convolvulus (2) | ||
| 青兰属Dracocephalum (1) | ||
| 车前属Plantago (1) | ||
| 亚菊属Ajania (1);蒿属Artemisia (11);紫菀木属Asterothamnus (1);蓝刺头属Echinops (1);旋覆花属Inula (1);花花柴属Karelinia (1);栉叶蒿属Neopallasia (1);鸦葱属Takhtajaniantha (2);苦苣菜属Sonchus (2);苦荬菜属Ixeris (1);绢蒿属Seriphidium (2);莴苣属Lactuca (2);蓟属Cirsium (1);紫菀属Aster (2);紫菀木属Asterothamnus (1)火绒草属Leontopodium (1);漏芦属Rhaponticum (1);飞蓬属Erigeron (1) | ||
| 水麦冬属Triglochin (1) | ||
| 芨芨草属Neotrinia (2);獐毛属Aeluropus (2);冰草属Agropyron (1);三芒草属Aristida (1);雀麦属Bromus (1);拂子茅属Calamagrostis (3);隐子草属Cleistogenes (1);披碱草属Elymus (6);九顶草属Enneapogon (1);旱麦草属Eremopyrum (1);洽草属Koeleria (1);狼尾草属Pennisetum (1);芦苇属Phragmites (1);狗尾草属Setaria (1);针茅属Stipa (7);稗属Echinochloa (1);甘蔗属Saccharum (1);狗牙根属Cynodon (1);虎尾草属Chloris (1);黄花茅属Anthoxanthum (1);剪股颖属Agrostis (1);碱茅属Puccinellia (1);孔颖草属Bothriochloa (1);赖草属Leymus (2);马唐属Digitaria (1);新麦草属Psathyrostachys (1);鸭茅属Dactylis (1);偃麦草属Elytrigia (1);燕麦属Avena (1);虉草属Phalaris (1);早熟禾属Poa (2);大麦属Hordeum (1);羊茅属Festuca (8);棒头草属Polypogon (1);画眉草属Eragrostis (1);荩草属Arthraxon (1);细柄茅属Ptilagrostis (1);异燕麦属Helictotrichon (1) | ||
| 榕属Ficus (1) | ||
| 扁穗草属Blysmus (2);薹草属Carex (7) | ||
| 泽泻属Alisma (1) | ||
| 葱属Allium (2) | ||
| 卫矛属Euonymus (1) | ||
| 香蒲属Typha (2) | ||
| 拉拉藤属Galium (1) | ||
| 牛舌草属Anchusa (1) | ||
| 灯芯草属Juncus (2) | ||
| 马齿苋属Portulaca (1) | ||
科类别 Categories of families | 科Family | 属Genus | 种Species | 属类别 Categories of genera | 属Genus | 种Species | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
数量 Number (No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量 Number(No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量 Number (No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量 Number (No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量Number (No.) | 占比Percentage (%) | ||
| 大型科Large family (≥10) | 6 | 15 | 196 | 73 | 107 | 70 | 大型属Large genus (≥10) | 1 | 1 | 11 | 4 |
| 中型科Medium-sized family (5~9) | 4 | 10 | 31 | 12 | 13 | 8 | 中型属Medium-sized genus (5~9) | 8 | 5 | 51 | 18 |
| 小型科Small family (2~4) | 8 | 20 | 19 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 小型属Small genus (2~4) | 42 | 27 | 105 | 39 |
| 单种科Monotypic family (1) | 23 | 55 | 23 | 8 | 23 | 15 | 单种属Monotypic genus (1) | 102 | 67 | 102 | 39 |
表2 塔里木河流域牧草植物科属分析
Table 2 Analysis of family and genus of forage plants in Tarim River Basin
科类别 Categories of families | 科Family | 属Genus | 种Species | 属类别 Categories of genera | 属Genus | 种Species | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
数量 Number (No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量 Number(No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量 Number (No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量 Number (No.) | 占比 Percentage (%) | 数量Number (No.) | 占比Percentage (%) | ||
| 大型科Large family (≥10) | 6 | 15 | 196 | 73 | 107 | 70 | 大型属Large genus (≥10) | 1 | 1 | 11 | 4 |
| 中型科Medium-sized family (5~9) | 4 | 10 | 31 | 12 | 13 | 8 | 中型属Medium-sized genus (5~9) | 8 | 5 | 51 | 18 |
| 小型科Small family (2~4) | 8 | 20 | 19 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 小型属Small genus (2~4) | 42 | 27 | 105 | 39 |
| 单种科Monotypic family (1) | 23 | 55 | 23 | 8 | 23 | 15 | 单种属Monotypic genus (1) | 102 | 67 | 102 | 39 |
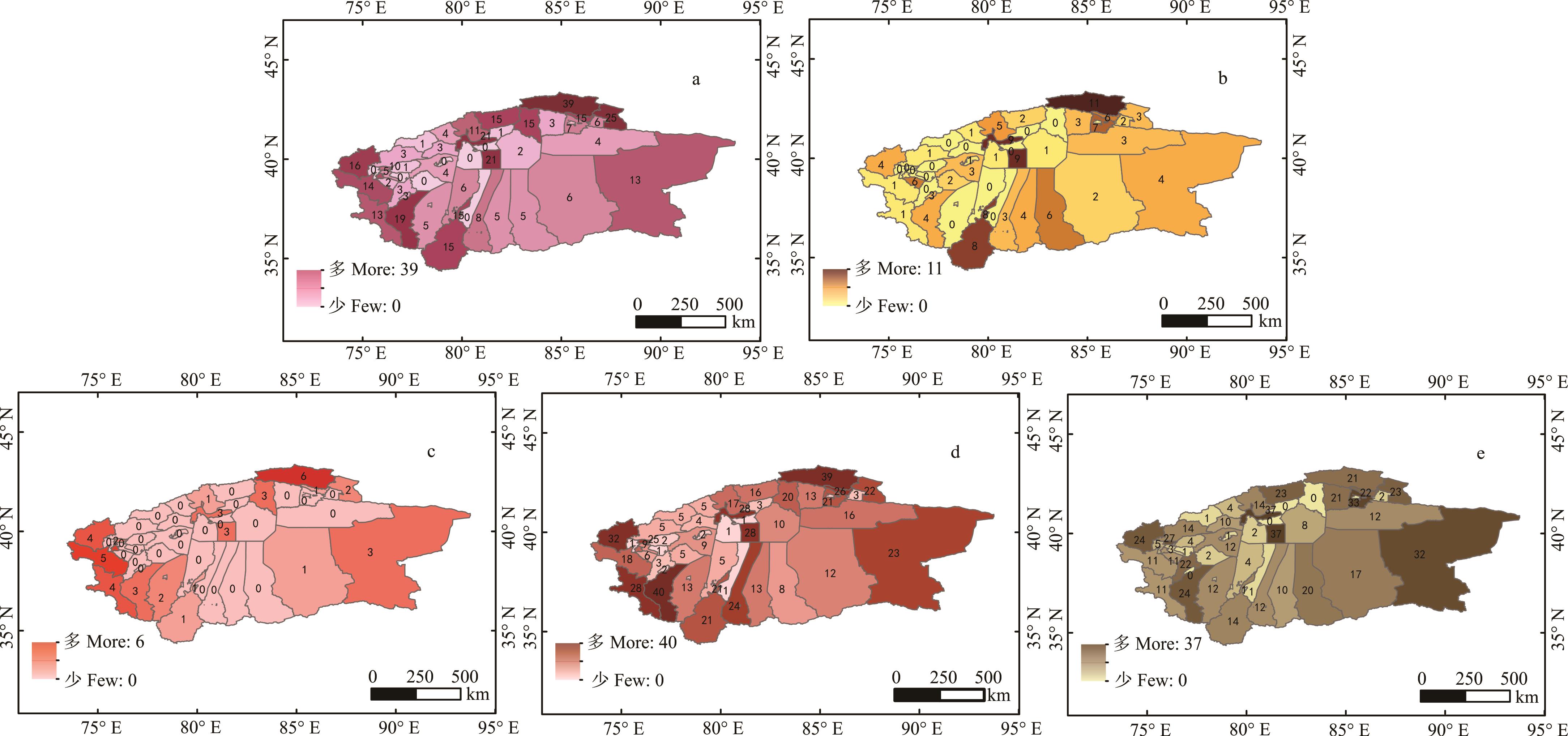
图2 塔里木河流域牧草植物类群分布a, b, c, d, e分别为禾本科、豆科、莎草科、其他科及灌木植物分布。a, b, c, d, e were the distribution of Poaceae forage plants, Leguminous forage plants, Cyperaceae forage plants, forage plants from other families and shrub plants. 基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2762号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2762 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.2 Distribution of forage plant communities in the Tarim River Basin
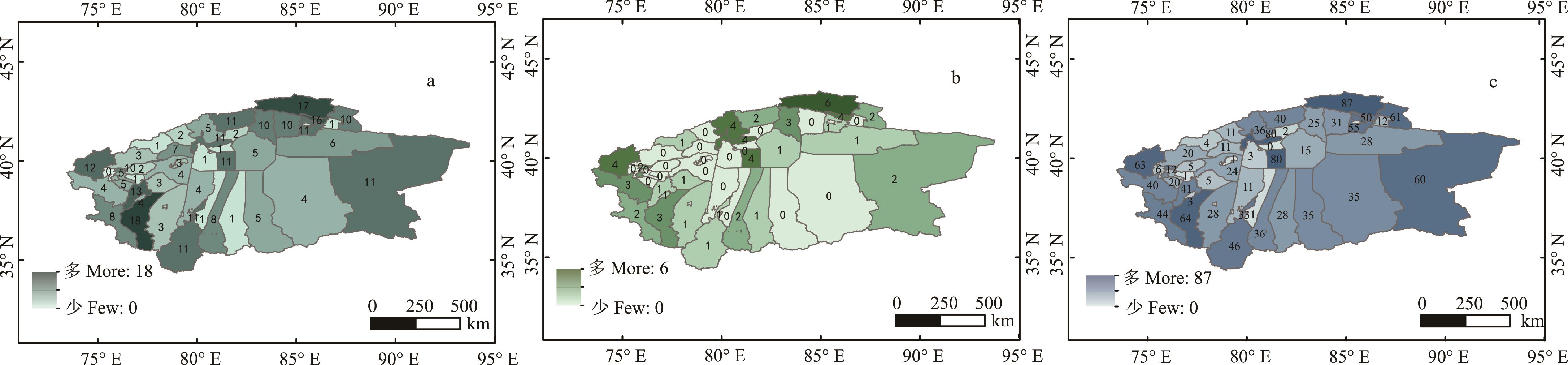
图3 塔里木河流域牧草植物生活型分布a、b、c分别代表一年生、两年生及多年生牧草植物分布。a, b, c were the distribution of annual forage plants, biennial forage plants and perennial forage plants. 基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2762号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2023) 2762 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.3 Life-form distribution of forage plants in the Tarim River Basin

图4 不同生活型物种数(a)和牧草类群物种数(b)与13个影响因子的相关性热图*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001.
Fig.4 Heatmap of correlation between 13 influencing factors and the number of species in different life forms (a) and the number of species of forage taxa (b)
生活型 Life forms | 年均温Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 年均降水Annual precipitation (AP) | pH | 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | 碱解氮Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN) | 速效钾Available potassium (AK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一年生Annual | -0.386* | / | -0.393** | 0.320* | 0.351* | -0.377* |
| 两年生Biennial | -0.526** | 0.525** | -0.460** | 0.413** | 0.497** | -0.384* |
| 多年生Perennial | -0.541*** | / | -0.423** | / | 0.336* | -0.374* |
表 3 对塔里木河流域不同生活型牧草植物分布具有显著影响的因子
Table 3 Factors that have significant impacts on the distribution of forage plants with different life forms in the Tarim River Basin
生活型 Life forms | 年均温Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 年均降水Annual precipitation (AP) | pH | 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | 碱解氮Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN) | 速效钾Available potassium (AK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一年生Annual | -0.386* | / | -0.393** | 0.320* | 0.351* | -0.377* |
| 两年生Biennial | -0.526** | 0.525** | -0.460** | 0.413** | 0.497** | -0.384* |
| 多年生Perennial | -0.541*** | / | -0.423** | / | 0.336* | -0.374* |
牧草类群 Forage plant groups | 年均温Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 年均降水Annual precipitation (AP) | 地方生产总值Gross domestic product (GDP) | pH | 土壤有机质Soil organic matter | 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | 碱解氮Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN) | 速效钾Available potassium (AK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 禾本科Poaceae | -0.582** | 0.473** | / | -0.602** | / | 0.414** | 0.555** | -0.457** |
| 豆科Fabaceae | -0.325* | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 莎草科Cyperaceae | -0.582** | 0.380* | / | -0.515** | 0.332* | 0.424** | 0.411** | -0.536** |
| 其他科Other family | -0.597** | / | / | -0.471** | / | 0.340* | 0.340* | -0.458** |
| 灌木Shrub | -0.321* | / | 0.334* | / | / | / | / | / |
表4 对塔里木河流域不同牧草类群牧草植物分布具有显著影响的因子
Table 4 Factors significantly influencing the distribution of pasture plants of different forage taxa in the Tarim River Basin
牧草类群 Forage plant groups | 年均温Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 年均降水Annual precipitation (AP) | 地方生产总值Gross domestic product (GDP) | pH | 土壤有机质Soil organic matter | 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | 碱解氮Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (AN) | 速效钾Available potassium (AK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 禾本科Poaceae | -0.582** | 0.473** | / | -0.602** | / | 0.414** | 0.555** | -0.457** |
| 豆科Fabaceae | -0.325* | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 莎草科Cyperaceae | -0.582** | 0.380* | / | -0.515** | 0.332* | 0.424** | 0.411** | -0.536** |
| 其他科Other family | -0.597** | / | / | -0.471** | / | 0.340* | 0.340* | -0.458** |
| 灌木Shrub | -0.321* | / | 0.334* | / | / | / | / | / |
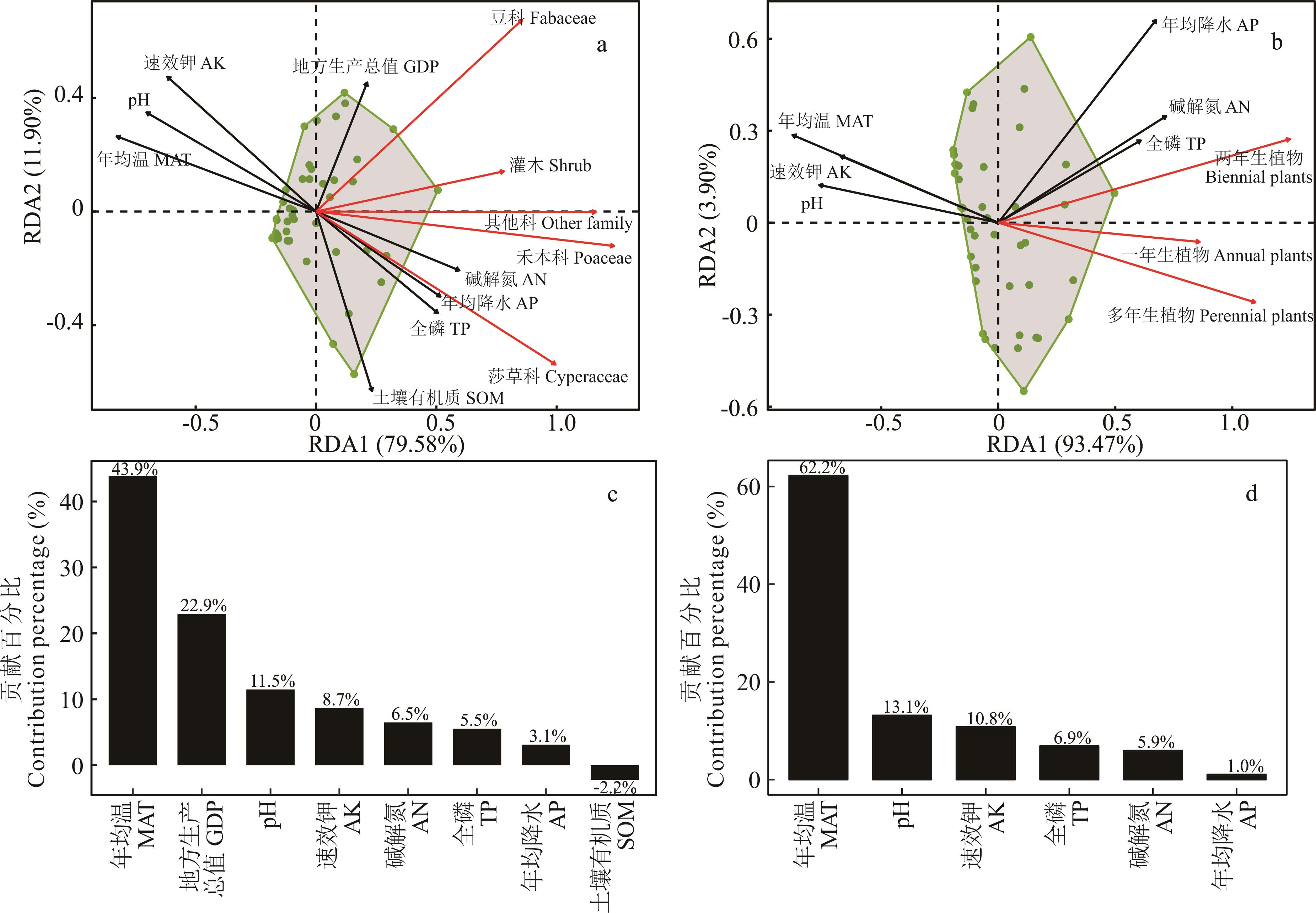
图5 牧草类群、生活型与环境因子冗余分析及影响其分布的环境因子贡献百分比a、b分别为牧草类群及生活型对环境因子的冗余分析,c、d分别为影响草本类群与生活型物种数的环境因子贡献百分比。a, b were redundancy analysis (RDA) showing the relationship between life forms and environmental factors; c, d were the percentage contribution of environmental factors with affecting the distribution of forage taxa and influencing the distribution of life forms.
Fig.5 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of forage groups, life forms, and environmental factors, along with the percentage contribution of environmental factors influencing
| [1] | Ma F J, Feng L S, Yang S, et al. Current status and development and utilization countermeasures of grazing germplasm resources in Liaoning Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(1): 50-54. |
| 马凤江, 冯良山, 杨姝, 等. 辽宁省牧草种质资源现状及开发利用对策.安徽农业科学, 2023, 51(1): 50-54. | |
| [2] | Yan Q, Ma Y S, Shi J J. Study on cold resistance of typical suitable cultivated forage grass in Sanjiangyuan region. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary, 2007(12): 64-66. |
| 严青, 马玉寿, 施建军. 三江源区典型适宜栽培牧草的抗寒性研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2007(12): 64-66. | |
| [3] | Zeng B, Zhang X Q, Peng Y, et al. Analysis on the drought tolerance of Dactylis glomerata in greenhouse. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2006(1): 103-106. |
| 曾兵, 张新全, 彭燕, 等. 优良牧草鸭茅的温室抗旱性研究. 湖北农业科学, 2006(1): 103-106. | |
| [4] | Zhang S Y, Wang S Z, Yang S L, et al. Study on salt endurance of turf-type Poa pratensis varieties. Journal of Zhelimu Animal Husbandry College, 1999(4): 2-6. |
| 张淑艳, 王世珍, 杨双连, 等. 坪用草地早熟禾品种耐盐性的比较研究. 哲里木畜牧学院学报, 1999(4): 2-6. | |
| [5] | Jing H C, Wang T, Lin R C, et al. Strengthen the research of forage basic biology to ensure forage seed industry and national food security. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 719-724. |
| 景海春, 王台, 林荣呈, 等. 加强饲草基础生物学研究,保障饲草种业与国家大粮食安全. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 719-724. | |
| [6] | Fang Y. Research on forage germplasm resources and breeding. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 27(20): 26-27. |
| 方媛. 牧草种质资源与育种研究概况. 安徽农学通报, 2021, 27(20): 26-27. | |
| [7] | Baoyin H X G, Wang Z W, Alata. Research progress of forage breeding in China. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2010, 31(Z1): 331-334. |
| 宝音贺希格, 王忠武, 阿拉塔. 我国牧草育种研究进展. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2010, 31(Z1): 331-334. | |
| [8] | Guo C Y, Fang Y Y, Yi F Y, et al. Current status of protection and utilization of pasture germplasm resources in China. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2024, 45(6): 81-86. |
| 郭呈宇, 房永雨, 伊风艳, 等. 我国牧草种质资源保护与利用现状. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2024, 45(6): 81-86. | |
| [9] | Wang Y H. The current situation and protection countermeasures of forage germplasm resources in Gansu Province. China Animal Industry, 2023(22): 28-29. |
| 王银花. 甘肃地区牧草种质资源现状及保护对策. 中国畜牧业, 2023(22): 28-29. | |
| [10] | Ma L X, Xin X Y, Sun Z Y, et al. Effect of phosphate fertilizer on forage yield in alpine meadow grassland. Grassland and Turf, 2018, 38(3): 17-22. |
| 马隆喜, 辛小云, 孙志英, 等. 施磷肥对高寒草甸草原牧草的增产效应研究. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(3): 17-22. | |
| [11] | Wang Y F. Mechanism of increasing yield of intercropping and mixed cropping patterns of (Medicago sativa L). and gramineous crops. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 王玉芬. 苜蓿与不同禾本科牧草间混作增产效应. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. | |
| [12] | Wang Y F, Zhuo X L, Wang L, et al. Effect of harvest period and processing method on the quality and in vitro digestibility of native grass products. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 145-154. |
| 王一凡, 卓兴良, 王磊, 等. 收割时间与加工方式对天然牧草产品品质和体外消化率的影响. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 145-154. | |
| [13] | Han Y, Feng W Q, Zhang T T, et al. Influence of ecological factors on the distribution of medicinal plants resources. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2023, 38(4): 1450-1453. |
| 韩颖, 冯婉庆, 张婷婷, 等. 生态因子对药用植物资源分布的影响. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(4): 1450-1453. | |
| [14] | Hu Z Z, Zhao J, Zhang Y L. Distribution patterns of rare and endangered plants in hot spots in Jiangxi under the influence of climate and terrain factors. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 24(22): 112-115. |
| 胡忠俊, 赵娟, 张一林. 气候地形因子影响下江西热点地区珍稀濒危植物分布格局研究. 安徽农学通报, 2018, 24(22): 112-115. | |
| [15] | Huang J X, Zheng M X, Huang Y Y, et al. Composition and distribution of semi-mangrove communities in coastal areas in western Guangdong and their influence factors. Wetland Science, 2020, 18(1): 91-100. |
| 黄嘉欣, 郑明轩, 黄颖彦, 等. 粤西沿海地区半红树植物群落组成和分布及其影响因子研究. 湿地科学, 2020, 18(1): 91-100. | |
| [16] | Lu J. The main forage resources of Qilian Mountains in Gansu and analysis on the soil. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2008. |
| 芦娟. 甘肃祁连山区草地主要牧草资源及其土壤生境分析. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2008. | |
| [17] | Lu X X, Chen T C, Wei J F, et al. Nutritional value of forages and their impact factors across different grassland types in Yili, Xinjiang. Pratacultural Science, (2024-12-19)[2025-06-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1069.S.20241219.1437.013.html. |
| 鲁星鑫, 陈天赐, 尉剑飞, 等. 新疆伊犁不同草地类型牧草营养价值及其影响因素. 草业科学, (2024-12-19)[2025-06-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1069.S.20241219.1437.013.html. | |
| [18] | Liu J P, Zhang N N, Zhao X S, et al. Comparative analysis of yield and nutritional value of six perennial Gramineae forage grasses in Alpine region of Qinghai. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(9): 3794-3806. |
| 刘金平, 张楠楠, 赵鑫盛, 等. 青海高寒地区6种多年生禾本科牧草产量及营养价值比较分析. 中国畜牧兽医, 2024, 51(9): 3794-3806. | |
| [19] | Liu D X, Peng W D, Wu Y F, et al. Evaluation on the production performance and feed value of seven grasses in arid areas. Grassland and Turf, 2024, 44(3): 108-115. |
| 刘定鑫, 彭文栋, 武育芳, 等. 干旱区7个禾本科牧草品种生产性能与饲用价值评价. 草原与草坪, 2024, 44(3): 108-115. | |
| [20] | Zhang J, Li Z G, Li J W, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and correspondence analysis of nutritional value of common grass species in Ewenki grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(5): 33-39. |
| 张军, 李治国, 李江文, 等. 鄂温克草原常见禾本科牧草营养价值的综合评价与对应分析.中国草地学报, 2019, 41(5): 33-39. | |
| [21] | Hou W F, Qi G Q, He L Z, et al. Comparative study on nutritional composition of eight native leguminous forage in Xing’an League. Feed Research, 2023, 46(12): 135-138. |
| 候伟峰, 其格其, 何刘柱, 等. 兴安盟8种乡土豆科牧草营养成分比较研究. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(12): 135-138. | |
| [22] | Peng Y, Ma S J, Sun J Y, et al. Comprehensive character evaluation of 12 wild legume forage germplasms in Tibet. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(12): 2429-2439. |
| 彭艳, 马素洁, 孙晶远, 等. 西藏12份野生豆科牧草种质资源综合性状评价. 草业科学, 2021, 38(12): 2429-2439. | |
| [23] | Zhang F F, Yu L, Zhang Q B, et al. Comprehensive assessment of the main legume forages’ nutritional value of natural mowing steppe in Shaertao Mountain, Zhaosu, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 51(10): 1907-1915. |
| 张凡凡, 于磊, 张前兵, 等. 沙尔套山天然割草场主要豆科牧草营养价值综合评价研究. 新疆农业科学, 2014, 51(10): 1907-1915. | |
| [24] | Yang R Q, Mu Z X, Huang M T, et al. Construction of ecological security pattern of Tarim River Basin based on ecosystem sustainability. Environmental Science, (2025-02-07)[2025-06-09]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202410268. |
| 杨荣钦, 穆振侠, 黄娩婷, 等. 基于生态系统可持续的塔里木河流域生态安全格局构建. 环境科学, (2025-02-07)[2025-06-09]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202410268. | |
| [25] | Xiong M Q, Liu X H, Zhang X H, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of soil conservation in the upper reaches of the Tarim River Basin based on the RUSLE model. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(4): 641-650. |
| 熊茂秋, 刘晓煌, 张雪辉, 等. 基于RUSLE模型的塔里木河流域上游土壤保持时空变化研究. 地质通报, 2024, 43(4): 641-650. | |
| [26] | Li L, Zhou Z L, Lv R H, et al. Soil physical and chemical properties of desert riparian forest in different areas of the Tarim River. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015, 43(11): 75-78, 87. |
| 李荔, 周正立, 吕瑞恒, 等. 塔里木河流域荒漠河岸林土壤理化性质. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(11): 75-78, 87. | |
| [27] | Lu Q, Wang J H, Chu J M. China desert plant map. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing, 2012. |
| 卢琦, 王建和, 褚建民. 中国荒漠植物图鉴. 北京: 中国林业出版, 2012. | |
| [28] | Chen M J, Jia S X. Chinese forage plants. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2002. |
| 陈默君, 贾慎修. 中国饲用植物. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002. | |
| [29] | Chen S. Grassland forage plant resources in China. Shenyang: Liaoning Ethnic Publishing House, 1994. |
| 陈山. 中国草地饲用植物资源. 沈阳: 辽宁民族出版社, 1994. | |
| [30] | National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook 2001-2022. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2001-2022. |
| 国家统计局. 2001-2022年中国统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2001-2022. | |
| [31] | Li J X, Liu Y Z, Ge G, et al. Study on the flora of seed plants in Jinpenshan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi Province. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(11): 2322-2331. |
| 李健星, 刘以珍, 葛刚, 等. 江西金盆山自然保护区种子植物区系研究. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(11): 2322-2331. | |
| [32] | Zhang D J. Evaluation on types and quality of natural grassland in Hainan Prefecture of Qinghai Province using forage nutrients by PCA method. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2011(9): 11-14. |
| 张东杰. 基于PCA方法以牧草营养成分评判青海省海南州天然草地类型质量初探. 草业与畜牧, 2011(9): 11-14. | |
| [33] | Tian B, Ma C, Geng Y W, et al. Evaluation of feeding value of different forage nutrients based on principal component analysis. Feed Industry, 2024, 45(7): 15-19. |
| 田斌, 马超, 耿怡雯, 等. 基于主成分分析法评价不同牧草营养成分饲用价值. 饲料工业, 2024, 45(7): 15-19. | |
| [34] | Xin Y C. The analysis of nutrition ingredient of grass in Qinghai natural grassland. Qinghai Prataculture, 2011, 20(1): 26-31, 9. |
| 辛玉春. 青海天然草地牧草营养成分分析. 青海草业, 2011, 20(1): 26-31, 9. | |
| [35] | Hou L F, Tang J W. Analysis of pastures’ nutrition component in Qinghai Province by principal component. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2018, 39(2): 42-44. |
| 侯留飞, 唐俊伟. 青海省天然草地牧草营养成分的主成分分析. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2018, 39(2): 42-44. | |
| [36] | An S Z. The content of elite wild herbage on the natural grassland in Xinjiang. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 1992(3): 15-20. |
| 安沙舟. 新疆天然草地优良野生牧草名录. 八一农学院学报, 1992(3): 15-20. | |
| [37] | An S Z. The saline forage resources on natural grassland in Xinjiang. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 1995(5): 73-77. |
| 安沙舟. 新疆天然草地盐生牧草资源. 中国草地, 1995(5): 73-77. | |
| [38] | Zhang H H, Jiang W L, Zhang X Z, et al. Investigation and collection of wild forage germplasm resources in Xinjiang. Grass-Feeding Livestock, 2015(4): 61-70. |
| 张荟荟, 姜万利, 张学洲, 等. 新疆野生牧草种质资源的调查与搜集. 草食家畜, 2015(4): 61-70. | |
| [39] | Ma Y B, Xu Z, Zhao L X, et al. Investigation and collection of wild forage germplasm resources in northern Xinjiang. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2007(11): 29-34. |
| 马玉宝, 徐柱, 赵来喜, 等. 新疆北疆地区野生牧草种质资源的考察与搜集. 草业与畜牧, 2007(11): 29-34. | |
| [40] | Zuriguli·Youliwas, Dong Z G, Zhang B. Utilization and development of wild forage germplasm resources in Xinjiang. Agricultural Development & Equipments, 2016(4): 44. |
| 祖日古丽·友力瓦斯, 董志国, 张博. 新疆野生牧草种质资源的利用与开发. 农业开发与装备, 2016(4): 44. | |
| [41] | Jazibira. Research overview of natural forage resources in Xinjiang. Contemporary Animal Husbandry, 2016(14): 35. |
| 孜比拉. 新疆天然牧草资源研究概况. 当代畜牧, 2016(14): 35. | |
| [42] | Li S S. Study on floristics of vascular plants and plant resources in Beita Mountain of Xinjiang. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. |
| 李珊珊. 新疆北塔山地区植物区系与植物资源研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2017. | |
| [43] | Saul·Abai Khan, Yimamu·Aishan. A brief study on natural forage resources in Xinjiang. Grass-Feeding Livestock, 2007(3): 51-52. |
| 沙吾列·阿拜汗, 衣马木·艾山. 新疆天然牧草资源研究概况. 草食家畜, 2007(3): 51-52. | |
| [44] | Zhang Y L, Yifu Layin·Yusufu, Marzia, et al. Collection and screening of wild forage germplasm resources in Xinjiang. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2017(2): 63-66, 83. |
| 张云玲, 依甫拉音·玉素甫, 玛尔孜亚, 等. 新疆豆科野生优良牧草种质资源搜集及筛选. 草学, 2017(2): 63-66, 83. | |
| [45] | Sui Y, Cui Q G, Dong M, et al. Contrasting responses of legume versus non-legume shrubs to soil water and nutrient shortages in the Mu Us Sandland. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2011, 4(4): 268-274. |
| [46] | Duan X B. Research and protection on the wild plant resources of Ebinur Lake watershed in Xinjiang. Wulumuqi: Xinjiang University, 2011. |
| 段小兵. 新疆艾比湖流域植物资源研究及其保护. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2011. | |
| [47] | Maestre F T, Cortina J, Bautista S, et al. Small scale environmental heterogeneity and spatiotemporal dynamics of seedling survival in a degraded semiarid ecosystem. Ecosystems, 2003(6): 630-643. |
| [48] | Lou A R. Ecological gradient analysis and environmental interpretation of mountain vegetation in the middle section of Tianshan Mountains. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 1998(4): 77-85. |
| 娄安如. 天山中段山地植被的生态梯度分析及环境解释. 植物生态学报, 1998(4): 77-85. | |
| [49] | Feng Y, Zhang Y M, Pan B R. Grassland types with environmental relations in middle zone of northern slope of Tianshan Mountains. Arid Land Geography, 2006(2): 237-242. |
| 冯缨, 张元明, 潘伯荣. 天山北坡中段草地类型的生态梯度组合格局与环境分析研究. 干旱区地理, 2006(2): 237-242. | |
| [50] | Li K H, Hu Y K, Fan Y G, et al. Influence of environmental factors on distribution of plant communities and composition of species in alpine grassland. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2007(4): 378-382. |
| 李凯辉, 胡玉昆, 范永刚, 等. 环境因子对高寒草地植物群落分布和物种组成的影响. 中国农业气象, 2007(4): 378-382. | |
| [51] | Wang X D. Distribution characteristics of plant communities and response to soil environmental factors in Shangduhe National Wetland Park, Zhenglanqi. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 王旭东. 正蓝旗上都河国家湿地公园植物群落分布特征对土壤环境因子的响应. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021. | |
| [52] | Liu X H, Zhang Q Q, Zhang G P, et al. Analysis of spatial distribution and influencing factors of plant communities in the lower reaches of the Tarim River. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(10): 131-144. |
| 刘星宏, 张青青, 张广鹏, 等. 塔里木河下游植物群落空间分布及影响因素分析. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(10): 131-144. | |
| [53] | Xu N, Yao Y L, Wang M, et al. Spatial distribution of plant communities and environmental interpretation in Xinjiang Bayanbulak marsh. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(2): 409-419. |
| 徐娜, 姚艳玲, 王铭, 等. 新疆巴音布鲁克高寒沼泽湿地植物群落空间分布与环境解释. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(2): 409-419. | |
| [54] | Qi D H. Types and characteristics of plant communities in the Otingdag Sandy Land. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2023. |
| 齐丹卉. 浑善达克沙地植被特征和分布格局. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2023. | |
| [55] | Aoguganmuqier, Tergeresayhan, Suyalatu, et al. Investigation and analysis of wild forage plant resource in nomadic grazing system of Arhorqin pastures-a case study of Hundleng summer base. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2017, 36(2): 66-69, 84. |
| 敖古干牧其尔, 特日格勒赛罕, 苏亚拉图, 等. 阿鲁科尔沁草原游牧系统野生饲用植物资源调查分析——以浑德伦夏营盘为例. 中国野生植物资源, 2017, 36(2): 66-69, 84. | |
| [56] | Duan D X, Gao C M, Wu T. Analysis on the composition of wild forage plant resources in Yellow River Delta. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2022, 41(4): 80-82, 89. |
| 段代祥, 高春明, 吴涛. 黄河三角洲地区野生饲用植物资源构成分析. 中国野生植物资源, 2022, 41(4): 80-82, 89. | |
| [57] | Meng Y, Dong J J, Ma Z C, et al. Research on wild forage resources in the area along the highway of Kalasu port in Xinjiang. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2022(19): 108-111, 124. |
| 孟岩, 董俊俊, 马占仓, 等. 新疆卡拉苏口岸公路沿线区域野生饲用植物资源研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2022(19): 108-111, 124. | |
| [58] | Liu J, Liu Y, Yan P, et al. Analysis of the composition of wild forage plant resources in low-mountain deserts of the upper and middle reaches of the Manas River in Xinjiang. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(5): 98-103. |
| 刘佳, 刘鸯, 阎平, 等. 新疆玛纳斯河中上游低山荒漠区野生饲用植物资源构成分析. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(5): 98-103. | |
| [59] | Zheng K, Gu H R, Shen Y X, et al. Evaluation system of forage quality and research advances in forage quality breeding. Pratacultural Science, 2006(5): 57-61. |
| 郑凯, 顾洪如, 沈益新, 等. 牧草品质评价体系及品质育种的研究进展. 草业科学, 2006(5): 57-61. | |
| [60] | Li Y Q, Xu M Y, Wang Z H, et al. Research advances in evaluation of forage quality. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008(11): 4485-4486, 4546. |
| 李艳琴, 徐敏云, 王振海, 等. 牧草品质评价研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 2008(11): 4485-4486, 4546. | |
| [61] | Wang D F, Han Y, Yuan C, et al. Conventional nutrient contents of 120 wild forages from southwest karst mountainous areas and their clustering analysis. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(8): 5255-5269. |
| 王德凤, 韩勇, 袁超, 等. 西南喀斯特山区120种野生牧草的常规营养成分含量及其聚类分析. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(8): 5255-5269. | |
| [62] | Xing H C, Jie Y C, Kang W L, et al. Botanical traits and nutrient composition analysis of 97 forage germplasm resources in Gramineae//Grassland Supervision Center, Ministry of Agriculture, China Grassland Society. 2009 China Grassland Development Forum Proceedings. Hefei: Ramie Research Institute, Hunan Agricultural University, College of Life Science and Technology, Hunan Agricultural University, 2009: 487-496. |
| 邢虎成, 揭雨成, 康万利, 等. 禾本科97份牧草种质资源植物学性状观察及营养成分分析//农业部草原监理中心, 中国草学会. 2009中国草原发展论坛论文集. 合肥: 湖南农业大学苎麻研究所, 湖南农业大学生命科学技术学院, 2009: 487-496. | |
| [63] | Wuyungaowa, Wu Y L, Yu H M, et al. Analysis of nutritional components of six gramineous forages in Hulun Buir, Inner Mongolia. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2017, 38(2): 50-52. |
| 乌云高娃, 吴艳玲, 余红梅, 等. 内蒙古呼伦贝尔地区6种禾本科牧草营养成分分析. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2017, 38(2): 50-52. |
| [1] | 安玉霞, 王文强, 余殿, 梁咏亮, 杨君珑, 李小伟. 基于优化MaxEnt模型的锁阳分布研究:现状评估与未来预测[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 1-12. |
| [2] | 龚昕, 霍新茹, 李雯, 杨彦东, 刘超, 秦伟春, 沈艳, 王国会, 马红彬. 宁夏罗山山地草原植被群落特征及其空间分异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 1-15. |
| [3] | 陶惠赟, 杨闰艳, 李延灿, 刘亚鹏, 祁鹤兴. 黄河源区矮嵩草根际土壤微生物多样性及对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 16-32. |
| [4] | 吕烨昕, 叶茂, 钱娇蓉, 陈维龙, 车静, 李苗苗, 曾国燕. 新疆哈巴河林区草地物种多样性和系统发育多样性分析及影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 50-61. |
| [5] | 于双, 李小伟, 王瑞霞, 杨君珑, 马龙. 灵武白芨滩不同年限柠条固沙林林下草本群落演替规律及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 13-23. |
| [6] | 韩雨轩, 王瑞, 郝丽芬, 袁海滨, 林克剑. 外来入侵植物长刺蒺藜草在我国的地理分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 34-44. |
| [7] | 王鹏, 金正, 余婷, 秦康强, 桑新亚, 陶建平, 罗唯学. 预测姜黄属植物在中国当前和未来气候情景下的潜在分布区变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 14-27. |
| [8] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [9] | 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| [10] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| [11] | 杨鑫, 曹文侠, 鱼小军, 汪海斌, 郝媛媛. 基于近20年MODIS NDVI日数据的青海省草地资源动态监测及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 1-14. |
| [12] | 蒙仲举, 陈颜洁, 包斯琴. 苏尼特右旗荒漠草原三种放牧方式下群落斑块特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 13-23. |
| [13] | 张敏, NIPAPAN Kanjana, 李铷, 傅杨, 汤东生. 环境因子对云南扁穗雀麦种子萌发和出苗的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 143-151. |
| [14] | 崔博超, 郑江华, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 段素素, 杜梦洁. 塔里木河流域草地净初级生产力时空分异特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. |
| [15] | 孙思思, 吴战平, 肖启涛, 于飞, 古书鸿, 方荻, 李浪, 赵兴炳. 云贵高原草地生态系统CO2通量变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 184-191. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||