

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 16-32.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025036
陶惠赟1,2( ), 杨闰艳2, 李延灿2, 刘亚鹏2, 祁鹤兴2(
), 杨闰艳2, 李延灿2, 刘亚鹏2, 祁鹤兴2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-13
修回日期:2025-04-15
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-10-20
通讯作者:
祁鹤兴
作者简介:E-mail: qhx390495559@126.com基金资助:
Hui-yun TAO1,2( ), Run-yan YANG2, Yan-can LI2, Ya-peng LIU2, He-xing QI2(
), Run-yan YANG2, Yan-can LI2, Ya-peng LIU2, He-xing QI2( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Revised:2025-04-15
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-10-20
Contact:
He-xing QI
摘要:
为探究不同海拔下矮嵩草根际土壤微生物群落组成特征及其环境因子影响因素,本研究以黄河源区海拔3000~5000 m矮嵩草根际土壤为对象,对其真菌和细菌进行Illumina MiSeq测序以及生物信息学分析,研究根际土壤微生物多样性差异、群落结构以及与环境因子之间的关系。结果表明黄河源区5个海拔下的微生物多样性、群落结构与环境因子之间的关系存在较大的差异。不同海拔的根际土壤中,在4027.0 m处的真菌多样性最高,而在4932.1 m处的细菌多样性最高,显示出真菌和细菌对海拔变化的不同响应模式。土壤微生物群落结构随着海拔上升具有不同的变化规律:随着海拔上升真菌群落中油壶菌门的相对丰度逐渐增大,蛙粪霉门只分布在海拔高于4500 m的采样点;细菌群落中随着海拔上升相对丰度逐渐增大的门分别是硝化螺旋菌门、蛭弧菌门、迷踪菌门、RCP2-54和SAR324_cladeMarine_group_B,随海拔上升相对丰度逐渐下降的是梭杆菌门。除了pH随着海拔的升高而降低,其他土壤理化因子随海拔上升都呈复杂的变化趋势。其中,在海拔4932.1 m处pH、全磷、速效氮、有机质与其余海拔具有显著差异(P<0.05);在海拔4027.0 m处全钾、速效磷、速效钾与其余海拔具有显著差异(P<0.05)。冗余分析表明,速效钾和海拔是影响真菌群落组成及其多样性的重要因子,而细菌群落受pH、全氮、全磷、速效氮、有机碳和海拔的影响更大,其中pH对细菌群落结构的影响最为显著。本研究通过Illumina MiSeq测序技术深入分析不同海拔下的矮嵩草根际土壤微生物多样性、群落结构及其环境影响因素,为黄河源区生态保护提供了土壤微生物层面的理论依据。
陶惠赟, 杨闰艳, 李延灿, 刘亚鹏, 祁鹤兴. 黄河源区矮嵩草根际土壤微生物多样性及对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 16-32.
Hui-yun TAO, Run-yan YANG, Yan-can LI, Ya-peng LIU, He-xing QI. Diversity of microorganisms in the rhizosphere soil of Kobresia humilis and their responses to environmental factors in the source region of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(12): 16-32.
采样地点 Sampling site | 样本 Sample | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 伴生植物 Companion plants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 共和县青海湖国家自然保护区Qinghai Lake National Nature Reserve in Gonghe County | S1 | 36°33′07.45″N 100°43′48.29″E | 3208.0 | 矮嵩草、芨芨草、鹅绒委陵菜、早熟禾、马蔺、野葱、车前草、薹草、茵陈蒿、毛建草、扁穗冰草、麻花秦艽、达乌里黄芪K.humilis, Achnatherum splendens, Potentilla anserina, Poa annua, Iris lactea, Allium chrysanthum, Plantago asiatica, Carex sp., Artemisia capillaris, Dracocephalum rupestre, Agropyron cristatum, Gentiana straminea, Astragalus dahuricus |
| 兴海县河卡镇Heka Town, Xinghai County | S2 | 35°45′45.90″N 99°53′41.52″E | 3519.9 | 矮嵩草、肉果草、垂穗披碱草、鹅绒委陵菜、蒲公英、火绒草、早熟禾、蕨麻、大戟、薹草K.humilis, Lancea tibetica, Elymus nutans, P.anserina, Taraxacum mongolicum, Leontopodium leontopodioides, P. annua, Argentina anserina, Euphorbia pekinensis, Carex. sp. |
| 兴海县子科滩镇Ziketan Town, Xinghai County | S3 | 35°36′17.56″N 99°32′50.16″E | 4027.0 | 矮嵩草、麻花秦艽、薹草、马尿泡、火绒草、鹅绒委陵菜、忍冬、黄花棘豆、全缘兔耳草、高山大戟、节节草K.humilis, G. straminea, Carex sp., Przewalskia tangutica, L. leontopodioides, P. anserina, Lonicera japonica, Oxytropis ochrocephala, Lagotis integra, Euphorbia stracheyi, Equisetum ramosissimum |
| 玛多县玛查理镇Marcharlie Town, Mardo County | S4 | 34°19′38.89″N 97°55′30.23″E | 4511.7 | 矮嵩草、高山嵩草、早熟禾、银叶火绒草、普式马先蒿、珠牙蓼、麦冬、小丛红景天、棘豆、紫菀、麻花秦艽、苣荬菜、毛茛、马蔺、金露梅K.humilis, K. pygmaea, P. annua, L. souliei, Pedicularis przewalskii, Polygonum viviparum, Ophiopogon japonicus, Rhodiola dumulosa, Oxytropis sp., Aster tataricus, G. straminea, Sonchus oleraceus, Ranunculus japonicus, I. lactea, Dasiphora fruticosa |
| 巴颜喀拉山Bayan Har Mountain | S5 | 34°07′55.19″N 97°39′27.49″E | 4932.1 | 矮嵩草、高山嵩草、皱叶娟毛苣、百里香、火绒草、多刺绿绒蒿、紫苑、麻花秦艽、委陵菜、毡毛雪莲、点地梅、香青、水母雪兔子、爪瓣虎耳草、高山龙胆K.humilis, K. pygmaea, Soroseris hookeriana, Thymus mongolicus, L. leontopodioides, Meconopsis horridula, A. tataricus, G. straminea, Potentilla sp., Saussurea velutina, Androsace umbellata, Anaphalis sinica, Saussurea medusa, Saxifraga unguiculata, Gentiana algida |
表1 土壤样本信息
Table 1 Basic information of soil sampling sites
采样地点 Sampling site | 样本 Sample | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 伴生植物 Companion plants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 共和县青海湖国家自然保护区Qinghai Lake National Nature Reserve in Gonghe County | S1 | 36°33′07.45″N 100°43′48.29″E | 3208.0 | 矮嵩草、芨芨草、鹅绒委陵菜、早熟禾、马蔺、野葱、车前草、薹草、茵陈蒿、毛建草、扁穗冰草、麻花秦艽、达乌里黄芪K.humilis, Achnatherum splendens, Potentilla anserina, Poa annua, Iris lactea, Allium chrysanthum, Plantago asiatica, Carex sp., Artemisia capillaris, Dracocephalum rupestre, Agropyron cristatum, Gentiana straminea, Astragalus dahuricus |
| 兴海县河卡镇Heka Town, Xinghai County | S2 | 35°45′45.90″N 99°53′41.52″E | 3519.9 | 矮嵩草、肉果草、垂穗披碱草、鹅绒委陵菜、蒲公英、火绒草、早熟禾、蕨麻、大戟、薹草K.humilis, Lancea tibetica, Elymus nutans, P.anserina, Taraxacum mongolicum, Leontopodium leontopodioides, P. annua, Argentina anserina, Euphorbia pekinensis, Carex. sp. |
| 兴海县子科滩镇Ziketan Town, Xinghai County | S3 | 35°36′17.56″N 99°32′50.16″E | 4027.0 | 矮嵩草、麻花秦艽、薹草、马尿泡、火绒草、鹅绒委陵菜、忍冬、黄花棘豆、全缘兔耳草、高山大戟、节节草K.humilis, G. straminea, Carex sp., Przewalskia tangutica, L. leontopodioides, P. anserina, Lonicera japonica, Oxytropis ochrocephala, Lagotis integra, Euphorbia stracheyi, Equisetum ramosissimum |
| 玛多县玛查理镇Marcharlie Town, Mardo County | S4 | 34°19′38.89″N 97°55′30.23″E | 4511.7 | 矮嵩草、高山嵩草、早熟禾、银叶火绒草、普式马先蒿、珠牙蓼、麦冬、小丛红景天、棘豆、紫菀、麻花秦艽、苣荬菜、毛茛、马蔺、金露梅K.humilis, K. pygmaea, P. annua, L. souliei, Pedicularis przewalskii, Polygonum viviparum, Ophiopogon japonicus, Rhodiola dumulosa, Oxytropis sp., Aster tataricus, G. straminea, Sonchus oleraceus, Ranunculus japonicus, I. lactea, Dasiphora fruticosa |
| 巴颜喀拉山Bayan Har Mountain | S5 | 34°07′55.19″N 97°39′27.49″E | 4932.1 | 矮嵩草、高山嵩草、皱叶娟毛苣、百里香、火绒草、多刺绿绒蒿、紫苑、麻花秦艽、委陵菜、毡毛雪莲、点地梅、香青、水母雪兔子、爪瓣虎耳草、高山龙胆K.humilis, K. pygmaea, Soroseris hookeriana, Thymus mongolicus, L. leontopodioides, Meconopsis horridula, A. tataricus, G. straminea, Potentilla sp., Saussurea velutina, Androsace umbellata, Anaphalis sinica, Saussurea medusa, Saxifraga unguiculata, Gentiana algida |
样本 Sample | 覆盖率Coverage (%) | ACE指数ACE index | Chao 指数Chao index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | |
| S1 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 394.75±68.78a | 2039.85±177.98b | 394.03±67.96a | 2031.69±170.98b |
| S2 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 394.84±97.25a | 2054.87±87.36b | 394.92±96.38a | 2048.15±85.42b |
| S3 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 593.65±257.14a | 2045.45±154.06b | 598.38±264.57a | 2033.58±149.47b |
| S4 | 99.9 | 99.6 | 442.21±257.34a | 2425.17±149.60ab | 443.86±260.80a | 2408.45±143.85ab |
| S5 | 99.9 | 99.3 | 380.50±86.68a | 2617.63±541.12a | 379.89±86.65a | 2586.61±519.20a |
样本 Sample | 香农指数Shannon index | 辛普森指数Simpson index | ||||
| 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | |||
| S1 | 4.05±0.67b | 6.97±0.03ab | 0.07±0.06a | 0.002±0.0007a | ||
| S2 | 4.04±0.29b | 7.01±0.02ab | 0.06±0.03a | 0.002±0.0005a | ||
| S3 | 4.35±0.79b | 6.84±0.19b | 0.05±0.04a | 0.004±0.0029a | ||
| S4 | 3.83±0.67ab | 7.07±0.07a | 0.07±0.05a | 0.002±0.0002a | ||
| S5 | 4.21±0.32a | 7.08±0.07a | 0.03±0.01a | 0.002±0.0001a | ||
表2 不同海拔下根际土壤微生物多样性指数
Table 2 Microbial diversity index of rhizosphere soil at different altitudes
样本 Sample | 覆盖率Coverage (%) | ACE指数ACE index | Chao 指数Chao index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | |
| S1 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 394.75±68.78a | 2039.85±177.98b | 394.03±67.96a | 2031.69±170.98b |
| S2 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 394.84±97.25a | 2054.87±87.36b | 394.92±96.38a | 2048.15±85.42b |
| S3 | 99.8 | 99.8 | 593.65±257.14a | 2045.45±154.06b | 598.38±264.57a | 2033.58±149.47b |
| S4 | 99.9 | 99.6 | 442.21±257.34a | 2425.17±149.60ab | 443.86±260.80a | 2408.45±143.85ab |
| S5 | 99.9 | 99.3 | 380.50±86.68a | 2617.63±541.12a | 379.89±86.65a | 2586.61±519.20a |
样本 Sample | 香农指数Shannon index | 辛普森指数Simpson index | ||||
| 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | |||
| S1 | 4.05±0.67b | 6.97±0.03ab | 0.07±0.06a | 0.002±0.0007a | ||
| S2 | 4.04±0.29b | 7.01±0.02ab | 0.06±0.03a | 0.002±0.0005a | ||
| S3 | 4.35±0.79b | 6.84±0.19b | 0.05±0.04a | 0.004±0.0029a | ||
| S4 | 3.83±0.67ab | 7.07±0.07a | 0.07±0.05a | 0.002±0.0002a | ||
| S5 | 4.21±0.32a | 7.08±0.07a | 0.03±0.01a | 0.002±0.0001a | ||
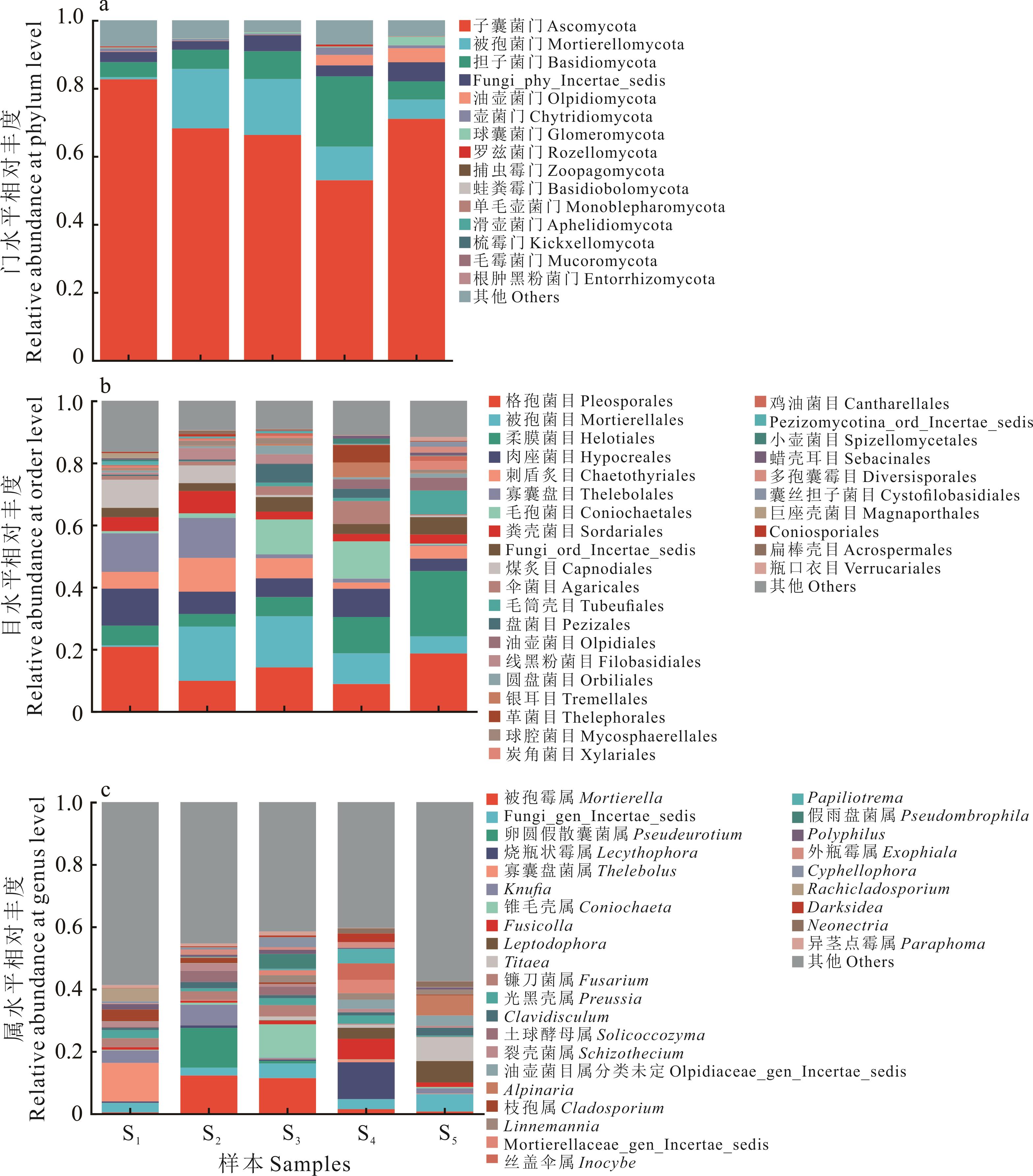
图4 不同海拔下门、目、属水平上的根际土壤真菌群落相对丰度分布
Fig.4 Abundance distribution of rhizosphere soil fungal community at phylum, order and genus levels under different altitudes

图5 不同海拔下门、目、属水平上的根际土壤细菌群落相对丰度分布
Fig.5 Abundance distribution of rhizosphere soil bacterial community at phylum, order and genus levels under different altitudes
样品 Sample | pH | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 速效氮 Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 8.01±0.00a | 2.15±0.04c | 0.566±0.01c | 6.919±0.20e | 7.390±0.42c | 156.761±0.13c | 146.18±2.82c | 54.427±0.35c |
| S2 | 7.83±0.01c | 2.01±0.01cd | 0.536±0.01d | 8.884±0.29d | 5.909±0.09d | 176.551±0.35b | 146.57±1.30c | 36.021±0.88e |
| S3 | 7.75±0.04d | 3.85±0.11b | 0.605±0.01b | 12.612±0.44a | 8.951±0.13a | 295.126±0.35a | 273.55±3.94b | 69.683±0.62b |
| S4 | 7.97±0.02b | 1.89±0.02d | 0.619±0.02b | 9.839±0.08c | 5.080±0.55e | 87.759±0.034e | 136.32±1.63d | 37.178±0.74d |
| S5 | 6.71±0.02e | 7.06±0.40a | 0.805±0.00a | 10.810±0.21b | 8.088±0.01b | 137.099±0.20d | 548.27±7.11a | 137.268±1.16a |
表3 不同海拔下根际土壤的环境因子
Table 3 Rhizosphere soil environment factors at different altitudes
样品 Sample | pH | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 速效氮 Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 8.01±0.00a | 2.15±0.04c | 0.566±0.01c | 6.919±0.20e | 7.390±0.42c | 156.761±0.13c | 146.18±2.82c | 54.427±0.35c |
| S2 | 7.83±0.01c | 2.01±0.01cd | 0.536±0.01d | 8.884±0.29d | 5.909±0.09d | 176.551±0.35b | 146.57±1.30c | 36.021±0.88e |
| S3 | 7.75±0.04d | 3.85±0.11b | 0.605±0.01b | 12.612±0.44a | 8.951±0.13a | 295.126±0.35a | 273.55±3.94b | 69.683±0.62b |
| S4 | 7.97±0.02b | 1.89±0.02d | 0.619±0.02b | 9.839±0.08c | 5.080±0.55e | 87.759±0.034e | 136.32±1.63d | 37.178±0.74d |
| S5 | 6.71±0.02e | 7.06±0.40a | 0.805±0.00a | 10.810±0.21b | 8.088±0.01b | 137.099±0.20d | 548.27±7.11a | 137.268±1.16a |
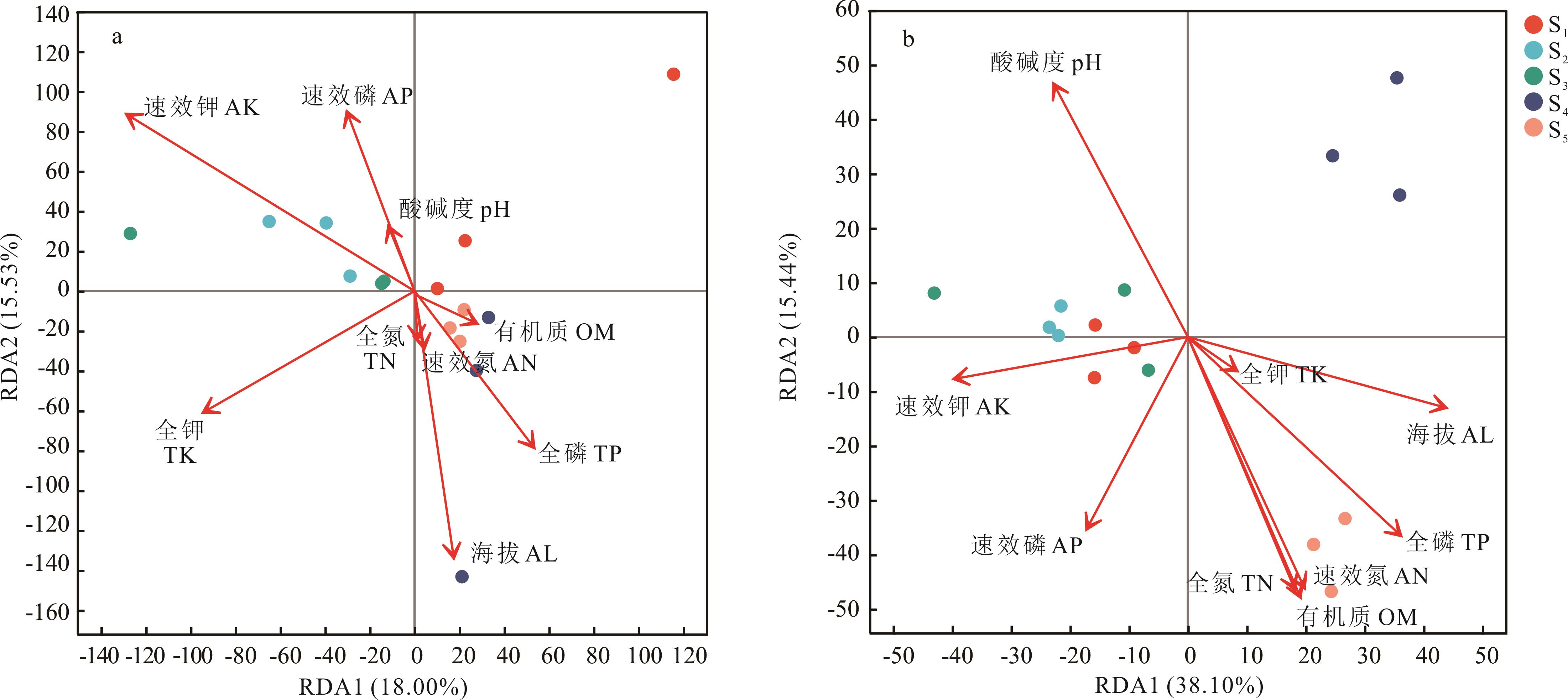
图7 不同海拔下根际土壤环境因子在属水平上的冗余分析A: 真菌Fungi; b: 细菌Bacteria.
Fig.7 Redundancy analysis for rhizosphere soil environment factors at genus levels under different altitudes
土壤理化因子 Soil physicochemical properties | RDA1 | RDA2 | r2 | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | |
| pH | -0.3263 | -0.4509 | 0.9453 | 0.8926 | 0.0219 | 0.8458 | 0.779 | 0.005 |
| 全氮Total N | 0.0505 | 0.3773 | -0.9987 | -0.9261 | 0.0104 | 0.7780 | 0.911 | 0.002 |
| 全磷Total P | 0.5476 | 0.7067 | -0.8367 | -0.7075 | 0.1808 | 0.8373 | 0.337 | 0.004 |
| 全钾Total K | -0.8309 | 0.8009 | -0.5564 | -0.5988 | 0.2522 | 0.0304 | 0.169 | 0.829 |
| 速效氮Available N | 0.1414 | 0.4063 | -0.9900 | -0.9138 | 0.0154 | 0.7920 | 0.870 | 0.004 |
| 速效磷Available P | -0.3073 | -0.4321 | 0.9516 | -0.9018 | 0.1819 | 0.4697 | 0.317 | 0.020 |
| 速效钾Available K | -0.8135 | -0.9845 | 0.5816 | -0.1751 | 0.4934 | 0.5064 | 0.011 | 0.010 |
| 有机质Organic matter | 0.8780 | 0.3836 | -0.4786 | -0.9235 | 0.0170 | 0.8342 | 0.843 | 0.002 |
| 海拔Altitude | 0.1242 | 0.9558 | -0.9923 | -0.2940 | 0.3746 | 0.6584 | 0.022 | 0.002 |
表4 不同海拔下根际土壤真菌和细菌冗余分析
Table 4 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of rhizosphere soil fungi and bacteria at different altitudes
土壤理化因子 Soil physicochemical properties | RDA1 | RDA2 | r2 | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | |
| pH | -0.3263 | -0.4509 | 0.9453 | 0.8926 | 0.0219 | 0.8458 | 0.779 | 0.005 |
| 全氮Total N | 0.0505 | 0.3773 | -0.9987 | -0.9261 | 0.0104 | 0.7780 | 0.911 | 0.002 |
| 全磷Total P | 0.5476 | 0.7067 | -0.8367 | -0.7075 | 0.1808 | 0.8373 | 0.337 | 0.004 |
| 全钾Total K | -0.8309 | 0.8009 | -0.5564 | -0.5988 | 0.2522 | 0.0304 | 0.169 | 0.829 |
| 速效氮Available N | 0.1414 | 0.4063 | -0.9900 | -0.9138 | 0.0154 | 0.7920 | 0.870 | 0.004 |
| 速效磷Available P | -0.3073 | -0.4321 | 0.9516 | -0.9018 | 0.1819 | 0.4697 | 0.317 | 0.020 |
| 速效钾Available K | -0.8135 | -0.9845 | 0.5816 | -0.1751 | 0.4934 | 0.5064 | 0.011 | 0.010 |
| 有机质Organic matter | 0.8780 | 0.3836 | -0.4786 | -0.9235 | 0.0170 | 0.8342 | 0.843 | 0.002 |
| 海拔Altitude | 0.1242 | 0.9558 | -0.9923 | -0.2940 | 0.3746 | 0.6584 | 0.022 | 0.002 |
| [1] | An H T, Sun C C, Dong Q M, et al. Characteristics of soil particle size fractals under livestock assembly in alpine meadows of the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2025, 33(4): 1106-1113. |
| 安海涛, 孙彩彩, 董全民, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸不同放牧方式下土壤粒径分形特征. 草地学报, 2025, 33(4): 1106-1113. | |
| [2] | Niu Y P, Gao X X, Yao S T, et al. Linkages of plant diversity and functional groups to aboveground productivity upon alpine grassland degradation. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2025, 49(1): 83-92. |
| 牛亚平, 高晓霞, 姚世庭, 等. 退化高寒草地植物多样性和功能群组成与地上生产力的关系.植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 83-92. | |
| [3] | Li Y. Stability of plant communities and their driving mechanisms in alpine grasslands, Qingzang Plateau. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 李洋. 青藏高原高寒草地植物群落稳定性及其驱动机制研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2023. | |
| [4] | Fan R J, Zhu Z H, Li Y N, et al. Grazing-tolerance of two major plant species in alpine Kobresia humilis meadow. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(6): 1052-1062. |
| 樊瑞俭, 朱志红, 李英年, 等. 高寒矮嵩草草甸两种主要植物耐牧性的比较. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(6): 1052-1062. | |
| [5] | Zhou X M. A preliminary study on the morphological-ecological characteristics of eight species of Kobresia in Qinghai-Tibet. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 1979, 21(2): 45-52. |
| 周兴民. 青藏高原嵩草属(Kobresia)八种植物的形态-生态学特性的初步研究. 植物学报, 1979, 21(2): 45-52. | |
| [6] | Li Q X. Genetic diversity of five Kobresia plants along the eastern of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in China. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2005. |
| 李巧峡. 青藏高原东部嵩草属五种植物的遗传多样性研究. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2005. | |
| [7] | Li Q X, Zhao Q F, Ma S R, et al. Research progress on Kobresia species. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science), 2006, 42(6): 78-82. |
| 李巧峡, 赵庆芳, 马世荣, 等. 嵩草属植物研究进展. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 42(6): 78-82. | |
| [8] | Zhu Z H, Sun S Q. Characteristic responsiveness of modular populations of Kobresia humilis to grazing in alpine meadow. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1996, 38(8): 653-660. |
| 朱志红, 孙尚奇. 高寒草甸矮嵩草种群的放牧中构件种群的反应特性. 植物学报, 1996, 38(8): 653-660. | |
| [9] | Yang Y W, Li X L, Li J L, et al. Growth response of Kobresia humilis to grazing disturbance on alpine meadow. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2011, 20(9): 18-24. |
| 杨元武, 李希来, 李积兰, 等. 高寒草甸矮嵩草对放牧扰动的生长反应. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(9): 18-24. | |
| [10] | Wang C. Propagation and expansion characteristics of Kobresia humilis plaques in artificial grassland of black soil beach. Xining: Qinghai University, 2021. |
| 王超. 黑土滩人工草地矮嵩草斑块繁殖与扩展特征. 西宁: 青海大学, 2021. | |
| [11] | Zhou X M, Wang Q J, Zhang Y Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of vegetation succession law of the alpine meadow under different grazing intensitie. Chinese Journal of the Plant Ecology, 1987(4): 276-285. |
| 周兴民, 王启基, 张堰青, 等. 不同放牧强度下高寒草甸植被演替规律的数量分析. 植物生态学报, 1987(4): 276-285. | |
| [12] | Wang Y, Ding T, Zhou L W, et al. Variation characteristics of rhizosphere soil microorganisms of Abiea yuanbaoshanensis along altitude gradient in winter. Guihaia, 2025, 45(1): 147-160. |
| 王莹, 丁涛, 周龙武, 等. 元宝山冷杉冬季根际土壤微生物沿海拔梯度的变化特征. 广西植物, 2025, 45(1): 147-160. | |
| [13] | Avis J T, Gravel V, Antoun H, et al. Multifaceted beneficial effects of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant health and productivity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 40(7): 1733-1740. |
| [14] | Pérez-Jaramillo J E, Mendes R, Raaijmakers J M. Impact of plant domestication on rhizosphere microbiome assembly and functions. Plant Molecular Biology, 2016, 90: 635-644. |
| [15] | Zhang X P, Liu Q, Wang J, et al. Progress on the mechanism of interaction between saline plants and inter-rooted soil microorganisms under saline stress. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2024, 55(4): 1119-1200. |
| 张旭萍, 刘强, 王锦, 等. 盐碱胁迫下盐生植物与根际土壤微生物交互作用机制研究进展. 土壤通报, 2024, 55(4): 1191-1200. | |
| [16] | Tang Y P, Song Y Q, Liu W H, et al. Characteristics of rhizosphere soil microbial communities in Gentiana rigescens Franch. based on high-throughput sequencing method. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 37(5): 1047-1055. |
| 唐运萍, 宋艳秋, 刘卫红, 等. 基于高通量测序分析滇龙胆根际土壤微生物群落特征. 西南农业学报, 2024, 37(5): 1047-1055. | |
| [17] | Yang Y, Liu B R. Distribution of soil nutrient and microbial biomass in rhizosphere versus nonrhizosphere area of different plant species in desertified steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(22): 7562-7570. |
| 杨阳, 刘秉儒. 荒漠草原不同植物根际与非根际土壤养分及微生物量分布特征. 生态学报, 2015, 35(22): 7562-7570. | |
| [18] | Jia H B. Biodegradetion of oil contaminated soil and the influence of biodegradation on soil bacterial community diversity. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2013. |
| 贾洪柏. 石油污染土壤的微生物修复及对相关土壤细菌群落多样性的影响. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2013. | |
| [19] | Lomolino M V. Elevation gradients of species-density: historical and prospective views. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2001, 10(1): 3-13. |
| [20] | Ma L W.Soil bacterial and fungal diversity patterns and the underlying mechanisms along an elevational gradient in Mountain Guanshan, China. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2022. |
| 马璐雯. 江西官山土壤细菌和真菌多样性海拔梯度格局及其影响因素. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2022. | |
| [21] | Xu M H. Altitudinal gradient pattern of soil microbial α diversity in warm temperate forest and its influencing factors. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 1-10[2025-05-13]. http: //kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1661.X.20250228.1737.008.html. |
| 徐茂宏. 暖温带森林土壤微生物α多样性海拔梯度格局及其影响因素. 生态环境学报, 1-10[2025-05-13]. http: //kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1661.X.20250228.1737.008.html. | |
| [22] | Wang J, Soininen J, Zhang Y, et al. Contrasting patterns in elevational diversity between microorganisms and macroorganisms. Journal of Biogeography, 2011, 38(3): 595-603. |
| [23] | Jiao K. Characteristics of soil microbial community along the soil profile of typical vegetation in Mount Segrila. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2021. |
| 焦克. 色季拉山典型植被深层土壤微生物群落特征研究. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2021. | |
| [24] | Chang L J. Research on soil microbial community structure and its influencing factors at different elevations in Wutai Mountain. Jinzhong: Taiyuan Normal University, 2024. |
| 常丽娟. 五台山不同海拔土壤微生物群落结构特征及其影响因素研究. 晋中: 太原师范学院, 2024. | |
| [25] | Huang S M, Zhou L, Jia W J, et al. Soil bacterial community diversity and PICRUSt function prediction of Meconopsis integrifolia at different altitudes. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1-10[2025-05-13]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1213.S.20250324.1513.006. |
| 黄顺满, 周麟, 贾维嘉, 等.不同海拔全缘叶绿绒蒿土壤细菌群落多样性及PICRUSt功能预测. 西南农业学报, 1-10[2025-05-13]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1213.S.20250324.1513.006. | |
| [26] | Ma J P, Pang D B, Chen L, et al. Characteristics of soil microbial community structure under vegetation at different altitudes in Helan Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(2): 667-676. |
| 马进鹏, 庞丹波, 陈林, 等.贺兰山不同海拔植被下土壤微生物群落结构特征. 生态学报, 2022, 42(2): 667-676. | |
| [27] | Li Z J, Fei X W, Tian Z, et al. Phytoplankton community composition and species diversity in nearshore bays of Hainan based on Illumina MiSeq. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2024, 55(9): 2798-2812. |
| 李智杰, 费小雯, 田冶, 等. 基于Illumina MiSeq的海南近岸海湾浮游植物群落组成及其物种多样性分析. 南方农业学报, 2024, 55(9): 2798-2812. | |
| [28] | He X B, Huang K P, Li J Y, et al. Structure and diversity of microbial community in rhizosphere soil of tobacco root rot caused by Fusarium. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 66(2): 411-420. |
| 何晓冰, 黄昆鹏, 李俊营, 等. 烟草镰刀菌根腐病根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性.浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(2): 411-420. | |
| [29] | Lu S E, Xiao B, Ren F M, et al. Fungal community structure and diversity of rhizosphere soil of Polygonatum sibiricum with root-rot analyzed by Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technology. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 13-19. |
| 卢圣鄂, 肖波, 任风鸣, 等. 基于Illumina Miseq分析黄精根腐病根际土壤真菌群落结构及多样性. 世界科学技术——中医药现代化, 2021, 23(1): 13-19. | |
| [30] | Li C M, Zhang D R, Xu G C, et al. Effects of alpine grassland degradation on soil microbial communities in Qilian Mountains of China. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2023, 23(1): 912-923. |
| [31] | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis.Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| [32] | Chen S F, Zhou Y Q, Chen Y R, et al. FASTP: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17): i884-i890. |
| [33] | Magoc T, Salzberg S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(21): 2957-2963. |
| [34] | Edgar R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature methods, 2013, 10(10): 996-998. |
| [35] | Huang X L, Chen J P, Mo X F, et al. Microbial diversity and chemical characteristics of rhizosphere soil associated with understory Cardiocrinum giganteum. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2023, 43(6): 596-605. |
| 黄晓露, 陈江平, 莫小锋, 等. 林下大百合根际土壤微生物及化学特征分析. 森林与环境学报, 2023, 43(6): 596-605. | |
| [36] | Schloss P D, Westcott S L, Ryabin T, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(23): 7537-7541. |
| [37] | Chang F, He S S, Dang C Y. Assisted selection of biomarkers by linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) in microbiome data. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2022(183): e61715. |
| [38] | Nicola S, Jacques I, Levi W, et al. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology, 2011, 12(6): R60. |
| [39] | Rong X S, He M, Wang C Y, et al. Analysis on the diversity of soil bacterial and fungal communities in the degraded alpine grassland in Northern Tibet Plateau. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(9): 1646-1651. |
| 荣新山, 何敏, 王从彦, 等. 藏北退化高寒草原土壤细菌和真菌多样性分析. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(9): 1646-1651. | |
| [40] | Ren C J, Zhou Z H, Guo Y X, et al. Contrasting patterns of microbial community and enzyme activity between rhizosphere and bulk soil along an elevation gradient. Catena, 2021, 196: 104921. |
| [41] | Luo Z R, Zheng W C, Tang Z S, et al. Soil microbial diversity and its influencing factors in the habitat of rare plant Emmenopterys henryi in Jiulongshan, Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2024, 41(5): 1013-1023. |
| 骆争荣, 郑伟成, 唐战胜, 等. 浙江九龙山香果树生境土壤微生物多样性及其影响因素. 浙江农林大学学报, 2024, 41(5): 1013-1023. | |
| [42] | Wu H K, Ji S, Qiu X X, et al. Structural characteristics of soil fungal communities at different altitudes on the Qilian Mountains. Journal of Forestry and Environment, 2024, 44(6): 571-580. |
| 吴昊坤, 戢爽, 邱巡巡, 等. 祁连山南坡不同海拔高度土壤真菌群落结构特征. 森林与环境学报, 2024, 44(6): 571-580. | |
| [43] | Ji S, Wu H K, Zhang S X, et al. Study on the variation of bacterial communities in alpine meadow soil along an altitudinal gradient and its influencing factors. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2025, 33(4): 1085-1094. |
| 戢爽, 吴昊坤, 张绍雄, 等. 不同海拔高寒草甸土壤细菌多样性特征及影响因素研究. 草地学报, 2025, 33(4): 1085-1094. | |
| [44] | Zhang L. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil microbial community structure in alpine grassland of Tibet Plateau. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. |
| 张路. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物群落结构特征及影响因素. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2022. | |
| [45] | Meng Z Y, Li M, Yang X J, et al. Composition of fungal community in rhizosphere soil of Picea crassifoila and its response to altitude change. Mycosystema, 2023, 42(7): 1635-1650. |
| 孟兆云, 李敏, 杨勋爵, 等.青海云杉根围土壤真菌群落组成及对海拔变化的响应. 菌物学报, 2023, 42(7): 1635-1650. | |
| [46] | van der Wal A, van Veen J A, Smant W, et al. Fungal biomass development in a chronosequence of land abandonment. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(1): 51-60. |
| [47] | Dequelamu. Vertical differentiation of plant and soil microbial diversity in Qilian Mountain National Park and its relationship with soil environment. Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2023. |
| 德却拉姆. 祁连山国家公园植物和土壤微生物多样性垂直分异及其与土壤环境的关系研究. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2023. | |
| [48] | Li H Y, Yao T, Gao Y M, et al. Relationship between soil fungal communities and soil environmental factors in degraded alpine grassland. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2019, 59(4): 678-688. |
| 李海云, 姚拓, 高亚敏, 等.退化高寒草地土壤真菌群落与土壤环境因子间相互关. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(4): 678-688. | |
| [49] | Xiang X, Yin H X, Zhu Z Y, et al. Differences and influencing factors of bacterial composition and diversity in seven typical extreme habitats on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023, 63(8): 3235-3251. |
| 向信, 殷恒霞, 朱肇宇, 等. 青藏高原极端生境细菌多样性差异及影响因素. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(8): 3235-3251. | |
| [50] | Li S J, Wang F X, Cong W Q, et al. Microbial community structure and environmental response of desert soil in Hexi corridor. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(6): 1718-1728. |
| 李善家, 王福祥, 从文倩, 等. 河西走廊荒漠土壤微生物群落结构及环境响应. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(6): 1718-1728. | |
| [51] | Li J K, Cao P X, Liu Y X, et al. Study on bacterial diversity in rhizosphere soil of Astragalus heydei in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environmental Ecology, 2020, 2(11): 18-24. |
| 李敬科, 曹鹏熙, 刘怡萱, 等. 青藏高原毛柱黄耆根际土壤细菌多样性研究. 环境生态学, 2020, 2(11): 18-24. | |
| [52] | Nozari R M, Ramos L M, da Luz L A, et al. Halotolerant Streptomyces spp. induce salt tolerance in maize through systemic induction of the antioxidant system and accumulation of proline. Rhizosphere, 2022, 24: 100623. |
| [53] | Yang P N, Li X L, Li C Y, et al. Response of soil microbial diversity to long-term enclosure in degraded patches of alpine meadow in the source zone of the Yellow River. Environmental Sciences, 2023, 44(4): 2293-2303. |
| 杨鹏年, 李希来, 李成一, 等. 黄河源区斑块化退化高寒草甸土壤微生物多样性对长期封育的响应. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4): 2293-2303. | |
| [54] | Wang C T, Long R J, Wang Q J, et al. Effects of altitude on plant-species diversity and productivity in an alpine meadow, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Australian Journal of Botany, 2007, 55(2): 110-117. |
| [55] | Zhang X F, Bai X, Zhang Q D, et al. Effect of grazing prohibition on bacterial community structure in the topsoil of Stipa krylovii grassland in Inner Mongolia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(11): 3376-3383. |
| 张晓馥, 白雪, 张起迪, 等. 禁牧对内蒙古克氏针茅草原表层土壤细菌群落结构的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(11): 3376-3383. | |
| [56] | Feng H H, Wu B, Wu G Q, et al. Characteristics and functions soil microbial communities under different vegetation types in Karst areas.Journal of Forest and Environment, 2024, 44(2): 148-156. |
| 冯汉华, 吴斌, 伍国清, 等. 喀斯特不同植被类型土壤细菌群落与功能特征. 森林与环境学报, 2024, 44(2): 148-156. | |
| [57] | Li Y F. Elevation pattern and community assembly of soil bacteria on the Mount Gangbala in Tibet, China. Lhasa: Tibet University, 2023. |
| 李伊凡. 西藏岗巴拉山土壤细菌多样性海拔分布格局与群落构建. 拉萨: 西藏大学, 2023. | |
| [58] | Liu J, Sui Y, Yu Z, et al. High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 70: 113-122. |
| [59] | Zhang S, Guo Y J, Qiu K Y. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of the fine roots and rhizosphere soil of dominant plants at different altitudes in the Helan Mountains. Pratacultural Science, 2025, 42(2): 316-328. |
| 张硕, 郭艳菊, 邱开阳. 贺兰山不同海拔优势植物细根-根际土壤生态化学计量特征. 草业科学, 2025, 42(2): 316-328. | |
| [60] | Li X X, Liu G M, Wu X L, et al. Elevational distribution of soil organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and their ecological stoichiometry on Maxian Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(3): 758-765. |
| 李新星, 刘桂民, 吴小丽, 等.马衔山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(3): 758-765. | |
| [61] | Xing S L. Comparative study of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau soil nitrogen mineralization process response to temperatures change. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2010. |
| 邢顺林. 青藏高原与黄土高原土壤氮素矿化过程对温度变化响应的比较研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. | |
| [62] | Li D W, Wang Z Q, Tian H X, et al. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of soils at different elevations in Taibai Mountains. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(1): 160-170. |
| 李丹维, 王紫泉, 田海霞, 等. 太白山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(1): 160-170. |
| [1] | 安玉霞, 王文强, 余殿, 梁咏亮, 杨君珑, 李小伟. 基于优化MaxEnt模型的锁阳分布研究:现状评估与未来预测[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 1-12. |
| [2] | 孔天赐, 马学青, 贺晨帮, 樊泰延, 芦光新, 祁鹤兴. 青贮玉米真菌性病害对青贮发酵微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 95-106. |
| [3] | 陈鑫珠, 林平冬, 岳稳, 杨雅妮, 邱水玲, 郑向丽. 不同添加剂对蚕豆秸秆青贮品质及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 164-174. |
| [4] | 姜安静, 董乙强, 周时杰, 聂婷婷, 吴悦, 柳泽宇, 单兴芸, 雷雅欣, 吴凯, 安沙舟. 草地植物多样性沿海拔梯度分布特征及其驱动因素——以天山北坡东段为例[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 29-40. |
| [5] | 龚昕, 霍新茹, 李雯, 杨彦东, 刘超, 秦伟春, 沈艳, 王国会, 马红彬. 宁夏罗山山地草原植被群落特征及其空间分异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 1-15. |
| [6] | 回金峰, 魏孔钦, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 伊犁河流域紫花苜蓿干草产量和营养品质对海拔高度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 41-50. |
| [7] | 申迪, 曾子铭, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 廖扬, 王迅, 黄伟华, 刘书杰, 杨英魁, 王书祥. 低精料日粮和高精料日粮对牦牛生长性能和瘤胃菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 155-165. |
| [8] | 于双, 李小伟, 王瑞霞, 杨君珑, 马龙. 灵武白芨滩不同年限柠条固沙林林下草本群落演替规律及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 13-23. |
| [9] | 王鹏, 金正, 余婷, 秦康强, 桑新亚, 陶建平, 罗唯学. 预测姜黄属植物在中国当前和未来气候情景下的潜在分布区变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 14-27. |
| [10] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [11] | 郁国梁, 马紫荆, 吕自立, 刘彬. 海拔和植物群落共同调节天山中段南坡巴伦台地区天然草场土壤化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 68-78. |
| [12] | 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| [13] | 黄业芸, 邱开阳, 朱亚超, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 杨壹, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 鲍平安. 贺兰山不同海拔植被生物量与土壤分形特征和土壤水分的相关关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 24-35. |
| [14] | 赵朋波, 邱开阳, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 李小伟, 陈林, 王继飞, 孟文芬, 黄业芸, 李小聪, 杨浩楠. 海拔梯度对贺兰山岩羊主要活动区植物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 79-90. |
| [15] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||