

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 12-23.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020064
刘万弟1( ), 李小伟1(
), 李小伟1( ), 黄文广2, 马惠成1, 马红英1, 王文晓1
), 黄文广2, 马惠成1, 马红英1, 王文晓1
收稿日期:2020-02-20
修回日期:2020-05-18
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-08
通讯作者:
李小伟
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: Lixiaowei@nxu.edu.cn基金资助:
Wan-di LIU1( ), Xiao-wei LI1(
), Xiao-wei LI1( ), Wen-guang HUANG2, Hui-cheng MA1, Hong-ying MA1, Wen-xiao WANG1
), Wen-guang HUANG2, Hui-cheng MA1, Hong-ying MA1, Wen-xiao WANG1
Received:2020-02-20
Revised:2020-05-18
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-08
Contact:
Xiao-wei LI
摘要:
物种多样性和生产力是草地生态系统的核心指标,是实现草地生态系统服务与功能的根本所在。宁夏温性草原位于干旱与半干旱的过渡区,针茅属植物是其优势种群,对水热变化敏感;因此,在全球气候变化背景下,探讨宁夏草原针茅属植物群落物种多样性与生产力的格局,在宏观尺度揭示其影响因素,不仅在生态学理论研究中具有重大价值,而且对宁夏天然草地生产与管理也具有指导意义。本研究以宁夏温性草原针茅属植物群落为对象,沿着环境梯度设置15个野外观测样地,调查了植物群落特征,测定土壤养分指标,结合各个样地的气候因子、土壤养分和空间数据,探讨了植物群落多样性和生产力空间分布格局及其对生态因子的响应,阐明植物群落物种多样性与生产力的关系。结果显示:1)宁夏针茅属群落生产力与纬度呈显著正相关,与海拔和经度显著负相关;物种多样性与纬度显著负相关,与海拔显著正相关,而与经度关系不显著;2)冗余分析(RDA)结果显示:土壤速效氮(SAN)、年均温度(MAT)、土壤有机碳(SOC)、土壤全氮(TN)、年均辐射(Ssrad)、土壤水分(SWC)、土壤容重(BD)、土壤全磷(TP)、年均降水量(MAP)、生长季月均降水量(GSP)、干旱季月均降水量(PDA)是影响物种多样性和生产力的主要因素;土壤因子对生产力、多样性及整体解释量分别为15.6%、17.8%、19.8%,水热因子对生产力、多样性及整体解释量分别为13.8%、37.9%、25.2%,共同解释量分别为68.7%、39.6%、50.6%。总体而言,水热及土壤因子是宁夏针茅属草原生产力及多样性格局的驱动因素,但对多样性和生产力解释比例不同,具有一定的倾向性;群落多样性与生产力呈正相关趋势,但不显著。本研究结果能为宁夏天然草原的生产与管理提供理论依据。
刘万弟, 李小伟, 黄文广, 马惠成, 马红英, 王文晓. 宁夏草原针茅属植物群落物种多样性和生产力格局及影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 12-23.
Wan-di LIU, Xiao-wei LI, Wen-guang HUANG, Hui-cheng MA, Hong-ying MA, Wen-xiao WANG. Community diversity, patterns of productivity, and factors influencing them in Stipa in Ningxia grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 12-23.
| 样地编号No. | 经度Longitude (E) | 纬度Latitude (N) | 海拔Elevation (m) | 优势种Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 106°29′06″ | 38°05′14″ | 1220.53 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S2 | 106°29′07″ | 38°05′13″ | 1233.42 | 沙生针茅S. caucasic |
| S3 | 107°17′55″ | 37°41′17″ | 1489.14 | 长芒草S. bungeana |
| S4 | 107°17′55″ | 37°41′15″ | 1486.94 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S5 | 106°16′07″ | 37°14′58″ | 1929.39 | 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica |
| S6 | 106°14′52″ | 37°14′58″ | 1675.94 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S7 | 106°01′55″ | 37°43′24″ | 1624.32 | 短花针茅S.breviflora |
| S8 | 105°11′43″ | 37°11′10″ | 2086.00 | 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica |
| S9 | 105°11′44″ | 37°11′10″ | 2085.01 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S10 | 105°30′44″ | 36°47′05″ | 1680.42 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S11 | 106°14′39″ | 36°39′55″ | 1676.49 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S12 | 106°29′47″ | 36°44′21″ | 1998.14 | 大针茅S. grandis |
| S13 | 106°17′51″ | 36°16′46″ | 1926.49 | 大针茅S. grandis |
| S14 | 106°24′40″ | 36°12′04″ | 1815.14 | 大针茅S. grandis |
| S15 | 105°37′46″ | 36°24′21″ | 2462.52 | 甘青针茅S. przewalskyi |
表1 各观测样点概况
Table 1 Overview of each observation sample point
| 样地编号No. | 经度Longitude (E) | 纬度Latitude (N) | 海拔Elevation (m) | 优势种Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 106°29′06″ | 38°05′14″ | 1220.53 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S2 | 106°29′07″ | 38°05′13″ | 1233.42 | 沙生针茅S. caucasic |
| S3 | 107°17′55″ | 37°41′17″ | 1489.14 | 长芒草S. bungeana |
| S4 | 107°17′55″ | 37°41′15″ | 1486.94 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S5 | 106°16′07″ | 37°14′58″ | 1929.39 | 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica |
| S6 | 106°14′52″ | 37°14′58″ | 1675.94 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S7 | 106°01′55″ | 37°43′24″ | 1624.32 | 短花针茅S.breviflora |
| S8 | 105°11′43″ | 37°11′10″ | 2086.00 | 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica |
| S9 | 105°11′44″ | 37°11′10″ | 2085.01 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S10 | 105°30′44″ | 36°47′05″ | 1680.42 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S11 | 106°14′39″ | 36°39′55″ | 1676.49 | 短花针茅S. breviflora |
| S12 | 106°29′47″ | 36°44′21″ | 1998.14 | 大针茅S. grandis |
| S13 | 106°17′51″ | 36°16′46″ | 1926.49 | 大针茅S. grandis |
| S14 | 106°24′40″ | 36°12′04″ | 1815.14 | 大针茅S. grandis |
| S15 | 105°37′46″ | 36°24′21″ | 2462.52 | 甘青针茅S. przewalskyi |
植物群落 Plant community | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | Simpson优势度指数Simpson dominance index (J) | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index ( | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (Y) | 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 短花针茅S. breviflora | 124.97±59.09c | 0.70±0.16bc | 1.47±0.47cd | 0.79±0.10bc | 6.89±2.75c |
| 长芒草S. bungeana | 110.05±62.18c | 0.85±0.20a | 2.19±0.09a | 0.87±0.24ab | 12.00±1.26ab |
| 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica | 241.53±27.44b | 0.74±0.68ab | 1.66±0.25bc | 0.82±0.59abc | 7.80±1.87c |
| 沙生针茅S.caucasica | 112.30±86.29c | 0.61±0.92c | 1.28±0.27d | 0.74±0.68c | 5.80±1.64c |
| 甘青针茅S. przewalskyi | 326.20±58.02a | 0.86±0.01a | 2.28±1.14a | 0.88±0.18a | 13.40±2.30a |
| 大针茅S. grandis | 198.74±51.15b | 0.80±0.06ab | 1.96±0.22ab | 0.83±0.67ab | 10.80±1.93b |
表2 宁夏草原针茅属植物群落多样性和生产力的整体分布
Table 2 The distribution of community diversity and productivity of Stipa in Ningxia grassland (mean±SD)
植物群落 Plant community | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | Simpson优势度指数Simpson dominance index (J) | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index ( | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (Y) | 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 短花针茅S. breviflora | 124.97±59.09c | 0.70±0.16bc | 1.47±0.47cd | 0.79±0.10bc | 6.89±2.75c |
| 长芒草S. bungeana | 110.05±62.18c | 0.85±0.20a | 2.19±0.09a | 0.87±0.24ab | 12.00±1.26ab |
| 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica | 241.53±27.44b | 0.74±0.68ab | 1.66±0.25bc | 0.82±0.59abc | 7.80±1.87c |
| 沙生针茅S.caucasica | 112.30±86.29c | 0.61±0.92c | 1.28±0.27d | 0.74±0.68c | 5.80±1.64c |
| 甘青针茅S. przewalskyi | 326.20±58.02a | 0.86±0.01a | 2.28±1.14a | 0.88±0.18a | 13.40±2.30a |
| 大针茅S. grandis | 198.74±51.15b | 0.80±0.06ab | 1.96±0.22ab | 0.83±0.67ab | 10.80±1.93b |
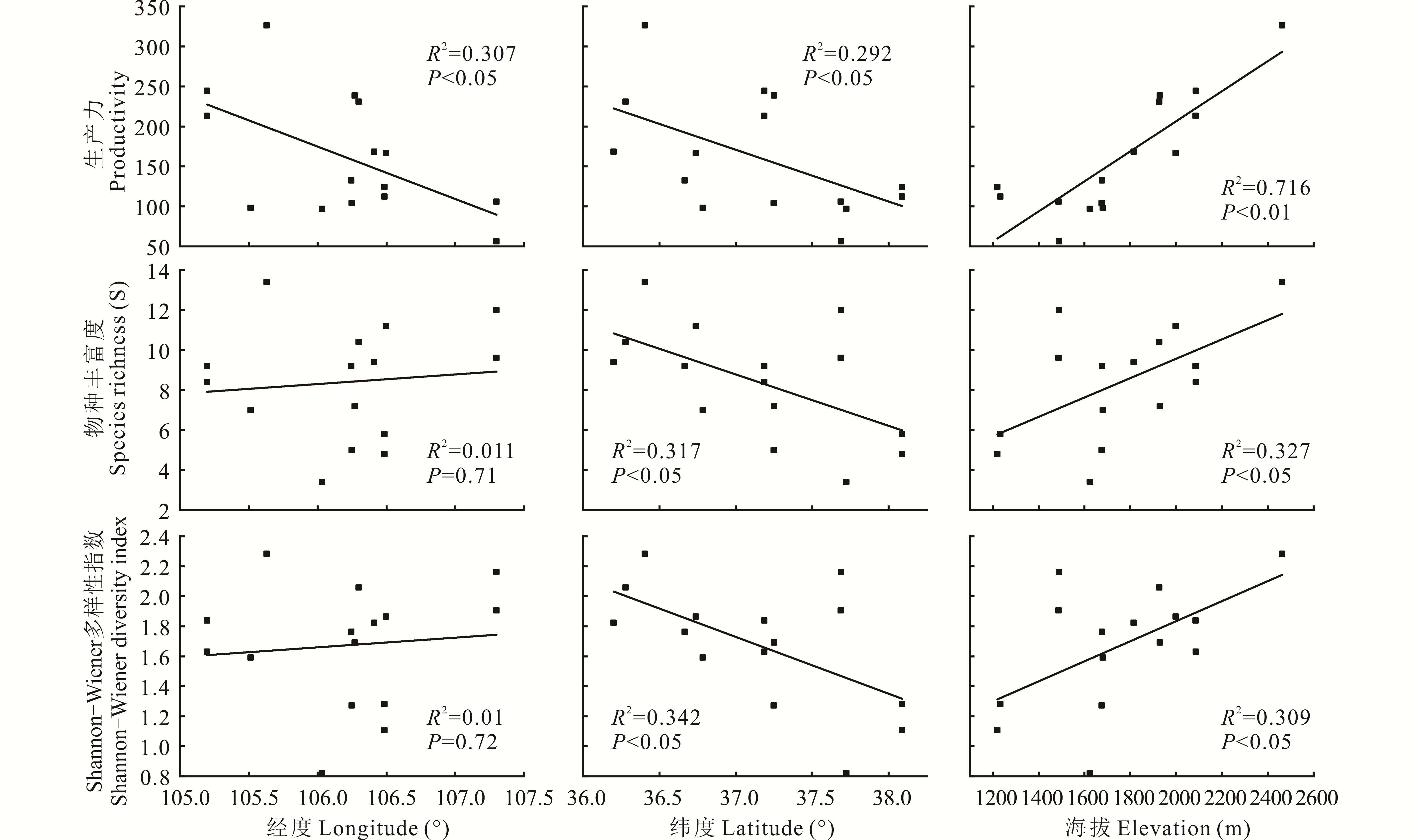
图2 宁夏草原针茅属群落生产力、物种丰富度、Shannon-Weiner多样性指数的空间分布格局
Fig.2 Spatial distribution patterns of productivity, species richness and Shannon-Weiner diversity indices of Stipa community in Ningxia grassland
| 样地编号No. | 土壤有机碳SOC (g?kg-1) | 土壤全氮 TN (g?kg-1) | 土壤全磷 TP (g?kg-1) | pH | 土壤速效氮 SAN (mg?kg-1) | 土壤速效磷 SAP (mg?kg-1) | 容重 BD (g?cm-3) | 土壤含水量SWC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2.34±0.51g | 0.03±0.00h | 0.22±0.02h | 8.14±0.03fg | 2.91±0.70gh | 10.75±4.94fg | 1.4007b | 3.35e |
| S2 | 2.87±0.62g | 0.03±0.00h | 0.24±0.00h | 8.08±0.03g | 2.10±0.73gh | 22.25±6.25def | 1.5451a | 3.78de |
| S3 | 2.65±0.33g | 0.04±0.00h | 0.20±0.01h | 8.16±0.02efg | 1.09±0.71h | 11.88±2.47fg | 1.3956b | 4.81de |
| S4 | 3.97±0.28g | 0.04±0.01h | 0.28±0.02g | 8.16±0.05efg | 3.61±2.64fgh | 8.49±2.99g | 1.1980d | 13.83c |
| S5 | 21.18±2.18d | 0.11±0.01f | 0.44±0.04e | 8.14±0.05fg | 12.01±1.60cd | 30.56±8.56cd | 1.2119d | 11.59c |
| S6 | 3.30±0.65g | 0.05±0.00h | 0.44±0.01e | 8.23±0.06def | 5.25±1.58fg | 43.75±3.12a | 1.1673def | 11.94c |
| S7 | 4.20±0.66g | 0.07±0.03g | 0.39±0.03f | 8.21±0.06ef | 4.20±3.16fg | 15.08±4.88efg | 1.3235bc | 4.24de |
| S8 | 13.29±3.77e | 0.10±0.02ef | 0.48±0.02d | 8.32±0.08bcd | 10.03±2.11de | 16.03±4.56efg | 1.1790de | 6.87de |
| S9 | 26.77±2.30c | 0.16±0.01d | 0.52±0.01c | 8.16±0.03efg | 15.05±0.73bc | 42.23±9.14ab | 1.1420defg | 6.55de |
| S10 | 11.70±0.58ef | 0.10±0.01ef | 0.52±0.01c | 8.23±0.02def | 6.88±2.05ef | 16.96±2.94efg | 1.2281cd | 4.19de |
| S11 | 8.38±1.65f | 0.08±0.01fg | 0.53±0.02c | 8.26±0.04cde | 4.90±1.73fg | 12.26±5.38fg | 1.2208d | 7.23d |
| S12 | 26.61±6.34c | 0.15±0.01d | 0.63±0.01ab | 8.35±0.06abc | 15.40±1.73bc | 24.69±2.91de | 1.1624def | 10.65c |
| S13 | 28.03±3.12c | 0.18±0.01c | 0.60±0.01b | 8.42±0.01a | 15.74±1.41b | 22.25±4.94def | 1.0851efg | 21.89b |
| S14 | 39.05±2.80a | 0.21±0.01b | 0.66±0.01a | 8.39±0.03ab | 18.54±0.73b | 38.11±12.47abc | 1.0546g | 19.35b |
| S15 | 35.34±3.97b | 0.30±0.01a | 0.63±0.01ab | 7.84±0.06h | 29.62±4.40a | 32.45±7.21bcd | 1.0661fg | 30.37a |
表3 宁夏草原针茅属植物群落(0~30 cm)土壤特征
Table 3 Soil characteristics of the community (0-30 cm) of Stipa in Ningxia grassland (mean±SD)
| 样地编号No. | 土壤有机碳SOC (g?kg-1) | 土壤全氮 TN (g?kg-1) | 土壤全磷 TP (g?kg-1) | pH | 土壤速效氮 SAN (mg?kg-1) | 土壤速效磷 SAP (mg?kg-1) | 容重 BD (g?cm-3) | 土壤含水量SWC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2.34±0.51g | 0.03±0.00h | 0.22±0.02h | 8.14±0.03fg | 2.91±0.70gh | 10.75±4.94fg | 1.4007b | 3.35e |
| S2 | 2.87±0.62g | 0.03±0.00h | 0.24±0.00h | 8.08±0.03g | 2.10±0.73gh | 22.25±6.25def | 1.5451a | 3.78de |
| S3 | 2.65±0.33g | 0.04±0.00h | 0.20±0.01h | 8.16±0.02efg | 1.09±0.71h | 11.88±2.47fg | 1.3956b | 4.81de |
| S4 | 3.97±0.28g | 0.04±0.01h | 0.28±0.02g | 8.16±0.05efg | 3.61±2.64fgh | 8.49±2.99g | 1.1980d | 13.83c |
| S5 | 21.18±2.18d | 0.11±0.01f | 0.44±0.04e | 8.14±0.05fg | 12.01±1.60cd | 30.56±8.56cd | 1.2119d | 11.59c |
| S6 | 3.30±0.65g | 0.05±0.00h | 0.44±0.01e | 8.23±0.06def | 5.25±1.58fg | 43.75±3.12a | 1.1673def | 11.94c |
| S7 | 4.20±0.66g | 0.07±0.03g | 0.39±0.03f | 8.21±0.06ef | 4.20±3.16fg | 15.08±4.88efg | 1.3235bc | 4.24de |
| S8 | 13.29±3.77e | 0.10±0.02ef | 0.48±0.02d | 8.32±0.08bcd | 10.03±2.11de | 16.03±4.56efg | 1.1790de | 6.87de |
| S9 | 26.77±2.30c | 0.16±0.01d | 0.52±0.01c | 8.16±0.03efg | 15.05±0.73bc | 42.23±9.14ab | 1.1420defg | 6.55de |
| S10 | 11.70±0.58ef | 0.10±0.01ef | 0.52±0.01c | 8.23±0.02def | 6.88±2.05ef | 16.96±2.94efg | 1.2281cd | 4.19de |
| S11 | 8.38±1.65f | 0.08±0.01fg | 0.53±0.02c | 8.26±0.04cde | 4.90±1.73fg | 12.26±5.38fg | 1.2208d | 7.23d |
| S12 | 26.61±6.34c | 0.15±0.01d | 0.63±0.01ab | 8.35±0.06abc | 15.40±1.73bc | 24.69±2.91de | 1.1624def | 10.65c |
| S13 | 28.03±3.12c | 0.18±0.01c | 0.60±0.01b | 8.42±0.01a | 15.74±1.41b | 22.25±4.94def | 1.0851efg | 21.89b |
| S14 | 39.05±2.80a | 0.21±0.01b | 0.66±0.01a | 8.39±0.03ab | 18.54±0.73b | 38.11±12.47abc | 1.0546g | 19.35b |
| S15 | 35.34±3.97b | 0.30±0.01a | 0.63±0.01ab | 7.84±0.06h | 29.62±4.40a | 32.45±7.21bcd | 1.0661fg | 30.37a |
因子 Factor | 生产力 Productivity | 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) | Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index (J) | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index ( | Pielou均匀度指数Pielou evenness index (Y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经度Longitude | -0.554* | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 纬度Latitude | -0.541* | -0.563* | -0.645** | -0.585* | -0.560* |
| 海拔Elevation | 0.846** | 0.572* | 0.576* | 0.556* | 0.509 |
| 年均温MAT | -0.841** | -0.604* | -0.603* | -0.586* | -0.533* |
| 年降水量MAP | NS | 0.700** | 0.705** | 0.691** | 0.593* |
| 年均辐射Ssrad | -0.626* | -0.643** | -0.684** | -0.646** | -0.584* |
| 生长季月均降水量GSP | NS | 0.716** | 0.722** | 0.709** | 0.601* |
| 干旱季月均降水量PDA | NS | 0.690** | 0.675** | 0.666** | 0.504* |
| 土壤有机质SOC | 0.750** | 0.578* | 0.572* | 0.576* | NS |
| 土壤全氮TN | 0.794** | 0.613* | 0.566* | 0.580* | NS |
| 土壤含水量SWC | 0.675** | 0.596* | 0.599* | 0.610* | 0.615* |
| 土壤全磷TP | 0.616* | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 土壤速效氮SAN | 0.857** | 0.593* | 0.537* | 0.567* | NS |
| 土壤速效磷SAP | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| pH | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
表4 宁夏草原针茅属植物群落与生态因子的相关分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of community and ecological factors of Stipa in Ningxia grassland
因子 Factor | 生产力 Productivity | 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) | Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index (J) | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index ( | Pielou均匀度指数Pielou evenness index (Y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经度Longitude | -0.554* | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 纬度Latitude | -0.541* | -0.563* | -0.645** | -0.585* | -0.560* |
| 海拔Elevation | 0.846** | 0.572* | 0.576* | 0.556* | 0.509 |
| 年均温MAT | -0.841** | -0.604* | -0.603* | -0.586* | -0.533* |
| 年降水量MAP | NS | 0.700** | 0.705** | 0.691** | 0.593* |
| 年均辐射Ssrad | -0.626* | -0.643** | -0.684** | -0.646** | -0.584* |
| 生长季月均降水量GSP | NS | 0.716** | 0.722** | 0.709** | 0.601* |
| 干旱季月均降水量PDA | NS | 0.690** | 0.675** | 0.666** | 0.504* |
| 土壤有机质SOC | 0.750** | 0.578* | 0.572* | 0.576* | NS |
| 土壤全氮TN | 0.794** | 0.613* | 0.566* | 0.580* | NS |
| 土壤含水量SWC | 0.675** | 0.596* | 0.599* | 0.610* | 0.615* |
| 土壤全磷TP | 0.616* | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 土壤速效氮SAN | 0.857** | 0.593* | 0.537* | 0.567* | NS |
| 土壤速效磷SAP | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| pH | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
RDA排序轴 RDA ordination | 第一轴 Axis 1 | 第二轴Axis 2 | 第三轴 Axis 3 | 第四轴Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 0.6621 | 0.2892 | 0.0042 | 0.0004 |
| 非典型相关Pseudo-canonical correlation | 0.9717 | 0.9920 | 0.9788 | 0.9714 |
物种数据方差累积百分比 Cumulative percentage variance of species data | 66.21 | 95.13 | 95.55 | 95.59 |
表5 宁夏草原针茅属植物群落物种与生态因子RDA排序
Table 5 RDA sequence of species and ecological factors of Stipa community in Ningxia grassland
RDA排序轴 RDA ordination | 第一轴 Axis 1 | 第二轴Axis 2 | 第三轴 Axis 3 | 第四轴Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 0.6621 | 0.2892 | 0.0042 | 0.0004 |
| 非典型相关Pseudo-canonical correlation | 0.9717 | 0.9920 | 0.9788 | 0.9714 |
物种数据方差累积百分比 Cumulative percentage variance of species data | 66.21 | 95.13 | 95.55 | 95.59 |
| 1 | Lauchlan H F, Jason P, Anke J, et al. Worldwide evidence of a unimodal relationship between productivity and plant species richness. Science, 2015, 349(6245): 302-305. |
| 2 | Li Y H. Grazing dynamics of the species diversity in a-nenrolepidium chinense steppe and Stipa grandis steppe. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 1993, 35(11): 877-884. |
| 李永宏. 放牧影响下羊草草原和大针茅草原植物多样性的变化. 植物学报, 1993, 35(11): 877-884. | |
| 3 | Ji J J, Huang M, Liu Q. Modeling studies of response mechanism of steppe productivity to climate change in middle latitude semiarid regions in China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2005, 63(3): 257-266. |
| 季劲钧, 黄玫, 刘青. 气候变化对中国中纬度半干旱草原生产力影响机理的模拟研究. 气象学报, 2005, 63(3): 257-266. | |
| 4 | Han G D, Jiao S Y, Biligetu, et al. Effects of plant species diversity and productivity under different stocking rates in the Stipa breviflora Griseb. desert steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(1): 182-188. |
| 韩国栋, 焦树英, 毕力格图, 等. 短花针茅草原不同载畜率对植物多样性和草地生产力的影响. 生态学报, 2007, 27(1): 182-188. | |
| 5 | Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, Zhao H L, et al. Changes of species diversity and productivity in relation to soil properties in sandy grassland in Horqin Sand Land. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(5): 945-951. |
| 左小安, 赵学勇, 赵哈林, 等. 科尔沁沙质草地群落物种多样性、生产力与土壤特性的关系. 环境科学, 2007, 28(5): 945-951. | |
| 6 | Wang C T, Long R J, Wang Q L, et al. Response of plant diversity and productivity to soil resources changing under grazing disturbance on an alpine meadow. Acta Ecologica Snica, 2008, 28(9): 4144-4152. |
| 王长庭, 龙瑞军, 王启兰, 等. 放牧扰动下高寒草甸植物多样性、生产力对土壤养分条件变化的响应. 生态学报, 2008, 28(9): 4144-4152. | |
| 7 | Yin Y T, Hou X Y, Yun X J. Advances in the climate change influencing grassland ecosystems in Inner Mongolia. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(6): 1132-1139. |
| 尹燕亭, 侯向阳, 运向军. 气候变化对内蒙古草原生态系统影响的研究进展. 草业科学, 2011, 28(6): 1132-1139. | |
| 8 | Zhang D J. Effect of precipitation and temperature on pasture yield of grassland with high elevation and cold climate in Three Rivers Source. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(1): 181-184. |
| 张东杰. 水热因子对三江源高寒草地牧草产量的影响. 贵州农业科学, 2011, 39(1): 181-184. | |
| 9 | Zhao P, Chen T, Wang Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of the impact of climate change and human activities on grassland ecosystem NPP in Xinjiang. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 37(1): 51-62. |
| 赵鹏, 陈桃, 王茜, 等. 气候变化和人类活动对新疆草地生态系统NPP影响的定量分析. 中国科学院大学学报, 2020, 37(1): 51-62. | |
| 10 | Brendan C, Steven J, Tim J B, et al. Global convergence in the vulnerability of forests to drought. Nature, 2012, 491(7426): 752-755. |
| 11 | Wu J G, Lü J J, Ai L. The impacts of climate change on the biodiversity: Vulnerability and adaptation. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(2): 693-703. |
| 吴建国, 吕佳佳, 艾丽. 气候变化对生物多样性的影响: 脆弱性和适应. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(2): 693-703. | |
| 12 | Bai Y F, Li L H, Wang Q B, et al. Changes in plant species diversity and productivity along gradients of precipitation and elevation in the xilin river basin, Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2000, 24(6): 667-673. |
| 白永飞, 李凌浩, 王其兵, 等. 锡林河流域草原群落植物多样性和初级生产力沿水热梯度变化的样带研究. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(6): 667-673. | |
| 13 | Baer S G, Blair J M, Collins S L, et al. Soil resources regulate productivity and diversity in newly established tallgrass prairie. Ecology, 2003, 84(3): 724-735. |
| 14 | Zhang Q G, Zhang D Y. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Recent advances and controversies. Biodiversity Science, 2002, 10(1): 49-60. |
| 张全国, 张大勇. 生物多样性与生态系统功能: 进展与争论. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(1): 49-60. | |
| 15 | Naeem S, Thompson LJ, Lawler S P, et al. Declining biodiversity can alter the performance of ecosystems. Nature, 1994, 368(6473): 734-737. |
| 16 | Fornara D A,Tilman D. Ecological mechanisms associated with the positive diversity-productivity relationship in an N-limited grassland. Ecology, 2009, 90(2): 408-418. |
| 17 | Ansgar K, Jörg P, Volker A, et al. Effects of plant diversity, community composition and environmental parameters on productivity in montane European grasslands. Oecologia, 2005, 142(4): 606-615. |
| 18 | Zhou H K, Zhao X Q, Wen J, et al. The characteristics of soil and vegetation of degenerated alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source Region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(5): 1-11. |
| 周华坤, 赵新全, 温军, 等. 黄河源区高寒草原的植被退化与土壤退化特征. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 1-11. | |
| 19 | Li W, He S Q, Zhang G X. Ecological importance, environmental crisis and cooperative protection of the Eurasian steppe. World Forestry Research, 2020, 33(3): 95-100. |
| 李伟, 何淑嫱, 张更新. 欧亚草原的生态作用、环境危机及合作保护. 世界林业研究, 2020, 33(3): 95-100. | |
| 20 | Bai Y, Wu J, Pan Q, et al. Positive linear relationship between productivity and diversity: Evidence from the Eurasian steppe. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 44(5): 1023-1034. |
| 21 | Zhu Y J, Qiao X G, Guo K, et al. Distribution, community characteristics and classification of Stipa tianschanica var. gobica steppe in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(7): 785-792. |
| 朱媛君, 乔鲜果, 郭柯, 等. 中国戈壁针茅草原的分布、群落特征和分类. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(7): 785-792. | |
| 22 | Qiao X G, Guo K, Zhao L Q, et al. Distribution, community characteristics and classification of Stipa tianschanica var. klemenzii steppe in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(2): 231-237. |
| 乔鲜果, 郭柯, 赵利清, 等. 中国石生针茅草原的分布、群落特征和分类. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(2): 231-237. | |
| 23 | Yang Y, Guo K, Li Q Z, et al. Community characteristics of Stipa roborowskyi steppe in Xizang. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(6): 635-639. |
| 杨瑶, 郭柯, 赵利清, 等. 西藏昆仑针茅草原的基本特征. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(6): 635-639. | |
| 24 | Ma H C, Li X W,Yang J L, et al. Study on the community classification and floristic composition of ammopiptanthus mongolicus. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 706-716. |
| 马惠成, 李小伟, 杨君珑, 等. 蒙古沙冬青群落区系组成及分类研究. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(4): 706-716. | |
| 25 | Liu L L, Sheng J D, Cheng J H, et al. Relationship between plant species characteristics and climate factors in different grassland types of Xinjiang. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(5): 1-12. |
| 刘利利, 盛建东, 程军回, 等. 新疆不同草地类型植物物种特征与水热因子的关系研究. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 1-12. | |
| 26 | Wang C T, Long R J, Cao G M, et al. The relationship between soil nutrients and diversity-productivity of different type grasslands in alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 39(1): 1-8. |
| 王长庭, 龙瑞军, 曹广民, 等. 高寒草甸不同类型草地土壤养分与物种多样性——生产力关系. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(1): 1-8. | |
| 27 | Miao Q L, Ding Y Y, Wang Y, et al. Impact of climate warming on the distribution of China’s thermal resources. Journal of Natural Resources, 2009, 24(5): 934-944. |
| 缪启龙, 丁园圆, 王勇, 等. 气候变暖对中国热量资源分布的影响分析. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24(5): 934-944. | |
| 28 | Ma J H, Liu Y, Yang X G, et al. Characteristics of climate resources under global climate change in the North China Plain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(14): 3818-3827. |
| 马洁华, 刘园, 杨晓光, 等. 全球气候变化背景下华北平原气候资源变化趋势. 生态学报, 2010, 30(14): 3818-3827. | |
| 29 | Li Q H, Chen Y N. Response of spatial and temporal distribution of NDVI to hydrothermal condition variation in arid regions of Northwest China during 1981-2006. Glacier Permafrost, 2014, 36(2): 327-334. |
| 李奇虎, 陈亚宁. 1981-2006年西北干旱区NDVI时空分布变化对水热条件的响应. 冰川冻土, 2014, 36(2): 327-334. | |
| 30 | Liang X H, Zhang K B, Qiao S. Relationship between soil moisture and nutrients and plant diversity of caragana microphylla community in semi-arid loess region. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(9): 1748-1756. |
| 梁香寒, 张克斌, 乔厦. 半干旱黄土区柠条林土壤水分和养分与群落多样性关系. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(9): 1748-1756. | |
| 31 | Wang Y L, Ma Y S, Shi J J, et al. Investigation of biomass and soil nutrition of different vegetation type at alpine meadow in Yellow River headwater area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(1): 1-6. |
| 王彦龙, 马玉寿, 施建军, 等. 黄河源区高寒草甸不同植被生物量及土壤养分状况研究. 草地学报, 2011, 19(1): 1-6. | |
| 32 | Wang S L, Wang R X, Jing W M, et al. Biomass of grassland and response to soil moisture on arid mountain land in the Qilian mountains. Arid Land Geography, 2017, 40(4): 772-779. |
| 王顺利, 王荣新, 敬文茂, 等. 祁连山干旱山地草地生物量对水分条件的响应. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(4): 772-779. | |
| 33 | Ma W J, Zhang Q, Niu J M, et al. Relationship of ecosystem primary productivity to species diversity and functional group diversity: Evidence from Stipa breviflora grassland in Nei Mongol. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2013, 37(7): 620-630 |
| 马文静, 张庆, 牛建明, 等. 物种多样性和功能群多样性与生态系统生产力的关系——以内蒙古短花针茅草原为例. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(7): 620-630. | |
| 34 | Wang C T, Wang Q J, Long R J, et al. Changes in plant species diversity and productivity along an elevation gradient in an alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2004, 28(2): 240-245. |
| 王长庭, 王启基, 龙瑞军, 等. 高寒草甸群落植物多样性和初级生产力沿海拔梯度变化的研究. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(2): 240-245. | |
| 35 | Wu H B, Shui H W, Hu G Z, et al. Species diversity and biomass distribution patterns of alpine grassland along an elevation gradient in the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(6): 1071-1079 |
| 吴红宝, 水宏伟, 胡国铮, 等. 海拔对藏北高寒草地物种多样性和生物量的影响. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(6): 1071-1079. | |
| 36 | Liu X, Yang F, Zhang M J, et al. Plant diversity and productivity of grassland communities at different altitudes of Jiucaiping Mountain, Guizhou. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(2): 207-213. |
| 柳鑫, 杨丰, 张明均, 等. 贵州韭菜坪山区不同海拔草地群落植物多样性和生产力. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(2): 207-213. | |
| 37 | Yang H, Zhou W, Shi P Q, et al. Analysis of temporal-spatial variations of NPP and coupling relationship with hydrothermal factors in grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(2): 234-240. |
| 杨晗, 周伟, 石佩琪, 等. 内蒙古草地NPP时空变化格局及其与水热因子耦合关系. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(2): 234-240. | |
| 38 | Wang W X, Huang W G, Yang J L, et al. Distribution patterns and climate explanation of plant species richness in Ningxia grasslands. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(5): 158-163. |
| 王文晓, 黄文广, 杨君珑, 等. 宁夏草原物种丰富度分布格局及其水热解释. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(5): 158-163. | |
| 39 | Zhao X, Xie K Y, Wang Y J, et al. Study of patches community diversity on salinization grassland in north of Shanxi Province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(4): 51-60. |
| 赵祥, 谢开云, 王妍君, 等. 晋北盐碱化草地群落斑块的多样性. 草业学报, 2011, 20(4): 51-60. | |
| 40 | Zhang W G, Huang W B, Yang Z Y. The study on the relationship between mini-patch and degradation of pasture. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2003, 12(3): 44-50. |
| 张卫国, 黄文冰, 杨振宇. 草地微斑块与草地退化关系的研究. 草业学报, 2003, 12(3): 44-50. |
| [1] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [2] | 王子欣, 胡国铮, 水宏伟, 葛怡情, 韩玲, 高清竹, 干珠扎布, 旦久罗布. 不同时期干旱对青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统碳交换的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 24-33. |
| [3] | 顾继雄, 郭天斗, 王红梅, 李雪颖, 梁丹妮, 杨青莲, 高锦月. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地转变过程土壤微生物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 46-57. |
| [4] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [5] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [6] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 杜雷, 刘念, 李丽, 马玉寿. 黄河源区发草适生地植物群落特征及其土壤因子解释[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 80-89. |
| [7] | 张超, 闫瑞瑞, 梁庆伟, 娜日苏, 李彤, 杨秀芳, 包玉海, 辛晓平. 不同利用方式下草地土壤理化性质及碳、氮固持研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 90-98. |
| [8] | 侯金伟, 陈焘, 南志标. 不同埋藏方式及杀菌剂处理对黄土高原3种植物种子存活的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 129-136. |
| [9] | 刘帅楠, 李广, 吴江琪, 马维伟, 杨传杰, 张世康, 姚瑶, 陆燕花, 魏星星, 张娟. 黄土丘陵区不同土地类型下土壤养分特征—基于生态化学计量学[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 200-207. |
| [10] | 李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 胡雷, 陈科宇, 杨文高. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| [11] | 刘斯莉, 王长庭, 张昌兵, 胡雷, 唐立涛, 潘攀. 川西北高原3种禾本科牧草根系特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [12] | 蒋翔, 马建霞. 我国草地生态恢复对不同因素响应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 14-31. |
| [13] | 熊梅, 乔荠瑢, 杨阳, 张峰, 郑佳华, 吴建新, 赵萌莉. 不同载畜率下短花针茅和土壤生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 212-219. |
| [14] | 王晓娇, 蔡立群, 齐鹏, 王雅芝, 陈晓龙, 武均, 张仁陟. 培肥措施对旱地农田土壤CO2排放和碳库管理指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 32-45. |
| [15] | 孙华方, 李希来, 金立群, 李成一, 张静. 黄河源人工草地土壤微生物多样性对建植年限的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||