

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 28-40.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020161
李洁1( ), 潘攀2, 王长庭2(
), 潘攀2, 王长庭2( ), 胡雷2, 陈科宇2, 杨文高2
), 胡雷2, 陈科宇2, 杨文高2
收稿日期:2020-04-08
修回日期:2020-06-29
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2021-03-09
通讯作者:
王长庭
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wangct@swun.edu.cn基金资助:
Jie LI1( ), Pan PAN2, Chang-ting WANG2(
), Pan PAN2, Chang-ting WANG2( ), Lei HU2, Ke-yu CHEN2, Wen-gao YANG2
), Lei HU2, Ke-yu CHEN2, Wen-gao YANG2
Received:2020-04-08
Revised:2020-06-29
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2021-03-09
Contact:
Chang-ting WANG
摘要:
根系动态特征能够反映人工草地植物利用土壤资源的效率和群落恢复演替的程度。本研究以三江源区不同建植年限(5、6、9和13年)人工草地植物根系为研究对象,利用“微根管”技术,连续两个生长季(2015年5-9月和2016年5-9月)探究了4个建植年限人工草地根系动态特征。结果表明:地上生物量和丰富度在建植5~9年呈下降趋势,建植9~13年显著上升;土壤理化性质呈“N”字型变化,不同建植年限间差异显著;随建植年限增加,根系寿命、累积生产量和累积死亡量均波动上升,根系的生长和死亡主要发生在0~10 cm土层;根系平均现存量随建植年限增加持续增加,建植6~9年趋于深层化;根系生产量、死亡量和现存量具有明显季节变化,6月为生长高峰期,7月为现存量高峰期,8月为死亡高峰期,建植9年人工草地根系正生长高峰期迟于其他建植年限;建植年限和土层深度直接影响根系寿命,其余环境因子通过影响土壤速效养分或地上生物量间接影响根系现存量。综上所述,建植人工草地能够增加地上生物量和丰富度,改善土壤质量,促进根系现存量的增加,建植6~9年人工草地的二次退化现象只是暂时性过渡阶段,可在此阶段制定合理的人工管理措施来保证土壤养分的稳定输入,加快群落正向演替的进程,从而提高人工草地的群落稳定性和恢复力。
李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 胡雷, 陈科宇, 杨文高. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40.
Jie LI, Pan PAN, Chang-ting WANG, Lei HU, Ke-yu CHEN, Wen-gao YANG. Root dynamics of artificial grassland for swards of differing ages in the ‘Three-River Source’ region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 28-40.
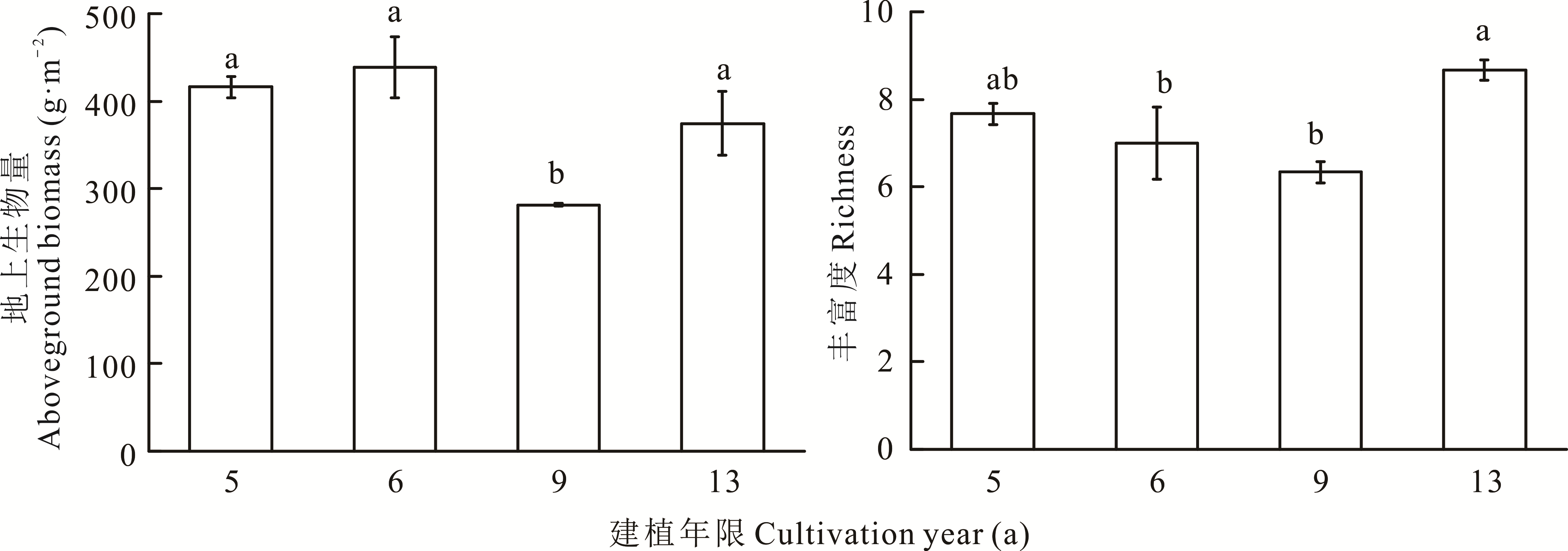
图1 不同建植年限人工草地植物群落特征变化不同小写字母表示不同年限间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different years (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Change of plant community characteristics in artificial grassland with different cultivation years
土层 Soil layer (cm) | 建植年限 Cultivation year (a) | pH | SM (%) | SOC (g·kg-1) | TN (g·kg-1) | TP (g·kg-1) | TK (g·kg-1) | AN (mg·kg-1) | AP (mg·kg-1) | AK (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 5 | 6.73± 0.01Bb | 13.68± 0.65Ab | 44.70± 0.44Ab | 7.84± 0.31Aab | 0.54± 0.03Ac | 19.18± 0.21Aa | 213.25± 4.08Ac | 2.55± 0.43Ac | 28.22± 0.76Ac |
| 6 | 7.34± 0.02Ba | 19.29± 0.90Aa | 48.78± 1.85Aa | 8.56± 0.27Aa | 0.73± 0.01Ab | 19.35± 0.20Aa | 316.25± 4.08Aa | 6.25± 0.76Ab | 33.54± 0.29Ab | |
| 9 | 6.28± 0.03Bc | 7.82± 0.11Ac | 30.47± 0.75Ac | 5.45± 0.17Ac | 0.54± 0.05Ac | 18.84± 0.21Aa | 263.91± 26.02Ab | 3.73± 0.38Ac | 29.76± 0.24Ac | |
| 13 | 6.13± 0.02Bd | 16.50± 1.51Aab | 45.50± 1.01Aab | 7.32± 0.31Ab | 0.87± 0.01Aa | 19.13± 0.16Ba | 286.86± 3.30Aab | 10.35± 0.54Aa | 49.38± 1.53Aa | |
| 10~20 | 5 | 7.16± 0.03Ac | 14.58± 3.55Aa | 38.61± 0.33Ba | 7.48± 0.18Aa | 0.63± 0.03Ab | 19.15± 0.10Ab | 174.01± 4.08Bc | 3.65± 0.42Aab | 12.62± 0.44Bd |
| 6 | 7.93± 0.04Aa | 14.32± 0.96Ba | 39.78± 0.34Ba | 7.28± 0.18Ba | 0.67± 0.02Bab | 18.86± 0.20Ab | 232.76± 4.08Bb | 3.68± 0.41Bab | 16.17± 0.65Bc | |
| 9 | 7.72± 0.06Ab | 7.12± 0.66Bc | 23.54± 0.24Ac | 5.09± 0.26Ac | 0.63± 0.06Ab | 19.26± 0.22Ab | 234.11± 3.17Ab | 3.08± 0.40Ab | 22.62± 0.92Bb | |
| 13 | 6.97± 0.02Ad | 10.58± 0.45Bb | 28.01± 1.46Bb | 5.99± 0.06Bb | 0.85± 0.21Aa | 20.38± 0.03Aa | 282.67± 4.09Aa | 4.81± 0.42Ba | 32.74± 0.91Ba |
表1 不同建植年限人工草地土壤理化特征
Table 1 Soil physical and chemical property in artificial grassland of different cultivation years
土层 Soil layer (cm) | 建植年限 Cultivation year (a) | pH | SM (%) | SOC (g·kg-1) | TN (g·kg-1) | TP (g·kg-1) | TK (g·kg-1) | AN (mg·kg-1) | AP (mg·kg-1) | AK (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 5 | 6.73± 0.01Bb | 13.68± 0.65Ab | 44.70± 0.44Ab | 7.84± 0.31Aab | 0.54± 0.03Ac | 19.18± 0.21Aa | 213.25± 4.08Ac | 2.55± 0.43Ac | 28.22± 0.76Ac |
| 6 | 7.34± 0.02Ba | 19.29± 0.90Aa | 48.78± 1.85Aa | 8.56± 0.27Aa | 0.73± 0.01Ab | 19.35± 0.20Aa | 316.25± 4.08Aa | 6.25± 0.76Ab | 33.54± 0.29Ab | |
| 9 | 6.28± 0.03Bc | 7.82± 0.11Ac | 30.47± 0.75Ac | 5.45± 0.17Ac | 0.54± 0.05Ac | 18.84± 0.21Aa | 263.91± 26.02Ab | 3.73± 0.38Ac | 29.76± 0.24Ac | |
| 13 | 6.13± 0.02Bd | 16.50± 1.51Aab | 45.50± 1.01Aab | 7.32± 0.31Ab | 0.87± 0.01Aa | 19.13± 0.16Ba | 286.86± 3.30Aab | 10.35± 0.54Aa | 49.38± 1.53Aa | |
| 10~20 | 5 | 7.16± 0.03Ac | 14.58± 3.55Aa | 38.61± 0.33Ba | 7.48± 0.18Aa | 0.63± 0.03Ab | 19.15± 0.10Ab | 174.01± 4.08Bc | 3.65± 0.42Aab | 12.62± 0.44Bd |
| 6 | 7.93± 0.04Aa | 14.32± 0.96Ba | 39.78± 0.34Ba | 7.28± 0.18Ba | 0.67± 0.02Bab | 18.86± 0.20Ab | 232.76± 4.08Bb | 3.68± 0.41Bab | 16.17± 0.65Bc | |
| 9 | 7.72± 0.06Ab | 7.12± 0.66Bc | 23.54± 0.24Ac | 5.09± 0.26Ac | 0.63± 0.06Ab | 19.26± 0.22Ab | 234.11± 3.17Ab | 3.08± 0.40Ab | 22.62± 0.92Bb | |
| 13 | 6.97± 0.02Ad | 10.58± 0.45Bb | 28.01± 1.46Bb | 5.99± 0.06Bb | 0.85± 0.21Aa | 20.38± 0.03Aa | 282.67± 4.09Aa | 4.81± 0.42Ba | 32.74± 0.91Ba |
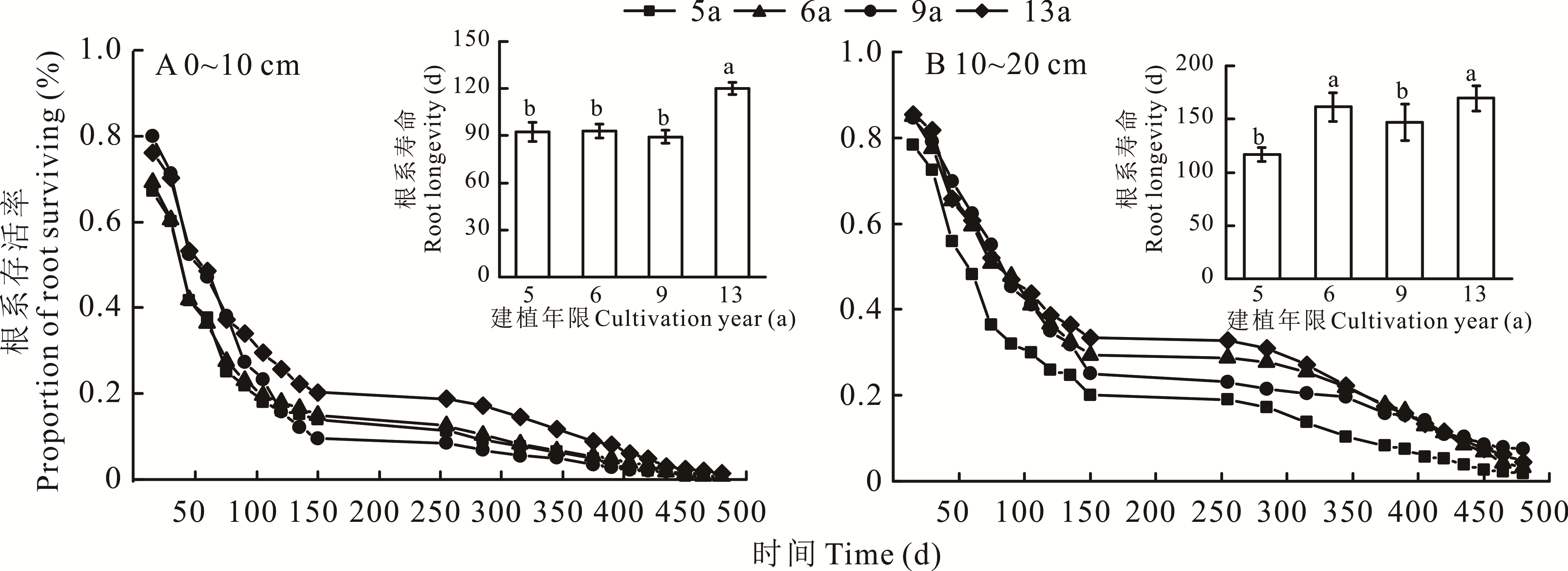
图2 不同建植年限人工草地根系存活率和平均寿命变化
Fig.2 Changes in proportion of root surviving and average longevity in artificial grassland with different cultivation years
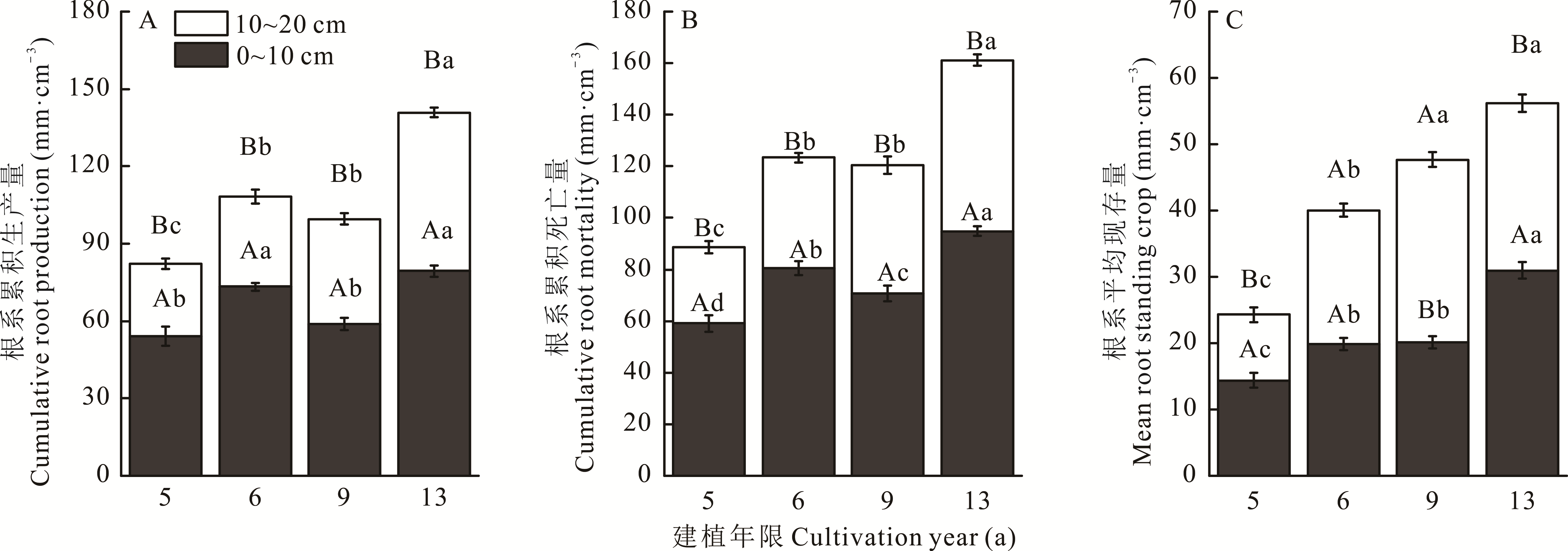
图5 不同建植年限人工草地根系累积生产量、累积死亡量和平均现存量变化不同大写字母表示不同土层间差异显著(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示不同年限间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different capital letters mean significant difference among different soil layers (P<0.05); Different lowercase letters mean significant difference among different cultivation years (P<0.05).
Fig.5 The changes of cumulative root production, cumulative root mortality and mean root standing crop of artificial grassland with different cultivation years
因子 Factor | 根系生产量 Root production | 根系死亡量 Root mortality | 根系现存量 Root standing crop | 根系寿命 Root longevity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass | -0.462** | -0.478** | -0.402* | -0.010 |
| 丰富度 Richness | -0.103 | 0.037 | 0.138 | 0.228 |
表2 根系特征与植物群落特征间的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between root characteristics and plant community characteristics
因子 Factor | 根系生产量 Root production | 根系死亡量 Root mortality | 根系现存量 Root standing crop | 根系寿命 Root longevity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass | -0.462** | -0.478** | -0.402* | -0.010 |
| 丰富度 Richness | -0.103 | 0.037 | 0.138 | 0.228 |
| 土层Soil layer | 因子Factor | pH | SM | SOC | TN | TP | TK | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 cm | 根系生产量Root production | -0.103 | 0.292 | 0.317 | 0.063 | 0.695** | 0.249 | 0.123 | 0.533* | 0.529* |
| 根系死亡量Root mortality | -0.251 | 0.095 | 0.148 | -0.126 | 0.601* | 0.342 | 0.153 | 0.522* | 0.490 | |
| 根系现存量Root standing crop | -0.375 | 0.156 | 0.028 | -0.286 | 0.533* | 0.186 | 0.336 | 0.535* | 0.476 | |
| 根系寿命Root longevity | -0.435 | 0.330 | 0.258 | 0.098 | 0.633** | 0.019 | 0.258 | 0.726** | 0.759** | |
| 10~20 cm | 根系生产量Root production | -0.398 | 0.146 | -0.333 | -0.248 | 0.491 | 0.629** | 0.678** | 0.565* | 0.753** |
| 根系死亡量Root mortality | -0.369 | -0.228 | -0.235 | -0.537* | 0.509* | 0.651** | 0.782** | 0.804** | 0.811** | |
| 根系现存量Root standing crop | 0.142 | -0.026 | -0.217 | -0.204 | 0.311 | 0.152 | 0.638** | -0.026 | 0.462 | |
| 根系寿命Root longevity | 0.437 | -0.158 | -0.308 | -0.378 | 0.030 | -0.136 | 0.395 | -0.188 | 0.220 |
表3 根系特征与土壤理化性质间的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between root characteristics and soil physical and chemical property
| 土层Soil layer | 因子Factor | pH | SM | SOC | TN | TP | TK | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 cm | 根系生产量Root production | -0.103 | 0.292 | 0.317 | 0.063 | 0.695** | 0.249 | 0.123 | 0.533* | 0.529* |
| 根系死亡量Root mortality | -0.251 | 0.095 | 0.148 | -0.126 | 0.601* | 0.342 | 0.153 | 0.522* | 0.490 | |
| 根系现存量Root standing crop | -0.375 | 0.156 | 0.028 | -0.286 | 0.533* | 0.186 | 0.336 | 0.535* | 0.476 | |
| 根系寿命Root longevity | -0.435 | 0.330 | 0.258 | 0.098 | 0.633** | 0.019 | 0.258 | 0.726** | 0.759** | |
| 10~20 cm | 根系生产量Root production | -0.398 | 0.146 | -0.333 | -0.248 | 0.491 | 0.629** | 0.678** | 0.565* | 0.753** |
| 根系死亡量Root mortality | -0.369 | -0.228 | -0.235 | -0.537* | 0.509* | 0.651** | 0.782** | 0.804** | 0.811** | |
| 根系现存量Root standing crop | 0.142 | -0.026 | -0.217 | -0.204 | 0.311 | 0.152 | 0.638** | -0.026 | 0.462 | |
| 根系寿命Root longevity | 0.437 | -0.158 | -0.308 | -0.378 | 0.030 | -0.136 | 0.395 | -0.188 | 0.220 |
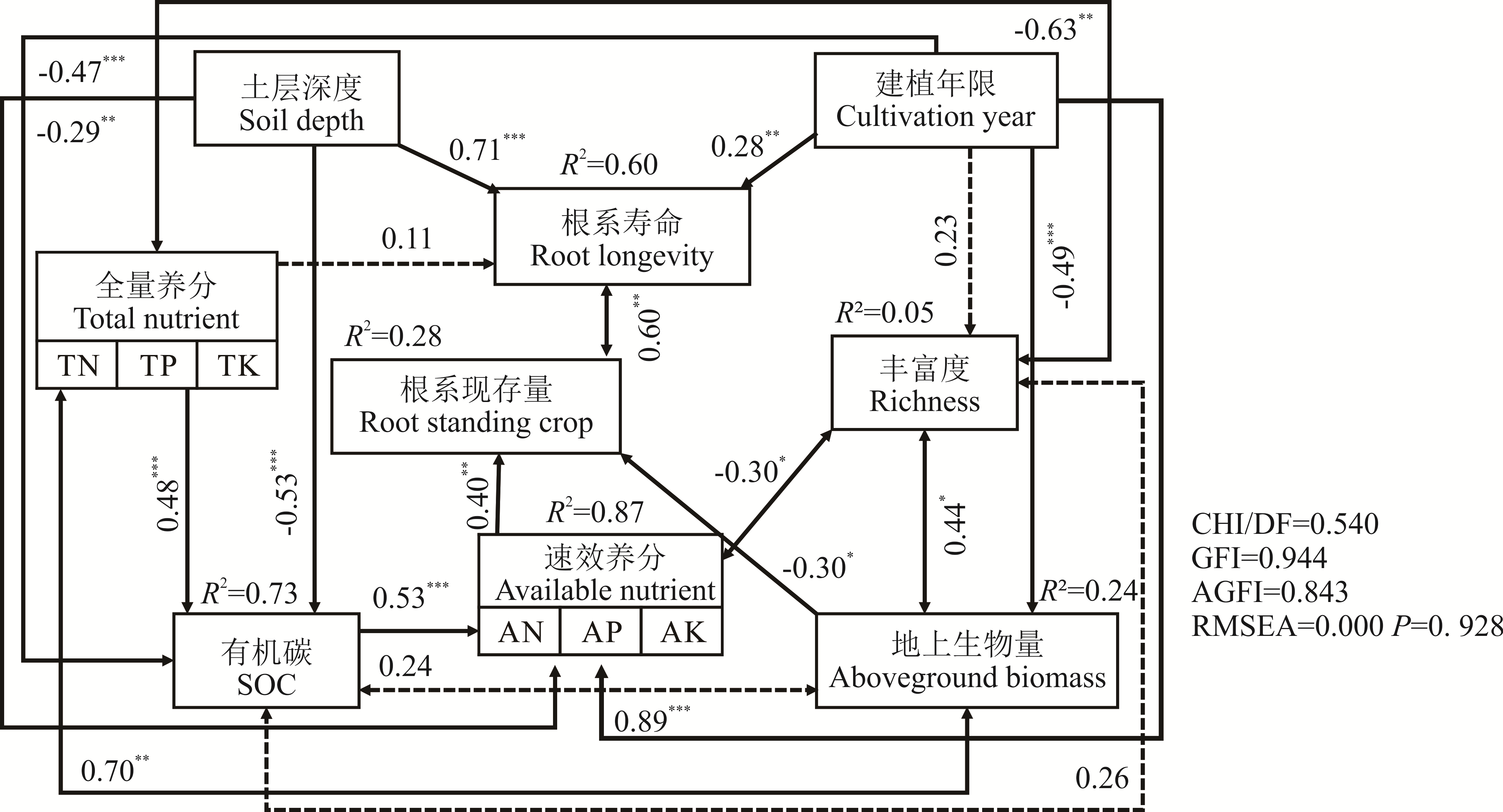
图6 根系寿命和现存量与环境因子结构方程模型“*”表示在P<0.05水平显著相关,“**”表示在P<0.01水平极显著相关,“***”表示在P<0.001水平极显著相关。实线代表相关显著,虚线代表相关不显著。R2表示解释率。 “*”means significant correlation at P<0.05, “**”means extremely significant correlation at P<0.01,“***”means extremely significant correlation at P<0.001. The solid line represents significant correlation, and the dotted line represents is not significant correlation. R2 means the rate of explanation.CHI: 卡方值Chi-Square; DF: 自由度Degrees of freedom; GFI: 适配度指数Goodness-of-fit; AGFI: 调整后适配度指数Adjusted goodness-of-fit index; RMSEA: 近似误差均方根Root mean square error of approximation.
Fig.6 The structural equation model of root longevity and standing crop and environmental factor
| 1 | Jiang C, Zhang L B. Climate change and its impact on the eco-environment of the Three-Rivers Headwater region on the Tibetan Plateau, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2015, 12(10): 12057-12081. |
| 2 | Xu M, Kang S C, Che X L, et al. Detection of hydrological variations and their impacts on vegetation from multiple satellite observations in the Three-River Source region of the Tibetan Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 1220-1232. |
| 3 | Chu H B, Wei J H, Qiu J, et al. Identification of the impact of climate change and human activities on rainfall-runoff relationship variation in the Three-River Headwaters region. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 106(11): 1-13. |
| 4 | Shao Q, Cao W, Fan J, et al. Effects of an ecological conservation and restoration project in the Three-River Source region, China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2017, 27(2): 183-204. |
| 5 | Wang X X, Dong S K, Li Y Y, et al. Effects of grassland degradation and artificial restoration on soil physicochemical properties in Three-River Headwater. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(4): 115-119, 124. |
| 王学霞, 董世魁, 李媛媛, 等. 三江源区草地退化与人工恢复对土壤理化性状的影响. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(4): 115-119, 124. | |
| 6 | Ma Y S, Zhang Z H, Dong Q M, et al. Application of restoration ecology in “black soil type” degraded grassland rebuilding. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2007, 42(2): 91-97. |
| 马玉寿, 张自和, 董全民, 等. 恢复生态学在 “黑土型” 退化草地植被改建中的应用. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2007, 42(2): 91-97. | |
| 7 | Cao G M, Long R J. The bottleneck and its resolutions to the natural recovery of black soil type degraded grassland in the Three River Source region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2009, 17(1): 4-9. |
| 曹广民, 龙瑞军. 三江源区 “黑土滩” 型退化草地自然恢复的瓶颈及解决途径. 草地学报, 2009, 17(1): 4-9. | |
| 8 | Zhang R, Wang Y, Ma L N, et al. Species diversities of plant communities of degraded artificial grassland, “Heitutan” and natural grassland in the “Three-River Headwaters” region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2014, 22(6): 1171-1178. |
| 张蕊, 王媛, 马丽娜, 等. 三江源区退化人工草地、“黑土滩” 和天然草地植物群落物种多样性. 草地学报, 2014, 22(6): 1171-1178. | |
| 9 | Yang X Z, Wang C T, Zi H B, et al. Soil microbial community structure characteristics in artificial grassland with different cultivation years in the headwater region of Three Rivers, China. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2015, 21(2): 341-349. |
| 杨希智, 王长庭, 字洪标, 等. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地土壤微生物群落结构特征. 应用与环境生物学报, 2015, 21(2): 341-349. | |
| 10 | Zhu L, Li Y Y, Wang X X, et al. Soil-quality effects of grassland degradation and restoration on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2012, 76(6): 2256-2264. |
| 11 | Wang C T, Wang G X, Liu W, et al. Effects of establishing an artificial grassland on vegetation characteristics and soil quality in a degraded meadow. Israel Journal of Ecology & Evolution, 2013, 59(3): 141-153. |
| 12 | Hu L, Zi H B, Wu P F, et al. Soil bacterial communities in grasslands revegetated using Elymus nutans are largely influenced by soil pH and total phosphorus across restoration time. Land Degradation and Development, 2019, 30(18): 2243-2256. |
| 13 | Zhang Y K, Zhang L F, Zhang X Z, et al. Effects of different range restorations on the root traits of vegetation in the alpine meadow. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2014, 50(1): 107-111. |
| 张燕堃, 张灵菲, 张新中, 等. 不同草地恢复措施对高寒草甸根系特征的影响. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(1): 107-111. | |
| 14 | Wang C T, Wang G X, Liu W, et al. Vegetation roots and soil physical and chemical characteristics in degeneration succession of the Kobresia pygmaea meadow. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2012, 21(3): 409-416. |
| 王长庭, 王根绪, 刘伟, 等. 植被根系及其土壤理化特征在高寒小嵩草草甸退化演替过程中的变化. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(3): 409-416. | |
| 15 | Gang H, Padilla F M, Xue Y Z, et al. Fine root dynamics and longevity of Artemisia halodendron reflect plant growth strategy in two contrasting habitats. Journal of Arid Environments, 2012, 79(4): 1-7. |
| 16 | Sullivan P F, Sommerkorn M, Rueth H M, et al. Climate and species affect fine root production with long-term fertilization in acidic tussock tundra near Toolik Lake, Alaska. Oecologia, 2007, 153(3): 643-652. |
| 17 | Bai W M, Zhou M, Fang Y, et al. Differences in spatial and temporal root lifespan of three Stipa grasslands in Northern China. Biogeochemistry, 2017, 132(3): 293-306. |
| 18 | Eissenstat D M, Wells C E, Yanai R D, et al. Building roots in a changing environment: Implications for root longevity. New Phytologist, 2000, 147(1): 33-42. |
| 19 | Brunner I, Bakker M R, Bjork R G, et al. Fine-root turnover rates of European forests revisited: An analysis of data from sequential coring and ingrowth cores. Plant and Soil, 2013, 362(1/2): 357-372. |
| 20 | Shi J W, Yu S Q, Yu L Z, et al. Application of minirhizotron in fine root studies. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(4): 715-719. |
| 史建伟, 于水强, 于立忠, 等. 微根管在细根研究中的应用. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(4): 715-719. | |
| 21 | Zi H B, Chen Y, Hu L, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on root dynamics in an alpine meadow, Northwestern Sichuan. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(1): 38-49. |
| 字洪标, 陈焱, 胡雷, 等. 氮肥添加对川西北高寒草甸植物群落根系动态的影响. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(1): 38-49. | |
| 22 | Bao S D. Analysis of agricultural chemistry. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 25-82. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 25-82. | |
| 23 | Wells C E, Glenn D M, Eissenstat D M. Changes in the risk of fine‐root mortality with age: A case study in peach, Prunus persica (Rosaceae). American Journal of Botany, 2002, 89(1): 79-87. |
| 24 | Burton A J, Hendrick K S P L. Relationships between fine root dynamics and nitrogen availability in Michigan Northern hardwood forests. Oecologia, 2000, 125(3): 389-399. |
| 25 | Majdi H, Andersson P. Fine root production and turnover in a Norway spruce stand in Northern Sweden: Effects of nitrogen and water manipulation. Ecosystems, 2005, 8(2): 191-199. |
| 26 | Wu Y B, Che R X, Ma S, et al. Estimation of root production and turnover in an alpine meadow: Comparison of three measurement methods. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(13): 3529-3537. |
| 吴伊波, 车荣晓, 马双, 等. 高寒草甸植被根系生产和周转的比较研究. 生态学报, 2014, 34(13): 3529-3537. | |
| 27 | Sanders J L, Brown D A A J. A new fiber optic technique for measuring root growth of soybeans under field conditions. Agronomy Journal, 1978, 70(6): 259-273. |
| 28 | Wang M B, Xun J J, Chen J W, et al. The net growth rate of fine roots of Caragana korshinskii seedlings in the Loess Plateau region, Northwest Shanxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(5): 1117-1124. |
| 王孟本, 荀俊杰, 陈建文, 等. 晋西北黄土区幼龄柠条根系的净生长速率. 生态学报, 2010, 30(5): 1117-1124. | |
| 29 | Ade L J, Zi H B, Liu M, et al. Response of belowground root growth dynamics to snow cover change in alpine meadow. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(20): 6773-6784. |
| 阿的鲁骥, 字洪标, 刘敏, 等. 高寒草甸地下根系生长动态对积雪变化的响应. 生态学报, 2017, 37(20): 6773-6784. | |
| 30 | Zi H B, Liu M, Ade L J, et al. Effects of cultivation duration on soil microbial functional diversity of artificial grassland in the Three-River Headwater region. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(4): 978-987. |
| 字洪标, 刘敏, 阿的鲁骥, 等. 三江源区不同建植年限对人工草地土壤微生物功能多样性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(4): 978-987. | |
| 31 | Xing Y F, Wang X L, Liu Y Q, et al. Characteristics of plant community and soil organic carbon and nitrogen in artificial grassland with different establishment years. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 521-528. |
| 邢云飞, 王晓丽, 刘永琦, 等. 不同建植年限人工草地植物群落和土壤有机碳氮特征. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 521-528. | |
| 32 | Kirk J L, Beaudette L A, Hart M, et al. Methods of studying soil microbial diversity. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2004, 58(2): 169-188. |
| 33 | Geng Y P, Pan X Y, Xu C Y, et al. Plasticity and ontogenetic drift of biomass allocation in response to above-and below-ground resource availabilities in perennial herbs: A case study of Alternanthera philoxeroides. Ecological Research, 2007, 22(2): 255-260. |
| 34 | Gedroc J J, McConnaughay K D M, Coleman J S. Plasticity in root/shoot partitioning: Optimal, ontogenetic, or both? Functional Ecology, 1996, 10(1): 44-50. |
| 35 | Ghestem M, Veylon G, Bernard A, et al. Influence of plant root system morphology and architectural traits on soil shear resistance. Plant and Soil, 2014, 377(1/2): 43-61. |
| 36 | Paetsch L, Mueller C W, Kogel-Knabner I, et al. Effect of in-situ aged and fresh biochar on soil hydraulic conditions and microbial C use under drought conditions. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 6852-6862. |
| 37 | Yang Y, Fang J, Smith P, et al. Changes in topsoil carbon stock in the Tibetan grasslands between the 1980s and 2004. Global Change Biology, 2009, 15(11): 2723-2729. |
| 38 | Wu L K, Lin X M, Lin W X. Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. |
| 吴林坤, 林向民, 林文雄. 根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物互作关系研究进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. | |
| 39 | Change J J, Xu L, Xue J Y, et al. Effects of grazing intensity on soil organic matter and microorganisms in the Zoige alpine meadow. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(1): 25-34. |
| 常晶晶, 徐丽, 薛晶月, 等. 放牧强度对若尔盖高寒草甸土壤有机质和微生物的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 25-34. | |
| 40 | Cammeraat E L H, Risch A C. The impact of ants on mineral soil properties and processes at different spatial scales. Journal of Applied Entomology, 2010, 132(4): 285-294. |
| 41 | Wang Q L, Wang C T, Liu W, et al. Changes in plant communities and soil microbial physiological groups of artificial grasslands established for different years in headwater region of Yangtze River and Yellow River. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(11): 2646-2651. |
| 王启兰, 王长庭, 刘伟, 等. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地植物群落与土壤微生物生理类群的变化. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(11): 2646-2651. | |
| 42 | Li A, Gu M H, Zhang S T, et al. Effects of species richness on weed invasion in an artificial grassland ecosystem in eastern Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(2): 177-181. |
| 李昂, 顾梦鹤, 张世挺, 等. 青藏高原东缘人工草地群落物种丰富度对杂草入侵的影响. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 177-181. | |
| 43 | Wang C T, Long R J, Wang Q L, et al. Community succession of differently aged artificial grasslands and their soil nutrient changes in Three Rivers’ Source Regions in Qinghai, China. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2009, 15(6): 3-10. |
| 王长庭, 龙瑞军, 王启兰, 等. 三江源区不同建植年代人工草地群落演替与土壤养分变化. 应用与环境生物学报, 2009, 15(6): 3-10. | |
| 44 | McCormack M L, Guo D L. Impacts of environmental factors on fine root lifespan. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5(6): 1-11. |
| 45 | Xu W J, Wang Z Q, Fan Z Q, et al. Effect of shading on the senescence of fine roots of Fraxinus mandshurica seedlings. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2006, 30(1): 104-111. |
| 46 | Rong L, Li S J, Li X W, et al. Carbon dynamics of fine root (grass root) decomposition and active soil organic carbon in various models of land use conversion from agricultural lands into forest lands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 31(1): 137-144. |
| 荣丽, 李守剑, 李贤伟, 等. 不同退耕模式细根(草根)分解过程中C动态及土壤活性有机碳的变化. 生态学报, 2010, 31(1): 137-144. | |
| 47 | Zhang Y Y, Liu B Y, Wang Y F, et al. Research progress of plant roots. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 22(11): 11-18. |
| 张鋆鋆, 刘冰洋, 王一凡, 等. 植物根系研究进展. 天津农业科学, 2016, 22(11): 11-18. | |
| 48 | Yavitt J B, Harms K E, Garcia M N, et al. Soil fertility and fine root dynamics in response to 4 years of nutrient (N, P, K) fertilization in a lowland tropical moist forest, Panama. Austral Ecology, 2011, 36(4): 433-445. |
| 49 | Zhao X C, Lai L M, Zhu L H, et al. Fine root biomass, decomposition and turnover of Reaumuria soongorica communities in the Sangong River basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(15): 4295-4303. |
| 赵学春, 来利明, 朱林海, 等. 三工河流域两种琵琶柴群落根系生物量、分解与周转. 生态学报, 2014, 34(15): 4295-4303. | |
| 50 | Xu M H, Liu M, Xue X, et al. Effects of warming and clipping on the growth of aboveground vegetation in an alpine meadow. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(2): 231-236. |
| 徐满厚, 刘敏, 薛娴, 等. 增温、刈割对高寒草甸地上植被生长的影响. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(2): 231-236. | |
| 51 | Zhang X P, Yin Y, Yu L Z, et al. Influence of water and soil nutrients on biomass and productivity of fine tree roots: A review. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 2010, 27(4): 606-613. |
| 张小朋, 殷有, 于立忠, 等. 土壤水分与养分对树木根系生物量及生产力的影响. 浙江林学院学报, 2010, 27(4): 606-613. | |
| 52 | Lopez B, Sabate S, Gracia C A. Annual and seasonal changes in fine root biomass of a Quercus ilex L. forest. Plant and Soil, 2001, 230(1): 125-134. |
| 53 | Pei Z Q, Zhou Y, Zheng Y R. Contribution of fine root turnover to the soil organic carbon cycling in a Reaumuria soongorica community in an arid ecosystem of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2011, 35(11): 1182-1191. |
| 54 | Leppalammi K J, Salemaa M, Kleja D B, et al. Fine root turnover and litter production of Norway spruce in a long-term temperature and nutrient manipulation experiment. Plant and Soil, 2014, 374(1/2): 73-88. |
| 55 | Searles P S, Saravia D A, Rousseaux M C. Root length density and soil water distribution in drip-irrigated olive orchards in Argentina under arid conditions. Crop and Pasture Science, 2009, 60(3): 280-288. |
| [1] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [2] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [3] | 张超, 闫瑞瑞, 梁庆伟, 娜日苏, 李彤, 杨秀芳, 包玉海, 辛晓平. 不同利用方式下草地土壤理化性质及碳、氮固持研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 90-98. |
| [4] | 刘斯莉, 王长庭, 张昌兵, 胡雷, 唐立涛, 潘攀. 川西北高原3种禾本科牧草根系特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [5] | 孙华方, 李希来, 金立群, 李成一, 张静. 黄河源人工草地土壤微生物多样性对建植年限的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. |
| [6] | 王琇瑜, 黄晓霞, 和克俭, 孙晓能, 吕曾哲舟, 张勇, 朱湄, 曾睿钦. 滇西北高寒草甸植物群落功能性状与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 6-17. |
| [7] | 梁军, 全小龙, 张杰雪, 史惠兰, 段中华, 乔有明. 3种禾草水提取液对其种子发芽和幼苗生长的潜在化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 81-89. |
| [8] | 邱月, 吴鹏飞, 魏雪. 三种人工草地小型土壤节肢动物群落多样性动态及其差异[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 21-32. |
| [9] | 官惠玲, 樊江文, 李愈哲. 不同人工草地对青藏高原温性草原群落生物量组成及物种多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 192-201. |
| [10] | 常海涛, 赵娟, 刘佳楠, 刘任涛, 罗雅曦, 张静. 退耕还林与还草对土壤理化性质及分形特征的影响——以宁夏荒漠草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 14-25. |
| [11] | 宿婷婷, 马红彬, 周瑶, 贾希洋, 张蕊, 张双乔, 胡艳莉. 黄土丘陵典型草原土壤理化性质对生态恢复措施的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 34-46. |
| [12] | 伍文宪, 张蕾, 黄小琴, 杨潇湘, 薛龙海, 刘勇. 川西北高寒牧区不同人工草地对土壤微生物多样性影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 29-41. |
| [13] | 刘玉祯, 曹文侠, 王金兰, 李文, 辛雨琼, 王世林, 王小军. 祁连山东段不同类型灌丛斑块土壤特征对围封的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 32-45. |
| [14] | 秦燕, 刘文辉, 何峰, 仝宗永, 李向林. 施肥与切根对退化羊草草原土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 5-14. |
| [15] | 赵涛,马春晖,王栋,景永元,席琳乔. 冬小麦套种草木樨土壤中根瘤菌分布与土壤理化性质的相关性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 45-55. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||