

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 53-61.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021036
撖冬荣( ), 姚拓(
), 姚拓( ), 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明
), 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明
收稿日期:2021-01-26
修回日期:2021-03-31
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
姚拓
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yaotuo@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Dong-rong HAN( ), Tuo YAO(
), Tuo YAO( ), Hai-yun LI, Min-hao CHEN, Ya-min GAO, Chang-ning LI, Jie BAI, Ming SU
), Hai-yun LI, Min-hao CHEN, Ya-min GAO, Chang-ning LI, Jie BAI, Ming SU
Received:2021-01-26
Revised:2021-03-31
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Tuo YAO
摘要:
为研究微生物肥料(MF)与化肥(CF)对垂穗披碱草的促生最佳施用配比,通过盆栽试验探究了化肥减量20%和40%分别配施5种剂量(60、90、120、150、180 kg·hm-2)微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草农艺性状、根系和营养品质的影响。结果表明:第1茬,80%CF (240 kg·hm-2)配施90 kg·hm-2MF,垂穗披碱草株高、茎粗、干草产量较对照(CK)分别提高34.86%、44.83%、3.08%;80%CF配施120 kg·hm-2MF,粗脂肪含量较CK提高22.97%,酸性洗涤纤维(ADF)含量较CK降低6.59%;80%CF配施150 kg·hm-2MF,粗蛋白含量较CK提高36.09%,80%CF配施90 kg·hm-2MF,中性洗涤纤维(NDF)含量降低15.64%。第2茬,80%CF配施60 kg·hm-2MF,垂穗披碱草总根长较CK增加34.77%;80%CF配施90 kg·hm-2MF,株高、茎粗、干草产量和总根表面积较CK分别提高80.43%、66.34%、13.08%和8.66%;80%CF配施120 kg·hm-2MF,粗蛋白和粗脂肪含量、总根体积、地下部鲜重和干重分别较CK提高25.30%、14.61%、45.54%、19.39%和51.04%;80%CF配施180 kg·hm-2MF,ADF和NDF含量分别较CK降低8.13%和8.88%。通过主成分分析,化肥减量20%(240 kg·hm-2)与微生物肥料(90 kg·hm-2)配施对垂穗披碱草促生效果最好。
撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61.
Dong-rong HAN, Tuo YAO, Hai-yun LI, Min-hao CHEN, Ya-min GAO, Chang-ning LI, Jie BAI, Ming SU. Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer and substitution with microbial fertilizer on the growth of Elymus nutans[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 53-61.
处理 Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 茎粗Thick stem (mm) | 干草产量Dry yield (g·m-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First harvest | 第2茬Second harvest | 第1茬First harvest | 第2茬Second harvest | 第1茬First harvest | 第2茬Second harvest | |
| CK | 37.67±0.35e | 26.77±0.67g | 1.45±0.04bc | 1.01±0.01bc | 290.20±15.93a | 113.75±10.19ab |
| B1 | 37.63±0.58e | 36.77±0.46e | 1.59±0.10bc | 1.19±0.10b | 259.21±7.73ab | 107.78±8.44b |
| B2 | 50.80±0.65a | 48.30±0.47a | 2.10±0.08a | 1.68±0.79a | 299.14±13.48a | 128.63±4.48a |
| B3 | 50.53±0.79a | 43.00±1.80bc | 2.03±0.04a | 1.66±0.14a | 260.84±21.24ab | 98.31±10.41bc |
| B4 | 43.63±0.52cd | 44.90±1.19b | 1.65±0.09bc | 1.25±0.12b | 226.81±9.03bc | 96.40±5.83bc |
| B5 | 45.50±0.95bc | 38.80±1.48de | 1.53±0.05bc | 1.09±0.07bc | 190.68±10.66cd | 82.30±4.47cd |
| C1 | 42.33±1.33cd | 28.20±1.87g | 1.56±0.06bc | 1.19±0.02b | 220.98±8.24bc | 81.75±3.92cd |
| C2 | 44.76±0.24bcd | 38.10±0.67de | 1.53±0.10bc | 1.09±0.04bc | 200.00±6.67cd | 75.43±1.04d |
| C3 | 47.07±1.73b | 40.70±0.45cd | 1.67±0.05b | 1.31±0.18b | 175.52±7.48d | 80.86±5.58cd |
| C4 | 43.83±0.67cd | 36.97±1.39e | 1.57±0.05bc | 1.23±0.02b | 222.14±7.60bc | 83.70±2.05cd |
| C5 | 46.77±0.85b | 32.40±0.83f | 1.23±0.04d | 0.81±0.13c | 192.31±18.62cd | 79.05±1.92cd |
表1 垂穗披碱草农艺性状特征变化
Table 1 Changes in agronomic characteristics of E. nutans
处理 Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 茎粗Thick stem (mm) | 干草产量Dry yield (g·m-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First harvest | 第2茬Second harvest | 第1茬First harvest | 第2茬Second harvest | 第1茬First harvest | 第2茬Second harvest | |
| CK | 37.67±0.35e | 26.77±0.67g | 1.45±0.04bc | 1.01±0.01bc | 290.20±15.93a | 113.75±10.19ab |
| B1 | 37.63±0.58e | 36.77±0.46e | 1.59±0.10bc | 1.19±0.10b | 259.21±7.73ab | 107.78±8.44b |
| B2 | 50.80±0.65a | 48.30±0.47a | 2.10±0.08a | 1.68±0.79a | 299.14±13.48a | 128.63±4.48a |
| B3 | 50.53±0.79a | 43.00±1.80bc | 2.03±0.04a | 1.66±0.14a | 260.84±21.24ab | 98.31±10.41bc |
| B4 | 43.63±0.52cd | 44.90±1.19b | 1.65±0.09bc | 1.25±0.12b | 226.81±9.03bc | 96.40±5.83bc |
| B5 | 45.50±0.95bc | 38.80±1.48de | 1.53±0.05bc | 1.09±0.07bc | 190.68±10.66cd | 82.30±4.47cd |
| C1 | 42.33±1.33cd | 28.20±1.87g | 1.56±0.06bc | 1.19±0.02b | 220.98±8.24bc | 81.75±3.92cd |
| C2 | 44.76±0.24bcd | 38.10±0.67de | 1.53±0.10bc | 1.09±0.04bc | 200.00±6.67cd | 75.43±1.04d |
| C3 | 47.07±1.73b | 40.70±0.45cd | 1.67±0.05b | 1.31±0.18b | 175.52±7.48d | 80.86±5.58cd |
| C4 | 43.83±0.67cd | 36.97±1.39e | 1.57±0.05bc | 1.23±0.02b | 222.14±7.60bc | 83.70±2.05cd |
| C5 | 46.77±0.85b | 32.40±0.83f | 1.23±0.04d | 0.81±0.13c | 192.31±18.62cd | 79.05±1.92cd |
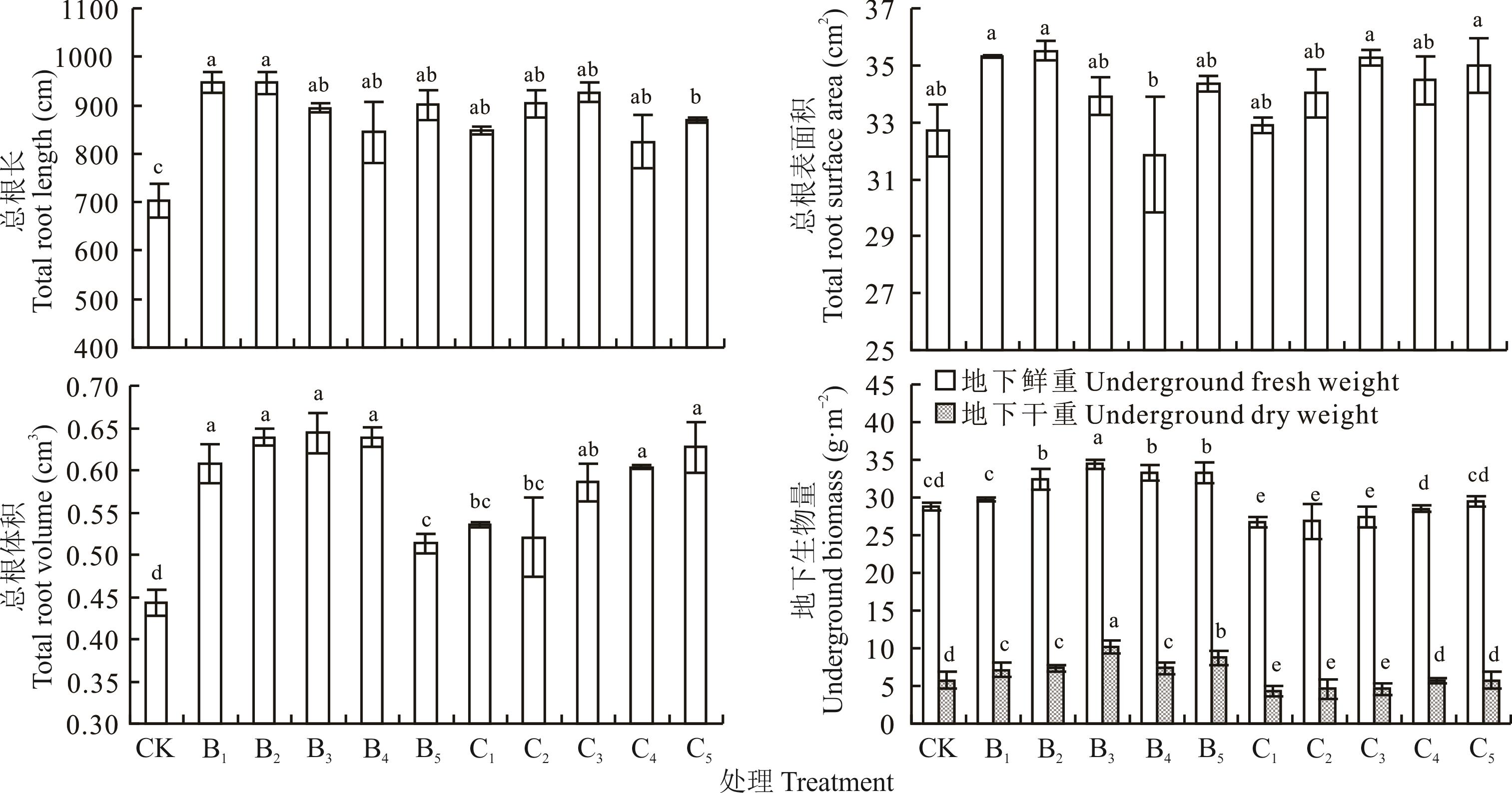
图1 垂穗披碱草根系的变化特征不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Root morphological characteristics of E. nutans
| 指标Index | CP | EE | ADF | NDF | PH | TS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | -0.201 | |||||
| ADF | 0.464 | -0.164 | ||||
| NDF | -0.167 | -0.151 | 0.702** | |||
| PH | 0.325 | -0.176 | -0.176 | -0.342 | ||
| TS | 0.053 | 0.180 | -0.436 | -0.664* | 0.525 | |
| DW | -0.351 | 0.475 | -0.561 | -0.475 | -0.159 | 0.354 |
表2 第1茬各指标之间的相关系数矩阵
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix of the indices in the first harvest
| 指标Index | CP | EE | ADF | NDF | PH | TS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | -0.201 | |||||
| ADF | 0.464 | -0.164 | ||||
| NDF | -0.167 | -0.151 | 0.702** | |||
| PH | 0.325 | -0.176 | -0.176 | -0.342 | ||
| TS | 0.053 | 0.180 | -0.436 | -0.664* | 0.525 | |
| DW | -0.351 | 0.475 | -0.561 | -0.475 | -0.159 | 0.354 |
主成分 Ingredient | 特征值 Eigenvalues | 贡献率Contribution rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方差Variance | 累计Cumulative | ||
| 1 | 2.860 | 40.851 | 40.851 |
| 2 | 1.876 | 26.796 | 67.647 |
表3 第1茬主成分分析的特征值与方差贡献率
Table 3 The eigenvalue and variance contribution rate of principal component analysis in the first harvest
主成分 Ingredient | 特征值 Eigenvalues | 贡献率Contribution rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方差Variance | 累计Cumulative | ||
| 1 | 2.860 | 40.851 | 40.851 |
| 2 | 1.876 | 26.796 | 67.647 |
处理 Treatment | 主成分 Principal component | 综合得分 Compodite score (F) | 综合排名 Total ranking | 处理 Treatment | 主成分 Principal component | 综合得分 Compodite score (F) | 综合排名 Total ranking | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (F1) | 2 (F2) | 1 (F1) | 2 (F2) | ||||||
| CK | 24.94 | -15.72 | 5.97 | 3 | C1 | 15.50 | -10.60 | 3.49 | 8 |
| B1 | 21.28 | -13.13 | 5.18 | 4 | C2 | 14.11 | -8.72 | 3.43 | 9 |
| B2 | 25.79 | -13.52 | 6.91 | 1 | C3 | 11.61 | -6.74 | 2.94 | 11 |
| B3 | 23.10 | -11.33 | 6.40 | 2 | C4 | 16.27 | -10.07 | 3.95 | 6 |
| B4 | 16.62 | -10.09 | 4.09 | 5 | C5 | 13.35 | -7.92 | 3.33 | 10 |
| B5 | 13.71 | -7.58 | 3.57 | 7 | |||||
表4 第1茬中不同处理各主成分综合得分及排名
Table 4 Comprehensive scores and rankings of the principal components of different treatments in the first harvest
处理 Treatment | 主成分 Principal component | 综合得分 Compodite score (F) | 综合排名 Total ranking | 处理 Treatment | 主成分 Principal component | 综合得分 Compodite score (F) | 综合排名 Total ranking | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (F1) | 2 (F2) | 1 (F1) | 2 (F2) | ||||||
| CK | 24.94 | -15.72 | 5.97 | 3 | C1 | 15.50 | -10.60 | 3.49 | 8 |
| B1 | 21.28 | -13.13 | 5.18 | 4 | C2 | 14.11 | -8.72 | 3.43 | 9 |
| B2 | 25.79 | -13.52 | 6.91 | 1 | C3 | 11.61 | -6.74 | 2.94 | 11 |
| B3 | 23.10 | -11.33 | 6.40 | 2 | C4 | 16.27 | -10.07 | 3.95 | 6 |
| B4 | 16.62 | -10.09 | 4.09 | 5 | C5 | 13.35 | -7.92 | 3.33 | 10 |
| B5 | 13.71 | -7.58 | 3.57 | 7 | |||||
| 指标Index | CP | EE | ADF | NDF | PH | TS | DW | TRL | TRS | TRV | UDW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | 0.241 | ||||||||||
| ADF | -0.257 | 0.005 | |||||||||
| NDF | -0.198 | -0.316 | 0.592* | ||||||||
| PH | 0.184 | 0.137 | -0.433 | -0.365 | |||||||
| TS | 0.198 | 0.389 | 0.043 | -0.292 | 0.656* | ||||||
| DW | 0.091 | 0.319 | -0.065 | -0.556 | 0.392 | 0.542 | |||||
| TRL | 0.160 | 0.175 | -0.074 | -0.141 | 0.484 | 0.283 | 0.297 | ||||
| TRS | 0.142 | -0.094 | 0.076 | 0.080 | 0.120 | -0.095 | 0.229 | 0.667* | |||
| TRV | 0.059 | -0.100 | -0.271 | -0.005 | 0.155 | -0.152 | -0.176 | 0.216 | 0.292 | ||
| UDW | 0.451 | 0.254 | -0.626* | -0.835 | 0.586* | 0.506 | 0.486 | 0.158 | -0.072 | -0.015 | |
| UFW | 0.507 | 0.356 | -0.584* | -0.816 | 0.578* | 0.515 | 0.500 | 0.270 | 0.067 | -0.016 | 0.930** |
表5 第2茬各指标之间的相关系数矩阵
Table 5 Correlation coefficient matrix of the indices in the second harvest
| 指标Index | CP | EE | ADF | NDF | PH | TS | DW | TRL | TRS | TRV | UDW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | 0.241 | ||||||||||
| ADF | -0.257 | 0.005 | |||||||||
| NDF | -0.198 | -0.316 | 0.592* | ||||||||
| PH | 0.184 | 0.137 | -0.433 | -0.365 | |||||||
| TS | 0.198 | 0.389 | 0.043 | -0.292 | 0.656* | ||||||
| DW | 0.091 | 0.319 | -0.065 | -0.556 | 0.392 | 0.542 | |||||
| TRL | 0.160 | 0.175 | -0.074 | -0.141 | 0.484 | 0.283 | 0.297 | ||||
| TRS | 0.142 | -0.094 | 0.076 | 0.080 | 0.120 | -0.095 | 0.229 | 0.667* | |||
| TRV | 0.059 | -0.100 | -0.271 | -0.005 | 0.155 | -0.152 | -0.176 | 0.216 | 0.292 | ||
| UDW | 0.451 | 0.254 | -0.626* | -0.835 | 0.586* | 0.506 | 0.486 | 0.158 | -0.072 | -0.015 | |
| UFW | 0.507 | 0.356 | -0.584* | -0.816 | 0.578* | 0.515 | 0.500 | 0.270 | 0.067 | -0.016 | 0.930** |
主成分 Ingredient | 特征值 Eigenvalues | 贡献率contribution rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方差Variance | 累计Cumulative | ||
| 1 | 4.650 | 38.750 | 38.750 |
| 2 | 1.884 | 15.701 | 54.451 |
| 3 | 1.640 | 13.671 | 68.122 |
| 4 | 1.008 | 8.399 | 76.521 |
表6 第2茬主成分分析的特征值与方差贡献率
Table 6 The eigenvalue and variance contribution rate of principal component analysis in the second harvest
主成分 Ingredient | 特征值 Eigenvalues | 贡献率contribution rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方差Variance | 累计Cumulative | ||
| 1 | 4.650 | 38.750 | 38.750 |
| 2 | 1.884 | 15.701 | 54.451 |
| 3 | 1.640 | 13.671 | 68.122 |
| 4 | 1.008 | 8.399 | 76.521 |
处理 Treatment | 第1主成分 Primary principal component (F1) | 第2主成分 Secondary principal component (F2) | 第3主成分 Thirdly principal component (F3) | 第4主成分 Fourth principal component (F4) | 综合得分 Compodite score (F) | 综合排名 Total ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 30.78 | 52.72 | 16.42 | -1.15 | 22.35 | 11 |
| B1 | 39.05 | 66.64 | 19.36 | -1.61 | 28.11 | 2 |
| B2 | 41.07 | 66.71 | 20.03 | -2.22 | 28.94 | 1 |
| B3 | 38.20 | 63.43 | 18.61 | -1.66 | 27.16 | 3 |
| B4 | 35.89 | 59.94 | 17.34 | -1.71 | 25.55 | 7 |
| B5 | 37.01 | 63.53 | 17.44 | -1.30 | 26.59 | 5 |
| C1 | 32.58 | 60.31 | 17.31 | -0.89 | 24.39 | 9 |
| C2 | 35.06 | 64.06 | 17.79 | -1.09 | 25.98 | 6 |
| C3 | 36.13 | 65.77 | 18.26 | -1.29 | 26.72 | 4 |
| C4 | 32.97 | 58.87 | 16.88 | -1.14 | 24.23 | 10 |
| C5 | 34.22 | 61.79 | 17.17 | -0.97 | 25.23 | 8 |
表7 第2茬中不同处理各主成分综合得分及排名
Table 7 Comprehensive scores and rankings of the principal components of different treatments in the second harvest
处理 Treatment | 第1主成分 Primary principal component (F1) | 第2主成分 Secondary principal component (F2) | 第3主成分 Thirdly principal component (F3) | 第4主成分 Fourth principal component (F4) | 综合得分 Compodite score (F) | 综合排名 Total ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 30.78 | 52.72 | 16.42 | -1.15 | 22.35 | 11 |
| B1 | 39.05 | 66.64 | 19.36 | -1.61 | 28.11 | 2 |
| B2 | 41.07 | 66.71 | 20.03 | -2.22 | 28.94 | 1 |
| B3 | 38.20 | 63.43 | 18.61 | -1.66 | 27.16 | 3 |
| B4 | 35.89 | 59.94 | 17.34 | -1.71 | 25.55 | 7 |
| B5 | 37.01 | 63.53 | 17.44 | -1.30 | 26.59 | 5 |
| C1 | 32.58 | 60.31 | 17.31 | -0.89 | 24.39 | 9 |
| C2 | 35.06 | 64.06 | 17.79 | -1.09 | 25.98 | 6 |
| C3 | 36.13 | 65.77 | 18.26 | -1.29 | 26.72 | 4 |
| C4 | 32.97 | 58.87 | 16.88 | -1.14 | 24.23 | 10 |
| C5 | 34.22 | 61.79 | 17.17 | -0.97 | 25.23 | 8 |
| 1 | Ma J G, Bowatte S, Wang Y F, et al. Differences in soil ammonia oxidizing bacterial communities under unpalatable (Stellera chamaejasme.)and palatable (Elymus nutans) plants growing on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 144: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107779. |
| 2 | Lin F, Liu X J, Tong C C, et al. Effects of intercropping on light energy utilization characteristics and productivity of different feed crops. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(10): 3452-3462. |
| 蔺芳, 刘晓静, 童长春, 等. 间作对不同类型饲料作物光能利用特征及生产能力的影响.应用生态学报, 2019, 30(10): 3452-3462. | |
| 3 | Kang Y J, Hao Y Y, Shen M, et al. Impacts of supplementing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers manufactured using pig manure as a substrate on the spread of tetracycline resistance genes in soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 130: 279-288. |
| 4 | Li Y H. Research on the development of chemical fertilizer industry in China. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. |
| 李勇海. 中国化肥行业发展对策研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. | |
| 5 | National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook-2018. [2019-04-06]. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2018/indexch.htm. |
| 国家统计局.中国统计年鉴-2018. [2019-04-06]. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2018/indexch.htm. | |
| 6 | Wang J B, Sun Y X, Li H Y, et al. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer and partial substitution of chemical fertilizer on wheat yield. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(36): 6-11. |
| 王家宝, 孙义祥, 李虹颖, 等. 生物有机肥用量及部分替代化肥对小麦产量效应的研究. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(36): 6-11. | |
| 7 | Li H Y, Jiang Y M, Yao T, et al. Isolation, screening, identification and growth promoting characteristics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria of vegetable crops. Journal of Plant Protection, 2018, 45(4): 836-845. |
| 李海云, 蒋永梅, 姚拓, 等. 蔬菜作物根际促生菌分离筛选、鉴定及促生特性测定. 植物保护学报, 2018, 45(4): 836-845. | |
| 8 | Wen C, Shan Y M, Jia W X, et al. Effects of bio-fertilizers on vegetation characteristics and stoichiometry of Leymus chinensis. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(9): 2192-2200. |
| 温超, 单玉梅, 贾伟星, 等. 微生物肥对羊草植被特征和化学计量学的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(9): 2192-2200. | |
| 9 | Li Y B, Li Y L, Guan G H, et al. Screening, identification of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and its effect on reducing fertilization while increasing efficiency in wheat (Triticum asetivum). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2020, 28(8): 1471-1476. |
| 李永斌, 李云龙, 关国华, 等. 植物根际促生菌的筛选、鉴定及其对小麦的减肥增产效果. 农业生物技术学报, 2020, 28(8): 1471-1476. | |
| 10 | Zhang X M, Cao Y R, Shen W Z, et al. Effects of microbial fertilizer on soil secondary salinization and tomato production in protected cultivation. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(5): 119-126. |
| 张绪美, 曹亚茹, 沈文忠, 等. 微生物肥对设施土壤次生盐渍化和番茄生产的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(5): 119-126. | |
| 11 | Yao Z Y, Li J, Song L Z, et al. Study on the effect of cross sowing of Elymus nutans and Medicago sativa in different periods. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1454-1459. |
| 姚泽英, 李军, 宋连昭, 等. 垂穗披碱草与紫花苜蓿不同时期交叉混播效果研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1454-1459. | |
| 12 | Li X K, Lu J W, Chen F. Rrimary study on fertilizer application of forage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008(2): 136-142. |
| 李小坤, 鲁剑巍, 陈防. 牧草施肥研究进展. 草业学报, 2008(2): 136-142. | |
| 13 | Wang P, Wang P, Sun W B, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of eight Elymus germplasms at seedling stage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 397-404. |
| 王平, 王沛, 孙万斌, 等. 8份披碱草属牧草苗期抗旱性综合评价. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 397-404. | |
| 14 | Li H Y, Qiu Y Z, Tuo Y, et al. Effects of PGPR microbial inoculants on the growth and soil properties of Avena sativa, Medicago sativa, and Cucumis sativus seedlings. Soil & Tillage Research, 2020, 199: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104577. |
| 15 | Wang G J, Chai Q, Zhang Y X, et al. Effects of maize special biofertilizer on maize growth in arid area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(1): 173-179. |
| 王国基, 柴强, 张玉霞, 等. 干旱区玉米专用菌肥对玉米生长特性的影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(1): 173-179. | |
| 16 | Chen L, Sun G Z, Yao T, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer partly replaced by microbial fertilizer on maize growth and soil microorganism in arid area. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(7): 108-113. |
| 陈龙, 孙广正, 姚拓, 等. 干旱区微生物肥料替代部分化肥对玉米生长及土壤微生物的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(7): 108-113. | |
| 17 | Ban Q, Huang L K, Zhang X Q, et al. Agronomic traits of 15 annual Ixeris polycephala varieties in the southwest of Sichuan Province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 37-46. |
| 班骞, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 等. 15个苦荬菜新品种(系)在川西南地区农艺性状综合评价. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 37-46. | |
| 18 | Sakshi P, Neelam C, Diksha G. Effect of malting on nutritional profile of alfalfa seeds and development of value added fermented products. International Journal of Fermented Foods, 2019, 8(2): 482-488. |
| 19 | Zhou H, Xia D, He Y Q. Rice grain quality-traditional traits for high quality rice and health-plus substances. Molecular Breeding: New Strategies in Plant Improvement, 2019, 40(45): 1-17. |
| 20 | Liu Q F, Xiong G R, Mao Z C, et al. Analyses for the colonization ability of Bacillus subtilis XF-1 in the rhizosphere. Journal of Plant Protection, 2012, 39(5): 425-430. |
| 刘庆丰, 熊国如, 毛自朝, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌XF-1的根围定殖能力分析. 植物保护学报, 2012, 39(5): 425-430. | |
| 21 | Chen C, Bauske E M, Musson G, et al. Biological control of Fusarium wilt on cotton by use of endophytic bacteria. Biological Control, 1995, 5(1): 83-91. |
| 22 | Sun Z, Zheng L, Qiu H B. Research advances on colonization of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(2): 8-15. |
| 孙真, 郑亮, 邱浩斌. 植物根际促生细菌定殖研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(2): 8-15. | |
| 23 | Yuan J, Zhang N, Huang Q W, et al. Organic acids from root exudates of banana help root colonization of PGPR strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NJN-6. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13438. |
| 24 | Pang Z Q, Yu D Q. Plant root system-microbial interaction system under drought stress and its application. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(2): 109-126. |
| 庞志强, 余迪求. 干旱胁迫下的植物根系-微生物互作体系及其应用. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(2): 109-126. | |
| 25 | Chen X B, Hu Y J, Qin H L, et al. Characteristics of soil nitrogen cycle and mechanisms underlying the increase in rice yield with partial substitution of mineral fertilizers with organic manure in a paddy ecosystem:A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(3): 1033-1042. |
| 陈香碧, 胡亚军, 秦红灵, 等. 稻作系统有机肥替代部分化肥的土壤氮循环特征及增产机制. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(3): 1033-1042. | |
| 26 | Xu R R, Chang S H, Jia Q M, et al. Effects of nitrogen application and utilization methods on the yield, quality and water use of grass-legume mixed grassland in Loess Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1744-1755. |
| 徐然然, 常生华, 贾倩民, 等. 施氮和利用方式对黄土高原禾豆混播草地产量、品质和水分利用的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1744-1755. | |
| 27 | Yanni Y G, Rizk R Y, E-l Fattah F K, et al. The beneficial plant growth-promoting association of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifoliiwith rice roots. Australian Journal Plant Physiology, 2001, 28: 845-870. |
| 28 | Han H W, Sun L N, Yao T, et al. Effects of bio-fertilizers with different PGPR strain combinations on yield and quality of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(5): 104-112. |
| 韩华雯, 孙丽娜, 姚拓, 等. 不同促生菌株组合对紫花苜蓿产量和品质的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 104-112. | |
| 29 | Li F F, Zhang F F, Wang X Z, et al. Effects of cutting date and crop growth stage on alfalfa silage quality. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 137-148. |
| 李菲菲, 张凡凡, 王旭哲, 等. 刈割茬次和生育期对苜蓿青贮品质的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 137-148. |
| [1] | 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 张静静, 申凤敏, 姜瑛, 张雪海, 孙娈姿, 杨芳, 刘振. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. |
| [2] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [3] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [4] | 刘丽英, 贾玉山, 范文强, 尹强, 成启明, 王志军. 影响苜蓿自然干燥的主要环境因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 121-132. |
| [5] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [6] | 白婕, 臧真凤, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 王可珍, 屈洋, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化及C、N特征对水分和N添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 213-220. |
| [7] | 邢强, 秦俊, 胡永红. 不同践踏强度对3种暖季型草坪草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 52-61. |
| [8] | 吴欣明, 方志红, 池惠武, 贾会丽, 刘建宁, 石永红, 王学敏. 30个青贮玉米在雁门关地区品种评比试验[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 唐立涛, 毛睿, 王长庭, 李洁, 胡雷, 字洪标. 氮磷添加对高寒草甸植物群落根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. |
| [10] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. |
| [11] | 徐强, 田新会, 杜文华. 高寒牧区黑麦和箭筈豌豆混播对草产量和营养品质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 49-59. |
| [12] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| [13] | 王云霞, 张萍, 葛蓓蕾, 雅蓉, 杨英, 靳磊. 渥丹百合农艺性状及活性成分对钾元素的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 205-213. |
| [14] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [15] | 肖逸, 杨忠富, 聂刚, 韩佳婷, 帅杨, 张新全. 12个多花黑麦草品种(系)在成都平原的生产性能和营养价值综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 174-185. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||