

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 124-134.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021087
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
刘亚男1( ), 于人杰2, 高燕丽3, 康俊梅1, 杨青川1, 武志海2(
), 于人杰2, 高燕丽3, 康俊梅1, 杨青川1, 武志海2( ), 王珍1(
), 王珍1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-15
修回日期:2021-03-25
出版日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-03-30
通讯作者:
武志海,王珍
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wangzhen@caas.cn, wuzhihai1116@163.com基金资助:
Ya-nan LIU1( ), Ren-jie YU2, Yan-li GAO3, Jun-mei KANG1, Qing-chuan YANG1, Zhi-hai WU2(
), Ren-jie YU2, Yan-li GAO3, Jun-mei KANG1, Qing-chuan YANG1, Zhi-hai WU2( ), Zhen WANG1(
), Zhen WANG1( )
)
Received:2021-03-15
Revised:2021-03-25
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-03-30
Contact:
Zhi-hai WU,Zhen WANG
摘要:
膜联蛋白(annexins)是一类进化保守的多基因家族蛋白,它们广泛存在于真核生物中,能通过Ca2+与膜磷脂的结合参与胁迫相关的多种生物学过程。早期对膜联蛋白的研究多集中于脊椎动物,对植物膜联蛋白的认识开始于番茄。关于豆科植物尤其是牧草中膜联蛋白的研究还鲜有报道。本研究分析了蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白与饲草紫花苜蓿同源蛋白的进化关系,研究了蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白基因MtANN2的表达模式,进一步利用拟南芥同源基因的突变体阐明了MtANN2在根系发育和盐胁迫中的功能。RT-qPCR结果显示,MtANN2在根中高丰度表达,且表达水平受NaCl诱导。RNA原位杂交表明MtANN2特异表达于幼苗侧根原基。拟南芥同源基因AtANN2的T-DNA插入突变体植株弱小、侧根数少、根鲜重低,且对盐(100 mmol·L-1)处理的敏感性显著高于野生型。超表达MtANN2于atann2后转基因植株的侧根数介于野生型与突变体之间,根鲜重接近野生型,表明MtANN2能在一定程度上互补该突变体的表型缺陷。在盐处理下,该转基因株系的发芽率和长势均恢复到类似野生型的水平。以上结果从分子水平上表明,蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2参与植物根系生长及盐胁迫响应,高水平表达该基因能够改善植物的耐盐性。本研究为紫花苜蓿耐盐分子育种提供了备选基因。
刘亚男, 于人杰, 高燕丽, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 武志海, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2基因的表达模式及盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 124-134.
Ya-nan LIU, Ren-jie YU, Yan-li GAO, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Zhi-hai WU, Zhen WANG. Expression pattern and biological functions of an annexin encoding gene MtANN2 in Medicago truncatula under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 124-134.
| 引物名称Primer | 序列5′-3′ Sequence 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| MtANN2 F | ATGGCGACATTGAAGATC |
| MtANN2 R | CTACTCATCACGTCCCATCAG |
| 1302-MtANN2 F | gaacacgggggactcttgaccATGGCGACATTGAAGATC |
| 1302-MtANN2 R | ctcctttactagtcagatctacCATCTCATCACGTCCCATCAG |
| 35S F | CTATCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTC |
| 1302 R | TTCCGTATGTTGCATCACCTT |
| LP | GATTGTGAAACTGTTGTATTTGGTG |
| RP | GATTGCGGAAGCTGTAGTTGC |
| T-DNA RB | GTGGATTGATGTGATATCTCC |
| qRT-Atactin F | TCCATCGATTGTTCACAGGA |
| qRT-Atactin R | TCACCACCACGAACCAGATA |
| qRT-MtANN2 F | GCGGTGCTTTTCAAGGATGG |
| qRT-MtANN2 R | ACCTTACGCTGAGCTGCATT |
| qRT-AtANN2 F | TCTTGTGAGCACTTTCAGGTAT |
| qRT-AtANN2 R | AGTTCTTGTTAATGGCGTTTCC |
| MtANN2-in situ F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTAGCTAATCAAGCAACTAAAATG |
| MtANN2-in situ R | ATTTAGGTGACACTATAGAATAGGGACTTTTTGAAACGGGCTTG |
表1 试验中所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in the study
| 引物名称Primer | 序列5′-3′ Sequence 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| MtANN2 F | ATGGCGACATTGAAGATC |
| MtANN2 R | CTACTCATCACGTCCCATCAG |
| 1302-MtANN2 F | gaacacgggggactcttgaccATGGCGACATTGAAGATC |
| 1302-MtANN2 R | ctcctttactagtcagatctacCATCTCATCACGTCCCATCAG |
| 35S F | CTATCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTC |
| 1302 R | TTCCGTATGTTGCATCACCTT |
| LP | GATTGTGAAACTGTTGTATTTGGTG |
| RP | GATTGCGGAAGCTGTAGTTGC |
| T-DNA RB | GTGGATTGATGTGATATCTCC |
| qRT-Atactin F | TCCATCGATTGTTCACAGGA |
| qRT-Atactin R | TCACCACCACGAACCAGATA |
| qRT-MtANN2 F | GCGGTGCTTTTCAAGGATGG |
| qRT-MtANN2 R | ACCTTACGCTGAGCTGCATT |
| qRT-AtANN2 F | TCTTGTGAGCACTTTCAGGTAT |
| qRT-AtANN2 R | AGTTCTTGTTAATGGCGTTTCC |
| MtANN2-in situ F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTAGCTAATCAAGCAACTAAAATG |
| MtANN2-in situ R | ATTTAGGTGACACTATAGAATAGGGACTTTTTGAAACGGGCTTG |

图1 拟南芥和2种苜蓿中膜联蛋白的进化关系分析红色圆点代表蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白,蓝色代表拟南芥膜联蛋白,黑色代表紫花苜蓿膜联蛋白。Red dots represent annexins in M. truncatula, blue for annexins in A. thaliana, and black for annexins in M. sativa.
Fig.1 Phylogenetic analysis of annexin proteins from Arabidopsis and two Medicago species
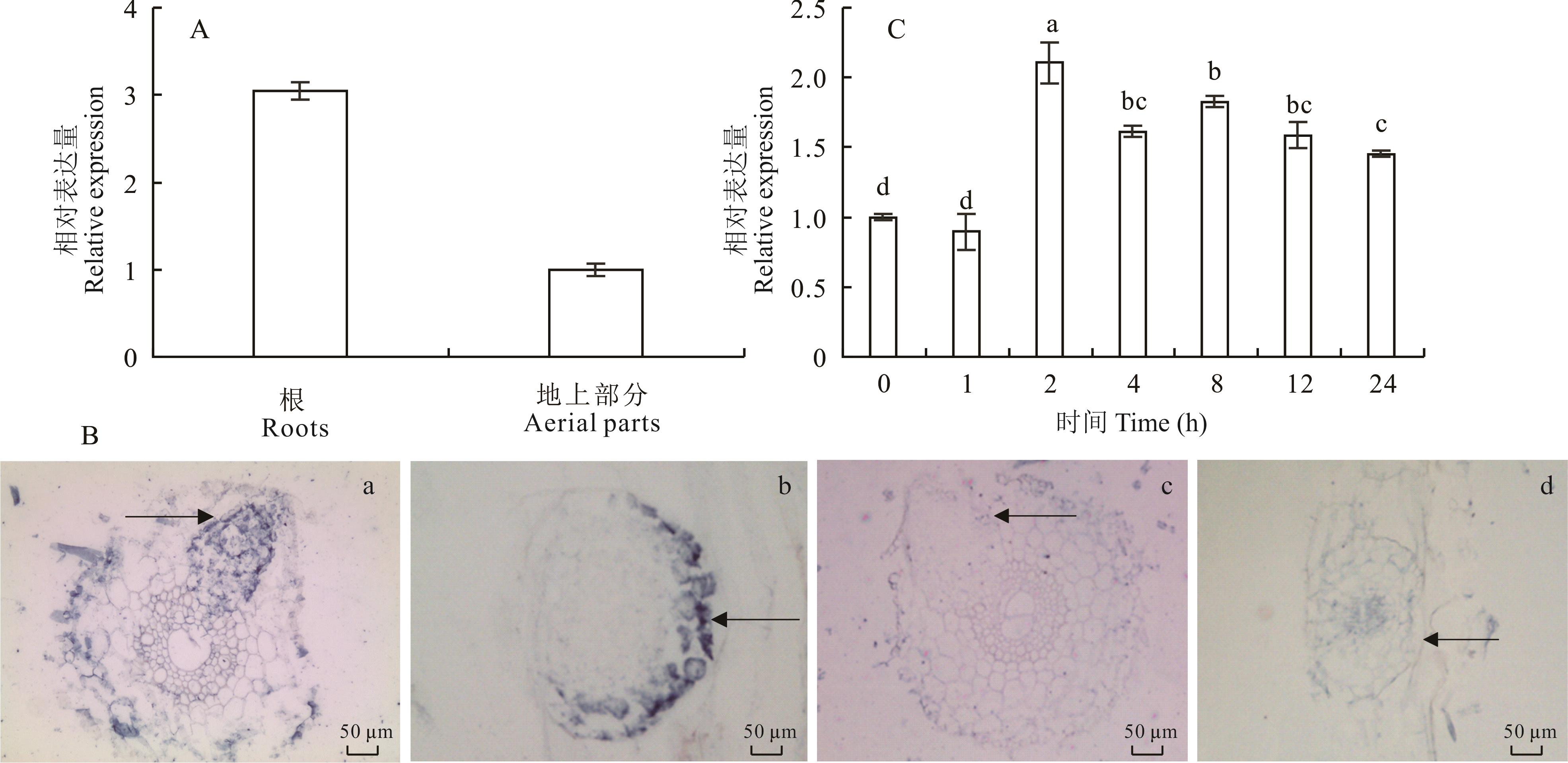
图2 MtANN2的表达模式分析A:RT-qPCR分析MtANN2在蒺藜苜蓿根及幼苗中的表达量;B:原位杂交分析MtANN2在根系组织中的表达。其中,a、b为反义探针杂交结果,c、d为正义探针杂交结果;a、c为根系横切,b、d为根系纵切;箭头表示侧根原基。其中,正义探针作为阴性对照;C:MtANN2对NaCl(200 mmol·L-1)处理的响应分析。标准误差来自3个生物重复,数据利用单因素方差分析及邓肯检验,不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。A: The relative expression of MtANN2 in roots and aerial tissues of M. truncatula; B: In situ hybridization of MtANN2 in roots of M. truncatula. a, b: Hybridization by the anti-sense probe; c, d:Hybridization by the sense probe; a, c: Root transection; b, d: Root longitudinal section; Arrows indicate lateral root primordial; Sense probe acts as a negative control; C: The relative expression of MtANN2 under NaCl treatment (200 mmol·L-1). Error bar represents mean±SD of three biological replicates. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA with Duncan’s test. Lowercase letters represent significant difference (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.2 Analysis of the expression pattern of MtANN2 in M. truncatula

图4 atann2突变体的鉴定及表型分析A:3周龄拟南芥;B:拟南芥AtANN2基因结构及atann2 T-DNA插入位点示意图,黑色块表示外显子,灰色块为非编码区(UTR),黑线为内含子,箭头代表基因型鉴定引物的位置,RB代表T-DNA的右边界,LP代表基因组侧翼序列上的上游引物,RP代表基因组侧翼序列上的下游引物,ATG代表起始密码子;C:atann2突变体基因型鉴定,Marker为分子大小标记;D:AtANN2表达水平分析;E:正常条件和盐处理(100 mmol·L-1 NaCl)下根系生长比较;F:相对一级侧根数统计;G:相对根长统计;H:相对根鲜重统计。图中列出盐处理后各指标减少的百分数,WT代表野生型,下同。A: Representative image of 3-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings; B: Schematic diagram of AtANN2 and the T-DNA insertion line of atann2, the boxes in black and gray represent exons and untranslated region, respectively, solid line indicates intron and arrow represents the location of primers used in screening; RB represents the right border of T-DNA, LP represents the forward primer of the genomic franking sequence, RP represents the reverse primer of the genomic franking sequence, ATG represents the start codon; C: PCR screening of the homozygous atann2; Marker represents the reference for DNA molecular size;D: Relative expression of AtANN2;E: Response to NaCl treatment;F: Statistical analysis of the relative No. of lateral roots; G: The relative length of roots; H: The relative fresh weight of roots. The subtraction between treatment and control was indicated by percentage, WT indicates wild types, the same below.
Fig.4 Screening and phenotypic analysis of atann2 mutant
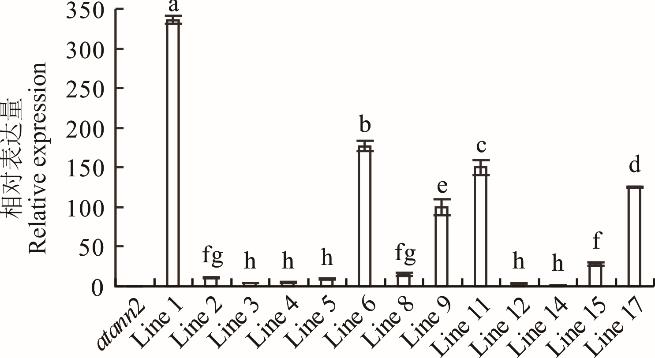
图5 异源表达MtANN2于拟南芥atann2转基因材料转录水平鉴定由于是异源表达,因此以阳性转基因株系中表达量最低者为1,从而计算其余株系的相对表达水平。The expression of the positive line with the lowest expression level was regarded as 1 to calculate the relative expression of others.
Fig.5 Identification of transcriptional level of MtANN2 in transgenic atann2

图6 异源表达MtANN2的atann2拟南芥对NaCl的响应A:盐处理(100 mmol·L-1 NaCl)下的发芽率比较,*代表该时间点atann2发芽率与其他株系差异显著(P<0.05);B:盐处理(100 mmol·L-1 NaCl)下的根系生长比较。A: Comparison of germination rate of the four genotypes under salt treatment (100 mmol·L-1 NaCl), * represents the significantly different germination rate of atann2 (P<0.05); B: Comparison of root growth of the four genotypeswith and without NaCl treatment.
Fig.6 Analysis of atann2 ectopically expressing MtANN2 under NaCl treatment
| 1 | Laohavisit A, Davies J M. Annexins. New Phytologist, 2011, 189(1): 40-53. |
| 2 | Davies J M. Annexin-mediated calcium signalling in plants. Plants (Basel), 2014, 3(1): 128-140. |
| 3 | Konopka P D, Clark G. Annexins as overlooked regulators of membrane trafficking in plant cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(4): 863. |
| 4 | Yan H, Yun L, Jiang Z, et al. Cloning and expression characterization of four annexin genes during germination and abiotic stress in Brassica rapa subsp. rapa ‘Tsuda’. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2015, 34(2): 467-482. |
| 5 | Ahmed I, Yadav D, Shukla P, et al. Heterologous expression of Brassica juncea annexin, AnnBj2 confers salt tolerance and ABA insensitivity in transgenic tobacco seedlings. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2018, 18: 569-579. |
| 6 | Xu L, Tang Y, Gao S, et al. Comprehensive analyses of the annexin gene family in wheat. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17: 415. |
| 7 | Li X, Zhang Q, Yang X, et al. OsANN3, a calcium-dependent lipid binding annexin is a positive regulator of ABA-dependent stress tolerance in rice. Plant Science, 2019, 284: 212-220. |
| 8 | Ma L, Ye J, Yang Y, et al. The SOS2-SCaBP8 complex generates and fine-tunes an AtANN4-dependent calcium signature under salt stress. Developmental Cell, 2019, 48(5): 697-709. |
| 9 | Yang Y, Guo Y. Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2018, 60(9): 58-66. |
| 10 | Kibria M G, Hoque M A. A review on plant responses to soil salinity and amelioration strategies. Open Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 9(11): 219-231. |
| 11 | Wei Z W, Gai J Y. Advances in genomic study on the legume model plant Medicago truncatula. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2006, 28(6): 83-90. |
| 魏臻武, 盖钧镒. 豆科模式植物蒺藜苜蓿基因组研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2006, 28(6): 83-90. | |
| 12 | Fernanda C N, Timmers A C J, Mireille C, et al. The nod factor-elicited annexin MtAnn1 is preferentially localised at the nuclear periphery in symbiotically activated root tissues of Medicago truncatula. Plant Journal, 2002, 32(3): 343-352. |
| 13 | Tanuja T, Karolina M G, Fernanda C N, et al. Annexins-calcium-and membrane-binding proteins in the plant kingdom: Potential role in nodulation and mycorrhization in Medicago truncatula. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 2009, 56(2): 199-210. |
| 14 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2- ΔΔ Ct method. Methods, 2001, 25: 402-408. |
| 15 | Zachgo S. In situ hybridization. Molecular Plant Biology. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2002: 41-63. |
| 16 | Branca A, Paape T D, Peng Z, et al. Whole-genome nucleotide diversity, recombination, and linkage disequilibrium in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(42): 864-870. |
| 17 | Chen H, Zeng Y, Yang Y, et al. Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2494. |
| 18 | Qiao B, Zhang Q, Liu D, et al. A calcium-binding protein, rice annexin OsANN1, enhances heat stress tolerance by modulating the production of H2O2. Journal Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(19): 5853-5866. |
| 19 | Cantero A, Barthakur S, Bushart T J, et al. Expression profiling of the Arabidopsis annexin gene family during germination, de-etiolation and abiotic stress. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 2006, 44(1): 13-24. |
| 20 | Jami S K, Clark G B, Ayele B T, et al. Identification and characterization of annexin gene family in rice. Plant Cell Reports, 2012, 31(5): 813-825. |
| 21 | Ahmed I, Yadav D, Shukla P, et al. Constitutive expression of Brassica juncea annexin, AnnBj2 confers salt tolerance and glucose and ABA insensitivity in transgenic plants. Plant Science, 2017, 265: 12-28. |
| 22 | Ijaz R, Ejaz J, Gao S, et al. Overexpression of annexin gene AnnSp2, enhances drought and salt tolerance through modulation of ABA synthesis and scavenging ROS in tomato. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 12087. |
| 23 | Saad B R, Harbaoui M, Romdhane B W, et al. Overexpression of Triticum durum TdAnn12 gene confers stress tolerance through scavenging reactive oxygen species in transgenic tobacco. Functional Plant Biology, 2019, 46(10): 885-895. |
| 24 | Shen C, Du H, Chen Z, et al. The chromosome-level genome sequence of the autotetraploid alfalfa and resequencing of core germplasms provide genomic resources for alfalfa research. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(9): 1250-1261. |
| 25 | Jami S K, Clark G B, Ayele B T, et al. Genome-wide comparative analysis of annexin superfamily in plants. PLoS One, 2012, 7(11): e47801. |
| 26 | Clark G B, Morgan R O, Fernandez M P, et al. Evolutionary adaptation of plant annexins has diversified their molecular structures, interactions and functional roles. New Phytologist, 2012, 196(3): 695-712. |
| 27 | Laohavisit A, Davies J M. Multifunctional annexins. Plant Science, 2009, 177(6): 532-539. |
| 28 | Lee S L E, Yang E J, Lee J E, et al. Proteomic identification of annexins, calcium-dependent membrane binding proteins that mediate osmotic stress and abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2004, 16(6): 1378-1391. |
| 29 | Wang Y Q, Zhang F, Li R M, et al. Cloning and expression of MeAnn1 gene from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Molecular Plant Breeding, 2015, 13(11): 2477-2483. |
| 王雨晴, 张帆, 李瑞梅, 等. 木薯MeAnn1基因的克隆及表达分析. 分子植物育种, 2015, 13(11): 2477-2483. | |
| 30 | Seigneurin-Berny D, Rolland N, Dorne A J, et al. Sulfolipid is a potential candidate for annexin binding to the outer surface of chloroplast. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 2000, 272(2): 519-524. |
| 31 | Seals D F, Parrish M L, Randall S K. A 42-kilodalton annexin-like protein is associated with plant vacuoles. Plant Physiology, 1994, 106(4): 1403-1412. |
| 32 | Ma L. The SOS pathway generates and fine-tunes an AtANN4-dependent calcium signature under salt stress. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 马亮. SOS途径通过膜联蛋白AtANN4介导盐胁迫下钙信号特异性调控机制的研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2019. | |
| 33 | Saad B R, Harbaoui M, omdhane B W, et al. The durum wheat annexin, TdAnn6, improves salt and osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis via modulation of antioxidant machinery. Protoplasma, 2021, 258(5): 1047-1059. |
| 34 | Mu C, Zhou L, Shan L, et al. Phosphatase GhDsPTP3a interacts with annexin protein GhANN8b to reversely regulate salt tolerance in cotton (Gossypium spp.). New Phytologist, 2019, 223(4): 1856-1872. |
| 35 | Deepanker Y, Ahmed I, Shukla P, et al. Overexpression of Arabidopsis AnnAt8 alleviates abiotic stress in transgenic Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plants, 2016, 5(2): 1-25. |
| 36 | Laohavisit A, Richards S L, Shabala L, et al. Salinity-induced calcium signaling and root adaptation in Arabidopsis require the calcium regulatory protein annexin1. Plant Physiology, 2013, 163(1): 253-262. |
| [1] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [2] | 吴彤, 刘云苗, 金军, 董伟峰, 才晓溪, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿cation/H+ exchanger基因家族鉴定及表达特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 181-194. |
| [3] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [4] | 汪芳珍, 杨成行, 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清. 盐处理下旱生植物沙芥蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 116-124. |
| [5] | 田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 朱永琪, 史晓艳, 李维弟, 李文瑞玉. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [6] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| [7] | 刘文文, 崔会婷, 尉春雪, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿叶绿素酸酯a加氧酶(MtCAO)基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 171-181. |
| [8] | 黄勇, 郭猛, 张红瑞, 周艳, 李贺敏, 高致明, 王盼盼. 盐胁迫对石竹种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 105-111. |
| [9] | 王桔红, 史生晶, 陈文, 甘桂媚, 陈赛娜, 李张伟. 枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草和鳢肠种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 112-120. |
| [10] | 何建军, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 边秀秀, 司二静, 杨轲, 王化俊, 马小乐, 李葆春, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄. 干旱和盐胁迫对盐生植物盐生草种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 129-140. |
| [11] | 李珍, 云岚, 石子英, 王俊, 张晨, 郭宏宇, 盛誉. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发及幼苗期生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. |
| [12] | 张智琦, 王珍, 张铁军, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 蒺藜苜蓿MtNSN1的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 200-208. |
| [13] | 伍国强, 李辉, 雷彩荣, 蔺丽媛, 金娟, 李善家. 添加KCl对高盐胁迫下红豆草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 45-55. |
| [14] | 孙亚男, 林茹, 潘晓阳, 陈月, 陶磊, 郭长虹. 紫花苜蓿MsZAT10基因的克隆及其在烟草中的功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 94-102. |
| [15] | 王小山, 季晓敏, 刘隆阳, 纪冰沁, 田银芳. EBR对NaCl胁迫下苜蓿属植物离子吸收和分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 110-119. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||