

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 24-34.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021299
收稿日期:2021-08-03
修回日期:2021-10-18
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-07-01
通讯作者:
张前兵,马春晖
作者简介:E-mail: chunhuima@126.com基金资助:
Jian-tao ZHAO( ), Ya-fei YUE(
), Ya-fei YUE( ), Qian-bing ZHANG(
), Qian-bing ZHANG( ), Chun-hui MA(
), Chun-hui MA( )
)
Received:2021-08-03
Revised:2021-10-18
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-07-01
Contact:
Qian-bing ZHANG,Chun-hui MA
摘要:
由于北疆地区冬季气候寒冷,常出现极端降雪情况,使得苜蓿遭受冷害和冻害的威胁,导致苜蓿生产性能下降,对畜牧业生产造成巨大损失。为探究不同秋眠级的紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性、越冬率及干草产量对北疆地区冬季覆雪厚度的响应,明确不同覆雪厚度下不同秋眠级苜蓿品种各抗寒指标的动态变化规律。选取秋眠级为1级的紫花苜蓿品种驯鹿、3级的康赛、5级的巨能551、7级的赛迪7和9级的WL656HQ,覆雪厚度设置为0、10及15 cm,对紫花苜蓿根冠层土壤温度变化、土壤表层(1~10 cm)日温度变化、表层土壤(0~15 cm)平均含水率变化、根颈中抗寒生理指标变化及越冬率进行观测和分析。发现冬季积雪可以维持紫花苜蓿的根冠部及根颈下土壤层的温度动态平衡,使得各秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种的越冬率在覆雪条件下均显著提高(P<0.05);与不覆雪相比,覆雪后各紫花苜蓿的丙二醛含量有所降低,可溶性蛋白、可溶性碳水化合物含量及干草产量均有所增加。通过主成分综合分析发现,覆雪15 cm处理下,秋眠级为5级的巨能551的越冬率、抗寒性指标及干草产量等综合评分表现优异,比较适宜在新疆北疆地区进行推广种植。
赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34.
Jian-tao ZHAO, Ya-fei YUE, Qian-bing ZHANG, Chun-hui MA. Relationship between cold resistance of alfalfa, degree of fall-dormancy and snow cover thickness in Northern Xinjiang[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 24-34.
| 品种Variety | 秋眠级FDG | 秋眠类型FDC | 种子来源Seed source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 驯鹿 AC Caribou | 1 | 高秋眠型 High-dormancy type | 北京克劳沃种业有限公司 Beijing Clover Seed Industry Co. , Ltd. |
| 康赛 Concept | 3 | 高秋眠型 High-dormancy type | 牧草青贮饲料研究所推广中心 Forage and Silage Research Development Center |
| 巨能551 Magnum 551 | 5 | 半秋眠型 Semi-dormancy type | 牧草青贮饲料研究所推广中心 Forage and Silage Research Development Center |
| 赛迪7 Sardi 7 | 7 | 非秋眠型 Non-dormancy type | 百绿国际草业(北京)有限公司 Barenbrug (Beijing) International Grass Co. , Ltd. |
| WL656HQ | 9 | 非秋眠型 Non-dormancy type | 北京正道生态科技有限公司 Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co. , Ltd. |
表1 供试苜蓿秋眠等级及来源
Table 1 Fall dormancy grade and source of alfalfa varieties for test
| 品种Variety | 秋眠级FDG | 秋眠类型FDC | 种子来源Seed source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 驯鹿 AC Caribou | 1 | 高秋眠型 High-dormancy type | 北京克劳沃种业有限公司 Beijing Clover Seed Industry Co. , Ltd. |
| 康赛 Concept | 3 | 高秋眠型 High-dormancy type | 牧草青贮饲料研究所推广中心 Forage and Silage Research Development Center |
| 巨能551 Magnum 551 | 5 | 半秋眠型 Semi-dormancy type | 牧草青贮饲料研究所推广中心 Forage and Silage Research Development Center |
| 赛迪7 Sardi 7 | 7 | 非秋眠型 Non-dormancy type | 百绿国际草业(北京)有限公司 Barenbrug (Beijing) International Grass Co. , Ltd. |
| WL656HQ | 9 | 非秋眠型 Non-dormancy type | 北京正道生态科技有限公司 Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co. , Ltd. |
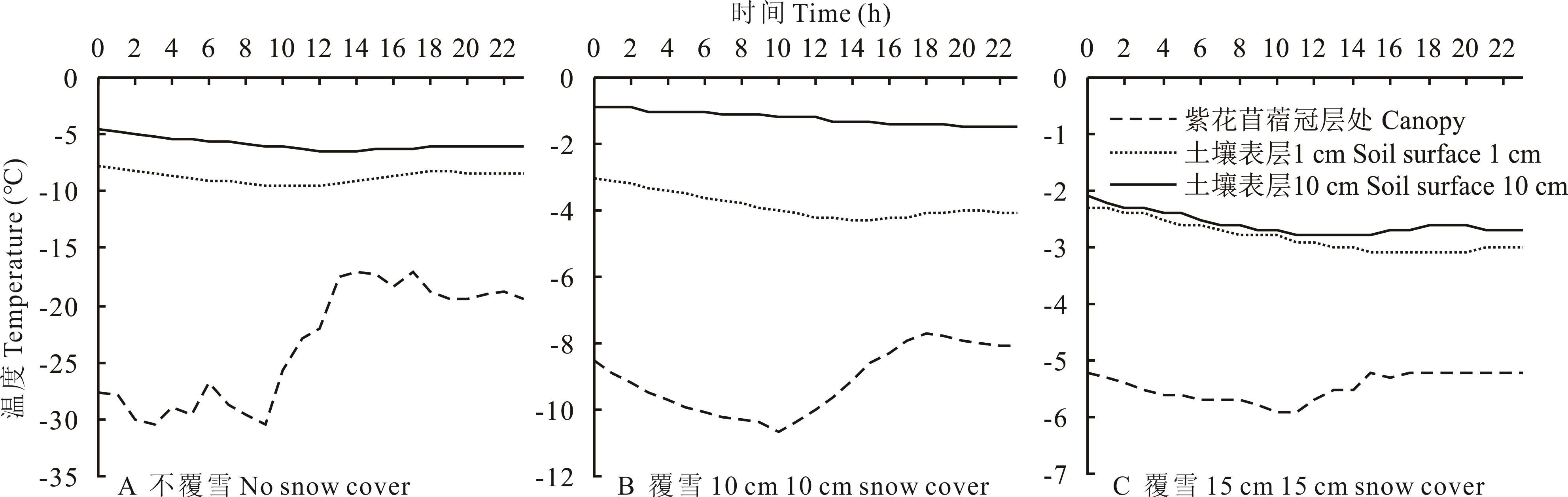
图2 冻结期不同覆雪厚度下紫花苜蓿冠层及土壤表层温度的日变化
Fig.2 Diurnal variation of the temperature of alfalfa canopy and soil surface under different snow cover thicknesses during the freezing period
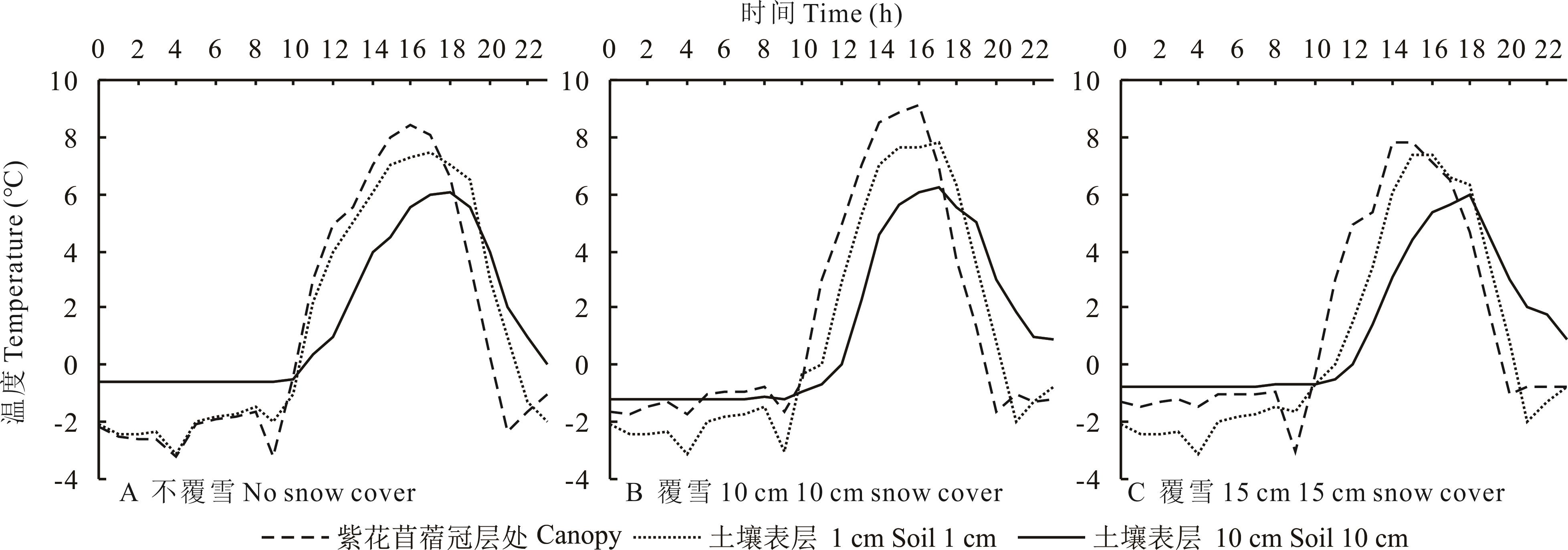
图3 融化期不同覆雪厚度下紫花苜蓿冠层及土壤表层温度的日变化
Fig.3 Diurnal changes in the temperature of alfalfa canopy and soil surface under different snow cover thicknesses during the melting period
指标 Index | 采样日期 Sampling date (月-日Month-day) | 覆雪厚度 Snow thickness (cm) | 品种 Varieties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
驯鹿 AC Caribou | 康赛 Concept | 巨能551 Magnum 551 | 赛迪7 Sardi 7 | WL656HQ | |||
可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein (mg·g-1 FW) | 11-26 | 0 | 55.60±1.13Ab | 58.54±0.40Aa | 53.91±0.51Ac | 59.40±0.37Aa | 51.58±3.24Ad |
| 10 | 55.85±0.55Ab | 58.45±0.84Aa | 53.80±0.63Ac | 59.36±0.98Aa | 50.51±1.21Ad | ||
| 15 | 55.87±0.65Ab | 58.33±0.79Aa | 54.06±1.01Ac | 59.63±1.07Aa | 50.10±0.85Ad | ||
| 12-31 | 0 | 71.78±0.45Aa | 68.05±0.55Aa | 68.85±0.51Aa | 65.03±0.49Ab | 62.65±0.53Ac | |
| 10 | 74.49±0.86Aa | 70.81±0.77Aa | 62.90±0.87Ab | 70.29±0.65Aa | 61.85±1.10Ac | ||
| 15 | 72.70±0.73Aa | 76.94±0.83Aa | 68.76±0.71Ab | 76.16±0.66Aa | 56.58±1.25Ac | ||
| 03-02 | 0 | 52.24±0.43Ca | 48.81±1.54Ca | 56.69±0.63Ba | 35.19±0.55Cb | 41.15±0.71Cb | |
| 10 | 56.31±0.78Ba | 58.76±1.52Ba | 45.55±0.60Cb | 50.10±0.92Aa | 49.47±0.67Bb | ||
| 15 | 61.45±0.63Aa | 60.87±0.89Aa | 57.10±1.01Aa | 49.74±0.63Bb | 52.94±0.91Ab | ||
可溶性碳水 化合物 Water soluble carbohydrate (g·100 g-1 DM) | 11-26 | 0 | 19.60±0.59Ad | 28.38±1.51Aa | 21.10±0.53Ac | 27.55±1.50Bb | 27.75±0.54Ab |
| 10 | 19.55±0.66Ad | 28.78±1.05Aa | 21.22±0.70Ac | 27.30±0.92Ab | 27.98±1.32Ab | ||
| 15 | 19.65±0.72Ad | 28.46±0.39Aa | 21.19±1.46Ac | 27.41±0.85Ab | 28.02±0.86Ab | ||
| 12-31 | 0 | 17.41±0.56Bab | 19.52±1.23Aa | 16.50±0.65ABb | 16.62±1.47Bb | 12.42±0.52Bb | |
| 10 | 16.38±0.53Bab | 17.51±0.69ABa | 15.79±1.21Bb | 18.98±0.82ABa | 18.62±1.71Aa | ||
| 15 | 18.58±1.08Aab | 16.65±0.63Bb | 17.36±0.78Ab | 20.70±0.79Aa | 17.23±0.86Ab | ||
| 03-02 | 0 | 10.64±0.60Bab | 13.48±0.43Ba | 13.55±1.65Ba | 11.48±1.58Bab | 6.31±0.73Bb | |
| 10 | 12.28±0.89Ab | 16.31±0.97Aa | 16.51±0.73Aa | 13.69±0.59Ab | 14.48±0.46Ab | ||
| 15 | 16.45±0.83Aa | 13.74±0.58Aa | 14.16±0.56Aa | 12.17±0.88Ab | 14.48±0.55Aa | ||
丙二醛 Malondialdehyde (mmol·g-1 DM) | 11-26 | 0 | 32.02±0.83Ae | 48.43±0.52Ad | 49.05±1.56Ac | 78.19±1.74Aa | 52.11±0.61Ab |
| 10 | 31.99±1.02Ae | 48.23±0.99Ad | 49.27±0.45Ac | 78.09±0.53Aa | 52.30±1.81Ab | ||
| 15 | 32.02±0.79Ae | 48.33±1.23Ad | 48.91±0.93Ac | 78.28±0.47Aa | 52.28±1.25Ab | ||
| 12-31 | 0 | 76.68±1.71Bd | 114.47±2.54Ac | 76.33±0.85Ae | 236.47±2.98Aa | 163.69±1.54Bb | |
| 10 | 98.64±1.74Ad | 135.57±1.76Ac | 60.07±0.91Be | 164.45±1.10Bb | 179.14±1.96Aa | ||
| 15 | 84.25±1.58Bc | 75.09±0.57Bd | 60.95±0.99Be | 165.45±1.65Ba | 160.56±1.55Bb | ||
| 03-02 | 0 | 57.60±0.63Aab | 56.26±0.67Aab | 73.39±0.86Aab | 52.33±0.98Ab | 74.79±1.23Aa | |
| 10 | 37.90±0.94Bb | 53.08±0.92Bab | 41.20±1.11Bb | 49.90±0.93Bb | 60.20±1.01Ba | ||
| 15 | 65.41±0.65Aa | 52.53±0.76Bab | 51.72±0.63Bab | 47.45±0.58Bb | 45.69±0.83Bb | ||
表2 不同覆雪厚度下各秋眠级苜蓿抗寒指标分析
Table 2 Analysis of cold resistance index of alfalfa at different fall dormancy levels under different snow cover thickness
指标 Index | 采样日期 Sampling date (月-日Month-day) | 覆雪厚度 Snow thickness (cm) | 品种 Varieties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
驯鹿 AC Caribou | 康赛 Concept | 巨能551 Magnum 551 | 赛迪7 Sardi 7 | WL656HQ | |||
可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein (mg·g-1 FW) | 11-26 | 0 | 55.60±1.13Ab | 58.54±0.40Aa | 53.91±0.51Ac | 59.40±0.37Aa | 51.58±3.24Ad |
| 10 | 55.85±0.55Ab | 58.45±0.84Aa | 53.80±0.63Ac | 59.36±0.98Aa | 50.51±1.21Ad | ||
| 15 | 55.87±0.65Ab | 58.33±0.79Aa | 54.06±1.01Ac | 59.63±1.07Aa | 50.10±0.85Ad | ||
| 12-31 | 0 | 71.78±0.45Aa | 68.05±0.55Aa | 68.85±0.51Aa | 65.03±0.49Ab | 62.65±0.53Ac | |
| 10 | 74.49±0.86Aa | 70.81±0.77Aa | 62.90±0.87Ab | 70.29±0.65Aa | 61.85±1.10Ac | ||
| 15 | 72.70±0.73Aa | 76.94±0.83Aa | 68.76±0.71Ab | 76.16±0.66Aa | 56.58±1.25Ac | ||
| 03-02 | 0 | 52.24±0.43Ca | 48.81±1.54Ca | 56.69±0.63Ba | 35.19±0.55Cb | 41.15±0.71Cb | |
| 10 | 56.31±0.78Ba | 58.76±1.52Ba | 45.55±0.60Cb | 50.10±0.92Aa | 49.47±0.67Bb | ||
| 15 | 61.45±0.63Aa | 60.87±0.89Aa | 57.10±1.01Aa | 49.74±0.63Bb | 52.94±0.91Ab | ||
可溶性碳水 化合物 Water soluble carbohydrate (g·100 g-1 DM) | 11-26 | 0 | 19.60±0.59Ad | 28.38±1.51Aa | 21.10±0.53Ac | 27.55±1.50Bb | 27.75±0.54Ab |
| 10 | 19.55±0.66Ad | 28.78±1.05Aa | 21.22±0.70Ac | 27.30±0.92Ab | 27.98±1.32Ab | ||
| 15 | 19.65±0.72Ad | 28.46±0.39Aa | 21.19±1.46Ac | 27.41±0.85Ab | 28.02±0.86Ab | ||
| 12-31 | 0 | 17.41±0.56Bab | 19.52±1.23Aa | 16.50±0.65ABb | 16.62±1.47Bb | 12.42±0.52Bb | |
| 10 | 16.38±0.53Bab | 17.51±0.69ABa | 15.79±1.21Bb | 18.98±0.82ABa | 18.62±1.71Aa | ||
| 15 | 18.58±1.08Aab | 16.65±0.63Bb | 17.36±0.78Ab | 20.70±0.79Aa | 17.23±0.86Ab | ||
| 03-02 | 0 | 10.64±0.60Bab | 13.48±0.43Ba | 13.55±1.65Ba | 11.48±1.58Bab | 6.31±0.73Bb | |
| 10 | 12.28±0.89Ab | 16.31±0.97Aa | 16.51±0.73Aa | 13.69±0.59Ab | 14.48±0.46Ab | ||
| 15 | 16.45±0.83Aa | 13.74±0.58Aa | 14.16±0.56Aa | 12.17±0.88Ab | 14.48±0.55Aa | ||
丙二醛 Malondialdehyde (mmol·g-1 DM) | 11-26 | 0 | 32.02±0.83Ae | 48.43±0.52Ad | 49.05±1.56Ac | 78.19±1.74Aa | 52.11±0.61Ab |
| 10 | 31.99±1.02Ae | 48.23±0.99Ad | 49.27±0.45Ac | 78.09±0.53Aa | 52.30±1.81Ab | ||
| 15 | 32.02±0.79Ae | 48.33±1.23Ad | 48.91±0.93Ac | 78.28±0.47Aa | 52.28±1.25Ab | ||
| 12-31 | 0 | 76.68±1.71Bd | 114.47±2.54Ac | 76.33±0.85Ae | 236.47±2.98Aa | 163.69±1.54Bb | |
| 10 | 98.64±1.74Ad | 135.57±1.76Ac | 60.07±0.91Be | 164.45±1.10Bb | 179.14±1.96Aa | ||
| 15 | 84.25±1.58Bc | 75.09±0.57Bd | 60.95±0.99Be | 165.45±1.65Ba | 160.56±1.55Bb | ||
| 03-02 | 0 | 57.60±0.63Aab | 56.26±0.67Aab | 73.39±0.86Aab | 52.33±0.98Ab | 74.79±1.23Aa | |
| 10 | 37.90±0.94Bb | 53.08±0.92Bab | 41.20±1.11Bb | 49.90±0.93Bb | 60.20±1.01Ba | ||
| 15 | 65.41±0.65Aa | 52.53±0.76Bab | 51.72±0.63Bab | 47.45±0.58Bb | 45.69±0.83Bb | ||
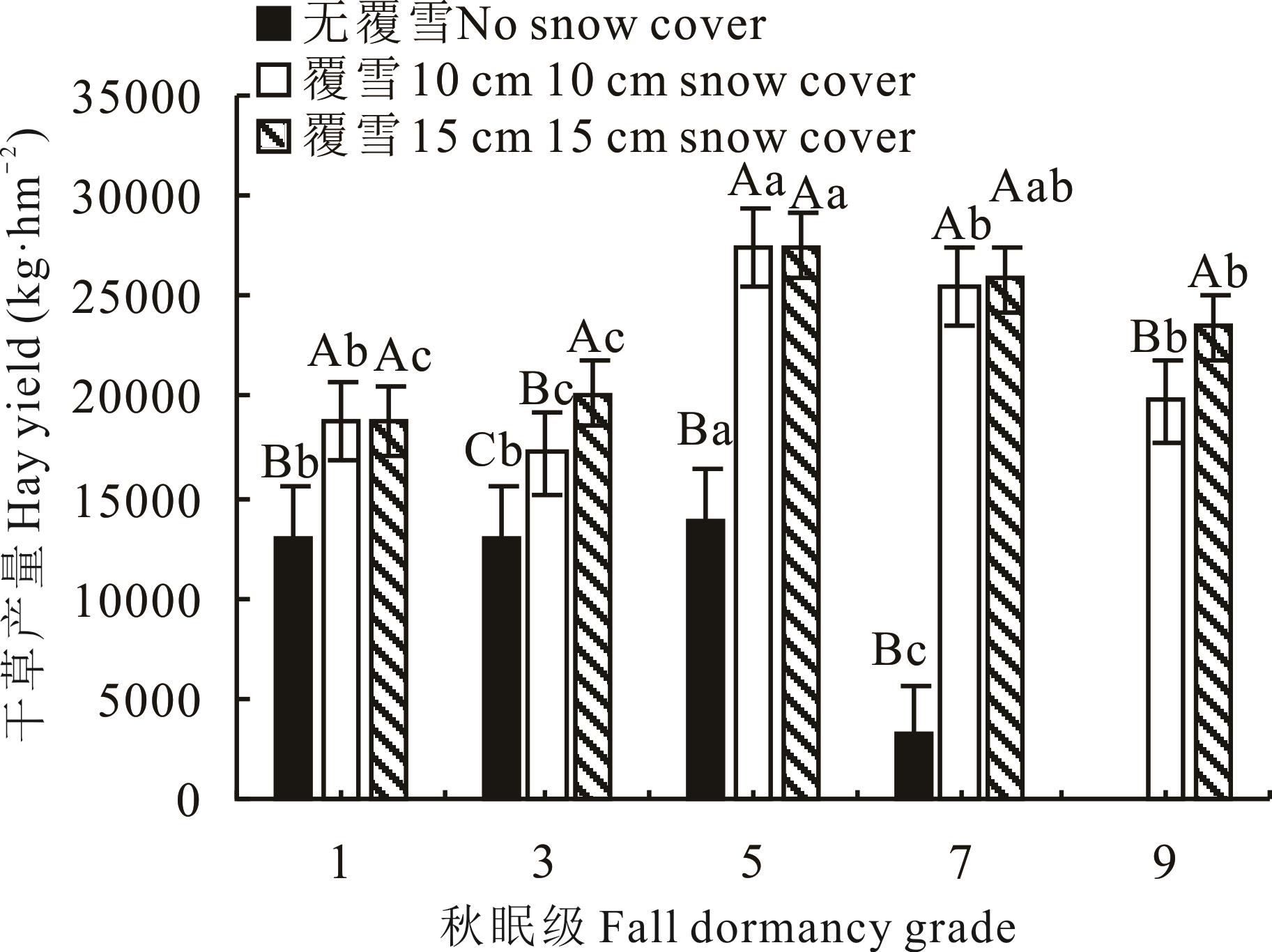
图6 不同覆雪处理下各秋眠级紫花苜蓿干草的年产量不同小写字母表示各品种间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示不同覆雪厚度间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different small letters indicate significant differences among varieties (P<0.05), and different capital letters indicate significant differences among snow cover thickness (P<0.05).
Fig.6 Annual hay yield of various fall dormancy grade alfalfa under different snow-covering treatments
| 指标 Index | 成分1 PCA1 | 成分2 PCA2 |
|---|---|---|
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.302 | 0.856 |
可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrate | 0.285 | 0.067 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde | -0.244 | 0.868 |
| 越冬率Winter survival rate | 0.971 | -0.150 |
| 干草产量 Hay yield | 0.984 | -0.054 |
表3 主成分得分系数矩阵
Table 3 Principal component score coefficient matrix
| 指标 Index | 成分1 PCA1 | 成分2 PCA2 |
|---|---|---|
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.302 | 0.856 |
可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrate | 0.285 | 0.067 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde | -0.244 | 0.868 |
| 越冬率Winter survival rate | 0.971 | -0.150 |
| 干草产量 Hay yield | 0.984 | -0.054 |
覆雪厚度 Snow thickness (cm) | 秋眠级 FDG | Y1 | Y2 | 综合得分 CS (Y) | 品种间排序 Ranking among varieties | 综合排序 Comprehensive ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | -0.667 | -0.174 | -0.328 | 3 | 13 |
| 3 | -0.539 | 0.021 | -0.217 | 1 | 11 | |
| 5 | -0.703 | 0.015 | -0.287 | 2 | 12 | |
| 7 | -2.871 | 0.620 | -1.005 | 4 | 14 | |
| 9 | -3.486 | 0.162 | -1.397 | 5 | 15 | |
| 10 | 1 | 0.457 | -0.119 | 0.154 | 4 | 9 |
| 3 | 0.600 | 0.291 | 0.336 | 2 | 5 | |
| 5 | 1.104 | -0.890 | 0.192 | 3 | 7 | |
| 7 | 1.091 | 0.313 | 0.546 | 1 | 2 | |
| 9 | 0.374 | -0.097 | 0.126 | 5 | 10 | |
| 15 | 1 | 0.642 | -0.015 | 0.262 | 4 | 6 |
| 3 | 0.896 | 0.166 | 0.421 | 3 | 4 | |
| 5 | 1.091 | 0.470 | 0.593 | 1 | 1 | |
| 7 | 1.329 | -0.415 | 0.427 | 2 | 3 | |
| 9 | 0.680 | -0.347 | 0.178 | 5 | 8 |
表4 各秋眠级苜蓿在不同覆雪厚度下的主成分、综合得分及排序
Table 4 Principal components, comprehensive scores (CS) and rankings of various fall dormancy grade alfalfa under different snow cover thickness
覆雪厚度 Snow thickness (cm) | 秋眠级 FDG | Y1 | Y2 | 综合得分 CS (Y) | 品种间排序 Ranking among varieties | 综合排序 Comprehensive ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | -0.667 | -0.174 | -0.328 | 3 | 13 |
| 3 | -0.539 | 0.021 | -0.217 | 1 | 11 | |
| 5 | -0.703 | 0.015 | -0.287 | 2 | 12 | |
| 7 | -2.871 | 0.620 | -1.005 | 4 | 14 | |
| 9 | -3.486 | 0.162 | -1.397 | 5 | 15 | |
| 10 | 1 | 0.457 | -0.119 | 0.154 | 4 | 9 |
| 3 | 0.600 | 0.291 | 0.336 | 2 | 5 | |
| 5 | 1.104 | -0.890 | 0.192 | 3 | 7 | |
| 7 | 1.091 | 0.313 | 0.546 | 1 | 2 | |
| 9 | 0.374 | -0.097 | 0.126 | 5 | 10 | |
| 15 | 1 | 0.642 | -0.015 | 0.262 | 4 | 6 |
| 3 | 0.896 | 0.166 | 0.421 | 3 | 4 | |
| 5 | 1.091 | 0.470 | 0.593 | 1 | 1 | |
| 7 | 1.329 | -0.415 | 0.427 | 2 | 3 | |
| 9 | 0.680 | -0.347 | 0.178 | 5 | 8 |
| 1 | Luo Z Z, Niu Y N, Li L L, et al. Soil moisture and alfalfa productivity response from different years of growth on the Loess Plateau of central Gansu. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(1): 31-38. |
| 罗珠珠, 牛伊宁, 李玲玲, 等. 陇中黄土高原不同种植年限苜蓿草地土壤水分及产量响应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(1): 31-38. | |
| 2 | Zhao Y H, Meng L D, Zhang X M, et al. Evaluation of physiological response and cold resistance of four alfalfa cultivars to low temperature stress. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(4): 683-692. |
| 赵一航, 孟令东, 张晓萌, 等. 4个紫花苜蓿品种对低温胁迫的生理响应及抗寒性评价. 草业科学, 2021, 38(4): 683-692. | |
| 3 | He Y, Liu Q W, Wang C Z, et al. The research on fall dormancy of alfalfa. Pratacultural Science, 2005, 22(11): 29-34. |
| 何云, 刘圈炜, 王成章, 等. 苜蓿秋眠性研究进展. 草业科学, 2005, 22(11): 29-34. | |
| 4 | Brummer E C, Shah M M, Luth D. Reexamining the relationship between fall dormancy and winter hardiness in alfalfa. Crop Science, 2000, 40(4): 971-977. |
| 5 | Li S S, Zhang Z Q, Wang Y F, et al. Effect of symbiotic rhizobium in alfalfa on physiological change under cold stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(2): 377-383. |
| 李莎莎, 张志强, 王亚芳, 等. 根瘤菌共生对低温胁迫下紫花苜蓿抗寒生理变化的影响. 草地学报, 2016, 24(2): 377-383. | |
| 6 | Anwar A, Bai L Q, Miao L, et al. 24-epibrassinolide ameliorates endogenous hormone levels to enhance low-temperature stress tolerance in cucumber seedlings.lnternational Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018,19(9): 2497. |
| 7 | Zhou J J, Wei W, Sang D, et al. Comparison between physiological characteristics and cold resistance of wild poa root during the overwintering period in alpine regions in northern Tibet. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(8): 2008-2016. |
| 周娟娟, 魏巍, 桑旦, 等. 藏北高寒区越冬期间野生早熟禾根系生理特征及抗寒性比较. 草业科学, 2019, 36(8): 2008-2016. | |
| 8 | Li Q, Li C H, Sun Q Z, et al. Study on cold resistance of three alfalfas successfully overwintered in Menyuan county. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(3): 631-634. |
| 李倩, 李长慧, 孙启忠, 等. 门源县越冬成功的3种紫花苜蓿抗寒性研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(3): 631-634. | |
| 9 | Shen X H, Jiang C, Li R L, et al. The study on the cold resistance and physiology change of root in meadow fescue-alfalfa mixture and monoculture in winter. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(2): 268-275. |
| 申晓慧, 姜成, 李如来, 等. 3种紫花苜蓿与草地羊茅单、混播越冬期根系生理变化及抗寒性. 草业科学, 2016, 33(2): 268-275. | |
| 10 | Li S M, Xu Q G, Yang Y, et al. Effects of low temperature stress on the antioxidant enzyme activities and fatty acid contents in zoysiagrass. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(4): 906-912. |
| 李双铭, 徐庆国, 杨勇, 等. 低温胁迫对结缕草抗氧化酶活性和脂肪酸含量的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(4): 906-912. | |
| 11 | Feng C J, Luo X Y, Sha W, et al. Effect of low temperature stress on SOD、POD activity and proline content of alfalfa. Pratacultural Science, 2005, 22(6): 29-32. |
| 冯昌军, 罗新义, 沙伟, 等. 低温胁迫对苜蓿品种幼苗SOD、POD活性和脯氨酸含量的影响. 草业科学, 2005, 22(6): 29-32. | |
| 12 | Shen Y P, Su H C, Wang G Y, et al. The responses of glaciers and snow cover to climate change in Xinjiang: Hazards effects. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2013, 35(6): 1355-1370. |
| 沈永平, 苏宏超, 王国亚, 等. 新疆冰川、积雪对气候变化的响应(Ⅱ): 灾害效应. 冰川冻土, 2013, 35(6): 1355-1370. | |
| 13 | Han C G. The characteristics of snow cover in Shihezi for past 58 years. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(32): 43-48. |
| 韩春光. 新疆石河子58年积雪变化特征. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(32): 43-48. | |
| 14 | Su L H, Zhang F F, Wang X Z, et al. Effects of snow cover on the yield and nutritional quality of alfalfa with different fall-dormancy levels. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(2): 356-363. |
| 苏力合, 张凡凡, 王旭哲, 等. 积雪覆盖对不同秋眠型紫花苜蓿产草量及营养品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(2): 356-363. | |
| 15 | Leep R H, Andresen J A, Jeranyama P. Fall dormancy and snow depth effects on winterkill of alfalfa. Agronomy Journal, 2001, 93(5): 1142-1148. |
| 16 | Annicchiarico P, Pecetti L, Tava A. Physiological and morphological traits associated with adaptation of lucerne (Medicago sativa) to severely drought-stressed and to irrigated environments. Annals of Applied Biology, 2013, 162(1): 27-40. |
| 17 | Hai B W, Ming G, Hu X, et al. Effects of chilling stress on the accumulation of soluble sugars and their key enzymes in Jatropha curcas seedlings. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2018, 24(5): 857-865. |
| 18 | Yang Y Z, Chen G, Peng F R, et al. Differences in water and osmoregulation substance contents in Toona sinensis from different provenances under low temperature stress and their correlation to cold tolerance. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2014, 23(4): 47-54. |
| 杨玉珍, 陈刚, 彭方仁, 等. 低温胁迫下不同种源香椿含水量和渗透调节物质含量差异及其与抗寒性的相关性.植物资源与环境学报, 2014, 23(4): 47-54. | |
| 19 | Niu Y, Liu Z J, He H, et al. Gene expression and metabolic changes of Momordica charantia L. seedlings in response to low temperature stress. Plos One, 2020, 15(5): e0233130. |
| 20 | Sun C Q, Yang Y J, Guo Z L, et al. Effects of fertilization and density on soluble sugar and protein and nitrate reductase of hybrid foxtail millet. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(5): 1169-1177. |
| 孙常青, 杨艳君, 郭志利, 等. 施肥和密度对杂交谷可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白及硝酸还原酶的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(5): 1169-1177. | |
| 21 | Qi C Y, Liu F Q, Liu J L, et al. Cluster analysis of antioxidant enzymes and soluble protein of alfalfa hybrid under low temperature stress. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(2): 53-58, 70. |
| 亓春宇, 刘凤歧, 刘杰淋, 等. 低温胁迫下紫花苜蓿杂交代抗氧化酶及可溶性蛋白的动态聚类分析. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(2): 53-58, 70. | |
| 22 | Xue Z M, Xue Q, Gao J H. The relationship of stomatal movement and photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfa seedlings under osmotic stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(2): 420-426. |
| 薛泽民, 薛琪, 高景慧. 渗透胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗气孔运动与光合作用的关系. 草地学报, 2018, 26(2): 420-426. | |
| 23 | Li Y Y, Zhao J, Zhang J, et al. Change of soluble sugar in skin and flesh tissues of radish taproot with low temperature storage.Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 1639-1646. |
| 李媛媛, 赵静, 张军, 等. 低温贮藏期间萝卜不同部位可溶性糖变化规律研究. 西北农业学报, 2019, 28(10): 1639-1646. | |
| 24 | Nan L L, Shi S L, Zhu X Q, et al. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of root in different root type alfalfa cultivars in field during overwintering period. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 25(2): 369-374. |
| 南丽丽, 师尚礼, 朱新强, 等. 田间越冬期不同根型苜蓿根系的生理生化特性. 核农学报, 2011, 25(2): 369-374. | |
| 25 | Xu H Y, Zhen L L, Li Y Y, et al. Effect of freeze-drying environment on freezing tolerance of alfalfa crowns.Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(4): 724-733. |
| 徐洪雨, 甄莉丽, 李钰莹, 等. 低温干旱环境对紫花苜蓿根颈耐寒性的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(4): 724-733. | |
| 26 | Sun X C, Hu C X, Tan Q L. Effects of molybdenum on antioxidative defense system and membrane lipid peroxidation in winter wheat under low temperature stress. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2006, 32(2): 175-182. |
| 27 | Zhao T H, Sun J W, Fu Y. Advances of research on metabolism of plant reactive oxygen species and exogenous regulation under abiotic stress. Crops, 2008(3): 10-13. |
| 赵天宏, 孙加伟, 付宇. 逆境胁迫下植物活性氧代谢及外源调控机理的研究进展. 作物杂志, 2008(3): 10-13. | |
| 28 | Ullah A, Sun H, Yang X, et al. Drought coping strategies in cotton: Increased crop per drop. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(3): 271-284. |
| 29 | Pu Y Y, Sun W C. The relationship between cold resistance of winter turnip rape varieties and its physiological characteristics. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2010, 8(2): 335-339. |
| 蒲媛媛, 孙万仓. 白菜型冬油菜抗寒性与生理生化特性关系. 分子植物育种, 2010, 8(2): 335-339. | |
| 30 | Shen X H. Study on the effects of mix-sowing with Bromus inermis on changes of physiological parameters of alfalfa root in wintering period. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(4): 901-904. |
| 申晓慧. 不同品种苜蓿与无芒雀麦单、混播越冬期根系生理指标变化研究. 草地学报, 2017, 25(4): 901-904. | |
| 31 | Li R L, Shen X H, Jiang C, et al. Effects of snow cover on alfalfa over-wintering and turning green. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(1): 67-73, 92. |
| 李如来, 申晓慧, 姜成, 等. 积雪覆盖对苜蓿越冬及返青生长的影响. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(1): 67-73, 92. | |
| 32 | Wang W D, Deng B, Wang X G, et al. Effect of the last harvest time on over-winter rate and root nutrient content of alfalfa in Horqin sandy land. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(4): 810-813. |
| 王伟东, 邓波, 王显国, 等. 末次刈割时间对科尔沁沙地苜蓿越冬率及根系营养物质含量的影响. 草地学报, 2017, 25(4): 810-813. | |
| 33 | Lu X S. The study on fall-dormancy of officially approved alfalfa cultivars in China. Grassland of China, 1998, 4(3): 2-6, 13. |
| 卢欣石. 中国苜蓿审定品种秋眠性研究. 中国草地, 1998, 4(3): 2-6, 13. | |
| 34 | Wang X L, Li H, Mi F G, et al. Comparison of production performance and winter survival rate of different fall dormancy alfalfa varieties. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(6): 82-92. |
| 王晓龙, 李红, 米福贵, 等. 不同秋眠级苜蓿生产性能及越冬率评价. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 82-92. | |
| 35 | Gao T, Sun Q Z, Wang C, et al. Effect of harvesting time in fall on productivity of different dormancy alfalfa varieties. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(1): 27-34. |
| 高婷, 孙启忠, 王川, 等. 秋季刈割时期对不同秋眠性苜蓿品种生产性能的影响. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(1): 27-34. | |
| 36 | Lu X Y, Hou C, Ji S R, et al. The yield difference and the relationship with shoot growth among alfalfa varieties varying in fall dormancy under a short-term cultivation system with spring sowing. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(2): 401-406. |
| 陆晓燕, 侯琛, 纪树仁, 等. 不同秋眠型紫花苜蓿春播短期栽培产量的差异及与地上部分枝的关系. 草地学报, 2017, 25(2): 401-406. |
| [1] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [2] | 王雪萌, 何欣, 张涵, 宋瑞, 毛培胜, 贾善刚. 基于多光谱成像技术快速无损检测紫花苜蓿人工老化种子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 197-208. |
| [3] | 李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75. |
| [4] | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [5] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| [6] | 欧成明, 赵美琦, 孙铭, 毛培胜. 抗坏血酸和水杨酸丸衣对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子发芽特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 93-101. |
| [7] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 赵雅姣, 王静. 内源异黄酮对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮及氮效率的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [8] | 张岳阳, 李芳, 梁维维, 李彦忠. 新疆昌吉32个紫花苜蓿品种的田间抗病性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 133-146. |
| [9] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| [10] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [11] | 白婕, 臧真凤, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 王可珍, 屈洋, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化及C、N特征对水分和N添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 213-220. |
| [12] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [13] | 徐睿智, 吴晓娟, 杨惠敏. 刈割后追肥对建植当年紫花苜蓿生长和生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 195-204. |
| [14] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [15] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||