

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 50-62.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021496
收稿日期:2021-12-28
修回日期:2022-03-09
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
王长庭
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wangct@swun.edu.cn基金资助:
Guo-hong YOU( ), Dan LIU, Yan-li WANG, Chang-ting WANG(
), Dan LIU, Yan-li WANG, Chang-ting WANG( )
)
Received:2021-12-28
Revised:2022-03-09
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Chang-ting WANG
摘要:
氮(N)是植物生长发育所需的基本元素,人为N添加已成为陆地生态系统N输入的主要形式。施N作为改善土壤养分条件的重要途径,可改变土壤理化性质,也会对植物叶片生态化学计量特征产生影响。本研究在2012年5月设置0(CK)、10(N10)、20(N20)、30(N30) g·m-2·a-1的N添加试验,并于2018年8月采集禾本科、莎草科、豆科和杂类草叶片,测定其碳(C)、N、磷(P)含量,分析不同水平N添加下植物叶片生态化学计量特征的差异,探索长期N添加下植物叶片生态化学计量特征变化的影响因素。结果表明:1)N添加显著提高了禾本科叶片碳(LC)含量而显著降低了豆科LC含量(P<0.05),莎草科和杂类草LC含量变化不显著(P>0.05)。随施N量增加,4种功能群叶片氮(LN)含量均显著增加(P<0.05),而叶片磷(LP)含量变化趋势不一致。2)N添加下4种功能群植物叶片碳氮比(LC/N)整体呈下降趋势,叶片氮磷比(LN/P)和叶片碳磷比(LC/P)呈上升趋势。3)土壤含水量(SMC)与植物叶片各项指标均显著相关(P<0.05),SMC对植物叶片生态化学计量特征变化的贡献率最高(10.28%,P<0.001)。4种功能群中,杂类草对SMC变化的响应最敏感,表现为杂类草LN、LN/P和LC/P随SMC增加显著降低而LC/N和LP显著升高。综上所述,4种功能群植物叶片生态化学计量特征对N添加的响应存在差异,N添加下影响植物叶片生态化学计量特征变化的重要因子是SMC。
游郭虹, 刘丹, 王艳丽, 王长庭. 高寒草甸植物叶片生态化学计量特征对长期氮肥添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 50-62.
Guo-hong YOU, Dan LIU, Yan-li WANG, Chang-ting WANG. Response of plant leaf ecological stoichiometric characteristics to long-term nitrogen addition in alpine meadow[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 50-62.
土层 Soil layer (cm) | 处理 Treatment | 全碳 Total carbon (TC, g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 Carbon nitrogen ratio (C/N) | 氮磷比 Nitrogen phosphorus ratio (N/P) | 碳磷比 Carbon phosphorus ratio (C/P) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content (SMC, %) | 土壤紧实度 Soil compactness (SC, Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | CK | 62.76±1.45Ab | 5.59±0.16Ab | 1.13±0.03Aa | 11.22±0.08Aab | 4.94±0.25Ab | 55.44±2.37Ab | 36.04±1.49Aa | 207.33±6.57Aa |
| N10 | 74.41±2.16Aa | 6.57±0.18Aa | 0.89±0.02Bc | 11.78±0.47Aa | 7.13±0.32Aa | 84.04±7.53Aa | 28.26±1.12Abc | 200.00±5.57Aa | |
| N20 | 61.24±1.62Ab | 5.75±0.16Ab | 1.13±0.02Aa | 10.68±0.90Aab | 5.10±0.13Ab | 54.34±3.97Ab | 31.61±0.16Ab | 209.00±10.79Aa | |
| N30 | 63.61±1.75Ab | 6.32±0.16Aab | 1.00±0.01Bb | 9.69±0.38Ab | 6.58±0.12Aa | 63.70±2.39Ab | 27.18±0.56Ac | 198.33±18.99Aa | |
| 10~20 | CK | 51.10±1.53Ba | 5.08±0.15Ba | 1.14±0.03Aa | 10.09±0.26Aa | 4.47±0.15Ba | 45.15±2.58Ba | 35.55±1.03Aa | 170.33±6.17Ab |
| N10 | 53.45±1.48Ba | 4.52±0.21Bb | 1.06±0.05Aa | 11.83±0.01Aa | 4.26±0.17Ba | 50.28±0.11Ba | 29.29±0.69Ab | 192.30±2.16Aa | |
| N20 | 55.26±0.66Ba | 5.14±0.26Ba | 1.16±0.01Aa | 10.76±0.04Aa | 4.45±0.10Ba | 47.82±0.72Ba | 34.15±0.41Aa | 193.20±2.69Aa | |
| N30 | 52.26±0.86Ba | 4.86±0.14Bab | 1.12±0.01Aa | 10.75±0.10Aa | 4.34±0.06Ba | 46.63±0.98Ba | 28.40±0.53Ab | 172.13±1.85Ab |
表1 不同梯度氮添加下土壤理化特征
Table 1 Soil physiochemical characteristics under different N addition gradients
土层 Soil layer (cm) | 处理 Treatment | 全碳 Total carbon (TC, g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 Carbon nitrogen ratio (C/N) | 氮磷比 Nitrogen phosphorus ratio (N/P) | 碳磷比 Carbon phosphorus ratio (C/P) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content (SMC, %) | 土壤紧实度 Soil compactness (SC, Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | CK | 62.76±1.45Ab | 5.59±0.16Ab | 1.13±0.03Aa | 11.22±0.08Aab | 4.94±0.25Ab | 55.44±2.37Ab | 36.04±1.49Aa | 207.33±6.57Aa |
| N10 | 74.41±2.16Aa | 6.57±0.18Aa | 0.89±0.02Bc | 11.78±0.47Aa | 7.13±0.32Aa | 84.04±7.53Aa | 28.26±1.12Abc | 200.00±5.57Aa | |
| N20 | 61.24±1.62Ab | 5.75±0.16Ab | 1.13±0.02Aa | 10.68±0.90Aab | 5.10±0.13Ab | 54.34±3.97Ab | 31.61±0.16Ab | 209.00±10.79Aa | |
| N30 | 63.61±1.75Ab | 6.32±0.16Aab | 1.00±0.01Bb | 9.69±0.38Ab | 6.58±0.12Aa | 63.70±2.39Ab | 27.18±0.56Ac | 198.33±18.99Aa | |
| 10~20 | CK | 51.10±1.53Ba | 5.08±0.15Ba | 1.14±0.03Aa | 10.09±0.26Aa | 4.47±0.15Ba | 45.15±2.58Ba | 35.55±1.03Aa | 170.33±6.17Ab |
| N10 | 53.45±1.48Ba | 4.52±0.21Bb | 1.06±0.05Aa | 11.83±0.01Aa | 4.26±0.17Ba | 50.28±0.11Ba | 29.29±0.69Ab | 192.30±2.16Aa | |
| N20 | 55.26±0.66Ba | 5.14±0.26Ba | 1.16±0.01Aa | 10.76±0.04Aa | 4.45±0.10Ba | 47.82±0.72Ba | 34.15±0.41Aa | 193.20±2.69Aa | |
| N30 | 52.26±0.86Ba | 4.86±0.14Bab | 1.12±0.01Aa | 10.75±0.10Aa | 4.34±0.06Ba | 46.63±0.98Ba | 28.40±0.53Ab | 172.13±1.85Ab |
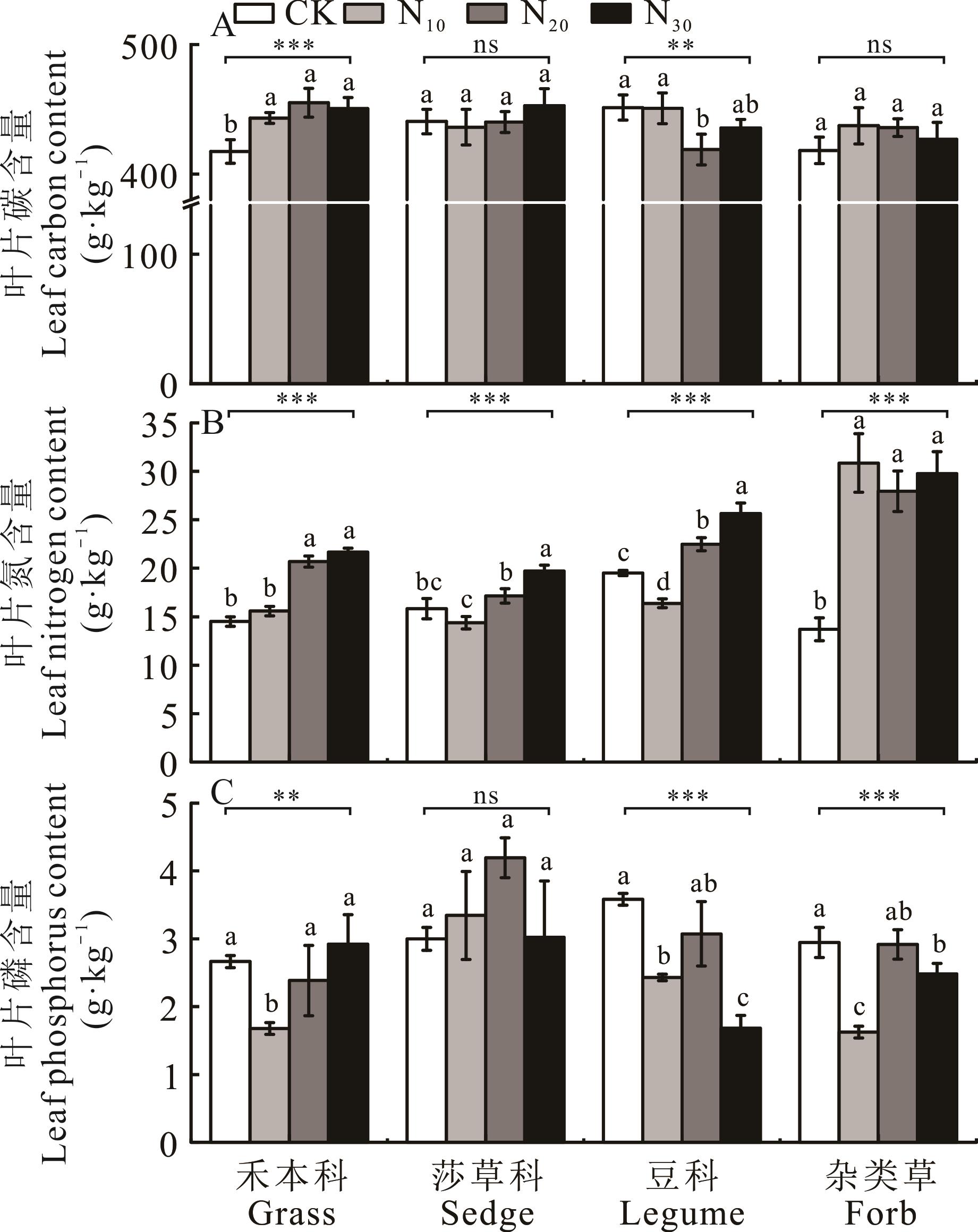
图1 不同梯度氮添加下植物LC、LN、LP含量的变化*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ns: 不显著Not significant. 不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Changes of LC, LN and LP contents of plants with different nitrogen gradients
| 指标Indicator | 叶片碳LC | 叶片氮LN | 叶片磷LP | 叶片碳氮比LC/N | 叶片氮磷比LN/P | 叶片碳磷比LC/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全碳Total carbon (TC) | 0.014 | 0.019 | -0.106 | -0.001 | 0.092 | 0.103 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | -0.014 | 0.086 | -0.026 | -0.104 | 0.067 | 0.040 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | -0.089 | -0.084 | 0.264** | 0.033 | -0.246** | -0.275** |
| 碳氮比Carbon nitrogen ratio (C/N) | 0.047 | -0.082 | -0.138* | 0.138* | 0.063 | 0.117 |
| 氮磷比Nitrogen phosphorus ratio (N/P) | 0.034 | 0.091 | -0.146* | -0.076 | 0.160* | 0.158* |
| 碳磷比Carbon phosphorus ratio (C/P) | 0.049 | 0.042 | -0.184** | -0.005 | 0.163* | 0.185** |
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (SMC) | -0.145* | -0.342** | 0.279** | 0.325** | -0.404** | -0.363** |
| 土壤紧实度Soil compactness (SC) | 0.040 | 0.004 | 0.022 | 0.002 | -0.008 | -0.001 |
表2 植物叶片生态化学计量特征值与环境因子的Pearson相关性
Table 2 Pearson correlations between ecological stoichiometric characteristics of plant leaves and environmental factors
| 指标Indicator | 叶片碳LC | 叶片氮LN | 叶片磷LP | 叶片碳氮比LC/N | 叶片氮磷比LN/P | 叶片碳磷比LC/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全碳Total carbon (TC) | 0.014 | 0.019 | -0.106 | -0.001 | 0.092 | 0.103 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | -0.014 | 0.086 | -0.026 | -0.104 | 0.067 | 0.040 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | -0.089 | -0.084 | 0.264** | 0.033 | -0.246** | -0.275** |
| 碳氮比Carbon nitrogen ratio (C/N) | 0.047 | -0.082 | -0.138* | 0.138* | 0.063 | 0.117 |
| 氮磷比Nitrogen phosphorus ratio (N/P) | 0.034 | 0.091 | -0.146* | -0.076 | 0.160* | 0.158* |
| 碳磷比Carbon phosphorus ratio (C/P) | 0.049 | 0.042 | -0.184** | -0.005 | 0.163* | 0.185** |
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (SMC) | -0.145* | -0.342** | 0.279** | 0.325** | -0.404** | -0.363** |
| 土壤紧实度Soil compactness (SC) | 0.040 | 0.004 | 0.022 | 0.002 | -0.008 | -0.001 |
变量 Variable | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (SMC) | 10.28 | 25.0047 | 0.001 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | 1.39 | 3.3714 | 0.021 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | 1.15 | 2.8028 | 0.058 |
表3 最优RDA模型中环境因子对植物叶片生态化学计量特征变异的贡献率
Table 3 Contribution rate of environmental factors to variation of ecological stoichiometry characteristics of plant leaves in the optimal RDA model
变量 Variable | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (SMC) | 10.28 | 25.0047 | 0.001 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | 1.39 | 3.3714 | 0.021 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | 1.15 | 2.8028 | 0.058 |
| 1 | He K J, Huang Y M, Qi Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on vegetation and soil and its linkages to plant diversity and productivity in a semi-arid steppe. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 778: 146299. |
| 2 | Galloway J N, Dentener F J, Capone D G, et al. Nitrogen cycles: Past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry, 2004, 70(2): 153-226. |
| 3 | Lu M, Yang Y H, Luo Y Q, et al. Responses of ecosystem nitrogen cycle to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. New Phytologist, 2011, 189(4): 1040-1050. |
| 4 | Li K H, Liu X J, Song L, et al. Response of alpine grassland to elevated nitrogen deposition and water supply in China. Oecologia, 2015, 177(1): 65-72. |
| 5 | Lebauer D S, Treseder K K. Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed. Ecology, 2008, 89(2): 371-379. |
| 6 | Tian D S, Niu S L. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environmental Research Letters, 2015, 10: 024019. |
| 7 | Sterner R W, Elser J J. Ecological stoichiometry: The biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2002. |
| 8 | Wang S Q, Yu G R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| 王绍强, 于贵瑞. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| 9 | Yang K, Huang J H, Dong D, et al. Canopy leaf N and P stoichiometry in grassland communities of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(1): 17-22. |
| 杨阔, 黄建辉, 董丹, 等. 青藏高原草地植物群落冠层叶片氮磷化学计量学分析. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(1): 17-22. | |
| 10 | Yang H, Luo Y C. Responses of the functional traits in Cleistogenes squarrosa to nitrogen addition and drought. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(1): 32-42. |
| 杨浩, 罗亚晨. 糙隐子草功能性状对氮添加和干旱的响应. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(1): 32-42. | |
| 11 | Zhang K, He M Z, Li X R, et al. Foliar carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of typical desert plants across the Alashan Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(22): 6538-6547. |
| 张珂, 何明珠, 李新荣, 等. 阿拉善荒漠典型植物叶片碳、氮、磷化学计量特征. 生态学报, 2014, 34(22): 6538-6547. | |
| 12 | Güsewell S. N∶P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytologist, 2004, 164: 243-266. |
| 13 | Koerselman W, Meuleman A M F. The vegetation N∶P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. Journal of Applied Ecology, 1996, 33(6): 1441-1450. |
| 14 | Zhang L X, Bai Y F, Han X G. Differential responses of N∶P stoichiometry of Leymus chinensis and Carex korshinskyi to N additions in a steppe ecosystem in Nei Mongol. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2004, 46(3): 259-270. |
| 15 | Su J Q, Li X R, Bao J T. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities in desertified steppe. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(3): 664-670. |
| 苏洁琼, 李新荣, 包婧婷. 施氮对荒漠化草原土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(3): 664-670. | |
| 16 | Zhou X. Influence of biochemical inhibitor combination on nitrogen transformation in yellow clayey soil and its ecological environment effect. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. |
| 周旋. 生化抑制剂组合对黄泥田土壤氮素转化的影响及其环境生态效应. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. | |
| 17 | Wang Q J, Bai L G. The causes and measures for nitrogen fertilizer caused soil acidification. Journal of Henan Science and Technology, 1991(7): 9, 16. |
| 王秋杰, 白乐高. 氮素化肥致使土壤酸化板结的原因及对策. 河南科技, 1991(7): 9, 16. | |
| 18 | Li M F. Effect of nitrogen addition on plant photosynthesis: A meta-analysis. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020. |
| 李孟帆. 氮添加对植物光合作用影响的整合分析. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. | |
| 19 | Li Q, Huang Y X, Zhou D W, et al. Mechanism of the trade-off between biological nitrogen fixation and phosphorus acquisition strategies of herbaceous legumes under nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2021, 45(3): 286-297. |
| 李强, 黄迎新, 周道玮, 等. 土壤氮磷添加下豆科草本植物生物固氮与磷获取策略的权衡机制. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(3): 286-297. | |
| 20 | Xi D, Weng H D, Hu Y L, et al. Effects of canopy nitrogen addition and understory removal on soil organic carbon fractions in a Chinese fir plantation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(21): 8525-8534. |
| 习丹, 翁浩东, 胡亚林, 等. 林冠氮添加和林下植被去除对杉木林土壤有机碳组分的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(21): 8525-8534. | |
| 21 | Whittinghill K A, Currie W S, Zak D R, et al. Anthropogenic N deposition increases soil C storage by decreasing the extent of litter decay: Analysis of field observations with an ecosystem model. Ecosystems, 2012, 15(3): 450-461. |
| 22 | Liu Y W, Geng X D, Tenzintarchen, et al. Divergence in ecosystem carbon fluxes and soil nitrogen characteristics across alpine steppe, alpine meadow and alpine swamp ecosystems in a biome transition zone. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 748: 142453. |
| 23 | Yuan Z Q, Jiang X J. Vegetation and soil covariation, not grazing exclusion, control soil organic carbon and nitrogen in density fractions of alpine meadows in a Tibetan permafrost region. Catena, 2021, 196: 104832. |
| 24 | Mou J, Bin Z J, Li Q X, et al. Effects of nitrogen and silicon addition on soil nitrogen mineralization in alpine meadows of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2019, 43(1): 77-84. |
| 牟静, 宾振钧, 李秋霞, 等. 氮硅添加对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤氮矿化的影响. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(1): 77-84. | |
| 25 | Chen X P, Zhang T, Guo R Y, et al. Fencing enclosure alters nitrogen distribution patterns and tradeoff strategies in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena, 2021, 197: 104948. |
| 26 | Zi H B, Hu L, Wang C T, et al. Responses of soil bacterial community and enzyme activity to experimental warming of an alpine meadow. European Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 69(3): 429-438. |
| 27 | Luo X, Wang Y T, Zhang J, et al. Responses of dominant species and rhizosphere soil stoichiometry to rainfall in typical steppe of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(3): 1002-1014. |
| 罗叙, 王誉涛, 张娟, 等. 黄土高原典型草原优势种植物及其根际土壤化学计量对降雨变化的响应. 生态学报, 2022, 42(3): 1002-1014. | |
| 28 | Zhang W, Fu Y, Li J F, et al. Comparative study on kjeldahl method and sumas combustion method for total nitrogen measurement in soil. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(35): 172-175. |
| 张薇, 付昀, 李季芳, 等. 基于凯氏定氮法与杜马斯燃烧法测定土壤全氮的比较研究. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(35): 172-175. | |
| 29 | Lu R K. Analysis methods of soil and agricultural chemistry. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 30 | Tang Z H, Xu W T, Zhou G Y, et al. Patterns of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration in relation to productivity in China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(16): 4033-4038. |
| 31 | Qing Y, Sun F D, Li Y, et al. Analysis of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in degraded alpine wetland, Zoige, southwest China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(3): 38-47. |
| 青烨, 孙飞达, 李勇, 等. 若尔盖高寒退化湿地土壤碳氮磷比及相关性分析. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 38-47. | |
| 32 | Wang J L, Zhong Z M, Wang Z H, et al. Soil C/P distribution characteristics of alpine steppe ecosystems in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(2): 9-19. |
| 王建林, 钟志明, 王忠红, 等. 青藏高原高寒草原生态系统土壤碳磷比的分布特征. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 9-19. | |
| 33 | Tian H Q, Chen G S, Zhang C, et al. Pattern and variation of C∶N∶P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 98(1/2/3): 139-151. |
| 34 | Bui E N, Henderson B L. C∶N∶P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant and Soil, 2013, 373(1/2): 553-568. |
| 35 | Zhang R Y. Variations of N∶P stoichiometry among functional groups in a sub-alpine meadow. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. |
| 张仁懿. 亚高寒草甸不同功能群植物N∶P化学计量特征差异研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010. | |
| 36 | Yang H Y. Study on the effect of stimulated N deposition on N2O emission and fate of nitrogen in a Stipa krylovii steppe. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017. |
| 杨涵越. 模拟氮沉降对克氏针茅草原N2O排放及氮去向的影响研究. 北京: 清华大学, 2017. | |
| 37 | Yang Z, Gamadaerji, Tan X R, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition amount and frequency on soil respiration and its components in a temperate semiarid grassland. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(10): 1059-1072. |
| 杨泽, 嘎玛达尔基, 谭星儒, 等. 氮添加量和施氮频率对温带半干旱草原土壤呼吸及组分的影响. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(10): 1059-1072. | |
| 38 | Fan M Z, Yin C, Fan F L, et al. Effects of different long-term fertilization on the activities of enzymes related to carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles in a red soil. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(3): 833-838. |
| 范淼珍, 尹昌, 范分良, 等. 长期不同施肥对红壤碳、氮、磷循环相关酶活性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3): 833-838. | |
| 39 | Wang G X, Shen Y P, Qian J, et al. Study on the influence of vegetation change on soil moisture cycle in alpine meadow. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2003, 25(6): 653-659. |
| 王根绪, 沈永平, 钱鞠, 等. 高寒草地植被覆盖变化对土壤水分循环影响研究. 冰川冻土, 2003, 25(6): 653-659. | |
| 40 | Wang H Y, Ding R, Wang Z H, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on C∶N∶P ecological stoichiometry in leaves and roots of different canopy species in Hulunbuir grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 37-45. |
| 王洪义, 丁睿, 王智慧, 等. 氮、磷添加对草地不同冠层植物叶片和根系生态化学计量特征的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 37-45. | |
| 41 | Li W J. Response of ecological stoichiometry characteristics of steppe plants to nitrogen addition on the Loess Plateau. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2019, 47(3): 208-213. |
| 李维军. 黄土高原斯泰普草原植物氮磷生态化学计量特征对氮素添加的响应. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(3): 208-213. | |
| 42 | Yue Z W, Li X Y, Li L, et al. Responses of soil, microbes and plant ecological stoichiometric characteristics to nitrogen addition in an alpine grassland of Kunlun Mountain. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(3): 1-8. |
| 岳泽伟, 李向义, 李磊, 等. 氮添加对昆仑山高山草地土壤、微生物和植物生态化学计量特征的影响. 生态科学, 2020, 39(3): 1-8. | |
| 43 | Bin Z J, Wang J J, Zhang W P, et al. Effects of N addition on ecological stoichiometric characteristics in six dominant plant species of alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(3): 231-237. |
| 宾振钧, 王静静, 张文鹏, 等. 氮肥添加对青藏高原高寒草甸6个群落优势种生态化学计量学特征的影响. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(3): 231-237. | |
| 44 | Yu H L, Li Y Z, Fan J W, et al. Leaf N and P contents of different functional groups in relation to precipitation and temperature in China Grassland Transect. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(11): 2867-2874. |
| 于海玲, 李愈哲, 樊江文, 等. 中国草地样带不同功能群植物叶片氮磷含量随水热因子的变化规律. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(11): 2867-2874. | |
| 45 | Xiong X S, Cai H Y, Li Y Q, et al. Seasonal dynamics of leaf C, N and P stoichiometry in plants of typical steppe in Nei Mongol, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(11): 1138-1153. |
| 熊星烁, 蔡宏宇, 李耀琪, 等. 内蒙古典型草原植物叶片碳氮磷化学计量特征的季节动态. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(11): 1138-1153. | |
| 46 | Gao Z B, Wang H Y, Lv X T, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on C∶N∶P stoichiometry in roots and leaves of four dominant plant species in a meadow steppe of Hulunbuir. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(1): 80-88. |
| 高宗宝, 王洪义, 吕晓涛, 等. 氮磷添加对呼伦贝尔草甸草原4种优势植物根系和叶片C∶N∶P化学计量特征的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(1): 80-88. | |
| 47 | Bin Z J, Zhang R Y, Zhang W P, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon addition on leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration of Elymus nutans of alpine meadow on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(14): 4699-4706. |
| 宾振钧, 张仁懿, 张文鹏, 等. 氮磷硅添加对青藏高原高寒草甸垂穗披碱草叶片碳氮磷的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(14): 4699-4706. | |
| 48 | Li D D. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on community and stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in grassland ecosystem of northern China. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. |
| 李冬冬. 氮磷添加对北方草原生态系统群落和碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020. | |
| 49 | Ågren G I. Stoichiometry and nutrition of plant growth in natural communities. Functional Plant Biology, 2008, 39: 153-170. |
| 50 | Chen W W, Kou L, Jiang L, et al. Short-term responses of foliar multi-element stoichiometry and nutrient resorption of slash pine to N addition in subtropical China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(4): 1094-1102. |
| 陈微微, 寇亮, 蒋蕾, 等. 亚热带湿地松叶片多元素化学计量与养分回收对氮添加的短期响应. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(4): 1094-1102. | |
| 51 | Ding X H, Luo S Z, Liu J W, et al. Longitude gradient changes on plant community and soil stoichiometry characteristics of grassland in Hulunbeir. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(11): 3467-3476. |
| 丁小慧, 罗淑政, 刘金巍, 等. 呼伦贝尔草地植物群落与土壤化学计量学特征沿经度梯度变化. 生态学报, 2012, 32(11): 3467-3476. | |
| 52 | Yu Q, Wu H H, He N P, et al. Testing the growth-rate hypothesis in vascular plants with above- and below-ground biomass. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e32162. |
| 53 | Han W X, Fang J Y, Guo D L, et al. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytologist, 2005, 168(2): 377-385. |
| 54 | Sadras V O. The N∶P stoichiometry of cereal, grain legume and oilseed crops. Field Crops Research, 2006, 95(1): 13-29. |
| 55 | Han W X, Tang L Y, Chen Y H, et al. Relationship between the relative limitation and resorption efficiency of nitrogen vs phosphorus in woody plants. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e83366. |
| 56 | Liu D, Zhang J, Bao Y L, et al. Effects of soil moisture on Phragmites australis leaves and soil C, N and P ecological stoichiometric characteristics in Yangguan wetland, Dunhuang. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(11): 3804-3812. |
| 刘冬, 张剑, 包雅兰, 等. 水分对敦煌阳关湿地芦苇叶片与土壤C、N、P生态化学计量特征的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(11): 3804-3812. | |
| 57 | Su Z X, Su B Q, Shangguan Z P. Response characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia leaf and soil ecological stoichiometric parameters to precipitation in the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(19): 7000-7008. |
| 苏卓侠, 苏冰倩, 上官周平. 黄土高原刺槐叶片-土壤生态化学计量参数对降雨量的响应特征. 生态学报, 2020, 40(19): 7000-7008. | |
| 58 | Luo Y, Gong L, Zhu M L, et al. Stoichiometry characteristics of leaves and soil of four shrubs in the upper reaches of the Tarim River Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(24): 8326-8335. |
| 罗艳, 贡璐, 朱美玲, 等. 塔里木河上游荒漠区4种灌木植物叶片与土壤生态化学计量特征. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24): 8326-8335. | |
| 59 | Xie L L, Hu X F, Liu Q H, et al. Response of C∶N stoichiometry of Picea asperata to soil water and nitrogen availabilities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(15): 5377-5387. |
| 谢路路, 胡雪凤, 刘庆华, 等. 云杉碳氮化学计量比对土壤水分和氮有效性的响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(15): 5377-5387. | |
| 60 | Zhang X N. Study on desert plant community succession and nutrient elements driving. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2014. |
| 张雪妮. 荒漠植物群落演替及其营养元素驱动研究. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2014. | |
| 61 | Shen Z X, Yang F T, Zhong H M. Preliminary studies on water content and degree of required water of main plants in Kobresia humilis meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 1991, 1(1): 133-141. |
| 沈振西, 杨福囤, 钟海民. 矮嵩草(Kobresia humilis)草甸主要植物含水量及需水程度的初步研究. 草地学报, 1991, 1(1): 133-141. | |
| 62 | Zhao L, Ma X, Liu H Q, et al. Responses of leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry of Carex muliensis to water table drawdown in an alpine marsh on the Ruoergai Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(7): 2426-2432. |
| 赵丽, 马骁, 刘宏强, 等. 若尔盖高寒草本沼泽木里薹草叶片碳氮磷化学计量特征对水位下降的响应. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(7): 2426-2432. | |
| 63 | Li Y C, Yu H L, Wang P, et al. Effects of precipitation on plant community diversity and C∶N∶P ecological stoichiometry in a desert steppe of Ningxia, northwestern China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(1): 117-126. |
| 李一春, 余海龙, 王攀, 等. 降水量对荒漠草原植物群落多样性和C∶N∶P生态化学计量特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(1): 117-126. | |
| 64 | Wright I J, Reich P B, Westoby M. Strategy shifts in leaf physiology, structure and nutrient content between species of high- and low-rainfall and high- and low-nutrient habitats. Functional Ecology, 2001, 15(4): 423-434. |
| 65 | Liu X D, Yin G L, Wu J, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on the physical properties of soil in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(10): 12-21. |
| 刘晓东, 尹国丽, 武均, 等. 青藏高原东部高寒草甸草地土壤物理性状对氮元素添加的响应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 12-21. | |
| 66 | Shen Z X, Zhou X M, Chen Z Z, et al. Response of plant groups to simulated rainfall and nitrogen supply in alpine Kobresia humilis meadow. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2002, 26(3): 288-294. |
| 沈振西, 周兴民, 陈佐忠, 等. 高寒矮嵩草草甸植物类群对模拟降水和施氮的响应. 植物生态学报, 2002, 26(3): 288-294. | |
| 67 | Chen Z, Wang H, Wang J Z, et al. Estimation on seasonal dynamics of alpine grassland aboveground biomass using phenology camera-derived NDVI. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2021, 45(5): 487-495. |
| 陈哲, 汪浩, 王金洲, 等. 基于物候相机归一化植被指数估算高寒草地植物地上生物量的季节动态. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(5): 487-495. | |
| 68 | Yang F T, Shen Z X, Zhong H M. A preliminary study on transpiration intensity of plants in Kobresia humilis meadow. Acta Phytoecologica Et Geobotanica Sinica, 1989, 13(2): 136-143. |
| 杨福囤, 沈振西, 钟海民. 矮嵩草草甸植物蒸腾强度的初步研究. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 1989, 13(2): 136-143. |
| [1] | 张丽苗, 谭雪, 董智, 郑杰, 袁中勋, 李昌晓. 喜旱莲子草入侵对三峡库区重庆主城河岸带植物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 13-25. |
| [2] | 彭艳, 孙晶远, 马素洁, 王向涛, 魏学红, 孙磊. 藏北不同退化阶段高寒草甸植物群落特征与土壤养分特性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 49-60. |
| [3] | 纪童, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波. 7种禾本科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 144-156. |
| [4] | 甘凤玲, 韦杰, 李沙沙. 紫色土埂坎典型草本根系摩阻特性对土壤含水率的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 28-37. |
| [5] | 张玉琢, 杨志贵, 于红妍, 张强, 杨淑霞, 赵婷, 许画画, 孟宝平, 吕燕燕. 基于STARFM的草地地上生物量遥感估测研究——以甘肃省夏河县桑科草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 23-34. |
| [6] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [7] | 蒋嘉瑜, 连学, 唐希明, 刘任涛, 张安宁. 干旱与半干旱区红砂枯落物分解初期节肢动物群落结构特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 156-168. |
| [8] | 王亚妮, 胡宜刚, 王增如, 李以康, 张振华, 周华坤. 沙化和人工植被重建对高寒草地土壤细菌群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 26-39. |
| [9] | 田英, 许喆, 朱丽珍, 王俊, 温学飞. 生长季不同月份平茬对柠条人工林地土壤细菌群落特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 40-50. |
| [10] | 刘咏梅, 董幸枝, 龙永清, 朱志梅, 王雷, 盖星华, 赵樊, 李京忠. 退化高寒草甸狼毒群落分类特征及其环境影响因子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 1-11. |
| [11] | 卫宏健, 丁杰, 张巨明, 杨文, 王咏琪, 刘天增. 践踏胁迫下狗牙根草坪土壤真菌群落结构的变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 102-112. |
| [12] | 金玲, 陆颖, 马红彬, 谢应忠, 沈艳. 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原植物群落的数量分类与排序[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 12-21. |
| [13] | 李鑫, 魏雪, 王长庭, 任晓, 吴鹏飞. 外源性养分添加对高寒草甸土壤节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 155-164. |
| [14] | 周磊, 魏雪, 王长庭, 吴鹏飞. 高寒草地小型土壤节肢动物群落特征及其对草地退化的指示作用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 34-46. |
| [15] | 潘占东, 马倩倩, 陈晓龙, 蔡立群, 蔡雪梅, 董博, 武均, 张仁陟. 添加生物质炭对黄土高原旱作农田土壤养分、腐殖质及其组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 14-24. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||