

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 53-63.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021414
靳旭妹( ), 王莹莹, 刘崇义, 陈新义, 龙明秀(
), 王莹莹, 刘崇义, 陈新义, 龙明秀( ), 何树斌(
), 何树斌( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-10
修回日期:2022-02-09
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-09-14
通讯作者:
龙明秀,何树斌
作者简介:E-mail: heshubin@nwsuaf.edu.cn基金资助:
Xu-mei JIN( ), Ying-ying WANG, Chong-yi LIU, Xin-yi CHEN, Ming-xiu LONG(
), Ying-ying WANG, Chong-yi LIU, Xin-yi CHEN, Ming-xiu LONG( ), Shu-bin HE(
), Shu-bin HE( )
)
Received:2021-11-10
Revised:2022-02-09
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-09-14
Contact:
Ming-xiu LONG,Shu-bin HE
摘要:
为探究不同生草模式对关中地区有机猕猴桃园土壤养分及细菌群落的影响,试验设置多年生黑麦草+毛苕子(Mode 1)、多年生黑麦草+草木樨(Mode 2)、多年生黑麦草+白三叶(Mode 3)及鼠茅草(Mode 4),以自然生草处理为对照(CK),观察草种生长特性、研究生草对果园耕层(0~20 cm)土壤养分影响,采用高通量测序法分析细菌群落结构。结果表明:鼠茅草越冬率最高,样地杂草株数最少。人工生草较自然生草有机质提高了6.46%~38.63%,以多年生黑麦草+毛苕子效果更为明显,且该处理提高土壤脲酶、蔗糖酶和碱性磷酸酶活性最为显著,分别为3.37、44.17和3.46 mg·d-1·g-1。同时,与自然生草相比,多年生黑麦草+毛苕子、多年生黑麦草+草木樨和多年生黑麦草+白三叶提高了土壤细菌群落的丰富度和多样性,多年生黑麦草+毛苕子存在最多差异显著的细菌分支。综上,关中地区有机猕猴桃园种植多年生黑麦草+毛苕子在一定程度上有助于提高土壤有机质及养分含量,改善土壤微生态环境。
靳旭妹, 王莹莹, 刘崇义, 陈新义, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 生草对关中地区有机猕猴桃园土壤养分及细菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 53-63.
Xu-mei JIN, Ying-ying WANG, Chong-yi LIU, Xin-yi CHEN, Ming-xiu LONG, Shu-bin HE. Effects on soil nutrients and bacterial communities of different cover crops in an organic kiwifruit orchard in the Guanzhong region of China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 53-63.
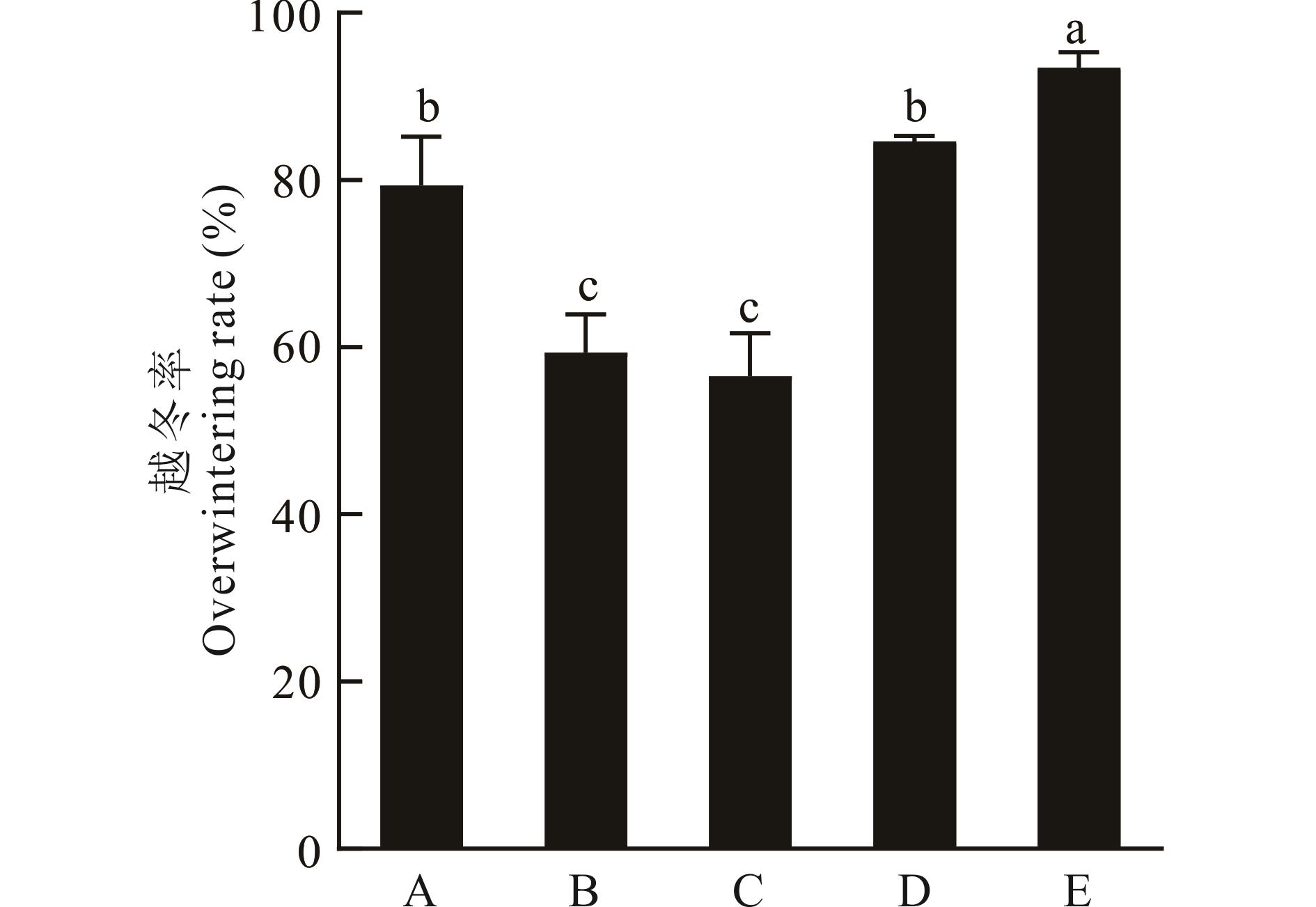
图 1 不同生草草种的越冬率A:多年生黑麦草L. perenne;B:毛苕子V. villosa;C:草木樨M. officinalis;D: 白三叶T. repens;E:鼠茅草V. myuros.不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著 (P<0.05) 。Different letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.1 Overwintering rate of different grass species
处理 Treatment | 杂草株数 Number of weeds (plant·m-2) | 地上部鲜草产量 Aboveground fresh yield (g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 197a | 742.01bc |
| Mode 1 | 108d | 1107.41a |
| Mode 2 | 129b | 705.57c |
| Mode 3 | 124c | 690.74c |
| Mode 4 | 49e | 885.18b |
表1 不同生草处理杂草发生情况和地上部鲜草产量
Table 1 Weed occurrence and aboveground fresh yield of different cover crops treatments
处理 Treatment | 杂草株数 Number of weeds (plant·m-2) | 地上部鲜草产量 Aboveground fresh yield (g·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 197a | 742.01bc |
| Mode 1 | 108d | 1107.41a |
| Mode 2 | 129b | 705.57c |
| Mode 3 | 124c | 690.74c |
| Mode 4 | 49e | 885.18b |
处理 Treatment | 土层 Soil layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 cm | 5~10 cm | 10~15 cm | 15~20 cm | |
| CK | 15.02±4.00a | 15.71±1.63a | 15.61±1.16a | 14.69±1.05a |
| Mode 1 | 18.39±3.74a | 16.90±1.94a | 16.64±1.22a | 16.58±1.33a |
| Mode 2 | 15.91±0.60a | 16.02±0.42a | 15.85±0.71a | 15.34±1.53a |
| Mode 3 | 16.35±0.58a | 16.18±1.33a | 15.64±0.75a | 15.73±0.87a |
| Mode 4 | 17.47±3.24a | 17.21±1.66a | 16.06±1.25a | 21.15±8.79a |
表2 不同生草处理对0~20 cm土层土壤含水量的影响
Table 2 Effect of different cover crops treatments on soil water content at a depth of 0-20 cm (%)
处理 Treatment | 土层 Soil layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 cm | 5~10 cm | 10~15 cm | 15~20 cm | |
| CK | 15.02±4.00a | 15.71±1.63a | 15.61±1.16a | 14.69±1.05a |
| Mode 1 | 18.39±3.74a | 16.90±1.94a | 16.64±1.22a | 16.58±1.33a |
| Mode 2 | 15.91±0.60a | 16.02±0.42a | 15.85±0.71a | 15.34±1.53a |
| Mode 3 | 16.35±0.58a | 16.18±1.33a | 15.64±0.75a | 15.73±0.87a |
| Mode 4 | 17.47±3.24a | 17.21±1.66a | 16.06±1.25a | 21.15±8.79a |
处理 Treatment | 酸碱度 pH | 有机质 Organic matter content (g·kg-1) | 微生物碳 Microbial biomass carbon(mg·kg-1) | 微生物氮 Microbial biomass nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 脲酶活性 Urease activity (mg·d-1·g-1) | 蔗糖酶活性 Sucrase activity (mg·d-1·g-1) | 碱性磷酸酶活性 Alkaline phosphatase activity (mg·d-1·g-1) | 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity (mL·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.08±0.03ab | 18.43±0.50d | 251.70±33.38a | 20.03±3.08b | 2.41±0.18c | 27.47±1.78d | 2.87±0.07b | 5.03±0.04b |
| Mode 1 | 8.09±0.02ab | 25.55±1.12a | 316.46±40.51a | 27.29±2.24a | 3.37±0.26a | 44.17±2.17a | 3.46±0.12a | 5.56±0.33ab |
| Mode 2 | 8.10±0.02a | 19.62±0.51cd | 263.40±48.33a | 23.04±2.29ab | 2.91±0.11b | 32.43±1.54c | 2.89±0.04b | 5.87±0.30a |
| Mode 3 | 8.09±0.06ab | 20.50±1.61c | 236.37±69.03a | 21.17±1.67b | 2.93±0.14b | 33.24±3.34bc | 2.97±0.01b | 5.48±0.41ab |
| Mode 4 | 8.01±0.05b | 22.72±0.90b | 237.53±44.16a | 21.60±2.53b | 3.20±0.07ab | 37.21±1.31b | 3.29±0.19a | 5.84±0.10a |
表3 不同生草处理对土壤养分与酶活性的影响
Table 3 Effects of different cover crops treatments on soil chemical and biological characteristics
处理 Treatment | 酸碱度 pH | 有机质 Organic matter content (g·kg-1) | 微生物碳 Microbial biomass carbon(mg·kg-1) | 微生物氮 Microbial biomass nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 脲酶活性 Urease activity (mg·d-1·g-1) | 蔗糖酶活性 Sucrase activity (mg·d-1·g-1) | 碱性磷酸酶活性 Alkaline phosphatase activity (mg·d-1·g-1) | 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity (mL·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.08±0.03ab | 18.43±0.50d | 251.70±33.38a | 20.03±3.08b | 2.41±0.18c | 27.47±1.78d | 2.87±0.07b | 5.03±0.04b |
| Mode 1 | 8.09±0.02ab | 25.55±1.12a | 316.46±40.51a | 27.29±2.24a | 3.37±0.26a | 44.17±2.17a | 3.46±0.12a | 5.56±0.33ab |
| Mode 2 | 8.10±0.02a | 19.62±0.51cd | 263.40±48.33a | 23.04±2.29ab | 2.91±0.11b | 32.43±1.54c | 2.89±0.04b | 5.87±0.30a |
| Mode 3 | 8.09±0.06ab | 20.50±1.61c | 236.37±69.03a | 21.17±1.67b | 2.93±0.14b | 33.24±3.34bc | 2.97±0.01b | 5.48±0.41ab |
| Mode 4 | 8.01±0.05b | 22.72±0.90b | 237.53±44.16a | 21.60±2.53b | 3.20±0.07ab | 37.21±1.31b | 3.29±0.19a | 5.84±0.10a |
处理 Treatment | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 特征序列数 Observed_otus | Goods_coverage指数 Goods_coverage index | Shannon指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2588.44±632.27a | 2420.33±535.99a | 0.98±0.01a | 10.38±0.29a |
| Mode 1 | 2870.95±282.03a | 2672.67±662.29a | 0.99±0.00a | 10.57±0.35a |
| Mode 2 | 2858.65±382.02a | 2688.33±258.54a | 0.98±0.01a | 10.54±0.18a |
| Mode 3 | 3040.59±771.79a | 2787.67±333.01a | 0.98±0.01a | 10.54±0.20a |
| Mode 4 | 2748.83±236.40a | 2557.67±202.23a | 0.99±0.01a | 10.38±0.21a |
表4 不同生草处理对土壤细菌Alpha多样性的影响
Table 4 Effect of different cover crops treatments on Alpha diversity of soil bacteria
处理 Treatment | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 特征序列数 Observed_otus | Goods_coverage指数 Goods_coverage index | Shannon指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2588.44±632.27a | 2420.33±535.99a | 0.98±0.01a | 10.38±0.29a |
| Mode 1 | 2870.95±282.03a | 2672.67±662.29a | 0.99±0.00a | 10.57±0.35a |
| Mode 2 | 2858.65±382.02a | 2688.33±258.54a | 0.98±0.01a | 10.54±0.18a |
| Mode 3 | 3040.59±771.79a | 2787.67±333.01a | 0.98±0.01a | 10.54±0.20a |
| Mode 4 | 2748.83±236.40a | 2557.67±202.23a | 0.99±0.01a | 10.38±0.21a |
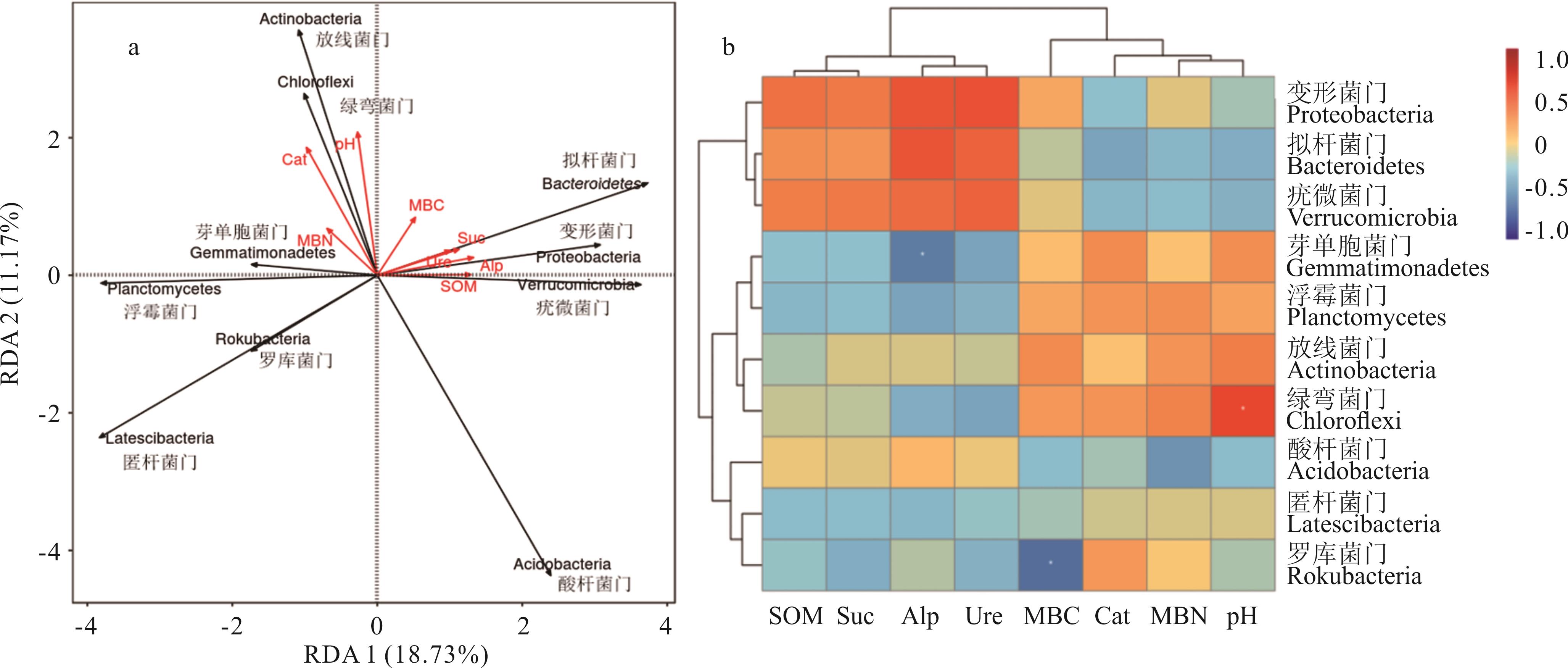
图6 土壤细菌群落结构与环境因子的关联性分析pH、SOM、MBC、MBN、Ure、Suc、Alp和Cat分别代表土壤pH、有机质、微生物碳、微生物氮、脲酶、蔗糖酶、碱性磷酸酶和过氧化氢酶活性,“*”代表显著相关(P<0.05)。pH,SOM,MBC,MBN,Ure,Suc,Alp and Cat represent soil pH, organic matter, microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen, urease, sucrase, alkaline phosphatase and catalase activity. “*” represents significant correlation (P<0.05).
Fig.6 Correlation analysis between soil bacterial community structure and environmental factors
| 1 | Seufert V, Ramankutty N, Foley J A. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature, 2012, 485(7397): 229. |
| 2 | Liu X M, Yu H J, Li Q, et al. Overview of organic agriculture development. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(4): 1303-1313. |
| 刘晓梅, 余宏军, 李强, 等. 有机农业发展概述. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(4): 1303-1313. | |
| 3 | Shen J B, Zhu Q C, Jiao X Q, et al. Agriculture green development: A model for China and the world. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(1): 5-13. |
| 沈建波, 朱启超, 焦晓强, 等. 农业绿色发展: 中国和世界的典范. 农业科学与工程前沿, 2020, 7(1): 5-13. | |
| 4 | Xie X J, Jin D Y, He P, et al. Research report on the development of kiwi fruit industry. China Rural Science and Technology, 2021(8): 56-59. |
| 谢学军, 金东艳, 何鹏, 等. 猕猴桃产业发展情况调研报告. 中国农村科技, 2021(8): 56-59. | |
| 5 | Jing Z B, Lei Y S, Li Y W, et al. Biotechnology and kiwifruit breeding in China. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2015, 31(7): 1-10. |
| 井赵斌, 雷玉山, 李永武, 等. 生物技术与我国猕猴桃育种. 生物技术通报, 2015, 31(7): 1-10. | |
| 6 | Tong Y A, Chen L L, Gao Y M, et al. Effect of fertilization on kiwifruit yield and quality. Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2011, 39(10): 171-176. |
| 同延安, 陈黎岭, 高义民, 等. 施肥对猕猴桃产量和品质的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报, 2011, 39(10): 171-176. | |
| 7 | Gu Y R, Zhang H L, Hu Y H. Effect of natural grasses cover on soil properties and yield and quality of peach. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(12): 103-107. |
| 谷艳蓉, 张海伶, 胡艳红. 果园自然生草覆盖对土壤理化性状及大桃产量和品质的影响. 草业科学, 2009, 26(12): 103-107. | |
| 8 | Yang M, Wang Y Y, Lu J Y, et al. Advances in typical patterns to include grass species in orchards and mechanisms to regulate resources within the orchard-grass system in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(9): 189-199. |
| 杨梅, 王亚亚, 陆姣云, 等. 典型果园生草模式及果草系统资源调控研究进展. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 189-199. | |
| 9 | Ma G H, Zeng M, Wang Y Y, et al. Research progress on orchard sod culture. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2005, 21(7): 273-277. |
| 马国辉, 曾明, 王羽玥, 等. 果园生草制研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(7): 273-277. | |
| 10 | Peck G M, Merwin I A, Thies J E, et al. Soil properties change during the transition to integrated and organic apple production in a New York orchard. Applied Soil Ecology, 2011, 48(1): 18-30. |
| 11 | Wang P, Wang Y, Wu Q S. Effects of soil tillage and planting grass on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal propagules and soil properties in citrus orchards in southeast China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2016, 155: 54-61. |
| 12 | Jiang L L, Gong Q T, Wu H B, et al. Effects of different grasses cultivation on apple orchard soil microbial community. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(10): 3482-3490. |
| 姜莉莉, 宫庆涛, 武海斌, 等. 不同生草处理对苹果园土壤微生物群落的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(10): 3482-3490. | |
| 13 | Wang Y J, Liu L, Luo Y, et al. Mulching practices alter the bacterial-fungal community and network in favor of soil quality in a semiarid orchard system. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 725: 138527. |
| 14 | Zheng J Y, Zhao J S, Shi Z H, et al. Soil aggregates are key factors that regulate erosion-related carbon loss in citrus orchards of southern China: Bare land vs. grass-covered land. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2021, 309: 107254. |
| 15 | Li C, Wang X L, Liu S, et al. Effects of natural herbage on soil-nutrients, enzyme activities and microorganisms in vineyard of Helan Mountain’s Eastern Foothill. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(3): 559-565. |
| 李超, 王晓玲, 刘思, 等. 贺兰山东麓葡萄园自然生草对土壤养分酶活性及微生物的影响. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(3): 559-565. | |
| 16 | Liu F T, Zhang L S, Li X W, et al. Effects of inter-row planting grasses on soil organic carbon fractions and soil microbial community of apple orchard in Weibei dryland. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(2): 355-363. |
| 刘富庭, 张林森, 李雪薇, 等. 生草对渭北旱地苹果园土壤有机碳组分及微生物的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(2):355-363. | |
| 17 | Wang G W, Song X. Response of integrated fertility of apricot orchard soil to artificial grass pattern and its environmental interpretation in the eastern Gansu Province of loess plateau. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2018, 36(4): 29-39. |
| 王根旺, 宋曦. 陇东黄土高原地区杏园土壤综合肥力对人工生草模式的响应及其环境解释. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(4): 29-39. | |
| 18 | Jiao R A, Jiao J, Li C Z. The effect of sod-culture on orchard soil properties and the floral physiology of olives. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(7): 133-144. |
| 焦润安, 焦健, 李朝周. 生草对油橄榄园土壤性质和油橄榄成花生理的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 133-144. | |
| 19 | Qian Y L, Liang Z T, Cao Q, et al. Effects of grass-planting on soil bacterial community composition of apple orchard in Longdong arid region. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(10): 3010-3017. |
| 钱雅丽, 梁志婷, 曹铨, 等. 陇东旱作果园生草对土壤细菌群落组成的影响. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(10): 3010-3017. | |
| 20 | Qian Y L, Wang X Z, Lai X F, et al. Effects of perennial forage on characteristics of the soil fungal community in an apple orchard. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(11): 124-132. |
| 钱雅丽, 王先之, 来兴发, 等. 多年生牧草种植对苹果园土壤真菌群落特征的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 124-132. | |
| 21 | Arentoft B W, Ali A, Streibig J C, et al. A new method to evaluate the weed-suppressing effect of mulches: A comparison between spruce bark and cocoa husk mulches. Weed Research, 2013, 53(3): 169-175. |
| 22 | Neilsen G, Forge T, Angers D, et al. Suitable orchard floor management strategies in organic apple orchards that augment soil organic matter and maintain tree performance. Plant and Soil, 2014, 378(1/2): 325-335. |
| 23 | Andersen L, Kühn B F, Bertelsen M, et al. Alternatives to herbicides in an apple orchard, effects on yield, earthworms and plant diversity. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 2013, 172: 1-5. |
| 24 | Wang Y T, Ji X H, Zhang Y M, et al. Effects of self-sown grass on soil physical properties and microbial diversity of pear orchards in yellow river delta. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(16): 5374-5384. |
| 王艳廷, 冀晓昊, 张艳敏, 等. 自然生草对黄河三角洲梨园土壤物理性状及微生物多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(16): 5374-5384. | |
| 25 | Fu X Q, Liu J R, Huang W X. Effects of natural grass on soil microbiology, nutrient and fruit quality of Nanfeng tangerine yard. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. |
| 付学琴, 刘琚珥, 黄文新. 南丰蜜橘园自然生草对土壤微生物和养分及果实品质的影响. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. | |
| 26 | Li C J, Peng H, Xie Y H, et al. Mulch grasses planting and management techniques in orchards of southern China based on different utilization purposes. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2019(3): 63-67, 72. |
| 李尝君, 彭华, 谢运河, 等. 基于不同用途的南方果园生草栽培及管理利用技术. 湖南农业科学, 2019(3): 63-67, 72. | |
| 27 | Zhu X B, Pan L, Wang H L, et al. Analysis of the ecological effects of grass-growing in kiwi fruit orchards in Shiyan, China. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(3): 381-388. |
| 朱先波, 潘亮, 王华玲, 等. 十堰猕猴桃果园生草生态效应的分析. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(3): 381-388. | |
| 28 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 30-34. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 30-34. | |
| 29 | Brookes P C, Landman A, Pruden G, et al. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1985, 17(6): 837-842. |
| 30 | Song J G, Wang J, Lin S. Determination of soil microbial biomass nitrogen by continuous flow analytical system. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 1999, 5(3): 282-287. |
| 宋建国, 王晶, 林杉. 用连续流动分析仪测定土壤微生物态氮的方法研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1999, 5(3): 282-287. | |
| 31 | Guan S Y. Soil enzyme and its research method. Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1986. |
| 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 32 | Logue Jürg B, Stedmon Colin A, Kellerman Anne M, et al. Experimental insights into the importance of aquatic bacterial community composition to the degradation of dissolved organic matter. The ISME Journal, 2016, 10(3): 533-545. |
| 33 | Wen M Z, Guo J X. Influences of litter on soil organisms in Northeastern Leymus chinensis grassland of China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2008, 30(5): 7-12. |
| 温明章, 郭继勋. 不同凋落物量对东北羊草草原土壤生物的影响. 中国草地学报, 2008, 30(5): 7-12. | |
| 34 | Shi B, Gao W, Jin G. Effects on rhizospheric and heterotrophic respiration of conversion from primary forest to secondary forest and plantations in northeast China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2015, 66: 11-18. |
| 35 | Li H J. Studies on soil respiration and its relations to environmental factors in different ecosystems. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2008. |
| 李洪建. 不同生态系统土壤呼吸与环境因子的关系研究. 太原: 山西大学, 2008. | |
| 36 | Yang L, Mao Y F, Hu Y L, et al. Effects of orchard grass on soil fertility and apple tree nutrition. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. |
| 杨露, 毛云飞, 胡艳丽, 等. 生草改善果园土壤肥力和苹果树体营养的效果. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. | |
| 37 | Yang Y H, Zhang S, Wang S, et al. Yield and nutrient concentration in common green manure crops and assessment of potential for nitrogen replacement in different regions of China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. |
| 杨叶华, 张松, 王帅, 等. 中国不同区域常见绿肥产量和养分含量特征及替代氮肥潜力评估. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. | |
| 38 | Xiao L T, Yang H L, Huang W X, et al. Effects of grass cultivation on soil microbial community structure and functional characteristics in Nanfeng tangerine orchard. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences. 2022, 36(1): 190-200. |
| 肖力婷, 杨慧林, 黄文新, 等. 生草栽培对南丰蜜橘园土壤微生物群落结构与功能特征的影响. 核农学报, 2022, 36(1): 190-200. | |
| 39 | Zhou L K. Soil enzymology. Beijing: Science Press, 1987. |
| 周礼恺. 土壤酶学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987. | |
| 40 | Compant S, Reiter B, Sessitsch A, et al. Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by plant growth-promoting bacterium Burkholderia sp. strain PsJN. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(3): 1685-1693. |
| 41 | Chen X S, Zhang R J, Wang Y T, et al. Effects of growing Hairy vetch (Vicia villosa) on the soil nutrient, enzyme activities and microorganisms in apple orchard. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2016, 43(12): 2325-2334. |
| 陈学森, 张瑞洁, 王艳廷, 等. 苹果园种植长柔毛野豌豆结合自然生草对土壤综合肥力的影响. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(12): 2325-2334. | |
| 42 | Lipson D A, Schmidt S K. Seasonal changes in an alpine soil bacterial community in the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(5): 2867-2879. |
| 43 | Wang F W, Wang X B, Li J C, et al. Effects of fertilization and straw incorporation on bacterial communities in lime concretion black soil. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(10): 1302-1311. |
| 王伏伟, 王晓波, 李金才, 等. 施肥及秸秆还田对砂姜黑土细菌群落的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(10): 1302-1311. | |
| 44 | Naether A, Foesel B U, Naegele V, et al. Environmental factors affect acidobacterial communities below the subgroup level in grassland and forest soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(20): 7398. |
| 45 | Dong H. Screening and characteristics of available grass species in orchard in Shanxi. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 董慧. 山西果园可利用草种的筛选及其特性研究. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2016. | |
| 46 | Chen H S, Liu S P, Liang G Q, et al. Effects of three cropping patterns on bacterial community structure and diversity in rhizosphere of broccoli. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(6): 1457-1465. |
| 陈海生, 刘守平, 梁国钱, 等. 3种西兰花种植方式对根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响研究. 核农学报, 2021, 35(6): 1457-1465. |
| [1] | 彭艳, 孙晶远, 马素洁, 王向涛, 魏学红, 孙磊. 藏北不同退化阶段高寒草甸植物群落特征与土壤养分特性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 49-60. |
| [2] | 潘占东, 马倩倩, 陈晓龙, 蔡立群, 蔡雪梅, 董博, 武均, 张仁陟. 添加生物质炭对黄土高原旱作农田土壤养分、腐殖质及其组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 14-24. |
| [3] | 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| [4] | 李文, 魏廷虎, 永措巴占, 才仁塔次, 周玉海, 张雁平, 李文浩, 郭卫兴. 混播比例对三江源人工草地植被和土壤养分特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 39-48. |
| [5] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [6] | 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 赵艳丽, 张裕年, 肖斌, 付贵全, 杜娟. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [7] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 王宏生. 围封和防除狼毒对狼毒斑块土壤理化性质和微生物量影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 63-72. |
| [8] | 黄玙璠, 舒英格, 肖盛杨, 陈梦军. 喀斯特山区不同草地土壤养分与酶活性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 93-104. |
| [9] | 魏鹏, 安沙舟, 董乙强, 孙宗玖, 别尔达吾列提·希哈依, 李超. 基于高通量测序的准噶尔盆地荒漠土壤细菌多样性及群落结构特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. |
| [10] | 王婷, 张永超, 赵之重. 青藏高原退化高寒湿地植被群落结构和土壤养分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 9-18. |
| [11] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [12] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [13] | 柳书俊, 姚新转, 赵德刚, 吕立堂. 湄潭茶园土壤养分特征及肥力质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 33-45. |
| [14] | 施颖, 胡廷花, 高红娟, 罗巧玉, 于应文. 两种放牧模式下高寒草甸群落植被构成及稳定性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 1-10. |
| [15] | 帅林林, 周青平, 陈有军, 苟小林, 周蓉. 高寒半湿润沙地草本修复期土壤微生物变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 11-22. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||