

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 71-84.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022251
安晓霞1( ), 张盈盈1, 马春晖1, 李曼2(
), 张盈盈1, 马春晖1, 李曼2( ), 张前兵1(
), 张前兵1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-15
修回日期:2022-07-28
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-04-21
通讯作者:
李曼,张前兵
作者简介:liman570510@126.com基金资助:
Xiao-xia AN1( ), Ying-ying ZHANG1, Chun-hui MA1, Man LI2(
), Ying-ying ZHANG1, Chun-hui MA1, Man LI2( ), Qian-bing ZHANG1(
), Qian-bing ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2022-05-15
Revised:2022-07-28
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
Man LI,Qian-bing ZHANG
摘要:
为探讨施磷及接种丛枝菌根真菌对苜蓿干物质产量、磷含量以及土壤碱性磷酸酶(AKP)活性的影响,分析接菌及施磷条件下紫花苜蓿土壤速效磷、全磷与干物质产量之间的关系,进而阐明接菌及施磷对紫花苜蓿干物质产量及各指标之间关系的影响机制。本试验采用双因素完全随机设计,设置4个施菌水平:单接种摩西管柄囊霉(Fm,T1)、幼套球囊霉(Ge,T2)、双接菌(Fm×Ge,T3)及未接菌处理(CK,T0),在施菌条件下设置4个施磷水平,分别为:施P2O5 0(P0)、50(P1)、100(P2)、150(P3) mg·kg-1,菌磷互作共16个处理,每个处理10次重复。结果表明:1)相同接菌处理,苜蓿的干物质产量、植株叶片、茎及根部磷含量、土壤pH值及碱性磷酸酶活性均随施磷量的增加呈先增加后降低的趋势,均在P2处理达到最大值,且施磷处理显著大于未施磷处理(P<0.05)。根际和非根际土壤速效磷和全磷含量均随施磷量的增加而逐渐增加,苜蓿的磷肥农学效率随施磷量的增加呈逐渐降低的趋势。2)相同施磷处理,单接菌及双接菌处理苜蓿的干物质产量、植株叶片、茎及根部磷含量、根际和非根际土壤速效磷、全磷含量、磷素利用效率及土壤中碱性磷酸酶活性均显著大于未接菌处理(P<0.05),土壤全磷及速效磷含量均在T3处理达到最大值。双接菌处理下土壤的pH值显著小于未接菌处理(P<0.05),且在T3处理达到最小值。因此,当施磷(P2O5)量为100 mg·kg-1时,混合接种两种丛枝菌根真菌可以有效促进苜蓿植株根系对土壤中速效磷的吸收,提高磷素利用效率,进而促进苜蓿干物质产量的形成。
安晓霞, 张盈盈, 马春晖, 李曼, 张前兵. 施磷与接种丛枝菌根真菌对苜蓿产量和磷素利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 71-84.
Xiao-xia AN, Ying-ying ZHANG, Chun-hui MA, Man LI, Qian-bing ZHANG. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on alfalfa yield and phosphorus use efficiency[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 71-84.
容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 碱解氮 Alkaline-nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available-potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.47 | 71.8 | 24.1 | 18.3 | 0.23 | 135.5 |
表1 试验地土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of test soil
容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 碱解氮 Alkaline-nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available-potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.47 | 71.8 | 24.1 | 18.3 | 0.23 | 135.5 |
编号 Number | 处理 Treatments | NH4H2PO4 (mg·pot-1) | CN2H4O (mg·pot-1) | 摩西球囊霉 F. mosseae (g·pot-1) | 幼套球囊酶 G. etunicatum (g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T0P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | T0P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | T0P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | T0P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | T1P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 10 | 0 |
| 6 | T1P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 10 | 0 |
| 7 | T1P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 10 | 0 |
| 8 | T1P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 10 | 0 |
| 9 | T2P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 0 | 10 |
| 10 | T2P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 0 | 10 |
| 11 | T2P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 0 | 10 |
| 12 | T2P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 0 | 10 |
| 13 | T3P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 5 | 5 |
| 14 | T3P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 | T3P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 5 | 5 |
| 16 | T3P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 5 | 5 |
表2 试验设计
Table 2 Experimental design
编号 Number | 处理 Treatments | NH4H2PO4 (mg·pot-1) | CN2H4O (mg·pot-1) | 摩西球囊霉 F. mosseae (g·pot-1) | 幼套球囊酶 G. etunicatum (g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T0P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | T0P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | T0P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | T0P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | T1P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 10 | 0 |
| 6 | T1P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 10 | 0 |
| 7 | T1P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 10 | 0 |
| 8 | T1P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 10 | 0 |
| 9 | T2P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 0 | 10 |
| 10 | T2P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 0 | 10 |
| 11 | T2P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 0 | 10 |
| 12 | T2P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 0 | 10 |
| 13 | T3P0 | 0.0 | 105.3 | 5 | 5 |
| 14 | T3P1 | 35.1 | 70.2 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 | T3P2 | 70.2 | 35.1 | 5 | 5 |
| 16 | T3P3 | 105.3 | 0.0 | 5 | 5 |
处理 Treatment | 第1茬 First cut | 第2茬 Second cut | 第3茬 Third cut |
|---|---|---|---|
| T0P0 | 14.03±0.95Cc | 16.22±0.70Bc | 11.63±0.92Db |
| T0P1 | 21.73±0.60Ba | 16.50±1.22Cc | 14.57±0.51Ca |
| T0P2 | 18.73±0.81Db | 21.67±0.51Ca | 14.47±0.55Ca |
| T0P3 | 21.57±0.61Ba | 18.13±0.90Bb | 13.43±0.55Ca |
| T1P0 | 17.73±0.85ABc | 17.05±0.78Bd | 15.23±0.40Bc |
| T1P1 | 22.95±0.84Bb | 21.67±0.51ABb | 15.78±0.62Bc |
| T1P2 | 25.90±0.80Ba | 23.85±0.65Ba | 18.65±0.56ABa |
| T1P3 | 23.07±0.87Ab | 19.30±0.69ABc | 17.35±0.65ABb |
| T2P0 | 16.63±0.61Bc | 16.89±0.64Bd | 13.93±0.85Cd |
| T2P1 | 21.80±0.50Bb | 20.50±1.06Bb | 15.03±0.90BCc |
| T2P2 | 23.43±0.61Ca | 21.90±0.72Ca | 18.10±0.80Ba |
| T2P3 | 22.57±0.76ABab | 18.17±0.76Bc | 16.32±0.51Bb |
| T3P0 | 19.03±0.70Ac | 19.00±0.66Ac | 16.77±0.58Ab |
| T3P1 | 24.38±0.94Ab | 22.47±0.55Ab | 17.30±0.72Ab |
| T3P2 | 27.23±0.83Aa | 25.87±0.68Aa | 19.45±0.56Aa |
| T3P3 | 23.70±0.79Ab | 20.13±0.75Ac | 17.58±0.45Ab |
| Fungus treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** |
| Phosphorus treatment (P) | ** | ** | ** |
| Fungus phosphorus interaction (T×P) | ** | ** | ** |
表3 不同处理下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量
Table 3 Dry matter yield of alfalfa under different treatments (g·pot-1)
处理 Treatment | 第1茬 First cut | 第2茬 Second cut | 第3茬 Third cut |
|---|---|---|---|
| T0P0 | 14.03±0.95Cc | 16.22±0.70Bc | 11.63±0.92Db |
| T0P1 | 21.73±0.60Ba | 16.50±1.22Cc | 14.57±0.51Ca |
| T0P2 | 18.73±0.81Db | 21.67±0.51Ca | 14.47±0.55Ca |
| T0P3 | 21.57±0.61Ba | 18.13±0.90Bb | 13.43±0.55Ca |
| T1P0 | 17.73±0.85ABc | 17.05±0.78Bd | 15.23±0.40Bc |
| T1P1 | 22.95±0.84Bb | 21.67±0.51ABb | 15.78±0.62Bc |
| T1P2 | 25.90±0.80Ba | 23.85±0.65Ba | 18.65±0.56ABa |
| T1P3 | 23.07±0.87Ab | 19.30±0.69ABc | 17.35±0.65ABb |
| T2P0 | 16.63±0.61Bc | 16.89±0.64Bd | 13.93±0.85Cd |
| T2P1 | 21.80±0.50Bb | 20.50±1.06Bb | 15.03±0.90BCc |
| T2P2 | 23.43±0.61Ca | 21.90±0.72Ca | 18.10±0.80Ba |
| T2P3 | 22.57±0.76ABab | 18.17±0.76Bc | 16.32±0.51Bb |
| T3P0 | 19.03±0.70Ac | 19.00±0.66Ac | 16.77±0.58Ab |
| T3P1 | 24.38±0.94Ab | 22.47±0.55Ab | 17.30±0.72Ab |
| T3P2 | 27.23±0.83Aa | 25.87±0.68Aa | 19.45±0.56Aa |
| T3P3 | 23.70±0.79Ab | 20.13±0.75Ac | 17.58±0.45Ab |
| Fungus treatment (T) | ** | ** | ** |
| Phosphorus treatment (P) | ** | ** | ** |
| Fungus phosphorus interaction (T×P) | ** | ** | ** |
处理 Treatment | 苜蓿叶片磷含量 Phosphorus content in alfalfa leaves (mg·kg-1) | 苜蓿茎磷含量 Phosphorus content in alfalfa stem (mg·kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 0.203±0.008Ba | 0.252±0.007Cb | 0.219±0.006Bb | 0.155±0.003Abc | 0.146±0.009Bc | 0.111±0.003Bb |
| T0P1 | 0.210±0.005Ba | 0.270±0.008Db | 0.284±0.014Ba | 0.175±0.002Ba | 0.182±0.003Cb | 0.141±0.013BCa |
| T0P2 | 0.207±0.008Da | 0.388±0.007Ba | 0.277±0.002Ba | 0.167±0.008Cab | 0.216±0.010Ba | 0.151±0.003Ca |
| T0P3 | 0.204±0.009Ca | 0.383±0.018Ba | 0.233±0.008Cb | 0.150±0.007Cc | 0.207±0.001Ba | 0.143±0.003Ca |
| T1P0 | 0.216±0.002ABb | 0.297±0.001Bc | 0.233±0.006Bb | 0.161±0.008Ac | 0.184±0.003Ac | 0.119±0.005Bc |
| T1P1 | 0.254±0.009Aa | 0.350±0.006Cb | 0.240±0.007Cb | 0.169±0.008Bbc | 0.216±0.004ABb | 0.149±0.005Bb |
| T1P2 | 0.232±0.002Cb | 0.378±0.015Ba | 0.288±0.007Ba | 0.193±0.010ABa | 0.237±0.006Aa | 0.190±0.007Ba |
| T1P3 | 0.226±0.011Bb | 0.377±0.011Ba | 0.281±0.006Ba | 0.179±0.005Bab | 0.219±0.006ABb | 0.186±0.005Aa |
| T2P0 | 0.209±0.004ABb | 0.286±0.013Bc | 0.223±0.009Bc | 0.153±0.007Ab | 0.196±0.001Ac | 0.114±0.002Bc |
| T2P1 | 0.245±0.010Aa | 0.374±0.019Bb | 0.249±0.004Cb | 0.176±0.009Ba | 0.208±0.008Bbc | 0.134±0.003Cb |
| T2P2 | 0.255±0.002Ba | 0.389±0.001ABa | 0.271±0.011Ba | 0.191±0.004Ba | 0.232±0.009Aa | 0.156±0.004Ca |
| T2P3 | 0.254±0.008Aa | 0.368±0.016Bb | 0.266±0.011Ba | 0.178±0.009Ba | 0.211±0.002Bb | 0.152±0.008Ca |
| T3P0 | 0.225±0.009Ab | 0.328±0.003Ab | 0.277±0.007Ac | 0.164±0.005Ac | 0.199±0.004Ac | 0.146±0.003Ac |
| T3P1 | 0.241±0.008Ab | 0.391±0.016Aa | 0.304±0.005Ab | 0.197±0.004Ab | 0.228±0.003Aab | 0.167±0.007Ab |
| T3P2 | 0.292±0.006Aa | 0.399±0.001Aa | 0.333±0.008Aa | 0.220±0.010Aab | 0.216±0.007Bb | 0.207±0.001Aa |
| T3P3 | 0.231±0.007Bb | 0.389±0.014Aa | 0.325±0.006Aa | 0.207±0.007Aa | 0.230±0.007Aa | 0.172±0.006Bb |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
处理 Treatment | 苜蓿根部磷含量 Phosphorus content in alfalfa roots (mg·kg-1) | 磷肥农学效率 Agronomic efficiency of phosphate fertilizer (%) | ||||
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | ||||
| T0P0 | 0.173±0.006Bc | 0.182±0.003Cc | 0.144±0.003Cb | — | ||
| T0P1 | 0.224±0.006Aa | 0.216±0.008Cb | 0.178±0.001Ba | 24.26±1.20Aa | ||
| T0P2 | 0.198±0.006Cb | 0.245±0.006Ca | 0.170±0.004Da | 14.43±0.70Bb | ||
| T0P3 | 0.190±0.002Db | 0.231±0.010Ca | 0.172±0.006Ca | 8.33±0.41Ac | ||
| T1P0 | 0.201±0.008Ac | 0.217±0.006Bc | 0.151±0.003Cd | — | ||
| T1P1 | 0.216±0.004Ab | 0.265±0.009ABa | 0.170±0.003Bc | 23.07±1.67Aa | ||
| T1P2 | 0.240±0.009ABa | 0.271±0.001Ba | 0.181±0.004Cb | 20.43±1.08Aa | ||
| T1P3 | 0.222±0.004Bb | 0.246±0.004Bb | 0.196±0.003Ba | 7.19±0.39Ab | ||
| T2P0 | 0.204±0.004Ab | 0.212±0.005Bb | 0.162±0.004Bc | — | ||
| T2P1 | 0.214±0.006Ab | 0.253±0.005Ba | 0.175±0.004Bb | 21.96±1.13Aa | ||
| T2P2 | 0.234±0.006Ba | 0.267±0.010Ba | 0.199±0.007Ba | 17.76±0.85ABb | ||
| T2P3 | 0.205±0.004Cb | 0.255±0.007Ba | 0.180±0.006Cb | 7.11±0.37Ac | ||
| T3P0 | 0.212±0.007Ac | 0.243±0.004Ac | 0.188±0.003Ac | — | ||
| T3P1 | 0.227±0.004Ab | 0.273±0.006Ab | 0.215±0.008Ab | 20.78±1.07Aa | ||
| T3P2 | 0.253±0.006Aa | 0.304±0.004Aa | 0.233±0.003Aa | 19.72±0.77Aa | ||
| T3P3 | 0.241±0.012Aa | 0.295±0.013Aa | 0.219±0.006Ab | 4.90±0.31Ab | ||
| T | ** | ** | ** | NS | ||
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| T×P | ** | NS | ** | * | ||
表4 不同处理下苜蓿不同部位磷含量及磷肥农学效率
Table 4 Phosphorus content in different parts of alfalfa and agronomic efficiency of phosphate fertilizer under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 苜蓿叶片磷含量 Phosphorus content in alfalfa leaves (mg·kg-1) | 苜蓿茎磷含量 Phosphorus content in alfalfa stem (mg·kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 0.203±0.008Ba | 0.252±0.007Cb | 0.219±0.006Bb | 0.155±0.003Abc | 0.146±0.009Bc | 0.111±0.003Bb |
| T0P1 | 0.210±0.005Ba | 0.270±0.008Db | 0.284±0.014Ba | 0.175±0.002Ba | 0.182±0.003Cb | 0.141±0.013BCa |
| T0P2 | 0.207±0.008Da | 0.388±0.007Ba | 0.277±0.002Ba | 0.167±0.008Cab | 0.216±0.010Ba | 0.151±0.003Ca |
| T0P3 | 0.204±0.009Ca | 0.383±0.018Ba | 0.233±0.008Cb | 0.150±0.007Cc | 0.207±0.001Ba | 0.143±0.003Ca |
| T1P0 | 0.216±0.002ABb | 0.297±0.001Bc | 0.233±0.006Bb | 0.161±0.008Ac | 0.184±0.003Ac | 0.119±0.005Bc |
| T1P1 | 0.254±0.009Aa | 0.350±0.006Cb | 0.240±0.007Cb | 0.169±0.008Bbc | 0.216±0.004ABb | 0.149±0.005Bb |
| T1P2 | 0.232±0.002Cb | 0.378±0.015Ba | 0.288±0.007Ba | 0.193±0.010ABa | 0.237±0.006Aa | 0.190±0.007Ba |
| T1P3 | 0.226±0.011Bb | 0.377±0.011Ba | 0.281±0.006Ba | 0.179±0.005Bab | 0.219±0.006ABb | 0.186±0.005Aa |
| T2P0 | 0.209±0.004ABb | 0.286±0.013Bc | 0.223±0.009Bc | 0.153±0.007Ab | 0.196±0.001Ac | 0.114±0.002Bc |
| T2P1 | 0.245±0.010Aa | 0.374±0.019Bb | 0.249±0.004Cb | 0.176±0.009Ba | 0.208±0.008Bbc | 0.134±0.003Cb |
| T2P2 | 0.255±0.002Ba | 0.389±0.001ABa | 0.271±0.011Ba | 0.191±0.004Ba | 0.232±0.009Aa | 0.156±0.004Ca |
| T2P3 | 0.254±0.008Aa | 0.368±0.016Bb | 0.266±0.011Ba | 0.178±0.009Ba | 0.211±0.002Bb | 0.152±0.008Ca |
| T3P0 | 0.225±0.009Ab | 0.328±0.003Ab | 0.277±0.007Ac | 0.164±0.005Ac | 0.199±0.004Ac | 0.146±0.003Ac |
| T3P1 | 0.241±0.008Ab | 0.391±0.016Aa | 0.304±0.005Ab | 0.197±0.004Ab | 0.228±0.003Aab | 0.167±0.007Ab |
| T3P2 | 0.292±0.006Aa | 0.399±0.001Aa | 0.333±0.008Aa | 0.220±0.010Aab | 0.216±0.007Bb | 0.207±0.001Aa |
| T3P3 | 0.231±0.007Bb | 0.389±0.014Aa | 0.325±0.006Aa | 0.207±0.007Aa | 0.230±0.007Aa | 0.172±0.006Bb |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
处理 Treatment | 苜蓿根部磷含量 Phosphorus content in alfalfa roots (mg·kg-1) | 磷肥农学效率 Agronomic efficiency of phosphate fertilizer (%) | ||||
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | ||||
| T0P0 | 0.173±0.006Bc | 0.182±0.003Cc | 0.144±0.003Cb | — | ||
| T0P1 | 0.224±0.006Aa | 0.216±0.008Cb | 0.178±0.001Ba | 24.26±1.20Aa | ||
| T0P2 | 0.198±0.006Cb | 0.245±0.006Ca | 0.170±0.004Da | 14.43±0.70Bb | ||
| T0P3 | 0.190±0.002Db | 0.231±0.010Ca | 0.172±0.006Ca | 8.33±0.41Ac | ||
| T1P0 | 0.201±0.008Ac | 0.217±0.006Bc | 0.151±0.003Cd | — | ||
| T1P1 | 0.216±0.004Ab | 0.265±0.009ABa | 0.170±0.003Bc | 23.07±1.67Aa | ||
| T1P2 | 0.240±0.009ABa | 0.271±0.001Ba | 0.181±0.004Cb | 20.43±1.08Aa | ||
| T1P3 | 0.222±0.004Bb | 0.246±0.004Bb | 0.196±0.003Ba | 7.19±0.39Ab | ||
| T2P0 | 0.204±0.004Ab | 0.212±0.005Bb | 0.162±0.004Bc | — | ||
| T2P1 | 0.214±0.006Ab | 0.253±0.005Ba | 0.175±0.004Bb | 21.96±1.13Aa | ||
| T2P2 | 0.234±0.006Ba | 0.267±0.010Ba | 0.199±0.007Ba | 17.76±0.85ABb | ||
| T2P3 | 0.205±0.004Cb | 0.255±0.007Ba | 0.180±0.006Cb | 7.11±0.37Ac | ||
| T3P0 | 0.212±0.007Ac | 0.243±0.004Ac | 0.188±0.003Ac | — | ||
| T3P1 | 0.227±0.004Ab | 0.273±0.006Ab | 0.215±0.008Ab | 20.78±1.07Aa | ||
| T3P2 | 0.253±0.006Aa | 0.304±0.004Aa | 0.233±0.003Aa | 19.72±0.77Aa | ||
| T3P3 | 0.241±0.012Aa | 0.295±0.013Aa | 0.219±0.006Ab | 4.90±0.31Ab | ||
| T | ** | ** | ** | NS | ||
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| T×P | ** | NS | ** | * | ||
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤速效磷含量 Available phosphorus content in rhizosphere soil (mg·kg-1) | 非根际土壤速效磷含量 Available phosphorus content in non-rhizosphere soil (mg·kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 6.09±0.26Cc | 8.15±0.38Cd | 9.41±0.39Ac | 10.43±0.45Cc | 10.08±0.19Ac | 8.24±0.25Bc |
| T0P1 | 13.54±0.27Bb | 11.38±0.37Bc | 10.17±0.44Cbc | 14.69±0.63Bb | 11.29±0.50Cbc | 10.08±0.45Cb |
| T0P2 | 14.52±0.52Cb | 13.12±0.57Cb | 11.11±0.26Cab | 16.90±0.56Ba | 12.14±0.58Db | 11.29±0.51Ca |
| T0P3 | 18.79±0.58Ca | 14.34±0.51Ca | 12.10±0.64Da | 17.93±0.64Ba | 14.29±0.44Da | 12.01±0.25Ca |
| T1P0 | 9.14±0.26Bc | 9.41±0.26Bc | 9.90±0.32Ad | 12.90±0.51Bc | 11.02±0.26Ad | 9.81±0.45Ad |
| T1P1 | 9.76±0.38Cc | 11.91±0.26Bb | 14.57±0.44Bc | 13.35±0.37Cbc | 16.55±0.70Bc | 14.75±0.58Bc |
| T1P2 | 13.27±0.63Cb | 12.73±0.38Cb | 17.57±0.77Bb | 14.26±0.64Db | 18.65±0.53Bb | 17.75±0.77Bb |
| T1P3 | 21.26±0.90Ba | 18.07±0.33Ba | 22.23±0.51Ba | 17.29±0.50Ba | 21.08±0.75Ba | 21.26±0.37Ba |
| T2P0 | 6.94±0.32Cc | 9.18±0.32Bd | 9.72±0.45Ad | 12.14±0.32Bd | 10.48±0.38Ab | 9.40±0.39Ad |
| T2P1 | 13.53±0.39Bb | 10.43±0.44Cc | 14.03±0.58Bc | 14.15±0.63BCc | 11.42±0.57Cb | 13.85±0.56Bc |
| T2P2 | 19.18±0.64Ba | 16.17±0.33Bb | 17.48±0.76Bb | 15.32±0.64Cb | 16.63±0.82Ca | 16.94±0.64Bb |
| T2P3 | 20.22±0.31Ba | 19.63±0.38Aa | 20.39±0.69Ca | 17.22±0.51Ba | 17.58±0.77Ca | 20.13±0.70Ba |
| T3P0 | 13.13±0.45Ad | 11.46±0.13Ad | 10.21±0.25Ad | 15.47±0.69Ac | 11.29±0.38Ac | 10.43±0.44Ad |
| T3P1 | 22.15±0.91Ac | 12.94±0.32Ac | 19.18±0.64Ac | 17.49±0.26Ab | 18.06±0.82Ab | 16.90±0.70Ac |
| T3P2 | 23.82±0.82Ab | 17.48±0.50Ab | 22.87±0.75Ab | 19.92±0.88Aa | 27.35±0.49Aa | 24.80±0.69Ab |
| T3P3 | 33.38±1.02Aa | 20.50±0.70Aa | 29.87±0.91Aa | 20.38±0.45Aa | 28.18±1.02Aa | 30.04±0.24Aa |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤全磷含量 Total phosphorus content in rhizosphere soil (g·kg-1) | 非根际土壤全磷含量 Total phosphorus content in non-rhizosphere soil (g·kg-1) | ||||
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 0.310±0.003Cb | 0.297±0.006Bc | 0.272±0.010Bc | 0.308±0.004Bc | 0.288±0.008Cc | 0.280±0.014Bc |
| T0P1 | 0.322±0.014Dab | 0.345±0.010Bb | 0.309±0.014Bb | 0.323±0.015Bc | 0.309±0.005Cc | 0.322±0.008Cb |
| T0P2 | 0.336±0.016Ba | 0.368±0.013Cab | 0.333±0.011Cab | 0.353±0.016Cb | 0.363±0.014Cb | 0.337±0.015Cb |
| T0P3 | 0.345±0.011Ca | 0.388±0.013Ba | 0.356±0.016Ba | 0.387±0.011Ca | 0.388±0.013Ba | 0.365±0.009Ba |
| T1P0 | 0.363±0.014Bc | 0.356±0.030Ab | 0.285±0.006Bc | 0.359±0.008Ac | 0.338±0.006Bc | 0.294±0.010Bd |
| T1P1 | 0.389±0.011Bb | 0.388±0.013Aa | 0.378±0.006Ab | 0.390±0.014Ab | 0.381±0.010Bb | 0.331±0.008Cc |
| T1P2 | 0.413±0.021Aa | 0.404±0.017ABa | 0.396±0.010Aab | 0.407±0.016Bb | 0.397±0.012Bab | 0.370±0.014Bb |
| T1P3 | 0.430±0.008Ba | 0.420±0.008Ba | 0.404±0.011Aa | 0.436±0.011Ba | 0.411±0.006Ba | 0.400±0.016Aa |
| T2P0 | 0.332±0.011Cc | 0.350±0.014Ab | 0.276±0.003Bd | 0.354±0.003Ac | 0.305±0.013Cc | 0.298±0.013Bc |
| T2P1 | 0.365±0.012Cb | 0.376±0.017ABab | 0.303±0.009Bc | 0.391±0.004Ab | 0.362±0.012Bb | 0.365±0.012Bb |
| T2P2 | 0.408±0.015Aa | 0.389±0.013BCa | 0.363±0.012Bb | 0.403±0.008Bb | 0.375±0.005Cb | 0.396±0.005Aa |
| T2P3 | 0.421±0.006Ba | 0.401±0.012Ba | 0.402±0.018Aa | 0.431±0.010Ba | 0.402±0.004Ba | 0.407±0.014Aa |
| T3P0 | 0.402±0.004Ac | 0.380±0.018Ac | 0.366±0.008Ab | 0.363±0.005Ac | 0.396±0.012Ac | 0.389±0.016Aa |
| T3P1 | 0.413±0.018Abc | 0.404±0.017Abc | 0.380±0.012Ab | 0.414±0.007Ab | 0.408±0.007Ac | 0.395±0.009Aa |
| T3P2 | 0.431±0.005Aab | 0.423±0.014Ab | 0.406±0.006Aa | 0.434±0.010Ab | 0.447±0.004Ab | 0.402±0.008Aa |
| T3P3 | 0.454±0.011Aa | 0.461±0.011Aa | 0.410±0.019Aa | 0.468±0.014Aa | 0.470±0.011Aa | 0.411±0.006Aa |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | NS | NS | ** | NS | * | ** |
表5 不同处理下根际土、非根际土速效磷及全磷含量
Table 5 Available phosphorus content and total phosphorus content of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤速效磷含量 Available phosphorus content in rhizosphere soil (mg·kg-1) | 非根际土壤速效磷含量 Available phosphorus content in non-rhizosphere soil (mg·kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 6.09±0.26Cc | 8.15±0.38Cd | 9.41±0.39Ac | 10.43±0.45Cc | 10.08±0.19Ac | 8.24±0.25Bc |
| T0P1 | 13.54±0.27Bb | 11.38±0.37Bc | 10.17±0.44Cbc | 14.69±0.63Bb | 11.29±0.50Cbc | 10.08±0.45Cb |
| T0P2 | 14.52±0.52Cb | 13.12±0.57Cb | 11.11±0.26Cab | 16.90±0.56Ba | 12.14±0.58Db | 11.29±0.51Ca |
| T0P3 | 18.79±0.58Ca | 14.34±0.51Ca | 12.10±0.64Da | 17.93±0.64Ba | 14.29±0.44Da | 12.01±0.25Ca |
| T1P0 | 9.14±0.26Bc | 9.41±0.26Bc | 9.90±0.32Ad | 12.90±0.51Bc | 11.02±0.26Ad | 9.81±0.45Ad |
| T1P1 | 9.76±0.38Cc | 11.91±0.26Bb | 14.57±0.44Bc | 13.35±0.37Cbc | 16.55±0.70Bc | 14.75±0.58Bc |
| T1P2 | 13.27±0.63Cb | 12.73±0.38Cb | 17.57±0.77Bb | 14.26±0.64Db | 18.65±0.53Bb | 17.75±0.77Bb |
| T1P3 | 21.26±0.90Ba | 18.07±0.33Ba | 22.23±0.51Ba | 17.29±0.50Ba | 21.08±0.75Ba | 21.26±0.37Ba |
| T2P0 | 6.94±0.32Cc | 9.18±0.32Bd | 9.72±0.45Ad | 12.14±0.32Bd | 10.48±0.38Ab | 9.40±0.39Ad |
| T2P1 | 13.53±0.39Bb | 10.43±0.44Cc | 14.03±0.58Bc | 14.15±0.63BCc | 11.42±0.57Cb | 13.85±0.56Bc |
| T2P2 | 19.18±0.64Ba | 16.17±0.33Bb | 17.48±0.76Bb | 15.32±0.64Cb | 16.63±0.82Ca | 16.94±0.64Bb |
| T2P3 | 20.22±0.31Ba | 19.63±0.38Aa | 20.39±0.69Ca | 17.22±0.51Ba | 17.58±0.77Ca | 20.13±0.70Ba |
| T3P0 | 13.13±0.45Ad | 11.46±0.13Ad | 10.21±0.25Ad | 15.47±0.69Ac | 11.29±0.38Ac | 10.43±0.44Ad |
| T3P1 | 22.15±0.91Ac | 12.94±0.32Ac | 19.18±0.64Ac | 17.49±0.26Ab | 18.06±0.82Ab | 16.90±0.70Ac |
| T3P2 | 23.82±0.82Ab | 17.48±0.50Ab | 22.87±0.75Ab | 19.92±0.88Aa | 27.35±0.49Aa | 24.80±0.69Ab |
| T3P3 | 33.38±1.02Aa | 20.50±0.70Aa | 29.87±0.91Aa | 20.38±0.45Aa | 28.18±1.02Aa | 30.04±0.24Aa |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤全磷含量 Total phosphorus content in rhizosphere soil (g·kg-1) | 非根际土壤全磷含量 Total phosphorus content in non-rhizosphere soil (g·kg-1) | ||||
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 0.310±0.003Cb | 0.297±0.006Bc | 0.272±0.010Bc | 0.308±0.004Bc | 0.288±0.008Cc | 0.280±0.014Bc |
| T0P1 | 0.322±0.014Dab | 0.345±0.010Bb | 0.309±0.014Bb | 0.323±0.015Bc | 0.309±0.005Cc | 0.322±0.008Cb |
| T0P2 | 0.336±0.016Ba | 0.368±0.013Cab | 0.333±0.011Cab | 0.353±0.016Cb | 0.363±0.014Cb | 0.337±0.015Cb |
| T0P3 | 0.345±0.011Ca | 0.388±0.013Ba | 0.356±0.016Ba | 0.387±0.011Ca | 0.388±0.013Ba | 0.365±0.009Ba |
| T1P0 | 0.363±0.014Bc | 0.356±0.030Ab | 0.285±0.006Bc | 0.359±0.008Ac | 0.338±0.006Bc | 0.294±0.010Bd |
| T1P1 | 0.389±0.011Bb | 0.388±0.013Aa | 0.378±0.006Ab | 0.390±0.014Ab | 0.381±0.010Bb | 0.331±0.008Cc |
| T1P2 | 0.413±0.021Aa | 0.404±0.017ABa | 0.396±0.010Aab | 0.407±0.016Bb | 0.397±0.012Bab | 0.370±0.014Bb |
| T1P3 | 0.430±0.008Ba | 0.420±0.008Ba | 0.404±0.011Aa | 0.436±0.011Ba | 0.411±0.006Ba | 0.400±0.016Aa |
| T2P0 | 0.332±0.011Cc | 0.350±0.014Ab | 0.276±0.003Bd | 0.354±0.003Ac | 0.305±0.013Cc | 0.298±0.013Bc |
| T2P1 | 0.365±0.012Cb | 0.376±0.017ABab | 0.303±0.009Bc | 0.391±0.004Ab | 0.362±0.012Bb | 0.365±0.012Bb |
| T2P2 | 0.408±0.015Aa | 0.389±0.013BCa | 0.363±0.012Bb | 0.403±0.008Bb | 0.375±0.005Cb | 0.396±0.005Aa |
| T2P3 | 0.421±0.006Ba | 0.401±0.012Ba | 0.402±0.018Aa | 0.431±0.010Ba | 0.402±0.004Ba | 0.407±0.014Aa |
| T3P0 | 0.402±0.004Ac | 0.380±0.018Ac | 0.366±0.008Ab | 0.363±0.005Ac | 0.396±0.012Ac | 0.389±0.016Aa |
| T3P1 | 0.413±0.018Abc | 0.404±0.017Abc | 0.380±0.012Ab | 0.414±0.007Ab | 0.408±0.007Ac | 0.395±0.009Aa |
| T3P2 | 0.431±0.005Aab | 0.423±0.014Ab | 0.406±0.006Aa | 0.434±0.010Ab | 0.447±0.004Ab | 0.402±0.008Aa |
| T3P3 | 0.454±0.011Aa | 0.461±0.011Aa | 0.410±0.019Aa | 0.468±0.014Aa | 0.470±0.011Aa | 0.411±0.006Aa |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | NS | NS | ** | NS | * | ** |
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤 pH pH of rhizosphere soil | 非根际土壤 pH pH of non-rhizosphere soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 8.56±0.03Aa | 8.27±0.12Ac | 8.19±0.01Ad | 8.13±0.02Ac | 8.15±0.02Ac | 8.17±0.04Ad |
| T0P1 | 8.59±0.04Aa | 8.41±0.01Ab | 8.31±0.02Ac | 8.23±0.05Ab | 8.23±0.02Ab | 8.28±0.03Ac |
| T0P2 | 8.62±0.04Aa | 8.57±0.05Aa | 8.48±0.02Aa | 8.36±0.03Aa | 8.32±0.01Aa | 8.52±0.01Aa |
| T0P3 | 8.56±0.03Aa | 8.36±0.02Ab | 8.40±0.02Ab | 8.16±0.02Ac | 8.17±0.06Abc | 8.38±0.01Ab |
| T1P0 | 8.23±0.07Bb | 8.15±0.02Bb | 8.13±0.03Bc | 8.03±0.05Bc | 8.03±0.01Bb | 8.11±0.02Bc |
| T1P1 | 8.31±0.03Cab | 8.20±0.02Bab | 8.23±0.04Bb | 8.14±0.01Bb | 8.13±0.07Ba | 8.20±0.03BCb |
| T1P2 | 8.38±0.02Ca | 8.24±0.03Ca | 8.41±0.03Ba | 8.22±0.03Ca | 8.16±0.05Ba | 8.35±0.03Ca |
| T1P3 | 8.27±0.10Bb | 8.17±0.03Bb | 8.26±0.03Bb | 8.08±0.03Bc | 8.08±0.09Bab | 8.24±0.04Bb |
| T2P0 | 8.48±0.01Aa | 8.26±0.02Ac | 8.14±0.01Bd | 8.13±0.04Ac | 8.11±0.02Abc | 8.16±0.01ABd |
| T2P1 | 8.49±0.04Ba | 8.38±0.03Ab | 8.28±0.01Ac | 8.21±0.01Ab | 8.21±0.06Aab | 8.24±0.05ABc |
| T2P2 | 8.50±0.10Ba | 8.48±0.03Ba | 8.45±0.02Aa | 8.28±0.03Ba | 8.28±0.02Aa | 8.43±0.01Ba |
| T2P3 | 8.48±0.10Aa | 8.33±0.04Abc | 8.37±0.02Ab | 8.17±0.02Abc | 8.17±0.03Abc | 8.35±0.03Ab |
| T3P0 | 8.15±0.02Bb | 8.02±0.01Cc | 8.06±0.01Cb | 7.88±0.01Cc | 7.88±0.01Cc | 8.05±0.02Cc |
| T3P1 | 8.23±0.05Cab | 8.11±0.02Cb | 8.21±0.03Ba | 8.00±0.02Cb | 7.96±0.06Cb | 8.18±0.06Cb |
| T3P2 | 8.26±0.04Da | 8.19±0.01Ca | 8.25±0.04Ca | 8.08±0.02Da | 8.11±0.05Ca | 8.28±0.01Da |
| T3P3 | 8.21±0.04Bab | 8.11±0.02Bb | 8.22±0.04Ca | 7.93±0.07Cc | 7.96±0.07Bb | 8.22±0.02Bb |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | NS | ** | ** | NS | NS | * |
表6 不同处理下根际及非根际土壤pH
Table 6 The pH value of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤 pH pH of rhizosphere soil | 非根际土壤 pH pH of non-rhizosphere soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 8.56±0.03Aa | 8.27±0.12Ac | 8.19±0.01Ad | 8.13±0.02Ac | 8.15±0.02Ac | 8.17±0.04Ad |
| T0P1 | 8.59±0.04Aa | 8.41±0.01Ab | 8.31±0.02Ac | 8.23±0.05Ab | 8.23±0.02Ab | 8.28±0.03Ac |
| T0P2 | 8.62±0.04Aa | 8.57±0.05Aa | 8.48±0.02Aa | 8.36±0.03Aa | 8.32±0.01Aa | 8.52±0.01Aa |
| T0P3 | 8.56±0.03Aa | 8.36±0.02Ab | 8.40±0.02Ab | 8.16±0.02Ac | 8.17±0.06Abc | 8.38±0.01Ab |
| T1P0 | 8.23±0.07Bb | 8.15±0.02Bb | 8.13±0.03Bc | 8.03±0.05Bc | 8.03±0.01Bb | 8.11±0.02Bc |
| T1P1 | 8.31±0.03Cab | 8.20±0.02Bab | 8.23±0.04Bb | 8.14±0.01Bb | 8.13±0.07Ba | 8.20±0.03BCb |
| T1P2 | 8.38±0.02Ca | 8.24±0.03Ca | 8.41±0.03Ba | 8.22±0.03Ca | 8.16±0.05Ba | 8.35±0.03Ca |
| T1P3 | 8.27±0.10Bb | 8.17±0.03Bb | 8.26±0.03Bb | 8.08±0.03Bc | 8.08±0.09Bab | 8.24±0.04Bb |
| T2P0 | 8.48±0.01Aa | 8.26±0.02Ac | 8.14±0.01Bd | 8.13±0.04Ac | 8.11±0.02Abc | 8.16±0.01ABd |
| T2P1 | 8.49±0.04Ba | 8.38±0.03Ab | 8.28±0.01Ac | 8.21±0.01Ab | 8.21±0.06Aab | 8.24±0.05ABc |
| T2P2 | 8.50±0.10Ba | 8.48±0.03Ba | 8.45±0.02Aa | 8.28±0.03Ba | 8.28±0.02Aa | 8.43±0.01Ba |
| T2P3 | 8.48±0.10Aa | 8.33±0.04Abc | 8.37±0.02Ab | 8.17±0.02Abc | 8.17±0.03Abc | 8.35±0.03Ab |
| T3P0 | 8.15±0.02Bb | 8.02±0.01Cc | 8.06±0.01Cb | 7.88±0.01Cc | 7.88±0.01Cc | 8.05±0.02Cc |
| T3P1 | 8.23±0.05Cab | 8.11±0.02Cb | 8.21±0.03Ba | 8.00±0.02Cb | 7.96±0.06Cb | 8.18±0.06Cb |
| T3P2 | 8.26±0.04Da | 8.19±0.01Ca | 8.25±0.04Ca | 8.08±0.02Da | 8.11±0.05Ca | 8.28±0.01Da |
| T3P3 | 8.21±0.04Bab | 8.11±0.02Bb | 8.22±0.04Ca | 7.93±0.07Cc | 7.96±0.07Bb | 8.22±0.02Bb |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | NS | ** | ** | NS | NS | * |
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤碱性磷酸酶AKP of rhizosphere soil | 非根际土壤碱性磷酸酶AKP of non-rhizosphere soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 7149±158Bb | 7672±328Cb | 7963±334Cb | 8680±170Bc | 8398±184Ab | 10390±144Bb |
| T0P1 | 7498±309Cb | 8869±228Ba | 8873±168Cb | 9684±476Bb | 8518±118Bb | 13159±600Ba |
| T0P2 | 8921±279Aa | 8933±212Ba | 9163±398Aa | 11048±184Aa | 9407±190Ba | 10762±192Bb |
| T0P3 | 7381±147Cb | 7834±170Bb | 8253±315Cb | 10064±175ABb | 8100±256Cb | 12551±269Aab |
| T1P0 | 8247±307Aa | 8325±204Bb | 8546±108BCb | 10026±285Aa | 8599±270Ac | 12155±177Ac |
| T1P1 | 8411±202Ba | 9666±157Aa | 8667±355Cb | 10054±105ABa | 8705±176Bc | 14130±243Aa |
| T1P2 | 8409±283Aa | 9887±173Aa | 9002±244Ab | 10164±162Ba | 10954±477Aa | 13161±517Ab |
| T1P3 | 8522±160Ba | 9652±298Aa | 11357±360Aa | 10591±315Aa | 9329±254Bb | 11708±253Bc |
| T2P0 | 8223±226Ab | 8020±372BCa | 9155±447ABb | 8805±306Bc | 8481±309Ab | 11074±391Bb |
| T2P1 | 8231±408Bb | 8272±353Ca | 10772±444Aa | 9068±155Cbc | 8596±315Bb | 11498±471Db |
| T2P2 | 8378±322Ab | 8402±215Ba | 9631±188Ab | 10680±278ABa | 9012±109Bb | 12638±625Aa |
| T2P3 | 9204±216Aa | 8182±268Ba | 8997±118Bb | 9661±213Bb | 10998±133Aa | 11471±450Bb |
| T3P0 | 8229±256Ab | 9241±335Ab | 9459±432Ab | 9862±335Abc | 8705±427Ac | 11922±320Ab |
| T3P1 | 10439±112Aa | 9706±126Aab | 9550±190Bb | 10325±180Aab | 9610±235Ab | 12280±203Cb |
| T3P2 | 8474±341Ab | 10277±195Aa | 9652±133Ab | 10493±431ABa | 11042±199Aa | 13231±126Aa |
| T3P3 | 8240±191Bb | 9825±318Aab | 11333±465Aa | 9614±267Bc | 8874±158Bc | 12499±159Aab |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** |
表7 不同处理下根际和非根际土壤碱性磷酸酶活性
Table 7 Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) activity of rhizosphere soil and non-rhizosphere soil under different treatments (U·g-1)
处理 Treatment | 根际土壤碱性磷酸酶AKP of rhizosphere soil | 非根际土壤碱性磷酸酶AKP of non-rhizosphere soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第3茬Third cut | |
| T0P0 | 7149±158Bb | 7672±328Cb | 7963±334Cb | 8680±170Bc | 8398±184Ab | 10390±144Bb |
| T0P1 | 7498±309Cb | 8869±228Ba | 8873±168Cb | 9684±476Bb | 8518±118Bb | 13159±600Ba |
| T0P2 | 8921±279Aa | 8933±212Ba | 9163±398Aa | 11048±184Aa | 9407±190Ba | 10762±192Bb |
| T0P3 | 7381±147Cb | 7834±170Bb | 8253±315Cb | 10064±175ABb | 8100±256Cb | 12551±269Aab |
| T1P0 | 8247±307Aa | 8325±204Bb | 8546±108BCb | 10026±285Aa | 8599±270Ac | 12155±177Ac |
| T1P1 | 8411±202Ba | 9666±157Aa | 8667±355Cb | 10054±105ABa | 8705±176Bc | 14130±243Aa |
| T1P2 | 8409±283Aa | 9887±173Aa | 9002±244Ab | 10164±162Ba | 10954±477Aa | 13161±517Ab |
| T1P3 | 8522±160Ba | 9652±298Aa | 11357±360Aa | 10591±315Aa | 9329±254Bb | 11708±253Bc |
| T2P0 | 8223±226Ab | 8020±372BCa | 9155±447ABb | 8805±306Bc | 8481±309Ab | 11074±391Bb |
| T2P1 | 8231±408Bb | 8272±353Ca | 10772±444Aa | 9068±155Cbc | 8596±315Bb | 11498±471Db |
| T2P2 | 8378±322Ab | 8402±215Ba | 9631±188Ab | 10680±278ABa | 9012±109Bb | 12638±625Aa |
| T2P3 | 9204±216Aa | 8182±268Ba | 8997±118Bb | 9661±213Bb | 10998±133Aa | 11471±450Bb |
| T3P0 | 8229±256Ab | 9241±335Ab | 9459±432Ab | 9862±335Abc | 8705±427Ac | 11922±320Ab |
| T3P1 | 10439±112Aa | 9706±126Aab | 9550±190Bb | 10325±180Aab | 9610±235Ab | 12280±203Cb |
| T3P2 | 8474±341Ab | 10277±195Aa | 9652±133Ab | 10493±431ABa | 11042±199Aa | 13231±126Aa |
| T3P3 | 8240±191Bb | 9825±318Aab | 11333±465Aa | 9614±267Bc | 8874±158Bc | 12499±159Aab |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| T×P | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** |
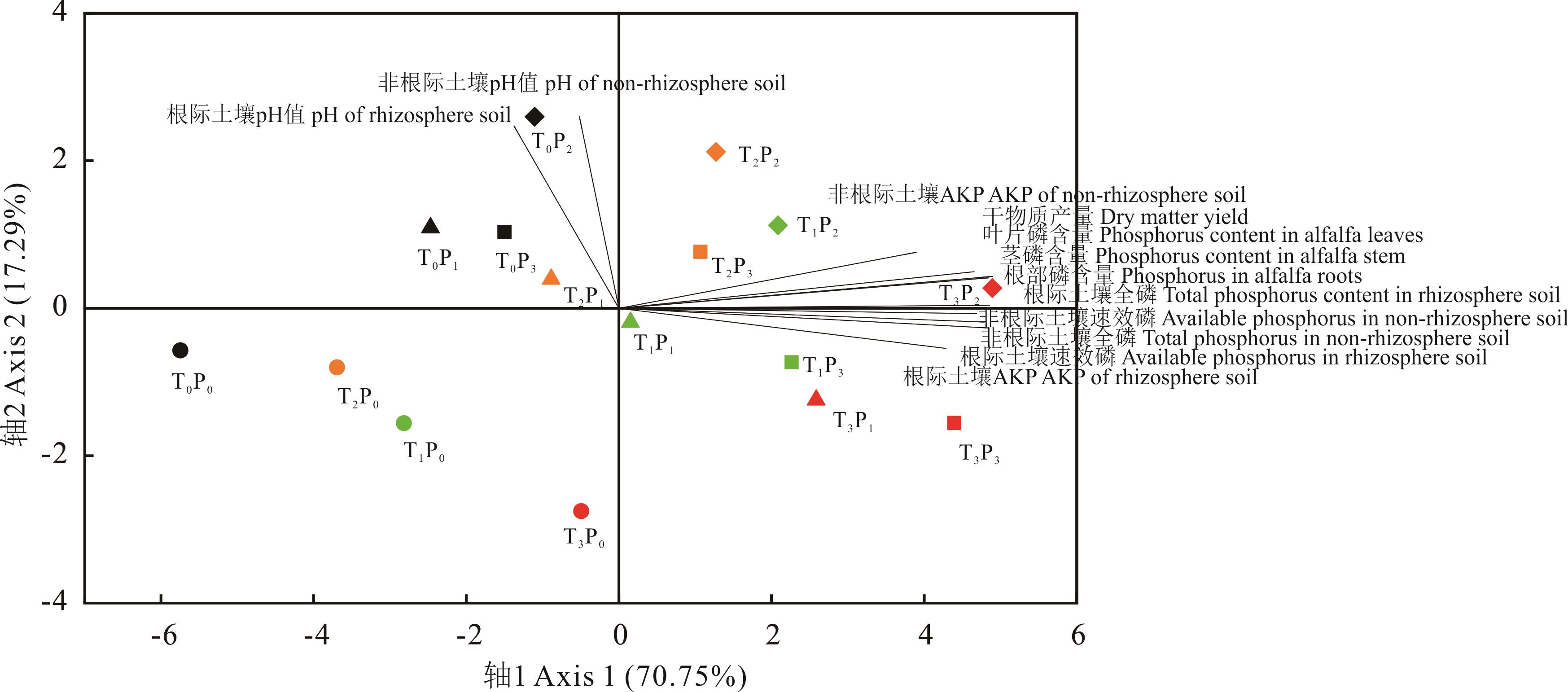
图1 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿各指标主成分分析●,▲,?和■分别代表P0、P1、P2和P3。黑色、红色、绿色和黄色分别代表T0、T1、T2和T3。●, ▲, ? and ■ represents P0, P1, P2, and P3, respectively. Black, red, green and yellow represents T0, T1, T2, and T3, respectively.
Fig.1 Principal component analysis of alfalfa under different fungal phosphorus treatment
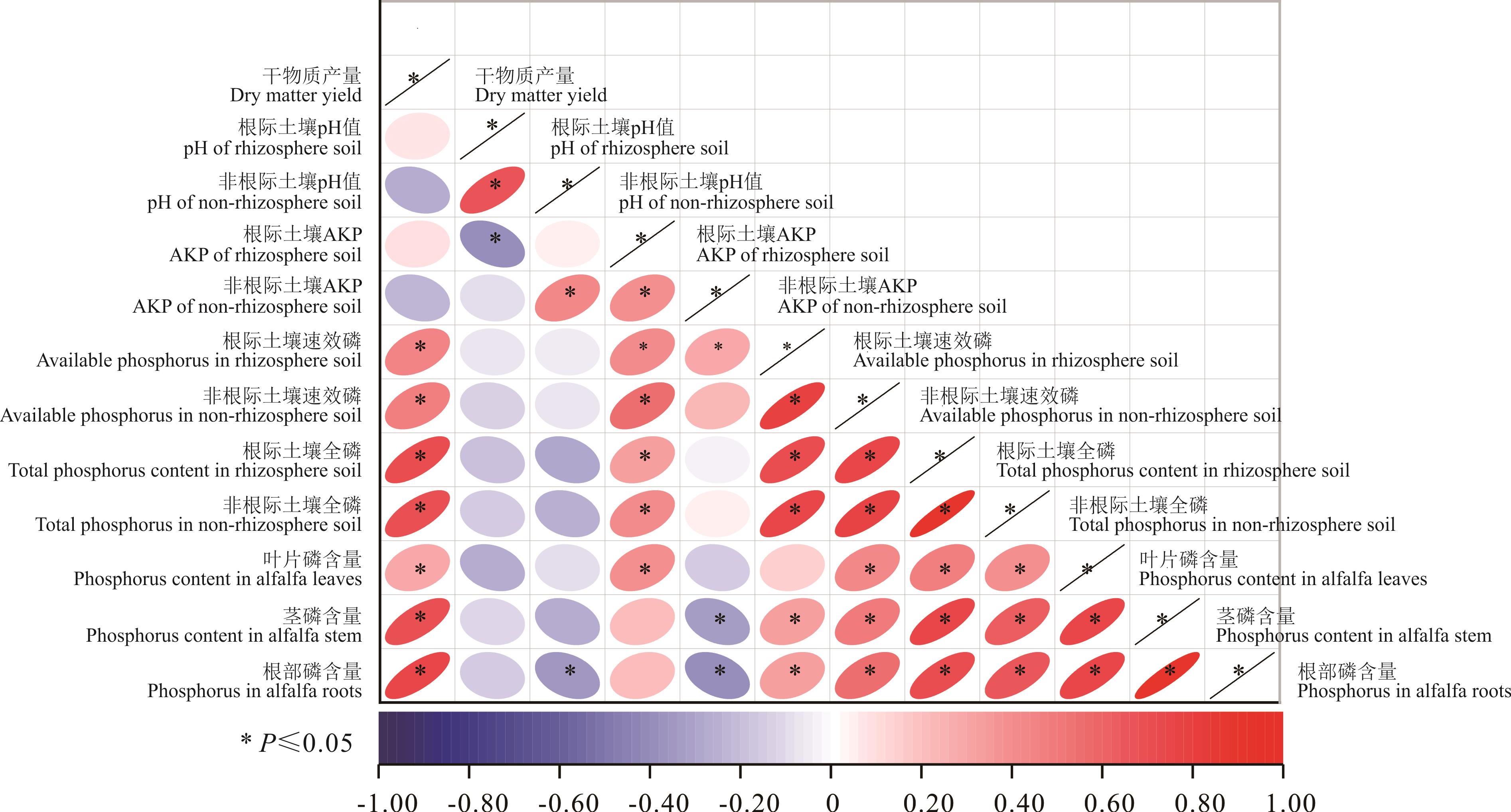
图2 苜蓿生长指标、土壤磷等生理参数相关性*: 在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。*: Significant correlation was found at the 0.05 level (bilateral).
Fig.2 Correlation between alfalfa growth index, soil phosphorus and other physiological parameters
| 1 | Liu X S, Zhao J W, Liu J Y, et al. Water-phosphorus coupling enhances fine root turnover and dry matter yield of alfalfa under drip irrigation. Agronomy Journal, 2021, 113(5): 4161-4175. |
| 2 | Zhang Q B, Liu J Y, Liu X S, et al. Optimizing water and phosphorus management to improve hay yield and water and phosphorus-use efficiency in alfalfa under drip irrigation. Food Science and Nutrition, 2020, 8(5): 2406-2418. |
| 3 | Liu J Y, Liu X S, Zhang Q B, et al. Response of alfalfa growth to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria under different phosphorus application levels. AMB Express, 2020, 10(1): 1-13. |
| 4 | Tshibangu K A, Lwalaba W L J, Kirika A B, et al. Effect of phosphorus and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation on growth and productivity of maize (Zea mays L.) in a tropical ferralsol. Gesunde Pflanzen, 2022, 74(1): 159-165. |
| 5 | Suriyagoda L D B, Ryan M H, Renton M, et al. Above- and belowground interactions of grass and pasture legume species when grown together under drought and low phosphorus availability. Plant and Soil, 2011, 348(1): 281-297. |
| 6 | Frosi G, Barros V A, Oliveira M T, et al. Increase in biomass of two woody species from a seasonal dry tropical forest in association with AMF with different phosphorus levels. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 102(2): 46-52. |
| 7 | Popescu G C, Popescu M. Role of combined inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, as a sustainable tool, for stimulating the growth, physiological processes, and flowering performance of lavender. Sustainability, 2022, 14(2): 951. |
| 8 | Chen M, Arato M, Borghi L, et al. Beneficial services of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-from ecology to application. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9(4): 1270-1284. |
| 9 | Shrivastava P, Kumar R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2015, 22(2): 123-131. |
| 10 | Kaschuk G, Kuyper T W, Leffelaar P A, et al. Are the rates of photosynthesis stimulated by the carbon sink strength of rhizobial and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbioses? Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2009, 41(6): 1233-1244. |
| 11 | Tshibangu K A, Baert G, Lwalaba W L J, et al. Increasing of NPK fertilizer efficiency by arbuscular mycorrhiza in common bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.). Gesunde Pflanzen, 2020, 72(4): 303-310. |
| 12 | Cofre N, Becerra A G, Marro N, et al. Soybean growth and foliar phosphorus concentration mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from soils under different no-till cropping systems. Rhizosphere, 2020, 16: 100254. |
| 13 | Lang M, Zhang C, Su W, et al. Long-term P fertilization significantly altered the diversity, composition and mycorrhizal traits of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in a wheat-maize rotation. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 170: 104261. |
| 14 | Meng L L, Srivastava A K, Kuča K, et al. Earthworm (Pheretima guillelmi)-mycorrhizal fungi (Funneliformis mosseae) association mediates rhizosphere responses in white clover. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 172: 104371. |
| 15 | Shan L W. Effects of AMF on photosynthetic characteristics and productivity of grassland plants under different treatment conditions. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2020. |
| 单立文. AMF在不同处理条件下对草地植物光合特征及其生产力影响的研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2020. | |
| 16 | Xie K Y, Sun L L, Zhang L W, et al. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobium inoculation on the biomass of alfalfa and smooth brome in mixed culture. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(1): 182-188. |
| 谢开云, 孙伶俐, 张力文, 等. 菌根真菌和根瘤菌接种对紫花苜蓿和无芒雀麦混播牧草生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(1): 182-188. | |
| 17 | Liu J Y, Hui J F, Sun M Y, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi (AMF) and phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) on dry matter yield and phosphorus use efficiency of alfalfa. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. |
| 刘俊英, 回金峰, 孙梦瑶, 等. 施磷水平和接种AMF与解磷细菌对苜蓿产量及磷素利用效率的影响. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. | |
| 18 | Fan J W, Du Y L, Wang B R, et al. Forage yield, soil water depletion, shoot nitrogen and phosphorus uptake and concentration, of young and old stands of alfalfa in response to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilisation in a semiarid environment. Field Crops Research, 2016, 198(11): 247-257. |
| 19 | Lu R K. Methods of soil agricultural chemical analysis. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 20 | Wang Q, Bao Y, Liu X, et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with glomalin-related soil protein and soil enzymes in different managed semiarid steppes. Mycorrhiza, 2014, 24(7): 525-538. |
| 21 | Bundrett M C, Ashwath N, Jasper D A. Mycorrhizas in the kakadu region of tropical Australia. Plant and Soil, 1996, 184(1): 173-184. |
| 22 | Xue Y F, Xia H Y, Christie P, et al. Crop acquisition of phosphorus iron and zinc from soil in cereal/legume intercropping systems: A critical review. Annals of Botany, 2016, 117(3): 363-377. |
| 23 | Pacheco I, Ferreira R, Correia P, et al. Microbial consortium increases maize productivity and reduces grain phosphorus concentration under field conditions. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2021, 28(1): 232-237. |
| 24 | Tran C T K, Watts-Williams S J, Smernik R J, et al. Effects of plant roots and arbuscular mycorrhizas on soil phosphorus leaching. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 722: 137847. |
| 25 | Sun T, Li Z, Wu Q, et al. Effects of alfalfa intercropping on crop yield, water use efficiency, and overall economic benefit in the corn belt of Northeast China. Field Crops Research, 2018, 216(7): 109-119. |
| 26 | Wang J, Liu X J, Hao F, et al. Study on nitrogen utilization characteristics of alfalfa with different nitrogen efficiency in different growth periods. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2461-2469. |
| 王静, 刘晓静, 郝凤, 等. 不同氮效率紫花苜蓿各生育期氮利用特征研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2461-2469. | |
| 27 | Drevon J J. Efficacité d’utilisation du phosphore pour la fixation symbiotique de l’azote et phytases des nodules de légumineuses. Innovations Agronomiques, 2017, 60: 3-10. |
| 28 | Hu J, Lin X, Bentivenga S P, et al. Intraradical and extraradical communities of AM fungi associated with alfalfa respond differently to long-term phosphorus fertilization. Flora, 2019, 258: 151424. |
| 29 | Beauregard M S, Hamel C, St-Arnaud M. Long-term phosphorus fertilization impacts soil fungal and bacterial diversity but not AM fungal community in alfalfa. Microbial Ecology, 2010, 59(2): 379-389. |
| 30 | Püschel D, Janoušková M, Voříšková A, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhiza stimulates biological nitrogen fixation in two Medicago spp. through improved phosphorus acquisition. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 390. |
| 31 | Liu S, Xu J, Huang H, et al. Changes in the mycorrhizal fungal community in host roots over five host generations under low and high phosphorus conditions. Plant and Soil, 2020, 456(1): 27-41. |
| 32 | Cavagnaro T R, Bender S F, Asghari H R, et al. The role of arbuscular mycorrhizas in reducing soil nutrient loss. Trends in Plant Science, 2015, 20(5): 283-290. |
| 33 | Darch T, Blackwell M S A, Chadwick D, et al. Assessment of bioavailable organic phosphorus in tropical forest soils by organic acid extraction and phosphatase hydrolysis. Geoderma, 2016, 284(8): 93-102. |
| 34 | Gessa C E, Mimmo T, Deiana S, et al. Effect of aluminium and pH on the mobility of phosphate through a soil-root interface model. Plant and Soil, 2005, 272(1): 301-311. |
| 35 | Tshibangu A K, Shutcha M N, Baert G, et al. Effect of soil properties on arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi (AMF) activity and assessment of some methods of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) inoculation in Lubumbashi region (DR. Congo). Scholars Bulletin, 2020, 6(8): 198-207. |
| [1] | 叶婷, 吴晓娟, 芦奕晓, 刘生娟, 姜卓慧, 杨惠敏. 混播比例对两种苜蓿混播草地产量和种群密度稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. |
| [2] | 李超男, 王磊, 周继强, 赵长兴, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣. 微塑料对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [3] | 张振粉, 黄荣, 姚博, 张旺东, 杨成德, 陈秀蓉. 欧美进口紫花苜蓿可培养种带细菌及其对动植物的致病性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 161-172. |
| [4] | 张士敏, 赵娇阳, 朱慧森, 卫凯, 王永新. 硒对不同品种紫花苜蓿发芽阶段物质转化和形态建成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 79-90. |
| [5] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [6] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [7] | 孙守江, 唐艺涵, 马馼, 李曼莉, 毛培胜. 紫花苜蓿种子吸胀期胚根线粒体AsA-GSH循环对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 152-162. |
| [8] | 赵艳兰, 曾鑫奕, 弓晋超, 李香君, 李旭旭, 刘珊, 张新全, 周冀琼. 丛枝菌根真菌接种对白车轴草耐盐性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 179-188. |
| [9] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| [10] | 苏乐乐, 秦燕, 王瞾敏, 张永超, 刘文辉. 氮磷添加对燕麦与箭筈豌豆不同种植方式草地土壤微生物-胞外酶化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 56-66. |
| [11] | 杜鹏冲, 潘昱臻, 侯双利, 王智慧, 王洪义. 氮磷添加对呼伦贝尔草地凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 44-53. |
| [12] | 王晓龙, 杨曌, 来永才, 李红, 钟鹏, 徐艳霞, 柴华, 李莎莎, 吴玥, 宋敏超, 周景明. 不同秋眠等级苜蓿根系性状对越冬的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 144-153. |
| [13] | 苗阳阳, 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民. 碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 107-117. |
| [14] | 赵俊威, 李生仪, 孙延亮, 刘选帅, 马春晖, 张前兵. 不同氮磷水平下不同土层中紫花苜蓿细根周转特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 118-128. |
| [15] | 陈卫东, 张玉霞, 张庆昕, 刘庭玉, 王显国, 王东儒. 末次刈割时间对苜蓿根颈抗氧化系统及抗寒性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 129-138. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||