

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 206-215.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022340
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
梁佳1,2( ), 胡朝阳3, 谢志明1,2, 马刘峰1,2, 陈芸1,2, 方志刚1,2(
), 胡朝阳3, 谢志明1,2, 马刘峰1,2, 陈芸1,2, 方志刚1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-26
修回日期:2022-10-20
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-05-26
通讯作者:
方志刚
作者简介:E-mail: fangyi20@126.com基金资助:
Jia LIANG1,2( ), Zhao-yang HU3, Zhi-ming XIE1,2, Liu-feng MA1,2, Yun CHEN1,2, Zhi-gang FANG1,2(
), Zhao-yang HU3, Zhi-ming XIE1,2, Liu-feng MA1,2, Yun CHEN1,2, Zhi-gang FANG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-08-26
Revised:2022-10-20
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-05-26
Contact:
Zhi-gang FANG
摘要:
为探究外源褪黑素缓解甜高粱幼苗干旱胁迫可能的生理机制,以甜高粱品种‘大力士’为材料,采用盆栽试验方法,分析自然干旱条件下,叶面喷施褪黑素(100 μmol·L-1)对甜高粱幼苗生长及生理特性的影响。结果表明,干旱胁迫导致植株地上部水分失衡,叶绿体结构受损,细胞产生氧化胁迫,显著抑制甜高粱幼苗的生长。喷施褪黑素可显著降低甜高粱叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量,积累更多的可溶性蛋白和脯氨酸,提高叶片含水量,使叶绿体基粒片层排列有序,光合色素含量升高;喷施褪黑素还能显著提高叶片过氧化物酶(POD)和硝酸还原酶活性。综合上述,喷施100 μmol·L-1褪黑素能进一步激发干旱环境中甜高粱叶片抗氧化系统的保护作用,通过渗透调节,维持植株水分平衡,改善叶绿体结构,提高光合色素含量,协同增强氮代谢,促进植株生长,从而缓解干旱对甜高粱幼苗的伤害。
梁佳, 胡朝阳, 谢志明, 马刘峰, 陈芸, 方志刚. 外源褪黑素缓解甜高粱幼苗干旱胁迫的生理效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 206-215.
Jia LIANG, Zhao-yang HU, Zhi-ming XIE, Liu-feng MA, Yun CHEN, Zhi-gang FANG. Exogenous melatonin alleviates the physiological effects of drought stress in sweet sorghum seedlings[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 206-215.
处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 叶面积 Leaf area (cm2) | 地上部干重 Shoot dry weight (g·plant-1) | 根系干重 Root dry weight (g·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 97.83±3.95a | 4.46±0.29a | 23.12±0.97a | 0.49±0.07ab | 0.10±0.02ab |
| D | 73.83±6.52b | 3.59±0.35c | 15.05±1.36b | 0.42±0.05b | 0.06±0.02b |
| CK+MT | 98.01±2.31a | 4.45±0.15ab | 24.60±1.57a | 0.49±0.04a | 0.11±0.01a |
| D+MT | 85.65±10.60ab | 3.91±0.24bc | 22.40±1.98a | 0.48±0.13ab | 0.08±0.03ab |
表1 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下甜高粱幼苗生长的影响
Table 1 Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth of sweet sorghum seedlings under drought stress
处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 叶面积 Leaf area (cm2) | 地上部干重 Shoot dry weight (g·plant-1) | 根系干重 Root dry weight (g·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 97.83±3.95a | 4.46±0.29a | 23.12±0.97a | 0.49±0.07ab | 0.10±0.02ab |
| D | 73.83±6.52b | 3.59±0.35c | 15.05±1.36b | 0.42±0.05b | 0.06±0.02b |
| CK+MT | 98.01±2.31a | 4.45±0.15ab | 24.60±1.57a | 0.49±0.04a | 0.11±0.01a |
| D+MT | 85.65±10.60ab | 3.91±0.24bc | 22.40±1.98a | 0.48±0.13ab | 0.08±0.03ab |
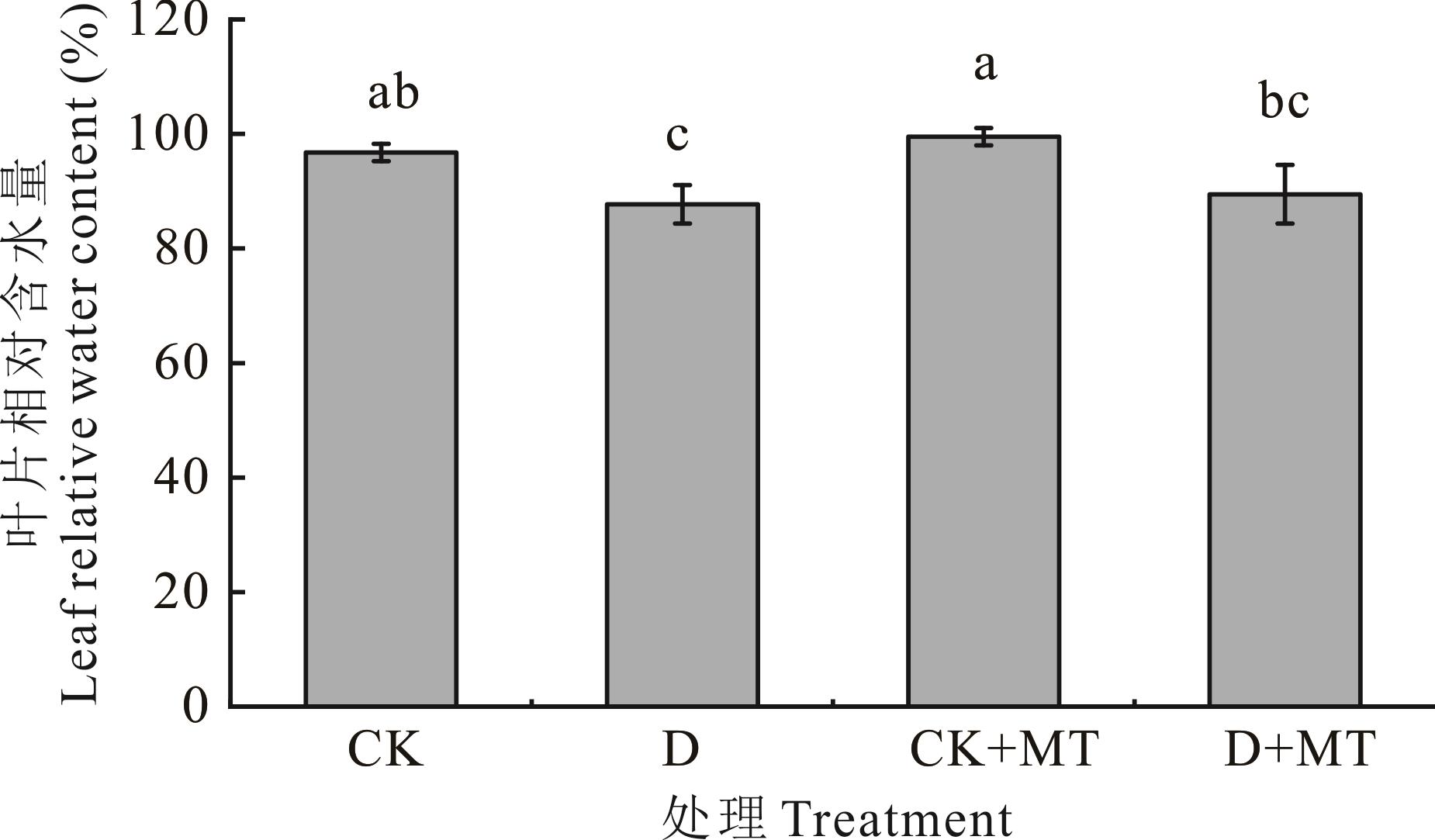
图1 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下甜高粱幼苗叶片相对含水量的影响CK:对照;D:干旱胁迫;CK+MT:正常供水条件下喷施100 μmol·L-1的褪黑素;D+MT:干旱胁迫条件下喷施100 μmol·L-1的褪黑素。数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差。不同小写字母表示不同处理在0.05水平差异显著。下同。CK: Control; D: Drought stress; CK+MT: Spraying 100 μmol·L-1 melatonin under normal water supply; D+MT: Spraying 100 μmol·L-1 melatonin under drought stress. Data were mean±standard deviation for three replicates. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of exogenous melatonin on leaf relative water content of sweet sorghum seedlings under drought stress
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | D | CK+MT | D+MT | |
| 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a (Chl a) | 10.09±0.47a | 5.69±0.36c | 9.19±0.23b | 8.92±0.48b |
| 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b (Chl b) | 4.00±0.52a | 2.72±0.38b | 4.00±0.53a | 3.55±0.42ab |
| 总叶绿素Total chlorophyll (T-Chl) | 14.10±0.72a | 8.42±0.41c | 13.20±0.71ab | 12.47±0.14b |
| 类胡萝卜素Carotenoid (Car) | 1.66±0.11a | 0.85±0.12c | 1.41±0.48ab | 1.02±0.10bc |
| Chl a/Chl b | 2.55±0.37a | 2.12±0.36a | 2.32±0.26a | 2.55±0.41a |
| T-Chl/Car | 8.57±0.98a | 9.96±1.44a | 10.20±3.78a | 12.30±1.42a |
表2 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下甜高粱幼苗叶绿素与类胡萝卜素含量及其比值的影响
Table 2 Effects of exogenous melatonin on chlorophyll and carotenoid contents and their ratios in sweet sorghum seedlings under drought stress
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | D | CK+MT | D+MT | |
| 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a (Chl a) | 10.09±0.47a | 5.69±0.36c | 9.19±0.23b | 8.92±0.48b |
| 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b (Chl b) | 4.00±0.52a | 2.72±0.38b | 4.00±0.53a | 3.55±0.42ab |
| 总叶绿素Total chlorophyll (T-Chl) | 14.10±0.72a | 8.42±0.41c | 13.20±0.71ab | 12.47±0.14b |
| 类胡萝卜素Carotenoid (Car) | 1.66±0.11a | 0.85±0.12c | 1.41±0.48ab | 1.02±0.10bc |
| Chl a/Chl b | 2.55±0.37a | 2.12±0.36a | 2.32±0.26a | 2.55±0.41a |
| T-Chl/Car | 8.57±0.98a | 9.96±1.44a | 10.20±3.78a | 12.30±1.42a |

图2 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下甜高粱幼苗叶片中叶绿体超微结构的影响A~B:对照(CK); C~D:干旱胁迫(D)处理; E~F:正常供水条件下喷施 100 μmol·L-1褪黑素(CK+MT)处理;G~H:干旱条件下,喷施 100 μmol·L-1褪黑素(D+MT)处理。A-B: Control (CK); C-D: Drought stress (D) treatment; E-F: Spraying 100 μmol·L-1 melatonin under normal water supply (CK+MT) treatment; G-H: Spraying 100 μmol·L-1 melatonin under drought stress (D+MT) treatment. Chl: Chloroplast; GL: Grana lamella; St: Starch grain; Pi: Osmophilic granules.
Fig.2 Effects of exogenous melatonin on chloroplast ultrastructure in leaves of sweet sorghum seedlings under drought stress
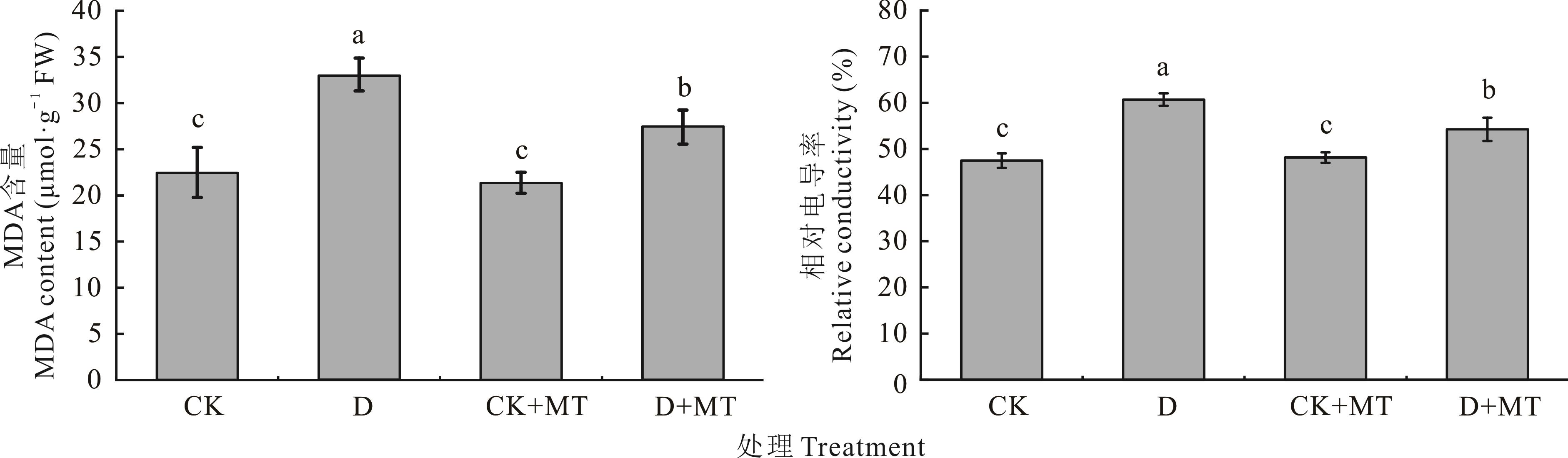
图3 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下甜高粱幼苗MDA含量与相对电导率的影响
Fig.3 Effects of exogenous melatonin on MDA contents and relative conductivity of sweet sorghum seedlings under drought stress
| 1 | Deng M J. National water conservation action is a key measure for alleviating water shortage in inland dry areas-A study on the development trend of water issues in the dry areas of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region and its allocation and regulation strategy. China Water Resource, 2018(6): 14-17. |
| 邓铭江. 破解内陆干旱区水资源紧缺问题的关键举措-新疆干旱区水问题发展趋势与调控策略. 中国水利, 2018(6): 14-17. | |
| 2 | Li D, Shen H T, Wang Y, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on photosynthetic carbon assimilation and endogenous hormones in tobacco seedlings under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. |
| 李冬, 申洪涛, 王艳, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗光合碳同化和内源激素的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. | |
| 3 | Seleiman M F, Al-Suhaibani N, Ali N, et al. Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants, 2021, 10(2): 259. |
| 4 | Vinutha K S, Lokesh H, Anil Kumar G S, et al. Performance of bmr 6 and 12 sorghum mutants in different wild backgrounds under salinity. Sugar Tech, 2018, 20(3): 293-304. |
| 5 | Si R, Liu B, Zhu Z C, et al. Optimal fertigation and irrigation for sweet sorghum production in arid regions in northwest China. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(5): 54-61. |
| 司瑞, 刘冰, 朱钊岑, 等. 西北干旱区甜高粱种植水肥配比模式研究. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(5): 54-61. | |
| 6 | Xie T T, Shan L S, Su P X, et al. Effects of different irrigation quantities at key growth stages on yield, quality and water use efficiency of sweet sorghum. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019(4): 51-57. |
| 解婷婷, 单立山, 苏培玺, 等. 关键生育期不同灌溉量对甜高粱产量、品质及水分利用效率的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019(4): 51-57. | |
| 7 | Khan I, Awan S A, Ikram R, et al. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on plant growth, antioxidants defense system, and endogenous hormones in two wheat varieties under drought stress. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 172(2): 696-706. |
| 8 | Sun C, Liu L, Wang L, et al. Melatonin: A master regulator of plant development and stress responses. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(1): 126-145. |
| 9 | Liu L, Li D, Ma Y L, et al. Alleviation of drought stress and the physiological mechanisms in the tobacco seedlings treated with exogenous melatonin. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(8): 95-105. |
| 刘领, 李冬, 马宜林, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烤烟幼苗生长的缓解效应与生理机制研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 95-105. | |
| 10 | Zhu C Q, Wei Q Q, Xiang X J, et al. Regulation effects of seedling raising by melatonin and methyl jasmonate substrate on low temperature stress tolerance in rice. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(8): 2016-2027. |
| 朱春权, 魏倩倩, 项兴佳, 等. 褪黑素和茉莉酸甲酯基质育秧对水稻耐低温胁迫的调控作用. 作物学报, 2022, 48(8): 2016-2027. | |
| 11 | Ma X H, Chen R M, Liu X Q, et al. Effects of melatonin on root growth and drought tolerance of maize seedlings. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(2): 1-14. |
| 马旭辉, 陈茹梅, 柳小庆, 等. 褪黑素对玉米幼苗根系发育和抗旱性的影响. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(2): 1-14. | |
| 12 | Li J J, Zeng L, Cheng Y, et al. Exogenous melatonin alleviates damage from drought stress in Brassica napus L. (rapeseed) seedlings. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2018, 40: 43. |
| 13 | Kabiri R, Hatami A, Oloumi H, et al. Foliar application of melatonin induces tolerance to drought stress in moldavian balm plants (Dracocephalum moldavica) through regulating the antioxidant system.Folia Horticulturae, 2018, 30: 155-167. |
| 14 | Liu J L. Influence of exogenous melatonin on tomato antioxidant system and yield and fruit quality under drought stress. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2015. |
| 刘建龙. 外源褪黑素处理对干旱胁迫下番茄抗氧化系统及产量和果实品质的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. | |
| 15 | Khan M N, Zhang J, Luo T, et al. Seed priming with melatonin coping drought stress in rapeseed by regulating reactive oxygen species detoxification: Antioxidant defense system, osmotic adjustment, stomatal traits and chloroplast ultrastructure perseveration. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 140: 111597. |
| 16 | Wang L, Feng C, Zheng X D, et al. Plant mitochondria synthesize melatonin and enhance the tolerance of plants to drought stress. Journal of Pineal Research, 2017, 63(3): e12429. |
| 17 | Liang J, Mayinu W S M, Fang Z G. Effects of exogenous growth substances on seed germination of sweet sorghum under drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(3): 610-617. |
| 梁佳, 马依努·吾斯曼, 方志刚. 外源生长物质对干旱胁迫条件下甜高粱种子萌发的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(3): 610-617. | |
| 18 | Zhao W S, Sun Y L, Liu X P.Effects of drought-rewatering-drought on photosynthesis and growth of maize. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(6): 594-603. |
| 赵文赛, 孙永林, 刘西平. 干旱-复水-再干旱处理对玉米光合能力和生长的影响. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(6):594-603. | |
| 19 | Liu H. Transcriptome analysis of cold-tolerant tomato germplasm under cold stress and functional characterization of cold responsive genes. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 刘辉. 番茄耐寒种质低温胁迫下的转录组分析及相关基因功能鉴定. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2012. | |
| 20 | Arivalagan M, Somasundaram R. Propiconazole and salicylic acid alleviate effect of drought stress in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) through biochemical and some physiological characters. Journal of Applied and Advanced Research, 2016, 1(3): 1-7. |
| 21 | Knudson L L, Tibbitts T W, Edwards G E. Measurement of ozone injury by determination of leaf chlorophyll concentration. PlantPhysiology, 1977, 60(4): 606-608. |
| 22 | Nxele X, Klein A, Ndimba B K. Drought and salinity stress alters ROS accumulation, water retention, and osmolyte content in sorghum plants. South African Journal of Botany, 2017, 108: 261-266. |
| 23 | Zhang R M, Sun Y K, Liu Z Y, et al. Effects of melatonin on seedling growth, mineral nutrition, and nitrogen metabolism in cucumber under nitrate stress. Journal of Pineal Research, 2017, 62(4): e12403. |
| 24 | Niu L M. Analyses of chlorophyll degradation and antioxidative characteristics of flag leaf and ear organs in wheat under water deficit. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2019. |
| 牛连梅. 水分亏缺对小麦旗叶和穗器官叶绿素降解及抗氧化特性的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. | |
| 25 | Wen J R, Ke Y P, Yu X J, et al. Evaluation of drought resistance in 54 maize inbred lines under 20% PEG-6000 stress seedling stages. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2021, 29(1): 46-53. |
| 文景茹, 柯永培, 余学杰, 等. 20%PEG-6000胁迫下54个玉米自交系苗期抗旱性评价. 玉米科学, 2021, 29(1): 46-53. | |
| 26 | Sarropoulou V N, Therios I N, Dimassi‐Theriou K N. Melatonin promotes adventitious root regeneration in in vitro shoot tip explants of the commercial sweet cherry rootstocks CAB‐6P (Prunus cerasus L.), Gisela 6 (P. cerasus×P. canescens), and M×M 60 (P. avium×P. mahaleb). Journal of Pineal Research, 2012, 52(1): 38-46. |
| 27 | Qiao Y, Ren J, Yin L, et al. Exogenous melatonin alleviates PEG-induced short-term water deficiency in maize by increasing hydraulic conductance. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 1-14. |
| 28 | Ankita S, Surinder K S, Alok K, et al. Proline content and membrane permeability index in response to water stress in recombinant inbred lines of lentil. Vegetos, 2017, 30: 2. |
| 29 | Sadak M S, Bakry B A. Alleviation of drought stress by melatonin foliar treatment on two flax varieties under sandy soil. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2020, 26(5): 907-919. |
| 30 | Cui G, Zhao X X, Liu S D, et al. Beneficial effects of melatonin in overcoming drought stress in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 118: 138-149. |
| 31 | Wang P, Sun X, Li C, et al. Long‐term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought‐induced leaf senescence in apple. Journal of Pineal Research, 2013, 54(3): 292-302. |
| 32 | Ma X Q, Zhang J, Burgess P, et al. Interactive effects of melatonin and cytokinin on alleviating drought-induced leaf senescence in creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2018, 145: 1-11. |
| 33 | Ahmad S, Wang G Y, Muhammad I, et al. Application of melatonin-mediated modulation of drought tolerance by regulating photosynthetic efficiency, chloroplast ultrastructure, and endogenous hormones in maize. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 2022, 9(1): 1-14. |
| 34 | Huang B, Chen Y E, Zhao Y Q, et al. Exogenous melatonin alleviates oxidative damages and protects photosystem II in maize seedlings under drought stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 677. |
| 35 | Guo J, Yang Y, Wang G, et al. Ecophysiological responses of Abies fabri seedlings to drought stress and nitrogen supply. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 139(4): 335-347. |
| 36 | He J H, Chen J Z, Xu J Q, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on physiological mechanism of drought resistance of tobacco seedlings. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(2): 50-57. |
| 贺嘉豪, 陈建中, 徐坚强, 等. 外源褪黑素对烟草幼苗抗旱性生理机制的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(2): 50-57. | |
| 37 | Meng J F, Xu T F, Wang Z Z, et al. The ameliorative effects of exogenous melatonin on grape cuttings under water‐deficient stress: Antioxidant metabolites, leaf anatomy, and chloroplast morphology. Journal of Pineal Research, 2014, 57(2): 200-212. |
| 38 | Fan H X, Zhao S, Xin G Q, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonine on the physiological characteristics of peony seedlings under drought stress. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(6): 63-72. |
| 范海霞, 赵飒, 辛国奇, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下牡丹幼苗生理特性的影响. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(6): 63-72. | |
| 39 | Su Z H, Zhou Z B, Jiang X L, et al. Physiological and biochemical characteristics and adaptability of Tamarix taklamakanensis in different ecological habitats in the Tarim Basin. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(1): 198-206. |
| 苏志豪, 周晓兵, 姜小龙, 等. 不同土壤水分条件下沙生柽柳(Tamarix taklamakanensis)的生理生化特征及适应性. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(1): 198-206. | |
| 40 | Gu X B, Lu L H, Song G H, et al. The mitigative effect of exogenous melatonin pretreatment on peach seedling growth under drought stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2022, 58(2): 309-318. |
| 古咸彬, 陆玲鸿, 宋根华, 等. 外源褪黑素预处理对干旱胁迫下桃苗生长的缓解效应. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(2): 309-318. | |
| 41 | Sharma A, Wang J, Xu D. Melatonin regulates the functional components of photosynthesis, antioxidant system, gene expression, and metabolic pathways to induce drought resistance in grafted Carya cathayensis plants. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 713: 136675. |
| 42 | Cao L. Regulatory effects of exogenous melatonin on carbon and nitrogen metabolism, yield and quality of soybean during grain filling under drought stress. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 曹亮. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下鼓粒期大豆碳氮代谢及产量品质的调控效应. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2020. | |
| 43 | Zhong C, Bai Z G, Zhu L F, et al. Nitrogen-mediated alleviation of photosynthetic inhibition under moderate water deficit stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2019, 157: 269-282. |
| 44 | Zhao C, Guo H, Wang J, et al. Melatonin enhances drought tolerance by regulating leaf stomatal behavior, carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and related gene expression in maize plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 779382. |
| [1] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [2] | 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 贺海明, 马霜, 马风华, 宋柯辰. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [3] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [4] | 张一龙, 喻启坤, 李雯, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根地上地下表型特征及内源激素对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [5] | 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 李满有, 倪旺, 冯琴, 妥昀昀, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| [6] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| [7] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 孙晓梵. 两类新疆狗牙根抗旱基因型抗氧化酶保护系统及其基因表达差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| [8] | 姚露花, 綦才, 杨建峰, 郭彦军. 种子引发对甜高粱角质层蜡质及其抗性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 185-196. |
| [9] | 金祎婷, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 梁国玲, 贾志锋. 全生育期干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 112-126. |
| [10] | 苏世平, 李毅, 刘小娥, 种培芳, 单立山, 后有丽. 外源脯氨酸对缓解红砂干旱胁迫的机理研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 127-138. |
| [11] | 孙晓梵, 张一龙, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同施氮量对干旱下狗牙根抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. |
| [12] | 杨德智, 王晨, 侯明杰, 王虎成. 饲用甜高粱和全株玉米青贮对肉羊前胃微生态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 145-154. |
| [13] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [14] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [15] | 吴雨涵, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 张永超. 干旱胁迫对燕麦幼苗叶片光合特性及活性氧清除系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 75-86. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 267
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 209
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||