

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 34-45.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023141
李俊瑶1,2( ), 蒋星驰1,3, 胡晋瑜4, 魏栋光5, 赵学勇1, 王少昆1(
), 蒋星驰1,3, 胡晋瑜4, 魏栋光5, 赵学勇1, 王少昆1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-28
修回日期:2023-06-05
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2023-12-27
通讯作者:
王少昆
作者简介:E-mail: wangsk@lzb.sc.cn基金资助:
Jun-yao LI1,2( ), Xing-chi JIANG1,3, Jin-yu HU4, Dong-guang WEI5, Xue-yong ZHAO1, Shao-kun WANG1(
), Xing-chi JIANG1,3, Jin-yu HU4, Dong-guang WEI5, Xue-yong ZHAO1, Shao-kun WANG1( )
)
Received:2023-04-28
Revised:2023-06-05
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Shao-kun WANG
摘要:
添加高效纤维素分解菌于农牧业有机冗余物中,通过有氧发酵制备出具有一定保水性、透气性和肥力的生物有机肥(MOF)。在乌拉特荒漠草原试验区进行MOF施加相关试验,施加量为1 kg·m-2。结果表明,MOF的施加可以通过促进植被生长、改良土壤理化性质以及增加微生物数量等方式对退化荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物系统起到快速恢复作用。其中,植被盖度增加了33%;土壤黏粉粒含量增加了2%,土壤全碳含量增加了9%,土壤全氮含量增加了0.9%;土壤细菌中11个门类数量变化差异显著,土壤真菌中1个门类数量变化差异显著;植被盖度增加的92%可由MOF的施加和土壤含水率共同解释,物种丰富度增加的84%可由MOF施加、土壤含水率和土壤电导率共同解释。试验结果为施加生物有机肥在干旱区荒漠草原产生的恢复作用提供了理论依据、数据支持以及技术支撑。
李俊瑶, 蒋星驰, 胡晋瑜, 魏栋光, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 生物有机肥施加对荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 34-45.
Jun-yao LI, Xing-chi JIANG, Jin-yu HU, Dong-guang WEI, Xue-yong ZHAO, Shao-kun WANG. The effect of microbial organic fertilizers application on vegetation-soil-microbe in desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 34-45.
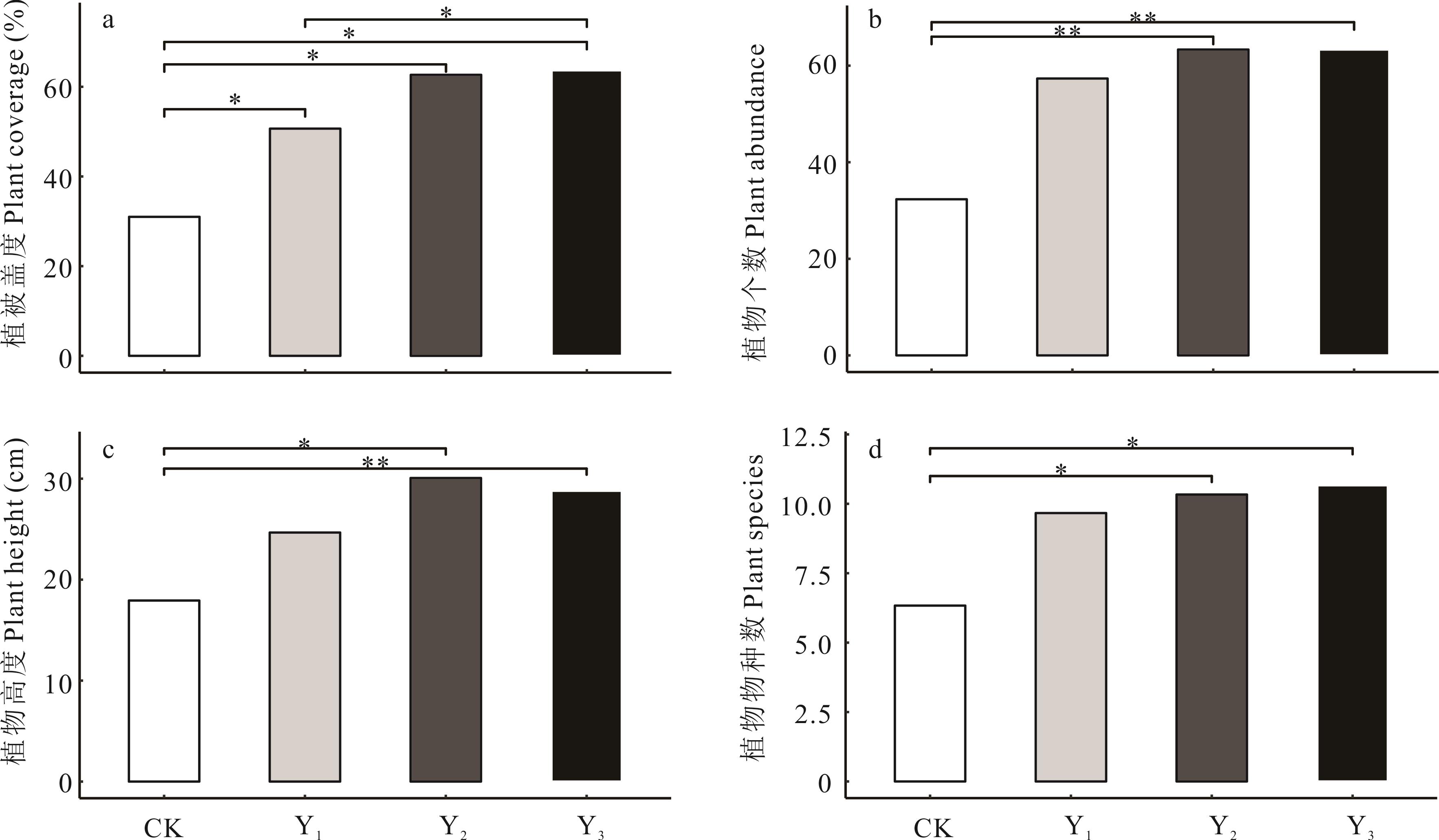
图1 施肥后不同恢复年限植被特征CK:对照Control;Y1:施肥后恢复1年Recovery after fertilization for 1 year;Y2:施肥后恢复2年Recovery after fertilization for 2 years;Y3:施肥后恢复3年Recovery after fertilization for 3 years. ***: P<0.001; **: P<0.01; *: P<0.05. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Vegetation characteristics in different restoration years after fertilization
处理 Treatment | 机械组成 Soil particle size distribution | 土壤含水率 Soil water content (SWC, %) | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductivity (EC, μS·cm-1) | 全碳含量 Total carbon content (TC, %) | 全氮含量 Total nitrogen content(TN, %) | 碳氮比 Carbon/ nitrogen (C/N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
粗砂 Coarse sand (CS, %) | 细砂 Fine sand (FS, %) | 黏粉粒 Silt and clay (SC, %) | |||||||
| CK | 81.7±1.4a | 15.6±1.2a | 2.7±0.8b | 2.4±0.3b | 8.93±0.04a | 48.00±8.39b | 5.7±1.6c | 0.3±0.1b | 16.54±2.75a |
| Y1 | 83.0±3.4a | 14.1±3.4a | 2.9±0.4b | 4.5±0.7a | 8.78±0.17ab | 88.17±47.57ab | 7.3±0.7bc | 0.5±0.0b | 15.31±0.23ab |
| Y2 | 81.1±0.4a | 15.1±1.0a | 3.8±0.7ab | 4.0±0.9a | 8.59±0.14b | 98.17±21.87ab | 10.1±2.1b | 0.6±0.1b | 17.57±0.86a |
| Y3 | 77.9±4.5a | 17.3±3.2a | 4.8±1.3a | 2.9±0.2b | 8.61±0.24b | 136.83±7.09ab | 15.3±2.8a | 1.2±0.3a | 12.76±0.82b |
表1 不同施肥处理荒漠草原土壤理化性质特征
Table 1 Physical properties of desert steppe soil in different fertilization treatments
处理 Treatment | 机械组成 Soil particle size distribution | 土壤含水率 Soil water content (SWC, %) | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductivity (EC, μS·cm-1) | 全碳含量 Total carbon content (TC, %) | 全氮含量 Total nitrogen content(TN, %) | 碳氮比 Carbon/ nitrogen (C/N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
粗砂 Coarse sand (CS, %) | 细砂 Fine sand (FS, %) | 黏粉粒 Silt and clay (SC, %) | |||||||
| CK | 81.7±1.4a | 15.6±1.2a | 2.7±0.8b | 2.4±0.3b | 8.93±0.04a | 48.00±8.39b | 5.7±1.6c | 0.3±0.1b | 16.54±2.75a |
| Y1 | 83.0±3.4a | 14.1±3.4a | 2.9±0.4b | 4.5±0.7a | 8.78±0.17ab | 88.17±47.57ab | 7.3±0.7bc | 0.5±0.0b | 15.31±0.23ab |
| Y2 | 81.1±0.4a | 15.1±1.0a | 3.8±0.7ab | 4.0±0.9a | 8.59±0.14b | 98.17±21.87ab | 10.1±2.1b | 0.6±0.1b | 17.57±0.86a |
| Y3 | 77.9±4.5a | 17.3±3.2a | 4.8±1.3a | 2.9±0.2b | 8.61±0.24b | 136.83±7.09ab | 15.3±2.8a | 1.2±0.3a | 12.76±0.82b |
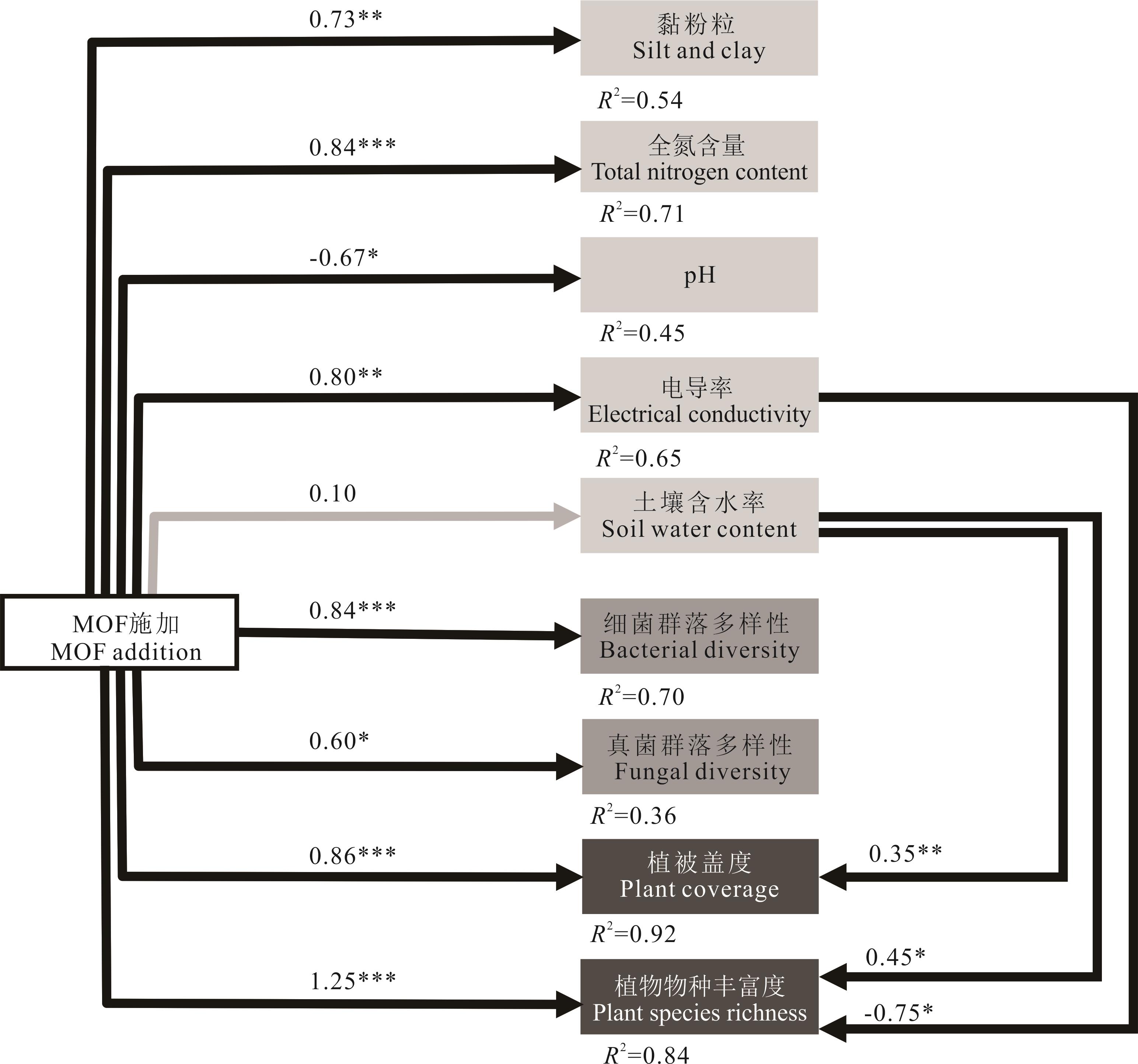
图6 分段结构方程模型箭头上的数值为标准差估计值,R2 表示解释度。整体模型Fisher’s C=53.102,P=0.874,AIC=113.102。The values on top of the arrows are standard deviation estimates and the asterisks indicate statistical significance, R2 means interpretation rate. Fisher’s C=53.102, P=0.874, AIC=113.102.
Fig.6 Piecewise structural equation model
| 1 | Kang L, Han X, Zhang Z, et al. Grassland ecosystems in China: review of current knowledge and research advancement. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 2007, 362(1482): 997-1008. |
| 2 | Wu H X, Wang Z Y, Yin Q, et al. Research progress on degradation of desert steppe in northern China. Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry Science & Technology, 2017, 43(2): 58-62. |
| 武海霞, 王则宇, 尹强, 等. 我国北方荒漠草原退化研究进展. 内蒙古林业科技, 2017, 43(2): 58-62. | |
| 3 | Wang Z, Yun X J, Wei Z J, et al. Responses of plant community and soil properties to inter-annual precipitation variability and grazing durations in a desert steppe in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2014, 13(6): 1171-1182. |
| 4 | Li S G, Harazono Y, Oikawa T, et al. Grassland desertification by grazing and the resulting micrometeorological changes in Inner Mongolia. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2000, 102(2000): 125-137. |
| 5 | Zhou P, Han G D, Wang C J, et al. Effects of stocking rates on carbon flux in the desert grassland ecological system of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 32(4): 59-64. |
| 周培, 韩国栋, 王成杰, 等. 不同放牧强度对内蒙古荒漠草地生态系统含碳温室气体交换的影响. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 32(4): 59-64. | |
| 6 | Wei L, Song N P, Fang K. Effects of grazing on communities diversity in desert steppe. Journal of Jianghan University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(4): 87-91. |
| 魏乐, 宋乃平, 方楷. 放牧对荒漠草原群落多样性的影响. 江汉大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(4): 87-91. | |
| 7 | Tang Z S, An H, Deng L, et al. Changes in the plant community and soil physical properties during grassland desertification of steppes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(4): 991-1000. |
| 唐庄生, 安慧, 邓蕾, 等. 荒漠草原沙漠化植物群落及土壤物理变化. 生态学报, 2016, 36(4): 991-1000. | |
| 8 | Chang H T, Zhao J, Liu J N, et al. Changes in soil physico-chemical properties and related fractal features during conversion of cropland into agroforestry and grassland: A case study of desertified steppe in Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(7): 14-25. |
| 常海涛, 赵娟, 刘佳楠, 等. 退耕还林与还草对土壤理化性质及分形特征的影响——以宁夏荒漠草原为例. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 14-25. | |
| 9 | Rong H, He J L, Zhang X, et al. Relationship between aboveground biomass and soil moisture of different vegetation restoration models on desert steppe. Grassland and Turf, 2018, 38(5): 71-76. |
| 荣浩, 何京丽, 张欣, 等. 荒漠草原不同植被恢复模式地上生物量与土壤水分的关系. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(5): 71-76. | |
| 10 | Wen X P, Zhang Y L, Li H J. The review of desert grassland restoration. Science Mosaic, 2013(12): 252-256. |
| 文小平, 张银玲, 李宏建. 荒漠草原恢复文献综述. 科技广场, 2013(12): 252-256. | |
| 11 | Tian X M, Ma C X, Xing E D. Restoration and management measures for degraded grasslands of family ranches in desert steppe area. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(36): 105-110. |
| 田秀民, 马春霞, 邢恩德. 荒漠草原区家庭牧场退化草地恢复管理措施研究. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(36): 105-110. | |
| 12 | Chun L, Han W J, Wang H, et al. Effect of fertilizations on vegetation of the degraded desert steppe. Grassland and Prataculture, 2015, 27(3): 22-26. |
| 春亮, 韩文军, 王海, 等. 施肥对荒漠草原退化草地植被特征的影响. 草原与草业, 2015, 27(3): 22-26. | |
| 13 | Li L H, Sun S G, Yang S L. Change of community characteristics in restoration degraded desert steppe. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2013, 41(10): 4526-4527. |
| 李兰花, 孙树光, 杨胜利. 退化荒漠草原恢复过程中植被生态学特性的变化. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(10): 4526-4527. | |
| 14 | Bayaertu, Na Y, Liu D Q, et al. Present situation and protection and utilization measures of natural grassland resources in Urat Middle Banner. Grassland and Prataculture, 2017, 1(29): 9-12. |
| 巴雅尓图, 那亚, 刘东庆, 等. 乌拉特中旗天然草地资源现状及保护利用措施. 草原与草业, 2017, 1(29): 9-12. | |
| 15 | Qiu B, Luo Y J. Effects of fertilizer gradients on productivity and species diversity in a degraded alpine meadow. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2004, 40(3): 56-59. |
| 邱波, 罗燕江. 不同施肥梯度对甘南退化高寒草甸生产力和物种多样性的影响. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 40(3): 56-59. | |
| 16 | Sun B. Three grassland improvement measures on alpine degraded grassland vegetation. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2005, 40(6): 797-801. |
| 孙斌. 三种改良措施对高寒退化草地植被的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2005, 40(6): 797-801. | |
| 17 | Cheng J M, Jia H Y, Peng X L. Biomass structure of fertilized grassland communities. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 1997, 6(2): 22-27. |
| 程积民, 贾恒义, 彭详林. 施肥草地群落生物量结构的研究. 草业学报, 1997, 6(2): 22-27. | |
| 18 | Cheng J M, Jia H Y, Peng X L. Study on vegetation community structure and its succession on fertilization grassland. Research on Soil and Water Conservation, 1996, 3(4): 124-128. |
| 程积民, 贾恒义, 彭详林. 施肥草地植被群落结构和演替的研究. 水土保持研究, 1996, 3(4): 124-128. | |
| 19 | Zhou G Y, Chen G C, Zhao Y L, et al. Comparative research on the influence of chemical fertilizer application and enclosure on alpine steppes in the Qinghai Lake area structure and species diversity of the plant community. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2004, 13(1): 26-31. |
| 周国英, 陈桂琛, 赵以莲, 等. 施肥和围栏封育对青海湖地区高寒草原影响的比较研究I群落结构及其物种多样性. 草业学报, 2004, 13(1): 26-31. | |
| 20 | Zhou G Y, Chen G C, Zhao Y L, et al. Comparative studies on the influence of chemical fertilizer application and enclosure on alpine steppes in Qinghai Lake area Ⅱ seasonal and annual biomass dynamics. Pratacultural Science, 2005, 22(1): 59-63. |
| 周国英, 陈桂琛, 赵以莲, 等. 施肥和围栏封育对青海湖地区高寒草原影响的比较研究Ⅱ地上生物量季节动态. 草业科学, 2005, 22(1): 59-63. | |
| 21 | Du Z Y, An H, Wang B, et al. Effects of nutrient addition and precipitation manipulation on plant species diversity and biomass of in a desert grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 1100-1110. |
| 杜忠毓, 安慧, 王波, 等. 养分添加和降水变化对荒漠草原植物群落物种多样性和生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 1100-1110. | |
| 22 | Lu H, Yao T, Li J H, et al. Vegetation and soil microorganism characteristics of degraded grasslands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(5): 34-43. |
| 卢虎, 姚拓, 李建宏, 等. 高寒地区不同退化草地植被和土壤微生物特性及其相关性研究. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 34-43. | |
| 23 | Li X, Wang Y C. The biodiversity of soil microbes and plants. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 6(37): 708-713. |
| 李骁, 王迎春. 土壤微生物多样性与植物多样性. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 6(37): 708-713. | |
| 24 | Li X Q, Liu Y G, Song G J, et al. Current situation and development trend of microbial organic fertilizer industry in China. China Fruit & Vegetable, 2019, 39(4): 35-38. |
| 李西强, 刘延刚, 宋国静, 等. 国内微生物有机肥生产现状与发展趋势. 中国果菜, 2019, 39(4): 35-38. | |
| 25 | Wang L G, Li W J, Qiu J, et al. Effect of biological organic fertilizer on crops growth, soil fertility and yield. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2004(5): 12-16. |
| 王立刚, 李维炯, 邱建, 等. 生物有机肥对作物生长、土壤肥力及产量的效应研究. 土壤肥料, 2004(5): 12-16. | |
| 26 | Yuan X M, Zhang G J, Cai M Q, et al. Effects of base application of microbial organic fertilizer on soil improvement and rice yield. Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020(5): 101-105. |
| 袁晓明, 张国江, 蔡明清, 等. 基施微生物有机肥对土壤改良效果及水稻产量的影响. 上海农业科技, 2020(5): 101-105. | |
| 27 | Kong D J. Effect on nitrogen and carbon content and microbial community structure of wheat soybean rotation soil under straw return and fertilizer application treatments. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2020. |
| 孔德杰. 秸秆还田和施肥对麦豆轮作土壤碳氮及微生物群落的影响. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020. | |
| 28 | Ai C. Distinct responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to changes in fertilization regime and crop rotation. Geoderma, 2018, 319(2018): 156-166. |
| 29 | Saha S, Mina B L, Gopinath K A, et al. Organic amendments affect biochemical properties of a subtemperate soil of the Indian Himalayas. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2008(80): 233-242. |
| 30 | Wang S K, Zhao X Y, Wang X J, et al. Organic compound and its utilization in sandy land restoration. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 36(4): 990-996. |
| 王少昆, 赵学勇, 王晓江, 等. 有机混合物的制备及其在退化沙地恢复方面的应用. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(4): 990-996. | |
| 31 | Lu T T, Zhai X J, Liu X J, et al. Influences of fertilizer, irrigation fire on community characteristics and soil nutrient in desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(3): 57-66. |
| 陆婷婷, 翟夏杰, 刘晓娟, 等. 施肥、灌溉及火烧对荒漠草原土壤养分和植物群落特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(3): 57-66. | |
| 32 | Qu G R. Effects of fertilization on vegetation characteristics of degraded grassland in desert steppe. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2021, 11(3): 45-49. |
| 屈革荣. 施肥对荒漠草原退化草地植被特征的影响研究. 农业灾害研究, 2021, 11(3): 45-49. | |
| 33 | Wang S K, Zhao X Y, Jia K F, et al. Soil bacterial diversity and its vertical distribution in Stipa klemenzii community of Urat Desert Steppe. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 6(36): 1564-1570. |
| 王少昆, 赵学勇, 贾昆峰, 等. 乌拉特荒漠草原小针茅(Stipa klemenzii)群落土壤细菌多样性及垂直分布特征. 中国沙漠, 2016, 6(36): 1564-1570. | |
| 34 | Jiang X C, Li J Y, Chen F, et al. Soil bacterial characteristics of six plant communities in the desert areas to the North of Yinshan Mountains. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(4): 1122-1132. |
| 蒋星驰, 李俊瑶, 陈峰, 等. 阴山北麓荒漠区6种植物群落的土壤细菌特征. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(4): 1122-1132. | |
| 35 | Jiao R X, Bu D S, Zhang T, et al. Evaluation of soil nutrient status in Alar cotton planting area of Xinjiang. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2023, 41(2): 160-167. |
| 焦润兴, 卜东升, 张涛, 等. 新疆阿拉尔植棉区土壤养分丰缺状况评价. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(2): 160-167. | |
| 36 | Mohd Yusoff M Z, Hu A Y, Feng C J, et al. Influence of pretreated activated sludge for electricity generation in microbial fuel cell application. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 145: 90-96. |
| 37 | Adams R I, Miletto M, Taylor J W, et al. Dispersal in microbes: fungi in indoor air are dominated by outdoor air and show dispersal limitation at short distances. The ISME Journal, 2013, 7(7): 1262-1273. |
| 38 | Chen S B, Ouyang Z Y, Xu W H, et al. A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 2010, 18(4): 323-335. |
| 39 | Ginestet C. Ggplot 2: Elegant graphics for data analysis: Book reviews. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society), 2011, 174(1): 245-246. |
| 40 | Lefcheck J S. PIECEWISESEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in R for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2016, 7(5): 573-579. |
| 41 | Liu S. Impact of manure on soil biochemical properties: A global synthesis. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 745: 1-15. |
| 42 | Shu X. Organic amendments enhance soil microbial diversity, microbial functionality and crop yields: A meta-analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 829: 1-9. |
| 43 | Maeder P, Fliessbach A, Dubois D, et al. Soil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming. Science, 2002, 296(1694): 1693-1697. |
| 44 | Richard D B, Wim H van der Putten. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 2014, 515: 505-511. |
| 45 | Gu S S, Hu Q L, Cheng Y Q, et al. Application of organic fertilizer improves microbial community diversity and alters microbial network structure in tea (Camellia sinensis) plantation soils. Soil & Tillage Research, 2019, 195: 1-10. |
| 46 | Jiang J Y, Liu R T, Zhang A N. Comparative analysis of soil fractal dimension and soil physical and chemical properties between Caragana korshinskii shrub plantations in arid and semi-arid desert steppe. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(4): 54-61, 69. |
| 蒋嘉瑜, 刘任涛, 张安宁. 干旱与半干旱荒漠草原区柠条灌丛土壤分形维数与理化性质对比分析. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(4): 54-61, 69. | |
| 47 | Semenov M V. Long-term fertilization rather than plant species shapes rhizosphere and bulk soil prokaryotic communities in agroecosystems. Applied Soil Ecology, 2020, 154(10): 103641. |
| 48 | Guo Z, Wan S, Hua K, et al. Fertilization regime has a greater effect on soil microbial community structure than crop rotation and growth stage in an agroecosystem. Applied Soil Ecology, 2020, 149: 103510. |
| [1] | 段鹏, 韦鎔宜, 王芳萍, 姚步青, 赵之重, 胡碧霞, 宋词, 杨萍, 王婷. 不同养分添加对黄河源区退化高寒湿地土壤微生物碳源利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 138-153. |
| [2] | 赵敏, 赵坤, 王赟博, 殷国梅, 刘思博, 闫宝龙, 孟卫军, 吕世杰, 韩国栋. 长期放牧干扰降低了短花针茅荒漠草原植物多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 39-49. |
| [3] | 刘欣雷, 杜鹤强, 刘秀帆, 范亚伟. 内蒙古荒漠草原地表风沙活动对放牧强度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 1-11. |
| [4] | 陈彦硕, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽, 张振杰. 荒漠草原不同年限灌丛引入过程土壤细菌碳源利用特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 30-44. |
| [5] | 李思媛, 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤有机碳及土壤微生物生物量生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 58-70. |
| [6] | 胡宇霞, 龚吉蕊, 朱趁趁, 矢佳昱, 张子荷, 宋靓苑, 张魏圆. 基于生态系统服务簇的内蒙古荒漠草原生态系统服务的空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 1-14. |
| [7] | 江奥, 敬路淮, 泽让东科, 田黎明. 放牧影响草地凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 208-220. |
| [8] | 李江文, 裴婧宏, 韩国栋, 何邦印, 李彩. 基于植物功能性状分析异常降水对不同载畜率下荒漠草原功能群多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 212-222. |
| [9] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波, 任小玢. 降水对荒漠草原地上生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 30-39. |
| [10] | 米扬, 郭蓉, 王媛, 王占军, 蒋齐, 俞鸿千, 马琨. 宁夏荒漠草原土壤细菌与真菌群落对降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 81-92. |
| [11] | 苏荣霞, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽. 荒漠草原不同间距灌丛引入对土壤细菌碳源利用和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 93-105. |
| [12] | 牛伟玲, 陈辉, 侯慧新, 郭晨睿, 马娇林, 武建双. 10年禁牧未改变藏西北高寒荒漠植物水氮利用效率[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [13] | 刘万龙, 许冬梅, 史佳梅, 许爱云. 不同群落生境蒙古冰草种群株丛结构和叶片功能性状的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. |
| [14] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [15] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||