

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 147-159.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024029
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-01-17
修回日期:2024-03-15
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
石凤翎
作者简介:E-mail: shifengling@imau.edu.cn基金资助:
Jing XING( ), Wen-qiang FAN, Jia-ni WANG, Feng-ling SHI(
), Wen-qiang FAN, Jia-ni WANG, Feng-ling SHI( )
)
Received:2024-01-17
Revised:2024-03-15
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Feng-ling SHI
摘要:
干旱作为一种严重影响植物生长发育和作物生产的环境因素之一,需要一种高效但不会对环境造成影响的方法来缓解其对植物带来的危害。通常土壤微生物被认为可以与植物进行互作从而改善环境带来的不良影响,但仍需验证在植物受到干旱胁迫时土壤微生物是否可以发挥关键性作用?通过对蒙农2号、蒙农1号扁蓿豆进行灭菌和未灭菌处理,测定其生长表型与生理特性的变化,以揭示土壤微生物在扁蓿豆应对胁迫时所发挥的作用,同时对正常浇水及干旱胁迫后的根际土壤进行16S rRNA高通量测序分析,以期明晰品种介导的扁蓿豆根际微生物对干旱胁迫的响应变化规律,并探究发挥关键作用的菌群。结果表明,干旱胁迫下未灭菌处理显著提高了蒙农2号和蒙农1号扁蓿豆的株高增量、地上干重、地下干重,同时显著降低了脯氨酸(Pro)与丙二醛(MDA)含量,增强了过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性。正常浇水条件下,蒙农2号与蒙农1号扁蓿豆其根际细菌中变形菌门占比分别为72.83%、67.65%,根瘤菌占比分别为5.28%、3.65%;干旱胁迫后蒙农2号与蒙农1号扁蓿豆根际细菌中变形菌门相对丰度下降了8.42%、4.76%,而根瘤菌相对丰度增加了1.69%和2.35%。同时推测根瘤菌为扁蓿豆抗旱相关的核心微生物,并且蒙农2号扁蓿豆在水分充足的情况下根际富集了比蒙农1号更多的根瘤菌,这使得其在受到干旱胁迫时能够更加快速地做出反应。总而言之,研究证明土壤微生物在植物抵抗干旱胁迫中发挥了积极作用,根际微生物可以提高扁蓿豆对干旱胁迫的耐受能力,微生物组成和丰度受干旱胁迫和植物宿主的调节,且各自效果差异较大,进一步说明微生物的富集过程与植物基因型密切相关。
邢静, 范文强, 王佳妮, 石凤翎. 干旱胁迫下 2个扁蓿豆品种根际细菌多样性及土壤灭菌对其生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 147-159.
Jing XING, Wen-qiang FAN, Jia-ni WANG, Feng-ling SHI. Rhizosphere bacterial diversity and the effects of soil sterilization on the growth of two varieties of Medicago ruthenica under drought stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 147-159.
| pH | 有机碳Organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 速效磷Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.27±0.03 | 17.25±0.30 | 276.98±4.69 | 11.46±0.55 | 0.91±0.04 | 1.17±0.04 |
表1 土壤理化性质
Table 1 Soil physical and chemical properties
| pH | 有机碳Organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 速效磷Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.27±0.03 | 17.25±0.30 | 276.98±4.69 | 11.46±0.55 | 0.91±0.04 | 1.17±0.04 |
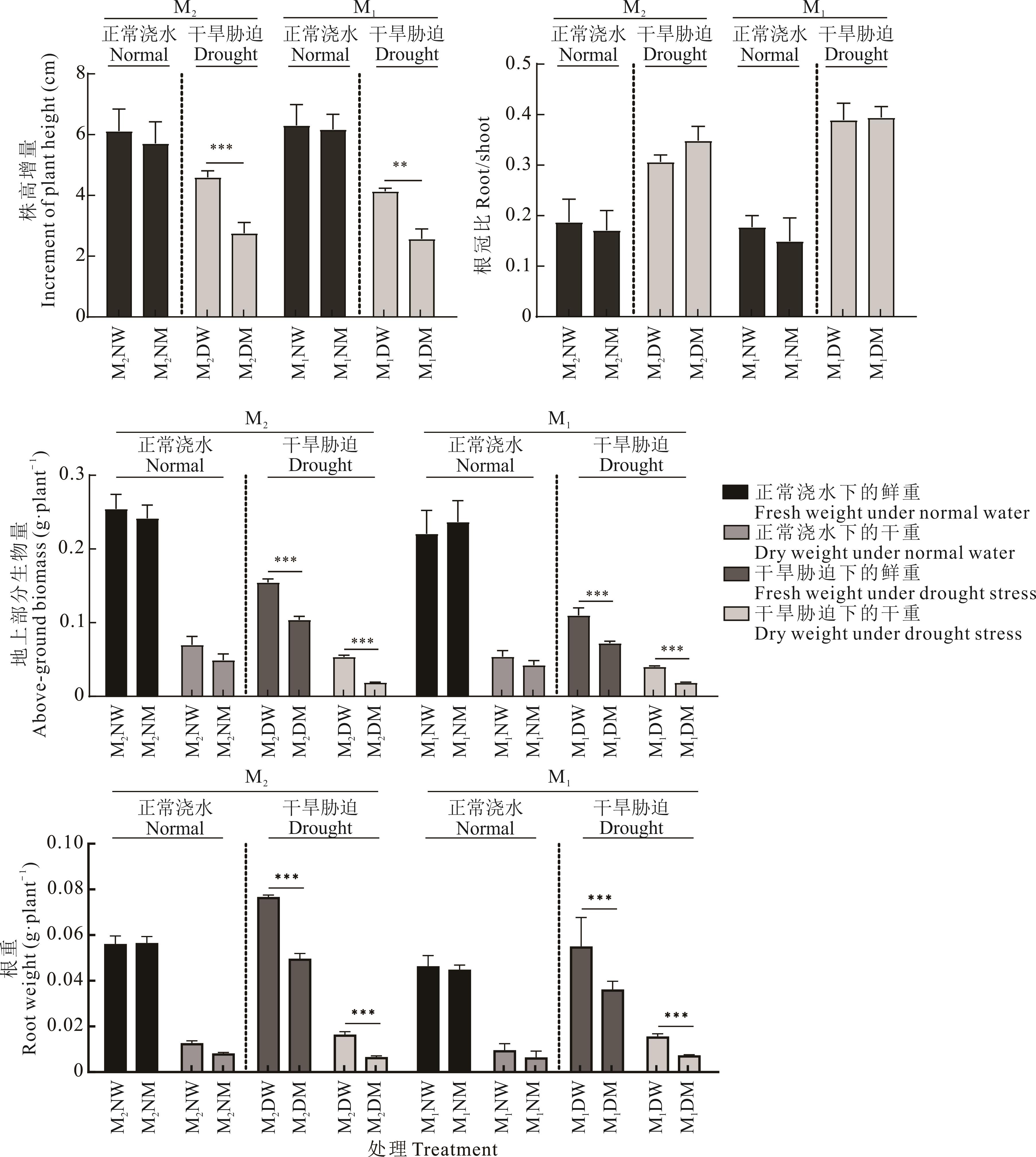
图1 干旱胁迫期间两个扁蓿豆品种未灭菌与灭菌处理下生长特性的变化数据为 15 个重复的均值,误差条表示标准差Datas are the mean of 15 replicates, and error bars represent standard deviations; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Changes in growth characteristics of two M. ruthenica varieties under unsterilized and sterilized treatments during drought stress

图2 干旱胁迫期间两个扁蓿豆品种未灭菌与灭菌处理下生理特性的变化
Fig.2 Changes in physiological characteristics of two M. ruthenica varieties under unsterilized and sterilized treatments during drought stress

图4 基于不同处理条件和扁蓿豆品种的微生物多样性差异分析A: 正常浇水和干旱胁迫下M2与M1的根际土壤样本中的重叠和不同的ASV数量Overlapping and different ASV numbers in rhizosphere soil samples of M2 and M1 under normal watering and drought stress; B: 基于weighted_unifrac距离的PCoA分析PCoA analysis based on weighted_unifrac distance.
Fig.4 Differences in microbial diversity under different treatment conditions and M. ruthenica varieties
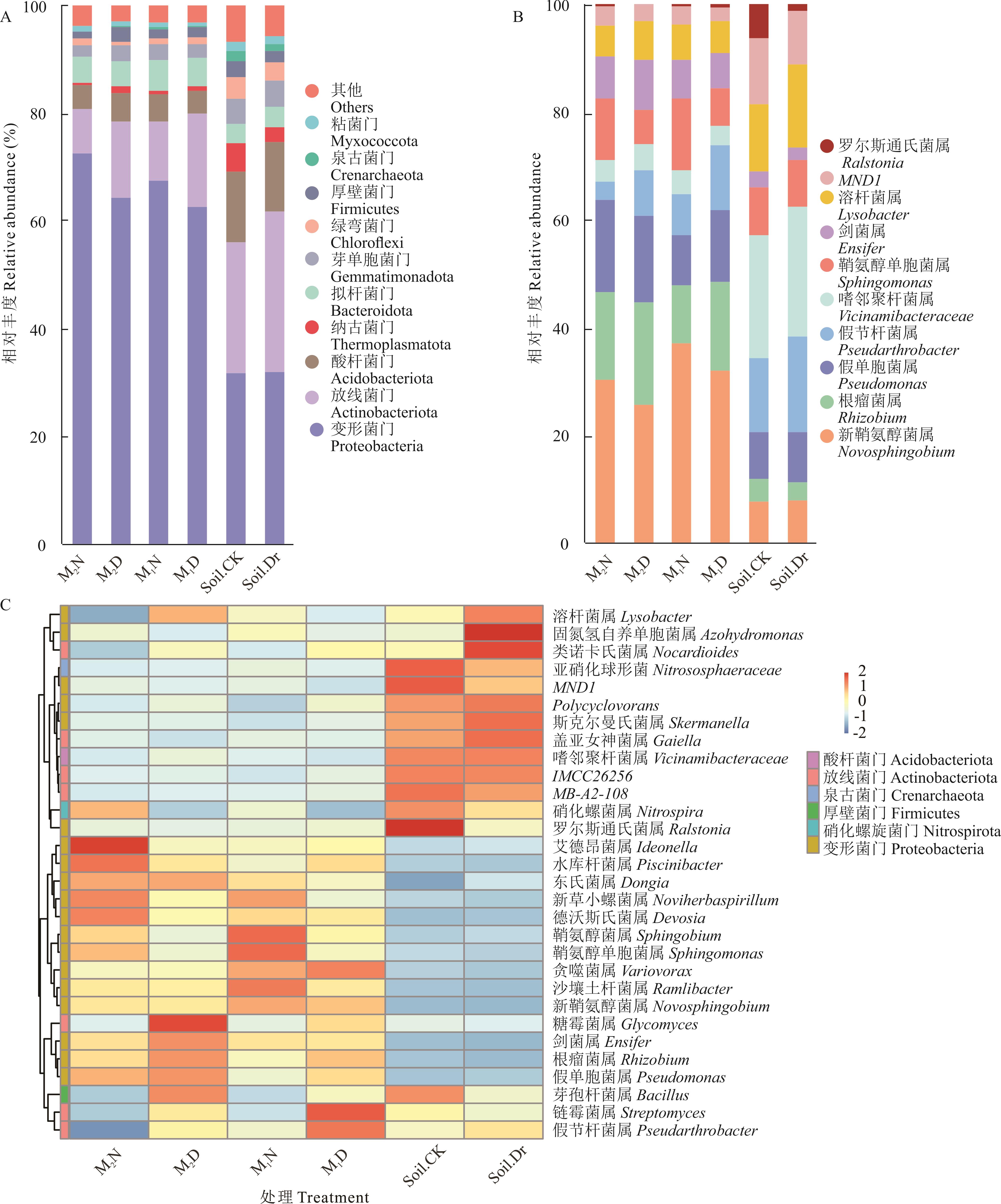
图5 不同水分条件处理下两个扁蓿豆品种根际土壤细菌群落组成的差异A: 门分类水平下的细菌群落相对丰度(相对丰度前10)Relative abundance of bacterial communities at phylum taxonomic level (top 10 relative abundances); B: 属分类水平下的细菌群落相对丰度(相对丰度前10)Relative abundance of bacterial communities at genus levels (top 10 relative abundances); C: 前30个属水平下细菌群落的平均相对丰度热图聚类Heatmap clustering of the average relative abundance of bacterial communities at the level of the top 30 genera.
Fig.5 Differences in the composition of rhizosphere soil bacterial communities between two M. ruthenica varieties under different water conditions
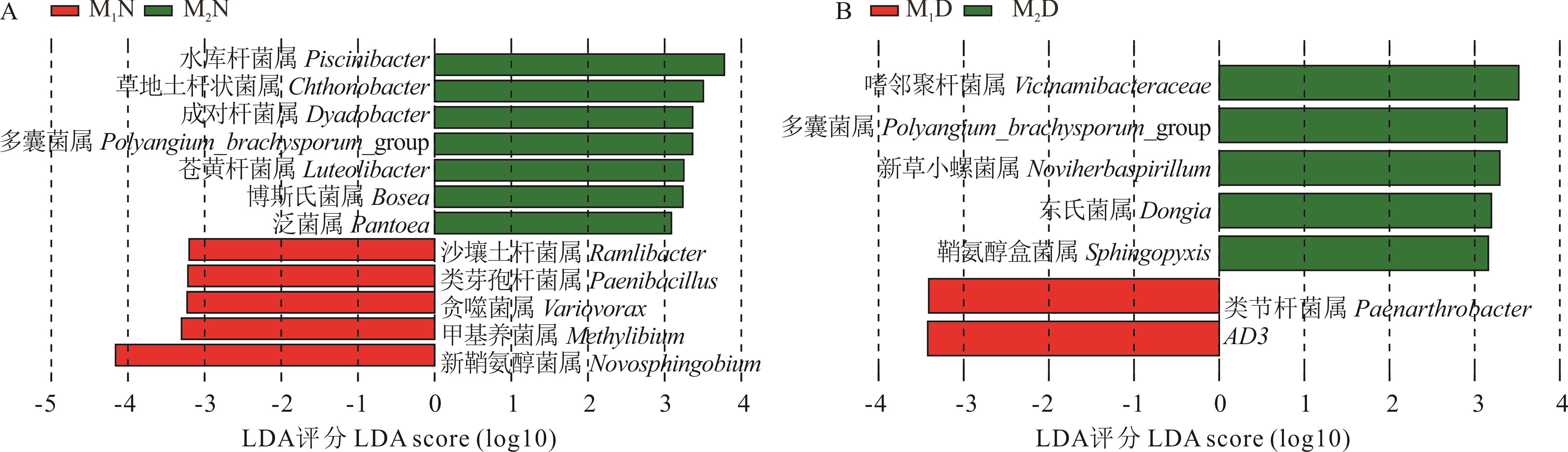
图6 根际土壤中鉴定的潜在生物标志物A: 属水平下正常浇水时的潜在生物标志物Potential biomarkers for normal watering at the genus level; B: 属水平下干旱胁迫时的潜在生物标志物Potential biomarkers under drought stress at the genus level.
Fig.6 Potential biomarkers identified in rhizosphere soils
| 1 | Chen Y N, Li Y P, Li Z, et al. Analysis of the impact of global climate change on dryland areas. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(2): 111-119. |
| 陈亚宁, 李玉朋, 李稚, 等. 全球气候变化对干旱区影响分析. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(2): 111-119. | |
| 2 | Stringer L C, Mirzabaev A, Benjaminsen T A, et al. Climate change impacts on water security in global drylands. One Earth, 2021, 4(6): 851-864. |
| 3 | Shi S G. The impact of climate change on the hydrological drought characteristics of the Weihe River Basin. Shaanxi Water Resources, 2023(9): 60-62. |
| 师晟国. 气候变化对渭河流域水文干旱特征的影响研究. 陕西水利, 2023(9): 60-62. | |
| 4 | Shayanmehr S, Porhajašová J I, Babošová M, et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and crop production in an arid region. Agriculture, 2022, 12(7): 1056. |
| 5 | Dong J Q, Yang Y T, Fan W Q, et al. Identification of Medicago ruthenica hybrids and heterosis analysis of main agronomic traits in F1 and F2. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 229-239. |
| 董佳琦, 杨艳婷, 范文强, 等. 扁蓿豆种内杂种鉴定及其F1和F2代主要农艺性状优势分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 229-239 . | |
| 6 | Wu R, Xu B, Shi F L. Leaf transcriptome analysis of Medicago ruthenica revealed its response and adaptive strategy to drought and drought recovery. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22(1): 562. |
| 7 | Liu W P, Li Y X, Li Z Y, et al. Study on relationship between leaf anatomical traits and drought resistance of four different ecological types of Medicago ruthenica in Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(6): 32-43. |
| 刘万鹏, 李悦煊, 李志勇, 等. 内蒙古四种不同生态类型扁蓿豆叶片解剖性状与抗旱性关系的研究. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(6): 32-43. | |
| 8 | Li Y Y, Wu D B, Cong B M, et al. Study on rhizosphere soil microbial community driving the successful invasion of cenchrus iongispinus. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(11): 62-74. |
| 李宇宇, 吴德宝, 丛百明, 等. 驱动长刺蒺藜草成功入侵的根际土壤微生物群落研究. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(11): 62-74. | |
| 9 | Rodriguez R J, Henson J, Van Volkenburgh E, et al. Stress tolerance in plants via habitat-adapted symbiosis. International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal, 2008, 2(4): 404-416. |
| 10 | Wu C H, Liu J Z. Research progress on influencing factors of rhizosphere microorganisms and their interaction with plants. Journal of Hebei Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 46(6): 603-613. |
| 吴昌昊, 刘敬泽. 根际微生物影响因素及其与植物互作研究进展. 河北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6): 603-613. | |
| 11 | Wu J Y. Pod biological characteristics study of Medicago ruthenica L. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. |
| 吴建禹. 扁蓿豆荚果生物学特性的研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. | |
| 12 | Gu R, Sudebilige, Shi F L, et al. Physiological and biochemical responses of Medicago ruthenicus (L.) Sojak cv. Zhilixing seedling to different salt stresses. Grassland and Prataculture, 2020, 32(3): 15-20. |
| 谷蕊, 苏德毕力格, 石凤翎, 等. 直立型扁蓿豆幼苗对不同盐胁迫的生理生化响应. 草原与草业, 2020, 32(3): 15-20. | |
| 13 | Wu R N, Xu B, Shi F L. Analysis of SSR characterizatics for Medicago ruthenicus ‘Zhilixing’ based on transcriptome data. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 1-8. |
| 乌日娜, 徐舶, 石凤翎. 基于转录组数据的直立型扁蓿豆SSR序列特征分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(5): 1-8. | |
| 14 | Zhou W J, Lyu D G, Qin S J. Research progress in interaction between plant and rhizosphere microorganism. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2016, 38(3): 253-260. |
| 周文杰, 吕德国, 秦嗣军. 植物与根际微生物相互作用关系研究进展. 吉林农业大学学报, 2016, 38(3): 253-260. | |
| 15 | Bulgarelli D, Schlaeppi K, Spaepen S, et al. Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2013, 64(1): 807-838. |
| 16 | Müller D B, Vogel C, Bai Y, et al. The plant microbiota: Systems-level insights and perspectives. Annual Review of Genetics, 2016, 50(1): 211-234. |
| 17 | Glick B R. Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiological Research, 2014, 169(1): 30-39. |
| 18 | Ding Z J, Bai Y. The current status and future studies on plant root development and root microbiota (in Chinese). Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2021, 51(10): 1447-1456. |
| 丁兆军, 白洋. 根系发育和微生物组研究现状及未来发展趋势. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2021, 51(10): 1447-1456. | |
| 19 | Bulgarelli D, Rott M, Schlaeppi K, et al. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature, 2012, 488: 91-95. |
| 20 | Waheed H, Javaid M M, Shahid A, et al. Impact of foliar-applied Hoagland’s nutrient solution on growth and yield of mash bean (Vigna mungo L.) under different growth stages. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2019, 42(10): 1133-1141. |
| 21 | Isai S G, Guilhem R, Paulina F, et al. Coordination between microbiota and root endodermis supports plant mineral nutrient homeostasis. Science, 2021, 371(6525): 10.1126/science. abd0695. |
| 22 | Li X, Zhang M, Liu C Z, et al. Effects of dialectric barrier discharge plasma treatment on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Astragalus sinicus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 129-140. |
| 李想, 张梦, 刘春增, 等. 等离子体处理对紫云英种子萌发和生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 129-140. | |
| 23 | Luo Y, Li C, Wang P, et al. Responses of different oat cultivars to low-nitrogen stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 等. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. | |
| 24 | Zou Q. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2000: 161-250. |
| 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 161-250. | |
| 25 | Carey S J, Becklund L E, Fabre P P, et al. Optimizing the lysis step in CTAB DNA extractions of silica-dried and herbarium leaf tissues. Applications in Plant Sciences, 2023, 11(3): e11522. |
| 26 | Feng S L, Li B Y, Lyu G L, et al. Response characteristics of leaf water potential in different growth stages of Amorpha fruticosa seedlings to drought stress and re-watering. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1363-1371. |
| 冯树林, 李博渊, 吕国利, 等. 紫穗槐幼苗不同生长阶段叶水势对干旱胁迫与复水的响应特征. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1363-1371. | |
| 27 | Sun C X, Gao X X, Chen X, et al. Metabolic and growth responses of maize to successive drought and re-watering cycles. Agricultural Water Management, 2016, 172: 62-73. |
| 28 | Yang Z D, Xu L, Yu S Z, et al. Effect of water stress on physiological characters and root morphology of Aquilaria sinensis seedlings. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2014, 43(1): 1-5. |
| 杨振德, 徐丽, 玉舒中, 等. 水分胁迫对土沉香生理生化特性及根系形态的影响. 西部林业科学, 2014, 43(1): 1-5. | |
| 29 | He F, Lyu G X, Meng Y D, et al. Effects of drought stress and rehydration on hormone contents of Eucommia ulmoides seedling. Plant Physiology Journal, 2021, 57(12): 2279-2290. |
| 何凤, 吕庚鑫, 孟益德, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对杜仲苗激素含量的影响. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(12): 2279-2290. | |
| 30 | Chen A P, Sui X Q, Wang Y X, et al. Effects of drought and re-watering on growth and physiological characteristics of Seriphidium transiliense seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1216-1225. |
| 陈爱萍, 隋晓青, 王玉祥, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对伊犁绢蒿幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1216-1225. | |
| 31 | Mishra R, Shteinberg M, Shkolnik D, et al. Interplay between abiotic (drought) and biotic (virus) stresses in tomato plants. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2022, 23(4): 475-488. |
| 32 | Liu C, Han L H, Song P B, et al. Effects of soil microorganisms on the growth of Eupatorium purpurea and local plants in Southwest China. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(7): 104-107. |
| 刘潮, 韩利红, 宋培兵, 等. 土壤微生物对紫茎泽兰与我国西南当地植物生长的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(7): 104-107. | |
| 33 | Guo Y P, Mi F G, Yan L J, et al. Physiological response to drought stresses and drought resistances evaluation of different Kentucky bluegrass varieties. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 220-228. |
| 郭郁频, 米福贵, 闫利军, 等. 不同早熟禾品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应及抗旱性评价. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 220-228. | |
| 34 | Wang Z J, Ji B, Ji T, et al. An evaluation of drought resistance of five forage legumes based on a quantile model. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. |
| 王占军, 季波, 纪童, 等. 5种豆科牧草抗旱性研究与评价. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. | |
| 35 | Yang Z D, Zhao Y Y, Yu S Z, et al. The variations of physiological and root morphological characteristics of Dalbergia odorifera seedlings under drought stress. Forestry Science and Technology Development, 2014, 28(3): 63-66. |
| 杨振德, 赵岩岩, 玉舒中, 等.干旱胁迫对降香黄檀幼苗生理特性及根系形态特征的影响. 林业科技开发, 2014, 28(3): 63-66. | |
| 36 | Tan J R, Zha T G, Zhang Z Y, et al. Leaf structure, physiology and transcriptome analysis of Salsola collina in response to drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 75-88. |
| 谭炯锐, 查同刚, 张泽宇, 等. 猪毛菜响应干旱胁迫的叶片结构、生理及转录组分析. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 75-88. | |
| 37 | Berendsen R L, Pieterse C M J, Bakker P A H M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in Plant Science, 2012, 17(8): 478-486. |
| 38 | Carrión V J, Perez-Jaramillo J, Cordovez V, et al. Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome. Science, 2019, 366: 606-612. |
| 39 | Shao W W. Effects of variety and soil on bacterial community and nitrogen cycling functional flora structure in the rhizosphere of soybean. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2024. |
| 邵玮玮. 品种和土壤对大豆根际细菌群落及氮循环功能菌群结构的影响. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2024. | |
| 40 | Niu B, Paulson J N, Zheng X Q, et al. Simplified and representative bacterial community of maize roots. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114: 2450-2459. |
| 41 | Ding H, Sun Y X, Dai L X, et al. Effects of drought stress and low nitrogen on bacterial community structure and diversity in peanut rhizosphere soil. Journal of Peanut Science, 2021, 50(3):11-18. |
| 丁红, 孙运霞, 戴良香, 等. 干旱胁迫和低氮对花生根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响. 花生学报, 2021, 50(3):11-18. | |
| 42 | Cao K F, Liu J W, Suo R Z, et al. Effect of rhizobia inoculation on nodule nitrogen fixation and growth of ‘Monnong Clover No.1’. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(12): 3876-3886. |
| 曹克璠, 刘嘉伟, 索荣臻, 等. 接种根瘤菌对‘蒙农三叶草1号’结瘤固氮及生长的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(12): 3876-3886. | |
| 43 | Ma Y J, Quan J P, Gan H L, et al. Assessment of the impact of rhizobial inoculation on production performance and nutritional value of different varieties of purple alfalfa. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 43(1): 27-33. |
| 马垭杰, 权金鹏, 甘辉林, 等. 接种根瘤菌对不同品种紫花苜蓿生产性能及营养价值的影响评价. 畜牧兽医杂志, 2024, 43(1): 27-33. | |
| 44 | Fitzpatrick C R, Copeland J, Wang P W, et al. Assembly and ecological function of the root microbiome across angiosperm plant species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(6): 1157-1165. |
| 45 | Liu T Y, Ye N, Wang X, et al. Drought stress and plant ecotype drive microbiome recruitment in switchgrass rhizosheath. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(10): 1753-1774. |
| [1] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [2] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [3] | 魏娜, 敬文茂, 许尔文, 王荣新, 赵晶忠, 马雪娥, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 白花草木樨MaERF058基因耐旱功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 159-169. |
| [4] | 曾露婧, 王国华. 干旱及复水对荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 41-57. |
| [5] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [6] | 王雨欣, 陶佳丽, 朱慧森, 许涛, 张逸飞, 岑慧芳. 异源表达偏关苜蓿miR397-5p增强烟草干旱胁迫耐受能力[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 123-134. |
| [7] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [8] | 王宝强, 马文静, 王贤, 朱晓林, 赵颖, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [9] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [10] | 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 贺海明, 马霜, 马风华, 宋柯辰. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [11] | 梁佳, 胡朝阳, 谢志明, 马刘峰, 陈芸, 方志刚. 外源褪黑素缓解甜高粱幼苗干旱胁迫的生理效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [12] | 董佳琦, 杨艳婷, 范文强, 王佳妮, 石凤翎. 扁蓿豆种内杂种鉴定及其F1和F2代主要农艺性状优势分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 229-239. |
| [13] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [14] | 张一龙, 喻启坤, 李雯, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根地上地下表型特征及内源激素对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [15] | 王占军, 季波, 纪童, 蒋齐. 5种豆科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||