

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 1-15.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024148
• 研究论文 •
龚昕1,3,4( ), 霍新茹1,3,4, 李雯1,3,4, 杨彦东1,3,4, 刘超2, 秦伟春2, 沈艳1,3,4, 王国会1,3,4, 马红彬1,3,4(
), 霍新茹1,3,4, 李雯1,3,4, 杨彦东1,3,4, 刘超2, 秦伟春2, 沈艳1,3,4, 王国会1,3,4, 马红彬1,3,4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-29
修回日期:2024-07-01
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
马红彬
作者简介:E-mail: ma_hb@nxu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xin GONG1,3,4( ), Xin-ru HUO1,3,4, Wen LI1,3,4, Yan-dong YANG1,3,4, Chao LIU2, Wei-chun QIN2, Yan SHEN1,3,4, Guo-hui WANG1,3,4, Hong-bin MA1,3,4(
), Xin-ru HUO1,3,4, Wen LI1,3,4, Yan-dong YANG1,3,4, Chao LIU2, Wei-chun QIN2, Yan SHEN1,3,4, Guo-hui WANG1,3,4, Hong-bin MA1,3,4( )
)
Received:2024-04-29
Revised:2024-07-01
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Hong-bin MA
摘要:
宁夏罗山国家级自然保护区是宁夏中部干旱带上唯一的水源涵养林区和区域绿色生态保护屏障,对该地区生物多样性保护、防治土壤侵蚀、维护生态安全具有重要作用,但目前对罗山草地植物群落特征鲜有报道,其草原植被群落特征及其与环境因子的关系还不清晰。本研究以罗山自然保护区草原为对象,研究了不同海拔和不同类型草地植物群落组成、多样性特征的空间分异规律及植被群落特征与环境因子的关系。结果表明:1) 罗山自然保护区草地植物群落由一、二年生草本、多年生草本和灌木、半灌木组成,其中多年生草本占比最大;荒漠草原与典型草原植物群落以禾本科和杂类草为主,草甸草原以杂类草为主;随着海拔的升高,除群落地上生物量外,所调查植被数量特征符合“中间高度膨胀”理论,在海拔1600~2100 m时均达到峰值。2) 草地植物Margarlef丰富度指数与Shannon-Wiener多样性指数随着海拔的升高,在2000~2100 m的草原样地达到最高,呈现先增加后减小的“单峰型”变化趋势(P<0.05);Simpson优势度指数与Pielou均匀度指数随海拔升高变化不显著(P>0.05);保护区草甸草原、典型草原和荒漠草原3种草原类型间物种多样性差异不明显。3) 年降水量、海拔、土壤全氮含量、土壤全磷含量、日均气温是影响研究区草地植被特征的重要环境因子,其中年降水量、海拔是主要环境因子,土壤全氮含量、土壤全磷含量以及日均气温是次要环境因子。研究为进一步了解罗山自然保护区草地植被分布特征提供了基础。
龚昕, 霍新茹, 李雯, 杨彦东, 刘超, 秦伟春, 沈艳, 王国会, 马红彬. 宁夏罗山山地草原植被群落特征及其空间分异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 1-15.
Xin GONG, Xin-ru HUO, Wen LI, Yan-dong YANG, Chao LIU, Wei-chun QIN, Yan SHEN, Guo-hui WANG, Hong-bin MA. Vegetation community characteristics and spatial differentiation in mountain grassland in Luoshan, Ningxia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 1-15.
草原类型 Grassland type | 分布区域 Distribution location | 土壤有机质含量 Soil organic matter content (g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮含量 Soil total nitrogen content (g·kg-1) | 土壤全磷含量 Soil total phosphorus content (g·kg-1) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤黏粒含量 Soil clay content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
荒漠草原 Desert steppe | 主要分布于大、小罗山东麓和同红公路两侧海拔1500~1800 m。It is mainly distributed in the east foot of Daluo Mountain and Xiaoluo Mountain, and the altitude of 1500-1800 m on both sides of Tonghong Highway. | 6.13 | 0.36 | 0.46 | 1.33 | 1.46 |
典型草原 Typical steppe | 主要分布于海拔1900 m左右小罗山最南边和大罗山西侧及1800~2000 m大罗山主峰西边阳坡、半阳坡和山脚下。It is mainly distributed in the southernmost part of Xiaoluo Mountain and the west side of Daluo Mountain at an altitude of about 1900 m, and in the west side of the main peak of Daluo Mountain at an altitude of 1800-2000 m. | 7.34 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 1.24 | 1.49 |
草甸草原 Meadow steppe | 主要分布于好汉峰林下区域 2368~2558 m。It is mainly distributed in the under forest area of Haohan Peak at an altitude of 2368-2558 m. | 21.86 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 1.11 | 3.56 |
表1 保护区草原类型分布及土壤主要性状
Table 1 Grassland type distribution and main soil properties in the protected area
草原类型 Grassland type | 分布区域 Distribution location | 土壤有机质含量 Soil organic matter content (g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮含量 Soil total nitrogen content (g·kg-1) | 土壤全磷含量 Soil total phosphorus content (g·kg-1) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤黏粒含量 Soil clay content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
荒漠草原 Desert steppe | 主要分布于大、小罗山东麓和同红公路两侧海拔1500~1800 m。It is mainly distributed in the east foot of Daluo Mountain and Xiaoluo Mountain, and the altitude of 1500-1800 m on both sides of Tonghong Highway. | 6.13 | 0.36 | 0.46 | 1.33 | 1.46 |
典型草原 Typical steppe | 主要分布于海拔1900 m左右小罗山最南边和大罗山西侧及1800~2000 m大罗山主峰西边阳坡、半阳坡和山脚下。It is mainly distributed in the southernmost part of Xiaoluo Mountain and the west side of Daluo Mountain at an altitude of about 1900 m, and in the west side of the main peak of Daluo Mountain at an altitude of 1800-2000 m. | 7.34 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 1.24 | 1.49 |
草甸草原 Meadow steppe | 主要分布于好汉峰林下区域 2368~2558 m。It is mainly distributed in the under forest area of Haohan Peak at an altitude of 2368-2558 m. | 21.86 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 1.11 | 3.56 |
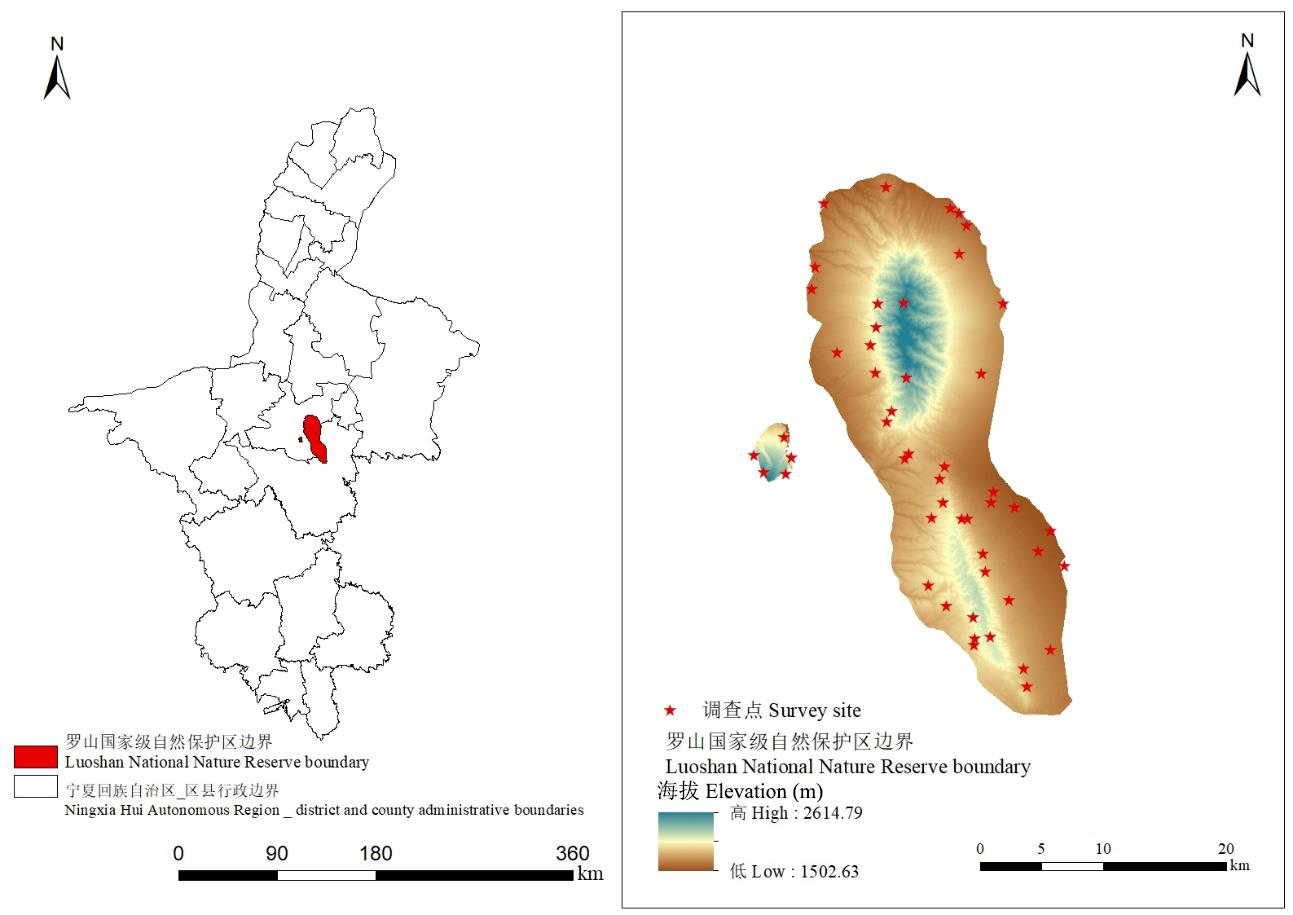
图1 样地基础信息基于宁夏回族自治区标准地图在线服务网站下载的审图号为宁S(2022)第001号的标准地图制作,底图无修改。Based on the standard map downloaded from the online service website of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region with the map number of Ning S (2022) No.001, the standard map was created without any modifications to the base map.
Fig.1 Basic information of sample plots
草原类型 Grassland type | 重要值排名前10的物种The top ten species in terms of importance value | 重要值 Importance value (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生活型Life style | 物种名Species name | ||
荒漠草原 Desert steppe | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 短花针茅 Stipa breviflora | 28.72 |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 银灰旋花 Convolvulus ammannii | 5.40 | |
| 半灌木 Subshrub | 蓍状亚菊 Ajania achilleoides | 4.85 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 隐子草 Cleistogenes serotina | 4.45 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 阿尔泰狗娃花 Aster altaicus | 4.31 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 冷蒿 Artemisia frigida | 4.11 | |
| 灌木 Shrub | 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor | 3.49 | |
| 半灌木 Subshrub | 牛枝子 Lespedeza potaninii | 3.31 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 长芒草 Stipa bungeana | 3.13 | |
| 半灌木 Subshrub | 二裂委陵菜 Sibbaldianthe bifurca | 2.06 | |
典型草原 Typical steppe | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 大针茅 Stipa grandis | 21.82 |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 长芒草 S. bungeana | 9.92 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 冷蒿 A. frigida | 6.14 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 6.09 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 短翼岩黄芪 Hedysarum brachypterum | 5.88 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 阿尔泰狗娃花 A. altaicus | 3.95 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 草原石头花 Gypsophila davurica | 3.55 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 星毛委陵菜 Potentilla acaulis | 2.56 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 隐子草 C. serotina | 2.22 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 针枝芸香 Haplophyllum tragacanthoides | 2.06 | |
草甸草原 Meadow steppe | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 干生薹草 Carex aridula | 25.92 |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 冷蒿 A. frigida | 8.95 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 黑柴胡 Bupleurum smithii | 8.08 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 花苜蓿 Medicago ruthenica | 7.13 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 串铃草 Phlomoides mongolica | 4.99 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 多序岩黄芪 Hedysarum polybotrys | 4.29 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 双花堇菜 Viola biflora | 3.21 | |
| 多年生草本Perennial herb | 洽草 Koeleria macrantha | 3.00 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 草原石头花 G. davurica | 2.92 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 黄花棘豆 Oxytropis ochrocephala | 2.89 | |
表2 不同草原类型植物生活型和重要值
Table 2 Life style and importance value of species in different grassland types
草原类型 Grassland type | 重要值排名前10的物种The top ten species in terms of importance value | 重要值 Importance value (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生活型Life style | 物种名Species name | ||
荒漠草原 Desert steppe | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 短花针茅 Stipa breviflora | 28.72 |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 银灰旋花 Convolvulus ammannii | 5.40 | |
| 半灌木 Subshrub | 蓍状亚菊 Ajania achilleoides | 4.85 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 隐子草 Cleistogenes serotina | 4.45 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 阿尔泰狗娃花 Aster altaicus | 4.31 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 冷蒿 Artemisia frigida | 4.11 | |
| 灌木 Shrub | 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor | 3.49 | |
| 半灌木 Subshrub | 牛枝子 Lespedeza potaninii | 3.31 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 长芒草 Stipa bungeana | 3.13 | |
| 半灌木 Subshrub | 二裂委陵菜 Sibbaldianthe bifurca | 2.06 | |
典型草原 Typical steppe | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 大针茅 Stipa grandis | 21.82 |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 长芒草 S. bungeana | 9.92 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 冷蒿 A. frigida | 6.14 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 6.09 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 短翼岩黄芪 Hedysarum brachypterum | 5.88 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 阿尔泰狗娃花 A. altaicus | 3.95 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 草原石头花 Gypsophila davurica | 3.55 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 星毛委陵菜 Potentilla acaulis | 2.56 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 隐子草 C. serotina | 2.22 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 针枝芸香 Haplophyllum tragacanthoides | 2.06 | |
草甸草原 Meadow steppe | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 干生薹草 Carex aridula | 25.92 |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 冷蒿 A. frigida | 8.95 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 黑柴胡 Bupleurum smithii | 8.08 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 花苜蓿 Medicago ruthenica | 7.13 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 串铃草 Phlomoides mongolica | 4.99 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 多序岩黄芪 Hedysarum polybotrys | 4.29 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 双花堇菜 Viola biflora | 3.21 | |
| 多年生草本Perennial herb | 洽草 Koeleria macrantha | 3.00 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 草原石头花 G. davurica | 2.92 | |
| 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 黄花棘豆 Oxytropis ochrocephala | 2.89 | |
植物功能群 Plant functional group | 荒漠草原Desert steppe | 典型草原Typical steppe | 草甸草原Meadow steppe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
物种数 Number of species | 物种比例 Species ratio (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 物种数 Number of species | 物种比例 Species ratio (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 物种数 Number of species | 物种比例 Species ratio (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) | |
| 灌木、半灌木Shrub,subshrub | 11 | 12.64 | 18.22 | 12 | 18.75 | 11.75 | 1 | 3.33 | 2.28 |
| 多年生草本Perennial herb | 64 | 73.56 | 76.80 | 51 | 79.69 | 66.43 | 27 | 90.00 | 96.97 |
| 一、二年生草本Annual,biennial herb | 12 | 13.80 | 4.98 | 1 | 1.56 | 21.82 | 2 | 6.67 | 0.75 |
| 禾本科Poaceae | 17 | 19.54 | 42.62 | 10 | 15.63 | 45.44 | 3 | 10.00 | 4.78 |
| 豆科Leguminosae | 20 | 22.99 | 13.19 | 11 | 17.19 | 10.55 | 4 | 13.33 | 16.14 |
| 菊科Compositae | 14 | 16.09 | 19.06 | 13 | 20.31 | 16.57 | 5 | 16.67 | 15.52 |
| 杂类草Forb | 36 | 41.38 | 25.13 | 30 | 46.88 | 27.44 | 18 | 60.00 | 63.56 |
表3 不同草地类型植物功能群物种数和重要值的变化
Table 3 Changes of species number and importance value of plant functional groups in different grassland types
植物功能群 Plant functional group | 荒漠草原Desert steppe | 典型草原Typical steppe | 草甸草原Meadow steppe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
物种数 Number of species | 物种比例 Species ratio (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 物种数 Number of species | 物种比例 Species ratio (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 物种数 Number of species | 物种比例 Species ratio (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) | |
| 灌木、半灌木Shrub,subshrub | 11 | 12.64 | 18.22 | 12 | 18.75 | 11.75 | 1 | 3.33 | 2.28 |
| 多年生草本Perennial herb | 64 | 73.56 | 76.80 | 51 | 79.69 | 66.43 | 27 | 90.00 | 96.97 |
| 一、二年生草本Annual,biennial herb | 12 | 13.80 | 4.98 | 1 | 1.56 | 21.82 | 2 | 6.67 | 0.75 |
| 禾本科Poaceae | 17 | 19.54 | 42.62 | 10 | 15.63 | 45.44 | 3 | 10.00 | 4.78 |
| 豆科Leguminosae | 20 | 22.99 | 13.19 | 11 | 17.19 | 10.55 | 4 | 13.33 | 16.14 |
| 菊科Compositae | 14 | 16.09 | 19.06 | 13 | 20.31 | 16.57 | 5 | 16.67 | 15.52 |
| 杂类草Forb | 36 | 41.38 | 25.13 | 30 | 46.88 | 27.44 | 18 | 60.00 | 63.56 |

图2 不同海拔植被特征变化图中阴影部分表示不同海拔植被数量特征值的分布范围;不同小写字母表示不同海拔梯度间植被特征存在显著差异(P<0.05)。The shaded part in the figure represents the distribution range of vegetation quantity characteristic values at different altitudes. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in vegetation characteristics among different altitude gradients (P<0.05).
Fig.2 Changes of vegetation characteristics at different altitudes

图3 不同海拔、草原类型物种多样性指数变化图内部大写字母表示:A:不同海拔;B:荒漠草原;C:典型草原;D:不同草地类型;DS:荒漠草原;TS:典型草原:MS:草甸草原。图中横轴大写字母表示:S:Margarlef丰富度指数;D:Simpson优势度指数;H:Shannon-Wiener多样性指数;J:Pielou均匀度指数。图中不同小写字母表示不同海拔或草地类型物种多样性指数差异显著(P<0.05)。The capital letters inside the figure indicate: A: Different altitude; B: Desert steppe; C: Typical steppe; D: Different grassland types; DS: Desert steppe; TS: Typical steppe; MS: Meadow steppe. The horizontal capital letters in the figure indicate: S: Margarlef richness index; D: Simpson dominance degree index; H: Shannon-Wiener diversity index; J: Pielou uniformity index. Different lowercase letters in the figure indicate that the species diversity index of different altitudes or grassland types is significantly different (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Species diversity index changes at different altitudes and grassland types

图4 植被特征、物种多样性指数与环境因子的Pearson相关性分析*表示在0.05水平相关性显著。**表示在0.01水平相关性显著。CC:群落盖度;CD:群落密度;CH:群落平均高度;CB:群落地上生物量;S:Margarlef丰富度指数;D:Simpson优势度指数;H:Shannon-Wiener多样性指数;J:Pielou均匀度指数;Alti:海拔;Prec:年降水量;ADT:日均温;TC:土壤有机质含量;TN:土壤全氮含量;TP:土壤全磷含量;SBD:土壤容重;SC:土壤黏粒含量。下同。* indicates a significant correlation at the 0.05 level. ** indicates a significant correlation at the 0.01 level. CC: Community coverage; CD: Community density; CH: Community average height; CB: Community above-ground biomass; S: Margarlef richness index; D: Simpson dominance degree index; H: Shannon-Wiener diversity index; J: Pielou uniformity index; Alti: Altitude; Prec: Annual precipitation; ADT: Average daily temperature; TC: Soil organic matter content; TN: Soil total nitrogen content; TP: Soil total phosphorus content; SBD: Soil bulk density; SC: Soil clay content. The same below.
Fig.4 Pearson correlation analysis of vegetation characteristics, species diversity index and environmental factors
| 1 | The 3rd National Land Survey Leading Group of the State Council, Ministry of Natural Resources, National Bureau of Statistics. A bulletin on the main data results of the third national land survey. Beijing: People’s Daily, 2021. |
| 国务院第三次全国国土调查领导小组办公室, 自然资源部, 国家统计局. 第三次全国国土调查主要数据公报. 北京: 人民日报, 2021. | |
| 2 | Yi M X, Sun Z G, Cong P F, et al. Research progress on the response of grassland ecosystem function to climate change. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(12): 112-120. |
| 羿明璇, 孙政国, 丛鹏飞, 等. 草地生态系统功能对气候变化的响应研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(12): 112-120. | |
| 3 | Chen G S, Tian H Q. Land use/cover change effects on carbon cycling in terrestrial ecosystems. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(2): 189-204. |
| 陈广生, 田汉勤. 土地利用/覆盖变化对陆地生态系统碳循环的影响. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(2): 189-204. | |
| 4 | Liu B, Sun Y L, Wang Z L, et al. Analysis of the vegetation cover change and the relative role of its influencing factors in north China. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30(1): 12-23. |
| 刘斌, 孙艳玲, 王中良, 等. 华北地区植被覆盖变化及其影响因子的相对作用分析. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(1): 12-23. | |
| 5 | Bai X H, Zhang J T, Cao K, et al. Relationship between forest communities and the environment in the Xiaowutai Mountain National Nature Reserve, Hebei. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 3683-3696. |
| 白晓航, 张金屯, 曹科, 等. 河北小五台山国家级自然保护区森林群落与环境的关系. 生态学报, 2017, 37(11): 3683-3696. | |
| 6 | Yang G G, Hao H X, Yue Y P, et al. Community characteristics, distribution and environment interpretation of Cupressus gigantea along Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2023, 59(1): 156-162. |
| 杨刚刚, 郝海霞, 岳艳鹏, 等. 雅鲁藏布江巨柏分布区植物群落特点、分布与环境解释. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(1): 156-162. | |
| 7 | Zheng D S, Liu Q J. Effects of environmental factors on forest community distribution in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve of northeastern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2023, 45(8): 57-64. |
| 郑东升, 刘琪璟. 环境因子对长白山自然保护区森林群落分布的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 2023, 45(8): 57-64. | |
| 8 | Huston M A. Hidden treatments in ecological experiments: re-evalutating the ecosystem function of biodiversity. Oecologia, 1997, 110(4): 449-460. |
| 9 | Nguyen H, Herbohn J, Firn J, et al. Biodiversity-productivity relationships in small-scale mixed-species plantations using native species in Leyte Province, Philippines. Forest Ecology & Management, 2012, 274(15): 81-90. |
| 10 | Carnicer J, Sardans J, Stefanescu C, et al. Global biodiversity, stoichiometry and ecosystem function responses to human-induced C-N-P imbalances. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 172(1): 82-91. |
| 11 | Chang X X, Zhao W Z, Zhao A F. Species diversity of pasture community at different altitude levels in Qilian Mountains. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(9): 1599-1603. |
| 常学向, 赵文智, 赵爱芬. 祁连山区不同海拔草地群落的物种多样性. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(9): 1599-1603. | |
| 12 | Wu H B, Shui H W, Hu G Z, et al. Species diversity and biomass distribution patterns of alpine grassland along an elevation gradient in the northern Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(6): 1071-1079. |
| 吴红宝, 水宏伟, 胡国铮, 等. 海拔对藏北高寒草地物种多样性和生物量的影响.生态环境学报, 2019, 28(6): 1071-1079. | |
| 13 | Hu Y K, Li K H, Adeli M D, et al. Plant species diversity of alpine grasslands on southern slope of Tianshan mountain along altitude gradient. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26(2): 182-186. |
| 胡玉昆, 李凯辉, 阿德力·麦地, 等. 天山南坡高寒草地海拔梯度上的植物多样性变化格局. 生态学杂志, 2007, 26(2): 182-186. | |
| 14 | Zhang K L, Ye M, Yin X K, et al. Species composition and diversity of grassland community in Habahe forest zone of Altai Mountains. Grassland and Turf, 2023, 43(5): 75-83. |
| 张凯丽, 叶茂, 殷锡凯, 等. 阿尔泰山哈巴河林区草地群落物种组成及多样性研究. 草原与草坪, 2023, 43(5): 75-83. | |
| 15 | Zhang Y Y. Variation characteristies of plant community diversity along the elevational gradient in the western Tianshan Mountains. Anqing: Anqing Normal University, 2023. |
| 张媛媛. 西天山植物群落多样性沿海拔梯度的变化特征. 安庆: 安庆师范大学, 2023. | |
| 16 | Huang Y G, Li L, Dai X A. Understory plant diversity of Zhangjiajie sandstone peak forest at different elevations and its relationship with soil factors. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023, 42(10): 2469-2476. |
| 黄炎根, 李丽, 戴兴安. 张家界砂岩峰林不同海拔林下植物多样性及其与土壤因子的关系. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(10): 2469-2476. | |
| 17 | Zhao X Y, An S Z, Cao G M, et al. Surveying desert major plant communities in China: implications, current status, and scheme. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 9-19. |
| 赵学勇, 安沙舟, 曹广民, 等. 中国荒漠主要植物群落调查的意义、现状及方案. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 9-19. | |
| 18 | Wang X B, Ma C, Chen D K, et al. Spatiotemporal change of NPP and its response to climate over Luoshan region in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region from 2004 to 2015. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 38(6): 358-364, 385. |
| 王夏冰, 马超, 陈登魁, 等. 宁夏罗山地区2004-2015年NPP时空变化及气候响应. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(6): 358-364, 385. | |
| 19 | Su J S, Cheng J M, Gao Y, et al. Fine root biomass of four main vegetation types in Daluo Mountain of Ningxia, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(3): 626-632. |
| 苏纪帅, 程积民, 高阳, 等. 宁夏大罗山4种主要植被类型的细根生物量. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(3): 626-632. | |
| 20 | Yang X X, Zhang Z Q. Countermeasures and measures to speed up the construction of Luoshan natural ecological barrier in the central arid zone of Ningxia. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008, 14(21): 85, 116. |
| 杨雪霞, 张占强. 加快建设宁夏中部干旱带罗山天然生态屏障的对策与措施. 安徽农学通报, 2008, 14(21): 85, 116. | |
| 21 | Yang J L, Zhang X L, Cao B, et al. Active organic carbon in soil of typical vegetation in Luoshan of Ningxia. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2017, 46(4): 61-66. |
| 杨君珑, 张学丽, 曹兵, 等. 宁夏罗山典型植被类型的土壤活性有机碳组分研究. 西部林业科学, 2017, 46(4): 61-66. | |
| 22 | Tian H G, Qin W C, Shi X H. Suggestions on the protection and utilization of forest resources in Luoshan Reserve. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 15(9): 16, 188. |
| 田会刚, 秦伟春, 施兴慧. 罗山保护区森林资源保护及利用建议. 安徽农学通报, 2009, 15(9): 16, 188. | |
| 23 | Zhou J, Yang H. Protection status, existing problems and countermeasures of plant resources in Luoshan, Ningxia. Regional Governance, 2019(32): 55-57. |
| 周静, 杨慧. 宁夏罗山植物资源的保护现状、存在的问题及对策. 区域治理, 2019(32): 55-57. | |
| 24 | Ren C B, Wu J, Shi S W. Structural analysis and optimization countermeasures of forest land of Luoshan National Nature Reserve. Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2012, 53(8): 56, 64. |
| 任成宝, 吴娟, 石少伟. 宁夏罗山国家级自然保护区林地结构现状及优化对策. 宁夏农林科技, 2012, 53(8): 56, 64. | |
| 25 | Wu X, Cheng X X, Ma Y K, et al. Chemical characteristics of groundwater Luoshan Nature Reserve. Ground Water, 2012, 34(1): 23-26, 79. |
| 吴玺, 程旭学, 马岳昆, 等. 罗山自然保护区地下水化学特征研究. 地下水, 2012, 34(1): 23-26, 79. | |
| 26 | Wang Y J, Ma Y Z, Zheng Y H, et al. Response of tree-ring width of Pinus tabulaeformis to climate factors in Luoshan Mountains of Ningxia. Journal of Desert Research, 2009, 29(5): 971-976. |
| 王亚军, 马玉贞, 郑影华, 等. 宁夏罗山油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)树轮宽度对气候因子的响应分析. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(5): 971-976. | |
| 27 | Jia X Y, Ma H B, Zhou Y, et al. Floristic quantitative classification and successional characteristics of typical grassland under different ecological restoration methods in the Loess Hilly Region of Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(2): 15-25. |
| 贾希洋, 马红彬, 周瑶, 等. 不同生态恢复措施下宁夏黄土丘陵区典型草原植物群落数量分类和演替. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 15-25. | |
| 28 | Jia X Y, Ma H B, Zhou Y, et al. Effect of different ecological restoration measures on the characteristics of typical grassland communities in loess hilly region of Ningxia. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(1): 51-60. |
| 贾希洋, 马红彬, 周瑶, 等. 不同生态恢复措施对宁夏黄土丘陵区典型草原植物群落特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(1): 51-60. | |
| 29 | Cai Y R, Lu Q, Wu W P, et al. Effects of fish-scale pit ecological restoration measures on plant community characteristics in a typical steppe in Ningxia. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(9): 2115-2126. |
| 蔡育蓉, 陆琪, 吴宛萍, 等. 鱼鳞坑生态恢复措施对宁夏典型草原植物群落特征的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(9): 2115-2126. | |
| 30 | Qin L. Statistical ecology. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2009. |
| 覃林. 统计生态学. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2009. | |
| 31 | Yang Y D, Ma J L, Ma H B, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on root trait characteristics of dominant plants in the desert steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(6): 1507-1517. |
| 杨彦东, 马静利, 马红彬, 等. 封育对荒漠草原优势植物根系性状特征的影响. 草业科学, 2023, 40(6): 1507-1517. | |
| 32 | Zhang X L, Zhou J H, Cai W T, et al. Diversity characteristics of plant communities in the arid desert of the Heihe basin under different moisture gradients. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(14): 4627-4635. |
| 张晓龙, 周继华, 蔡文涛, 等. 水分梯度下黑河流域荒漠植物群落多样性特征. 生态学报, 2017, 37(14): 4627-4635. | |
| 33 | Magurran A E. Ecological diversity and its measurement. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1988. |
| 34 | Jia W X, Liu Y R, Zhang Y S, et al. Species diversity and biomass of meadow steppe in Qilian Mountains and their relationships with climate factors. Arid Zone Research, 2015, 32(6): 1167-1172. |
| 贾文雄, 刘亚荣, 张禹舜, 等. 祁连山草甸草原物种多样性和生物量与气候要素的关系. 干旱区研究, 2015, 32(6): 1167-1172. | |
| 35 | Niu Y J, Zhou J W, Yang S W, et al. Quantitative apportionment of slope aspect and altitude to soil moisture and temperature and plant distribution on alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(5): 1489-1497. |
| 牛钰杰, 周建伟, 杨思维, 等. 坡向和海拔对高寒草甸山体土壤水热和植物分布格局的定量分解. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(5): 1489-1497. | |
| 36 | Zhang Q D, Wei W, Chen L D, et al. Spatial variation of soil moisture and species diversity patterns along a precipitation gradient in the grasslands of the Loess Plateau. Journal of Natural Resources, 2018, 33(8): 1351-1362. |
| 张钦弟, 卫伟, 陈利顶, 等. 黄土高原草地土壤水分和物种多样性沿降水梯度的分布格局. 自然资源学报, 2018, 33(8): 1351-1362. | |
| 37 | Dong Y L, Zhang D G, Chen J G, et al. Comparison of community structure and biodiversity of alpine meadow at different habitats in Eastern Qilian Mountains: A case study in Zhuaxixiulong township of Tianzhu county, Gansu province. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2014, 22(3): 481-487. |
| 董云龙, 张德罡, 陈建纲, 等. 东祁连山高寒草地不同生境条件下植物群落结构特征及多样性比较——以甘肃省天祝抓喜秀龙乡为例. 草地学报, 2014, 22(3): 481-487. | |
| 38 | Chen G L. Study on community structure and plant diversity of shrubby grass of Luoshan in Ningxia. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2023. |
| 陈改莲. 宁夏罗山灌草群落结构及植物多样性研究. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2023. | |
| 39 | He M Z. Composition and distribution of desert vegetation in Alxa plateau and its environmental interpretation:Ⅲ. Response of plant functional group diversity to environmental factors. Journal of Desert Research, 2010, 30(2): 278-286. |
| 何明珠. 阿拉善高原荒漠植被组成分布特征及其环境解释: Ⅲ.植物功能群多样性对环境因素的响应. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(2): 278-286. | |
| 40 | He M Z, Zhang Z S, Li X J, et al. Environmental effects on distribution and composition of desert vegetations in Alxa plateau: Ⅱ. Correlation between C4 plants distribution and environmental factors. Journal of Desert Research, 2010, 30(1): 57-62. |
| 何明珠, 张志山, 李小军, 等. 阿拉善高原荒漠植被组成分布特征及其环境解释: Ⅱ.C4植物组成、分布特征与环境的关系. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(1): 57-62. | |
| 41 | Chen D L. Processes and mechanisms of abandoned croplands recovery succession across different steppe in the northern Yinshan Mountain. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 陈大岭. 阴山北麓不同草原区弃耕地恢复演替过程及其机理研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2023. | |
| 42 | Wang L F, Wu X Y, Chang J C, et al. Effects of seasonal grazing rest on spatial distribution pattern of plant communities in meadow steppe. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(8): 1944-1953. |
| 王利锋, 吴秀扬, 常杰超, 等. 季节性休牧对草甸草原植物群落空间分布格局的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8): 1944-1953. | |
| 43 | Jia W X, Chen J H, Zhang Y S, et al. The relationship of characteristics of meadow communities with soil moisture and temperature in the northern slope of Qilian Mountains. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3): 661-667. |
| 贾文雄, 陈京华, 张禹舜, 等. 祁连山北坡草地植物群落特征与土壤水热因子的关系. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3): 661-667. | |
| 44 | Li Q, He G X, Liu Z G, et al. Responses of vegetation characteristics and biodiversity to habitat in alpine meadows in eastern Qilian Mountains. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(1): 169-177. |
| 李强, 何国兴, 刘志刚, 等. 东祁连山高寒草甸植被特征和生物多样性对生境的响应. 草地学报, 2022, 30(1): 169-177. | |
| 45 | Jin Z L, Liu G P, Zhou M T, et al. Elevation characteristics of grassland community diversity and effect of soil physical and chemical properties in Karst Mountain grassland. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(4): 661-668. |
| 金章利, 刘高鹏, 周明涛, 等. 喀斯特山地草地群落多样性海拔特征及土壤理化性质特征. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(4): 661-668. | |
| 46 | Wang X R, Xing Y J. Research progress on the effects of environmental factors and community dynamics on plant species diversity. International Journal of Ecology, 2021, 10(4): 608-617. |
| 王心茹, 邢亚娟. 环境因子及群落动态对植物物种多样性影响研究进展. 世界生态学, 2021, 10(4): 608-617. | |
| 47 | Kitayama K. An altitudinal transect study of the vegetation on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Vegetation, 1992, 102(2): 149-171. |
| 48 | Yu S J, Wang J, He H Y, et al. Driving factors of the temporal stability of biomass of mixed broadleaf-conifer forest. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2022, 58(11): 181-190. |
| 于水今, 王娟, 何海燕, 等. 针阔混交林生物量稳定性驱动因子. 林业科学, 2022, 58(11): 181-190. | |
| 49 | Li G X, Su J D, Zhao X J. Response relationship between plant community diversity and altitude in Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve, Gansu Province. Natural Protected Areas, 2024, 4(1): 110-122. |
| 李国霞, 苏军德, 赵晓冏. 甘肃祁连山国家自然保护区植物群落多样性与海拔的响应关系. 自然保护地, 2024, 4(1): 110-122. | |
| 50 | Liu Y J. Characteristies and influencing factors of the phylogenetic structure of herbaceous plant communities in the middle-eastern Qilian Mountains. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 刘永靖. 祁连山中东部草本植物群落谱系结构特征及其影响因素. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| 51 | He Y Q, Zeng J Y, Chen G J, et al. Characteristics and species diversity of typical forest community in Dalian island of Pingtan, Fujian, China. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(3): 759-769. |
| 何雅琴, 曾纪毅, 陈国杰, 等. 福建平潭大练岛典型森林群落特征及物种多样性. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(3): 759-769. | |
| 52 | Li T T, Ji L Z, Yu D P, et al. Forest community classification, ordination, and comparison of species diversity in broadleaved-Korean pine mixed forests of Northeast China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(2): 620-628. |
| 李婷婷, 姬兰柱, 于大炮, 等. 东北阔叶红松林群落分类、排序及物种多样性比较. 生态学报, 2019, 39(2): 620-628. | |
| 53 | Xu J X, Wang J Z. Correlation between vegetation community and soil physical-chemical factors in water-level fluctuation zone of Xiangxi River of the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(12): 3661-3669. |
| 徐建霞, 王建柱. 三峡库区香溪河消落带植被群落特征与土壤环境相关性. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(12): 3661-3669. | |
| 54 | Hu Y X, Huang J L, Du Y, et al. Monitoring wetland vegetation pattern response to water-level change resulting from the Three Gorges Project in the two largest freshwater lakes of China. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 74: 274-285. |
| 55 | Yue P P, Lu X F, Ye R R, et al. Quantitative classification and ordination of Stipa purpurea steppe community in source region of the Yangtze River. Guihaia, 2014, 34(5): 635-641. |
| 岳鹏鹏, 卢学峰, 叶润蓉, 等. 长江源区紫花针茅草原群落数量分类与排序. 广西植物, 2014, 34(5): 635-641. |
| [1] | 张聪, 王娅, 周立华, 裴孝东, 李军豪, 石贵. 牲畜饲养结构的时空分布特征及驱动因素——以宁夏为例[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 37-49. |
| [2] | 刘倩, 丁彦芬, 宋杉杉, 许文婕, 杨威. 南京明城墙绿带草本层自生植物群落数量分类与排序分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 1-15. |
| [3] | 于双, 李小伟, 王瑞霞, 杨君珑, 马龙. 灵武白芨滩不同年限柠条固沙林林下草本群落演替规律及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 13-23. |
| [4] | 石昊, 杨彩红, 夏菲, 王军强, 魏巍, 王敬龙, 薛云尹, 郑晒坤, 吴皓阳, 冉林灵, 严双, 姜晓敏. 短期增温对修复过程中藏北高寒退化草地生产力的初期影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 30-45. |
| [5] | 王鹏, 金正, 余婷, 秦康强, 桑新亚, 陶建平, 罗唯学. 预测姜黄属植物在中国当前和未来气候情景下的潜在分布区变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 14-27. |
| [6] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [7] | 郁国梁, 马紫荆, 吕自立, 刘彬. 海拔和植物群落共同调节天山中段南坡巴伦台地区天然草场土壤化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 68-78. |
| [8] | 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| [9] | 刘彩凤, 段媛媛, 王玲玲, 王乙茉, 郭正刚. 高原鼠兔干扰对高寒草甸植物物种多样性与土壤生态化学计量比间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 157-166. |
| [10] | 马婧, 郭方君, 邹枝慧, 孙琳, 陈芳. 腾格里沙漠南缘不同恢复阶段沙质草地植被的季节变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 203-210. |
| [11] | 李美慧, 李玉华, 晏昕辉, 拓行行, 杨梦茹, 王子临, 李伟. 半灌木扩张驱动的草地植物多样性与地上生产力特征及其关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 27-39. |
| [12] | 黄业芸, 邱开阳, 朱亚超, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 杨壹, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 鲍平安. 贺兰山不同海拔植被生物量与土壤分形特征和土壤水分的相关关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 24-35. |
| [13] | 周娟娟, 刘云飞, 王敬龙, 魏巍. 短期养分添加对西藏沼泽化高寒草甸地上生物量、植物多样性和功能性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 17-29. |
| [14] | 虎雅玲, 哈斯额尔敦, 满良, 杨一, 张萍. 小叶锦鸡儿灌丛地植被对沙源供给的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [15] | 张丽苗, 谭雪, 董智, 郑杰, 袁中勋, 李昌晓. 喜旱莲子草入侵对三峡库区重庆主城河岸带植物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 13-25. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||