

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 60-72.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023247
李鸿飞1( ), 周帮伟1, 张淼1, 施树楠2, 李志坚1(
), 周帮伟1, 张淼1, 施树楠2, 李志坚1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-18
修回日期:2023-08-28
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-01-15
通讯作者:
李志坚
作者简介:E-mail: lizj004@nenu.edu.cn基金资助:
Hong-fei LI1( ), Bang-wei ZHOU1, Miao ZHANG1, Shu-nan SHI2, Zhi-jian LI1(
), Bang-wei ZHOU1, Miao ZHANG1, Shu-nan SHI2, Zhi-jian LI1( )
)
Received:2023-07-18
Revised:2023-08-28
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-01-15
Contact:
Zhi-jian LI
摘要:
为筛选出适宜在呼伦贝尔地区种植的优质饲用燕麦品种,在该地引进18份燕麦种质资源作为供试材料并测试其区域适应性。本试验基于该地区田间种植环境,采取随机区组设计,对供试燕麦的主要生产性能、农艺性状、营养品质等指标进行分析比较,采用灰色关联度分析法对供试品种的各项指标进行综合评价,旨在为该地区燕麦种质资源的适应性研究提供一定参考。结果表明:18份供试燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区均能发育成熟,生育期在76~109 d,生长速率呈“慢-快-慢”的趋势。随着生育期的推进,供试燕麦的干草产量逐步增高并于灌浆期达到最大,伽利略(13.18 t·hm-2)干草产量最高,其次是甜燕3号(12.32 t·hm-2)、贝勒(12.25 t·hm-2),显著高于其他燕麦品种(P<0.05)。贝勒(120 cm)株高最高,甜燕3号(117 cm)次之,二者显著高于其他供试燕麦品种(P<0.05)。福燕1号鲜干比(4.98)最高,白燕7号(1.74)茎叶比最低,说明二者具有较好的适口性。福燕1号的粗蛋白含量最高(13.46%),福燕2号的中性洗涤纤维及酸性洗涤纤维含量均为最低,说明二者具有较好的饲用品质。灰色关联度分析表明,本地区种植的燕麦应选择具有鲜干比大、叶片较大、茎秆粗壮、粗蛋白含量高、草产量高等特征的燕麦品种。甜燕3号、伽利略、福燕2号综合表现位居前列,可作为优良的饲用燕麦品种在当地推广种植。
李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72.
Hong-fei LI, Bang-wei ZHOU, Miao ZHANG, Shu-nan SHI, Zhi-jian LI. Adaptability evaluation of different oat varieties introduced in the Hulunbuir region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 60-72.
品种 Variety | 生育期 Phenological stages (月-日 Month-day) | 生育周期 Growth duration (d) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
播种期 Sowing stage | 出苗期 Seedling stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 灌浆期 Pustulation stage | 完熟期 Mature stage | ||
| A | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-26 | 09-06 | 09-20 | 10-05 | 104 |
| B | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-26 | 09-07 | 09-21 | 10-06 | 105 |
| C | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-06 | 07-20 | 08-09 | 08-14 | 08-27 | 09-22 | 91 |
| D | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-16 | 08-21 | 09-01 | 09-24 | 92 |
| E | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-20 | 08-25 | 09-05 | 09-25 | 94 |
| F | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-22 | 08-16 | 08-23 | 09-10 | 09-22 | 91 |
| G | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-07 | 07-21 | 08-14 | 08-23 | 09-03 | 09-18 | 87 |
| H | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 09-04 | 09-12 | 09-24 | 10-10 | 109 |
| I | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-28 | 09-10 | 09-23 | 10-10 | 109 |
| J | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-22 | 08-29 | 09-10 | 09-22 | 10-09 | 108 |
| K | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-12 | 08-21 | 08-31 | 09-19 | 88 |
| L | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-19 | 08-09 | 08-14 | 08-24 | 09-13 | 82 |
| M | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-12 | 08-19 | 08-31 | 09-16 | 85 |
| N | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-18 | 08-23 | 09-05 | 09-23 | 92 |
| O | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-16 | 08-21 | 09-03 | 09-21 | 90 |
| P | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 09-03 | 09-09 | 09-22 | 10-09 | 108 |
| Q | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-12 | 08-21 | 09-01 | 09-15 | 84 |
| R | 06-23 | 06-28 | 07-06 | 07-19 | 08-08 | 08-13 | 08-21 | 09-05 | 76 |
表1 不同燕麦品种生育期
Table 1 The phenological stages of different oat varieties
品种 Variety | 生育期 Phenological stages (月-日 Month-day) | 生育周期 Growth duration (d) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
播种期 Sowing stage | 出苗期 Seedling stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 灌浆期 Pustulation stage | 完熟期 Mature stage | ||
| A | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-26 | 09-06 | 09-20 | 10-05 | 104 |
| B | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-26 | 09-07 | 09-21 | 10-06 | 105 |
| C | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-06 | 07-20 | 08-09 | 08-14 | 08-27 | 09-22 | 91 |
| D | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-16 | 08-21 | 09-01 | 09-24 | 92 |
| E | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-20 | 08-25 | 09-05 | 09-25 | 94 |
| F | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-22 | 08-16 | 08-23 | 09-10 | 09-22 | 91 |
| G | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-07 | 07-21 | 08-14 | 08-23 | 09-03 | 09-18 | 87 |
| H | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 09-04 | 09-12 | 09-24 | 10-10 | 109 |
| I | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-28 | 09-10 | 09-23 | 10-10 | 109 |
| J | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-22 | 08-29 | 09-10 | 09-22 | 10-09 | 108 |
| K | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-12 | 08-21 | 08-31 | 09-19 | 88 |
| L | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-19 | 08-09 | 08-14 | 08-24 | 09-13 | 82 |
| M | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-12 | 08-19 | 08-31 | 09-16 | 85 |
| N | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-18 | 08-23 | 09-05 | 09-23 | 92 |
| O | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 08-16 | 08-21 | 09-03 | 09-21 | 90 |
| P | 06-23 | 06-30 | 07-08 | 07-21 | 09-03 | 09-09 | 09-22 | 10-09 | 108 |
| Q | 06-23 | 06-29 | 07-07 | 07-20 | 08-12 | 08-21 | 09-01 | 09-15 | 84 |
| R | 06-23 | 06-28 | 07-06 | 07-19 | 08-08 | 08-13 | 08-21 | 09-05 | 76 |
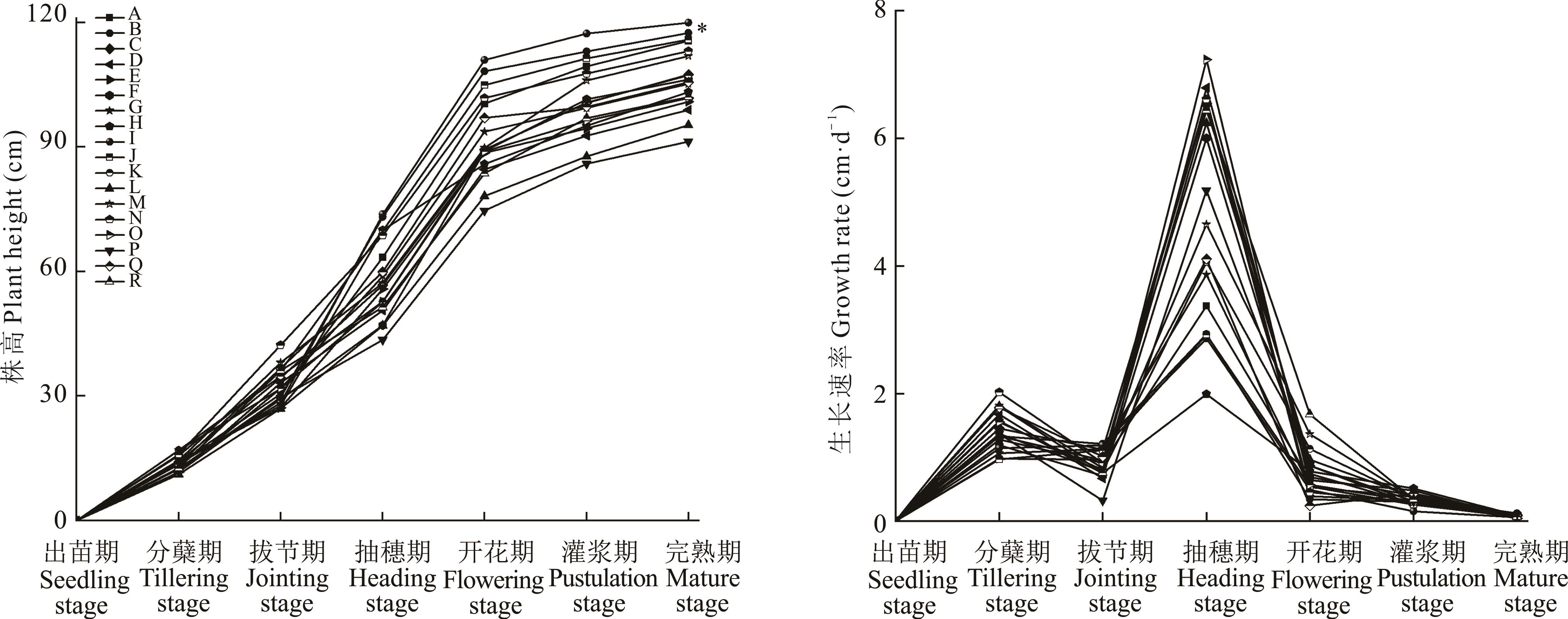
图2 不同燕麦品种株高及生长速率比较*表示在0.05水平下,完熟期贝勒和甜燕3号的株高显著高于其他品种。* indicate that the plant height of Baylor and Tianyan No. 3 at the mature stage was significantly higher than that other varieties at the level of 0.05.
Fig.2 Comparison of plant height and growth rate of different oat varieties
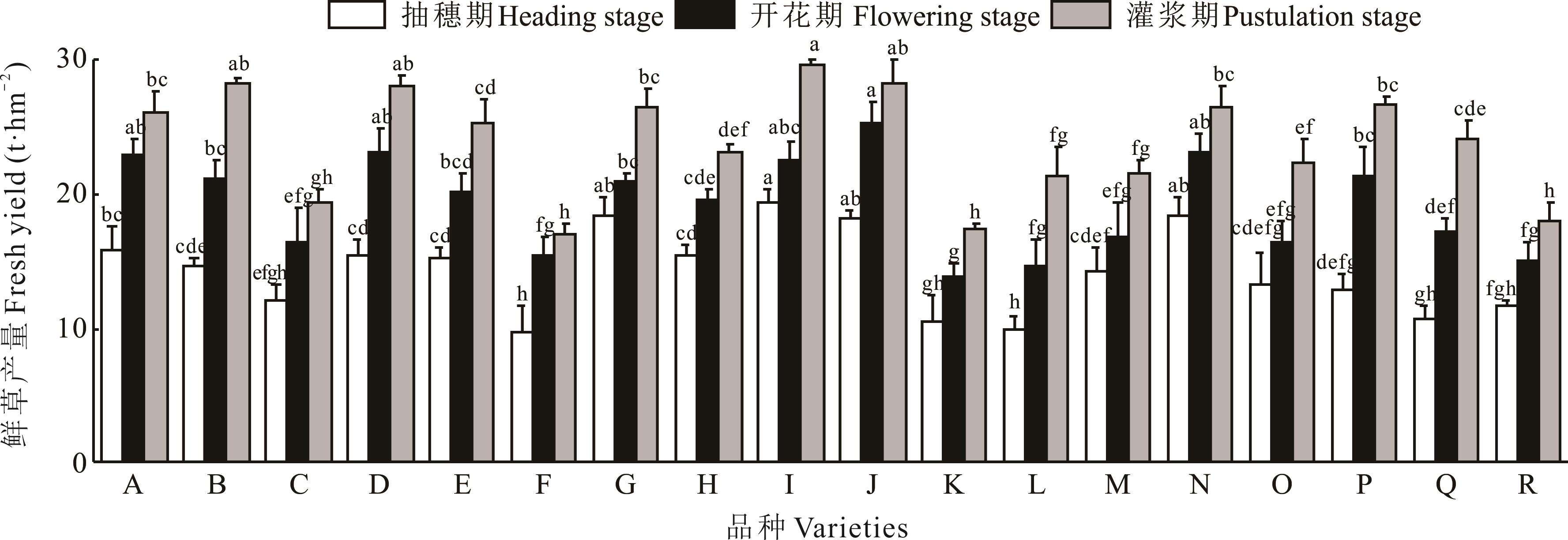
图3 不同燕麦品种鲜草产量比较不同小写字母表示不同品种在相同生育期内差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different varieties within the same growth period (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.3 Comparison of different oat varieties fresh yield
品种 Variety | 茎粗 Plant diameter (cm) | 茎节数 Stalk pitch (No.) | 穗长 | 旗叶长 Flag leaf length (cm) | 旗叶宽 Flag leaf width (cm) | 旗叶面积 Flag leaf area (cm2) | 鲜干比 Fresh/dry | 茎叶比 Stem/leaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.79±0.05cd | 6.33±0.58a | 24.97±0.87d | 29.20±1.30f | 2.83±0.15b | 68.70±0.83b | 3.73±0.23ef | 2.23±0.03fgh |
| B | 0.94±0.05b | 6.67±0.58a | 35.03±1.17a | 31.33±0.15de | 3.53±0.15a | 92.08±4.06a | 3.13±0.03hi | 2.30±0.04f |
| C | 0.69±0.07ef | 4.00±0.00e | 14.87±0.60j | 17.07±0.45j | 1.57±0.06i | 22.23±0.48i | 4.98±0.12a | 1.90±0.05k |
| D | 0.64±0.03fg | 4.33±0.58de | 30.70±1.61c | 33.47±0.57bc | 1.93±0.06efg | 53.81±1.62c | 3.83±0.06e | 2.17±0.03hij |
| E | 0.49±0.05i | 5.33±0.58bc | 23.03±1.12e | 25.03±1.20i | 1.63±0.06hi | 34.04±2.74gh | 3.64±0.26efg | 2.12±0.05j |
| F | 0.65±0.05efg | 4.67±0.58cde | 21.07±1.25fg | 27.23±0.83gh | 1.63±0.06hi | 37.01±2.25efgh | 3.96±0.09de | 1.74±0.05l |
| G | 0.64±0.03fg | 5.00±0.00cd | 20.23±0.93gh | 30.37±0.87ef | 1.53±0.06i | 38.75±2.41defg | 3.91±0.08e | 2.85±0.04a |
| H | 0.66±0.05efg | 6.00±0.00ab | 18.03±0.45i | 29.50±0.60ef | 2.23±0.15d | 54.83±4.60c | 3.43±0.06fgh | 2.15±0.04ij |
| I | 0.69±0.05ef | 5.33±0.58bc | 32.50±0.80b | 34.40±0.62b | 2.00±0.10def | 57.25±3.88c | 3.27±0.11hi | 2.24±0.02fgh |
| J | 1.04±0.05a | 6.00±0.00ab | 29.87±0.95c | 32.47±1.12cd | 2.67±0.15bc | 71.91±1.68b | 3.04±0.05i | 2.22±0.04ghi |
| K | 0.59±0.05gh | 5.00±0.00cd | 19.23±0.55hi | 31.20±0.66de | 1.57±0.06i | 40.63±0.80def | 4.59±0.06bc | 2.77±0.02b |
| L | 0.73±0.03de | 4.67±0.58cde | 17.87±0.32i | 27.27±1.17g | 1.87±0.15fgh | 42.24±1.93de | 4.71±0.14ab | 2.37±0.04e |
| M | 0.52±0.02hi | 4.33±0.58de | 22.57±0.40ef | 29.70±1.37ef | 1.70±0.20ghi | 42.09±6.27de | 4.27±0.32cd | 2.69±0.04c |
| N | 0.81±0.02cd | 5.33±0.58bc | 30.67±0.96c | 43.03±1.06a | 2.50±0.10c | 89.54±5.76a | 3.72±0.21ef | 2.46±0.04d |
| O | 0.87±0.02bc | 4.67±0.58cde | 20.13±0.80gh | 25.37±0.42hi | 1.63±0.15hi | 34.43±2.74fgh | 3.66±0.13efg | 1.92±0.04k |
| P | 0.82±0.05c | 6.00±0.00ab | 20.60±0.26gh | 24.20±0.66i | 2.00±0.10def | 40.23±1.61defg | 3.35±0.13ghi | 2.25±0.06fg |
| Q | 0.73±0.03de | 4.67±0.58cde | 19.20±0.30hi | 24.90±0.30i | 2.17±0.15de | 44.90±3.69d | 3.42±0.21fgh | 2.76±0.01bc |
| R | 0.61±0.03fg | 4.33±0.58de | 21.23±0.35fg | 23.93±1.46i | 1.57±0.06i | 31.17±1.97h | 4.28±0.30cd | 2.16±0.03hij |
表2 灌浆期不同燕麦品种农艺性状比较
Table 2 Comparison of different oat varieties agronomic traits during pustulation stage
品种 Variety | 茎粗 Plant diameter (cm) | 茎节数 Stalk pitch (No.) | 穗长 | 旗叶长 Flag leaf length (cm) | 旗叶宽 Flag leaf width (cm) | 旗叶面积 Flag leaf area (cm2) | 鲜干比 Fresh/dry | 茎叶比 Stem/leaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.79±0.05cd | 6.33±0.58a | 24.97±0.87d | 29.20±1.30f | 2.83±0.15b | 68.70±0.83b | 3.73±0.23ef | 2.23±0.03fgh |
| B | 0.94±0.05b | 6.67±0.58a | 35.03±1.17a | 31.33±0.15de | 3.53±0.15a | 92.08±4.06a | 3.13±0.03hi | 2.30±0.04f |
| C | 0.69±0.07ef | 4.00±0.00e | 14.87±0.60j | 17.07±0.45j | 1.57±0.06i | 22.23±0.48i | 4.98±0.12a | 1.90±0.05k |
| D | 0.64±0.03fg | 4.33±0.58de | 30.70±1.61c | 33.47±0.57bc | 1.93±0.06efg | 53.81±1.62c | 3.83±0.06e | 2.17±0.03hij |
| E | 0.49±0.05i | 5.33±0.58bc | 23.03±1.12e | 25.03±1.20i | 1.63±0.06hi | 34.04±2.74gh | 3.64±0.26efg | 2.12±0.05j |
| F | 0.65±0.05efg | 4.67±0.58cde | 21.07±1.25fg | 27.23±0.83gh | 1.63±0.06hi | 37.01±2.25efgh | 3.96±0.09de | 1.74±0.05l |
| G | 0.64±0.03fg | 5.00±0.00cd | 20.23±0.93gh | 30.37±0.87ef | 1.53±0.06i | 38.75±2.41defg | 3.91±0.08e | 2.85±0.04a |
| H | 0.66±0.05efg | 6.00±0.00ab | 18.03±0.45i | 29.50±0.60ef | 2.23±0.15d | 54.83±4.60c | 3.43±0.06fgh | 2.15±0.04ij |
| I | 0.69±0.05ef | 5.33±0.58bc | 32.50±0.80b | 34.40±0.62b | 2.00±0.10def | 57.25±3.88c | 3.27±0.11hi | 2.24±0.02fgh |
| J | 1.04±0.05a | 6.00±0.00ab | 29.87±0.95c | 32.47±1.12cd | 2.67±0.15bc | 71.91±1.68b | 3.04±0.05i | 2.22±0.04ghi |
| K | 0.59±0.05gh | 5.00±0.00cd | 19.23±0.55hi | 31.20±0.66de | 1.57±0.06i | 40.63±0.80def | 4.59±0.06bc | 2.77±0.02b |
| L | 0.73±0.03de | 4.67±0.58cde | 17.87±0.32i | 27.27±1.17g | 1.87±0.15fgh | 42.24±1.93de | 4.71±0.14ab | 2.37±0.04e |
| M | 0.52±0.02hi | 4.33±0.58de | 22.57±0.40ef | 29.70±1.37ef | 1.70±0.20ghi | 42.09±6.27de | 4.27±0.32cd | 2.69±0.04c |
| N | 0.81±0.02cd | 5.33±0.58bc | 30.67±0.96c | 43.03±1.06a | 2.50±0.10c | 89.54±5.76a | 3.72±0.21ef | 2.46±0.04d |
| O | 0.87±0.02bc | 4.67±0.58cde | 20.13±0.80gh | 25.37±0.42hi | 1.63±0.15hi | 34.43±2.74fgh | 3.66±0.13efg | 1.92±0.04k |
| P | 0.82±0.05c | 6.00±0.00ab | 20.60±0.26gh | 24.20±0.66i | 2.00±0.10def | 40.23±1.61defg | 3.35±0.13ghi | 2.25±0.06fg |
| Q | 0.73±0.03de | 4.67±0.58cde | 19.20±0.30hi | 24.90±0.30i | 2.17±0.15de | 44.90±3.69d | 3.42±0.21fgh | 2.76±0.01bc |
| R | 0.61±0.03fg | 4.33±0.58de | 21.23±0.35fg | 23.93±1.46i | 1.57±0.06i | 31.17±1.97h | 4.28±0.30cd | 2.16±0.03hij |
品种 Variety | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
抽穗期 Heading stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 灌浆期 Pustulation stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 灌浆期 Pustulation stage | |
| A | 64.00±2.56cdefg | 61.95±1.09bcd | 59.80±0.64cdef | 39.54±2.84abcd | 34.20±2.55cde | 33.95±1.98bcd |
| B | 65.74±1.06abc | 62.21±2.47bcd | 60.63±0.26bcd | 37.02±2.03bcde | 34.30±0.86cde | 32.32±1.26cd |
| C | 65.11±0.49abcd | 60.30±0.98cde | 60.37±1.52bcd | 39.80±0.59abc | 36.93±1.42abcd | 37.06±0.79ab |
| D | 59.35±1.58ij | 56.84±1.18fgh | 54.28±2.92g | 31.99±3.36f | 31.53±1.23e | 29.88±0.98d |
| E | 61.27±1.47ghi | 58.92±0.49defg | 58.06±0.68cdefg | 36.22±1.52cde | 34.81±0.91cde | 36.06±3.49abc |
| F | 61.32±1.33ghi | 57.35±2.78defg | 56.12±1.40efg | 36.15±0.77cde | 35.35±1.91bcde | 34.32±3.09bcd |
| G | 67.68±1.34ab | 66.97±1.86a | 65.49±2.08a | 40.63±2.70ab | 39.80±2.33a | 40.23±1.26a |
| H | 62.06±1.70fghi | 59.46±1.02defg | 56.30±2.83efg | 38.65±1.93abcde | 36.75±1.15abcd | 34.12±1.53bcd |
| I | 64.79±1.17cdef | 62.07±1.97bcd | 60.98±1.61bc | 37.10±0.58bcde | 36.46±0.67abcd | 35.84±1.14abc |
| J | 60.06±1.27ij | 55.40±0.78h | 56.01±0.97fg | 35.49±1.43ef | 33.75±2.72cde | 34.32±2.19bcd |
| K | 69.48±0.28a | 64.19±1.23ab | 59.95±2.21cde | 36.73±2.42bcde | 36.82±0.75abcd | 38.18±0.85ab |
| L | 66.46±0.90bc | 63.90±0.45ab | 63.98±0.28ab | 41.63±0.68a | 39.43±1.65ab | 36.38±1.24abc |
| M | 58.32±1.82j | 62.80±2.24bc | 61.29±2.15bc | 36.72±1.72bcde | 37.69±1.74abc | 36.16±3.33abc |
| N | 63.25±1.35defg | 59.93±2.47cdef | 61.14±2.93bc | 38.72±1.94abcde | 37.58±1.31abc | 36.69±1.81abc |
| O | 60.24±1.56hij | 54.98±1.36h | 55.77±0.56g | 36.03±1.15cde | 35.23±1.96bcde | 34.19±0.63bcd |
| P | 62.96±0.42efgh | 56.44±0.65gh | 55.87±0.45g | 35.66±1.37def | 32.61±2.04de | 36.30±0.51abc |
| Q | 65.19±1.26abcd | 60.55±1.50cde | 56.85±3.46defg | 36.60±1.23cde | 35.21±1.37bcde | 36.12±0.43abc |
| R | 66.36±0.65bc | 61.64±1.84bcd | 56.92±1.78defg | 39.58±0.89abcd | 36.58±1.18abcd | 35.23±0.39bc |
表3 不同燕麦品种中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维比较
Table 3 Comparison of different oat varieties neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber (%)
品种 Variety | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
抽穗期 Heading stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 灌浆期 Pustulation stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 灌浆期 Pustulation stage | |
| A | 64.00±2.56cdefg | 61.95±1.09bcd | 59.80±0.64cdef | 39.54±2.84abcd | 34.20±2.55cde | 33.95±1.98bcd |
| B | 65.74±1.06abc | 62.21±2.47bcd | 60.63±0.26bcd | 37.02±2.03bcde | 34.30±0.86cde | 32.32±1.26cd |
| C | 65.11±0.49abcd | 60.30±0.98cde | 60.37±1.52bcd | 39.80±0.59abc | 36.93±1.42abcd | 37.06±0.79ab |
| D | 59.35±1.58ij | 56.84±1.18fgh | 54.28±2.92g | 31.99±3.36f | 31.53±1.23e | 29.88±0.98d |
| E | 61.27±1.47ghi | 58.92±0.49defg | 58.06±0.68cdefg | 36.22±1.52cde | 34.81±0.91cde | 36.06±3.49abc |
| F | 61.32±1.33ghi | 57.35±2.78defg | 56.12±1.40efg | 36.15±0.77cde | 35.35±1.91bcde | 34.32±3.09bcd |
| G | 67.68±1.34ab | 66.97±1.86a | 65.49±2.08a | 40.63±2.70ab | 39.80±2.33a | 40.23±1.26a |
| H | 62.06±1.70fghi | 59.46±1.02defg | 56.30±2.83efg | 38.65±1.93abcde | 36.75±1.15abcd | 34.12±1.53bcd |
| I | 64.79±1.17cdef | 62.07±1.97bcd | 60.98±1.61bc | 37.10±0.58bcde | 36.46±0.67abcd | 35.84±1.14abc |
| J | 60.06±1.27ij | 55.40±0.78h | 56.01±0.97fg | 35.49±1.43ef | 33.75±2.72cde | 34.32±2.19bcd |
| K | 69.48±0.28a | 64.19±1.23ab | 59.95±2.21cde | 36.73±2.42bcde | 36.82±0.75abcd | 38.18±0.85ab |
| L | 66.46±0.90bc | 63.90±0.45ab | 63.98±0.28ab | 41.63±0.68a | 39.43±1.65ab | 36.38±1.24abc |
| M | 58.32±1.82j | 62.80±2.24bc | 61.29±2.15bc | 36.72±1.72bcde | 37.69±1.74abc | 36.16±3.33abc |
| N | 63.25±1.35defg | 59.93±2.47cdef | 61.14±2.93bc | 38.72±1.94abcde | 37.58±1.31abc | 36.69±1.81abc |
| O | 60.24±1.56hij | 54.98±1.36h | 55.77±0.56g | 36.03±1.15cde | 35.23±1.96bcde | 34.19±0.63bcd |
| P | 62.96±0.42efgh | 56.44±0.65gh | 55.87±0.45g | 35.66±1.37def | 32.61±2.04de | 36.30±0.51abc |
| Q | 65.19±1.26abcd | 60.55±1.50cde | 56.85±3.46defg | 36.60±1.23cde | 35.21±1.37bcde | 36.12±0.43abc |
| R | 66.36±0.65bc | 61.64±1.84bcd | 56.92±1.78defg | 39.58±0.89abcd | 36.58±1.18abcd | 35.23±0.39bc |
指标 Index | 权重系数 Weighting coefficient | 排序 Rank | 指标 Index | 权重系数 Weighting coefficient | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 0.096 | 7 | 茎叶比 Stem/leaf | 0.101 | 6 |
| 鲜草产量 Fresh yield | 0.114 | 5 | 粗蛋白 CP | 0.116 | 4 |
| 干草产量 Hay yield | 0.119 | 3 | 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF | 0.064 | 10 |
| 旗叶面积Flag leaf area | 0.124 | 2 | 中性洗涤纤维 NDF | 0.071 | 8 |
| 鲜干比 Fresh/dry | 0.131 | 1 | 相对饲喂价值 RFV | 0.065 | 9 |
表4 不同指标的权重
Table 4 Weights of the different index
指标 Index | 权重系数 Weighting coefficient | 排序 Rank | 指标 Index | 权重系数 Weighting coefficient | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 0.096 | 7 | 茎叶比 Stem/leaf | 0.101 | 6 |
| 鲜草产量 Fresh yield | 0.114 | 5 | 粗蛋白 CP | 0.116 | 4 |
| 干草产量 Hay yield | 0.119 | 3 | 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF | 0.064 | 10 |
| 旗叶面积Flag leaf area | 0.124 | 2 | 中性洗涤纤维 NDF | 0.071 | 8 |
| 鲜干比 Fresh/dry | 0.131 | 1 | 相对饲喂价值 RFV | 0.065 | 9 |
品种 Variety | 等权Equal weight | 加权Weighted | 品种 Variety | 等权Equal weight | 加权Weighted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | ||
| 甜燕1号 Tianyan No.1 | 0.697 | 9 | 0.685 | 8 | 伽利略 Galileo | 0.759 | 3 | 0.746 | 2 |
| 甜燕3号 Tianyan No.3 | 0.769 | 1 | 0.767 | 1 | B5-2 | 0.618 | 17 | 0.612 | 17 |
| 福燕1号 Fuyan No.1 | 0.706 | 6 | 0.708 | 6 | Song | 0.623 | 16 | 0.623 | 16 |
| 福燕2号 Fuyan No.2 | 0.765 | 2 | 0.730 | 3 | 东燕1号 Dongyan No.1 | 0.637 | 15 | 0.629 | 15 |
| 丹燕111 Danyan No.111 | 0.683 | 12 | 0.672 | 11 | 牧王 Haymaker | 0.704 | 7 | 0.709 | 5 |
| 白燕7号 Baiyan No.7 | 0.693 | 10 | 0.670 | 12 | Ca-1 | 0.712 | 5 | 0.686 | 7 |
| 蒙饲燕4号 Mengsiyan No.4 | 0.608 | 18 | 0.612 | 17 | 爱沃126 Ever leaf 126 | 0.687 | 11 | 0.673 | 10 |
| 爱沃 Ever leaf | 0.699 | 8 | 0.680 | 9 | Mogan | 0.661 | 13 | 0.645 | 13 |
| 贝勒 Baylor | 0.721 | 4 | 0.717 | 4 | 甜燕60号 Tianyan No.60 | 0.658 | 14 | 0.639 | 14 |
表5 供试燕麦品种关联度及排名
Table 5 Correlation degree and ranking of oat varieties tested
品种 Variety | 等权Equal weight | 加权Weighted | 品种 Variety | 等权Equal weight | 加权Weighted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | 关联度 Correlation degree | 排序 Rank | ||
| 甜燕1号 Tianyan No.1 | 0.697 | 9 | 0.685 | 8 | 伽利略 Galileo | 0.759 | 3 | 0.746 | 2 |
| 甜燕3号 Tianyan No.3 | 0.769 | 1 | 0.767 | 1 | B5-2 | 0.618 | 17 | 0.612 | 17 |
| 福燕1号 Fuyan No.1 | 0.706 | 6 | 0.708 | 6 | Song | 0.623 | 16 | 0.623 | 16 |
| 福燕2号 Fuyan No.2 | 0.765 | 2 | 0.730 | 3 | 东燕1号 Dongyan No.1 | 0.637 | 15 | 0.629 | 15 |
| 丹燕111 Danyan No.111 | 0.683 | 12 | 0.672 | 11 | 牧王 Haymaker | 0.704 | 7 | 0.709 | 5 |
| 白燕7号 Baiyan No.7 | 0.693 | 10 | 0.670 | 12 | Ca-1 | 0.712 | 5 | 0.686 | 7 |
| 蒙饲燕4号 Mengsiyan No.4 | 0.608 | 18 | 0.612 | 17 | 爱沃126 Ever leaf 126 | 0.687 | 11 | 0.673 | 10 |
| 爱沃 Ever leaf | 0.699 | 8 | 0.680 | 9 | Mogan | 0.661 | 13 | 0.645 | 13 |
| 贝勒 Baylor | 0.721 | 4 | 0.717 | 4 | 甜燕60号 Tianyan No.60 | 0.658 | 14 | 0.639 | 14 |
| 1 | Zhao X F, Rong Y P, Zhao L X. The collection and evaluation of oat (Avena sativa) in China. Pratacultural Science, 2007, 24(3): 36-40. |
| 赵秀芳, 戎郁萍, 赵来喜. 我国燕麦种质资源的收集和评价. 草业科学, 2007, 24(3): 36-40. | |
| 2 | Hou L Y, Zhu Z Y, Yang J, et al. Current status, problems and potentials of forage oat in China. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 45(3): 248-253. |
| 侯龙鱼, 朱泽义, 杨杰, 等. 我国饲草用燕麦现状、问题和潜力. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 45(3): 248-253. | |
| 3 | Yang C, Wang G G, Wang M L. Production and trade of wild oat forage in China. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(5): 1129-1135. |
| 杨春, 王国刚, 王明利. 我国的燕麦草生产和贸易. 草业科学, 2017, 34(5): 1129-1135. | |
| 4 | Qi X D. Nutritional value and evaluation of oat in alpine pasture. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2012, 31(4): 100-101. |
| 祁学东. 高寒牧区燕麦营养价值及其评价. 畜牧兽医杂志, 2012, 31(4): 100-101. | |
| 5 | Pan Q M, Xue J G, Tao J, et al. Current status of grassland degradation and measures for grassland restoration in northern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(17): 1642-1650. |
| 潘庆民, 薛建国, 陶金, 等. 中国北方草原退化现状与恢复技术. 科学通报, 2018, 63(17): 1642-1650. | |
| 6 | Lin B Q, Chen W H, Jiang W B. Present situation and prospect of forage crop development in Hulunbuir. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2002(S1): 24-26. |
| 林宝奇, 陈文贺, 蒋万波. 呼伦贝尔市发展饲草作物的现状和前景. 内蒙古农业科技, 2002(S1): 24-26. | |
| 7 | Ding W Q, Li P, Yin Y T, et al. Vulnerability of herder households under the framework of sustainable livelihoods in the grassland of Northern China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(8): 1-11. |
| 丁文强, 李平, 尹燕亭, 等. 可持续生计视角下中国北方草原区牧户脆弱性评价研究. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 1-11. | |
| 8 | Perez H N, Diaz S, Garnier E, et al. New handbook for stand-ardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Australian Journal of Botany, 2013, 61(3): 167-234. |
| 9 | Liang G L, Qin Y, Wei X X, et al. Evaluation on productivity and quality of oat strain I-D in the alpine regions of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(4): 917-927. |
| 梁国玲, 秦燕, 魏小星, 等. 青藏高原高寒区I-D燕麦品系饲草生产性能及品质评价. 草地学报, 2018, 26(4): 917-927. | |
| 10 | Guan Y X, Liu D, Zhang K C. Comparison of two kinds of nitrogen analyzers for determination of crude protein content in feed. Shanghai Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2012, 181(3): 6-8. |
| 管姚香, 刘丹, 张克春. 两种定氮仪测定饲料粗蛋白含量的比较. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2012, 181(3): 6-8. | |
| 11 | Chen J Y, Huang L J, Jin X W, et al. Determination of crude fiber in feeds by filter bag fiber analyzer. China Feed, 2023, 721(5): 87-91. |
| 陈建勇, 黄丽俊, 金晓威, 等. 滤袋式纤维分析仪检测饲料中粗纤维. 中国饲料, 2023, 721(5): 87-91. | |
| 12 | Ling S L. Evaluation on the nutritional value of high-quality forage grass in desert steppe of Ordos by using RFV. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2014, 35(10): 15-16, 19. |
| 凌树礼. 应用RFV评价鄂尔多斯荒漠草原优势牧草营养价值. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2014, 35(10): 15-16, 19. | |
| 13 | Chen X, Wu B, Zhang Z W. Evaluation of adaptability and stability for important agronomic traits of oat (Avena spp.) germplasm resources. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2016, 17(4): 577-585. |
| 陈新, 吴斌, 张宗文. 燕麦种质资源重要农艺性状适应性和稳定性评价. 植物遗传资源学报, 2016, 17(4): 577-585. | |
| 14 | Liu G, Zhao G Q, Wei L M. Primary application of the entropy weight-based gray systematic theory to integrated evaluation of oat. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2007, 156(3): 84-89. |
| 刘刚, 赵桂琴, 魏黎明. 基于熵权赋权法的灰色系统理论在燕麦品种综合评价中的应用. 中国草地学报, 2007, 156(3): 84-89. | |
| 15 | Hu D P. Study on adaptability of different Avena sativa varieties in Yanmenguan Pass area. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 胡东鹏. 雁门关地区不同饲用燕麦品种的适应性研究. 太谷: 山西农业大学, 2016. | |
| 16 | Zhang W, Zhou Q P, Chen Y J, et al. Comparison of production performance and forage quality of ten introduced oat varieties in Hulunbuir, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 129-142. |
| 张伟, 周青平, 陈有军, 等. 呼伦贝尔地区10个引进燕麦品种生产性能及饲草品质比较. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 129-142. | |
| 17 | Na Y, Wu R C, Li F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of production performance of 15 oat varieties in south bank of Yellow River in western Inner Mongolia. Feed Research, 2022, 45(24): 97-101. |
| 那亚, 乌仁曹, 李峰, 等. 15个燕麦品种在内蒙古西部黄河南岸地区生产性能综合评价. 饲料研究, 2022, 45(24): 97-101. | |
| 18 | Wang Y C, Song L, Zhang F F, et al. Comparative study on production performance of 10 oat varieties. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(2): 254-263. |
| 王彦超, 宋磊, 张凡凡, 等. 不同燕麦品种生育期农艺性状、生产性能及品质的比较. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(2): 254-263. | |
| 19 | Wang X, Li M, Zheng Y H, et al. Study on introduced forage oat varieties. Grassland and Prataculture, 2016, 28(3): 34-42. |
| 王玺, 李敏, 郑轶慧, 等. 饲用燕麦适应性鉴定与评价. 草原与草业, 2016, 28(3): 34-42. | |
| 20 | Cao L X, Zhao S F, Zhao Y G, et al. Effects of variety diversity on yield stability of oat seeds in Bashang region of Hebei Province. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 43(2): 48-55. |
| 曹丽霞, 赵世峰, 赵艳格, 等. 品种多样性对冀北坝上地区燕麦种子产量稳定性的影响. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43(2): 48-55. | |
| 21 | Bai S S, Zhang W J, Wang Z F, et al. Investigation on the production and utilization of oat and rye forage in the Yellow River Delta. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2020(3): 63-68. |
| 柏杉杉, 张文娟, 王兆凤, 等. 黄河三角洲地区麦类饲草生产利用情况调研报告. 草学, 2020(3): 63-68. | |
| 22 | Zhang Y, Chen Z F, Zhang X N, et al. Influence of mowing time on yield and quality of spring and autumn sown oat hay. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(11): 124-135. |
| 张莹, 陈志飞, 张晓娜, 等. 不同刈割期对春播、秋播燕麦干草产量和品质的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 124-135. | |
| 23 | Wang W. Assessment of productive performance and nutritive value of 21 oat genotypes in western Jilin Province. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2016. |
| 王巍. 吉林省西部地区21个燕麦品种生产性能和营养价值评价. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2016. | |
| 24 | Gao Y M, Sa R N, Sun L L, et al. Preliminary study on introduction experiment of oats in Tongliao area of Inner Mongolia. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2017, 38(5): 32-35. |
| 高亚敏, 萨日娜, 孙琳丽, 等. 内蒙古通辽地区燕麦引种试验初步研究. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2017, 38(5): 32-35. | |
| 25 | Zhuang K Z, Wu R H, Zhang C Y, et al. Evaluation of productivity of 11 oat varieties in Lunan region. Crop Research, 2022, 36(4): 313-319, 326. |
| 庄克章, 吴荣华, 张春艳, 等. 11个饲用燕麦品种在鲁南地区的生产性能评价. 作物研究, 2022, 36(4): 313-319, 326. | |
| 26 | Duan L X, Ma X, Ju Z L, et al. Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with organic fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of Avena sativa ‘Qinghai’. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(2): 471-478. |
| 段连学, 马祥, 琚泽亮, 等. 减氮配施有机肥对‘青海甜燕麦’光合特性和产量的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(2): 471-478. | |
| 27 | Wang Q, Li Z J, Li J, et al. Evaluation of agronomic and forage quality traits of a range of oat cultivars. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 149-158. |
| 王茜, 李志坚, 李晶, 等. 不同类型燕麦农艺和饲草品质性状分析. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 149-158. | |
| 28 | Zhou B W, Serret M D, Elazab A, et al. Wheat ear carbon assimilation and nitrogen remobilization contribute significantly to grain yield. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2016, 58(11): 914-926. |
| 29 | Chai J K, Zhao G Q, Hu K J, et al. Effect of eco-environment in different planting areas on oat nutritive value and hay production. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(3): 421-425, 476. |
| 柴继宽, 赵桂琴, 胡凯军, 等. 不同种植区生态环境对燕麦营养价值及干草产量的影响. 草地学报, 2010, 18(3): 421-425, 476. | |
| 30 | Yang Y G, Cheng T L, Yang X J, et al. Effects of different growth stages of three oat cultivars on the nutritive value of silage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(4): 683-688. |
| 杨云贵, 程天亮, 杨雪娇, 等. 3个燕麦品种不同收获期对青贮饲草营养价值的影响. 草地学报, 2013, 21(4): 683-688. |
| [1] | 赵洁, 陈恒光, 裴晓蒙, 于昊, 徐银莹, 茆达干. 围产期日粮添加白藜芦醇对山羊生产性能、血液指标及炎症因子基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 210-220. |
| [2] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [3] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [4] | 鲍根生, 李媛, 冯晓云, 张鹏, 孟思宇. 高寒区氮添加和间作种植互作对燕麦和豌豆根系构型影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 73-84. |
| [5] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [6] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [7] | 张睿, 韩重阳, 蔡家邦, 汪阳, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 聂刚. 6个苇状羊茅(型)品种在成都平原区的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 138-148. |
| [8] | 李文龙, 李峰, 张仲鹃, 王殿清, 王欢, 靳慧卿, 特木热, 胡志玲, 陶雅. 鄂尔多斯高原北部一年两季燕麦种植模式生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 159-168. |
| [9] | 张珈敏, 关皓, 李海萍, 贾志锋, 马祥, 刘文辉, 陈有军, 陈仕勇, 蒋永梅, 甘丽, 周青平, 杨丽雪. 混播比例及乳酸菌剂对燕麦-饲用豌豆发酵TMR品质及瘤胃降解特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 169-181. |
| [10] | 任春燕, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 段嘉蕾. 青藏高原高寒地区早熟燕麦资源筛选和适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 116-129. |
| [11] | 石永红, 高鹏, 方志红, 赵祥, 韩伟, 魏江铭, 刘琳, 李锦臻. 15个进口饲用燕麦品种炭疽病的抗病性评价及损失分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 130-142. |
| [12] | 党浩千, 覃娟清, 郭宇康, 张富, 王迎港, 刘庆华. 不同添加剂发酵笋壳对湖羊生产性能及瘤胃发酵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 135-148. |
| [13] | 蒋丛泽, 受娜, 高玮, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区不同青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 216-228. |
| [14] | 张振粉, 黄荣, 李向阳, 姚博, 赵桂琴. 基于Illumina MiSeq高通量测序的燕麦种带细菌多样性及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 96-108. |
| [15] | 叶婷, 吴晓娟, 芦奕晓, 刘生娟, 姜卓慧, 杨惠敏. 混播比例对两种苜蓿混播草地产量和种群密度稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||