

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 74-85.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023362
桑瑞娟1( ), 崔超杰4(
), 崔超杰4( ), 何云5, 张晓霞6, 姚晋1, 董春阳1, 孙浩1,2,3, 史莹华1,2,3, 朱晓艳1,2,3, 李德锋1,2,3(
), 何云5, 张晓霞6, 姚晋1, 董春阳1, 孙浩1,2,3, 史莹华1,2,3, 朱晓艳1,2,3, 李德锋1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-26
修回日期:2023-10-30
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
李德锋
作者简介:E-mail: Leadephone@126.com基金资助:
Rui-juan SANG1( ), Chao-jie CUI4(
), Chao-jie CUI4( ), Yun HE5, Xiao-xia ZHANG6, Jin YAO1, Chun-yang DONG1, Hao SUN1,2,3, Ying-hua SHI1,2,3, Xiao-yan ZHU1,2,3, De-feng LI1,2,3(
), Yun HE5, Xiao-xia ZHANG6, Jin YAO1, Chun-yang DONG1, Hao SUN1,2,3, Ying-hua SHI1,2,3, Xiao-yan ZHU1,2,3, De-feng LI1,2,3( )
)
Received:2023-09-26
Revised:2023-10-30
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
De-feng LI
摘要:
为了解秋播饲用燕麦在豫北地区的抗倒伏特性和生产性能,本研究测定了18个品种的干草产量、分蘖数、越冬率和不同时期倒伏率,分析了燕麦倒伏与株高、穗位高及茎秆形态的关系。结果表明:80%的燕麦品种从抽穗期开始倒伏,乳熟中期收获时倒伏率为10.0%~95.0%,其中,贝利和大富豪两个品种倒伏率较低;第1节和第2节茎粗、第2节干重等反映茎秆强度的指标与倒伏率呈显著负相关(P<0.05);18个燕麦品种生育期为182~207 d,干草产量、株高、越冬率和返青期分蘖数分别为11.99~20.46 t·hm-2、1.11~1.52 m、83.7%~96.6%和5.3~8.5个·株-1,贝利、爱沃和燕王3个品种干草产量较高,达20 t·hm-2。综合抗倒伏特性、干草产量和营养品质,本研究认为贝利、燕王和大富豪3个品种适宜在豫北地区秋播种植。
桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85.
Rui-juan SANG, Chao-jie CUI, Yun HE, Xiao-xia ZHANG, Jin YAO, Chun-yang DONG, Hao SUN, Ying-hua SHI, Xiao-yan ZHU, De-feng LI. Lodging resistance and production performance of 18 autumn-sown forage oat varieties in northern Henan Province[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(8): 74-85.
品种 Varieties | 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | 净度 Purity (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 播种量 Seeding rate (kg·hm-2) | 原产地 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESK | 47.0 | 96.9 | 34.3 | 197.4 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| LAMPTON | 65.0 | 94.6 | 36.5 | 145.8 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 75.0 | 96.5 | 33.2 | 125.0 | 美国America |
| 贝利Baler | 90.0 | 97.8 | 44.4 | 102.0 | 加拿大Canada |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 41.0 | 89.3 | 40.1 | 246.6 | 加拿大Canada |
| 贝勒2号Baler Ⅱ | 51.0 | 98.8 | 40.1 | 178.6 | 加拿大Canada |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 56.0 | 95.8 | 41.9 | 167.4 | 加拿大Canada |
| 海威Haiwee | 81.0 | 92.8 | 44.5 | 119.5 | 加拿大Canada |
| 伽利略Galileo | 61.0 | 98.6 | 27.0 | 149.0 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 47.0 | 86.5 | 41.0 | 220.1 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| 凯速Souris | 81.0 | 82.3 | 35.7 | 135.5 | 美国America |
| 蒙特Mengte | 58.0 | 92.8 | 40.5 | 166.9 | 美国America |
| 莫妮达Monida | 98.0 | 79.2 | 32.2 | 116.3 | 加拿大Canada |
| 牧王Haymaker | 90.0 | 96.0 | 44.2 | 104.2 | 加拿大Canada |
| 挑战者Challengers | 64.0 | 93.0 | 38.0 | 151.2 | 加拿大Canada |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 78.0 | 97.4 | 55.7 | 119.0 | 加拿大Canada |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 44.0 | 99.4 | 39.3 | 206.6 | 加拿大Canada |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 80.0 | 96.8 | 31.8 | 116.0 | 美国America |
表1 18个燕麦品种发芽率、净度、千粒重、播种量及原产地
Table 1 Germination rate, purity, thousand grain weight, seeding rate and origin of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | 净度 Purity (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 播种量 Seeding rate (kg·hm-2) | 原产地 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESK | 47.0 | 96.9 | 34.3 | 197.4 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| LAMPTON | 65.0 | 94.6 | 36.5 | 145.8 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 75.0 | 96.5 | 33.2 | 125.0 | 美国America |
| 贝利Baler | 90.0 | 97.8 | 44.4 | 102.0 | 加拿大Canada |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 41.0 | 89.3 | 40.1 | 246.6 | 加拿大Canada |
| 贝勒2号Baler Ⅱ | 51.0 | 98.8 | 40.1 | 178.6 | 加拿大Canada |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 56.0 | 95.8 | 41.9 | 167.4 | 加拿大Canada |
| 海威Haiwee | 81.0 | 92.8 | 44.5 | 119.5 | 加拿大Canada |
| 伽利略Galileo | 61.0 | 98.6 | 27.0 | 149.0 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 47.0 | 86.5 | 41.0 | 220.1 | 澳大利亚Australia |
| 凯速Souris | 81.0 | 82.3 | 35.7 | 135.5 | 美国America |
| 蒙特Mengte | 58.0 | 92.8 | 40.5 | 166.9 | 美国America |
| 莫妮达Monida | 98.0 | 79.2 | 32.2 | 116.3 | 加拿大Canada |
| 牧王Haymaker | 90.0 | 96.0 | 44.2 | 104.2 | 加拿大Canada |
| 挑战者Challengers | 64.0 | 93.0 | 38.0 | 151.2 | 加拿大Canada |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 78.0 | 97.4 | 55.7 | 119.0 | 加拿大Canada |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 44.0 | 99.4 | 39.3 | 206.6 | 加拿大Canada |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 80.0 | 96.8 | 31.8 | 116.0 | 美国America |
品种 Varieties | 抽穗期Heading stage (Month-day) | 乳熟中期Mid-milk maturity (Month-day) | 生育期Growth period (d) | 熟性 Maturity | 分蘖数Tiller number (No·plant-1) | 越冬率Winter survival rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒙特Mengte | 04-05 | 04-28 | 182 | 特早熟SEM | 7.9±1.8abcd | 96.1±5.5a |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 04-23 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 6.6±0.6abcd | 92.0±7.2a |
| LAMPTON | 04-28 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 8.4±0.4ab | 95.3±6.1a |
| 挑战者Challengers | 04-28 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 7.0±2.0abcd | 96.6±4.9a |
| 海威Haiwee | 04-29 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 6.7±0.7abcd | 83.7±7.2a |
| ESK | 05-01 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 8.5±3.0a | 92.9±7.1a |
| 莫妮达Monida | 05-01 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 7.6±1.8abcd | 87.5±2.4a |
| 凯速Souris | 05-02 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 6.7±2.3abcd | 92.9±9.4a |
| 伽利略Galileo | 04-30 | 05-15 | 199 | 中熟MM | 8.1±1.7abc | 94.6±6.4a |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 05-03 | 05-15 | 199 | 中熟MM | 5.7±0.4bcd | 91.0±10.8a |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 05-01 | 05-19 | 203 | 中熟MM | 6.9±1.3abcd | 89.7±6.9a |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 05-02 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 5.3±1.5d | 88.9±10.7a |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 05-02 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 6.2±1.1abcd | 87.8±8.6a |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 05-06 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 8.1±0.9abc | 94.9±5.9a |
| 贝利Baler | 05-06 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 6.6±0.9abcd | 94.3±7.1a |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 05-07 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 7.4±1.1abcd | 94.4±5.5a |
| 牧王Haymaker | 05-03 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 5.9±1.7abcd | 93.1±8.4a |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 05-09 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 5.7±0.2cd | 92.5±8.2a |
表2 18个燕麦品种生育期、熟性、分蘖数与越冬率
Table 2 The growth period, maturity, tiller number and winter survival rate of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 抽穗期Heading stage (Month-day) | 乳熟中期Mid-milk maturity (Month-day) | 生育期Growth period (d) | 熟性 Maturity | 分蘖数Tiller number (No·plant-1) | 越冬率Winter survival rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒙特Mengte | 04-05 | 04-28 | 182 | 特早熟SEM | 7.9±1.8abcd | 96.1±5.5a |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 04-23 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 6.6±0.6abcd | 92.0±7.2a |
| LAMPTON | 04-28 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 8.4±0.4ab | 95.3±6.1a |
| 挑战者Challengers | 04-28 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 7.0±2.0abcd | 96.6±4.9a |
| 海威Haiwee | 04-29 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 6.7±0.7abcd | 83.7±7.2a |
| ESK | 05-01 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 8.5±3.0a | 92.9±7.1a |
| 莫妮达Monida | 05-01 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 7.6±1.8abcd | 87.5±2.4a |
| 凯速Souris | 05-02 | 05-12 | 196 | 早熟EM | 6.7±2.3abcd | 92.9±9.4a |
| 伽利略Galileo | 04-30 | 05-15 | 199 | 中熟MM | 8.1±1.7abc | 94.6±6.4a |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 05-03 | 05-15 | 199 | 中熟MM | 5.7±0.4bcd | 91.0±10.8a |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 05-01 | 05-19 | 203 | 中熟MM | 6.9±1.3abcd | 89.7±6.9a |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 05-02 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 5.3±1.5d | 88.9±10.7a |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 05-02 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 6.2±1.1abcd | 87.8±8.6a |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 05-06 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 8.1±0.9abc | 94.9±5.9a |
| 贝利Baler | 05-06 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 6.6±0.9abcd | 94.3±7.1a |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 05-07 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 7.4±1.1abcd | 94.4±5.5a |
| 牧王Haymaker | 05-03 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 5.9±1.7abcd | 93.1±8.4a |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 05-09 | 05-23 | 207 | 晚熟LM | 5.7±0.2cd | 92.5±8.2a |
品种 Varieties | 株高 Plant height (m) | 鲜草产量 Fresh yield (t·hm–2) | 干草产量 Hay yield (t·hm–2) | 干鲜比 Dry/fresh | 茎叶比 Stem/leaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利Baler | 1.50±0.05a | 73.60±3.33bc | 20.46±1.87a | 0.28±0.02a | 2.15±1.16abc |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 1.32±0.03bc | 74.83±4.54abc | 19.89±3.06a | 0.27±0.04ab | 1.03±0.33c |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 1.33±0.10bc | 72.39±20.51bc | 19.52±4.55a | 0.26±0.02ab | 1.76±0.79abc |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 1.34±0.03bc | 72.64±1.14bc | 19.19±0.93ab | 0.26±0.02ab | 0.96±0.27c |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 1.52±0.03a | 61.91±7.82cde | 17.17±2.65abc | 0.28±0.03a | 1.20±0.12bc |
| 牧王Haymaker | 1.47±0.02ab | 62.45±12.83cde | 16.75±2.40abc | 0.28±0.04a | 1.11±0.26bc |
| 伽利略Galileo | 1.30±0.02bc | 76.63±11.95ab | 15.68±3.90bcd | 0.20±0.03de | 1.36±0.26abc |
| 贝勒2号Baler Ⅱ | 1.49±0.06a | 62.43±5.54cde | 15.67±1.82bcd | 0.25±0.03abc | 0.86±0.42c |
| LAMPTON | 1.29±0.29bc | 67.23±11.32bcd | 15.63±2.84bcd | 0.23±0.01bcd | 2.27±1.51abc |
| 海威Haiwee | 1.34±0.26abc | 72.34±4.20bc | 15.56±0.82bcd | 0.22±0.02cd | 2.90±1.27a |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 1.45±0.03ab | 58.31±5.85de | 15.32±1.32cd | 0.26±0.02ab | 1.38±0.37abc |
| 凯速Souris | 1.24±0.24bc | 88.03±3.13a | 15.09±2.50cd | 0.17±0.02e | 2.40±2.26abc |
| ESK | 1.11±0.21bc | 80.18±11.47ab | 15.06±2.22cd | 0.19±0.01de | 1.57±0.81abc |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 1.13±0.29bc | 51.30±3.52e | 14.98±1.18cd | 0.29±0.04a | 1.03±0.29c |
| 蒙特Mengte | 1.15±0.02c | 51.35±2.56e | 14.25±1.10cd | 0.28±0.02a | 1.64±0.13abc |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 1.32±0.06bc | 67.14±2.99bcd | 12.61±1.65d | 0.19±0.03de | 1.17±0.13bc |
| 莫妮达Monida | 1.21±0.28bc | 74.82±8.02abc | 12.52±1.68d | 0.17±0.01e | 1.34±0.14abc |
| 挑战者Challengers | 1.17±0.08c | 57.76±4.69de | 11.99±1.11d | 0.21±0.02de | 2.79±2.66ab |
表3 18个燕麦品种生产性能
Table 3 Production performance of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 株高 Plant height (m) | 鲜草产量 Fresh yield (t·hm–2) | 干草产量 Hay yield (t·hm–2) | 干鲜比 Dry/fresh | 茎叶比 Stem/leaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利Baler | 1.50±0.05a | 73.60±3.33bc | 20.46±1.87a | 0.28±0.02a | 2.15±1.16abc |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 1.32±0.03bc | 74.83±4.54abc | 19.89±3.06a | 0.27±0.04ab | 1.03±0.33c |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 1.33±0.10bc | 72.39±20.51bc | 19.52±4.55a | 0.26±0.02ab | 1.76±0.79abc |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 1.34±0.03bc | 72.64±1.14bc | 19.19±0.93ab | 0.26±0.02ab | 0.96±0.27c |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 1.52±0.03a | 61.91±7.82cde | 17.17±2.65abc | 0.28±0.03a | 1.20±0.12bc |
| 牧王Haymaker | 1.47±0.02ab | 62.45±12.83cde | 16.75±2.40abc | 0.28±0.04a | 1.11±0.26bc |
| 伽利略Galileo | 1.30±0.02bc | 76.63±11.95ab | 15.68±3.90bcd | 0.20±0.03de | 1.36±0.26abc |
| 贝勒2号Baler Ⅱ | 1.49±0.06a | 62.43±5.54cde | 15.67±1.82bcd | 0.25±0.03abc | 0.86±0.42c |
| LAMPTON | 1.29±0.29bc | 67.23±11.32bcd | 15.63±2.84bcd | 0.23±0.01bcd | 2.27±1.51abc |
| 海威Haiwee | 1.34±0.26abc | 72.34±4.20bc | 15.56±0.82bcd | 0.22±0.02cd | 2.90±1.27a |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 1.45±0.03ab | 58.31±5.85de | 15.32±1.32cd | 0.26±0.02ab | 1.38±0.37abc |
| 凯速Souris | 1.24±0.24bc | 88.03±3.13a | 15.09±2.50cd | 0.17±0.02e | 2.40±2.26abc |
| ESK | 1.11±0.21bc | 80.18±11.47ab | 15.06±2.22cd | 0.19±0.01de | 1.57±0.81abc |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 1.13±0.29bc | 51.30±3.52e | 14.98±1.18cd | 0.29±0.04a | 1.03±0.29c |
| 蒙特Mengte | 1.15±0.02c | 51.35±2.56e | 14.25±1.10cd | 0.28±0.02a | 1.64±0.13abc |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 1.32±0.06bc | 67.14±2.99bcd | 12.61±1.65d | 0.19±0.03de | 1.17±0.13bc |
| 莫妮达Monida | 1.21±0.28bc | 74.82±8.02abc | 12.52±1.68d | 0.17±0.01e | 1.34±0.14abc |
| 挑战者Challengers | 1.17±0.08c | 57.76±4.69de | 11.99±1.11d | 0.21±0.02de | 2.79±2.66ab |
品种 Varieties | 倒伏率Lodging rate (%) | 穗位高 Ear height (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孕穗期Booting stage | 抽穗期Heading stage | 乳熟初期Early-milk maturity | 乳熟中期Mid-milk maturity | ||
| LAMPTON | 37.5±5.6a | 66.3±23.3a | 90.0±0.0a | 95.0±3.5a | 1.04±0.07bcde |
| ESK | 6.3±5.8c | 51.3±29.7ab | 87.5±4.3a | 88.8±6.5ab | 1.00±0.02de |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 38.8±19.5a | 50.0±23.5ab | 75.0±8.7abc | 77.5±16.8abc | 1.03±0.03cde |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 7.0±7.5c | 21.3±15.2cdef | 78.8±11.4ab | 76.3±10.8abc | 1.12±0.05abc |
| 伽利略Galileo | 27.5±13.5ab | 33.8±7.4bc | 52.5±22.8cd | 72.5±24.9abc | 1.11±0.04abcd |
| 海威Haiwee | 1.3±2.2c | 3.8±6.5f | 55.0±21.8bcd | 62.5±27.7bcd | 1.12±0.03abc |
| 凯速Souris | 0.8±1.3c | 7.5±8.3ef | 60.0±21.5bcd | 61.3±23.0bcd | 1.08±0.01abcd |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 3.3±4.0c | 2.5±4.3f | 23.8±15.2efg | 40.0±14.1def | 1.11±0.06abcd |
| 挑战者Challengers | 0.0±0.0c | 1.3±2.2f | 27.5±19.2ef | 32.5±26.1ef | 0.96±0.04e |
| 蒙特Mengte | 0.0±0.0c | 10.0±7.9def | 22.5±5.6efg | 30.0±7.9ef | 0.97±0.01e |
| 燕王Forage plus | 0.0±0.0c | 0.0±0.0f | 11.3±9.6fg | 28.8±7.4ef | 1.12±0.02abc |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 1.3±2.2c | 8.8±7.4def | 10.0±7.9fg | 21.3±7.4f | 1.14±0.03ab |
| 莫妮达Monida | 0.0±0.0c | 12.5±8.3cdef | 18.8±10.2fg | 21.3±17.1f | 1.05±0.02bcde |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 0.8±0.8c | 1.3±2.2f | 5.0±8.7fg | 18.8±10.2f | 1.17±0.02a |
| 牧王Haymaker | 0.0±0.0c | 0.0±0.0f | 1.3±2.2g | 17.5±7.5f | 1.19±0.02a |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 0.0±0.0c | 0.0±0.0f | 10.0±12.2fg | 16.3±11.4f | 1.11±0.03abcd |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 0.0±0.0c | 3.8±4.1f | 2.5±2.5fg | 13.8±7.4f | 1.15±0.05ab |
| 贝利 Baler | 0.0±0.0c | 2.5±4.3f | 7.5±8.3fg | 10.0±6.1f | 1.12±0.07abc |
表4 18个燕麦品种倒伏率及穗位高
Table 4 Lodging rate and ear height of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 倒伏率Lodging rate (%) | 穗位高 Ear height (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孕穗期Booting stage | 抽穗期Heading stage | 乳熟初期Early-milk maturity | 乳熟中期Mid-milk maturity | ||
| LAMPTON | 37.5±5.6a | 66.3±23.3a | 90.0±0.0a | 95.0±3.5a | 1.04±0.07bcde |
| ESK | 6.3±5.8c | 51.3±29.7ab | 87.5±4.3a | 88.8±6.5ab | 1.00±0.02de |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 38.8±19.5a | 50.0±23.5ab | 75.0±8.7abc | 77.5±16.8abc | 1.03±0.03cde |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 7.0±7.5c | 21.3±15.2cdef | 78.8±11.4ab | 76.3±10.8abc | 1.12±0.05abc |
| 伽利略Galileo | 27.5±13.5ab | 33.8±7.4bc | 52.5±22.8cd | 72.5±24.9abc | 1.11±0.04abcd |
| 海威Haiwee | 1.3±2.2c | 3.8±6.5f | 55.0±21.8bcd | 62.5±27.7bcd | 1.12±0.03abc |
| 凯速Souris | 0.8±1.3c | 7.5±8.3ef | 60.0±21.5bcd | 61.3±23.0bcd | 1.08±0.01abcd |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 3.3±4.0c | 2.5±4.3f | 23.8±15.2efg | 40.0±14.1def | 1.11±0.06abcd |
| 挑战者Challengers | 0.0±0.0c | 1.3±2.2f | 27.5±19.2ef | 32.5±26.1ef | 0.96±0.04e |
| 蒙特Mengte | 0.0±0.0c | 10.0±7.9def | 22.5±5.6efg | 30.0±7.9ef | 0.97±0.01e |
| 燕王Forage plus | 0.0±0.0c | 0.0±0.0f | 11.3±9.6fg | 28.8±7.4ef | 1.12±0.02abc |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 1.3±2.2c | 8.8±7.4def | 10.0±7.9fg | 21.3±7.4f | 1.14±0.03ab |
| 莫妮达Monida | 0.0±0.0c | 12.5±8.3cdef | 18.8±10.2fg | 21.3±17.1f | 1.05±0.02bcde |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 0.8±0.8c | 1.3±2.2f | 5.0±8.7fg | 18.8±10.2f | 1.17±0.02a |
| 牧王Haymaker | 0.0±0.0c | 0.0±0.0f | 1.3±2.2g | 17.5±7.5f | 1.19±0.02a |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 0.0±0.0c | 0.0±0.0f | 10.0±12.2fg | 16.3±11.4f | 1.11±0.03abcd |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 0.0±0.0c | 3.8±4.1f | 2.5±2.5fg | 13.8±7.4f | 1.15±0.05ab |
| 贝利 Baler | 0.0±0.0c | 2.5±4.3f | 7.5±8.3fg | 10.0±6.1f | 1.12±0.07abc |
品种 Varieties | 第1节The first internode of stem | 第2节The second internode of stem | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
节间长LI (cm) | 茎粗SD (mm) | 壁厚WT (mm) | 干重DW (g) | 节间长LI (cm) | 茎粗SD (mm) | 壁厚WT (mm) | 干重DW (g) | |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 5.70±1.82ab | 3.80±0.14def | 0.14±0.01b | 0.06±0.02bcd | 11.93±6.19abcd | 4.90±0.42bcd | 0.13±0.01b | 0.13±0.04b |
| LAMPTON | 3.09±0.10c | 3.21±0.25f | 0.28±0.08ab | 0.01±0.00d | 11.52±3.73abcd | 3.41±0.30de | 0.32±0.00ab | 0.18±0.01ab |
| 挑战者Challengers | 1.52±0.36c | 4.55±0.47abc | 0.70±0.25a | 0.03±0.01d | 9.11±0.82abcd | 3.46±1.93de | 0.26±0.05ab | 0.19±0.04ab |
| 海威Haiwee | 7.47±2.06a | 3.37±0.38f | 0.38±0.03ab | 0.02±0.01d | 12.96±2.50abc | 4.22±0.64cde | 0.43±0.12ab | 0.23±0.23ab |
| ESK | 2.78±1.47c | 3.45±0.48ef | 0.57±0.51ab | 0.07±0.03bcd | 8.67±1.27bcd | 3.79±0.70cde | 0.27±0.22ab | 0.14±0.06b |
| 莫妮达Monida | 3.18±0.25c | 3.18±0.03f | 0.45±0.30ab | 0.05±0.03bcd | 11.71±0.04abcd | 4.05±0.35cde | 0.28±0.18ab | 0.28±0.11ab |
| 凯速Souris | 3.15±1.84c | 3.41±0.57f | 0.70±0.49a | 0.06±0.04bcd | 6.66±1.12d | 3.51±0.01de | 0.22±0.10b | 0.10±0.01b |
| 伽利略Galileo | 2.62±1.05c | 3.37±0.16f | 0.40±0.12ab | 0.03±0.01d | 12.01±2.38abcd | 3.01±0.74e | 0.32±0.12ab | 0.14±0.05b |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 1.56±0.28c | 3.29±0.15f | 0.27±0.07ab | 0.02±0.01d | 9.25±2.04abcd | 3.60±0.15de | 0.25±0.08ab | 0.11±0.04b |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 5.69±1.70ab | 3.80±0.31def | 0.15±0.03b | 0.17±0.01a | 13.63±0.62ab | 3.71±0.23de | 0.28±0.28ab | 0.20±0.04ab |
| 燕王Forage plus | 2.03±0.59c | 3.55±0.48ef | 0.16±0.03b | 0.03±0.01d | 10.23±2.24abcd | 3.85±0.84cde | 0.15±0.00b | 0.10±0.03b |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 3.50±0.30bc | 4.29±0.03bcd | 0.58±0.21ab | 0.10±0.00b | 11.60±0.63abcd | 4.59±0.83bcde | 0.58±0.31a | 0.28±0.06ab |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 2.34±0.38c | 4.91±0.13a | 0.27±0.14ab | 0.05±0.03bcd | 9.65±3.11abcd | 6.45±1.92a | 0.31±0.02ab | 0.23±0.07ab |
| 贝利 Baler | 1.50±0.61c | 4.20±0.42bcd | 0.36±0.24ab | 0.04±0.00cd | 8.44±1.66bcd | 5.87±0.76ab | 0.38±0.03ab | 0.18±0.08ab |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 3.78±0.46bc | 4.47±0.19abc | 0.51±0.30ab | 0.10±0.04b | 10.29±4.70abcd | 4.14±0.68cde | 0.47±0.10ab | 0.35±0.20a |
| 牧王Haymaker | 5.66±1.95ab | 4.81±0.13ab | 0.62±0.19ab | 0.09±0.07bc | 14.41±0.43a | 5.39±0.04abc | 0.43±0.18ab | 0.28±0.04ab |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 2.50±0.78c | 4.04±0.07cde | 0.28±0.03ab | 0.03±0.00d | 9.88±1.09abcd | 4.89±0.34bcd | 0.26±0.04ab | 0.24±0.06ab |
表5 18个燕麦品种茎秆形态特征
Table 5 Morphological characteristics of the stem of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 第1节The first internode of stem | 第2节The second internode of stem | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
节间长LI (cm) | 茎粗SD (mm) | 壁厚WT (mm) | 干重DW (g) | 节间长LI (cm) | 茎粗SD (mm) | 壁厚WT (mm) | 干重DW (g) | |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 5.70±1.82ab | 3.80±0.14def | 0.14±0.01b | 0.06±0.02bcd | 11.93±6.19abcd | 4.90±0.42bcd | 0.13±0.01b | 0.13±0.04b |
| LAMPTON | 3.09±0.10c | 3.21±0.25f | 0.28±0.08ab | 0.01±0.00d | 11.52±3.73abcd | 3.41±0.30de | 0.32±0.00ab | 0.18±0.01ab |
| 挑战者Challengers | 1.52±0.36c | 4.55±0.47abc | 0.70±0.25a | 0.03±0.01d | 9.11±0.82abcd | 3.46±1.93de | 0.26±0.05ab | 0.19±0.04ab |
| 海威Haiwee | 7.47±2.06a | 3.37±0.38f | 0.38±0.03ab | 0.02±0.01d | 12.96±2.50abc | 4.22±0.64cde | 0.43±0.12ab | 0.23±0.23ab |
| ESK | 2.78±1.47c | 3.45±0.48ef | 0.57±0.51ab | 0.07±0.03bcd | 8.67±1.27bcd | 3.79±0.70cde | 0.27±0.22ab | 0.14±0.06b |
| 莫妮达Monida | 3.18±0.25c | 3.18±0.03f | 0.45±0.30ab | 0.05±0.03bcd | 11.71±0.04abcd | 4.05±0.35cde | 0.28±0.18ab | 0.28±0.11ab |
| 凯速Souris | 3.15±1.84c | 3.41±0.57f | 0.70±0.49a | 0.06±0.04bcd | 6.66±1.12d | 3.51±0.01de | 0.22±0.10b | 0.10±0.01b |
| 伽利略Galileo | 2.62±1.05c | 3.37±0.16f | 0.40±0.12ab | 0.03±0.01d | 12.01±2.38abcd | 3.01±0.74e | 0.32±0.12ab | 0.14±0.05b |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 1.56±0.28c | 3.29±0.15f | 0.27±0.07ab | 0.02±0.01d | 9.25±2.04abcd | 3.60±0.15de | 0.25±0.08ab | 0.11±0.04b |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 5.69±1.70ab | 3.80±0.31def | 0.15±0.03b | 0.17±0.01a | 13.63±0.62ab | 3.71±0.23de | 0.28±0.28ab | 0.20±0.04ab |
| 燕王Forage plus | 2.03±0.59c | 3.55±0.48ef | 0.16±0.03b | 0.03±0.01d | 10.23±2.24abcd | 3.85±0.84cde | 0.15±0.00b | 0.10±0.03b |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 3.50±0.30bc | 4.29±0.03bcd | 0.58±0.21ab | 0.10±0.00b | 11.60±0.63abcd | 4.59±0.83bcde | 0.58±0.31a | 0.28±0.06ab |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 2.34±0.38c | 4.91±0.13a | 0.27±0.14ab | 0.05±0.03bcd | 9.65±3.11abcd | 6.45±1.92a | 0.31±0.02ab | 0.23±0.07ab |
| 贝利 Baler | 1.50±0.61c | 4.20±0.42bcd | 0.36±0.24ab | 0.04±0.00cd | 8.44±1.66bcd | 5.87±0.76ab | 0.38±0.03ab | 0.18±0.08ab |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 3.78±0.46bc | 4.47±0.19abc | 0.51±0.30ab | 0.10±0.04b | 10.29±4.70abcd | 4.14±0.68cde | 0.47±0.10ab | 0.35±0.20a |
| 牧王Haymaker | 5.66±1.95ab | 4.81±0.13ab | 0.62±0.19ab | 0.09±0.07bc | 14.41±0.43a | 5.39±0.04abc | 0.43±0.18ab | 0.28±0.04ab |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 2.50±0.78c | 4.04±0.07cde | 0.28±0.03ab | 0.03±0.00d | 9.88±1.09abcd | 4.89±0.34bcd | 0.26±0.04ab | 0.24±0.06ab |
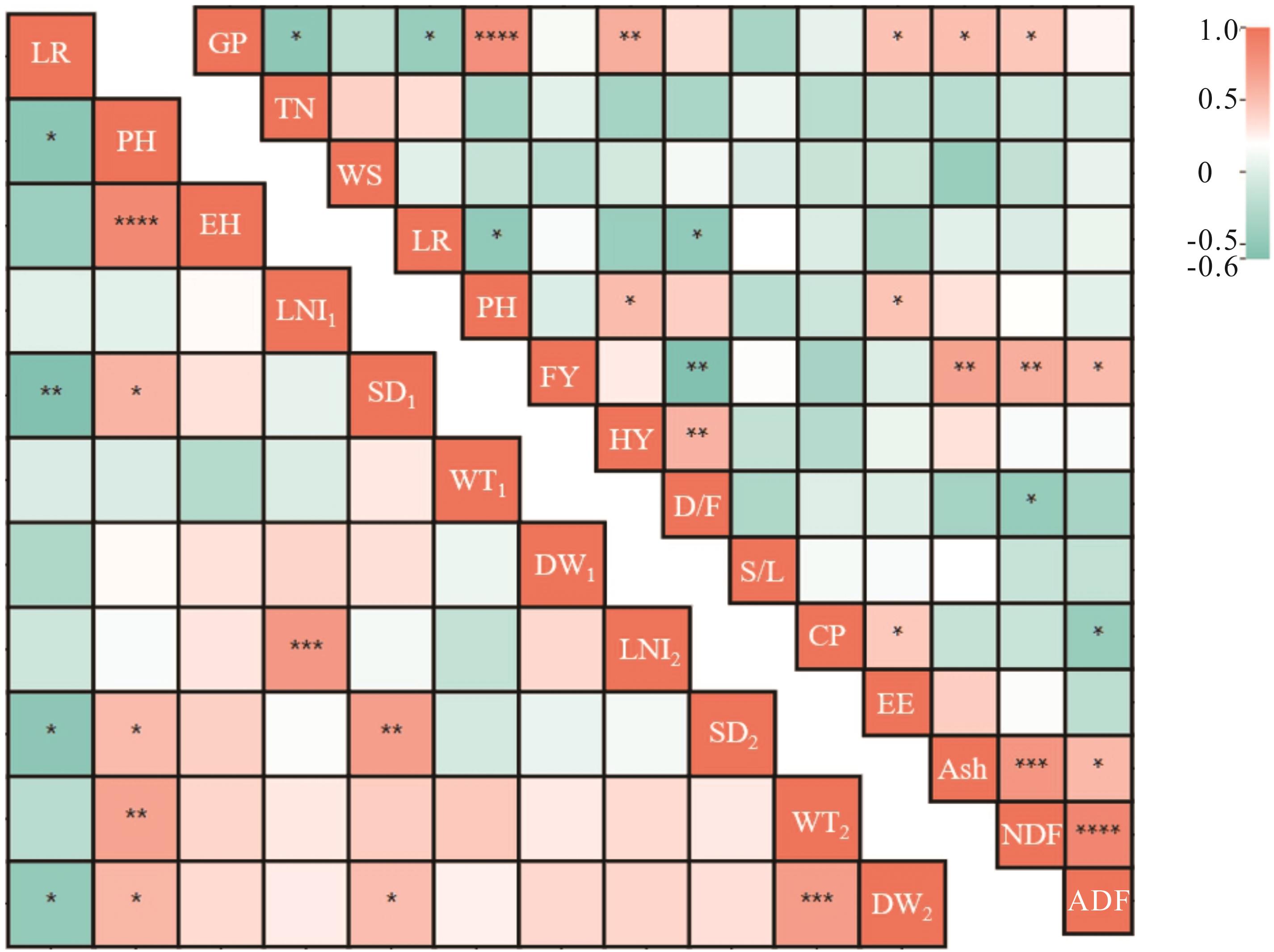
图1 燕麦倒伏率、株高、茎秆形态、生育期、分蘖数、越冬率、干草产量等之间的相关性GP: 生育期Growth period; TN: 分蘖数Tiller number; WS: 越冬率Winter survival rate; PH: 株高Plant height; FY: 鲜草产量Fresh yield; HY: 干草产量Hay yield; D/F: 干鲜比Dry/fresh; S/L: 茎叶比Stem/leaf; CP: 粗蛋白Crude protein; EE: 粗脂肪Ether extract; Ash: 粗灰分Crude ash; NDF: 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber; ADF: 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber; LR: 倒伏率Lodging rate; EH: 穗位高Ear height; LNI1: 第1节间长The 1st internode length; SD1: 第1节茎粗The 1st internode stem diameter; WT1: 第1节壁厚The 1st internode wall thick; DW1: 第1节干重The 1st internode dry weight; LNI2: 第2节间长The 2nd internode length; SD2: 第2节茎粗The 2nd internode stem diameter; WT2: 第2节壁厚The 2nd internode wall thick; DW2: 第2节干重The 2nd internode dry weight. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ****: P<0.0001.
Fig.1 Correlation among lodging rate, plant height, stem morphology, growth period, tiller number, winter survival rate and hay yield in oats
品种 Varieties | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%) | 粗脂肪 Ether extract (%) | 粗灰分 Crude ash (%) | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber(%) | 主成分得分 Principal components score | 分级 Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 10.28±0.84a | 2.51±0.19a | 11.31±1.18abcd | 60.28±3.41a | 35.29±0.65ab | 1.02 | 二级SL |
| LAMPTON | 9.51±0.54a | 2.24±0.23ab | 10.35±0.22cde | 58.45±3.37a | 34.63±2.16b | 0.84 | 三级TL |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 10.14±1.19a | 1.73±0.06b | 7.31±0.28f | 57.33±1.82a | 35.39±0.02ab | 0.69 | 二级SL |
| 莫妮达Monida | 9.97±2.70a | 2.22±0.20ab | 9.87±0.42e | 61.35±5.35a | 35.22±3.20ab | 0.69 | 三级TL |
| 蒙特Mengte | 8.58±0.24a | 1.88±0.08b | 7.25±0.01f | 54.55±0.68a | 34.56±0.08ab | 0.67 | 三级TL |
| 贝利 Baler | 9.51±1.87a | 2.27±0.39ab | 10.29±0.77cde | 60.33±3.26a | 35.83±2.66ab | 0.54 | 三级TL |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 9.70±1.40a | 2.33±0.37ab | 11.78±0.66a | 61.97±4.15a | 36.26±2.44ab | 0.38 | 三级TL |
| 挑战者Challengers | 10.21±1.03a | 2.22±0.18ab | 10.30±0.66cde | 62.79±3.98a | 37.47±1.76ab | 0.24 | 三级TL |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 8.43±0.57a | 2.07±0.02ab | 10.06±0.31de | 59.67±1.07a | 35.77±0.43ab | 0.11 | 三级TL |
| 甜燕2号 Haywire | 9.38±1.46a | 2.16±0.47ab | 10.40±0.12bcde | 62.61±1.10a | 37.28±0.63ab | -0.01 | 三级TL |
| 牧王Haymaker | 8.60±0.64a | 2.25±0.03ab | 10.27±0.45cde | 61.34±1.96a | 37.49±2.11ab | -0.11 | 三级TL |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 8.75±0.36a | 2.11±0.15ab | 9.97±0.64e | 63.22±0.67a | 37.60±0.07ab | -0.32 | 三级TL |
| 凯速Souris | 8.78±0.88a | 1.96±0.18b | 10.83±0.40abcde | 61.53±0.48a | 37.32±0.94ab | -0.33 | 三级TL |
| 海威Haiwee | 8.55±1.13a | 1.97±0.24b | 11.93±0.92a | 61.43±1.89a | 37.03±1.36ab | -0.39 | 三级TL |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 9.11±0.80a | 2.07±0.18ab | 11.62±0.44ab | 64.07±3.14a | 38.05±1.15a | -0.48 | 三级TL |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 8.47±0.89a | 1.92±0.11b | 10.98±0.80abcde | 62.71±1.75a | 38.03±1.02ab | -0.67 | 三级TL |
| 伽利略Galileo | 8.35±1.19a | 2.11±0.06ab | 11.00±0.45abcde | 64.23±2.24a | 38.28±0.82a | -0.82 | 三级TL |
| ESK | 8.06±0.40a | 2.01±0.31b | 11.42±0.27abc | 62.83±0.98a | 38.44±1.22a | -1.02 | 三级TL |
表6 18个燕麦品种营养成分含量、主成分得分及品质分级
Table 6 Nutritional content, principal component scores and quality grading of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%) | 粗脂肪 Ether extract (%) | 粗灰分 Crude ash (%) | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber(%) | 主成分得分 Principal components score | 分级 Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 10.28±0.84a | 2.51±0.19a | 11.31±1.18abcd | 60.28±3.41a | 35.29±0.65ab | 1.02 | 二级SL |
| LAMPTON | 9.51±0.54a | 2.24±0.23ab | 10.35±0.22cde | 58.45±3.37a | 34.63±2.16b | 0.84 | 三级TL |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 10.14±1.19a | 1.73±0.06b | 7.31±0.28f | 57.33±1.82a | 35.39±0.02ab | 0.69 | 二级SL |
| 莫妮达Monida | 9.97±2.70a | 2.22±0.20ab | 9.87±0.42e | 61.35±5.35a | 35.22±3.20ab | 0.69 | 三级TL |
| 蒙特Mengte | 8.58±0.24a | 1.88±0.08b | 7.25±0.01f | 54.55±0.68a | 34.56±0.08ab | 0.67 | 三级TL |
| 贝利 Baler | 9.51±1.87a | 2.27±0.39ab | 10.29±0.77cde | 60.33±3.26a | 35.83±2.66ab | 0.54 | 三级TL |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 9.70±1.40a | 2.33±0.37ab | 11.78±0.66a | 61.97±4.15a | 36.26±2.44ab | 0.38 | 三级TL |
| 挑战者Challengers | 10.21±1.03a | 2.22±0.18ab | 10.30±0.66cde | 62.79±3.98a | 37.47±1.76ab | 0.24 | 三级TL |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 8.43±0.57a | 2.07±0.02ab | 10.06±0.31de | 59.67±1.07a | 35.77±0.43ab | 0.11 | 三级TL |
| 甜燕2号 Haywire | 9.38±1.46a | 2.16±0.47ab | 10.40±0.12bcde | 62.61±1.10a | 37.28±0.63ab | -0.01 | 三级TL |
| 牧王Haymaker | 8.60±0.64a | 2.25±0.03ab | 10.27±0.45cde | 61.34±1.96a | 37.49±2.11ab | -0.11 | 三级TL |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 8.75±0.36a | 2.11±0.15ab | 9.97±0.64e | 63.22±0.67a | 37.60±0.07ab | -0.32 | 三级TL |
| 凯速Souris | 8.78±0.88a | 1.96±0.18b | 10.83±0.40abcde | 61.53±0.48a | 37.32±0.94ab | -0.33 | 三级TL |
| 海威Haiwee | 8.55±1.13a | 1.97±0.24b | 11.93±0.92a | 61.43±1.89a | 37.03±1.36ab | -0.39 | 三级TL |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 9.11±0.80a | 2.07±0.18ab | 11.62±0.44ab | 64.07±3.14a | 38.05±1.15a | -0.48 | 三级TL |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 8.47±0.89a | 1.92±0.11b | 10.98±0.80abcde | 62.71±1.75a | 38.03±1.02ab | -0.67 | 三级TL |
| 伽利略Galileo | 8.35±1.19a | 2.11±0.06ab | 11.00±0.45abcde | 64.23±2.24a | 38.28±0.82a | -0.82 | 三级TL |
| ESK | 8.06±0.40a | 2.01±0.31b | 11.42±0.27abc | 62.83±0.98a | 38.44±1.22a | -1.02 | 三级TL |
品种 Varieties | 抗倒伏性 Lodging resistance | 干草产量 Hay yield | 营养品质 Nutritional quality | 综合评价 Comprehensive evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利Baler | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 0.95 |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.69 | 0.79 |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.26 | 0.79 |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.17 | 0.78 |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 0.87 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.73 |
| 牧王Haymaker | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.45 | 0.71 |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 0.90 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.65 |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 0.65 | 0.39 | 1.00 | 0.63 |
| 蒙特Mengte | 0.76 | 0.27 | 0.84 | 0.64 |
| 莫妮达Monida | 0.87 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 0.62 |
| 挑战者Challengers | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.49 |
| 海威Haiwee | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.38 |
| 凯速Souris | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.83 | 0.37 |
| LAMPTON | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.91 | 0.31 |
| 伽利略Galileo | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.26 |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 0.23 |
| ESK | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.16 |
表7 18个燕麦品种综合评价
Table 7 Comprehensive evaluation of the 18 oat varieties
品种 Varieties | 抗倒伏性 Lodging resistance | 干草产量 Hay yield | 营养品质 Nutritional quality | 综合评价 Comprehensive evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贝利Baler | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 0.95 |
| 燕王Forage Plus | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.69 | 0.79 |
| 大富豪Millionaire | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.26 | 0.79 |
| 爱沃Everleaf | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.17 | 0.78 |
| 贝利2 Baler 2 | 0.87 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.73 |
| 牧王Haymaker | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.45 | 0.71 |
| 贝勒2号 Baler Ⅱ | 0.90 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.65 |
| 甜燕1号Sweety | 0.65 | 0.39 | 1.00 | 0.63 |
| 蒙特Mengte | 0.76 | 0.27 | 0.84 | 0.64 |
| 莫妮达Monida | 0.87 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 0.62 |
| 挑战者Challengers | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.49 |
| 海威Haiwee | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.38 |
| 凯速Souris | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| 兰普顿Lampton | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.83 | 0.37 |
| LAMPTON | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.91 | 0.31 |
| 伽利略Galileo | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.26 |
| 甜燕2号Haywire | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 0.23 |
| ESK | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.16 |
| 1 | Nan M, Li J, Zhao G Q, et al. Relationship between lodging resistance of oats and the basal internode stem characteristics and lignin synthesis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 172-180. |
| 南铭, 李晶, 赵桂琴, 等. 茎秆基部节间特性和木质素合成与燕麦抗倒伏的关系. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 172-180. | |
| 2 | Ye X L, Gan Z, Wan Y, et al. Advances and perspectives in forage oat breeding. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 等. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. | |
| 3 | Nan M, Zhao G Q, Chai J K. Study on lodging resistance of 20 forage oat (Avena sativa) varieties. Grassland and Turf, 2019, 39(5): 62-68. |
| 南铭, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽. 20份饲草型燕麦品种的抗倒伏性研究. 草原与草坪, 2019, 39(5): 62-68. | |
| 4 | Laude H H, Pauli A W. Influence of lodging on yield and other characters in winter wheat. Agronomy Journal, 1956, 48(10): 452-455. |
| 5 | Sisler W W, Olson P J. A study of methods of influencing lodging in barley and the effect of lodging upon yield and certain quality characteristics. Scientific Agriculture, 2016, 31(5): 177-186. |
| 6 | Norden A J. Factors associated with lodging resistance in oats. Agronomy Journal, 1959, 51(6): 335-338. |
| 7 | Mulder E G. Effect of mineral nutrition on lodging of cereals. Plant and Soil, 1954, 5(3): 246-306. |
| 8 | Welton F A. Lodging in oats and wheat. Botanical Gazette, 1928, 85(2): 121-151. |
| 9 | Tubbs F R. Physiological studies in plant nutrition: Ⅱ. The effect of manurial deficiency upon the mechanical strength of barley straw. Annals of Botany, 1930, 44(1): 147-160. |
| 10 | Garber R J, Olson P J. A study of the relation of some morphological characters to lodging in cereals. Agronomy Journal, 1919, 11(5): 173-186. |
| 11 | Purvis O N. The effect of potassium salts on the anatomy of Dactylis glomerata. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1919, 9(4): 338-365. |
| 12 | Hamilton D G. Certain oat culm characters and their relationship to lodging. Scientific Agriculture, 2016, 21(10): 646-676. |
| 13 | Liang G L, Zhang Y C, Jia Z F, et al. A study of the relationship between phenotypic traits, stem mechanical traits and lodging resistance of oat varieties for alpine regions. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(4): 58-69. |
| 梁国玲, 张永超, 贾志锋, 等. 高寒区不同燕麦品种(系)表型性状和茎秆力学特征与抗倒伏性的关系研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 58-69. | |
| 14 | Yang J, Liu W H, Liang G L, et al. Traits correlated with lodging resistance of oat strains in the alpine region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 50-60. |
| 杨晶, 刘文辉, 梁国玲, 等. 高寒地区不同燕麦品系抗倒伏相关性状分析. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 50-60. | |
| 15 | Rohweder D A, Barnes R F, Neal J. Proposed hay grading standards based on laboratory analyses for evaluating quality. Journal of Animal Science, 1978, 47(3): 747-759. |
| 16 | China Animal Agriculture Association. Oats hay quality grade, T/CAAA 002-2018. Beijing: China Animal Agriculture Association, 2019. |
| 中国畜牧业协会. 燕麦干草质量分级, T/CAAA 002-2018. 北京: 中国畜牧业协会, 2019. | |
| 17 | Yao J, He Y, Lu J D, et al. Winter survival rate, tillering characteristics, and production performance of autumn-sown forage oats in Henan Province. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(2): 528-539. |
| 姚晋, 何云, 卢家顶, 等. 河南省秋播饲用燕麦的越冬率、分蘖特性及其生产性能. 草地学报, 2023, 31(2): 528-539. | |
| 18 | Guo Y. Review of weight determination methods. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2018, 29(8): 252-253. |
| 郭昱. 权重确定方法综述. 农村经济与科技, 2018, 29(8): 252-253. | |
| 19 | Berry P M, Kendall S, Rutterford Z, et al. Historical analysis of the effects of breeding on the height of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum) and consequences for lodging. Euphytica, 2015, 203(2): 375-383. |
| 20 | Ma J, Ma W B, Tian Y H, et al. The culm lodging resistance of heavy panicle type of rice. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2004, 30(2): 143-148. |
| 马均, 马文波, 田彦华, 等. 重穗型水稻植株抗倒伏能力的研究. 作物学报, 2004, 30(2): 143-148. | |
| 21 | Gong J J, Zhao G Q, Ma X Q. Effects of plant growth regulator on plant height, yield and yield components of oat. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 25(5): 74-77. |
| 龚建军, 赵桂琴, 马雪琴. 矮壮素与乙烯利对燕麦株高、产量及其构成因素的调节作用. 草业科学, 2008, 25(5): 74-77. | |
| 22 | Hamilton D G. Culm, crown and root development in oats as related to lodging. Scientific Agriculture, 2016, 31(7): 286-315. |
| 23 | Brunava L, Alsina I, Treija S, et al. Lodging cause height at the centre of gravity changes during vegetation period for oat. Jelgava: Latvia University of Agriculture, 2014: 56-60. |
| 24 | Nan M, Zhao G Q, Li J, et al. Research of lodging-resistance and the stem morphological characteristics of different Avena sative L. varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(6): 1382-1391. |
| 南铭, 赵桂琴, 李晶, 等. 不同燕麦品种茎秆形态特征与抗倒伏性的关系. 草地学报, 2018, 26(6): 1382-1391. | |
| 25 | Ge J Y, Zhang B, Wang X, et al. Evaluation on the stem lodging resistance of different types of naked oat varieties. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2018, 41(5): 7-12. |
| 葛军勇, 张斌, 王霞, 等. 不同应用类型裸燕麦品种的茎秆抗倒伏特性评价. 河北农业大学学报, 2018, 41(5): 7-12. | |
| 26 | Sun H E, Tan X L, Zhang J C, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rate and plant growth regulator on lodging resistance, yield and quality of Qingyin No.2 oats. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2022(3): 24-30. |
| 孙怀恩, 谭旭良, 张俊超, 等. 施氮量和植物生长调节剂对青引2号燕麦抗倒能力及产量品质的影响. 草学, 2022(3): 24-30. | |
| 27 | Wu Y, Zhang W H, Chen M H, et al. Productive performance comparison of different oat varieties in Yangzhou region. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(7): 1728-1733. |
| 吴亚, 张卫红, 陈鸣晖, 等. 不同品种燕麦在扬州地区的生产性能. 草业科学, 2018, 35(7): 1728-1733. | |
| 28 | Nan M. Study expression of genes in stem lignin synthesis and intrinsic physiological mechanism of lodging resistance in oat (Avena sative L.). Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 南铭. 燕麦抗倒伏生理机制及茎秆木质素合成基因表达研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2021. | |
| 29 | Derick R A, Hamilton D G. Root development in oat varieties. Scientific Agriculture, 2016, 22(8): 503-508. |
| 30 | Liu Q, Lu H Z, Ma Y, et al. Effects of sowing date on oat production performance in winter fallow fields in Anning River Basin. Sichuan Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(8): 28-31, 38. |
| 柳茜, 卢寰宗, 马英, 等. 播期对安宁河流域冬闲田燕麦生产性能的影响. 四川农业科技, 2022(8): 28-31, 38. | |
| 31 | Xu Y D, Zhu R F, Ran Q F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation about production performance and feed value of 19 oat varieties in Chongqing. Feed Research, 2022, 45(19): 109-113. |
| 徐远东, 朱瑞芬, 冉启凡, 等. 19份燕麦品种(系)在重庆地区的生产性能与饲用价值综合评价. 饲料研究, 2022, 45(19): 109-113. | |
| 32 | Zhuang K Z, Wu R H, Zhang C Y, et al. Comparison of production performance between autumn sowing and spring sowing of low-temperature tolerant fodder oat in southern Shandong. Feed Research, 2021, 44(15): 105-108. |
| 庄克章, 吴荣华, 张春艳, 等. 鲁南地区耐低温饲用燕麦秋播和春播生产性能比较. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(15): 105-108. | |
| 33 | Li J, Liu Y M, Zhang C J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the yield, quality and feeding performance on different oat varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 1089-1098. |
| 李晶, 刘彦明, 张成君, 等. 不同燕麦品种产量和品质及饲喂性能综合评价. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 1089-1098. | |
| 34 | Zhang H H, Liang W W, Zhang X Z, et al. Production performance evaluation of 10 fodder oat varieties in the desert area of northern Xinjiang plain. Grass-Feeding Livestock, 2020(1): 31-35. |
| 张荟荟, 梁维维, 张学洲, 等. 10份饲用燕麦品种在北疆平原荒漠区的生产性能评价. 草食家畜, 2020(1): 31-35. | |
| 35 | Wooten D R, Livingston D, Jellen E N, et al. An intergenomic reciprocal translocation associated with oat winter hardiness component traits. Crop Science, 2007, 47(5): 1832-1840. |
| 36 | Sofronova V E, Chepalov V A, Dymova O V, et al. Functional condition of photosystem Ⅱ in leaves of spring oats during autumnal decrease in temperature. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 67(4): 661-670. |
| 37 | Pan B G, Nong Q X, Zhong Y H, et al. Study on nitrogen application technology of oats in winter fallow land in Youjiang River Valley. Modern Agriculture, 2022(11): 32-35. |
| 潘炳高, 农秋霞, 钟毅华, 等. 右江河谷地区冬闲地燕麦施氮技术研究. 现代化农业, 2022(11): 32-35. | |
| 38 | Wang G L, Wu B, Zhang J H, et al. The comparison of productivity of different oat varieties in the Yellow River Delta. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(6): 141-148. |
| 王国良, 吴波, 张进红, 等. 黄河三角洲地区不同品种燕麦生产性能比较. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(6): 141-148. | |
| 39 | Liang W P, Li S E, He C G, et al. Present situation of promotion and utilization status of alfalfa and oat in Qingyang City. China Cattle Science, 2021, 47(4): 82-83, 88. |
| 梁万鹏, 李世恩, 贺春贵, 等. 庆阳市紫花苜蓿和燕麦推广利用现状. 中国牛业科学, 2021, 47(4): 82-83, 88. | |
| 40 | Guo X, Qi S, Niu H, et al. Production performance and agronomic traits of four oat varieties in the Yellow River beach area. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2019, 40(8): 38-41. |
| 郭孝, 齐爽, 牛晖, 等. 4个燕麦品种在黄河滩区生产性能和农艺性状的研究. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2019, 40(8): 38-41. | |
| 41 | Nan C Q, Li J S, Meng Q L, et al. The adaptability evaluation of Canadian oat germplasm. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2013, 22(3): 75-81. |
| 南春芹, 李建设, 孟庆立, 等. 加拿大燕麦种质在陕西杨凌的适应性评价. 西北农业学报, 2013, 22(3): 75-81. | |
| 42 | Zhuang K Z, Wu R H, Zhang C Y, et al. Evaluation of productivity of 11 oat varieties in Lunan region. Crop Research, 2022, 36(4): 313-319, 326. |
| 庄克章, 吴荣华, 张春艳, 等. 11个饲用燕麦品种在鲁南地区的生产性能评价. 作物研究, 2022, 36(4): 313-319, 326. | |
| 43 | Lou C H, Wang B, Li D F, et al. Comparison of production performance and nutritional value of 16 oat varieties in Yellow River beach area. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(7): 1843-1851. |
| 娄春华, 王博, 李德锋, 等. 黄河滩区16个春播燕麦品种的生产性能和营养品质. 草业科学, 2019, 36(7): 1843-1851. | |
| 44 | Xu C L. A study on growth characteristics of different cultivars of oat (Avena sative) in alpine region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(2): 280-285. |
| 徐长林. 高寒牧区不同燕麦品种生长特性比较研究. 草业学报, 2012, 21(2): 280-285. | |
| 45 | Wu H Y, Qu N, Qu Z, et al. Comparison of crop yield and forage quality of six oat varieties in Angren County, Shigatse. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 72-80. |
| 吴海艳, 曲尼, 曲珍, 等. 6个燕麦品种在昂仁县的生产性能及饲草品质比较. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 72-80. | |
| 46 | Zhang Q Q, Liang Q W, Yang X F, et al. Production performance of 12 oat varieties in the Aru kerqin banner. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(3): 23-29, 38. |
| 张晴晴, 梁庆伟, 杨秀芳, 等. 12份燕麦品种在阿鲁科尔沁旗地区的生产性能研究. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(3): 23-29, 38. | |
| 47 | Wang S S, Gu H T, Xie H F, et al. Evaluation of forage yield and quality traits of 113 forage hexaploid triticale germplasm lines. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 192-202. |
| 王珊珊, 谷海涛, 谢慧芳, 等. 113份饲草型六倍体小黑麦种质饲草产量与品质性状的评价. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 192-202. | |
| 48 | Xiong X, Shao L Z, Dong J X, et al. Comparison of production performance and feeding value of different oat varieties in Yudaokou, Bashang, Chengde. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(7): 1412-1418. |
| 熊雪, 邵玲智, 董建新, 等. 承德坝上御道口地区不同燕麦品种生产性能及饲用价值. 草业科学, 2022, 39(7): 1412-1418. | |
| 49 | Yang M, Xu S H, Rao X, et al. Evaluation of agronomic traits and nutritional quality of forage oats in the Wumeng Mountain cold area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 1071-1080. |
| 杨敏, 徐树花, 饶雄, 等. 乌蒙山冷凉山区饲用燕麦农艺性状与营养品质评价. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 1071-1080. | |
| 50 | Cao X J, Wu J Y, Li W X, et al. Effects of different additives on fermentation quality and nutritional components of oat silage. China Feed, 2022(21): 60-65. |
| 曹晓娟, 武俊英, 李文旭, 等. 不同添加剂对青贮燕麦发酵品质和营养成分的影响. 中国饲料, 2022(21): 60-65. | |
| 51 | Zhao G Q, Ju Z L, Chai J K. Effects of altitude and variety on nutrient levels and epiphytes of oats. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 147-157. |
| 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 柴继宽. 海拔和品种对燕麦营养品质及表面附着微生物的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 147-157. | |
| 52 | Li F, Li X, Zhang Z J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on productivity of 16 spring sowing oat varieties in Songnen Plain. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(6): 52-59. |
| 李峰, 李雪, 张仲鹃, 等. 16个春播燕麦品种在松嫩平原的生产力综合评价. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(6): 52-59. | |
| 53 | Ren L J, Chen Y K, Shan L Y, et al. Analysis of comprehensive quality of whole plant corn silage based on principal component and grey correlation degree. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48(4): 1211-1221. |
| 任丽娟, 陈雅坤, 单丽燕, 等. 基于主成分和灰色关联度对全株玉米青贮综合品质的分析. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48(4): 1211-1221. |
| [1] | 李中利, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 高玮, 受娜, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区5个饲用甜高粱品种生产适宜性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 50-62. |
| [2] | 赵洁, 陈恒光, 裴晓蒙, 于昊, 徐银莹, 茆达干. 围产期日粮添加白藜芦醇对山羊生产性能、血液指标及炎症因子基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 210-220. |
| [3] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [4] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [5] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [6] | 李文龙, 李峰, 张仲鹃, 王殿清, 王欢, 靳慧卿, 特木热, 胡志玲, 陶雅. 鄂尔多斯高原北部一年两季燕麦种植模式生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 159-168. |
| [7] | 任春燕, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 段嘉蕾. 青藏高原高寒地区早熟燕麦资源筛选和适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 116-129. |
| [8] | 党浩千, 覃娟清, 郭宇康, 张富, 王迎港, 刘庆华. 不同添加剂发酵笋壳对湖羊生产性能及瘤胃发酵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 135-148. |
| [9] | 叶婷, 吴晓娟, 芦奕晓, 刘生娟, 姜卓慧, 杨惠敏. 混播比例对两种苜蓿混播草地产量和种群密度稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. |
| [10] | 王梓凡, 张晓庆, 钟志明, 权欣. 燕麦草捆和草块对彭波半细毛羊采食行为及生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 171-179. |
| [11] | 刘爱瑜, 王超, 吴占军, 赵寿培, 赵俐辰, 李晓宇, 张伟涛, 王乐天, 高玉红. 热应激对断奶绵羔羊生长性能、抗氧化性能和瘤胃菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 173-182. |
| [12] | 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 李满有, 倪旺, 冯琴, 妥昀昀, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| [13] | 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 向达兵, 邬晓勇, 吴琪, 刘长英, 范昱, 邹亮. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| [14] | 南铭, 王兴荣, 李晶, 刘彦明, 张成君, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴. 燕麦抗倒伏性状的基因型差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 106-118. |
| [15] | 李峰, 李文龙, 李雪, 张仲鹃, 白林坡, 赵雨霏, 陶雅. 黑龙江中南部16个饲用燕麦品种生产性能综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 82-92. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||