
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 13-25.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025113
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yang LIU( ), Hong XIAO(
), Hong XIAO( ), Chang-lin XU, Ming-yue DENG, Wen-qiang WEI, Ao HAN, Kai MA, Yun WANG
), Chang-lin XU, Ming-yue DENG, Wen-qiang WEI, Ao HAN, Kai MA, Yun WANG
Received:2025-04-01
Revised:2025-06-25
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Hong XIAO
Yang LIU, Hong XIAO, Chang-lin XU, Ming-yue DENG, Wen-qiang WEI, Ao HAN, Kai MA, Yun WANG. Impact of Salix oritrepha shrub encroachment on characteristics of herbaceous plant communities in the alpine meadows of the Eastern Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 13-25.
| 灌丛特征Shrub characteristics | 灌丛化程度Degree of shrub encroachment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | |
| 高度Height (cm) | 45.67±1.20c | 71.67±1.20b | 127.67±1.45a |
| 冠幅面积Crown area (m2) | 0.19±0.05c | 0.48±0.10b | 1.44±0.41a |
| 地上生物量Aboveground biomass (g·clump-1) | 194.61±22.69c | 587.28±85.84b | 2395.89±101.44a |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 5.12±0.81c | 6.75±0.33b | 12.38±0.14a |
| 分蘖株数Tillering number (No.) | 24.00±1.15c | 45.00±2.31a | 29.67±0.67b |
Table 1 Growth characteristics of S. oritrepha shrub under varying degrees of shrub encroachment
| 灌丛特征Shrub characteristics | 灌丛化程度Degree of shrub encroachment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | |
| 高度Height (cm) | 45.67±1.20c | 71.67±1.20b | 127.67±1.45a |
| 冠幅面积Crown area (m2) | 0.19±0.05c | 0.48±0.10b | 1.44±0.41a |
| 地上生物量Aboveground biomass (g·clump-1) | 194.61±22.69c | 587.28±85.84b | 2395.89±101.44a |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 5.12±0.81c | 6.75±0.33b | 12.38±0.14a |
| 分蘖株数Tillering number (No.) | 24.00±1.15c | 45.00±2.31a | 29.67±0.67b |
物种名 Species name | 科 Family | 灌丛斑块Shrub patch | 草地斑块Grass patch | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | ||
| 铃铃香青A. hancockii | 菊科Asteraceae | 4.00 | 1.67 | 1.33 | 15.67 | 9.67 | — |
| 钝苞雪莲Saussurea nigrescens | 菊科Asteraceae | — | 20.33 | 4.00 | — | — | — |
| 球花蒿A. smithii | 菊科Asteraceae | 1.00 | — | — | 12.00 | — | — |
| 黄帚橐吾Ligularia virgaurea | 菊科Asteraceae | — | — | — | — | — | 12.33 |
| 翻白草P. discolor | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 9.67 | 8.33 | — | 13.00 | 18.33 | 0.67 |
| 鹅绒委陵菜Potentilla anserina | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | — | — | — | — | 24.00 | 8.33 |
| 北方獐牙菜S. diluta | 龙胆科Gentianaceae | 4.00 | 0.67 | — | 6.33 | — | — |
| 珠芽蓼B. vivipara | 蓼科Polygonaceae | 18.00 | 7.00 | 11.67 | 46.33 | 51.33 | 17.67 |
| 银莲花Anemone cathayensis | 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 5.33 | 6.67 | 8.67 | 13.00 | 13.33 | 9.00 |
| 肉果草L. tibetica | 通泉草科Primulaceae | 1.33 | 3.33 | — | — | 0.33 | 1.67 |
| 问荆E. arvense | 木贼科Equisetaceae | — | 2.33 | 40.67 | — | 5.67 | 57.00 |
| 小米草Euphrasia pectinata | 玄参科Scrophulariaceae | — | — | — | 1.67 | 8.67 | 15.00 |
Table 2 Coverage of dominant forbs in shrub and grass patches across different intensities of shrub encroachment (%)
物种名 Species name | 科 Family | 灌丛斑块Shrub patch | 草地斑块Grass patch | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | ||
| 铃铃香青A. hancockii | 菊科Asteraceae | 4.00 | 1.67 | 1.33 | 15.67 | 9.67 | — |
| 钝苞雪莲Saussurea nigrescens | 菊科Asteraceae | — | 20.33 | 4.00 | — | — | — |
| 球花蒿A. smithii | 菊科Asteraceae | 1.00 | — | — | 12.00 | — | — |
| 黄帚橐吾Ligularia virgaurea | 菊科Asteraceae | — | — | — | — | — | 12.33 |
| 翻白草P. discolor | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 9.67 | 8.33 | — | 13.00 | 18.33 | 0.67 |
| 鹅绒委陵菜Potentilla anserina | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | — | — | — | — | 24.00 | 8.33 |
| 北方獐牙菜S. diluta | 龙胆科Gentianaceae | 4.00 | 0.67 | — | 6.33 | — | — |
| 珠芽蓼B. vivipara | 蓼科Polygonaceae | 18.00 | 7.00 | 11.67 | 46.33 | 51.33 | 17.67 |
| 银莲花Anemone cathayensis | 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 5.33 | 6.67 | 8.67 | 13.00 | 13.33 | 9.00 |
| 肉果草L. tibetica | 通泉草科Primulaceae | 1.33 | 3.33 | — | — | 0.33 | 1.67 |
| 问荆E. arvense | 木贼科Equisetaceae | — | 2.33 | 40.67 | — | 5.67 | 57.00 |
| 小米草Euphrasia pectinata | 玄参科Scrophulariaceae | — | — | — | 1.67 | 8.67 | 15.00 |
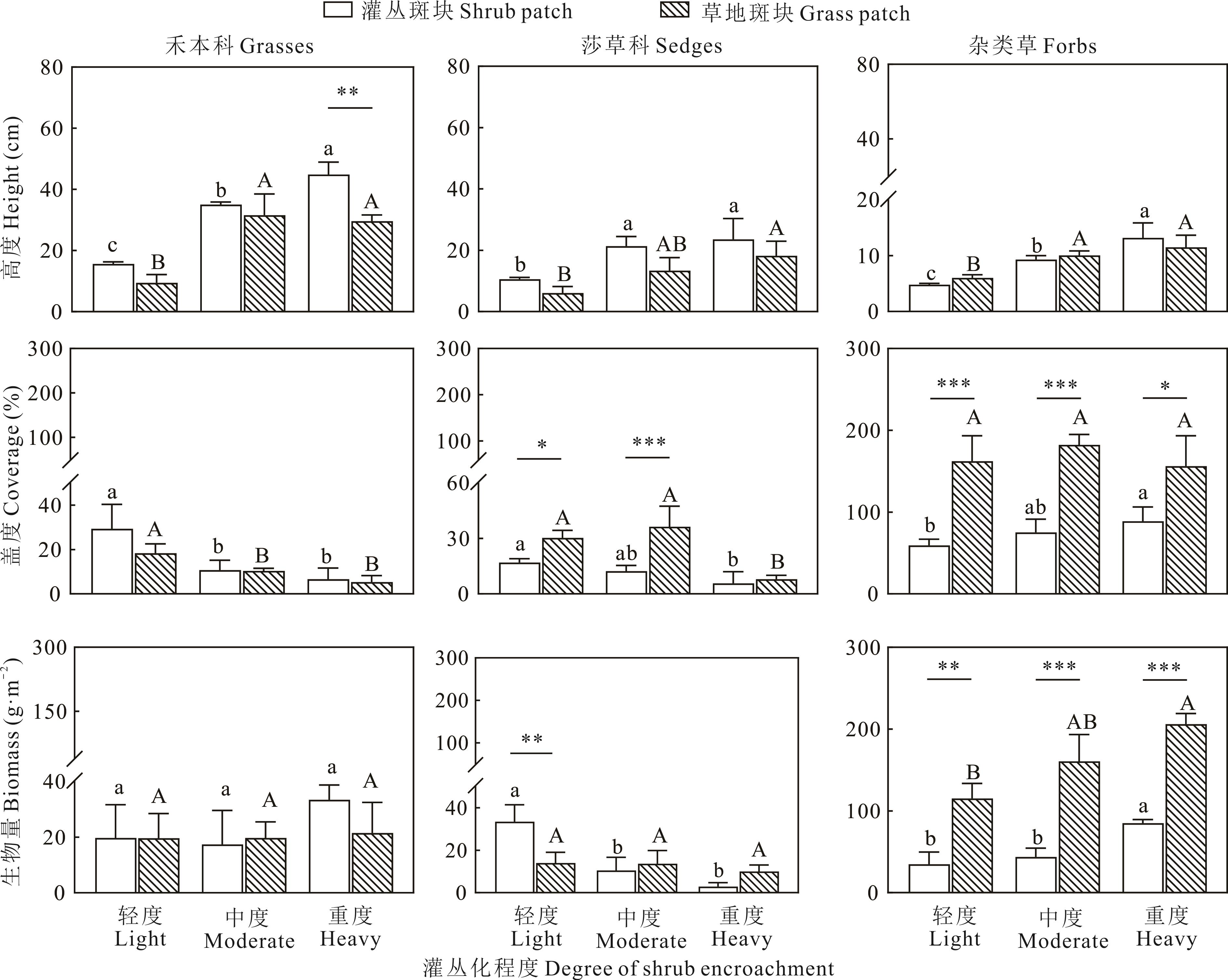
Fig.3 Variations in height, coverage, and biomass of herbaceous plant functional groups in shrub patches and grass patches across different intensities of shrub encroachment

Fig.5 Changes in species diversity index of herbaceous communities in shrub patches and grass patches across different intensities of shrub encroachment

Fig.7 Relationship among the growth characteristics of S. oritrepha and the height, coverage, aboveground biomass, and community species diversity indexes of herbaceous plant functional groups

Fig.8 Linear relationships between coverage of S. oritrepha and the height, coverage, and biomass of herbaceous plant functional groups in shrub patches and grass patches
| [1] | Maestre F T, Bowker M A, Puche M D, et al. Shrub encroachment can reverse desertification in semi-arid Mediterranean grasslands. Ecology Letters, 2009, 12(9): 930-941. |
| [2] | Zhao L R, Li K X, Zhu N, et al. Shrub encroachment accelerates the processes of moisture redistribution in alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma, 2025, 454: 117196. |
| [3] | Maestre T F, Cortina J. Remnant shrubs in Mediterranean semi-arid steppes: effects of shrub size, abiotic factors and species identity on understorey richness and occurrence. Acta Oecologica, 2004, 27(3): 161-169. |
| [4] | Dang Y L, Zhang P, Jiang P X, et al. Temperature-dependent variations in under-canopy herbaceous foliar diseases following shrub encroachment in grasslands. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 1131. |
| [5] | Zhu Y K, Shen H H, Akinyemi D S, et al. Increased precipitation attenuates shrub encroachment by facilitating herbaceous growth in a Mongolian grassland. Functional Ecology, 2022, 36(9): 2356-2366. |
| [6] | Shi H J, Jiang S J, Bian J H, et al. Livestock exclusion enhances shrub encroachment in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 2023, 34(5): 1390-1402. |
| [7] | Zhou L H, Shen H H, Chen L Y, et al. Ecological consequences of shrub encroachment in the grasslands of Northern China. Landscape Ecology, 2019, 34(1): 119-130. |
| [8] | Chen L Y, Li H, Zhang P J, et al. Climate and native grassland vegetation as drivers of the community structures of shrub-encroached grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Landscape Ecology, 2015, 30(9): 1627-1641. |
| [9] | Howard S K, Eldridge J D, Soliveres S. Positive effects of shrubs on plant species diversity do not change along a gradient in grazing pressure in an arid shrubland. Basic and Applied Ecology, 2012, 13(2): 159-168. |
| [10] | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Li G Y, et al. Shrub encroachment with increasing anthropogenic disturbance in the semiarid Inner Mongolian grasslands of China. Catena, 2013, 109: 39-48. |
| [11] | Liu Y Y, Ding J Y. Research progress on shrub encroachment in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2025, 47(4): 127-141. |
| 刘奕吟, 丁婧祎. 中国草地灌丛化研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2025, 47(4): 127-141. | |
| [12] | Ding J Y, Eldridge D. The success of woody plant removal depends on encroachment stage and plant traits. Nature Plants, 2022, 9(1): 58-67. |
| [13] | Yang W, Qu G P, Kelly A R, et al. Positive effects of leguminous shrub encroachment on multiple ecosystem functions of alpine meadows and steppes greatly depended on increasing soil nutrient. Catena, 2024, 236: 107745. |
| [14] | Liu Y F, Zhang Z C, Liu Y, et al. Shrub encroachment enhances the infiltration capacity of alpine meadows by changing the community composition and soil conditions. Catena, 2022, 213: 106222. |
| [15] | Zhao Y D, Hu X, Pan P Y. Positive feedback relationship between shrub encroachment and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the Inner Mongolia grassland of northern China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 177: 104525. |
| [16] | Zhang J M, Zhu N, Cai Y R, et al. Effects of Caragana microphylla on herbaceous community characteristics. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(21): 8830-8839. |
| 张敬敏, 珠娜, 蔡育蓉, 等. 小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)灌丛对草本群落特征的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(21): 8830-8839. | |
| [17] | Ding J Y, Yin C C, Han Y, et al. Research progress and perspectives on the impact of shrub encroachment on ecosystem multifunctionality. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(20): 8257-8267. |
| 丁婧祎, 尹彩春, 韩逸, 等. 草原灌丛化对生态系统多功能性的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(20): 8257-8267. | |
| [18] | Li Y, Hu Z Z, Wang Z T. Studies on distribution pattern of Salix oritrepha population at alpine area in east Qilian mountain. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2002, 11(3): 48-54. |
| 李毅, 胡自治, 王志泰. 东祁连山高寒地区山生柳种群分布格局研究. 草业学报, 2002, 11(3): 48-54. | |
| [19] | Zhou C Y, Yang X Y, Shao X Q, et al. Relationship between plant species diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality in alpine meadow with different degradation degrees. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(12): 3410-3422. |
| 周宸宇, 杨晓渊, 邵新庆, 等. 不同退化程度高寒草甸植物物种多样性与生态系统多功能性关系. 草地学报, 2022, 30(12): 3410-3422. | |
| [20] | Li X Q. A brief overview of the main economic groups of grassland plants in Qinghai. Qinghai Prataculture, 2019, 28(1): 42-45. |
| 李旭谦. 青海草地植物主要经济类群简述. 青海草业, 2019, 28(1): 42-45. | |
| [21] | Peng S L. Studies on succession of plant community II. methods for dynamics research. Ecological Science, 1994(2): 117-119. |
| 彭少麟. 植物群落演替研究: II. 动态研究的方法. 生态科学, 1994(2): 117-119. | |
| [22] | Liu Y F, Fan H, Shi J J, et al. Climate change-induced shrub encroachment changes soil hydraulic properties and inhibits herbaceous growth in alpine meadows. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2023, 340: 109629. |
| [23] | Ma X X, Gao Y Z. Impact of shrub encroachment on soil hydrological processes in grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 212-222. |
| 马学喜, 高英志. 灌丛化对草地土壤水文过程影响的研究进展. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 212-222. | |
| [24] | Saixiyala, Ding Y, Zhang S D, et al. Facilitation by a spiny shrub on a rhizomatous clonal herbaceous in Thicketization-grassland in northern China: increased soil resources or shelter from herbivores. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 809. |
| [25] | Wang Y L, Wang X L, Ma Y S, et al. Effect of slope aspect on vegetation growth and soil nutrient characteristics of alpine grassland in the source region of Yangtze River. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(10): 2336-2346. |
| 王彦龙, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 等. 坡向对长江源区高寒草地植被生长和土壤养分特征的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(10): 2336-2346. | |
| [26] | Zhao H L, Su Y Z, Zhang H, et al. Multiple effects of shrub on soil properties and understory vegetation in Horqin sand land, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(3): 385-390. |
| 赵哈林, 苏永中, 张华, 等. 灌丛对流动沙地土壤特性和草本植物的影响. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(3): 385-390. | |
| [27] | Qu W L, Yang X P, Zhang C T, et al. Shrub-mediated “fertile island” effects in arid and semi arid grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4): 201-207. |
| 瞿王龙, 杨小鹏, 张存涛, 等. 干旱、半干旱地区天然草原灌木及其肥岛效应研究进展. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 201-207. | |
| [28] | Liu T, Ji M F, Deng Y, et al. Progress in asymmetric light competition research. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(1): 156-167. |
| 刘涛, 姬明飞, 邓燕, 等. 植物非对称性光竞争研究进展. 草业科学, 2020, 37(1): 156-167. | |
| [29] | Li Y F, Sun B, Nan Z B, et al. Classification system of inter-silva grasslands in northern China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(3): 175-188. |
| 李毅夫, 孙斌, 南志标, 等. 中国北方林间草地分类体系研究. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 175-188. | |
| [30] | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Tong S Y, et al. Effects of shrub encroachment on biomass and biodiversity in the typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(22): 7221-7229. |
| 彭海英, 李小雁, 童绍玉, 等. 内蒙古典型草原灌丛化对生物量和生物多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(22): 7221-7229. | |
| [31] | Guan J X, Li X Q, Zhang M W, et al. Effects of Caragana microphylla encroachment on mineral element concentrations in leaves and aboveground biomass accumulation of herbaceous plants along an aridity gradient. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(19): 8047-8056. |
| 关家欣, 李小琴, 张明伟, 等. 沿干旱梯度小叶锦鸡儿灌丛化对草本植物叶片矿质元素浓度及地上生物量累积的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(19): 8047-8056. | |
| [32] | Yu L, Wang H M, Guo T D, et al. Bistable-state of vegetation shift in the desert grassland-shrubland anthropogenic mosaic area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(24): 9773-9783. |
| 于露, 王红梅, 郭天斗, 等. 荒漠草原-灌丛镶嵌体的植被稳态转变特征. 生态学报, 2021, 41(24): 9773-9783. | |
| [33] | Chen J, Li F C, Jia B, et al. Regulation of soil nitrogen cycling by shrubs in grasslands. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2024, 191: 109327. |
| [34] | Ravolainen T V, Bråthen A K, Ims A R, et al. Shrub patch configuration at the landscape scale is related to diversity of adjacent herbaceous vegetation. Plant Ecology & Diversity, 2013, 6(2): 257-268. |
| [35] | Beck J J. Variation in plant-soil interactions among temperate forest herbs. Plant Ecology, 2021, 222(11): 1225-1238. |
| [36] | Jezequel A, Delaby L, Finn A J, et al. Sward species diversity impacts on pasture productivity and botanical composition under grazing systems. Grass and Forage Science, 2024, 79(4): 651-665. |
| [37] | Knapp K A, Briggs M J, Collins L S, et al. Shrub encroachment in North American grasslands: shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs. Global Change Biology, 2008, 14(3): 615-623. |
| [38] | Zhao J X, Yang W, Awei J S, et al. Shrub encroachment increases soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in alpine grassland ecosystems of the central Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma, 2023, 433: 116468. |
| [39] | Wu G L, Liu Y F, Wang D, et al. Divergent successions to shrubs- and forbs-dominated meadows decrease ecosystem multifunctionality of hillside alpine meadow. Catena, 2024, 236: 107718. |
| [1] | Shi-jie ZHOU, Yi-lian WANG, Pan SUN, Jing SHANG, Wen-yu YANG, Xue-gui WANG, Ji-zhi YANG. Analysis of weed species and community characteristics in soybean-maize fields with a banded compound planting pattern in Sichuan Province [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 143-154. |
| [2] | Jia-qi HE, Lin WU, Zhi-min QIU, Xu-yong GAO, Lun-lun GAO, Shuang-bin FU, Yan-ping YANG, Pei-long WANG, Wan XU, Zhuang ZHOU. Species diversity and community characteristics of weeds on the banks of the Wenzhou expressway [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 40-53. |
| [3] | Shuang YAN, Fei XIA, Wei WEI, Jing-long WANG, Hao-yang WU, Lin-ling RAN, Yun-yin XUE, Hao SHI, Shai-kun ZHENG, Jun-qiang WANG, Jun-dong HE. Differences along an erosion gradient in alpine meadow plant community diversity and factors influencing diversity [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(6): 1-13. |
| [4] | Shun-hua LUO, Xin-yu LIU, Bao-ping MENG, Xuan-li CHEN, Ren-jie HU, Hong-yan YU, Xian-ying WANG, Bo ZHANG, Yu QIN. A study of functional group diversity and productivity of alpine grassland in Qilian Mountain National Park [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(6): 14-26. |
| [5] | Xue-ping LI, Shi-yang XU, Jian-jun LI, Yong-hong QI. Bacterial diversity and community structural changes in rhizosphere soil of naked barley disturbed by root rot [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(5): 118-129. |
| [6] | Shou-xing WANG, Hua-kun ZHOU, Li-peng OU, Cheng-xian LI, Yan-he WANG, Xiao-chun NING, Qiang GU, Dai-jun WEI, Ming-xin YANG. Vegetation and soil microbial diversity and their relationships with soil factors in different grassland types of the three river headwaters region [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 16-26. |
| [7] | Xue-xi MA, Ying-zhi GAO. Impact of shrub encroachment on soil hydrological processes in grassland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 212-222. |
| [8] | Xin GONG, Xin-ru HUO, Wen LI, Yan-dong YANG, Chao LIU, Wei-chun QIN, Yan SHEN, Guo-hui WANG, Hong-bin MA. Vegetation community characteristics and spatial differentiation in mountain grassland in Luoshan, Ningxia [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 1-15. |
| [9] | Yu-du JING, Xiao-wei LIU, Ke LIANG, Jun-hao FENG, Qiang YU, Liang GUO. Impacts of shrub encroachment on the fraction and stability of soil organic carbon of grassland on the Loess Plateau, and the underlying microbial mechanisms [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(12): 1-15. |
| [10] | Ye-xin LYU, Mao YE, Jiao-rong QIAN, Wei-long CHEN, Jing CHE, Miao-miao LI, Guo-yan ZENG. Biodiversity and phylogenetic diversity of grasslands in the Habahe forest area of Xinjiang and analysis of the influencing factors [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(12): 50-61. |
| [11] | Ze-hua LIU, Lin CHEN, Ya-qi ZHANG, Jin-xiao LONG, Xue-bin LI, Dan-bo PANG. The impact of shrub encroachment on species niches and interspecific associations of the Artemisia scoparia community in desert grassland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 1-15. |
| [12] | Qian LIU, Yan-fen DING, Shan-shan SONG, Wen-jie XU, Wei YANG. Quantitative classification and ordination analysis of spontaneous vegetation communities in herb layer along the green belt of Nanjing Ming City Wall [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 1-15. |
| [13] | Ya-nan ZHAO, Hong-mei WANG, Zhi-li LI, Zhen-jie ZHANG, Yan-shuo CHEN, Rong-xia SU. Responses of spatial pattern and driving factors for soil water deficit of desert grassland-shrubland transition sites [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. |
| [14] | Hao SHI, Cai-hong YANG, Fei XIA, Jun-qiang WANG, Wei WEI, Jing-long WANG, Yun-yin XUE, Shai-kun ZHENG, Hao-yang WU, Lin-ling RAN, Shuang YAN, Xiao-min JIANG. Initial effects of short-term warming on the productivity of alpine degraded grassland in northern Tibet during the restoration process [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 30-45. |
| [15] | Dong ZHANG, Chen HOU, Wen-ming MA, Chang-ting WANG, Zhuo-ma DENGZENG, Ting ZHANG. Study on soil enzyme activities under shrub encroachment gradients in alpine grassland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||