
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 1-12.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025159
Lei JIN1( ), Yan-ping WANG1, Narisu2(
), Yan-ping WANG1, Narisu2( ), Yong-sheng BAO1, Jing-chao ZHANG1
), Yong-sheng BAO1, Jing-chao ZHANG1
Received:2025-04-24
Revised:2025-06-04
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Narisu
Lei JIN, Yan-ping WANG, Narisu, Yong-sheng BAO, Jing-chao ZHANG. Impacts of daily-scale hydrothermal factor variations on productivity of Hulun Buir meadow steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 1-12.
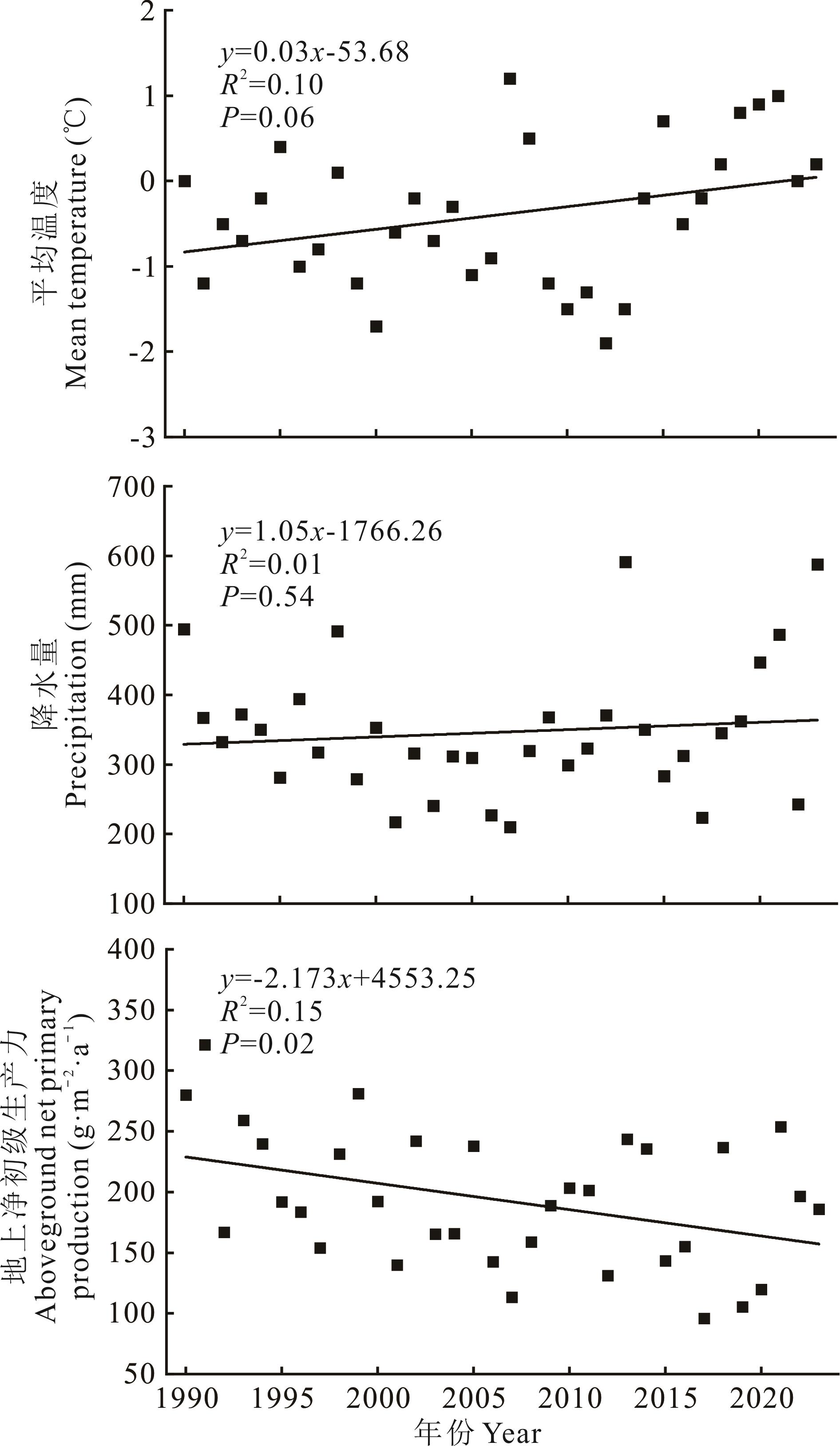
Fig.2 Interannual variability of mean annual temperature, annual precipitation, and aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) in the study area, 1990-2023
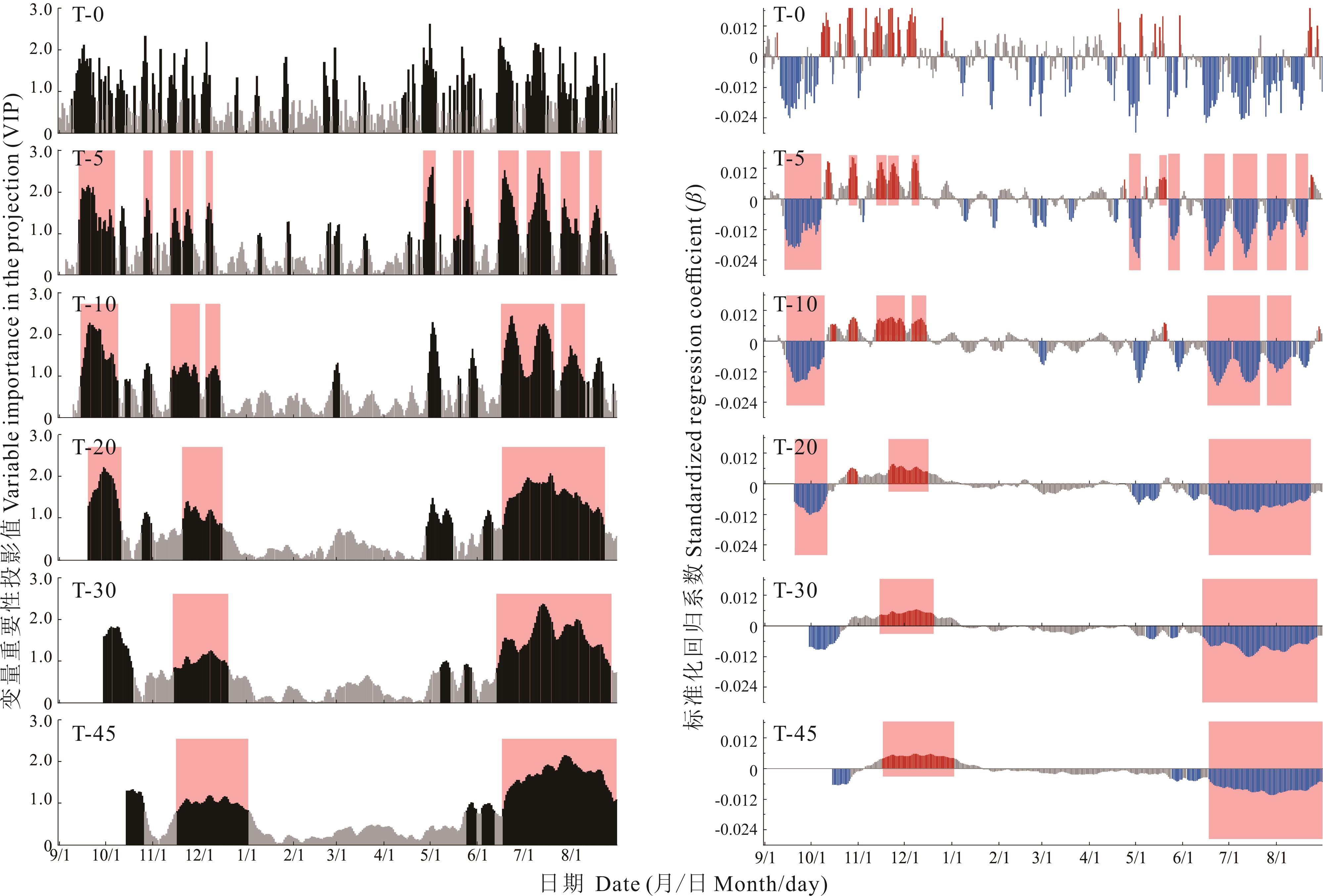
Fig.3 Partial least squares regression (PLSR) between aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) and multi-temporal daily air temperature averages in the study area, 1990-2023
| 气温窗口Temperature windows | R2 | 均方根误差Root mean square error (RMSE) | 平均绝对误差Mean absolute error (MAE) | 样本量 Sample size (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-0 | 0.821 | 23.113 | 19.196 | 34 |
| T-5 | 0.697 | 30.044 | 24.517 | |
| T-10 | 0.588 | 35.046 | 28.209 | |
| T-20 | 0.475 | 39.556 | 31.754 | |
| T-30 | 0.460 | 40.098 | 31.976 | |
| T-45 | 0.426 | 41.338 | 32.956 |
Table 1 Overall explanatory power of partial least squares regression (PLSR) between aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) and temperature across daily temporal scales
| 气温窗口Temperature windows | R2 | 均方根误差Root mean square error (RMSE) | 平均绝对误差Mean absolute error (MAE) | 样本量 Sample size (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-0 | 0.821 | 23.113 | 19.196 | 34 |
| T-5 | 0.697 | 30.044 | 24.517 | |
| T-10 | 0.588 | 35.046 | 28.209 | |
| T-20 | 0.475 | 39.556 | 31.754 | |
| T-30 | 0.460 | 40.098 | 31.976 | |
| T-45 | 0.426 | 41.338 | 32.956 |

Fig.4 Partial least squares regression (PLSR) between aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) and multi-temporal daily precipitation in the study area, 1990-2023
| 降水窗口Precipitation windows | R2 | 均方根误差Root mean square error (RMSE) | 平均绝对误差Mean absolute error (MAE) | 样本量Sample size (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-0 | 0.891 | 18.044 | 14.815 | 34 |
| P-5 | 0.742 | 27.715 | 22.172 | |
| P-10 | 0.690 | 30.369 | 24.039 | |
| P-20 | 0.597 | 34.627 | 27.532 | |
| P-30 | 0.507 | 38.300 | 31.136 | |
| P-45 | 0.407 | 42.012 | 34.520 |
Table 2 Overall explanatory power of partial least squares regression (PLSR) between aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) and precipitation across daily temporal scales
| 降水窗口Precipitation windows | R2 | 均方根误差Root mean square error (RMSE) | 平均绝对误差Mean absolute error (MAE) | 样本量Sample size (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-0 | 0.891 | 18.044 | 14.815 | 34 |
| P-5 | 0.742 | 27.715 | 22.172 | |
| P-10 | 0.690 | 30.369 | 24.039 | |
| P-20 | 0.597 | 34.627 | 27.532 | |
| P-30 | 0.507 | 38.300 | 31.136 | |
| P-45 | 0.407 | 42.012 | 34.520 |

Fig.5 Linear regression analysis between aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) and critical periods of multi-temporal daily air temperature averages and precipitation
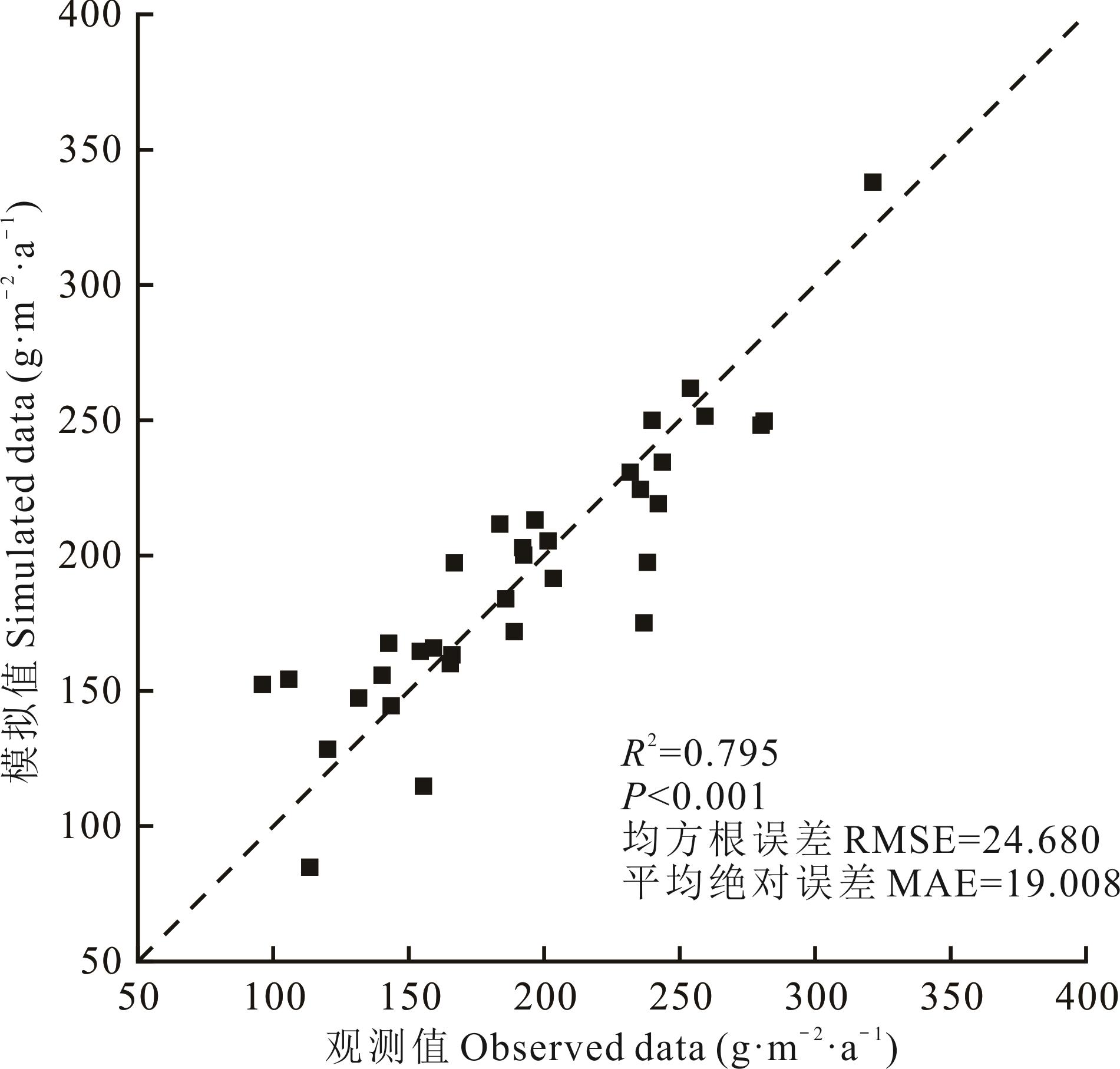
Fig.7 Accuracy validation of stepwise regression for modeled aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) using critical period air temperature and precipitation
| [1] | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change 2021:The physical science basis. Geneva: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2021. |
| [2] | Yan H, Xie G, Niu Z, et al. Impact of human activities and climate change on grassland productivity in Xilingol League. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2024, 15(5): 1134-1146. |
| [3] | Zhou X F, Peng B B, Zhou Y, et al. Quantifying the influence of climate change and anthropogenic activities on the net primary productivity of China’s grasslands. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(19): 4844. |
| [4] | Huang Y, Song H Q, Wu H, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of vegetation carbon use efficiency and its relationship with hydrothermal factors in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 44(5): 358-368. |
| 皇彦, 宋海清, 吴昊, 等. 内蒙古自治区植被碳利用效率时空动态及其与水热因子的关系. 水土保持通报, 2024, 44(5): 358-368. | |
| [5] | Luo S H, Liu X Y, Meng B P, et al. A study of functional group diversity and productivity of alpine grassland in Qilian Mountain National Park. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(6): 14-26. |
| 罗顺华, 刘新宇, 孟宝平, 等. 祁连山国家公园高寒草地功能群多样性与生产力研究. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 14-26. | |
| [6] | Chen C, Jing C Q, Zhao W K, et al. Grassland quality response to climate change in Xinjiang and predicted future trends. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 1-16. |
| 陈宸, 井长青, 赵苇康, 等. 新疆草地质量对气候变化的响应及其变化趋势. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 1-16. | |
| [7] | Kuang M M, Zhou G S, Zhou M Z. Environmental driving mechanism of species diversity and productivity in Tibetan alpine grasslands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(14): 6254-6264. |
| 匡苗苗, 周广胜, 周梦子. 西藏高寒草地物种多样性和生产力的环境驱动机制. 生态学报, 2024, 44(14): 6254-6264. | |
| [8] | Tu H Y, Guli·Jiapaer, Yu T, et al. Analysis of spatio-temporal variation characteristics and influencing factors of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(3): 1219-1233. |
| 涂海洋, 古丽·加帕尔, 于涛, 等. 中国陆地生态系统净初级生产力时空变化特征及影响因素. 生态学报, 2023, 43(3): 1219-1233. | |
| [9] | Huang L, Li J H, Zhang H Y, et al. Accounting and assessment of grassland ecological values. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 47-63. |
| 黄麟, 李佳慧, 张海燕, 等. 草原生态价值的内涵、核算及评估. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 47-63. | |
| [10] | Yao L J, Zhang J N, Zhang H R, et al. Sustainable utilization of natural resources in Inner Mongolia based on ecological footprint. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(8): 1525-1536. |
| 姚林杰, 张佳宁, 张恒瑞, 等. 基于生态足迹的内蒙古自然资源可持续利用分析. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1525-1536. | |
| [11] | Li Z Y, Yang Q, Ma Z G, et al. Responses of vegetation to climate change and human activities in the arid and semiarid regions of northern China. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2024, 48(3): 859-874. |
| 李卓忆, 杨庆, 马柱国, 等. 中国北方干旱半干旱区植被对气候变化和人类活动的响应. 大气科学, 2024, 48(3): 859-874. | |
| [12] | Wang Y, Wang J S, Zhang Q. Drought risk status of grassland in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 1-12. |
| 王莺, 王健顺, 张强. 中国草原干旱灾害风险特征研究. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 1-12. | |
| [13] | Yang C Y, Ding Y, Ma F L, et al. Climate change affects plant aboveground biomass by regulating the growth periods in alpine grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 35(5): 1260-1268. |
| 杨聪颖, 丁颖, 马扶林, 等. 气候变化通过调控青藏高原高寒草原植物生育期影响地上生物量积累. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(5): 1260-1268. | |
| [14] | Geng X D, Xu R. Ecosystem carbon exchange of an alpine meadow under simulated gradient warming in the Tibetan Plateau, China. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(12): 2407-2415. |
| 耿晓东, 旭日. 梯度增温对青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统碳交换的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(12): 2407-2415. | |
| [15] | Wang J T, Yang Y C, Yang M H. Spatial and temporal variation and driving forces of NPP on the Loess Plateau based on geodetector. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 2023, 39(1): 12-20. |
| 王江涛, 杨永崇, 杨梅焕. 基于地理探测器的黄土高原NPP时空变化及驱动力研究. 西安理工大学学报, 2023, 39(1): 12-20. | |
| [16] | Yang Y, Zhou D C, Gong Z N, et al. Ecological vulnerability and its drivers of the Loess Plateau based on vegetation productivity. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(10): 1951-1958. |
| 杨艳, 周德成, 宫兆宁, 等. 基于植被生产力的黄土高原地区生态脆弱性及其控制因子分析. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1951-1958. | |
| [17] | Zhao X X, Wang G X, Yang K, et al. Research on seed germination, seedling survival, and establishment of alpine plants in response to climate change: A review. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(2): 213-225. |
| 赵小祥, 王根绪, 杨凯, 等. 高山植物种子萌发、幼苗存活和定居对气候变化的响应. 草业科学, 2020, 37(2): 213-225. | |
| [18] | Yuan Y M, Liu J Y, Gao X L, et al. Root traits of seven Stipa species and their relations with environmental factors in temperate grasslands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(21): 8784-8794. |
| 袁野梅, 柳隽瑶, 高秀丽, 等. 温带草原7种针茅植物根系特征及其对环境因子变化的适应. 生态学报, 2022, 42(21): 8784-8794. | |
| [19] | Xu L L, Niu B, Zhang X Z, et al. Climate responses of carbon fluxes in two adjacent alpine grasslands in northern Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 1-16. |
| 徐玲玲, 牛犇, 张宪洲, 等. 藏北两个临近不同高寒草地碳通量对气候条件的响应. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 1-16. | |
| [20] | Lin X D, Chang L, Feng D. Remote-sensing estimation of vegetation gross primary productivity and its spatiotemporal changes in Qinghai Province from 2000 to 2019. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 16-27. |
| 林小丁, 常乐, 冯丹. 2000-2019年青海地区植被总初级生产力遥感估算及时空变化分析. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 16-27. | |
| [21] | Qiao L, Xia H. The impact of drought time scales and characteristics on gross primary productivity in China from 2001 to 2020. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2025, 28(1): 284-302. |
| [22] | Yu Z W, Liu Q, Zhang Y Y, et al. Changes of NDVI and driving factors in different grasslands in the Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(22): 10068-10082. |
| 余志巍, 刘强, 张宇阳, 等. 内蒙古不同草地NDVI变化及其驱动要素. 生态学报, 2024, 44(22): 10068-10082. | |
| [23] | Su R H, Guo E L, Wang Y F, et al. Extreme climate changes in the Inner Mongolia and their impacts on vegetation dynamics during 1982-2020. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(1): 419-431. |
| 苏日罕, 郭恩亮, 王永芳, 等. 1982-2020年内蒙古地区极端气候变化及其对植被的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(1): 419-431. | |
| [24] | Xiao F, Sang J, Wang H M. Effects of climate change on typical grassland plant phenology in Ewenki, Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(8): 2784-2792. |
| 肖芳, 桑婧, 王海梅. 气候变化对内蒙古鄂温克旗典型草原植物物候的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(8): 2784-2792. | |
| [25] | Zheng H J, Yang X F, Song C Q, et al. Distinct environmental controls on above- and below-ground net primary productivity in northern China’s grasslands. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 167: 112717. |
| [26] | Qu X B, Li D, Tian Y, et al. Distribution of net ecosystem productivity in the Hulunbuir region from 2001 to 2021 and its relationship with temperature and precipitation. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2024, 40(4): 100-106. |
| 曲学斌, 李丹, 田野, 等. 2001-2021年呼伦贝尔地区净生态系统生产力分布及其与气温和降水的关系. 气象与环境学报, 2024, 40(4): 100-106. | |
| [27] | Wang Z X, Hu G Z, Shui H W, et al. Effect of seasonal timing of drought on carbon exchange in the alpine meadow ecosystem of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(4): 24-33. |
| 王子欣, 胡国铮, 水宏伟, 等. 不同时期干旱对青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统碳交换的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 24-33. | |
| [28] | Zhang W, Wang L C, Xiang F F, et al. Vegetation dynamics and the relations with climate change at multiple time scales in the Yangtze River and Yellow River Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 110: 105892. |
| [29] | Yang Z G, Zhang J G, Li J R, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamic variation of temperate grassland classes in Inner Mongolia in the last 20 years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 1-16. |
| 杨志贵, 张建国, 李锦荣, 等. 内蒙古温性草原草地类型近20年时空动态变化研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 1-16. | |
| [30] | Jin L, Wang Y F. The impact of drought on biomass of forage grass in Hulunbuir grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(5): 80-90. |
| 金磊, 王永芳. 干旱对呼伦贝尔草原牧草生物量的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(5): 80-90. | |
| [31] | Ye S Y, Hu X X, Si X S, et al. Reliability assessment method for complex systems using sliding window and Kriging interpolation algorithm. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2023, 57(4): 171-179. |
| 叶爽怡, 扈晓翔, 司小胜, 等. 采用滑动窗口与克里金插值算法的复杂系统可靠性评估方法. 西安交通大学学报, 2023, 57(4): 171-179. | |
| [32] | Zhong Z Q, He B, Wang Y P, et al. Disentangling the effects of vapor pressure deficit on northern terrestrial vegetation productivity. Science Advances, 2023, 9(32): eadf3166. |
| [33] | Li P H, Zhang R Q, Xu L P. Three-dimensional ecological footprint based on ecosystem service value and their drivers: a case study of Urumqi. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 131: 108117. |
| [34] | Wang L, Yu H Y, Zhang Q, et al. Responses of aboveground biomass of alpine grasslands to climate changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2018, 28(12): 1953-1964. |
| [35] | Ma F L, Liu X W, Duo Y, et al. Effects of daily variation of hydro-thermal factors on alpine grassland productivity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(9): 3719-3728. |
| 马扶林, 刘小伟, 朵莹, 等. 日尺度下水热因子变化对青藏高原高寒草原生产力的影响特征. 生态学报, 2023, 43(9): 3719-3728. | |
| [36] | Cui B C, Zheng J H, Tuerxun·Hasimu, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics of grassland net primary productivity (NPP) in the Tarim River basin. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. |
| 崔博超, 郑江华, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 等. 塔里木河流域草地净初级生产力时空分异特征研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. | |
| [37] | Zhang R P, Guo J, Zhang Y L. Spatial distribution pattern of NPP of Xinjiang grassland and its response to climatic changes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(15): 5318-5326. |
| 张仁平, 郭靖, 张云玲. 新疆草地净初级生产力(NPP)空间分布格局及其对气候变化的响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(15): 5318-5326. | |
| [38] | Sun B, Wang Y, Guo Y, et al. The spatiotemporal dynamics and influencing factors of vegetation cover in the Xilin Gol grassland (2000-2020). Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(11): 11-22. |
| 孙斌, 王燕, 郭晔, 等. 2000-2020年锡林郭勒草原植被覆盖时空动态变化及影响因素分析. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(11): 11-22. | |
| [39] | Chang Y R, Zhang C, Wei J C, et al. Impacts of climate change and human activities on the net primary productivity of vegetation in Inner Mongolia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(11): 3444-3452. |
| 常屹冉, 张弛, 魏嘉诚, 等. 气候变化和人类活动对内蒙古植被净初级生产力的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(11): 3444-3452. | |
| [40] | Wang Z F, Wang J Y, Wang W L, et al. An explanation of the differences in grassland NDVI change in the eastern route of the China-Mongolia-Russia economic corridor. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(5): 867. |
| [41] | Zhang T K, Wang J B, Ye H, et al. Vulnerability of alpine ecosystems and its response to climate change and human activities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(1): 154-170. |
| 张庭康, 王军邦, 叶辉, 等. 高寒生态系统脆弱性及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应. 生态学报, 2024, 44(1): 154-170. | |
| [42] | Geng Y B, Wang S, Hu X D. Responses of aboveground net primary productivity of the alpine meadow steppe to climate change: simulations based on the CENTURY model. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(1): 1-13. |
| 耿元波, 王松, 胡雪荻. 高寒草甸草原净初级生产力对气候变化响应的模拟. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 1-13. | |
| [43] | Chen B, Li L G, Chen Z J. Spatio-temporal variation of climate productivity of vegetation and its responses to climate change in three provinces of northeast China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 35(12): 3339-3348. |
| 陈博, 李丽光, 陈振举. 东北三省植被气候生产力的时空变化及对气候变化的响应. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(12): 3339-3348. | |
| [44] | He Y J, Kong Z, Hu X, et al. Water and heat conditions seperately controlled inter-annual variation and growth trend of NDVI in the temperate grasslands in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(2): 766-777. |
| 何玉杰, 孔泽, 户晓, 等. 水热条件分别控制了中国温带草地 NDVI 的年际变化和增长趋势. 生态学报, 2022, 42(2): 766-777. | |
| [45] | Lin H L, Fan D, Feng Q S, et al. New focus for the study of the comprehensive sequential classification system for grassland: A review from 2008 to 2020 and prospects for future research. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 201-213. |
| 林慧龙, 范迪, 冯琦胜, 等. 草地综合顺序分类法研究新热点:2008-2020年回顾与展望. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 201-213. | |
| [46] | Zhang T L, Jiang L L, Liu B, et al. Quantitative analysis of vegetation sensitivity to climate change in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2025, 45(5): 2412-2423. |
| 张韬略, 姜亮亮, 刘冰, 等. 中国植被对气候变化的敏感性定量分析. 生态学报, 2025, 45(5): 2412-2423. |
| [1] | Ke GONG, Gui-li JIN, Wen-hao LIU, Jian MA, Zhi-biao LIU, Jia-xin LI, Ying LI. Effects of simulated warming on growth characteristics of Bromus inermis [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 93-103. |
| [2] | Peng-chong DU, Yu-zhen PAN, Shuang-li HOU, Zhi-hui WANG, Hong-yi WANG. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on litter decomposition in Hulunber steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 44-53. |
| [3] | Meng-han WANG, Li-li DONG, Fu-cui LI, Lie-bao HAN, Xiang WANG. Effects of different organic ∶inorganic nitrogen addition ratios on nitrogen distribution and transformation in a grassland soil [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 36-46. |
| [4] | Jing-jing ZHANG, Zun-chi LIU, Chuang YAN, Yun-xia WANG, Kai LIU, Xin-rong SHI, Zhi-you YUAN. Effects of soil pH on soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus ecological stoichiometry in three types of steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 69-81. |
| [5] | Wen-hui GUO, Run-yuan GU, Feng DING. Spring phenological characteristics of dandelion and plantain in Shandong Province and their responses to climate change [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 27-38. |
| [6] | Ying-ying NIE, Jin-qiang CHEN, Xiao-ping XIN, Li-jun XU, Gui-xia YANG, Xu WANG. Responses of niche characteristics and species diversity of main plant populations to duration of enclosure in the Hulun Buir meadow steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 15-25. |
| [7] | NIE Ying-ying, XU Li-jun, XIN Xiao-ping, CHEN Bao-rui, ZHANG Bao-hui. Effects of fence enclosure on the plant community composition and niche characteristics in a temperate meadow steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 11-22. |
| [8] | GENG Yuan-bo, WANG Song, HU Xue-di. Responses of aboveground net primary productivity of the alpine meadow steppe to climate change: simulations based on the CENTURY model [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(1): 1-13. |
| [9] | NA Ya, SUN Qi-Zhong, WANG Hong-Mei. Fatty acid characteristics of forage silages from the Hulunbeir Meadow Steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(2): 215-223. |
| [10] | CUI Xia, SONG Qing-Jie, ZHANG Yao-Yao, XU Gang, MENG Bao-Ping, GAO Jin-Long. Estimation of soil organic carbon content in alpine grassland using hyperspectral data [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(10): 20-29. |
| [11] | HU Fei-Long, YAN Yan, LU Xiao-Qiang, WU Jun, DING Hui, LIU Zhi-Min. Biomass allocation patterns in the temperate meadow steppe in Inner Mongolia [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(4): 36-44. |
| [12] | WANG Song, GENG Yuan-Bo, MU Yue. Responses of aboveground net primary productivity of the typical steppe to climate change-a simulation based on the CENTURY Model [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(12): 4-13. |
| [13] | LI Hui-Xia, PENG Huan, PENG De-Liang, ZHU Rui-Dong, XU Peng-Gang, LI Jian-Rong. Identification of cyst nematode in alpine meadow steppe, Gansu [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(8): 174-180. |
| [14] | TAN Hongyan, YAN Ruirui, YAN Yuchun, CHEN Baorui, XIN Xiaoping. Phospholipid fatty acid analysis of soil microbial communities under different grazing intensities in meadow steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(3): 115-121. |
| [15] | LIU Yan-shu,FAN Jiang-wen,LI Yu-zhe,ZHANG Liang-xia. Plant community productivity and diversity on alpine meadow steppe in the Three River Headwater Region, Qinghai Province under different denudation levels [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 1-7. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||