
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 43-52.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Li-min GAO( ), Chun CHEN, Yi-xin SHEN(
), Chun CHEN, Yi-xin SHEN( )
)
Received:2021-01-20
Revised:2021-07-05
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Yi-xin SHEN
Li-min GAO, Chun CHEN, Yi-xin SHEN. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer rates on forage dry matter yield and regrowth of alfalfa in seasonal cultivation systems[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 43-52.
处理 Treatments | 干物质产量 Forage dry matter yield (kg·hm-2) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 一级分枝数 Shoot number | 叶面积 Leaf area (m2·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| P0N0 | 4096fg | 4428e | 49.50ef | 32.84g | 2.00c | 1.75bcdef | 40097def | 21034ghi |
| P0N1 | 3375g | 5665cde | 63.35bcd | 38.97efg | 2.20c | 1.83bcdef | 27259f | 15930i |
| P0N2 | 4533ef | 6955bc | 64.56bcd | 44.30def | 2.93c | 2.17bcd | 76270b | 29256bcd |
| P0N3 | 6105c | 6712bcd | 57.76cde | 40.83efg | 3.40bc | 1.42def | 73059bc | 26442ghi |
| P1N0 | 3912fg | 4598de | 38.45g | 36.72fg | 3.27bc | 1.25ef | 36947f | 15279hi |
| P1N1 | 4638ef | 5460cde | 51.93ef | 34.80fg | 5.00a | 1.83bcdef | 56077bcd | 24400fghi |
| P1N2 | 5632cd | 8304ab | 55.79cde | 49.02cde | 5.20a | 1.58cdef | 67582bcd | 33067abc |
| P1N3 | 7718b | 7268bc | 71.91ab | 55.18abcd | 4.87ab | 2.25bcd | 86037a | 28540bcd |
| P2N0 | 4073fg | 5750cde | 54.25de | 40.39efg | 2.80c | 2.42abc | 39956ef | 19922efgh |
| P2N1 | 8424ab | 7471bc | 65.09abc | 39.71efg | 1.93c | 1.92bcdef | 65403bcd | 22406ghi |
| P2N2 | 8311ab | 8512ab | 62.41bcd | 45.71def | 2.53c | 1.17f | 91705a | 25461fghi |
| P2N3 | 8398ab | 8323ab | 73.93a | 52.34cd | 5.47a | 3.08a | 74188b | 21481abc |
| P3N0 | 5100de | 7072bc | 54.82de | 57.45abc | 2.60c | 2.08bcde | 63022bcd | 36461ab |
| P3N1 | 8670a | 9950a | 68.44ab | 65.43abc | 2.80c | 1.83bcdef | 121390a | 41234ab |
| P3N2 | 8696a | 10093a | 70.21ab | 70.21a | 3.27bc | 2.50ab | 88658a | 45876a |
| P3N3 | 8702a | 8864ab | 68.61ab | 68.61ab | 4.73ab | 1.92bcdef | 73415bc | 40759ab |
| P | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** |
| N | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** |
| P×N | *** | ns | *** | * | ns | *** | *** | *** |
Table 1 Effects of N and P fertilizer on the forage dry matter yield and yield components of alfalfa
处理 Treatments | 干物质产量 Forage dry matter yield (kg·hm-2) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 一级分枝数 Shoot number | 叶面积 Leaf area (m2·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| P0N0 | 4096fg | 4428e | 49.50ef | 32.84g | 2.00c | 1.75bcdef | 40097def | 21034ghi |
| P0N1 | 3375g | 5665cde | 63.35bcd | 38.97efg | 2.20c | 1.83bcdef | 27259f | 15930i |
| P0N2 | 4533ef | 6955bc | 64.56bcd | 44.30def | 2.93c | 2.17bcd | 76270b | 29256bcd |
| P0N3 | 6105c | 6712bcd | 57.76cde | 40.83efg | 3.40bc | 1.42def | 73059bc | 26442ghi |
| P1N0 | 3912fg | 4598de | 38.45g | 36.72fg | 3.27bc | 1.25ef | 36947f | 15279hi |
| P1N1 | 4638ef | 5460cde | 51.93ef | 34.80fg | 5.00a | 1.83bcdef | 56077bcd | 24400fghi |
| P1N2 | 5632cd | 8304ab | 55.79cde | 49.02cde | 5.20a | 1.58cdef | 67582bcd | 33067abc |
| P1N3 | 7718b | 7268bc | 71.91ab | 55.18abcd | 4.87ab | 2.25bcd | 86037a | 28540bcd |
| P2N0 | 4073fg | 5750cde | 54.25de | 40.39efg | 2.80c | 2.42abc | 39956ef | 19922efgh |
| P2N1 | 8424ab | 7471bc | 65.09abc | 39.71efg | 1.93c | 1.92bcdef | 65403bcd | 22406ghi |
| P2N2 | 8311ab | 8512ab | 62.41bcd | 45.71def | 2.53c | 1.17f | 91705a | 25461fghi |
| P2N3 | 8398ab | 8323ab | 73.93a | 52.34cd | 5.47a | 3.08a | 74188b | 21481abc |
| P3N0 | 5100de | 7072bc | 54.82de | 57.45abc | 2.60c | 2.08bcde | 63022bcd | 36461ab |
| P3N1 | 8670a | 9950a | 68.44ab | 65.43abc | 2.80c | 1.83bcdef | 121390a | 41234ab |
| P3N2 | 8696a | 10093a | 70.21ab | 70.21a | 3.27bc | 2.50ab | 88658a | 45876a |
| P3N3 | 8702a | 8864ab | 68.61ab | 68.61ab | 4.73ab | 1.92bcdef | 73415bc | 40759ab |
| P | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** |
| N | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** |
| P×N | *** | ns | *** | * | ns | *** | *** | *** |
处理 Treatments | 氮含量N content (%) | 磷含量P content (%) | 氮累积量N accumulation (kg·hm-2) | 磷累积量P accumulation (kg·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| P0N0 | 2.15c | 2.61abcd | 0.17b | 0.21a | 87.90fg | 135.43efg | 7.03e | 9.33cde |
| P0N1 | 2.14c | 2.61abcd | 0.19ab | 0.18ab | 72.16g | 149.50efg | 6.88e | 9.86cde |
| P0N2 | 2.54a | 2.70abc | 0.22ab | 0.18ab | 114.79de | 187.17cde | 9.95cde | 12.48bcd |
| P0N3 | 2.50a | 2.54bcde | 0.24ab | 0.13bc | 152.95c | 170.54def | 14.70abcd | 9.03cde |
| P1N0 | 2.15c | 2.28g | 0.18ab | 0.17ab | 84.27g | 94.85g | 7.14e | 6.45e |
| P1N1 | 2.44ab | 2.51bcdef | 0.21ab | 0.22a | 113.40e | 115.22fg | 9.17de | 9.80cde |
| P1N2 | 2.40ab | 2.72ab | 0.27a | 0.19ab | 135.32cd | 225.96abcd | 15.10abcd | 15.44ab |
| P1N3 | 2.54a | 2.62abcd | 0.23ab | 0.17ab | 196.17ab | 191.05cde | 19.30a | 12.51bcd |
| P2N0 | 1.85d | 2.31fg | 0.23ab | 0.16bc | 75.51g | 139.14efg | 10.53cde | 9.33cde |
| P2N1 | 2.26bc | 2.35efg | 0.22ab | 0.15bc | 190.41b | 136.31efg | 18.16ab | 8.65de |
| P2N2 | 2.49a | 2.46defg | 0.28a | 0.19ab | 206.96ab | 143.36efg | 17.27abc | 10.74cde |
| P2N3 | 2.52a | 2.49cdefg | 0.18ab | 0.15bc | 211.65ab | 149.72efg | 13.66abcde | 9.24cde |
| P3N0 | 2.10c | 2.74ab | 0.23ab | 0.14bc | 107.47ef | 221.06bcd | 11.64bcde | 11.01bcde |
| P3N1 | 2.35ab | 2.73ab | 0.16b | 0.14bc | 203.77ab | 271.25ab | 14.80abcd | 13.76bc |
| P3N2 | 2.51a | 2.80a | 0.17b | 0.11c | 218.21a | 283.43a | 12.47abcde | 11.40bcde |
| P3N3 | 2.52a | 2.64abcd | 0.24ab | 0.21a | 219.33a | 234.09abc | 18.90ab | 18.53a |
| P | ** | ** | ns | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| N | *** | *** | ns | ns | *** | *** | *** | ** |
| P×N | * | ** | ns | ns | *** | ns | ** | *** |
Table 2 Effects of N and P fertilizer on the content and accumulation of N and P
处理 Treatments | 氮含量N content (%) | 磷含量P content (%) | 氮累积量N accumulation (kg·hm-2) | 磷累积量P accumulation (kg·hm-2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| P0N0 | 2.15c | 2.61abcd | 0.17b | 0.21a | 87.90fg | 135.43efg | 7.03e | 9.33cde |
| P0N1 | 2.14c | 2.61abcd | 0.19ab | 0.18ab | 72.16g | 149.50efg | 6.88e | 9.86cde |
| P0N2 | 2.54a | 2.70abc | 0.22ab | 0.18ab | 114.79de | 187.17cde | 9.95cde | 12.48bcd |
| P0N3 | 2.50a | 2.54bcde | 0.24ab | 0.13bc | 152.95c | 170.54def | 14.70abcd | 9.03cde |
| P1N0 | 2.15c | 2.28g | 0.18ab | 0.17ab | 84.27g | 94.85g | 7.14e | 6.45e |
| P1N1 | 2.44ab | 2.51bcdef | 0.21ab | 0.22a | 113.40e | 115.22fg | 9.17de | 9.80cde |
| P1N2 | 2.40ab | 2.72ab | 0.27a | 0.19ab | 135.32cd | 225.96abcd | 15.10abcd | 15.44ab |
| P1N3 | 2.54a | 2.62abcd | 0.23ab | 0.17ab | 196.17ab | 191.05cde | 19.30a | 12.51bcd |
| P2N0 | 1.85d | 2.31fg | 0.23ab | 0.16bc | 75.51g | 139.14efg | 10.53cde | 9.33cde |
| P2N1 | 2.26bc | 2.35efg | 0.22ab | 0.15bc | 190.41b | 136.31efg | 18.16ab | 8.65de |
| P2N2 | 2.49a | 2.46defg | 0.28a | 0.19ab | 206.96ab | 143.36efg | 17.27abc | 10.74cde |
| P2N3 | 2.52a | 2.49cdefg | 0.18ab | 0.15bc | 211.65ab | 149.72efg | 13.66abcde | 9.24cde |
| P3N0 | 2.10c | 2.74ab | 0.23ab | 0.14bc | 107.47ef | 221.06bcd | 11.64bcde | 11.01bcde |
| P3N1 | 2.35ab | 2.73ab | 0.16b | 0.14bc | 203.77ab | 271.25ab | 14.80abcd | 13.76bc |
| P3N2 | 2.51a | 2.80a | 0.17b | 0.11c | 218.21a | 283.43a | 12.47abcde | 11.40bcde |
| P3N3 | 2.52a | 2.64abcd | 0.24ab | 0.21a | 219.33a | 234.09abc | 18.90ab | 18.53a |
| P | ** | ** | ns | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| N | *** | *** | ns | ns | *** | *** | *** | ** |
| P×N | * | ** | ns | ns | *** | ns | ** | *** |
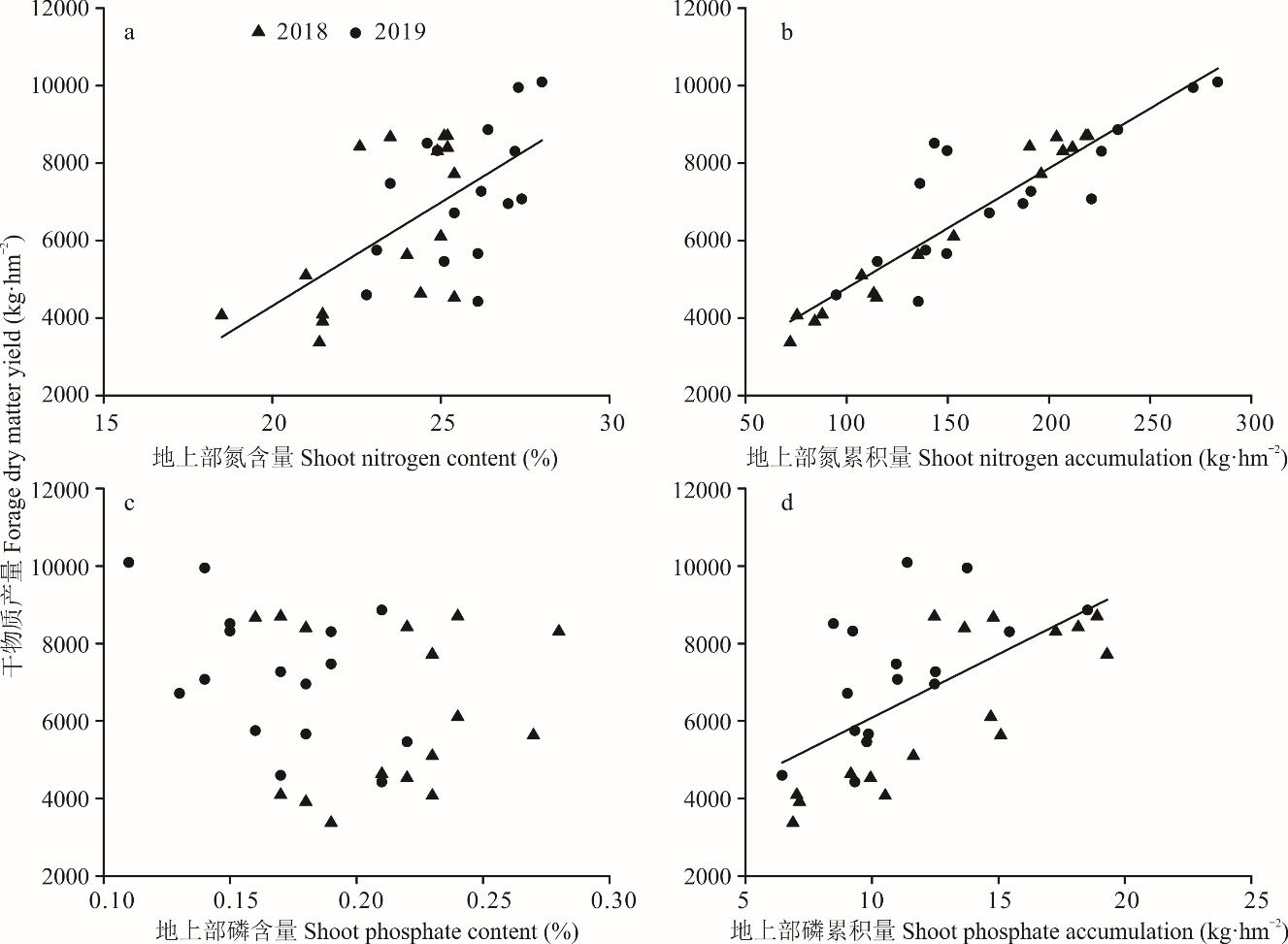
Fig.1 The relationships between shoot nitrogen content, nitrogen accumulation, phosphate content, phosphate accumulation and forage dry matter yield of alfalfa
处理 Treatments | 刈割后第6天 After cutting for 6 d | 刈割后第12天After cutting for 12 d | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
芽数Bud number (×106·hm-2) | 再生芽芽长Shoot length (cm) | 叶面积Leaf area (m2·hm-2) | 芽数Bud number (×106·hm-2) | 再生芽芽长Shoot length (cm) | 叶面积Leaf area (m2·hm-2) | |||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| P0N0 | 11.78g | 10.43bcd | 3.30f | 7.70cd | 1470h | 5170efg | 14.92de | 10.16abcd | 9.19d | 15.19cdef | 18105e | 9325gh |
| P0N1 | 11.48g | 10.14bcd | 5.35de | 7.62cd | 1367h | 5279efg | 13.78e | 10.14abcd | 14.32bc | 11.94f | 18024e | 9725gh |
| P0N2 | 14.77efg | 10.57bcd | 6.54abcde | 7.94cd | 7031abcd | 6061defg | 22.69bc | 12.08abcd | 14.82bc | 15.31cdef | 40644abc | 13500ef |
| P0N3 | 20.31cdef | 14.26a | 6.59abcde | 6.38d | 7341abcd | 6268defg | 20.35bcde | 14.60a | 17.82ab | 12.69ef | 36518abcd | 16952cd |
| P1N0 | 12.01g | 8.11cd | 4.99ef | 9.52bcd | 2520gh | 3580g | 19.52bcde | 8.11d | 10.64cd | 14.49def | 18350e | 8964h |
| P1N1 | 12.94fg | 8.32cd | 7.12abcd | 9.18bcd | 5962bcdef | 6363defg | 17.05cde | 9.45bcd | 12.15cd | 13.17ef | 22964de | 10560fgh |
| P1N2 | 21.14cde | 10.96bc | 7.58ab | 9.53bcd | 7645abc | 6428defg | 22.73bc | 10.63abcd | 21.56a | 14.59def | 45712a | 11878fgh |
| P1N3 | 17.81defg | 9.99bcd | 6.56abcde | 10.22abc | 5340cdef | 7488def | 22.26bc | 10.26abcd | 19.87a | 13.98def | 43381ab | 9559gh |
| P2N0 | 21.54bcde | 7.14d | 5.50cde | 7.78cd | 4553efg | 4349fg | 21.70bcd | 8.99cd | 10.72cd | 15.82cde | 24023cde | 12303fg |
| P2N1 | 23.56abcd | 10.57bcd | 5.62bcde | 9.40bcd | 7834ab | 6615defg | 23.47bc | 10.76abcd | 11.37cd | 15.84cde | 30728abcde | 17841cd |
| P2N2 | 22.44abcd | 10.70bc | 8.02a | 9.47bcd | 6046bcdef | 6172defg | 22.01bc | 10.52abcd | 13.02cd | 17.22cd | 26611bcde | 15896de |
| P2N3 | 17.48defg | 10.21bcd | 7.65ab | 10.01abc | 5104def | 4502fg | 18.60bcde | 10.13abcd | 17.81ab | 18.58bc | 26923bcde | 15578de |
| P3N0 | 22.99abcd | 11.31bc | 6.06abcde | 11.57ab | 4129fg | 11316bc | 25.29b | 11.18abcd | 10.16cd | 18.50bc | 16391e | 18252cd |
| P3N1 | 29.65ab | 10.64bc | 7.62ab | 11.30ab | 6901abcde | 9316cd | 32.99a | 12.84abc | 13.49bcd | 18.09c | 40429abc | 19224c |
| P3N2 | 24.27abc | 12.62b | 7.17abcd | 11.61ab | 6316bcdef | 13541b | 24.80bc | 12.44abc | 13.88bcd | 21.57b | 28529bcde | 28076b |
| P3N3 | 28.40ab | 13.14b | 7.51abc | 13.00a | 8784a | 18971a | 28.35b | 13.14ab | 14.08bc | 25.62a | 27039bcde | 35511a |
| P | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | * | *** | ns | *** |
| N | * | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** | ns | ns | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| P*N | * | * | * | ns | *** | ** | *** | ns | * | ** | * | *** |
Table 3 Effects of N and P fertilizers on alfalfa regrowth after cutting for 6 and 12 days
处理 Treatments | 刈割后第6天 After cutting for 6 d | 刈割后第12天After cutting for 12 d | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
芽数Bud number (×106·hm-2) | 再生芽芽长Shoot length (cm) | 叶面积Leaf area (m2·hm-2) | 芽数Bud number (×106·hm-2) | 再生芽芽长Shoot length (cm) | 叶面积Leaf area (m2·hm-2) | |||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| P0N0 | 11.78g | 10.43bcd | 3.30f | 7.70cd | 1470h | 5170efg | 14.92de | 10.16abcd | 9.19d | 15.19cdef | 18105e | 9325gh |
| P0N1 | 11.48g | 10.14bcd | 5.35de | 7.62cd | 1367h | 5279efg | 13.78e | 10.14abcd | 14.32bc | 11.94f | 18024e | 9725gh |
| P0N2 | 14.77efg | 10.57bcd | 6.54abcde | 7.94cd | 7031abcd | 6061defg | 22.69bc | 12.08abcd | 14.82bc | 15.31cdef | 40644abc | 13500ef |
| P0N3 | 20.31cdef | 14.26a | 6.59abcde | 6.38d | 7341abcd | 6268defg | 20.35bcde | 14.60a | 17.82ab | 12.69ef | 36518abcd | 16952cd |
| P1N0 | 12.01g | 8.11cd | 4.99ef | 9.52bcd | 2520gh | 3580g | 19.52bcde | 8.11d | 10.64cd | 14.49def | 18350e | 8964h |
| P1N1 | 12.94fg | 8.32cd | 7.12abcd | 9.18bcd | 5962bcdef | 6363defg | 17.05cde | 9.45bcd | 12.15cd | 13.17ef | 22964de | 10560fgh |
| P1N2 | 21.14cde | 10.96bc | 7.58ab | 9.53bcd | 7645abc | 6428defg | 22.73bc | 10.63abcd | 21.56a | 14.59def | 45712a | 11878fgh |
| P1N3 | 17.81defg | 9.99bcd | 6.56abcde | 10.22abc | 5340cdef | 7488def | 22.26bc | 10.26abcd | 19.87a | 13.98def | 43381ab | 9559gh |
| P2N0 | 21.54bcde | 7.14d | 5.50cde | 7.78cd | 4553efg | 4349fg | 21.70bcd | 8.99cd | 10.72cd | 15.82cde | 24023cde | 12303fg |
| P2N1 | 23.56abcd | 10.57bcd | 5.62bcde | 9.40bcd | 7834ab | 6615defg | 23.47bc | 10.76abcd | 11.37cd | 15.84cde | 30728abcde | 17841cd |
| P2N2 | 22.44abcd | 10.70bc | 8.02a | 9.47bcd | 6046bcdef | 6172defg | 22.01bc | 10.52abcd | 13.02cd | 17.22cd | 26611bcde | 15896de |
| P2N3 | 17.48defg | 10.21bcd | 7.65ab | 10.01abc | 5104def | 4502fg | 18.60bcde | 10.13abcd | 17.81ab | 18.58bc | 26923bcde | 15578de |
| P3N0 | 22.99abcd | 11.31bc | 6.06abcde | 11.57ab | 4129fg | 11316bc | 25.29b | 11.18abcd | 10.16cd | 18.50bc | 16391e | 18252cd |
| P3N1 | 29.65ab | 10.64bc | 7.62ab | 11.30ab | 6901abcde | 9316cd | 32.99a | 12.84abc | 13.49bcd | 18.09c | 40429abc | 19224c |
| P3N2 | 24.27abc | 12.62b | 7.17abcd | 11.61ab | 6316bcdef | 13541b | 24.80bc | 12.44abc | 13.88bcd | 21.57b | 28529bcde | 28076b |
| P3N3 | 28.40ab | 13.14b | 7.51abc | 13.00a | 8784a | 18971a | 28.35b | 13.14ab | 14.08bc | 25.62a | 27039bcde | 35511a |
| P | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | * | *** | ns | *** |
| N | * | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** | ns | ns | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| P*N | * | * | * | ns | *** | ** | *** | ns | * | ** | * | *** |
刈割后天数 Days after cutting (d) | 年份 Year | 再生芽数 Bud number | 再生芽芽长Shoot length | 叶面积 Leaf area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 2018 | 0.642 | 0.843** | 0.767** |
| 2019 | 0.378 | 0.696** | 0.692** | |
| 12 | 2018 | 0.483 | 0.490 | 0.506* |
| 2019 | 0.488 | 0.604 | 0.702** |
Table 4 Correlation analyses between alfalfa shoot biomass and related components after cutting for 6 and 12 days in 2018 and 2019
刈割后天数 Days after cutting (d) | 年份 Year | 再生芽数 Bud number | 再生芽芽长Shoot length | 叶面积 Leaf area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 2018 | 0.642 | 0.843** | 0.767** |
| 2019 | 0.378 | 0.696** | 0.692** | |
| 12 | 2018 | 0.483 | 0.490 | 0.506* |
| 2019 | 0.488 | 0.604 | 0.702** |
| 1 | Feng X C, Zeng J, Wang W, et al. The current situation and existing problems of alfalfa industry development in our country. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medcine, 2018(2): 135-137. |
| 冯骁骋, 曾洁, 王伟, 等. 我国苜蓿产业发展现状及存在的问题. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018(2): 135-137. | |
| 2 | Zhang Y J, Shen Y X. Development potential and planting mode of alfalfa in farming regions of southern China. Grassland and Turf, 2010, 30(1): 84-88. |
| 张艳娟, 沈益新. 南方农区紫花苜蓿发展潜力与种植模式研究进展. 草原与草坪, 2010, 30(1): 84-88. | |
| 3 | He F, Zhao Z X, Kang J M, et al. Effects of N, P and K fertilizer on alfalfa hay yield and quality. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(5): 24-32. |
| 何飞, 赵忠祥, 康俊梅, 等. 氮磷钾配比施肥对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(5): 24-32. | |
| 4 | Fan J W, Du Y L, Wang B R, et al. Forage yield, soil water depletion, shoot nitrogen and phosphorus uptake and concentration, of young and old stands of alfalfa in response to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilisation in a semiarid environment. Field Crops Research, 2016, 198: 247-257. |
| 5 | Wan L Q, Wang D, He F, et al. Effects of different nitrogen application levels on alfalfa growth. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 27(3): 1175-1180. |
| 万里强, 王丹, 何锋, 等. 不同氮素添加水平对紫花苜蓿生长性能的影响. 西南农业学报, 2014, 27(3): 1175-1180. | |
| 6 | Fishbeck K A, Phillips D A. Combined nitrogen and vegetative regrowth of symbiotically-grown alfalfa. Agronomy Journal, 1981, 73(6): 975-978. |
| 7 | Hannaway D, Shuler P. Nitrogen fertilization in alfalfa production. Journal of Production Agriculture, 1993, 6(1): 80-85. |
| 8 | Macdowall F. Effects of root environment on the kinetics of 1st month growth and nodulation of alfalfa. Canadian Journal of Botany, 1982, 60(6): 888-896. |
| 9 | Ding X Q, Fan Z H, Shen Y X. Effect of water stress on root growth of alfalfa seedlings and on nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies after water stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(5): 92-99. |
| 丁晓青, 樊子菡, 沈益新. 紫花苜蓿苗期根系生长的水分胁迫损伤及氮磷的修复生长作用. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 92-99. | |
| 10 | Chen Y, Qiao J, Shen Y X. Analysis of the relationship between root traits and plant growth traits of alfalfa in spring. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012, 35(1):108-112. |
| 陈艳, 乔璟, 沈益新. 春季紫花苜蓿根系性状与地上部生长性状的相关性分析. 南京农业大学学报, 2012, 35(1): 108-112. | |
| 11 | Zhang K, Qu H, Xue Z, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on the forage dry matter yield and quality of alfalfa with seasonal cultivation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(4): 844-849. |
| 张昆, 渠晖, 薛峥, 等. 施氮水平对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿饲草干物质产量和品质的影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(4): 844-849. | |
| 12 | Yu T F, Liu X J, Hao F. Effects of phosphate fertilizer application on alfalfa yield, nutritive value and N and P use efficiency. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(3): 154-163. |
| 于铁峰, 刘晓静, 郝凤. 施用磷肥对紫花苜蓿营养价值和氮磷利用效率的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 154-163. | |
| 13 | Valentine A J, Kleinert A, Benedito V A. Adaptive strategies for nitrogen metabolism in phosphate deficient legume nodules. Plant Science, 2017, 256: 46-52. |
| 14 | Jia J, Han Q F, Zhou F, et al. Effects of different N/P ratio on forage yield components and nutritional composites in non-irrigated land. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2009, 31(3): 77-82. |
| 贾珺, 韩清芳, 周芳, 等. 氮磷配比对旱地紫花苜蓿产量构成因子及营养成分的影响. 中国草地学报, 2009, 31(3): 77-82. | |
| 15 | Gao L M, Su J, Chen C, et al. Increases in forage legume biomass as a response to nitrogen input depend on temperature, soil characters and planting system: A meta analysis. Grass and Forage Science, 2021, 76: 309-319. |
| 16 | Hu W, Zhang Y H, Li P, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen supply under drip irrigation on the production performance rate and water and nitrogen use efficiency of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(2): 41-50. |
| 胡伟, 张亚红, 李鹏, 等. 水氮供应对地下滴灌紫花苜蓿生产性能及水氮利用效率的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 41-50. | |
| 17 | Zhang J X, Li W Q, Liu X J, et al. Effects of different nitrogen levels on alfalfa productivity in different growing years. Grassland and Turf, 2014, 34(3): 46-50. |
| 张进霞, 李文卿, 刘晓静, 等. 施氮对紫花苜蓿生长特性的影响. 草原与草坪, 2014, 34(3): 46-50. | |
| 18 | Wang Q, Ji S R, Shen Y X. Interactive effects of soil moisture and nitrogen application rate on seedling growth of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(12): 48-55. |
| 王茜, 纪树仁, 沈益新. 土壤水分和施氮水平对紫花苜蓿苗期生长的互作效应分析. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 48-55. | |
| 19 | Gao L M, Su J, Tian Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen accumulation and root nitrogenase activity in Medicago sativa at different soil water contents. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. |
| 高丽敏, 苏晶, 田倩, 等. 施氮对不同水分条件下紫花苜蓿氮素吸收及根系固氮酶活性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. | |
| 20 | Wang Y Y, Zhang H X, Jin C J, et al. Effects of phosphorus fertilizer on alfalfa productivity: A review. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(35): 72-77. |
| 王园园, 张红香, 金成吉, 等. 磷肥对紫花苜蓿生产力影响的研究概述. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(35): 72-77. | |
| 21 | Xie Y, Sun H R, Zhang X Q, et al. Effects of N, P and K fertilizer on alfalfa and recommended fertilizer rate in Bashang area. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2012, 34(2): 52-57. |
| 谢勇, 孙洪仁, 张新全, 等. 坝上地区紫花苜蓿氮、磷、钾肥料效应与推荐施肥量. 中国草地学报, 2012, 34(2): 52-57. | |
| 22 | Zhang J X, Li S. A study on N and P applied of alfalfa. Pratacultural Science, 1990, 7(4): 70-72. |
| 张积祥, 李松. 紫花苜蓿NP肥配施研究. 草业科学, 1990, 7(4): 70-72. | |
| 23 | Yang H H, Xi L Q, Wang D, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on the yield of alfalfa under drip irrigation. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(6): 1099-1106. |
| 杨浩宏, 席琳乔, 王栋, 等. 滴灌条件下氮、磷、钾肥效应对紫花苜蓿草产量的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(6): 1099-1106. | |
| 24 | Xiao Y Z, Wurenqiqige, Meng K, et al. Effects of formula fertilizer on the productivity of alfalfa. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(1): 174-178. |
| 肖燕子, 乌仁其其格, 孟凯, 等. 配方施肥对苜蓿生产性能的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(1): 174-178. | |
| 25 | Chen X Y, Liu P, Cheng Y, et al. The root-layer regulation based on the depth of phosphate fertilizer application of summer maize improves soil nitrogen absorption and utilization. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 238-248. |
| 陈晓影, 刘鹏, 程乙, 等. 基于磷肥施用深度的夏玉米根层调控提高土壤氮素吸收利用.作物学报, 2020, 46(2): 238-248. | |
| 26 | Batterman S A, Wurzburger N, Hedin L O, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus interact to control tropical symbiotic N2 fixation: A test in Inga punctata. Journal of Ecology, 2013, 101(6): 1400-1408. |
| 27 | Yu T Y, Li X L, Lu Y, et al. Effect of phosphorus (P) on nitrogen (N) uptake and utilization in peanut. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 912-921. |
| 于天一, 李晓亮, 路亚, 等. 磷对花生氮素吸收和利用的影响. 作物学报, 2019, 45(6): 912-921. | |
| 28 | Moez J, Mohamed E A, Helene P, et al. Nodule conductance varied among common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) genotypes under phosphorus deficiency. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2005, 162: 309-315. |
| 29 | Li X K, Lu J W, Chen F. Primary study on fertilizer application of forage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(2): 136-142. |
| 李小坤, 鲁剑巍, 陈防. 牧草施肥研究进展. 草业学报, 2008, 17(2): 136-142. | |
| 30 | Hou P, Liu Z X, Liu Y S, et al. Screening of fertilization combination for alfalfa in Beijing area. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(1): 144-149. |
| 侯湃, 刘自学, 刘艺杉, 等. 北京平原区紫花苜蓿施肥组合试验. 草业科学, 2014, 31(1): 144-149. | |
| 31 | Wei X J. Effect of fertilization on the leaf area and specific leaf weight (SLW) of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) in its flowering. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 7: 50-53. |
| 卫新菊. 施肥对苜蓿开花期叶面积及比叶重的影响. 中国农学通报, 2007, 7: 50-53. |
| [1] | Huan ZHANG, Yi-xiao MU, Gui-jie ZHANG. Effects of Lycium barbarum by-products on fermentation quality and microbial diversity of alfalfa silage [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 136-144. |
| [2] | Hong-ren SUN, Xian-guo WANG, Yao-jun BU, Nan QIAO, Bo REN. Preliminary study of a sufficiency index of soil N and recommended N fertilizer application rates for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [3] | Chang-chun TONG, Xiao-jing LIU, Yong WU, Ya-jiao ZHAO, Jing WANG. Regulation of endogenous isoflavones on alfalfa nodulation and nitrogen fixation and nitrogen use efficiency [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [4] | Yu-huan WU, Zi-kui WANG, Ya-nan LIU, Qian-hu MA. Effects of row configuration on characteristics of the light environment and light use efficiency in maize/alfalfa intercropping [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 144-155. |
| [5] | Li-ying LIU, Yu-shan JIA, Wen-qiang FAN, Qiang YIN, Qi-ming CHENG, Zhi-jun WANG. An investigation of the main environmental factors affecting the natural drying of alfalfa for hay, and hay quality [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 121-132. |
| [6] | Bin WANG, Yu-qi YANG, Man-you LI, Wang NI, Yi-rui HAI, Shun-xiang ZHANG, Xiu DONG, Jian LAN. The effect of sowing rate and row spacing on the yield and quality of alfalfa in the Ningxia Yellow River irrigation area [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| [7] | Hui-hui ZHANG, Shang-li SHI, Bei WU, Zi-li LI, Xiao-long LI. A study of yield interactions in mixed sowings of alfalfa and three perennial grasses [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [8] | Jie BAI, Zhen-feng ZANG, Cong LIU, Kan-zhuo ZAN, Ming-xiu LONG, Ke-zhen WANG, Yang QU, Shu-bin HE. Lipid peroxidation and carbon and nitrogen characteristics in leaves and roots of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) in response to water and nitrogen addition [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 213-220. |
| [9] | Bin WANG, Man-you LI, Xin-pan WANG, Xiu DONG, Jun-bao PANG, Jian LAN. Combined ploughing and tilling to improve degraded alfalfa (Medicago sativa) stands in a semi-arid region [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 107-117. |
| [10] | Na WEI, Yan-peng LI, Yi-tong MA, Wen-xian LIU. Genome-wide identification of the alfalfa TCP gene family and analysis of gene transcription patterns in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [11] | Xiao-fan YIN, Na WEI, Shu-wen ZHENG, Wen-xian LIU. Genome-wide development and utilization of LTR retrotransposon-based IRAP markers in Medicago truncatula [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 131-144. |
| [12] | Jia-ju ZHANG, Jie YU, Ming-na LI, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG. Identification and functional analysis of lncRNA167 and its cleavage product miR167c in Medicago truncatula [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 164-180. |
| [13] | Yan-zhong LI, Jun-qiang YU, Ming LI. Preliminary evaluation of 48 alfalfa varieties for resistance to three diseases [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 62-75. |
| [14] | Jing-dong ZHAO, Yan-tao SONG, Xin-lei XU, Wuyunna. Effects of nitrogen application and mowing on yield and quality of forage in degraded grassland in northwest Liaoning Province [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 36-48. |
| [15] | Xue WANG, Xiao-jing LIU, Ya-jiao ZHAO, Jing WANG. Nitrogen utilization and interspecific feedback characteristics of intercropped alfalfa/oat with different root barriers [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||