

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1-17.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021386
• 研究论文 •
收稿日期:2021-10-28
修回日期:2022-01-10
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-09-14
通讯作者:
冯琦胜
作者简介:E-mail: fengqsh@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhe-ren JIN( ), Qi-sheng FENG(
), Qi-sheng FENG( ), Rui-jing WANG, Tian-gang LIANG
), Rui-jing WANG, Tian-gang LIANG
Received:2021-10-28
Revised:2022-01-10
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-09-14
Contact:
Qi-sheng FENG
摘要:
青藏高原位于我国西部,又被称为“世界第三极”,对我国和世界的生态以及气候变化影响显著。为了评估2000-2020年青藏高原草地地上生物量(aboveground biomass,AGB)的变化情况,本研究采用多种机器学习方法结合MCD43A4产品数据模拟了草地地上生物量,并对该区域草地地上生物量的时空特征进行分析。结果表明:1)构建的机器学习模型中,Rborist模型精度最高,基于筛选后变量的R2 达到0.6484。“prec_05”、“prec_06”、“tp_12”、“NDPI”、“prec_04”、“tmax_01”、“prec_08”、“prec_12”这8个变量与生物量相关;2)青藏高原东南部的生物量要高于西北部,呈现由东南向西北递减趋势;3)2000-2020年间青藏高原草地生物量稳步增长,整体向好发展。青藏高原61.38%的草地变化趋势不具有可持续性,4.67%的草地持续性轻微恶化,持续性明显恶化的区域占比1.19%,呈稳定或恢复趋势的区域占比32.76%。
金哲人, 冯琦胜, 王瑞泾, 梁天刚. 基于MODIS数据与机器学习的青藏高原草地地上生物量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 1-17.
Zhe-ren JIN, Qi-sheng FENG, Rui-jing WANG, Tian-gang LIANG. A study of grassland aboveground biomass on the Tibetan Plateau using MODIS data and machine learning[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 1-17.
| 序号Number | 植被指数Vegetation index | 名称 Full name | 公式 Equation | 引用 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NDVI | 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index | [ | |
| 2 | EVI | 增强型植被指数Enhanced vegetation index | [ | |
| 3 | EVI2 | 增强型植被指数2 Enhanced vegetation index two | [ | |
| 4 | DVI | 差值植被指数Difference vegetation index | [ | |
| 5 | RVI | 比值植被指数Ratio vegetation index | [ | |
| 6 | SAVI | 土壤调整植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index | [ | |
| 7 | MSAVI | 修改型土壤调节植被指数Modified soil adjusted vegetation index | [ | |
| 8 | OSAVI | 优化土壤调整植被指数Optimized soil adjusted vegetation index | [ | |
| 9 | SATVI | 土壤调整总植被指数Soil adjusted total vegetation index | [ | |
| 10 | NDPI | 归一化物候指数Normalized difference phenology index | [ |
表1 本研究中使用的植被指数
Table 1 The vegetation index used in this study
| 序号Number | 植被指数Vegetation index | 名称 Full name | 公式 Equation | 引用 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NDVI | 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index | [ | |
| 2 | EVI | 增强型植被指数Enhanced vegetation index | [ | |
| 3 | EVI2 | 增强型植被指数2 Enhanced vegetation index two | [ | |
| 4 | DVI | 差值植被指数Difference vegetation index | [ | |
| 5 | RVI | 比值植被指数Ratio vegetation index | [ | |
| 6 | SAVI | 土壤调整植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index | [ | |
| 7 | MSAVI | 修改型土壤调节植被指数Modified soil adjusted vegetation index | [ | |
| 8 | OSAVI | 优化土壤调整植被指数Optimized soil adjusted vegetation index | [ | |
| 9 | SATVI | 土壤调整总植被指数Soil adjusted total vegetation index | [ | |
| 10 | NDPI | 归一化物候指数Normalized difference phenology index | [ |
| 草地类型Grassland type | 风干重Dry weight (kg·hm-2) | 盖度Cover degree (%) | 高度Height (cm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值Minimum value | 最大值Maximum value | 平均值Mean | 标准偏差Standard deviation | 最小值Minimum value | 最大值Maximum value | 平均值Mean | 标准偏差Standard deviation | 最小值Minimum value | 最大值Maximum value | 平均值Mean | 标准偏差Standard deviation | |
| A | 104.00 | 2420.00 | 808.42 | 604.83 | 15.00 | 99.00 | 55.10 | 31.58 | 4.26 | 52.00 | 26.12 | 14.66 |
| B | 106.00 | 2384.00 | 604.35 | 486.25 | 9.00 | 100.00 | 52.70 | 31.08 | 2.00 | 16.20 | 4.74 | 3.35 |
| C | 57.00 | 5858.00 | 1533.51 | 922.10 | 1.00 | 100.00 | 83.15 | 16.27 | 0.86 | 92.00 | 11.62 | 8.85 |
| D | 50.00 | 4154.00 | 588.59 | 519.72 | 5.00 | 100.00 | 55.60 | 23.31 | 1.00 | 53.00 | 8.74 | 5.89 |
| E | 11.00 | 1585.00 | 406.76 | 280.79 | 2.00 | 94.00 | 29.16 | 19.51 | 1.50 | 17.00 | 4.92 | 3.14 |
| F | 140.00 | 500.00 | 304.06 | 89.62 | 15.00 | 99.00 | 53.09 | 17.18 | 1.00 | 85.00 | 12.98 | 13.91 |
| G | 179.00 | 2927.00 | 1276.86 | 812.90 | 10.00 | 95.00 | 52.00 | 33.77 | 4.70 | 34.20 | 13.80 | 7.80 |
| H | 790.00 | 1633.00 | 1153.33 | 433.37 | 61.00 | 71.00 | 66.33 | 5.03 | 10.10 | 11.40 | 10.93 | 0.72 |
| I | 281.00 | 4816.00 | 2001.48 | 928.60 | 15.00 | 100.00 | 87.13 | 13.37 | 1.60 | 96.70 | 18.61 | 11.88 |
| J | 143.00 | 969.00 | 456.15 | 242.65 | 15.00 | 60.00 | 35.62 | 13.90 | 3.00 | 28.00 | 10.00 | 7.56 |
| K | 113.00 | 1771.00 | 672.83 | 306.59 | 4.00 | 80.00 | 50.23 | 19.24 | 3.00 | 33.20 | 11.87 | 5.89 |
| L | 210.00 | 3009.00 | 831.73 | 462.44 | 7.00 | 97.00 | 61.01 | 19.83 | 1.00 | 81.00 | 15.66 | 9.82 |
| M | 8.00 | 1096.00 | 393.85 | 281.47 | 1.00 | 83.00 | 25.24 | 20.01 | 0.95 | 48.00 | 14.85 | 9.21 |
| N | 883.00 | 3684.00 | 1812.50 | 966.50 | 48.00 | 99.00 | 75.50 | 21.92 | 0.95 | 25.13 | 8.25 | 8.27 |
| 总计Total | 8.00 | 5858.00 | 1359.28 | 950.42 | 1.00 | 100.00 | 76.16 | 22.53 | 0.86 | 96.70 | 12.18 | 9.44 |
表2 不同草地类型的调查样本数据基本情况
Table 2 Survey sample data and basic statistics of different grassland type
| 草地类型Grassland type | 风干重Dry weight (kg·hm-2) | 盖度Cover degree (%) | 高度Height (cm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值Minimum value | 最大值Maximum value | 平均值Mean | 标准偏差Standard deviation | 最小值Minimum value | 最大值Maximum value | 平均值Mean | 标准偏差Standard deviation | 最小值Minimum value | 最大值Maximum value | 平均值Mean | 标准偏差Standard deviation | |
| A | 104.00 | 2420.00 | 808.42 | 604.83 | 15.00 | 99.00 | 55.10 | 31.58 | 4.26 | 52.00 | 26.12 | 14.66 |
| B | 106.00 | 2384.00 | 604.35 | 486.25 | 9.00 | 100.00 | 52.70 | 31.08 | 2.00 | 16.20 | 4.74 | 3.35 |
| C | 57.00 | 5858.00 | 1533.51 | 922.10 | 1.00 | 100.00 | 83.15 | 16.27 | 0.86 | 92.00 | 11.62 | 8.85 |
| D | 50.00 | 4154.00 | 588.59 | 519.72 | 5.00 | 100.00 | 55.60 | 23.31 | 1.00 | 53.00 | 8.74 | 5.89 |
| E | 11.00 | 1585.00 | 406.76 | 280.79 | 2.00 | 94.00 | 29.16 | 19.51 | 1.50 | 17.00 | 4.92 | 3.14 |
| F | 140.00 | 500.00 | 304.06 | 89.62 | 15.00 | 99.00 | 53.09 | 17.18 | 1.00 | 85.00 | 12.98 | 13.91 |
| G | 179.00 | 2927.00 | 1276.86 | 812.90 | 10.00 | 95.00 | 52.00 | 33.77 | 4.70 | 34.20 | 13.80 | 7.80 |
| H | 790.00 | 1633.00 | 1153.33 | 433.37 | 61.00 | 71.00 | 66.33 | 5.03 | 10.10 | 11.40 | 10.93 | 0.72 |
| I | 281.00 | 4816.00 | 2001.48 | 928.60 | 15.00 | 100.00 | 87.13 | 13.37 | 1.60 | 96.70 | 18.61 | 11.88 |
| J | 143.00 | 969.00 | 456.15 | 242.65 | 15.00 | 60.00 | 35.62 | 13.90 | 3.00 | 28.00 | 10.00 | 7.56 |
| K | 113.00 | 1771.00 | 672.83 | 306.59 | 4.00 | 80.00 | 50.23 | 19.24 | 3.00 | 33.20 | 11.87 | 5.89 |
| L | 210.00 | 3009.00 | 831.73 | 462.44 | 7.00 | 97.00 | 61.01 | 19.83 | 1.00 | 81.00 | 15.66 | 9.82 |
| M | 8.00 | 1096.00 | 393.85 | 281.47 | 1.00 | 83.00 | 25.24 | 20.01 | 0.95 | 48.00 | 14.85 | 9.21 |
| N | 883.00 | 3684.00 | 1812.50 | 966.50 | 48.00 | 99.00 | 75.50 | 21.92 | 0.95 | 25.13 | 8.25 | 8.27 |
| 总计Total | 8.00 | 5858.00 | 1359.28 | 950.42 | 1.00 | 100.00 | 76.16 | 22.53 | 0.86 | 96.70 | 12.18 | 9.44 |

图3 各变量之间的相关系数情况***表示极显著相关(P<0.001),下同。 *** indicate extremely significant correlation(P<0.001), the same below. Biomass: 草地生物量 Aboveground biomass, AGB; NDPI: 归一化物候指数Normalized difference phenology index; prec_04: 4月降水量 Precipitation in April; prec_05: 5月降水量Precipitation in May; prec_06: 6月降水量 Precipitation in June; prec_08: 8月降水量 Precipitation in August; prec_12: 12月降水量 Precipitation in December; tmax_01: 1月最高温度 The highest temperature in January; tp_12: 12月平均温度 Average temperature in December.
Fig.3 Correlation coefficient among the variables
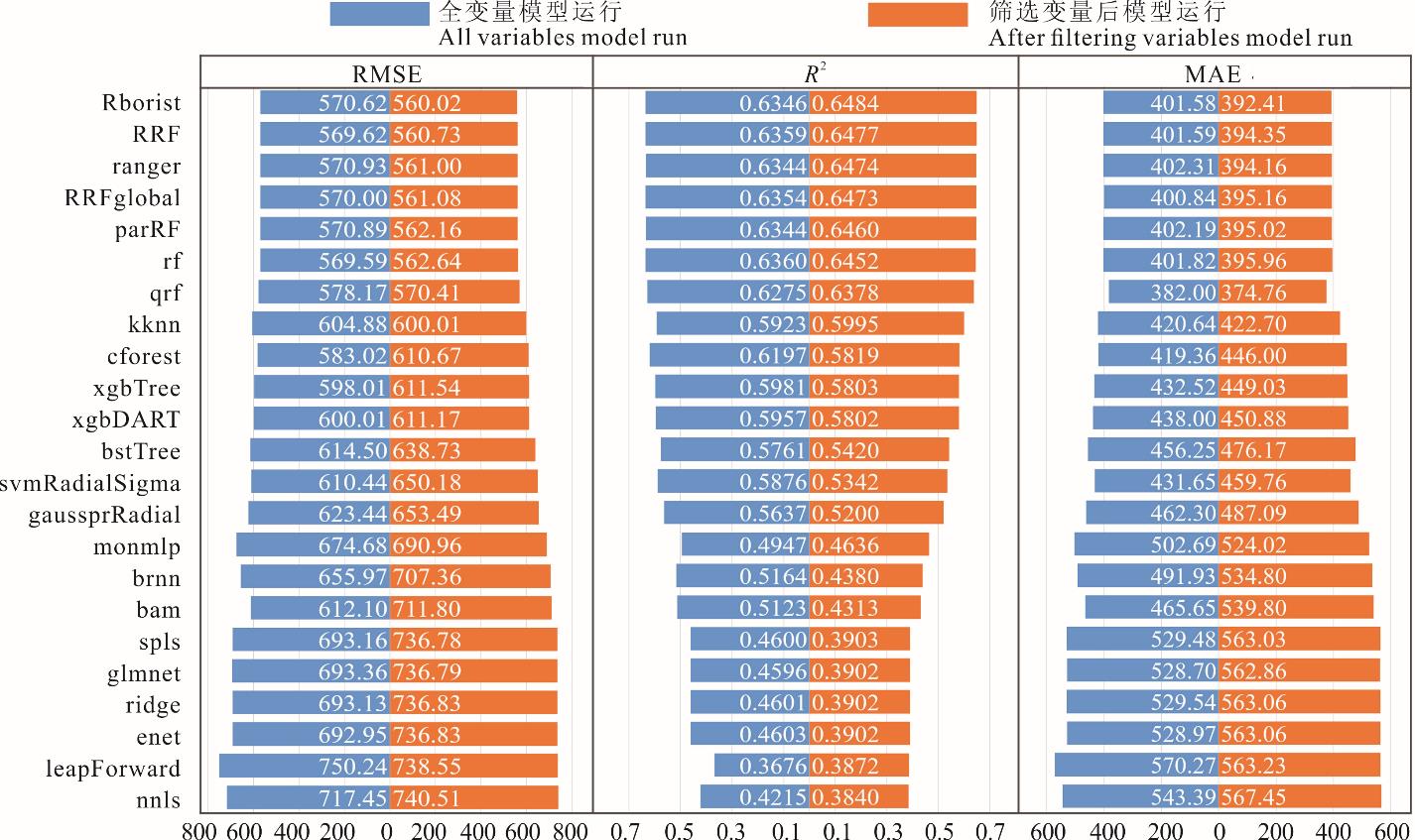
图4 筛选前后变量的模型运行情况bam:基于样条函数的广义加性模型 Generalized additive model using splines;brnn:贝叶斯规整化神经网络 Bayesian regularized neural networks;bstTree:提升树 Boosted tree;enet:弹性网络 Elasticnet;gaussprRadial:基于径向基函数核的高斯过程 Gaussian process with radial basis function kernel;glmnet:广义线性模型网 Generalized linear model net;kknn:k-临近算法 k-nearest neighbors;leapForward:基于正向选择的线性回归 Linear regression with forward selection;monmlp:单调多层感知机神经网络 Monotone multi-layer perceptron neural network;nnls:非负最小二乘 Non-negative least squares;ridge:岭回归 Ridge regression;svmRadialSigma:基于径向基函数核的支持向量机 Support vector machines with radial basis function kernel;spls:稀疏偏最小二乘 Sparse partial least squares;cforest:条件推断随机森林 Conditional inference random forest;parRF:平行随机森林 Parallel random forest;qrf:分位数随机森林 Quantile random forest;ranger:基于ranger的随机森林 Random forest;Rborist:基于Rborist的随机森林 Random forest;rf:基于randomForest的随机森林 Random forest;RRF:基于randomForest和RRF的正则化随机森林 Regularized random forest;RRFglobal:基于RRF的正则化随机森林 Regularized random forest;xgbDART:极端的梯度提升1 Extreme gradient boosting 1;xgbTree:极端的梯度提升2 Extreme gradient boosting 2. RMSE:均方根差Root mean square error, R2:决定系数Determination coefficient, MAE:平均绝对误差Mean absolute error.
Fig.4 Filter variables before and after the model runs
| 方法Method | 筛选变量前的参数Parameters of variables before filtering | 筛选变量后的参数Parameters of variables after filtering |
|---|---|---|
| Rborist | predFixed=34 and minNode=3 | predFixed=2 and minNode=3 |
| RRF | mtry=34, coefReg=0.505 and coefImp=0.5 | mtry=2, coefReg=1 and coefImp=0.5 |
| ranger | mtry=34, splitrule=variance and min.node.size=5 | mtry=2, splitrule=variance and min.node.size=5 |
| RRFglobal | mtry=67 and coefReg=0.505 | mtry=2 and coefReg=0.01 |
| parRF | mtry=34 | mtry=2 |
| rf | mtry=34 | mtry=2 |
| qrf | mtry=34 | mtry=2 |
| kknn | kmax=9, distance=2 and kernel=optimal | kmax=9, distance=2 and kernel=optimal |
| cforest | mtry=67 | mtry=8 |
| xgbTree | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.3, gamma=0, colsample_bytree=0.6, min_child_weight=1 and subsample=1 | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.4, gamma=0, colsample_bytree=0.8, min_child_weight=1 and subsample=1 |
| xgbDART | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.3, gamma=0, subsample=1, colsample_bytree= 0.8, rate_drop=0.5, skip_drop=0.95 and min_child_weight=1 | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.3, gamma=0, subsample=1, colsample_bytree= 0.8, rate_drop=0.5, skip_drop=0.95 and min_child_weight=1 |
| bstTree | mstop=150, maxdepth=3 and nu=0.1 | mstop=150, maxdepth=3 and nu=0.1 |
| svmRadialSigma | sigma=0.03387348 and C=1 | sigma=0.2790061 and C=1 |
| gaussprRadial | - | - |
| monmlp | hidden1=5 and n.ensemble=1 | hidden1=5 and n.ensemble=1 |
| brnn | neurons=3 | neurons=3 |
| bam | select=TRUE and method=GCV.Cp | select=FALSE and method=GCV.Cp |
| spls | K=24, eta=0.5 and kappa=0.5 | K=7, eta=0.9 and kappa=0.5 |
| glmnet | alpha=0.1 and lambda=1.112425 | alpha=1 and lambda=1.112425 |
| enet | fraction=0.525 and lambda=0.0001 | fraction=1 and lambda=0.0001 |
| ridge | lambda=0.0001 | lambda=0.0001 |
| leapForward | nvmax=4 | nvmax=4 |
| nnls | - | - |
表3 各机器学习方法参数取值情况
Table 3 Parameters of different machine learning methods
| 方法Method | 筛选变量前的参数Parameters of variables before filtering | 筛选变量后的参数Parameters of variables after filtering |
|---|---|---|
| Rborist | predFixed=34 and minNode=3 | predFixed=2 and minNode=3 |
| RRF | mtry=34, coefReg=0.505 and coefImp=0.5 | mtry=2, coefReg=1 and coefImp=0.5 |
| ranger | mtry=34, splitrule=variance and min.node.size=5 | mtry=2, splitrule=variance and min.node.size=5 |
| RRFglobal | mtry=67 and coefReg=0.505 | mtry=2 and coefReg=0.01 |
| parRF | mtry=34 | mtry=2 |
| rf | mtry=34 | mtry=2 |
| qrf | mtry=34 | mtry=2 |
| kknn | kmax=9, distance=2 and kernel=optimal | kmax=9, distance=2 and kernel=optimal |
| cforest | mtry=67 | mtry=8 |
| xgbTree | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.3, gamma=0, colsample_bytree=0.6, min_child_weight=1 and subsample=1 | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.4, gamma=0, colsample_bytree=0.8, min_child_weight=1 and subsample=1 |
| xgbDART | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.3, gamma=0, subsample=1, colsample_bytree= 0.8, rate_drop=0.5, skip_drop=0.95 and min_child_weight=1 | nrounds=150, max_depth=3, eta=0.3, gamma=0, subsample=1, colsample_bytree= 0.8, rate_drop=0.5, skip_drop=0.95 and min_child_weight=1 |
| bstTree | mstop=150, maxdepth=3 and nu=0.1 | mstop=150, maxdepth=3 and nu=0.1 |
| svmRadialSigma | sigma=0.03387348 and C=1 | sigma=0.2790061 and C=1 |
| gaussprRadial | - | - |
| monmlp | hidden1=5 and n.ensemble=1 | hidden1=5 and n.ensemble=1 |
| brnn | neurons=3 | neurons=3 |
| bam | select=TRUE and method=GCV.Cp | select=FALSE and method=GCV.Cp |
| spls | K=24, eta=0.5 and kappa=0.5 | K=7, eta=0.9 and kappa=0.5 |
| glmnet | alpha=0.1 and lambda=1.112425 | alpha=1 and lambda=1.112425 |
| enet | fraction=0.525 and lambda=0.0001 | fraction=1 and lambda=0.0001 |
| ridge | lambda=0.0001 | lambda=0.0001 |
| leapForward | nvmax=4 | nvmax=4 |
| nnls | - | - |

图7 2000-2020年青藏高原草地地上生物量持续性变化空间分布
Fig.7 Spatial distribution of grassland above-ground biomass on the Tibetan Plateau from 2000-2020 based on trend and Hurst index
行政区划 Administrative divisions | 草地类型 Grassland type | 变化趋势不稳定Trend instability | 持续性轻微降低 Sustained insignificant decrease | 持续性明显降低 Sustained significant decrease | 持续性稳定不变 Continuous stability | 持续性轻微增加 Sustained insignificant increase | 持续性明显增加Sustained significant increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
甘肃省 Gansu Province | A | 68.10 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 10.30 | 2.49 | 18.61 |
| C | 51.06 | 3.61 | 0.97 | 7.99 | 25.00 | 11.38 | |
| D | 22.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.90 | 18.67 | 36.36 | |
| F | 31.64 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.55 | 25.03 | 21.78 | |
| K | 53.02 | 2.22 | 0.42 | 4.42 | 21.12 | 18.79 | |
| M | 40.54 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.06 | 11.41 | 26.98 | |
| O | 30.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 13.57 | 12.62 | 43.13 | |
| P | 43.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.06 | 6.57 | 27.99 | |
| Q | 61.59 | 6.54 | 0.37 | 7.40 | 19.11 | 4.99 | |
| 小计Total | 43.70 | 1.99 | 0.48 | 11.92 | 20.71 | 21.20 | |
青海省 Qinghai Province | A | 65.06 | 1.04 | 0.88 | 14.37 | 6.96 | 11.68 |
| B | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| C | 53.26 | 6.01 | 1.45 | 13.94 | 18.42 | 6.92 | |
| D | 40.10 | 2.72 | 1.55 | 22.69 | 18.60 | 14.34 | |
| E | 26.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 19.38 | 30.78 | 23.64 | |
| F | 49.28 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 21.65 | 19.30 | 9.76 | |
| G | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| K | 55.03 | 7.53 | 1.67 | 7.44 | 18.08 | 10.26 | |
| M | 73.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.28 | 3.28 | 20.13 | |
| N | 50.82 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 8.67 | 13.04 | 26.73 | |
| P | 55.90 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 25.97 | 6.72 | 10.60 | |
| Q | 24.96 | 1.05 | 1.59 | 13.42 | 23.16 | 35.83 | |
| 小计Total | 50.72 | 4.41 | 1.31 | 16.36 | 17.11 | 10.09 | |
四川省 Sichuan Province | A | 41.74 | 2.57 | 0.98 | 2.08 | 42.35 | 10.28 |
| C | 56.24 | 10.71 | 1.32 | 11.26 | 16.26 | 4.21 | |
| G | 68.78 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 2.94 | 8.81 | 17.31 | |
| I | 75.56 | 3.58 | 0.25 | 2.47 | 7.65 | 10.49 | |
| J | 62.72 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 1.88 | 13.35 | 21.32 | |
| K | 59.16 | 7.39 | 1.23 | 7.67 | 16.53 | 8.02 | |
| N | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Q | 58.08 | 8.00 | 0.70 | 6.67 | 17.89 | 8.65 | |
| 小计Total | 57.14 | 9.66 | 1.27 | 10.10 | 16.37 | 5.45 | |
西藏自治区 Tibet Autonomous Region | A | 71.53 | 3.69 | 1.41 | 7.92 | 7.97 | 7.48 |
| D | 66.97 | 2.14 | 0.84 | 25.61 | 2.10 | 2.34 | |
| E | 55.60 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 38.09 | 2.02 | 4.08 | |
| F | 52.75 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 39.32 | 2.06 | 5.61 | |
| G | 71.46 | 10.42 | 3.97 | 5.46 | 7.94 | 0.74 | |
| H | 81.37 | 7.12 | 1.71 | 6.69 | 2.57 | 0.54 | |
| I | 76.61 | 4.44 | 0.00 | 4.03 | 6.85 | 8.06 | |
| J | 94.64 | 2.82 | 0.47 | 1.69 | 0.38 | 0.00 | |
| K | 59.33 | 15.57 | 3.79 | 14.00 | 6.50 | 0.80 | |
| L | 52.50 | 23.98 | 9.44 | 12.45 | 1.46 | 0.16 | |
| M | 79.63 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 10.42 | 4.39 | 5.36 | |
| N | 70.30 | 10.60 | 5.02 | 8.84 | 3.58 | 1.65 | |
| O | 76.71 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 7.84 | 10.58 | 4.76 | |
| P | 61.43 | 0.70 | 0.34 | 26.64 | 2.96 | 7.93 | |
| Q | 55.84 | 8.04 | 0.79 | 27.76 | 3.47 | 4.10 | |
| 小计Total | 63.61 | 2.30 | 0.89 | 27.98 | 2.30 | 2.93 | |
新疆维吾尔自治区 Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region | A | 57.58 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 19.66 | 2.95 | 18.95 |
| C | 59.28 | 4.55 | 1.69 | 23.21 | 5.79 | 5.49 | |
| D | 58.78 | 2.56 | 0.70 | 28.41 | 4.12 | 5.42 | |
| E | 69.46 | 3.34 | 1.40 | 19.38 | 2.73 | 3.70 | |
| F | 65.48 | 1.36 | 0.63 | 27.55 | 2.04 | 2.94 | |
| K | 61.40 | 3.49 | 0.62 | 21.36 | 8.42 | 4.72 | |
| M | 55.24 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 21.74 | 8.97 | 13.90 | |
| N | 73.08 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 8.66 | 6.70 | 11.14 | |
| O | 67.54 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 14.21 | 7.42 | 10.32 | |
| P | 75.68 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 9.14 | 4.76 | 10.31 | |
| 小计Total | 66.31 | 1.93 | 0.72 | 20.08 | 4.32 | 6.65 | |
云南省 Yunnan Province | A | 91.82 | 6.36 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.00 |
| C | 91.80 | 1.27 | 0.03 | 3.65 | 2.90 | 0.36 | |
| G | 96.45 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.81 | 1.62 | 0.97 | |
| H | 92.66 | 1.74 | 0.13 | 2.94 | 2.54 | 0.00 | |
| I | 89.41 | 1.91 | 0.00 | 1.04 | 4.77 | 2.86 | |
| N | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 小计Total | 91.84 | 1.31 | 0.03 | 3.38 | 2.94 | 0.50 |
表4 2000-2020年青藏高原各类草地变化特征分析
Table 4 The change characteristic analysis of different grassland from 2000-2020 on the Tibetan Plateau (%)
行政区划 Administrative divisions | 草地类型 Grassland type | 变化趋势不稳定Trend instability | 持续性轻微降低 Sustained insignificant decrease | 持续性明显降低 Sustained significant decrease | 持续性稳定不变 Continuous stability | 持续性轻微增加 Sustained insignificant increase | 持续性明显增加Sustained significant increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
甘肃省 Gansu Province | A | 68.10 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 10.30 | 2.49 | 18.61 |
| C | 51.06 | 3.61 | 0.97 | 7.99 | 25.00 | 11.38 | |
| D | 22.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.90 | 18.67 | 36.36 | |
| F | 31.64 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.55 | 25.03 | 21.78 | |
| K | 53.02 | 2.22 | 0.42 | 4.42 | 21.12 | 18.79 | |
| M | 40.54 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.06 | 11.41 | 26.98 | |
| O | 30.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 13.57 | 12.62 | 43.13 | |
| P | 43.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.06 | 6.57 | 27.99 | |
| Q | 61.59 | 6.54 | 0.37 | 7.40 | 19.11 | 4.99 | |
| 小计Total | 43.70 | 1.99 | 0.48 | 11.92 | 20.71 | 21.20 | |
青海省 Qinghai Province | A | 65.06 | 1.04 | 0.88 | 14.37 | 6.96 | 11.68 |
| B | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| C | 53.26 | 6.01 | 1.45 | 13.94 | 18.42 | 6.92 | |
| D | 40.10 | 2.72 | 1.55 | 22.69 | 18.60 | 14.34 | |
| E | 26.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 19.38 | 30.78 | 23.64 | |
| F | 49.28 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 21.65 | 19.30 | 9.76 | |
| G | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| K | 55.03 | 7.53 | 1.67 | 7.44 | 18.08 | 10.26 | |
| M | 73.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.28 | 3.28 | 20.13 | |
| N | 50.82 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 8.67 | 13.04 | 26.73 | |
| P | 55.90 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 25.97 | 6.72 | 10.60 | |
| Q | 24.96 | 1.05 | 1.59 | 13.42 | 23.16 | 35.83 | |
| 小计Total | 50.72 | 4.41 | 1.31 | 16.36 | 17.11 | 10.09 | |
四川省 Sichuan Province | A | 41.74 | 2.57 | 0.98 | 2.08 | 42.35 | 10.28 |
| C | 56.24 | 10.71 | 1.32 | 11.26 | 16.26 | 4.21 | |
| G | 68.78 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 2.94 | 8.81 | 17.31 | |
| I | 75.56 | 3.58 | 0.25 | 2.47 | 7.65 | 10.49 | |
| J | 62.72 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 1.88 | 13.35 | 21.32 | |
| K | 59.16 | 7.39 | 1.23 | 7.67 | 16.53 | 8.02 | |
| N | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Q | 58.08 | 8.00 | 0.70 | 6.67 | 17.89 | 8.65 | |
| 小计Total | 57.14 | 9.66 | 1.27 | 10.10 | 16.37 | 5.45 | |
西藏自治区 Tibet Autonomous Region | A | 71.53 | 3.69 | 1.41 | 7.92 | 7.97 | 7.48 |
| D | 66.97 | 2.14 | 0.84 | 25.61 | 2.10 | 2.34 | |
| E | 55.60 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 38.09 | 2.02 | 4.08 | |
| F | 52.75 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 39.32 | 2.06 | 5.61 | |
| G | 71.46 | 10.42 | 3.97 | 5.46 | 7.94 | 0.74 | |
| H | 81.37 | 7.12 | 1.71 | 6.69 | 2.57 | 0.54 | |
| I | 76.61 | 4.44 | 0.00 | 4.03 | 6.85 | 8.06 | |
| J | 94.64 | 2.82 | 0.47 | 1.69 | 0.38 | 0.00 | |
| K | 59.33 | 15.57 | 3.79 | 14.00 | 6.50 | 0.80 | |
| L | 52.50 | 23.98 | 9.44 | 12.45 | 1.46 | 0.16 | |
| M | 79.63 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 10.42 | 4.39 | 5.36 | |
| N | 70.30 | 10.60 | 5.02 | 8.84 | 3.58 | 1.65 | |
| O | 76.71 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 7.84 | 10.58 | 4.76 | |
| P | 61.43 | 0.70 | 0.34 | 26.64 | 2.96 | 7.93 | |
| Q | 55.84 | 8.04 | 0.79 | 27.76 | 3.47 | 4.10 | |
| 小计Total | 63.61 | 2.30 | 0.89 | 27.98 | 2.30 | 2.93 | |
新疆维吾尔自治区 Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region | A | 57.58 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 19.66 | 2.95 | 18.95 |
| C | 59.28 | 4.55 | 1.69 | 23.21 | 5.79 | 5.49 | |
| D | 58.78 | 2.56 | 0.70 | 28.41 | 4.12 | 5.42 | |
| E | 69.46 | 3.34 | 1.40 | 19.38 | 2.73 | 3.70 | |
| F | 65.48 | 1.36 | 0.63 | 27.55 | 2.04 | 2.94 | |
| K | 61.40 | 3.49 | 0.62 | 21.36 | 8.42 | 4.72 | |
| M | 55.24 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 21.74 | 8.97 | 13.90 | |
| N | 73.08 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 8.66 | 6.70 | 11.14 | |
| O | 67.54 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 14.21 | 7.42 | 10.32 | |
| P | 75.68 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 9.14 | 4.76 | 10.31 | |
| 小计Total | 66.31 | 1.93 | 0.72 | 20.08 | 4.32 | 6.65 | |
云南省 Yunnan Province | A | 91.82 | 6.36 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.00 |
| C | 91.80 | 1.27 | 0.03 | 3.65 | 2.90 | 0.36 | |
| G | 96.45 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.81 | 1.62 | 0.97 | |
| H | 92.66 | 1.74 | 0.13 | 2.94 | 2.54 | 0.00 | |
| I | 89.41 | 1.91 | 0.00 | 1.04 | 4.77 | 2.86 | |
| N | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 小计Total | 91.84 | 1.31 | 0.03 | 3.38 | 2.94 | 0.50 |
| 1 | Piao S L, Wang X H, Ciais P, et al. Changes in satellite-derived vegetation growth trend in temperate and boreal Eurasia from 1982 to 2006. Global Change Biology, 2011, 17: 3228-3239. |
| 2 | Li B. Achievements and prospects of grassland ecological research in China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1992(3): 3-9. |
| 李博. 我国草地生态研究的成就与展望. 生态学杂志, 1992(3): 3-9. | |
| 3 | Ren J Z, Liang T G, Lin H L, et al. Study on grassland’s responses to global climate change and its carbon sequestration potentials. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(2): 1-22. |
| 任继周, 梁天刚, 林慧龙, 等. 草地对全球气候变化的响应及其碳汇潜势研究. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 1-22. | |
| 4 | Zhang L Y, Wang G, Bao L R, et al. Temporal changes of MODIS-NDVI vegetation index and forage biomass in Xilinguole grassland——Taking the change from April to September in 2005 as a sample. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 25(3): 6-11. |
| 张连义, 王刚, 宝路如, 等. 锡林郭勒盟草地MODIS-NDVI植被指数和估产牧草产量季节变化特征——以2005年4-9月的变化为例. 草业科学, 2008, 25(3): 6-11. | |
| 5 | Liang T G, Yang S X, Feng Q S, et al. Multi-factor modeling of above-ground biomass in alpine grassland: A case study in the Three-River Headwaters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 186: 164-172. |
| 6 | Zhao H F, Li X D, Zhang D, et al. Aboveground biomass in grasslands in Qinghai Province estimated from MODIS data and its influencing factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 5-16. |
| 赵慧芳, 李晓东, 张东, 等. 基于MODIS数据的青海省草地地上生物量估算及影响因素研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 5-16. | |
| 7 | Qiao H Q, Duo D, Li X D, et al. Estimation of the grass yield of Sunan County, Gansu grassland based on MODIS. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 54(6): 817-823. |
| 乔蕻强, 朵丹, 李晓丹, 等. 基于MODIS数据的甘肃省肃南裕固族自治县草地产草量估算. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 817-823. | |
| 8 | Du Y E, Liu B K, Guo Z G. Changes of forage biomass of grasslands during the growing season in the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS data. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(6): 7. |
| 杜玉娥, 刘宝康, 郭正刚. 基于MODIS的青藏高原牧草生长季草地生物量动态. 草业科学, 2011, 28(6): 7. | |
| 9 | Ma Q Q, Chai L R, Ma H L, et al. Monitoring of grazing intensity in Maqu alpine meadow by remote sensing. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(5): 941-948. |
| 马青青, 柴林荣, 马海玲, 等. 玛曲高寒草甸放牧强度的遥感监测. 草业科学, 2018, 35(5): 941-948. | |
| 10 | Lu Y, Yang S X, Li X H. Monitoring of grassland herbage accumulation by using remote sensing in Gannan Prefecture. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(1): 32-43. |
| 陆荫, 杨淑霞, 李晓红. 甘南州高寒天然草地生长状况遥感监测. 草业科学, 2021, 38(1): 32-43. | |
| 11 | Yao X C, Qu T T, Chang W J, et al. Estimation of grassland biomass using MODIS data and plant community characteristics. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(4): 530-541. |
| 姚兴成, 曲恬甜, 常文静, 等. 基于 MODIS 数据和植被特征估算草地生物量. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(4): 530-541. | |
| 12 | Gao X X, Dong S K, Li S, et al. Using the random forest model and validated MODIS with the field spectrometer measurement promote the accuracy of estimating aboveground biomass and coverage of alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 112: 106114. |
| 13 | Zeng N, Ren X L, He H L, et al. Estimating grassland aboveground biomass on the Tibetan Plateau using a random forest algorithm. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102: 479-487. |
| 14 | Zhou W, Li H R, Xie L J, et al. Remote sensing inversion of grassland aboveground biomass based on high accuracy surface modeling. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 121: 107215. |
| 15 | Chen Y, Guerschman J, Shendryk Y, et al. Estimating pasture biomass using Sentinel-2 imagery and machine learning. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13: 603. |
| 16 | Zhang Y L, Li B Y, Liu L S, et al. Redetermine the region and boundaries of Tibetan Plateau. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(6): 1543-1553. |
| 张镱锂, 李炳元, 刘林山, 等. 再论青藏高原范围. 地理研究, 2021, 40(6): 1543-1553. | |
| 17 | Xia L, Song X N, Cai S H, et al. Role of surface hydrothermal elements in grassland degradation over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 4618-4631. |
| 夏龙, 宋小宁, 蔡硕豪, 等. 地表水热要素在青藏高原草地退化中的作用. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11): 4618-4631. | |
| 18 | Mo X G, Liu W, Meng C C, et al. Variations of grassland yield and forage-livestock balance over the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(7): 2415-2425. |
| 莫兴国, 刘文, 孟铖铖, 等. 青藏高原草地产量与草畜平衡变化. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(7): 2415-2425. | |
| 19 | Sun H L, Zheng D, Yao T D, et al. Protection and construction of the national ecological security shelter zone on Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(1): 3-12. |
| 孙鸿烈, 郑度, 姚檀栋, 等. 青藏高原国家生态安全屏障保护与建设. 地理学报, 2012, 67(1): 3-12. | |
| 20 | Xia J Z, Ma M N, Liang T G, et al. Estimates of grassland biomass and turnover time on the Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Research Letters, 2018, 13: 14020. |
| 21 | Peng S Z, Ding Y X, Liu W Z, et al. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth System Science Data, 2019, 11: 1931-1946. |
| 22 | Tucker C J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sensing and Environment, 1979, 8(2): 127-150. |
| 23 | Liu H Q, Huete A R. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(2): 457-465. |
| 24 | Jiang Z, Huete A R, Didan K, et al. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2008, 112(10): 3833-3845. |
| 25 | Richardson A J, Wiegand C L. Distinguishing vegetation from soil background information. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1977, 43(12): 1541-1552. |
| 26 | Jordan C F. Derivation of leaf-area index from quality of light on the forest floor. Ecology, 1969, 50(4): 663-666. |
| 27 | Huete A R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sensing of Environment, 1988, 25: 295-309. |
| 28 | Qi J, Chehbouni A, Huete A R, et al. A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1994, 48: 119-126. |
| 29 | Rondeaux G, Steven M, Baret F. Optimization of soil-adjusted vegetation indices. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1996, 55: 95-107. |
| 30 | Marsett R C, Qi J G, Heilman P, et al. Remote sensing for grassland management in the arid Southwest. Rangeland Ecology & Management, 2006, 59(5): 530-540. |
| 31 | Wang C, Chen J, Wu J, et al. A snow-free vegetation index for improved monitoring of vegetation spring green-up date in deciduous ecosystems. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 196: 1-12. |
| 32 | Yuan L H, Jiang W G, Shen W M, et al. The spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2010. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(24): 7798-7806. |
| 袁丽华, 蒋卫国, 申文明, 等. 2000-2010 年黄河流域植被覆盖的时空变化. 生态学报, 2013, 33(24): 7798-7806. | |
| 33 | Piao S L, Fang J Y. Dynamic vegetation cover change over the last 18 years in China. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(4): 294-302. |
| 朴世龙, 方精云. 最近18年来中国植被覆盖的动态变化. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(4): 294-302. | |
| 34 | Xu Z X, Li J Y, Liu C M. Long-term trend analysis for major climate variables in the Yellow River basin. Hydrological Processes, 2007, 21: 1935-1948. |
| 35 | Fu G B, Chen S L, Liu C M, et al. Hydro-climatic trends of the Yellow River basin for the last 50 years. Climatic Change, 2004, 65: 149-178. |
| 36 | Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B. Canadian streamflow trend detection: Impacts of serial and cross-correlation. International Association of Scientific Hydrology Bulletin, 2003, 48(1): 51-63. |
| 37 | Fang L, Wang W J, Jiang W G, et al. Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover and its responses to climate change in the Heilongjiang basin of China from 2000 to 2014. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 1745-1754. |
| 方利, 王文杰, 蒋卫国, 等. 2000-2014年黑龙江流域(中国)植被覆盖时空变化及其对气候变化的响应. 地理科学, 2017, 37(11): 1745-1754. | |
| 38 | Meng B P, Liang T G, Yi S H, et al. Modeling alpine grassland above ground biomass based on remote sensing data and machine learning algorithm: A case study in the east of Tibetan Plateau, China. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2986-2995. |
| 39 | Lin X C, Chen J J, Lou P Q, et al. Improving the estimation of alpine grassland fractional vegetation cover using optimized algorithms and multi-dimensional features. Plant Methods, 2021, 17: 96. |
| 40 | Tang R, Zhao Y T, Lin H L. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of aboveground biomass in the headwater of the Yellow River based on machine learning. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13: 3404. |
| 41 | Barrett B, Nitze I, Green S, et al. Assessment of multi-temporal, multi-sensor radar and ancillary spatial data for grasslands monitoring in ireland using machine learning approaches. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 152: 109-124. |
| 42 | Zhang Y, Yin X J, Wang W Q, et al. Estimation of grassland aboveground biomass using Landsat 8 OLI satellite image in the Northern Hillside of Tianshan Mountain. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2017, 32(6): 1012-1021. |
| 张雅, 尹小君, 王伟强, 等. 基于Landsat 8 OLI遥感影像的天山北坡草地地上生物量估算. 遥感技术与应用, 2017, 32(6): 1012-1021. | |
| 43 | Ge J, Meng B P, Yang S X, et al. Monitoring of above-ground biomass in alpine grassland based on agricultural digital camera and MODIS remote sensing data: A case study in the Yellow River Headwater Region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 23-34. |
| 葛静, 孟宝平, 杨淑霞, 等. 基于ADC和MODIS遥感数据的高寒草地地上生物量监测研究—以黄河源区为例. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 23-34. | |
| 44 | Gan L Q, Cao X, Chen X H, et al. Comparison of MODIS-based vegetation indices and methods for winter wheat green-up date detection in Huanghuai region of China. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2020, 288/289: 108019. |
| 45 | Su K, Yu Q, Hu Y H, et al. Inversion and effect research on dust distribution of urban forests in Beijing. Forests, 2019, 10: 418. |
| 46 | An C C, Dong Z, Li H L, et al. Assessment of vegetation phenological extractions derived from three satellite-derived vegetation indices based on different extraction algorithms over the Tibetan Plateau. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2021, 9: 794189. |
| 47 | Xu D W, Wang C, Chen J, et al. The superiority of the normalized difference phenology index (NDPI) for estimating grassland aboveground fresh biomass. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 264: 112578. |
| 48 | Zhuo G, Chen S R, Zhou B. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation coverage over the Tibetan Plateau and its responses to climatic factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(9): 3208-3218. |
| 卓嘎, 陈思蓉, 周兵. 青藏高原植被覆盖时空变化及其对气候因子的响应. 生态学报, 2018, 38(9): 3208-3218. | |
| 49 | Zhang L, Guo H D, Ji L, et al. Vegetation greenness trend (2000 to 2009) and the climate controls in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2013, 7: 073572. |
| 50 | Shen M G, Tang Y H, Chen J, et al. Influences of temperature and precipitation before the growing season on spring phenology in grasslands of the central and eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2011, 151: 1711-1722. |
| 51 | Han B H, Zhou B R, Yan Y Q, et al. Analysis of vegetation coverage change and its driving factors over Tibetan Plateau from 2000 to 2018. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1651-1658. |
| 韩炳宏, 周秉荣, 颜玉倩, 等. 2000-2018年间青藏高原植被覆盖变化及其与气候因素的关系分析. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1651-1658. |
| [1] | 厉方桢, 钟华平, 欧阳克蕙, 赵小敏, 李愈哲. 基于机器学习的阿勒泰地区草地地下生物量估测与数字制图[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 13-23. |
| [2] | 赵翊含, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 高宏元, 梁天刚, 贺金生, 钱大文. 基于Landsat 8和随机森林的青海门源天然草地地上生物量遥感估算[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 1-14. |
| [3] | 王瑞泾, 冯琦胜, 金哲人, 刘洁, 赵玉婷, 葛静, 梁天刚. 青藏高原退化草地的恢复潜势研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 11-22. |
| [4] | 沈江龙, 陈吉军, 阿布都瓦里 ·伊玛木, 杨坤, 郭雅婷, 郑江华. 新疆荒漠草地亮柔伪步甲虫害与草地变化关系研究—以昌吉州南山草场为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 163-177. |
| [5] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [6] | 蔺豆豆, 琚泽亮, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴. 青藏高原燕麦附着耐低温乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 103-114. |
| [7] | 秦格霞, 吴静, 李纯斌, 吉珍霞, 邱政超, 李颖. 基于机器学习算法的天祝藏族自治县草地地上生物量反演[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 177-188. |
| [8] | 刘佳丽, 范建容, 张茜彧, 杨超, 徐富宝, 张晓雪, 梁博. 高寒草地生长季/非生长季植被盖度遥感反演[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 15-26. |
| [9] | 付刚, 王俊皓, 李少伟, 何萍. 藏北高寒草地牧草营养品质对放牧的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 38-50. |
| [10] | 张亦然, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 吴宇辰. 基于XGBoost算法的草甸地上生物量的高光谱遥感反演[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 1-12. |
| [11] | 南志标, 王彦荣, 聂斌, 李春杰, 张卫国, 夏超. 春箭筈豌豆新品种“兰箭3号”选育与特性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 111-120. |
| [12] | 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 秦燕, 魏小星, 刘敏洁. 青藏高原老芒麦落粒性及农艺性状相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 130-139. |
| [13] | 石明明, 王晓敏, 陈奇, 韩炳宏, 周秉荣, 肖建设, 肖宏斌. 高寒草地干湿生态系统土壤水分及入渗对降水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 49-58. |
| [14] | 邱月, 吴鹏飞, 魏雪. 三种人工草地小型土壤节肢动物群落多样性动态及其差异[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 21-32. |
| [15] | 赵慧芳, 李晓东, 张东, 校瑞香. 基于MODIS数据的青海省草地地上生物量估算及影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 5-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||