

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 100-111.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022275
收稿日期:2022-06-28
修回日期:2022-07-29
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-04-21
通讯作者:
彭燕
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: pengyanlee@163.com基金资助:
Hua-hao FENG( ), Han WANG, Jian-zhen ZHOU, Han ZHANG, Tao TANG, Yan PENG(
), Han WANG, Jian-zhen ZHOU, Han ZHANG, Tao TANG, Yan PENG( )
)
Received:2022-06-28
Revised:2022-07-29
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
Yan PENG
摘要:
为评价西南地区白三叶种质耐铝性强弱,发掘优异材料,试验以采自四川、贵州地区的82份白三叶种质和生产中应用广泛的国审品种‘海法’(Haifa)、‘胡依阿’(Huia)为供试材料,使用水培方法,观测不同种质在铝胁迫(4 mmol·L-1)15 d的生长状况,利用隶属函数法初步筛选耐铝性差异材料。试验进一步通过观测9份初筛种质铝胁迫下的生长及生理变化,采用隶属函数法计算不同种质耐铝得分,采用主成分分析法分析不同耐铝评价指标贡献率,结合根尖苏木精染色结果,对白三叶种质进行耐铝性综合评价。结果表明:铝胁迫可引起供试白三叶株高、根长、干重、绿值、相对叶片含水量、叶绿素含量、最大光能转化效率及叶片健康指数显著下降(P<0.05);相对电导率和丙二醛含量显著增加(P<0.05);根尖活性铝含量增加。材料Tr016、Tr056、Tr060、Tr062、Tr077生长指标相对值的隶属函数得分排名靠前;而Tr009、Tr021、Tr040、Tr048、Tr075得分排名靠后。综合评价结果显示,材料Tr016、Tr060具有较强的耐铝性,而Tr021耐铝性较弱;主成分分析表明,铝胁迫下白三叶相对株高、相对根长和相对干重可作为生长鉴定指标,而光合参数(叶绿素含量、最大光能转化效率、叶片健康指数)及丙二醛含量可作为生理鉴定指标。该研究可为白三叶种质资源苗期耐铝性评价和新品种选育提供参考与基础材料。
冯华昊, 王涵, 周建祯, 张晗, 唐韬, 彭燕. 白三叶耐铝种质筛选及耐铝评价指标分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 100-111.
Hua-hao FENG, Han WANG, Jian-zhen ZHOU, Han ZHANG, Tao TANG, Yan PENG. Screening of Al-tolerant white clover germplasm and analysis of Al-tolerance evaluation indexes[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 100-111.
| 材料编号NO. | 采集地点Collection sites | 地理坐标Geographical coordinates | 生境Habitat | 海拔Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr001~Tr004 | 康定二郎山Erlang Mountain, Kangding | 29°51′ N,102°17′-102°18′ E | 山麓Piedmont | 2144~2200 |
| Tr005~Tr014 | 康定G318公路G318 Road, Kangding | 29°51′N,102°03′-102°20′ E | 路边Roadside | 1548~2120 |
| Tr015~Tr028 | 康定雅拉乡Yala Country, Kangding | 30°05′-30°13′ N,102°53′-102°57′ E | 河谷Valley,田坎Fields | 2576~2969 |
| Tr029~Tr035 | 康定折多山Zheduo Mountain, Kangding | 29°00′-30°02′ N,102°49′-102°56′ E | 路边Roadside | 2910~3807 |
| Tr036~Tr046 | 贵州贵阳Guiyang, Guizhou | 26°34′-27°41′ N,106°06′-106°91′ E | 河谷Valley,田坎Fields,路边Roadside,山坡Hillside | 1029~1394 |
| Tr047~Tr053 | 贵州遵义Zunyi, Guizhou | 27°73′-28°29′ N,106°02′-108°21′ E | 路边Roadside,河谷Valley,田坎Fields | 561~1213 |
| Tr054~Tr060 | 贵州毕节Bijie, Guizhou | 26°39′-27°17′ N,104°42′-106°41′ E | 路边Roadside,田坎Fields,山坡Hillside | 1020~1527 |
| Tr061 | 贵州铜仁Tongren, Guizhou | 27°23′ N,108°88′ E | 路边Roadside | 357 |
| Tr062~Tr064 | 贵州六盘水Liupanshui, Guizhou | 25°47′-26°24′ N,104°49′-105°28′ E | 田坎Fields,山坡Hillside | 1193~1532 |
| Tr065~Tr072 | 贵州安顺Anshun, Guizhou | 25°42′-26°13′ N,105°38′-106°05′ E | 路边Roadside,山坡Hillside,田坎Fields | 1049~1326 |
| Tr073~Tr074 | 贵州黔东南Qiandongnan, Guizhou | 26°22′-26°61′ N,107°83′-107°91′ E | 路边Roadside | 822~883 |
| Tr075~Tr078 | 贵州黔南Qiannan, Guizhou | 26°00′-26°38′ N,106°26′-107°21′ E | 田坎Fields,草原Grassland,山坡Hillside | 980~1639 |
| Tr079~Tr082 | 贵州黔西南Qianxinan, Guizhou | 25°04′-25°52′ N,104°56′-105°24′ E | 路边Roadside,田坎Fields | 986~1599 |
| Haifa | 购于百绿(天津)国际草业有限公司 Seeds were purchased from Barenbrug Company (Tianjin) | |||
| Huia | 购于百绿(天津)国际草业有限公司 Seeds were purchased from Barenbrug Company (Tianjin) | |||
表1 供试白三叶种质资源信息
Table 1 Information of white clover germplasm resources
| 材料编号NO. | 采集地点Collection sites | 地理坐标Geographical coordinates | 生境Habitat | 海拔Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr001~Tr004 | 康定二郎山Erlang Mountain, Kangding | 29°51′ N,102°17′-102°18′ E | 山麓Piedmont | 2144~2200 |
| Tr005~Tr014 | 康定G318公路G318 Road, Kangding | 29°51′N,102°03′-102°20′ E | 路边Roadside | 1548~2120 |
| Tr015~Tr028 | 康定雅拉乡Yala Country, Kangding | 30°05′-30°13′ N,102°53′-102°57′ E | 河谷Valley,田坎Fields | 2576~2969 |
| Tr029~Tr035 | 康定折多山Zheduo Mountain, Kangding | 29°00′-30°02′ N,102°49′-102°56′ E | 路边Roadside | 2910~3807 |
| Tr036~Tr046 | 贵州贵阳Guiyang, Guizhou | 26°34′-27°41′ N,106°06′-106°91′ E | 河谷Valley,田坎Fields,路边Roadside,山坡Hillside | 1029~1394 |
| Tr047~Tr053 | 贵州遵义Zunyi, Guizhou | 27°73′-28°29′ N,106°02′-108°21′ E | 路边Roadside,河谷Valley,田坎Fields | 561~1213 |
| Tr054~Tr060 | 贵州毕节Bijie, Guizhou | 26°39′-27°17′ N,104°42′-106°41′ E | 路边Roadside,田坎Fields,山坡Hillside | 1020~1527 |
| Tr061 | 贵州铜仁Tongren, Guizhou | 27°23′ N,108°88′ E | 路边Roadside | 357 |
| Tr062~Tr064 | 贵州六盘水Liupanshui, Guizhou | 25°47′-26°24′ N,104°49′-105°28′ E | 田坎Fields,山坡Hillside | 1193~1532 |
| Tr065~Tr072 | 贵州安顺Anshun, Guizhou | 25°42′-26°13′ N,105°38′-106°05′ E | 路边Roadside,山坡Hillside,田坎Fields | 1049~1326 |
| Tr073~Tr074 | 贵州黔东南Qiandongnan, Guizhou | 26°22′-26°61′ N,107°83′-107°91′ E | 路边Roadside | 822~883 |
| Tr075~Tr078 | 贵州黔南Qiannan, Guizhou | 26°00′-26°38′ N,106°26′-107°21′ E | 田坎Fields,草原Grassland,山坡Hillside | 980~1639 |
| Tr079~Tr082 | 贵州黔西南Qianxinan, Guizhou | 25°04′-25°52′ N,104°56′-105°24′ E | 路边Roadside,田坎Fields | 986~1599 |
| Haifa | 购于百绿(天津)国际草业有限公司 Seeds were purchased from Barenbrug Company (Tianjin) | |||
| Huia | 购于百绿(天津)国际草业有限公司 Seeds were purchased from Barenbrug Company (Tianjin) | |||
材料编号 NO. | 相对株高 RSL | 相对根长 RRL | 相对干重 RDW | 相对绿值 RG | 材料编号 NO. | 相对株高 RSL | 相对根长 RRL | 相对干重 RDW | 相对绿值 RG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr001 | 37.00k | 43.19ef | 12.93c | 47.37f~i | Tr043 | 73.74ab | 47.32a~f | 13.46c | 30.00n~r |
| Tr002 | 56.18e~j | 43.94ef | 11.75ij | 48.15f~i | Tr044 | 57.55a~h | 46.88a~f | 12.23f~h | 34.78l~p |
| Tr003 | 75.44a~d | 45.85ef | 12.74c~e | 66.67d | Tr045 | 60.25a~h | 43.42ef | 12.35f~h | 28.57p~s |
| Tr004 | 65.34a~g | 44.44d~f | 13.53c | 68.18d | Tr046 | 55.20b~h | 43.10ef | 12.35f~h | 28.57p~s |
| Tr005 | 54.26e~k | 42.70f | 12.76c~e | 36.36j~n | Tr047 | 69.78a~c | 43.90ef | 10.86o~q | 33.33l~p |
| Tr006 | 76.76ab | 44.14ef | 11.13l~o | 40.00j~m | Tr048 | 58.40a~h | 43.12ef | 10.54q~s | 20.00t~x |
| Tr007 | 59.34c~i | 46.82a~f | 11.08m~p | 40.00j~m | Tr049 | 55.32b~h | 52.24a~f | 10.62qr | 15.00v~x |
| Tr008 | 52.62f~k | 39.90f | 9.98tu | 50.00f~h | Tr050 | 66.04a~f | 42.07f | 12.86cd | 20.00t~w |
| Tr009 | 57.98d~i | 44.93d~f | 11.09m~p | 5.56y | Tr051 | 45.81gh | 42.80ef | 11.27k~n | 42.11h~k |
| Tr010 | 54.20e~k | 43.91ef | 11.76ij | 52.00e~g | Tr052 | 56.86a~h | 48.60a~f | 12.89cd | 26.32q~t |
| Tr011 | 61.93b~i | 45.75d~f | 10.99n~p | 52.17ef | Tr053 | 64.59a~g | 52.44a~f | 16.24a | 17.65v~x |
| Tr012 | 53.02e~k | 43.72ef | 10.63qr | 52.38ef | Tr054 | 56.98a~h | 42.65f | 11.37k~m | 25.00r~u |
| Tr013 | 64.38b~g | 43.35ef | 11.06m~p | 26.32q~t | Tr055 | 54.98b~h | 47.43a~f | 12.22gh | 10.53xy |
| Tr014 | 51.24f~k | 49.04a~f | 10.43rs | 20.00t~w | Tr056 | 58.23a~h | 56.14ab | 12.49e~g | 38.10j~n |
| Tr015 | 59.98b~i | 43.54f | 11.49j~l | 44.00g~j | Tr057 | 64.49a~g | 44.52f | 10.25st | 65.00d |
| Tr016 | 65.72a~f | 42.40f | 12.81c~e | 85.00b | Tr058 | 48.31e~h | 48.32a~f | 11.22l~o | 22.22r~u |
| Tr017 | 81.16a | 42.36f | 11.71ij | 85.00b | Tr059 | 55.44b~h | 49.86a~f | 10.50st | 29.41o~r |
| Tr018 | 54.00e~k | 45.85b~f | 13.55c | 25.00r~u | Tr060 | 59.20a~h | 50.80a~f | 10.45rs | 80.00bc |
| Tr019 | 71.04a~e | 50.12a~f | 9.61uv | 26.09q~t | Tr061 | 61.22a~h | 47.24a~f | 13.43c | 15.79v~x |
| Tr020 | 46.36g~k | 45.70b~f | 10.43rs | 30.43n~r | Tr062 | 47.22f~h | 51.09a~f | 12.13gh | 100.00a |
| Tr021 | 39.18jk | 44.35d~f | 10.91o~q | 28.00p~s | Tr063 | 53.26c~h | 56.83a~d | 12.12gh | 21.05s~v |
| Tr022 | 63.46b~g | 51.41a~f | 10.77qr | 80.00bc | Tr064 | 62.56d~f | 55.38a~d | 10.45rs | 35.00l~p |
| Tr023 | 54.66e~k | 41.92f | 14.68b | 25.00r~u | Tr065 | 53.41c~h | 44.92c~f | 12.75c~e | 15.00v~x |
| Tr024 | 54.64e~k | 43.40ef | 13.67c | 30.43n~r | Tr066 | 57.77a~h | 47.02a~f | 9.10w | 40.00j~m |
| Tr025 | 44.84i~k | 43.89ef | 12.57d~f | 44.00g~j | Tr067 | 50.21e~h | 47.02a~f | 9.75uv | 22.22s~v |
| Tr026 | 55.90e~j | 43.61ef | 12.93c | 30.43n~r | Tr068 | 61.22a~h | 48.36a~f | 10.33st | 40.91i~l |
| Tr027 | 61.96b~h | 45.41b~f | 12.18gh | 25.00r~u | Tr069 | 53.17c~h | 49.13a~f | 9.19w | 31.82n~r |
| Tr028 | 61.50b~i | 49.12a~f | 12.26f~h | 11.76xy | Tr070 | 74.95a | 51.22a~f | 12.97c | 19.05v~x |
| Tr029 | 48.14f~k | 47.43a~f | 12.53e~g | 30.43n~r | Tr071 | 62.57d~f | 46.01a~f | 9.57uv | 31.82n~r |
| Tr030 | 51.54f~k | 46.35a~f | 13.02c | 30.43n~r | Tr072 | 67.05c | 45.67b~f | 9.35vw | 48.00fi |
| Tr031 | 59.04c~i | 42.57f | 10.76qr | 32.00n~r | Tr073 | 53.16c~h | 57.27a~c | 13.01c | 6.25y |
| Tr032 | 65.50a~f | 43.35ef | 10.89o~q | 14.29wx | Tr074 | 43.98h | 50.29a~f | 13.01c | 8.70xy |
| Tr033 | 56.86e~i | 45.90a~f | 13.38c | 21.74s~v | Tr075 | 55.52b~h | 44.01f | 8.11x | 13.04wx |
| Tr034 | 55.46e~k | 45.19b~f | 12.17gh | 16.67v~x | Tr076 | 51.83c~h | 43.58ef | 11.58i~k | 36.00k~o |
| Tr035 | 75.90a~c | 42.57f | 11.46j~l | 28.57p~s | Tr077 | 63.58de | 48.83a~f | 10.01tu | 80.00bc |
| Tr036 | 50.41f~k | 43.08ef | 10.11t | 40.00j~m | Tr078 | 55.92j~m | 46.98a~f | 10.24st | 75.00c |
| Tr037 | 58.83d~i | 42.81f | 11.04m~p | 52.63ef | Tr079 | 66.49c | 48.53a~f | 12.19gh | 55.00e |
| Tr038 | 50.02f~k | 45.75b~f | 12.37f~h | 27.78p~s | Tr080 | 53.48mn | 47.77a~f | 12.36f~h | 76.19c |
| Tr039 | 40.12i~k | 58.27a | 12.50e~g | 13.33wx | Tr081 | 69.45b | 44.81c~f | 10.61qr | 31.58n~r |
| Tr040 | 51.54f~k | 43.83ef | 11.07m~p | 13.64wx | Tr082 | 69.97b | 46.92a~f | 9.70uv | 29.41o~r |
| Tr041 | 45.64h~k | 47.87a~f | 10.81qr | 6.67xy | Haifa | 63.34de | 45.61b~f | 9.99tu | 27.78p~s |
| Tr042 | 50.59d~h | 46.51a~f | 11.90hi | 30.00n~r | Huia | 54.59l~n | 46.14a~f | 12.10g | 47.62f~i |
表2 铝胁迫下白三叶的生长表现
Table 2 Growth performance of white clover under Al tolerance (%)
材料编号 NO. | 相对株高 RSL | 相对根长 RRL | 相对干重 RDW | 相对绿值 RG | 材料编号 NO. | 相对株高 RSL | 相对根长 RRL | 相对干重 RDW | 相对绿值 RG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr001 | 37.00k | 43.19ef | 12.93c | 47.37f~i | Tr043 | 73.74ab | 47.32a~f | 13.46c | 30.00n~r |
| Tr002 | 56.18e~j | 43.94ef | 11.75ij | 48.15f~i | Tr044 | 57.55a~h | 46.88a~f | 12.23f~h | 34.78l~p |
| Tr003 | 75.44a~d | 45.85ef | 12.74c~e | 66.67d | Tr045 | 60.25a~h | 43.42ef | 12.35f~h | 28.57p~s |
| Tr004 | 65.34a~g | 44.44d~f | 13.53c | 68.18d | Tr046 | 55.20b~h | 43.10ef | 12.35f~h | 28.57p~s |
| Tr005 | 54.26e~k | 42.70f | 12.76c~e | 36.36j~n | Tr047 | 69.78a~c | 43.90ef | 10.86o~q | 33.33l~p |
| Tr006 | 76.76ab | 44.14ef | 11.13l~o | 40.00j~m | Tr048 | 58.40a~h | 43.12ef | 10.54q~s | 20.00t~x |
| Tr007 | 59.34c~i | 46.82a~f | 11.08m~p | 40.00j~m | Tr049 | 55.32b~h | 52.24a~f | 10.62qr | 15.00v~x |
| Tr008 | 52.62f~k | 39.90f | 9.98tu | 50.00f~h | Tr050 | 66.04a~f | 42.07f | 12.86cd | 20.00t~w |
| Tr009 | 57.98d~i | 44.93d~f | 11.09m~p | 5.56y | Tr051 | 45.81gh | 42.80ef | 11.27k~n | 42.11h~k |
| Tr010 | 54.20e~k | 43.91ef | 11.76ij | 52.00e~g | Tr052 | 56.86a~h | 48.60a~f | 12.89cd | 26.32q~t |
| Tr011 | 61.93b~i | 45.75d~f | 10.99n~p | 52.17ef | Tr053 | 64.59a~g | 52.44a~f | 16.24a | 17.65v~x |
| Tr012 | 53.02e~k | 43.72ef | 10.63qr | 52.38ef | Tr054 | 56.98a~h | 42.65f | 11.37k~m | 25.00r~u |
| Tr013 | 64.38b~g | 43.35ef | 11.06m~p | 26.32q~t | Tr055 | 54.98b~h | 47.43a~f | 12.22gh | 10.53xy |
| Tr014 | 51.24f~k | 49.04a~f | 10.43rs | 20.00t~w | Tr056 | 58.23a~h | 56.14ab | 12.49e~g | 38.10j~n |
| Tr015 | 59.98b~i | 43.54f | 11.49j~l | 44.00g~j | Tr057 | 64.49a~g | 44.52f | 10.25st | 65.00d |
| Tr016 | 65.72a~f | 42.40f | 12.81c~e | 85.00b | Tr058 | 48.31e~h | 48.32a~f | 11.22l~o | 22.22r~u |
| Tr017 | 81.16a | 42.36f | 11.71ij | 85.00b | Tr059 | 55.44b~h | 49.86a~f | 10.50st | 29.41o~r |
| Tr018 | 54.00e~k | 45.85b~f | 13.55c | 25.00r~u | Tr060 | 59.20a~h | 50.80a~f | 10.45rs | 80.00bc |
| Tr019 | 71.04a~e | 50.12a~f | 9.61uv | 26.09q~t | Tr061 | 61.22a~h | 47.24a~f | 13.43c | 15.79v~x |
| Tr020 | 46.36g~k | 45.70b~f | 10.43rs | 30.43n~r | Tr062 | 47.22f~h | 51.09a~f | 12.13gh | 100.00a |
| Tr021 | 39.18jk | 44.35d~f | 10.91o~q | 28.00p~s | Tr063 | 53.26c~h | 56.83a~d | 12.12gh | 21.05s~v |
| Tr022 | 63.46b~g | 51.41a~f | 10.77qr | 80.00bc | Tr064 | 62.56d~f | 55.38a~d | 10.45rs | 35.00l~p |
| Tr023 | 54.66e~k | 41.92f | 14.68b | 25.00r~u | Tr065 | 53.41c~h | 44.92c~f | 12.75c~e | 15.00v~x |
| Tr024 | 54.64e~k | 43.40ef | 13.67c | 30.43n~r | Tr066 | 57.77a~h | 47.02a~f | 9.10w | 40.00j~m |
| Tr025 | 44.84i~k | 43.89ef | 12.57d~f | 44.00g~j | Tr067 | 50.21e~h | 47.02a~f | 9.75uv | 22.22s~v |
| Tr026 | 55.90e~j | 43.61ef | 12.93c | 30.43n~r | Tr068 | 61.22a~h | 48.36a~f | 10.33st | 40.91i~l |
| Tr027 | 61.96b~h | 45.41b~f | 12.18gh | 25.00r~u | Tr069 | 53.17c~h | 49.13a~f | 9.19w | 31.82n~r |
| Tr028 | 61.50b~i | 49.12a~f | 12.26f~h | 11.76xy | Tr070 | 74.95a | 51.22a~f | 12.97c | 19.05v~x |
| Tr029 | 48.14f~k | 47.43a~f | 12.53e~g | 30.43n~r | Tr071 | 62.57d~f | 46.01a~f | 9.57uv | 31.82n~r |
| Tr030 | 51.54f~k | 46.35a~f | 13.02c | 30.43n~r | Tr072 | 67.05c | 45.67b~f | 9.35vw | 48.00fi |
| Tr031 | 59.04c~i | 42.57f | 10.76qr | 32.00n~r | Tr073 | 53.16c~h | 57.27a~c | 13.01c | 6.25y |
| Tr032 | 65.50a~f | 43.35ef | 10.89o~q | 14.29wx | Tr074 | 43.98h | 50.29a~f | 13.01c | 8.70xy |
| Tr033 | 56.86e~i | 45.90a~f | 13.38c | 21.74s~v | Tr075 | 55.52b~h | 44.01f | 8.11x | 13.04wx |
| Tr034 | 55.46e~k | 45.19b~f | 12.17gh | 16.67v~x | Tr076 | 51.83c~h | 43.58ef | 11.58i~k | 36.00k~o |
| Tr035 | 75.90a~c | 42.57f | 11.46j~l | 28.57p~s | Tr077 | 63.58de | 48.83a~f | 10.01tu | 80.00bc |
| Tr036 | 50.41f~k | 43.08ef | 10.11t | 40.00j~m | Tr078 | 55.92j~m | 46.98a~f | 10.24st | 75.00c |
| Tr037 | 58.83d~i | 42.81f | 11.04m~p | 52.63ef | Tr079 | 66.49c | 48.53a~f | 12.19gh | 55.00e |
| Tr038 | 50.02f~k | 45.75b~f | 12.37f~h | 27.78p~s | Tr080 | 53.48mn | 47.77a~f | 12.36f~h | 76.19c |
| Tr039 | 40.12i~k | 58.27a | 12.50e~g | 13.33wx | Tr081 | 69.45b | 44.81c~f | 10.61qr | 31.58n~r |
| Tr040 | 51.54f~k | 43.83ef | 11.07m~p | 13.64wx | Tr082 | 69.97b | 46.92a~f | 9.70uv | 29.41o~r |
| Tr041 | 45.64h~k | 47.87a~f | 10.81qr | 6.67xy | Haifa | 63.34de | 45.61b~f | 9.99tu | 27.78p~s |
| Tr042 | 50.59d~h | 46.51a~f | 11.90hi | 30.00n~r | Huia | 54.59l~n | 46.14a~f | 12.10g | 47.62f~i |
编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank | 编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank | 编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank | 编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr001 | 0.381 | 42 | Tr022 | 0.692 | 2 | Tr043 | 0.450 | 22 | Tr064 | 0.547 | 12 |
| Tr002 | 0.415 | 32 | Tr023 | 0.310 | 73 | Tr044 | 0.422 | 30 | Tr065 | 0.300 | 75 |
| Tr003 | 0.572 | 9 | Tr024 | 0.350 | 56 | Tr045 | 0.335 | 63 | Tr066 | 0.410 | 33 |
| Tr004 | 0.545 | 13 | Tr025 | 0.388 | 41 | Tr046 | 0.321 | 69 | Tr067 | 0.330 | 67 |
| Tr005 | 0.350 | 56 | Tr026 | 0.347 | 58 | Tr047 | 0.362 | 51 | Tr068 | 0.459 | 21 |
| Tr006 | 0.409 | 35 | Tr027 | 0.359 | 54 | Tr048 | 0.156 | 84 | Tr069 | 0.409 | 35 |
| Tr007 | 0.432 | 25 | Tr028 | 0.374 | 44 | Tr049 | 0.418 | 31 | Tr070 | 0.449 | 23 |
| Tr008 | 0.319 | 70 | Tr029 | 0.402 | 38 | Tr050 | 0.288 | 78 | Tr071 | 0.374 | 44 |
| Tr009 | 0.248 | 82 | Tr030 | 0.393 | 39 | Tr051 | 0.345 | 60 | Tr072 | 0.425 | 28 |
| Tr010 | 0.427 | 27 | Tr031 | 0.313 | 72 | Tr052 | 0.425 | 28 | Tr073 | 0.501 | 17 |
| Tr011 | 0.466 | 19 | Tr032 | 0.264 | 80 | Tr053 | 0.514 | 16 | Tr074 | 0.364 | 50 |
| Tr012 | 0.410 | 33 | Tr033 | 0.360 | 52 | Tr054 | 0.289 | 77 | Tr075 | 0.223 | 83 |
| Tr013 | 0.316 | 71 | Tr034 | 0.309 | 74 | Tr055 | 0.325 | 68 | Tr076 | 0.347 | 58 |
| Tr014 | 0.369 | 47 | Tr035 | 0.333 | 65 | Tr056 | 0.616 | 6 | Tr077 | 0.639 | 4 |
| Tr015 | 0.392 | 40 | Tr036 | 0.335 | 63 | Tr057 | 0.492 | 18 | Tr078 | 0.598 | 7 |
| Tr016 | 0.569 | 10 | Tr037 | 0.408 | 37 | Tr058 | 0.369 | 47 | Tr079 | 0.558 | 11 |
| Tr017 | 0.580 | 8 | Tr038 | 0.360 | 52 | Tr059 | 0.432 | 25 | Tr080 | 0.634 | 5 |
| Tr018 | 0.371 | 46 | Tr039 | 0.524 | 15 | Tr060 | 0.670 | 3 | Tr081 | 0.345 | 60 |
| Tr019 | 0.437 | 24 | Tr040 | 0.251 | 81 | Tr061 | 0.368 | 49 | Tr082 | 0.358 | 55 |
| Tr020 | 0.342 | 62 | Tr041 | 0.286 | 79 | Tr062 | 0.761 | 1 | Haifa | 0.333 | 65 |
| Tr021 | 0.300 | 75 | Tr042 | 0.380 | 43 | Tr063 | 0.545 | 13 | Huia | 0.465 | 20 |
表3 隶属函数综合指数得分排名
Table 3 Rank of the subordinate function index score
编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank | 编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank | 编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank | 编号 NO. | U值 U values | 排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr001 | 0.381 | 42 | Tr022 | 0.692 | 2 | Tr043 | 0.450 | 22 | Tr064 | 0.547 | 12 |
| Tr002 | 0.415 | 32 | Tr023 | 0.310 | 73 | Tr044 | 0.422 | 30 | Tr065 | 0.300 | 75 |
| Tr003 | 0.572 | 9 | Tr024 | 0.350 | 56 | Tr045 | 0.335 | 63 | Tr066 | 0.410 | 33 |
| Tr004 | 0.545 | 13 | Tr025 | 0.388 | 41 | Tr046 | 0.321 | 69 | Tr067 | 0.330 | 67 |
| Tr005 | 0.350 | 56 | Tr026 | 0.347 | 58 | Tr047 | 0.362 | 51 | Tr068 | 0.459 | 21 |
| Tr006 | 0.409 | 35 | Tr027 | 0.359 | 54 | Tr048 | 0.156 | 84 | Tr069 | 0.409 | 35 |
| Tr007 | 0.432 | 25 | Tr028 | 0.374 | 44 | Tr049 | 0.418 | 31 | Tr070 | 0.449 | 23 |
| Tr008 | 0.319 | 70 | Tr029 | 0.402 | 38 | Tr050 | 0.288 | 78 | Tr071 | 0.374 | 44 |
| Tr009 | 0.248 | 82 | Tr030 | 0.393 | 39 | Tr051 | 0.345 | 60 | Tr072 | 0.425 | 28 |
| Tr010 | 0.427 | 27 | Tr031 | 0.313 | 72 | Tr052 | 0.425 | 28 | Tr073 | 0.501 | 17 |
| Tr011 | 0.466 | 19 | Tr032 | 0.264 | 80 | Tr053 | 0.514 | 16 | Tr074 | 0.364 | 50 |
| Tr012 | 0.410 | 33 | Tr033 | 0.360 | 52 | Tr054 | 0.289 | 77 | Tr075 | 0.223 | 83 |
| Tr013 | 0.316 | 71 | Tr034 | 0.309 | 74 | Tr055 | 0.325 | 68 | Tr076 | 0.347 | 58 |
| Tr014 | 0.369 | 47 | Tr035 | 0.333 | 65 | Tr056 | 0.616 | 6 | Tr077 | 0.639 | 4 |
| Tr015 | 0.392 | 40 | Tr036 | 0.335 | 63 | Tr057 | 0.492 | 18 | Tr078 | 0.598 | 7 |
| Tr016 | 0.569 | 10 | Tr037 | 0.408 | 37 | Tr058 | 0.369 | 47 | Tr079 | 0.558 | 11 |
| Tr017 | 0.580 | 8 | Tr038 | 0.360 | 52 | Tr059 | 0.432 | 25 | Tr080 | 0.634 | 5 |
| Tr018 | 0.371 | 46 | Tr039 | 0.524 | 15 | Tr060 | 0.670 | 3 | Tr081 | 0.345 | 60 |
| Tr019 | 0.437 | 24 | Tr040 | 0.251 | 81 | Tr061 | 0.368 | 49 | Tr082 | 0.358 | 55 |
| Tr020 | 0.342 | 62 | Tr041 | 0.286 | 79 | Tr062 | 0.761 | 1 | Haifa | 0.333 | 65 |
| Tr021 | 0.300 | 75 | Tr042 | 0.380 | 43 | Tr063 | 0.545 | 13 | Huia | 0.465 | 20 |
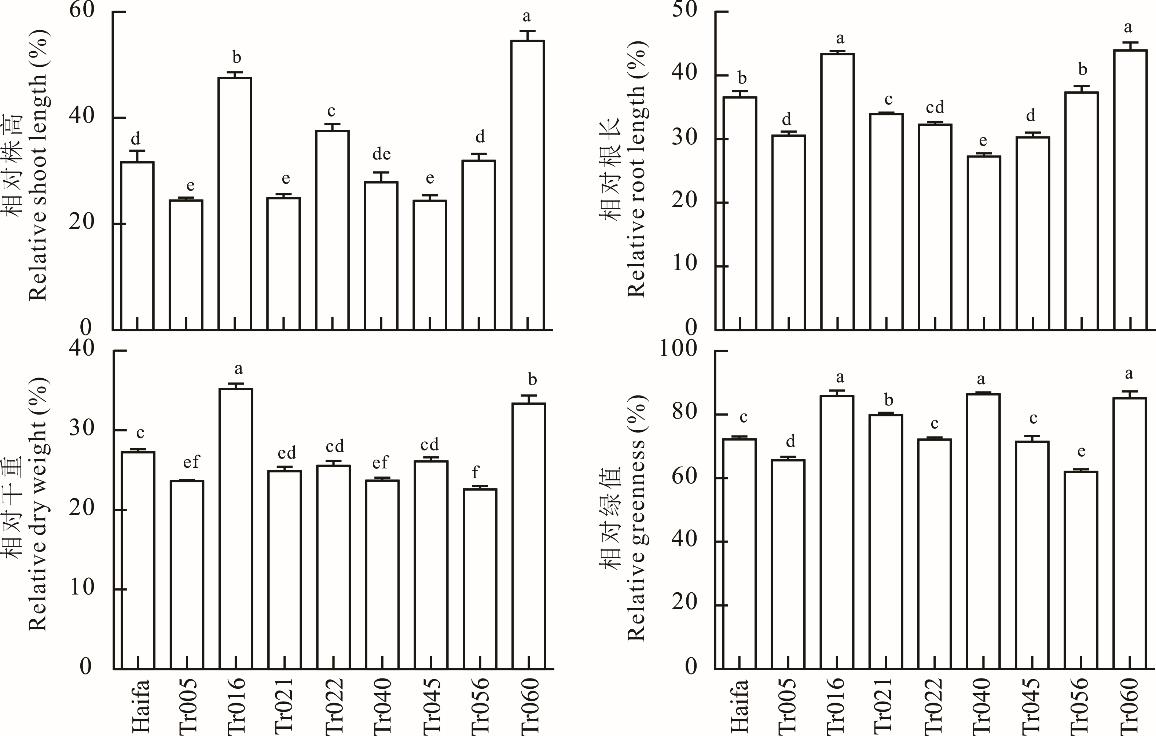
图1 铝胁迫对白三叶生长指标的影响不同小写字母代表不同材料间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences between materials at 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of Al tolerance on growth indexes of white clover
材料编号 NO. | 相对株高 RSL | 相对根长 RRL | 相对干重 RDW | 相对绿值 RG | 相对含水量 RWC | 相对电导率 EL | 丙二醛 MDA | 叶绿素 Chl | 最大光能转化效率 Fv/Fm | 叶片健康指数 PI | 得分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haifa | 0.241 | 0.558 | 0.369 | 0.316 | 0.597 | 0.565 | 0.525 | 0.221 | 0.291 | 0.523 | 0.421 |
| Tr005 | 0.002 | 0.197 | 0.085 | 0.000 | 0.278 | 0.717 | 0.464 | 0.099 | 0.409 | 0.576 | 0.283 |
| Tr016 | 0.768 | 0.964 | 1.000 | 0.892 | 0.819 | 1.000 | 0.987 | 0.732 | 0.793 | 1.000 | 0.896 |
| Tr021 | 0.018 | 0.399 | 0.183 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.406 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.114 |
| Tr022 | 0.438 | 0.298 | 0.236 | 0.315 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.343 | 0.064 | 0.192 |
| Tr040 | 0.116 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 0.003 | 0.236 | 0.168 | 0.669 | 0.432 | 0.262 | 0.360 | 0.233 |
| Tr045 | 0.000 | 0.180 | 0.280 | 0.040 | 0.875 | 0.094 | 0.259 | 0.343 | 0.122 | 0.200 | 0.239 |
| Tr056 | 0.251 | 0.601 | 0.000 | 0.247 | 0.736 | 0.000 | 0.480 | 0.428 | 0.280 | 0.700 | 0.372 |
| Tr060 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.852 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.561 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.887 | 0.930 |
表4 白三叶种质耐铝评价隶属函数得分
Table 4 Subordinate function score of Al tolerance evaluation of white clover germplasms
材料编号 NO. | 相对株高 RSL | 相对根长 RRL | 相对干重 RDW | 相对绿值 RG | 相对含水量 RWC | 相对电导率 EL | 丙二醛 MDA | 叶绿素 Chl | 最大光能转化效率 Fv/Fm | 叶片健康指数 PI | 得分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haifa | 0.241 | 0.558 | 0.369 | 0.316 | 0.597 | 0.565 | 0.525 | 0.221 | 0.291 | 0.523 | 0.421 |
| Tr005 | 0.002 | 0.197 | 0.085 | 0.000 | 0.278 | 0.717 | 0.464 | 0.099 | 0.409 | 0.576 | 0.283 |
| Tr016 | 0.768 | 0.964 | 1.000 | 0.892 | 0.819 | 1.000 | 0.987 | 0.732 | 0.793 | 1.000 | 0.896 |
| Tr021 | 0.018 | 0.399 | 0.183 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.406 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.114 |
| Tr022 | 0.438 | 0.298 | 0.236 | 0.315 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.343 | 0.064 | 0.192 |
| Tr040 | 0.116 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 0.003 | 0.236 | 0.168 | 0.669 | 0.432 | 0.262 | 0.360 | 0.233 |
| Tr045 | 0.000 | 0.180 | 0.280 | 0.040 | 0.875 | 0.094 | 0.259 | 0.343 | 0.122 | 0.200 | 0.239 |
| Tr056 | 0.251 | 0.601 | 0.000 | 0.247 | 0.736 | 0.000 | 0.480 | 0.428 | 0.280 | 0.700 | 0.372 |
| Tr060 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.852 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.561 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.887 | 0.930 |

图3 铝胁迫综合指标系数及贡献率RSL: Relative shoot length; RRL: Relative root length; RDW: Relative dry weight; RG: Relative greenness; RWC: Relative water content; EL: Electrolyte leakage; MDA: Malondialdehyde; Chl: Chlorophyll; Fv/Fm: Photochemical efficiency; PI: Performance index.
Fig.3 Comprehensive index coefficient and contribution rate of Al tolerance
材料编号 NO. | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | U1 | U2 | D值 D values | 综合排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haifa | -0.020 | -0.457 | 0.417 | 0.439 | 0.420 | 3 |
| Tr005 | -0.451 | -0.769 | 0.286 | 0.208 | 0.275 | 5 |
| Tr016 | 1.633 | 0.367 | 0.894 | 0.908 | 0.896 | 2 |
| Tr021 | -0.935 | 1.238 | 0.116 | 0.101 | 0.114 | 9 |
| Tr022 | -0.785 | 0.435 | 0.193 | 0.206 | 0.195 | 8 |
| Tr040 | -0.396 | 1.350 | 0.245 | 0.166 | 0.234 | 7 |
| Tr045 | -0.582 | -0.590 | 0.238 | 0.285 | 0.245 | 6 |
| Tr056 | -0.221 | -1.771 | 0.375 | 0.430 | 0.383 | 4 |
| Tr060 | 1.758 | 0.196 | 0.933 | 0.962 | 0.937 | 1 |
| 权重 Weight | 0.858 | 0.142 |
表5 白三叶种质综合评价
Table 5 Comprehensive evaluation of white clover germplasms
材料编号 NO. | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | U1 | U2 | D值 D values | 综合排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haifa | -0.020 | -0.457 | 0.417 | 0.439 | 0.420 | 3 |
| Tr005 | -0.451 | -0.769 | 0.286 | 0.208 | 0.275 | 5 |
| Tr016 | 1.633 | 0.367 | 0.894 | 0.908 | 0.896 | 2 |
| Tr021 | -0.935 | 1.238 | 0.116 | 0.101 | 0.114 | 9 |
| Tr022 | -0.785 | 0.435 | 0.193 | 0.206 | 0.195 | 8 |
| Tr040 | -0.396 | 1.350 | 0.245 | 0.166 | 0.234 | 7 |
| Tr045 | -0.582 | -0.590 | 0.238 | 0.285 | 0.245 | 6 |
| Tr056 | -0.221 | -1.771 | 0.375 | 0.430 | 0.383 | 4 |
| Tr060 | 1.758 | 0.196 | 0.933 | 0.962 | 0.937 | 1 |
| 权重 Weight | 0.858 | 0.142 |
| 1 | Zhang L Y, Zhao X Q, Shen R F. Soil acidification and its ecological effects. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(6): 1900-1908. |
| 张玲玉, 赵学强, 沈仁芳. 土壤酸化及其生态效应. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(6): 1900-1908. | |
| 2 | Taylor G J. The physiology of aluminum tolerance in higher plants. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1988, 19(7): 1179-1194. |
| 3 | Foy C D. Plant adaptation to acid, aluminum-toxic soils. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1988, 19(7): 959-987. |
| 4 | Rahman M, Lee S H, Ji H, et al. Importance of mineral nutrition for mitigating aluminum toxicity in plants on acidic soils: Current status and opportunities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(10): 1-12. |
| 5 | Zhang P, Ding Z, Zhong Z, et al. Transcriptomic analysis for indica and japonica rice varieties under aluminum toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(4): 12-19. |
| 6 | Ali B, Hasan S A, Hayat S, et al. A role for brassinosteroids in the amelioration of aluminum stress through antioxidant system in mung bean (Vigna radiata). Environmental Experimental Botany, 2008, 62(2): 153-159. |
| 7 | Qi G X, Wang J G, Yang X D, et al. Progresses in improvement of Trifolium repens L. by genetic engineering. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(11): 1-4. |
| 齐广勋, 王金刚, 杨向东, 等. 白三叶基因工程改良研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(11): 1-4. | |
| 8 | Ouyang L, Xu H Q, Yang Z J. Effects of different dosages of soil modifiers on physical and chemical properties of southern acidic soil and growth of Trifolium repens. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science, 2016, 44(11): 168-170, 208. |
| 欧阳玲, 徐华勤, 杨知建. 不同施用量土壤改良剂对南方酸性土壤理化性状及白三叶生长的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(11): 168-170, 208. | |
| 9 | Du Y, Zheng D C, Wang T Q. Investigation on ecological adaptability of wild Trifolium repens L. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 1983(4): 37-40. |
| 杜逸, 郑德成, 王天群. 野生白三叶生态适应性的调查. 中国草地学报, 1983(4): 37-40. | |
| 10 | Zhu B C. White clover resources in China. Pratacultural Science, 1986, 3(1): 4-9. |
| 朱邦长. 中国的白三叶草资源. 草业科学, 1986, 3(1): 4-9. | |
| 11 | Mao P C, Meng L, Gao H W, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of 39 Bromus inermis germplasms at the seedling stage. Pratacultural Science, 2010, 27(11): 82-88. |
| 毛培春, 孟林, 高洪文, 等. 39份无芒雀麦种质材料苗期抗旱性综合评价. 草业科学, 2010, 27(11): 82-88. | |
| 12 | Tian X X, Mao P C, Zheng M L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the salt tolerance of Melilotus officinalis at the seedling stage. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(1): 123-132. |
| 田小霞, 毛培春, 郑明利, 等. 黄花草木樨苗期耐盐性综合评价. 草业科学, 2022, 39(1): 123-132. | |
| 13 | Wang C Q, Liu W H, Zhang Y C, et al. Drought tolerance of wild Elymus nutans during germination and seedling establishment. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. |
| 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 等. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. | |
| 14 | Zhang H S, Gao Q, Zhang T T, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of copper tolerance of 30 germplasm resources of red clover (Trifolium pratense). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 117-128. |
| 张鹤山, 高秋, 张婷婷, 等. 30份红三叶种质资源耐铜性综合评价. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 117-128. | |
| 15 | Lin D D, Zhao G Q, Ju Z L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of 15 oat varieties at the seedling stage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 等. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. | |
| 16 | Jiang N, Tang M, Han B, et al. Effects of aluminum stress on different germplasm materials of alfalfa and its comprehensive evaluation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(3): 620-627. |
| 姜娜, 唐敏, 韩博, 等. 铝胁迫对紫花苜蓿不同种质材料的影响及综合评价. 草地学报, 2019, 27(3): 620-627. | |
| 17 | Chen Z. Evaluation of aluminum tolerance and aluminum tolerance mechanism of Cynodon dactylo on germplasm resources. Haikou: Hainan University, 2015. |
| 陈振. 狗牙根种质资源耐铝性评价及耐铝机理研究. 海口: 海南大学, 2015. | |
| 18 | Yan J, Liu J X. Advance in studies on aluminum tolerance of grass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(6): 148-155. |
| 阎君, 刘建秀. 草类植物耐铝性的研究进展. 草业学报, 2008, 17(6): 148-155. | |
| 19 | Lin X Y, Zhu B L, Zhang Y S, et al. Applicability of using shoot growth parameters as indices of screening for the tolerance of wheat genotypes to aluminum. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2002, 28(3): 260-266. |
| 林咸永, 朱炳良, 章永松, 等. 地上部生长性状指标在小麦耐铝性筛选中的应用. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2002, 28(3): 260-266. | |
| 20 | Wu J X, Zhang Z F, Zhang H S, et al. Study on the screening germplasm resources of acid-aluminum tolerance in white clover. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(2): 497-504. |
| 武建新, 张志飞, 张鹤山, 等. 白三叶耐酸铝种质资源筛选研究. 草地学报, 2018, 26(2): 497-504. | |
| 21 | Barrs H. A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficits in leaves. Australian Journal of Biological Sciences, 1962, 15(3): 413-428. |
| 22 | Blarney F P C, Nishizawa N K, Yoshimura E. Timing, magnitude, and location of initial soluble aluminum injuries to mungbean roots. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2004, 50(1): 67-76. |
| 23 | Li Z, Zhang Y, Peng D, et al. The inhibition of polyamine biosynthesis weakens the drought tolerance in white clover (Trifolium repens) associated with the alteration of extensive proteins. Protoplasma, 2018, 255(3): 803-817. |
| 24 | Li Z, Yong B, Cheng B Z, et al. Nitric oxide, γ-aminobutyric acid, and mannose pretreatment influence metabolic profiles in white clover under water stress. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2019, 61(12): 1255-1273. |
| 25 | Wang T, Amee M, Wang G, et al. FaHSP17.8-CII orchestrates lead tolerance and accumulation in shoots via enhancing antioxidant enzymatic response and PSII activity in tall fescue. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 223(1): 112568. |
| 26 | Sun G, Zhu H, Wen S, et al. Citrate synthesis and exudation confer Al resistance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant and Soil, 2020, 449(1): 319-329. |
| 27 | Samuels T D, Kucukakyuz K, Magaly R Z. Al partitioning patterns and root growth as related to Al sensitivity and Al tolerance in wheat. Plant Physiology, 1997, 113(2): 527-534. |
| 28 | Liu Y. Characteristics of soil water content and water-soluble calcium distribution in typical karst areas of Guizhou and analysis of water-calcium relationship. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2021. |
| 刘洋. 贵州典型喀斯特区土壤含水量与水溶性钙分布特征及水-钙关系分析. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2021. | |
| 29 | Bose J, Babourina O, Shabala S, et al. Low-pH and aluminum resistance in Arabidopsis correlates with high cytosolic magnesium content and increased magnesium uptake by plant roots. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2013, 54(7): 1093-1104. |
| 30 | Sun W J, Tang M, Ren J, et al. The physiological tolerance response of 8 alfalfa species in Yunnan to aluminum stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(5): 151-158. |
| 孙文君, 唐敏, 任健, 等. 8份云南苜蓿属优异种质资源对铝胁迫的生理耐受响应研究. 草地学报, 2018, 26(5): 151-158. | |
| 31 | Liu J L, Bai C J, Yan L L, et al. Evaluation on the aluminum tolerance of sixteen Stylosanthes varieties. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2014, 35(3): 476-482. |
| 刘建乐, 白昌军, 严琳玲, 等. 16份柱花草材料的耐铝性评价. 热带作物学报, 2014, 35(3): 476-482. | |
| 32 | Zhang Z F, Wu J X, Zeng N B, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance of 66 white clover germplasm resources at the germination stage. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(9): 2157-2165. |
| 张志飞, 武建新, 曾宁波, 等. 66份白三叶种质资源萌发期耐盐性综合评价. 草业科学, 2018, 35(9): 2157-2165. | |
| 33 | Chen F, Zhao S Y, Zhang H S, et al. Evaluation of copper tolerance of 103 white clover germplasm resources at germination stage. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(14): 4829-4839. |
| 陈菲, 赵思怡, 张鹤山, 等. 103份白三叶种质资源萌发期耐铜性评价. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(14): 4829-4839. |
| [1] | 哈雪, 张金青, 白方旭, 马祥荣, 王安琦, 马晖玲. 甘肃野生草地早熟禾种质种子产量相关性状分析及其对矿质元素利用效应评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 54-67. |
| [2] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [3] | 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 向达兵, 邬晓勇, 吴琪, 刘长英, 范昱, 邹亮. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| [4] | 戈建珍, 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村. 多菌灵在果园白三叶青贮中的降解及其对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 64-75. |
| [5] | 南志标, 王彦荣, 贺金生, 胡小文, 刘志鹏, 李春杰, 聂斌, 夏超. 我国草种业的成就、挑战与展望[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 1-10. |
| [6] | 韩重阳, 王栓, 左粟田, 闫三博, 汪阳, 蔡家邦, 马骢毓, 张新全, 聂刚. 10个白三叶品种在成都平原的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 105-117. |
| [7] | 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献, 张吉宇, 谢文刚, 方龙发, 王彦荣, 南志标. 中国牧草育种中的若干科学问题[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 184-193. |
| [8] | 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 宫文龙. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| [9] | 王如月, 袁世力, 文武武, 周鹏, 安渊. 磷对铝胁迫紫花苜蓿幼苗根系生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 53-62. |
| [10] | 杨凯, 史娟, 袁玉涛, 王立婷. 白三叶草叶片感染白粉病的细胞生理变化及其病原鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 92-104. |
| [11] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 贾瑜琀. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. |
| [12] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| [13] | 侯洁茹, 段晓玥, 李州, 彭燕. 白三叶TrSAMDC1克隆及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 170-178. |
| [14] | 雷雄, 游明鸿, 白史且, 陈丽丽, 邓培华, 熊毅, 熊艳丽, 余青青, 马啸, 杨建, 张昌兵. 川西北高原50份燕麦种质农艺性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 131-142. |
| [15] | 魏勇, 王晓瑜, 李应德, 段廷玉. AM真菌在白三叶-黑麦草体系中对抗逆信号的传导作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 138-146. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||