

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 180-189.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022354
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-08-31
修回日期:2022-10-10
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-03-20
通讯作者:
刘秦华
作者简介:E-mail: liuqinhua@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Meng-qi LIANG( ), Qi-feng WU, Tao SHAO, Ai-li WU, Qin-hua LIU(
), Qi-feng WU, Tao SHAO, Ai-li WU, Qin-hua LIU( )
)
Received:2022-08-31
Revised:2022-10-10
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-03-20
Contact:
Qin-hua LIU
摘要:
为提高多花黑麦草青贮发酵品质,减少α-生育酚、β-胡萝卜素含量损失,以无添加为对照,研究了添加剂:0.4%丙酸(PA)、植物乳杆菌(LP)、环状芽孢杆菌(BC)、植物乳杆菌和环状芽孢杆菌菌株混合添加(LP+BC)对青贮发酵品质、α-生育酚和β-胡萝卜素的影响,在青贮3、7、35和70 d后开窖取样,检测发酵品质、营养成分、α-生育酚和β-胡萝卜素含量。结果表明:添加剂对多花黑麦草发酵品质有显著影响(P<0.05),LP+BC组提高青贮发酵品质的效果最好,其次为LP组。青贮70 d后,与对照组相比,添加剂组均降低了饲料的pH,且pH都在4.0以下。LP、BC和LP+BC组提高了乳酸含量和乳酸乙酸比(P<0.05);PA组在青贮初期抑制了乳酸发酵,后期提高了青贮发酵品质,但提高效果不如其余3种添加剂。在各个青贮时期,PA组的α-生育酚含量均显著高于其余4组(P<0.05);在青贮35和70 d时,除PA组外,LP组α-生育酚含量最高(P<0.05)。青贮7 d后,各添加剂组β-胡萝卜素含量均显著高于对照组(P<0.05),LP组在青贮7和35 d时β-胡萝卜素含量最高(P<0.05)。综上所述,LP组处理下多花黑麦草青贮发酵品质良好且减少了α-生育酚含量损失,增加了β-胡萝卜素含量。
梁梦琪, 武齐丰, 邵涛, 吴艾丽, 刘秦华. 添加剂对多花黑麦草青贮发酵品质、α-生育酚和β-胡萝卜素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 180-189.
Meng-qi LIANG, Qi-feng WU, Tao SHAO, Ai-li WU, Qin-hua LIU. Effects of additives on the fermentation quality and α-tocopherol and β-carotene contents in Italian ryegrass silage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(5): 180-189.
| 项目Items | 含量Content |
|---|---|
| pH | 6.07 |
| 缓冲能Buffering capacity (mEq·kg-1 DM) | 49.2 |
| 干物质Dry matter (g·kg-1 FW) | 302 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (g·kg-1 DM) | 7.23 |
| 水溶性碳水化合物Water soluble carbohydrates (g·kg-1 DM) | 233 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fibre (g·kg-1 DM) | 556 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fibre (g·kg-1 DM) | 306 |
| 酸性洗涤木质素Acid detergent lignin (g·kg-1 DM) | 57.4 |
| 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | 6.87 |
| 好氧性细菌Aerobic bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | 7.35 |
| 酵母菌Yeasts (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | 6.40 |
| 霉菌Mold (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | <1.00 |
| α-生育酚α-tocopherol (mg·kg-1 DM) | 15.3 |
| β-胡萝卜素β-carotene (mg·kg-1 DM) | 57.4 |
表1 青贮前多花黑麦草化学和微生物组成
Table 1 Chemical and microbial compositions ofItalian ryegrass before silage
| 项目Items | 含量Content |
|---|---|
| pH | 6.07 |
| 缓冲能Buffering capacity (mEq·kg-1 DM) | 49.2 |
| 干物质Dry matter (g·kg-1 FW) | 302 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (g·kg-1 DM) | 7.23 |
| 水溶性碳水化合物Water soluble carbohydrates (g·kg-1 DM) | 233 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fibre (g·kg-1 DM) | 556 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fibre (g·kg-1 DM) | 306 |
| 酸性洗涤木质素Acid detergent lignin (g·kg-1 DM) | 57.4 |
| 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | 6.87 |
| 好氧性细菌Aerobic bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | 7.35 |
| 酵母菌Yeasts (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | 6.40 |
| 霉菌Mold (lg cfu·g-1 FW) | <1.00 |
| α-生育酚α-tocopherol (mg·kg-1 DM) | 15.3 |
| β-胡萝卜素β-carotene (mg·kg-1 DM) | 57.4 |
青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | 添加剂 Additive | pH | 乳酸 Lactic acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 乙酸 Acetic acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 丙酸 Propionic acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 丁酸 Butyric acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 乙醇 Ethanol (g·kg-1 DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 4.79a | 78.0jkl | 6.76g | 2.83cde | 9.31defg | 0.016 |
| PA | 4.84a | 71.1kl | 8.21fg | 16.08a | 5.75efg | 0.012 | |
| LP | 4.18c | 126.2fgh | 8.63efg | 2.72cde | 6.51efg | 0.020 | |
| BC | 4.19c | 106.9ghij | 6.87fg | 2.78cde | 7.79efg | 0.003 | |
| LP+BC | 4.07d | 138.6defg | 8.22fg | 2.73cde | 7.55efg | ND | |
| 7 | CK | 4.46b | 97.3hijk | 7.86fg | 2.02cde | 12.18cd | 0.040 |
| PA | 4.54b | 82.9ijkl | 9.43defg | 17.15a | 8.80defg | 0.053 | |
| LP | 3.90efg | 162.7cde | 10.17cdefg | 1.83de | 8.20defg | 0.003 | |
| BC | 3.85g | 168.8bcd | 8.72efg | 2.25cde | 8.38defg | ND | |
| LP+BC | 3.87fg | 157.3cdef | 8.75efg | 1.80de | 8.76defg | 0.038 | |
| 35 | CK | 3.98def | 124.6gh | 13.52abc | 1.39e | 18.03a | 0.012 |
| PA | 3.93efg | 127.2fgh | 16.99a | 15.46a | 13.67bc | ND | |
| LP | 3.58ij | 197.1ab | 12.43cde | 4.16c | 8.05defg | ND | |
| BC | 3.74h | 185.2bc | 10.33cdefg | 4.05cd | 9.54def | 0.007 | |
| LP+BC | 3.55j | 183.3bc | 10.91cdef | 2.73cde | 7.75efg | 0.038 | |
| 70 | CK | 4.25c | 61.0l | 6.35g | 1.16e | 16.49ab | 0.006 |
| PA | 4.00de | 110.7ghi | 16.30ab | 11.24b | 10.08cde | 0.006 | |
| LP | 3.71h | 130.6fg | 9.09efg | 2.18cde | 5.58fg | 0.037 | |
| BC | 3.71h | 135.1efg | 8.25fg | 2.77cde | 4.93g | 0.025 | |
| LP+BC | 3.68hi | 217.3a | 13.06bcd | 3.19cde | 8.99defg | 0.007 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time (d) | |||||||
| 3 | 4.41a | 104.2c | 7.74c | 5.43a | 7.38b | 0.010 | |
| 7 | 4.12b | 133.8b | 8.98bc | 5.01a | 9.26ab | 0.027 | |
| 35 | 3.76c | 163.5a | 12.84a | 5.56a | 11.41a | 0.011 | |
| 70 | 3.87c | 130.9b | 10.61b | 4.11b | 9.22ab | 0.016 | |
| 添加剂Additive | |||||||
| CK | 4.37a | 90.2c | 8.62b | 1.85b | 14.00a | 0.018 | |
| PA | 4.33a | 97.9c | 12.73a | 14.98a | 9.58b | 0.018 | |
| LP | 3.85b | 154.2ab | 10.08b | 2.72b | 7.08b | 0.015 | |
| BC | 3.87b | 148.9b | 8.54b | 2.96b | 7.67b | 0.009 | |
| LP+BC | 3.79b | 174.1a | 10.24b | 2.61b | 8.27b | 0.021 | |
| 标准误Standard error | 0.04 | 5.16 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.472 | |
| 显著性Significance | |||||||
| 添加剂Additive | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.785 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.255 | |
| 交互作用Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.110 | |
表2 添加剂和青贮时间对多花黑麦草pH和有机酸含量的影响
Table 2 Effects of additive and ensiling time on the pH and organic acid content of Italian ryegrass silage
青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | 添加剂 Additive | pH | 乳酸 Lactic acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 乙酸 Acetic acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 丙酸 Propionic acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 丁酸 Butyric acid (g·kg-1 DM) | 乙醇 Ethanol (g·kg-1 DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 4.79a | 78.0jkl | 6.76g | 2.83cde | 9.31defg | 0.016 |
| PA | 4.84a | 71.1kl | 8.21fg | 16.08a | 5.75efg | 0.012 | |
| LP | 4.18c | 126.2fgh | 8.63efg | 2.72cde | 6.51efg | 0.020 | |
| BC | 4.19c | 106.9ghij | 6.87fg | 2.78cde | 7.79efg | 0.003 | |
| LP+BC | 4.07d | 138.6defg | 8.22fg | 2.73cde | 7.55efg | ND | |
| 7 | CK | 4.46b | 97.3hijk | 7.86fg | 2.02cde | 12.18cd | 0.040 |
| PA | 4.54b | 82.9ijkl | 9.43defg | 17.15a | 8.80defg | 0.053 | |
| LP | 3.90efg | 162.7cde | 10.17cdefg | 1.83de | 8.20defg | 0.003 | |
| BC | 3.85g | 168.8bcd | 8.72efg | 2.25cde | 8.38defg | ND | |
| LP+BC | 3.87fg | 157.3cdef | 8.75efg | 1.80de | 8.76defg | 0.038 | |
| 35 | CK | 3.98def | 124.6gh | 13.52abc | 1.39e | 18.03a | 0.012 |
| PA | 3.93efg | 127.2fgh | 16.99a | 15.46a | 13.67bc | ND | |
| LP | 3.58ij | 197.1ab | 12.43cde | 4.16c | 8.05defg | ND | |
| BC | 3.74h | 185.2bc | 10.33cdefg | 4.05cd | 9.54def | 0.007 | |
| LP+BC | 3.55j | 183.3bc | 10.91cdef | 2.73cde | 7.75efg | 0.038 | |
| 70 | CK | 4.25c | 61.0l | 6.35g | 1.16e | 16.49ab | 0.006 |
| PA | 4.00de | 110.7ghi | 16.30ab | 11.24b | 10.08cde | 0.006 | |
| LP | 3.71h | 130.6fg | 9.09efg | 2.18cde | 5.58fg | 0.037 | |
| BC | 3.71h | 135.1efg | 8.25fg | 2.77cde | 4.93g | 0.025 | |
| LP+BC | 3.68hi | 217.3a | 13.06bcd | 3.19cde | 8.99defg | 0.007 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time (d) | |||||||
| 3 | 4.41a | 104.2c | 7.74c | 5.43a | 7.38b | 0.010 | |
| 7 | 4.12b | 133.8b | 8.98bc | 5.01a | 9.26ab | 0.027 | |
| 35 | 3.76c | 163.5a | 12.84a | 5.56a | 11.41a | 0.011 | |
| 70 | 3.87c | 130.9b | 10.61b | 4.11b | 9.22ab | 0.016 | |
| 添加剂Additive | |||||||
| CK | 4.37a | 90.2c | 8.62b | 1.85b | 14.00a | 0.018 | |
| PA | 4.33a | 97.9c | 12.73a | 14.98a | 9.58b | 0.018 | |
| LP | 3.85b | 154.2ab | 10.08b | 2.72b | 7.08b | 0.015 | |
| BC | 3.87b | 148.9b | 8.54b | 2.96b | 7.67b | 0.009 | |
| LP+BC | 3.79b | 174.1a | 10.24b | 2.61b | 8.27b | 0.021 | |
| 标准误Standard error | 0.04 | 5.16 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.472 | |
| 显著性Significance | |||||||
| 添加剂Additive | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.785 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.255 | |
| 交互作用Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.110 | |
青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | 添加剂 Additive | 干物质 Dry matter (g·kg-1) | 氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia nitrogen/ total nitrogen (g·kg-1 N) | 乳酸/乙酸 Lactic acid/ acetic acid (LA/AA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 278 | 58.4g | 11.71fgh |
| PA | 286 | 83.9efg | 8.79hi | |
| LP | 285 | 62.5g | 14.90cde | |
| BC | 282 | 111.3cde | 15.57bcd | |
| LP+BC | 276 | 162.4b | 16.97abcd | |
| 7 | CK | 275 | 152.4bc | 12.39efg |
| PA | 285 | 202.8a | 8.96hi | |
| LP | 281 | 154.4b | 16.41abcd | |
| BC | 264 | 138.9bcd | 19.39a | |
| LP+BC | 284 | 128.7bcd | 18.49ab | |
| 35 | CK | 283 | 87.1efg | 9.25hi |
| PA | 285 | 134.2bcd | 7.50i | |
| LP | 283 | 105.5def | 16.07bcd | |
| BC | 286 | 106.3def | 18.00abc | |
| LP+BC | 284 | 67.0fg | 16.97abcd | |
| 70 | CK | 280 | 131.3bcd | 9.86ghi |
| PA | 285 | 168.5ab | 6.89i | |
| LP | 283 | 73.1efg | 14.27def | |
| BC | 285 | 141.0bcd | 16.87abcd | |
| LP+BC | 284 | 149.7bc | 16.64abcd | |
| 青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | ||||
| 3 | 282 | 95.7c | 13.59b | |
| 7 | 278 | 155.5a | 15.13a | |
| 35 | 284 | 100.0c | 13.56b | |
| 70 | 283 | 132.8b | 12.91b | |
| 添加剂 Additive | ||||
| CK | 279 | 107.3cd | 10.80c | |
| PA | 285 | 147.4a | 8.04d | |
| LP | 283 | 99.0d | 15.41b | |
| BC | 279 | 121.7bc | 17.46a | |
| LP+BC | 282 | 124.4b | 17.27a | |
| 标准误Standard error | 1.10 | 5.08 | 0.25 | |
| 显著性Significance | ||||
| 添加剂Additive | 0.322 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time | 0.204 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 交互作用Interaction | 0.509 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
表3 添加剂和青贮时间对多花黑麦草干物质、氨态氮/总氮和乳酸/乙酸的影响
Table 3 Effects of additive and ensiling time on the dry matter, ammonia nitrogen/total nitrogen and lactic acid/acetic acid of Italian ryegrass silage
青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | 添加剂 Additive | 干物质 Dry matter (g·kg-1) | 氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia nitrogen/ total nitrogen (g·kg-1 N) | 乳酸/乙酸 Lactic acid/ acetic acid (LA/AA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 278 | 58.4g | 11.71fgh |
| PA | 286 | 83.9efg | 8.79hi | |
| LP | 285 | 62.5g | 14.90cde | |
| BC | 282 | 111.3cde | 15.57bcd | |
| LP+BC | 276 | 162.4b | 16.97abcd | |
| 7 | CK | 275 | 152.4bc | 12.39efg |
| PA | 285 | 202.8a | 8.96hi | |
| LP | 281 | 154.4b | 16.41abcd | |
| BC | 264 | 138.9bcd | 19.39a | |
| LP+BC | 284 | 128.7bcd | 18.49ab | |
| 35 | CK | 283 | 87.1efg | 9.25hi |
| PA | 285 | 134.2bcd | 7.50i | |
| LP | 283 | 105.5def | 16.07bcd | |
| BC | 286 | 106.3def | 18.00abc | |
| LP+BC | 284 | 67.0fg | 16.97abcd | |
| 70 | CK | 280 | 131.3bcd | 9.86ghi |
| PA | 285 | 168.5ab | 6.89i | |
| LP | 283 | 73.1efg | 14.27def | |
| BC | 285 | 141.0bcd | 16.87abcd | |
| LP+BC | 284 | 149.7bc | 16.64abcd | |
| 青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | ||||
| 3 | 282 | 95.7c | 13.59b | |
| 7 | 278 | 155.5a | 15.13a | |
| 35 | 284 | 100.0c | 13.56b | |
| 70 | 283 | 132.8b | 12.91b | |
| 添加剂 Additive | ||||
| CK | 279 | 107.3cd | 10.80c | |
| PA | 285 | 147.4a | 8.04d | |
| LP | 283 | 99.0d | 15.41b | |
| BC | 279 | 121.7bc | 17.46a | |
| LP+BC | 282 | 124.4b | 17.27a | |
| 标准误Standard error | 1.10 | 5.08 | 0.25 | |
| 显著性Significance | ||||
| 添加剂Additive | 0.322 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time | 0.204 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 交互作用Interaction | 0.509 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | 添加剂 Additive | 好氧性细菌 Aerobic bacteria | 酵母菌 Yeasts | 霉菌 Mold | 乳酸菌 Lactic acid bacteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 6.71a | <3.00g | <3.00b | 9.25ab |
| PA | 6.52ab | <3.00g | 4.68a | 9.48ab | |
| LP | 6.19b | 4.75efg | 4.68a | 9.36ab | |
| BC | 6.37ab | 6.31a | <3.00b | 9.33ab | |
| LP+BC | 6.54ab | 4.81efg | <3.00b | 9.48ab | |
| 7 | CK | 6.73a | 5.60bcd | <3.00b | 9.39ab |
| PA | 6.62a | 5.06defg | 4.68a | 9.60a | |
| LP | 4.83d | 4.68fg | <3.00b | 9.37ab | |
| BC | 6.36ab | 5.32cde | 4.72a | 9.10b | |
| LP+BC | 4.93d | 4.68fg | <3.00b | 9.14ab | |
| 35 | CK | 5.51c | 5.88abc | <3.00b | 8.34cd |
| PA | 5.65c | 5.52bcd | <3.00b | 8.60c | |
| LP | 5.44c | 5.73bc | 4.75a | 9.22ab | |
| BC | 5.55c | 5.49bcd | <3.00b | 9.15ab | |
| LP+BC | 4.90d | 5.94ab | <3.00b | 9.19ab | |
| 70 | CK | 4.87d | 4.68fg | 4.68a | 7.92de |
| PA | 4.79d | 4.62g | <3.00b | 8.08d | |
| LP | 4.72d | 5.00defg | <3.00b | 7.60e | |
| BC | 4.60d | 5.04defg | <3.00b | 7.53e | |
| LP+BC | 4.87d | 5.28cdef | <3.00b | 7.60e | |
| 青贮时间 Ensiling time(d) | |||||
| 3 | 6.47a | 5.02b | 3.43a | 9.38a | |
| 7 | 5.89b | 5.07b | 3.44a | 9.32a | |
| 35 | 5.41c | 5.71a | 3.03b | 8.90b | |
| 70 | 4.77d | 4.92b | 3.02c | 7.75c | |
| 添加剂 Additive | |||||
| CK | 5.95a | 5.19b | 3.12b | 8.72 | |
| PA | 5.90ab | 4.95b | 3.64a | 8.94 | |
| LP | 5.29c | 5.04b | 3.66a | 8.89 | |
| BC | 5.72b | 5.54a | 3.13b | 8.78 | |
| LP+BC | 5.31c | 5.18b | <3.00c | 8.85 | |
| 标准误Standard error | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.08 | |
| 显著性Significance | |||||
| 添加剂Additive | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.247 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 交互作用Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
表4 添加剂和青贮时间对多花黑麦草微生物组成的影响
Table 4 Effects of additive and ensiling time on the microbial composition of Italian ryegrass silage (lg cfu·g-1 FW)
青贮时间 Ensiling time (d) | 添加剂 Additive | 好氧性细菌 Aerobic bacteria | 酵母菌 Yeasts | 霉菌 Mold | 乳酸菌 Lactic acid bacteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 6.71a | <3.00g | <3.00b | 9.25ab |
| PA | 6.52ab | <3.00g | 4.68a | 9.48ab | |
| LP | 6.19b | 4.75efg | 4.68a | 9.36ab | |
| BC | 6.37ab | 6.31a | <3.00b | 9.33ab | |
| LP+BC | 6.54ab | 4.81efg | <3.00b | 9.48ab | |
| 7 | CK | 6.73a | 5.60bcd | <3.00b | 9.39ab |
| PA | 6.62a | 5.06defg | 4.68a | 9.60a | |
| LP | 4.83d | 4.68fg | <3.00b | 9.37ab | |
| BC | 6.36ab | 5.32cde | 4.72a | 9.10b | |
| LP+BC | 4.93d | 4.68fg | <3.00b | 9.14ab | |
| 35 | CK | 5.51c | 5.88abc | <3.00b | 8.34cd |
| PA | 5.65c | 5.52bcd | <3.00b | 8.60c | |
| LP | 5.44c | 5.73bc | 4.75a | 9.22ab | |
| BC | 5.55c | 5.49bcd | <3.00b | 9.15ab | |
| LP+BC | 4.90d | 5.94ab | <3.00b | 9.19ab | |
| 70 | CK | 4.87d | 4.68fg | 4.68a | 7.92de |
| PA | 4.79d | 4.62g | <3.00b | 8.08d | |
| LP | 4.72d | 5.00defg | <3.00b | 7.60e | |
| BC | 4.60d | 5.04defg | <3.00b | 7.53e | |
| LP+BC | 4.87d | 5.28cdef | <3.00b | 7.60e | |
| 青贮时间 Ensiling time(d) | |||||
| 3 | 6.47a | 5.02b | 3.43a | 9.38a | |
| 7 | 5.89b | 5.07b | 3.44a | 9.32a | |
| 35 | 5.41c | 5.71a | 3.03b | 8.90b | |
| 70 | 4.77d | 4.92b | 3.02c | 7.75c | |
| 添加剂 Additive | |||||
| CK | 5.95a | 5.19b | 3.12b | 8.72 | |
| PA | 5.90ab | 4.95b | 3.64a | 8.94 | |
| LP | 5.29c | 5.04b | 3.66a | 8.89 | |
| BC | 5.72b | 5.54a | 3.13b | 8.78 | |
| LP+BC | 5.31c | 5.18b | <3.00c | 8.85 | |
| 标准误Standard error | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.08 | |
| 显著性Significance | |||||
| 添加剂Additive | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.247 | |
| 青贮时间Ensiling time | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 交互作用Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
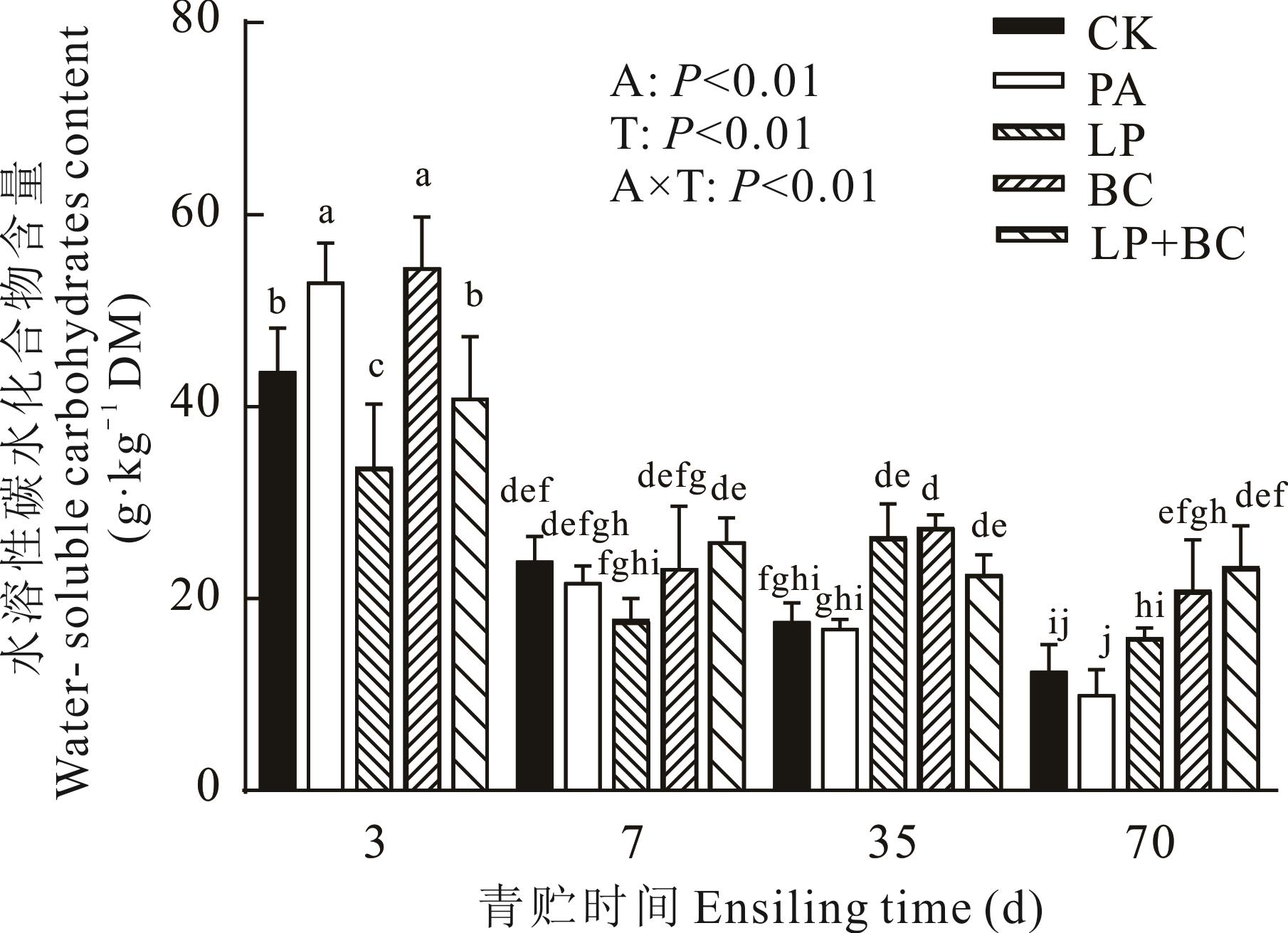
图1 添加剂和青贮时间对多花黑麦草青贮饲料水溶性碳水化合物含量的影响CK: 无添加No addition; PA: 0.4%丙酸0.4% propionic acid; LP: 植物乳杆菌L. plantarum B11; BC: 环状芽孢杆菌B. circulans 12; LP+BC: 植物乳杆菌及环状芽孢杆菌L. plantarum B11 and B. circulans 12. 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). A: 添加剂Additive; T: 贮藏时间Ensiling time; A×T: 添加剂和贮藏时间交互作用Interaction between additive and ensiling time. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of additive and ensiling time on the water-soluble carbohydrates content of Italian ryegrass silage
| 1 | Chen T D, Zhao X D, Li Y S, et al. Research progress of nutritional quality and animal feeding of Lolium multiflorum. Feed Research, 2020, 10(43): 146-149. |
| 陈腾达, 赵晓登, 李玉帅, 等. 多花黑麦草营养品质及在动物饲养方面的研究进展. 饲料研究, 2020, 10(43): 146-149. | |
| 2 | Yang J. Effects of complex silage additive treatments on fermentation quality of Italian ryegrass silage. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2007. |
| 杨杰. 复合青贮剂处理对多花黑麦草青贮品质的影响. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2007. | |
| 3 | Ding C L. Function and cultivation technique of Italian ryegrass in the agriculture system of rural area of South China. Chinese Journal of Rabbit Farming, 2008(11): 15-17. |
| 丁成龙. 多花黑麦草在南方农区农业结构中的作用及其栽培利用技术. 中国养兔杂志, 2008(11): 15-17. | |
| 4 | Liu Q H, Li X Y, Li J F, et al. Effect of temperature and additives on fermentation and α-tocopherol and β-carotene content of Pennisetum purpureum silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(7): 116-122. |
| 刘秦华, 李湘玉, 李君风, 等. 温度和添加剂对象草青贮发酵品质、α-生育酚和β-胡萝卜素的影响. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 116-122. | |
| 5 | Lindqvist H, Nadeau E, Jensen S K. Alpha-tocopherol and β-carotene in legume-grass mixtures as influenced by wilting, ensiling and type of silage additive. Grass & Forage Science, 2012, 67(1): 119-128. |
| 6 | Nadeau E, Johanssonb B, Jensen S K, et al. Vitamin content of forages as influenced by harvest and ensiling techniques. Grassland and Science in Europe, 2004, 9(1): 891-893. |
| 7 | Zhang Y X, Ke W C, Bal J, et al. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici J17 with high-antioxidant activity on antioxidant, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, fatty acids, and fermentation profiles of alfalfa silage ensiled at two different dry matter contents. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2020, 268: 114614. |
| 8 | Liu Q H, Wu J X, Shao T. Roles of microbes and lipolytic enzymes in changing the fatty acid profile, α-tocopherol and β-carotene of whole-crop oat silages during ensiling and after exposure to air. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2019, 253(48): 81-92. |
| 9 | Zong C, Zhang J, Shao T, et al. Effects of additives on fermentation quality of alfalfa silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 180-187. |
| 宗成, 张健, 邵涛, 等. 添加剂对紫花苜蓿青贮饲料发酵品质的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 180-187. | |
| 10 | Susanti E. Production optimization and cellulose system characterization of Bacillus circulans local strain using inducer avicel. Jurnal Ilmu Dasar, 2012, 12(1): 40-49. |
| 11 | Aamod A N, Sharad L, Shilpa P, et al. Evaluation of Bacillus circulans in imparting aerobic stability to silage. International Journal of Modern Science and Technology, 2017, 2(12): 391-396. |
| 12 | Xiao S H, Yuan X J, Dong Z H, et al. Effects of inoculant and molasses additives on fermentation quality of mixed silages of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) and common vetch (Vicia sativa L.). Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016, 39(6): 1017-1022. |
| 肖慎华, 原现军, 董志浩, 等. 添加乳酸菌制剂和糖蜜对箭筈豌豆和苇状羊茅混合青贮发酵品质的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 2016, 39(6): 1017-1022. | |
| 13 | Zhu J G, Zhang J, Shao T, et al. The effects of additives on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of whole-plant oat silage. Acta Agrestia Sincia, 2020, 28(6): 1756-1761. |
| 朱九刚, 张健, 邵涛, 等. 添加剂对全株燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质和有氧稳定性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1756-1761. | |
| 14 | Guo H M, Xia T C, Zhu W, et al. Effect of additives on the quality and aerobic stability of rice straw silage. Acta Prataculturae Sincia, 2017, 26(2): 190-196. |
| 郭海明, 夏天婵, 朱雯, 等. 青贮添加剂对稻草青贮品质和有氧稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 190-196. | |
| 15 | Liu Q H, Zhang J G, Lu X L. The effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculation on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of king grass silage. Acta Prataculturae Sincia, 2009, 18(4): 131-137. |
| 刘秦华, 张建国, 卢小良. 乳酸菌添加剂对王草青贮发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2009, 18(4): 131-137. | |
| 16 | Liu Q H, Li X Y, Seare T D, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and fibrolytic enzyme on the fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of total mixed rations silage including rape straw. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(9): 2087-2096. |
| 17 | Zhang Z X, Shao T. The effect of propionic acid addition on the dynamic fermentation changes of Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 18(2): 102-107. |
| 张增欣, 邵涛. 丙酸对多花黑麦草青贮发酵动态变化的影响. 草业学报, 2009, 18(2): 102-107. | |
| 18 | Hou M L, Du Z M, Fan W Q, et al. The effects of treating with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase on silage fermentation of natural grasses in meadow steppe. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2017, 48(5): 871-880. |
| 侯美玲, 杜珠梅, 范文强, 等. 乳酸菌与纤维素酶对草甸草原天然牧草青贮品质的影响. 畜牧兽医学报, 2017, 48(5): 871-880. | |
| 19 | Sun X L, Jian F C, Xu L P, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus plantarum on the quality of silage sorghum. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57(9): 159-163. |
| 孙向丽, 菅复春, 许来鹏, 等. 布氏乳杆菌和植物乳杆菌对高粱青贮品质的影响. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(9): 159-163. | |
| 20 | Kalac P. Carotenoids, ergosterol and tocopherols in fresh and preserved herbage and their transfer to bovine milk fat and adipose tissues: A review. Journal of Agrobiology, 2012, 29(1): 1-13. |
| 21 | Dunne P G, Monahan F, O’Mara F P, et al. Colour of bovine subcutaneous adipose tissue: A review of contributory factors, associations with carcass and meat quality and its potential utility in authentication of dietary history. Meat Science, 2009, 81(1): 28-45. |
| [1] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [2] | 李影正, 程榆林, 徐璐璐, 李万松, 严旭, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 周阳, 郑军军, 汪星宇, 张德龙, 程明军, 夏运红, 何建美, 唐祈林. 不同玉米品种(系)的全株、果穗与秸秆青贮特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [3] | 吴永杰, 丁浩, 邵涛, 赵杰, 董东, 代童童, 尹雪敬, 宗成, 李君风. 酶制剂对水稻秸秆青贮发酵品质及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 167-177. |
| [4] | 李君风, 赵杰, 唐小月, 代童童, 董东, 宗成, 邵涛. 瘤胃纤维素降解菌系对灭菌水稻秸秆结构性碳水化合物降解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. |
| [5] | 郭香, 吴硕, 郑明扬, 陈德奎, 邹璇, 陈晓阳, 周玮, 张庆. 添加黄梁木叶和壳寡糖对甘蔗梢青贮饲料发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 202-210. |
| [6] | 周迪, 杨帅, 张欣欣, 袁婧, 高艳霞, 李建国, 汪波, 周广生, 傅廷栋, 叶俊, 杨利国, 滑国华. 添加剂种类和组合对晾晒后全株油菜青贮效果的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 124-135. |
| [7] | 张欢, 牟怡晓, 张桂杰. 添加枸杞副产物对紫花苜蓿青贮发酵品质及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 136-144. |
| [8] | 李海萍, 关皓, 贾志锋, 刘文辉, 马祥, 刘勇, 汪辉, 马力, 周青平. 抗冻融乳酸菌的筛选及其对燕麦青贮品质和有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 158-170. |
| [9] | 王挺, 宋磊, 王旭哲, 马春晖, 杜保军, 张凡凡. 复合乳酸菌对番茄皮渣与苜蓿混合青贮发酵品质及瘤胃降解率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 167-177. |
| [10] | 郑娟善, 丁考仁青, 李新圃, 梁泽毅, 张剑搏, 杜梅, 丁学智. 瘤胃微生物在木质纤维素价值化利用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 182-192. |
| [11] | 杨冬梅, 李俊年, 陶双伦. 添加单宁酸对青贮葛藤有氧稳定性和霉菌毒素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 164-170. |
| [12] | 郭香, 陈德奎, 陈娜, 李云, 陈晓阳, 张庆. 含水量和添加剂对黄梁木叶青贮发酵品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 199-205. |
| [13] | 尹祥, 王咏琪, 李鑫琴, 田静, 王晓亚, 张建国. 不同水分吸附材料对象草青贮发酵品质及好氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 133-138. |
| [14] | 肖逸, 杨忠富, 聂刚, 韩佳婷, 帅杨, 张新全. 12个多花黑麦草品种(系)在成都平原的生产性能和营养价值综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 174-185. |
| [15] | 袁洁, 马冉冉, 张文洁, 许能祥, 赵冉冉, 顾洪如, 丁成龙. 自然青贮多花黑麦草优良乳酸菌的筛选及对多花黑麦草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 132-143. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||