

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 129-140.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022437
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
李想1( ), 张梦2, 刘春增2, 朱益飞3, 叶晓馨1(
), 张梦2, 刘春增2, 朱益飞3, 叶晓馨1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-03
修回日期:2022-12-07
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
叶晓馨
作者简介:E-mail: yexx@ahu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xiang LI1( ), Meng ZHANG2, Chun-zeng LIU2, Yi-fei ZHU3, Xiao-xin YE1(
), Meng ZHANG2, Chun-zeng LIU2, Yi-fei ZHU3, Xiao-xin YE1( )
)
Received:2022-11-03
Revised:2022-12-07
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-07-26
Contact:
Xiao-xin YE
摘要:
为打破紫云英种子硬实,提高种子活力和发芽一致性,本研究以赣紫75-3-51和信紫1号为供试材料,采用室内发芽试验探讨了不同剂量等离子体处理(7、8、9 kV电压分别处理1、3、5、10 min)对紫云英种子活力、幼苗生长、抗氧化酶活性以及渗透调节物质含量的影响,以期为紫云英种子播前处理技术提供参考。结果表明:等离子体处理对2种紫云英种子的发芽率和发芽势没有显著影响,但提高了紫云英种子活力。不同品种紫云英对等离子体处理的响应存在差异。等离子体处理对赣紫75-3-51生长存在低促高抑的现象,幼苗鲜重以及胚芽长度均随处理时间增加呈单峰曲线变化。信紫1号幼苗鲜重在高剂量(9 kV处理10 min)等离子体处理条件下显著降低,较对照降低了20.5%。赣紫75-3-51幼苗的超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物酶的活性随处理电压和时间的增加均表现为先升高后下降的变化趋势。信紫1号的两种抗氧化酶活性在低电压下(7 kV)随处理时间增加呈上升趋势,而在高电压下无显著变化。此外,低剂量等离子体处理提高了2种紫云英幼苗渗透调节物质含量。虽然等离子体处理对供试紫云英萌发无显著影响,但适宜的等离子体处理可激发紫云英种子抗氧化酶活性,促进大分子糖类和蛋白质的溶解,从而提高紫云英种子活力,促进幼苗生长。
李想, 张梦, 刘春增, 朱益飞, 叶晓馨. 等离子体处理对紫云英种子萌发和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 129-140.
Xiang LI, Meng ZHANG, Chun-zeng LIU, Yi-fei ZHU, Xiao-xin YE. Effects of dialectric barrier discharge plasma treatment on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Astragalus sinicus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 129-140.
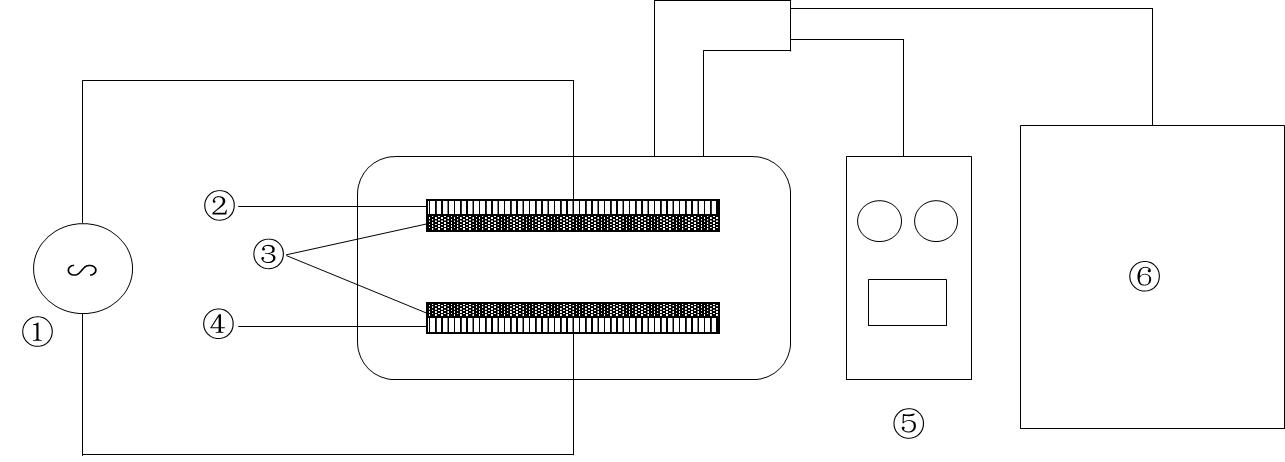
图1 低温等离子体种子处理装置原理① 纳秒脉冲等离子源 Nanosecond pulsed plasma; ② 高压电极 High voltage electrode; ③ 绝缘介质 Insulating medium; ④ 接地电极 Earth electrode; ⑤ 气压计 Barometer; ⑥ 真空泵 Vacuum pump.
Fig.1 Schematic of low-temperature plasma seed treatment device
因素 Factor | df | 信紫Xinzi | 赣紫Ganzi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
发芽率 Germination rate | 发芽势 Germination potential | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Vigor index | 发芽率 Germination rate | 发芽势 Germination potential | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Vigor index | ||
| 电压Voltage | 2 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 1.63 | 0.23 | 1.03 | 1.62 |
| 时间Time | 4 | 1.13 | 0.68 | 2.88* | 1.98 | 0.50 | 0.85 | 3.69** | 7.97*** |
电压 Voltage | 8 | 1.28 | 0.52 | 1.96 | 2.20* | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 2.00 |
表1 等离子体处理对不同品种紫云英种子发芽指标影响的双因素方差分析
Table 1 Two-way ANOVA of the effect of plasma treatments on the germination of two cultivars of A. sinicus seeds
因素 Factor | df | 信紫Xinzi | 赣紫Ganzi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
发芽率 Germination rate | 发芽势 Germination potential | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Vigor index | 发芽率 Germination rate | 发芽势 Germination potential | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Vigor index | ||
| 电压Voltage | 2 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 1.63 | 0.23 | 1.03 | 1.62 |
| 时间Time | 4 | 1.13 | 0.68 | 2.88* | 1.98 | 0.50 | 0.85 | 3.69** | 7.97*** |
电压 Voltage | 8 | 1.28 | 0.52 | 1.96 | 2.20* | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 2.00 |

图2 等离子体处理对信紫和赣紫发芽指数和活力指数的影响不同字母表示相同电压下不同处理时间之间差异显著(P<0.05), 误差线表示标准误,下同。Different letters indicate significant differences among different treatment times under the same voltage at 0.05 level, error lines represent standard errors, the same below.
Fig.2 Effect of plasma treatment on germination index and seed vigor index of Xinzi and Ganzi
品种 Variety | 电压 Voltage (kV) | 时间 Time (min) | 胚根长 Radicle length (mm) | 胚芽长 Germ length (mm) | 根芽比 Root bud ratio | 鲜重 Fresh weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
信紫 Xinzi | CK | 24.6±1.4ab | 35.8±0.7a | 0.69±0.05ab | 0.88±0.04ab | |
| 7 | 1 | 24.5±1.1ab | 36.4±0.5a | 0.67±0.03ab | 0.83±0.01abcd | |
| 3 | 24.3±0.7ab | 37.2±1.0a | 0.66±0.03ab | 0.84±0.04abc | ||
| 5 | 24.6±0.8ab | 36.9±1.0a | 0.67±0.03ab | 0.90±0.03ab | ||
| 10 | 27.1±0.6a | 35.2±1.1a | 0.78±0.03a | 0.95±0.03a | ||
| 8 | 1 | 24.0±1.3ab | 38.1±1.3a | 0.64±0.04b | 0.86±0.03abc | |
| 3 | 22.4±1.0b | 36.2±0.4a | 0.62±0.02b | 0.90±0.01ab | ||
| 5 | 23.5±0.7ab | 36.7±0.6a | 0.64±0.02b | 0.84±0.04abc | ||
| 10 | 23.0±1.0b | 36.0±0.9a | 0.64±0.04b | 0.72±0.06cd | ||
| 9 | 1 | 23.9±1.0ab | 36.1±0.7a | 0.66±0.03ab | 0.86±0.02abc | |
| 3 | 23.6±0.8ab | 34.9±1.1a | 0.68±0.04ab | 0.90±0.06ab | ||
| 5 | 23.8±1.3ab | 37.2±0.7a | 0.64±0.03b | 0.80±0.05bcd | ||
| 10 | 22.3±1.0b | 35.1±0.9a | 0.64±0.04b | 0.70±0.04d | ||
赣紫 Ganzi | CK | 31.8±0.8a | 40.2±1.2e | 0.80±0.03a | 0.93±0.03bcd | |
| 7 | 1 | 30.6±0.8ab | 43.6±0.9bcd | 0.70±0.02bcd | 0.96±0.02ab | |
| 3 | 30.4±0.6ab | 45.9±0.7abcd | 0.66±0.02cdef | 0.98±0.03ab | ||
| 5 | 31.9±0.7a | 42.7±0.6de | 0.75±0.02ab | 1.01±0.02ab | ||
| 10 | 29.4±0.6ab | 46.3±1.7abc | 0.64±0.03def | 0.92±0.03bcd | ||
| 8 | 1 | 31.9±1.0a | 44.1±0.5bcd | 0.72±0.03bc | 0.98±0.02ab | |
| 3 | 30.0±0.4ab | 46.5±0.7ab | 0.65±0.01def | 1.01±0.03ab | ||
| 5 | 31.8±0.5a | 48.2±0.7a | 0.66±0.01cdef | 1.03±0.03a | ||
| 10 | 29.5±0.6ab | 43.4±0.5bcd | 0.68±0.01bcde | 0.87±0.03d | ||
| 9 | 1 | 28.9±0.8b | 48.2±0.9a | 0.60±0.01f | 0.97±0.02ab | |
| 3 | 31.0±1.0ab | 45.1±0.9abcd | 0.69±0.02bcde | 0.95±0.02abc | ||
| 5 | 30.9±0.5ab | 43.1±1.0cde | 0.72±0.02bcd | 0.86±0.02d | ||
| 10 | 29.0±0.9b | 46.7±0.7ab | 0.62±0.02ef | 0.87±0.03cd |
表2 等离子体处理对两个紫云英品种幼苗生长的影响
Table 2 Effect of plasma treatment on the growth of two cultivars of A. sinicus
品种 Variety | 电压 Voltage (kV) | 时间 Time (min) | 胚根长 Radicle length (mm) | 胚芽长 Germ length (mm) | 根芽比 Root bud ratio | 鲜重 Fresh weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
信紫 Xinzi | CK | 24.6±1.4ab | 35.8±0.7a | 0.69±0.05ab | 0.88±0.04ab | |
| 7 | 1 | 24.5±1.1ab | 36.4±0.5a | 0.67±0.03ab | 0.83±0.01abcd | |
| 3 | 24.3±0.7ab | 37.2±1.0a | 0.66±0.03ab | 0.84±0.04abc | ||
| 5 | 24.6±0.8ab | 36.9±1.0a | 0.67±0.03ab | 0.90±0.03ab | ||
| 10 | 27.1±0.6a | 35.2±1.1a | 0.78±0.03a | 0.95±0.03a | ||
| 8 | 1 | 24.0±1.3ab | 38.1±1.3a | 0.64±0.04b | 0.86±0.03abc | |
| 3 | 22.4±1.0b | 36.2±0.4a | 0.62±0.02b | 0.90±0.01ab | ||
| 5 | 23.5±0.7ab | 36.7±0.6a | 0.64±0.02b | 0.84±0.04abc | ||
| 10 | 23.0±1.0b | 36.0±0.9a | 0.64±0.04b | 0.72±0.06cd | ||
| 9 | 1 | 23.9±1.0ab | 36.1±0.7a | 0.66±0.03ab | 0.86±0.02abc | |
| 3 | 23.6±0.8ab | 34.9±1.1a | 0.68±0.04ab | 0.90±0.06ab | ||
| 5 | 23.8±1.3ab | 37.2±0.7a | 0.64±0.03b | 0.80±0.05bcd | ||
| 10 | 22.3±1.0b | 35.1±0.9a | 0.64±0.04b | 0.70±0.04d | ||
赣紫 Ganzi | CK | 31.8±0.8a | 40.2±1.2e | 0.80±0.03a | 0.93±0.03bcd | |
| 7 | 1 | 30.6±0.8ab | 43.6±0.9bcd | 0.70±0.02bcd | 0.96±0.02ab | |
| 3 | 30.4±0.6ab | 45.9±0.7abcd | 0.66±0.02cdef | 0.98±0.03ab | ||
| 5 | 31.9±0.7a | 42.7±0.6de | 0.75±0.02ab | 1.01±0.02ab | ||
| 10 | 29.4±0.6ab | 46.3±1.7abc | 0.64±0.03def | 0.92±0.03bcd | ||
| 8 | 1 | 31.9±1.0a | 44.1±0.5bcd | 0.72±0.03bc | 0.98±0.02ab | |
| 3 | 30.0±0.4ab | 46.5±0.7ab | 0.65±0.01def | 1.01±0.03ab | ||
| 5 | 31.8±0.5a | 48.2±0.7a | 0.66±0.01cdef | 1.03±0.03a | ||
| 10 | 29.5±0.6ab | 43.4±0.5bcd | 0.68±0.01bcde | 0.87±0.03d | ||
| 9 | 1 | 28.9±0.8b | 48.2±0.9a | 0.60±0.01f | 0.97±0.02ab | |
| 3 | 31.0±1.0ab | 45.1±0.9abcd | 0.69±0.02bcde | 0.95±0.02abc | ||
| 5 | 30.9±0.5ab | 43.1±1.0cde | 0.72±0.02bcd | 0.86±0.02d | ||
| 10 | 29.0±0.9b | 46.7±0.7ab | 0.62±0.02ef | 0.87±0.03cd |
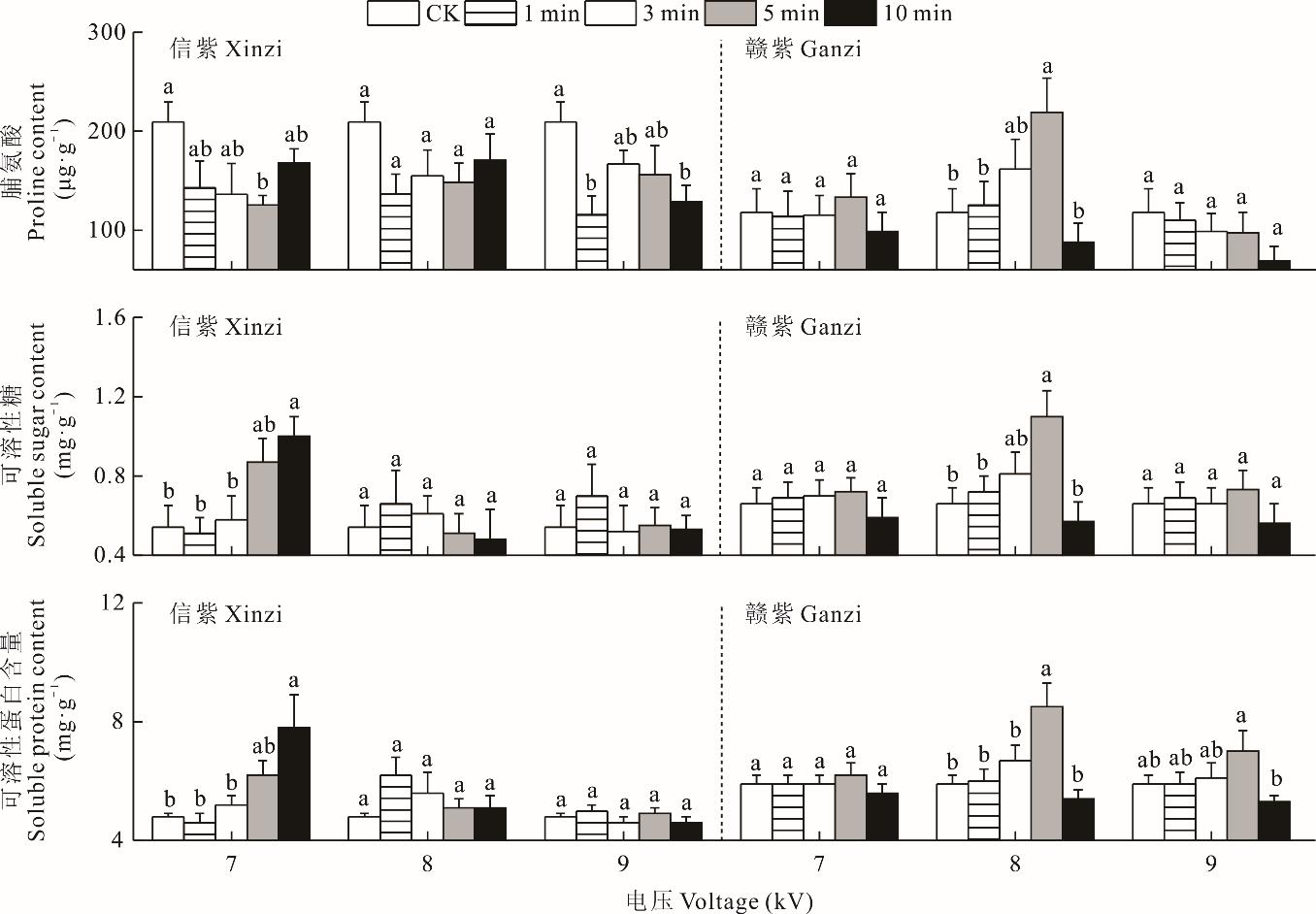
图6 等离子体处理对信紫和赣紫脯氨酸、可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白含量的影响
Fig.6 Effect of plasma treatment on the content of proline, soluble sugar and soluble protein in Xinzi and Ganzi seedlings
| 1 | Lin D H, Gu R S. Milk vetch in China. Fuzhou: Fujian Science and Technology Publishing House, 2000. |
| 林多胡, 顾荣申. 中国紫云英. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 2000. | |
| 2 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 3 | Lin X J, Cao W D, Wu Y Q, et al. Advance in Astragalus sinicus research. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(1): 135-140. |
| 林新坚, 曹卫东, 吴一群, 等. 紫云英研究进展. 草业科学, 2011, 28(1): 135-140. | |
| 4 | Ji C J, Li W, Liu S Y, et al. Development prospect of Chinese milk vetch under the background of ecological agriculture development. Contemporary Horticulture, 2021, 44(19): 66-67. |
| 季晨婕, 李薇, 刘深云, 等. 生态农业发展背景下紫云英的开发前景. 现代园艺, 2021, 44(19): 66-67. | |
| 5 | Li C X. A preliminary study on the characteristics of hard seeds of Chinese milk vetch. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 1982(3): 19-21. |
| 李长喜. 紫云英种子硬粒特性的初步研究. 河南农林科技, 1982(3): 19-21. | |
| 6 | Zhang M, Li B Y, Liu C Z, et al. A study of stratified maturity characteristics of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) pods and their seed yield. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(2): 64-72. |
| 张梦, 李本银, 刘春增, 等. 紫云英荚果分层成熟特性及其种子产量研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 64-72. | |
| 7 | Guo Q, Meng Y R, Qu G Z, et al. Improvement of wheat seed vitality by dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. Bioelectromagnetics, 2018, 39(2): 120-131. |
| 8 | Song J S, Kim S B, Ryu S, et al. Emerging plasma technology that alleviates crop stress during the early growth stages of plants: A review. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 988. |
| 9 | Jiresova J, Sera B, Scholtz V, et al. The dormancy overcoming and affection of early growth stages of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seeds by non-thermal plasma and plasma activated water. Romanian Reports in Physics, 2021, 73(4): 711. |
| 10 | Mazandarani A, Goudarzi S, Ghafoorifard H, et al. Evaluation of DBD plasma effects on barley seed germination and seedling growth. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(9): 3115-3121. |
| 11 | Fan Y J, Lu G X, Xu C T, et al. Effects of low-temperature plasma on seed germination and seeding characteristics of two kind of leguminous forage. Seed, 2016, 35(8): 47-49. |
| 范月君, 芦光新, 徐成体, 等. 冷等离子体处理对2种豆科牧草种子发芽及幼苗生长的影响. 种子, 2016, 35(8): 47-49. | |
| 12 | Xie C S. Preliminary study on the mechanism of air cold plasma promoting maize seed germination. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2020. |
| 谢成燊. 空气冷等离子体促进玉米种子萌发的机制的初步研究. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2020. | |
| 13 | Dobrin D, Magureanu M, Mandache N B, et al. The effect of non-thermal plasma treatment on wheat germination and early growth. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2015, 29: 255-260. |
| 14 | Ge Y Q, Wang M J, Zhou Z D. Study on stress resistance of plasma seed treatment technology. Agriculture Machinery Technology Extension, 2013(7): 44, 46. |
| 葛永群, 王明俊, 周志丹. 等离子体种子处理技术抗逆性研究. 农机科技推广, 2013(7): 44, 46. | |
| 15 | Tang X T, Zeng X D, Zhuo Y N, et al. Effects of air plasma treatment on seed germination, seeding and plant growth, and stress-tolerance of Andrographis paniculate (Burm.F.) Nees. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2017, 28(3): 383-387. |
| 汤小婷, 曾湘达, 卓一南, 等. 等离子体对穿心莲种子萌发、幼苗和植株生长及抗逆性的影响. 中药新药与临床药理, 2017, 28(3): 383-387. | |
| 16 | Guo Q, Wang Y, Zhang H R, et al. Alleviation of adverse effects of drought stress on wheat seed germination using atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-14. |
| 17 | Liu C Z, Lv Y H, Pan Z L, et al. Breeding of Xinzi No. 1, a new Chinese milk vetch cultivar with high yield and high quality. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2010(11): 42-44. |
| 刘春增, 吕玉虎, 潘兹亮, 等. 高产优质紫云英新品种信紫1号的选育. 河南农业科学, 2010(11): 42-44. | |
| 18 | Su J P, Liu C P, Wang X M, et al. Germplasm resources of green manure crops in Jiangxi and their application. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2012, 24(5): 100-103, 107. |
| 苏金平, 刘成鹏, 王晓明, 等. 江西绿肥作物种质资源及其应用. 江西农业学报, 2012, 24(5): 100-103, 107. | |
| 19 | Zhang M, Shi P F, Li B Y, et al. Phenotypic diversity and podding characteristics of 70 Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) germplasm lines cultivated in Southern Henan. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 168-180. |
| 张梦, 史鹏飞, 李本银, 等. 70份紫云英种质资源表型多样性及其在豫南地区的结实特征. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 168-180. | |
| 20 | Tao Q B, Sun J P, Nie Y T, et al. Evaluation of seed vigor and prediction of field seeding emergence of Chinese milk vetch(Astragalus sinicus L.) by conductivity method. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 95-103. |
| 陶奇波, 孙继鹏, 聂宇婷, 等. 电导率法评价紫云英种子活力并预测田间出苗表现. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 95-103. | |
| 21 | Li X Y, Chen H Z, Han R. Effect of UV-B irradiation on seed germination and seeding growth of Arabidopsis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 52-58. |
| 李晓阳, 陈慧泽, 韩榕. UV-B辐射对拟南芥种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 植物学报, 2013, 48(1): 52-58. | |
| 22 | Xu X M, Lv P H, Zhao Y J, et al. On seed vigor of Astragaius sinicus with different colors through low temperature germination. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 2021, 36(2): 16-19. |
| 徐小萌, 吕鹏辉, 赵阳佳, 等. 利用低温萌发试验评价不同颜色紫云英种子的活力. 北京农学院学报, 2021, 36(2): 16-19. | |
| 23 | Qi W C, Zhang L, Feng W S, et al. ROS and ABA signaling are involved in the growth stimulation induced by low-dose gamma irradiation in Arabidopsis seedling. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2015, 175(3): 1490-1506. |
| 24 | Gao J X, Wang Y N, Li P X, et al. Effects of lacquer wax coating on postharvest browning of fresh lotus pods. Food Science, 2016, 37(18): 275-282. |
| 高建晓, 王毓宁, 李鹏霞, 等. 漆蜡涂膜对鲜莲蓬采后褐变的影响. 食品科学, 2016, 37(18): 275-282. | |
| 25 | Zou Q. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: Beijing Agricultural Publishing House, 2000: 161-250. |
| 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 北京农业出版社, 2000: 161-250. | |
| 26 | Nalwa C, Thakur A K. Seed quality enhancement through plasma treatment: A review. Indian Journal of Ecology, 2018, 45: 814-821. |
| 27 | Sera B, Sery M, Stranak V, et al. Does cold plasma affect breaking dormancy and seed germination? A study on seeds of Lamb’s Quarters (Chenopodium album agg.). Plasma Science and Technology, 2009, 11(6): 749-754. |
| 28 | Wang M, Yang S Z, Chen Q Y, et al. Effects of atmospheric pressure plasma on seed germination and seedling growth of cucumber. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2007, 23(2): 195-200. |
| 王敏, 杨思泽, 陈青云, 等. 大气压等离子体处理对黄瓜种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(2): 195-200. | |
| 29 | Li L, Jiang J F, Li J G, et al. Effects of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4(1): 1-7. |
| 30 | Argerich C A, Bradford K J. The effects of priming and ageing on seed vigour in tomato. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1989, 40(5): 599-607. |
| 31 | Staric P, Grobelnik M S, Junkar I. Response of two different wheat varieties to glow and afterglow oxygen plasma. Plants, 2021, 10(8): 1728. |
| 32 | Rasooli Z, Barzin G, Mahabadi T D, et al. Stimulating effects of cold plasma seed priming on germination and seedling growth of cumin plant. South African Journal of Botany, 2021, 142: 106-113. |
| 33 | Cui D J, Yin Y, Wang J Q, et al. Research on the physio-biochemical mechanism of non-thermal plasma-regulated seed germination and early seedling development in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1332. |
| 34 | Wang J M, Huang M M, Qiao W W, et al. Disinfection technology of cold plasma and its application in food. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(5): 55-62. |
| 王佳媚, 黄明明, 乔维维, 等. 冷源等离子体冷杀菌技术及其在食品中的应用研究. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(5): 55-62. | |
| 35 | Zhang L, Wang S R, Jiao L X, et al. Physiological response of a submerged plant (Myriophyllum spicatum) to different NH4Cl concentrations in sediments. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 58: 91-98. |
| 36 | Yuan G F, Jia C G, Li Z, et al. Effect of brassinosteroids on drought resistance and abscisic acid concentration in tomato under water stress. Scientia Horticulturae, 2010, 126(2): 103-108. |
| 37 | Li Y J, Wang T C, Meng Y R, et al. Air atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma induced germination and growth enhancement of wheat seed. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2017, 37(6): 1621-1634. |
| 38 | Xu J J. Study on the effects of different chemical priming on seed germination and seedling characteristics in non-heading Chinese cabbage. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 徐金金. 不同化学引发剂对不结球白菜种子引发效果的研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. | |
| 39 | Yin M Q, Huang M J, Ma B Z, et al. Stimulating effects of seed treatment by magnetized plasma on tomato growth and yield. Plasma Science and Technology, 2005, 7(6): 3143-3147. |
| 40 | Salem K F M, El-Zanaty A M, Esmail R M. Assessing wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genetic diversity using morphological characters and microsatellite markers. World Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 4(5): 538-544. |
| 41 | Gill P K, Sharma A D, Singh P, et al. Changes in germination, growth and soluble sugar contents of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench seeds under various abiotic stresses. Plant Growth Regulation, 2003, 40(2): 157-162. |
| 42 | Peng X B, Yan H A, Zhang S X. Allelopathy effects of water extracts of walnut leaf on balloonflower. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2011, 20(9): 143-149. |
| 彭晓邦, 闫红安, 张硕新. 核桃叶水浸液对不同产地桔梗的化感效应. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(9): 143-149. | |
| 43 | Ma H Y, Zhang W E, Pan X J, et al. Review on the potential of applying the allelopathic effect of Juglandaceae. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(20): 57-63, 74. |
| 马红叶, 张文娥, 潘学军, 等. 胡桃科植物的化感作用及其应用前景综述. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(20): 57-63, 74. | |
| 44 | Xue Y. Study on the changes of nitrogenous compounds and microbial community characteristics during food waste composting. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021. |
| 薛映. 厨余垃圾堆肥过程含氮物质变化及微生物群落特征研究. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. | |
| 45 | Li K, Zhong C H, Shi Q H, et al. Cold plasma seed treatment improves chilling resistance of tomato plants through hydrogen peroxide and abscisic acid signaling pathway. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2021, 172: 286-297. |
| [1] | 马绍英, 陈桂平, 王娜, 马蕾, 连荣芳, 李胜, 张绪成. 豌豆土壤中潜在自毒物质的鉴定及自毒效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. |
| [2] | 张士敏, 赵娇阳, 朱慧森, 卫凯, 王永新. 硒对不同品种紫花苜蓿发芽阶段物质转化和形态建成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 79-90. |
| [3] | 许浩宇, 赵颖, 阮倩, 朱晓林, 王宝强, 魏小红. 不同混合盐碱下藜麦幼苗的抗性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 122-130. |
| [4] | 郭英姿, 贾文庆, 何松林, 王政. 花叶滇苦菜浸提液对3种花卉种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 96-106. |
| [5] | 刘思林, 陈俊雪, 杨阳, 陈中文, 卢玲玲, 牟英辉. 紫云英腐解液对牛筋草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 209-219. |
| [6] | 苏世平, 李毅, 刘小娥, 种培芳, 单立山, 后有丽. 外源脯氨酸对缓解红砂干旱胁迫的机理研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 127-138. |
| [7] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [8] | 刘春增, 郑春风, 聂良鹏, 张琳, 张济世, 吕玉虎, 李本银, 曹卫东. 现蕾期叶面喷素对紫云英籽粒数和籽粒重的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 76-83. |
| [9] | 张梦, 史鹏飞, 李本银, 刘春增, 郑春风, 张成兰, 郭晓彦, 张丽霞, 吕玉虎, 何春梅, 曹卫东. 70份紫云英种质资源表型多样性及其在豫南地区的结实特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 168-180. |
| [10] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 刘静, 金媛媛, 魏学凯. Epichloë内生真菌对禾草种子萌发影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 192-206. |
| [11] | 任文静, 吕玉虎, 周国朋, 常单娜, 向春阳, 曹卫东. 一个紫云英F4重组自交系群体的农艺性状与养分吸收评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 101-110. |
| [12] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [13] | 常单娜, 马晓彤, 周国朋, 高嵩涓, 刘蕊, 曹卫东. 不同根瘤菌与紫云英主栽品种的共生匹配性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 171-180. |
| [14] | 穆海婷, 王英哲, 苗一凡, 郁伟杰, 徐博. 重金属铜和铅胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 139-146. |
| [15] | 赵欣桐, 陈晓东, 李子吉, 张巨明, 刘天增. 植物内生肠杆菌对狗牙根耐盐性的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 127-136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||