

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 22-34.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023209
赵亚楠1,2( ), 王红梅1,3(
), 王红梅1,3( ), 李志丽1, 张振杰1, 陈彦硕1, 苏荣霞1
), 李志丽1, 张振杰1, 陈彦硕1, 苏荣霞1
收稿日期:2023-06-23
修回日期:2023-07-11
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-01-15
通讯作者:
王红梅
作者简介:E-mail: whm_826@nxu.edu.cn基金资助:
Ya-nan ZHAO1,2( ), Hong-mei WANG1,3(
), Hong-mei WANG1,3( ), Zhi-li LI1, Zhen-jie ZHANG1, Yan-shuo CHEN1, Rong-xia SU1
), Zhi-li LI1, Zhen-jie ZHANG1, Yan-shuo CHEN1, Rong-xia SU1
Received:2023-06-23
Revised:2023-07-11
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-01-15
Contact:
Hong-mei WANG
摘要:
草地灌丛化对生态系统结构、功能与服务产生重要影响,目前已经认识到其对土壤水分的负面影响,但还缺乏其在区域尺度的定量评价及其驱动机制研究。在宁夏荒漠草原选取43块成对样地(即荒漠草地和灌丛地),引入样地土壤水分相对亏缺指数(PCSWDI)评价荒漠草原向灌丛转变后土壤水分亏缺空间格局现状及其驱动因子。结果表明:荒漠草原转变为灌丛后0~100 cm和100~200 cm土壤含水量分别显著下降了27.80%和57.92%,0~100 cm灌丛地的PCSWDI显著低于荒漠草地,表明0~100 cm灌丛地目前不存在土壤水分亏缺现象。地统计学分析表明,荒漠草地和灌丛地的0~100 cm土壤水分相对亏缺指数的结构方差比分别为94.73%和95.29%,均属于强空间自相关,主要受结构性因子控制。此外,地理探测器的因子探测发现0~100 cm土壤储水量、坡向和田间持水量是影响灌丛地土壤水分相对亏缺指数的主导因子;交互探测表明,灌丛地0~100 cm土壤水分相对亏缺指数空间分异是多因子共同作用的结果。尽管分析得到0~100 cm灌丛地不存在土壤水分亏缺,但100~200 cm土壤含水量显著下降已经预示了深层土壤水分的消耗。因此,干旱半干旱地区的植被恢复必须考虑其植被承载力和水分阈值,基于自然的解决方案可能是未来植被恢复的主流思路。
赵亚楠, 王红梅, 李志丽, 张振杰, 陈彦硕, 苏荣霞. 荒漠草原灌丛转变过程土壤水分亏缺空间特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 22-34.
Ya-nan ZHAO, Hong-mei WANG, Zhi-li LI, Zhen-jie ZHANG, Yan-shuo CHEN, Rong-xia SU. Responses of spatial pattern and driving factors for soil water deficit of desert grassland-shrubland transition sites[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 22-34.

图2 荒漠草地向灌丛地转变后土壤属性变化WS: 储水量Water storage; FC: 田间持水量Field capacity; BD: 容重Bulk density; STN: 土壤全氮Soil total nitrogen; SOC: 土壤有机碳Soil organic carbon; SWC 0-100: 0~100 cm土层土壤含水量Soil water content in 0-100 cm; SWC100-200: 100~200 cm土层土壤含水量Soil water content in 100-200 cm; PCSWDI: 样地土壤水分相对亏缺指数Plot compared soil water deficit index; 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Changes of soil properties after desert grassland transition to shrubland
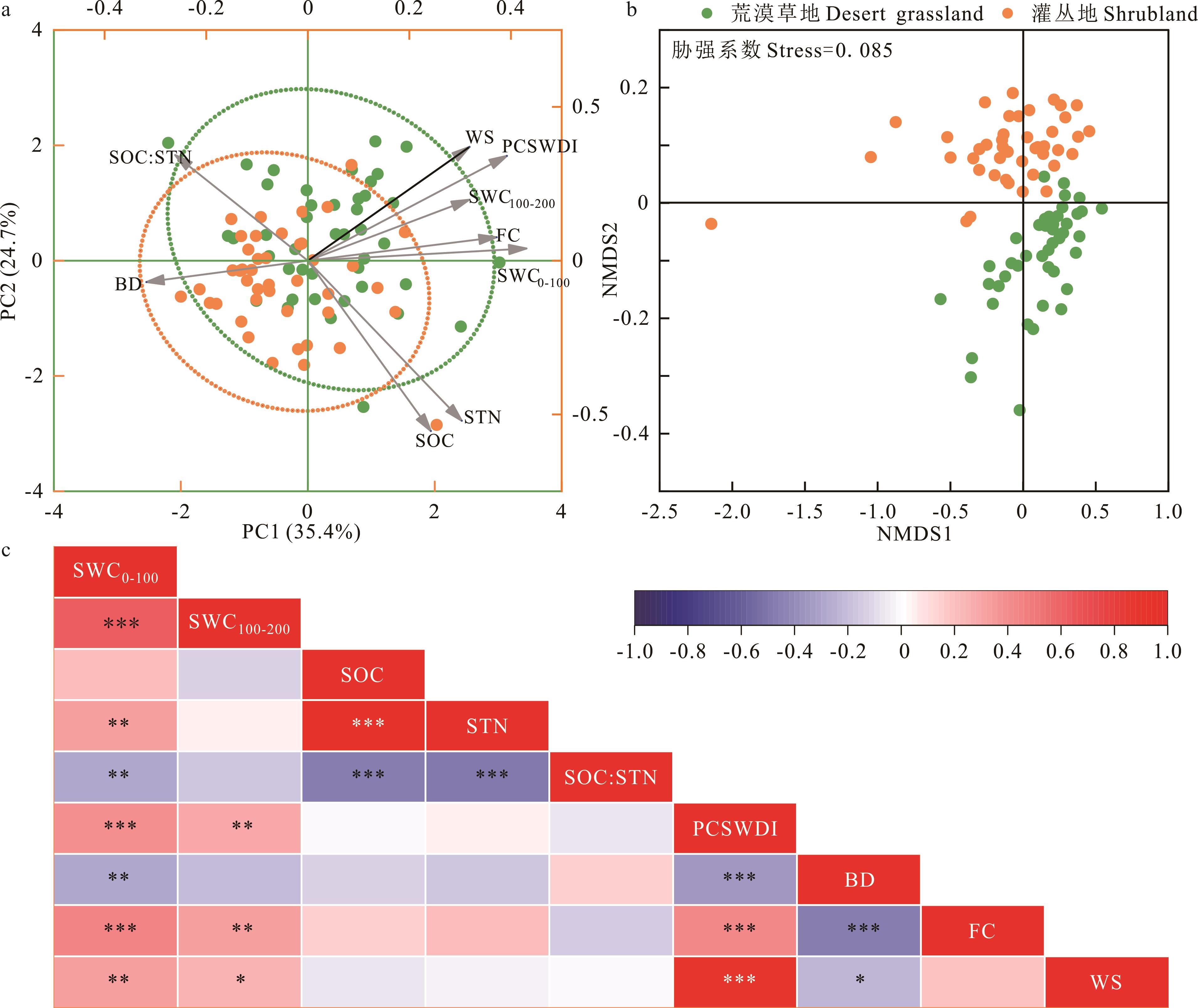
图3 应用主成分分析(a)、非度量多维标度分析(b)和相关性分析(c)研究荒漠草地向灌丛地转变后土壤属性的相互关系*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; 下同 The same below.
Fig.3 Interrelationship of soil properties after desert grassland transition to shrubland using principal component analysis (a), non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis (b) and correlation analysis (c)
样地类型 Site type | 块金值 Nugget | 基台值 Sill | 变程 Range (km) | C/(C0+C) (%) | 最优模型 Best model | R2 | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 荒漠草地Desert grassland | 0.0003 | 0.0057 | 8.88 | 94.73 | 高斯模型Gaussian model | 0.858 | 5.654×10-6 |
| 灌丛地Shrubland | 0.0004 | 0.0085 | 12.21 | 95.29 | 球状模型Spherical model | 0.579 | 4.111×10-5 |
表1 样地土壤水分相对亏缺指数半变异函数理论模型及相关参数
Table 1 Theoretical model of plot compared soil water deficit index semi-variation and correlation parameters
样地类型 Site type | 块金值 Nugget | 基台值 Sill | 变程 Range (km) | C/(C0+C) (%) | 最优模型 Best model | R2 | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 荒漠草地Desert grassland | 0.0003 | 0.0057 | 8.88 | 94.73 | 高斯模型Gaussian model | 0.858 | 5.654×10-6 |
| 灌丛地Shrubland | 0.0004 | 0.0085 | 12.21 | 95.29 | 球状模型Spherical model | 0.579 | 4.111×10-5 |

图4 荒漠草地和灌丛地土壤水分相对亏缺指数半变异函数(a, b)和空间插值结果(c, d)
Fig.4 Semi-variogram (a, b) and spatial interpolation (c, d) of plot compared soil water deficit index in desert grassland and shrubland

图5 灌丛地土壤水分相对亏缺指数的因子q值AGB: 地上植被生物量Above-ground vegetation biomass; 下同The same below.
Fig.5 The q values of driving factors on the plot compared soil water deficit index of shrubland
| 1 | Eldridge D J, Bowker M A, Maestre F T, et al. Impacts of shrub encroachment on ecosystem structure and functioning: Towards a global synthesis. Ecology Letters, 2011, 14(7): 709-722. |
| 2 | Maestre F T, Eldridge D J, Soliveres S, et al. Structure and functioning of dryland ecosystems in a changing world. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics, 2016, 47(1): 215-237. |
| 3 | Van Auken O W. Shrub invasions of North American semiarid grasslands. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics, 2000, 31(1): 197-215. |
| 4 | Cao X, Liu Y, Cui X, et al. Mechanisms, monitoring and modeling of shrub encroachment into grassland: A review. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2019, 12(6): 625-641. |
| 5 | Belayneh A, Tessema Z K. Mechanisms of bush encroachment and its inter-connection with rangeland degradation in semi-arid African ecosystems: A review. Journal of Arid Land, 2017, 9(2): 299-312. |
| 6 | Bestelmeyer B T, Peters D P C, Archer S R, et al. The grassland-shrubland regime shift in the Southwestern United States: Misconceptions and their implications for management. BioScience, 2018, 68(9): 678-690. |
| 7 | Briske D D. Rangeland Systems: processes, management and challenges. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 25-84. |
| 8 | Daryanto S, Fu B, Zhao W. Evaluating the use of fire to control shrub encroachment in global drylands: A synthesis based on ecosystem service perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 648: 285-292. |
| 9 | D’Odorico P, Okin G S, Bestelmeyer B T. A synthetic review of feedbacks and drivers of shrub encroachment in arid grasslands. Ecohydrology, 2012, 5(5): 520-530. |
| 10 | Rutten G, Prati D, Hemp A, et al. Plant-soil feedback in East-African savanna trees. Ecology, 2016, 97(2): 294-301. |
| 11 | Naikwade P. Changes in soil carbon sequestration during woody plant encroachment in arid ecosystems. Plantae Scientia, 2021, 4(4/5): 266-276. |
| 12 | Rashid H, Robert S, Neville A, et al. Ecosystems and human well-being: current state and trends: Findings of the condition and trends working group (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Series). Washington: Island Press, 2005: 623-662. |
| 13 | Reynolds J F, Smith D M S, Lambin E F, et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science, 2007, 316(5826): 847-851. |
| 14 | Guo Z S. Soil water carrying capacity for vegetation. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 32(14): 3801-3811. |
| 15 | Du L, Zeng Y, Ma L, et al. Effects of anthropogenic revegetation on the water and carbon cycles of a desert steppe ecosystem. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2021, 300: 108339. |
| 16 | Yang Y, Liu B. Effects of planting Caragana shrubs on soil nutrients and stoichiometries in desert steppe of Northwest China.Catena, 2019, 183: 104213. |
| 17 | Zhao Y N, Zhou Y R, Wang H M. Spatial heterogeneity of soil water content under introduced shrub (Caragana korshinskii) in desert grassland of the eastern Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(11): 3577-3586. |
| 赵亚楠, 周玉蓉, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原灌丛引入下土壤水分空间异质性. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(11): 3577-3586. | |
| 18 | Zhao Y N, Du Y Y, Ma Y P, et al. Soil organic carbon dynamics and the prediction of their spatial changes in response to anthropogenically introduced shrub encroachment in desert steppe of the Eastern Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(6): 1927-1935. |
| 赵亚楠, 杜艳艳, 马彦平, 等. 宁夏东部荒漠草原灌丛引入过程中土壤有机碳变化及其空间格局预测. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(6): 1927-1935. | |
| 19 | Zhao Y N, Zhao Y F, Wang H M, et al. Response of spatial heterogeneity and threshold value for soil water and aboveground biomass of desert grassland-shrubland anthropogenic transition in desert steppe of Ningxia, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2021, 57(12): 1-12. |
| 赵亚楠, 赵亚峰, 王红梅, 等. 荒漠草原灌丛转变土壤水分与地上生物量空间异质性及阈值响应. 林业科学, 2021, 57(12): 1-12. | |
| 20 | Yu L, Wang H M, Guo T D, et al. Bistable-state of vegetation shift in the desert grassland-shrubland anthropogenic Mosaic area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(24): 9773-9783. |
| 于露, 王红梅, 郭天斗, 等. 荒漠草原-灌丛镶嵌体的植被稳态转变特征. 生态学报, 2021, 41(24): 9773-9783. | |
| 21 | Yu L, Zhou Y R, Zhao Y N, et al. Responses of the soil seed bank to simulated rainfall levels and anthropogenically introduced shrub encroachment in the desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 等. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. | |
| 22 | Zhang S, Yang D, Yang Y, et al. Excessive afforestation and soil drying on China’s Loess Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2018, 123(3): 923-935. |
| 23 | Shao M, Wang Y, Xia Y, et al. Soil drought and water carrying capacity for vegetation in the critical zone of the Loess Plateau: A review. Vadose Zone Journal, 2018, 17(1): 170077. |
| 24 | Guo Z, Zhang W. Impact of initial planting density on soil water resource use limit by plants. Geoinformatics & Geostatistics: An Overview, 2016, 4(1): 1000137. |
| 25 | Shao R, Zhang B, Su T, et al. Estimating the increase in regional evaporative water consumption as a result of vegetation restoration over the Loess Plateau, China.Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2019, 124(22): 11783-11802. |
| 26 | Huang L, Shao M. Advances and perspectives on soil water research in China’s Loess Plateau. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 199: 102962. |
| 27 | Wang Y, Shao M, Zhu Y, et al. A new index to quantify dried soil layers in water-limited ecosystems: A case study on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma, 2018, 322: 1-11. |
| 28 | Wang Y, Shao M, Zhu Y, et al. Impacts of land use and plant characteristics on dried soil layers in different climatic regions on the Loess Plateau of China. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2011, 151(4): 437-448. |
| 29 | Jia X, Shao M, Zhu Y, et al. Soil moisture decline due to afforestation across the Loess Plateau, China.Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 546: 113-122. |
| 30 | Breshears D D, Cobb N S, Rich P M, et al. Regional vegetation die-off in response to global-change-type drought. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2005, 102(42): 15144-15148. |
| 31 | García I, Mendoza R, Pomar M C. Deficit and excess of soil water impact on plant growth of Lotus tenuis by affecting nutrient uptake and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Plant and Soil, 2008, 304(1/2): 117-131. |
| 32 | Zhao Y N, Yu L, Zhou Y R, et al. Soil moisture dynamics and deficit of desert grassland with anthropogenic introduced shrub encroachment in the eastern Ningxia, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1305-1315. |
| 赵亚楠, 于露, 周玉蓉, 等. 宁夏东部荒漠草原灌丛引入对土壤水分动态及亏缺的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1305-1315. | |
| 33 | Wang Y Q, Shao M A, Liu Z P. Large-scale spatial variability of dried soil layers and related factors across the entire Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma, 2010, 159(1/2): 99-108. |
| 34 | Huo Z, Shao M, Horton R. Impact of gully on soil moisture of shrubland in wind-water erosion crisscross region of the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere, 2008, 18(5): 674-680. |
| 35 | Western A W, Blöschl G, Grayson R B. Geostatistical characterisation of soil moisture patterns in the Tarrawarra catchment. Journal of Hydrology, 1998, 205(1/2): 20-37. |
| 36 | Yang Y, Dou Y, Liu D, et al. Spatial pattern and heterogeneity of soil moisture along a transect in a small catchment on the Loess Plateau. Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 550: 466-477. |
| 37 | Wang J F, Zhang T L, Fu B J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 67: 250-256. |
| 38 | Wang J F, Xu C D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1): 116-134. |
| 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 116-134. | |
| 39 | Zheng Q Q, Du L T, Gong F, et al. Landscape characteristics of Caragana intermedia plantation based on GF-1 remote sensing image in Yanchi. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Science), 2019, 39(1): 152-159. |
| 郑琪琪, 杜灵通, 宫菲, 等. 基于GF-1遥感影像的宁夏盐池柠条人工林景观特征研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 39(1): 152-159. | |
| 40 | Dan Y, Du L T, Wang L, et al. Effects of artificial vegetation reconstruction on regional ecosystem evapotranspiration in desert steppe of Yanchi County. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(5): 8-15, 39. |
| 丹杨, 杜灵通, 王乐, 等. 盐池县荒漠草原人工植被重建对区域生态系统蒸散的影响. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(5): 8-15, 39. | |
| 41 | Wang L, Du L T, Ma L L, et al. Effects of planted shrub encroachment on carbon storage of desert steppe ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(1): 246-254. |
| 王乐, 杜灵通, 马龙龙, 等. 人工灌丛化对荒漠草原生态系统碳储量的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(1): 246-254. | |
| 42 | Song N P, Yang X G, He X Z, et al. Soil nutrient effect of desert steppe reconstructed by artificial Caragana microphylla stand. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(4): 21-26. |
| 宋乃平, 杨新国, 何秀珍, 等. 荒漠草原人工柠条林重建的土壤养分效应. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(4): 21-26. | |
| 43 | Li Z L, Wang H M, Sun Z C, et al. Responses of soil nitrogen to the transition from desert grassland to shrubland in eastern Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(4): 1230-1240. |
| 李志丽, 王红梅, 孙忠超, 等. 宁夏东部荒漠草原-灌丛地转变过程土壤氮素响应. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(4): 1230-1240. | |
| 44 | Bao S D. Soil agro-chemistrical analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 45 | Moreno-de las Heras M, Turnbull L, Wainwright J. Seed-bank structure and plant- recruitment conditions regulate the dynamics of a grassland-shrubland Chihuahuan ecotone. Ecology, 2016, 97(9): 2303-2318. |
| 46 | Yang L, Wei W, Mo B R, et al. Soil water deficit under different artificial vegetation restoration in the semi-arid hilly region of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(11): 3060-3068. |
| 杨磊, 卫伟, 莫保儒, 等. 半干旱黄土丘陵区不同人工植被恢复土壤水分的相对亏缺. 生态学报, 2011, 31(11): 3060-3068. | |
| 47 | Cambardella C A, Moorman T B, Novak J M, et al. Field-scale variability of soil properties in central lowa soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1994, 58(5): 1501-1511. |
| 48 | Webster R, Oliver M A. Geostatistics for environmental scientists. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2007. |
| 49 | Matheron G. Principles of geostatistics. Economic Geology, 1963, 58(8): 1246-1266. |
| 50 | Samui P, Bui D T, Chakraborty S, et al. Handbook of probabilistic models. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2020: 229-242. |
| 51 | Wang J, Li X, Christakos G, et al. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2010, 24(1): 107-127. |
| 52 | Wang J F, Hu Y. Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2012, 33: 114-115. |
| 53 | Cui Y, Wang X, Zhang X, et al. Soil moisture mediates microbial carbon and phosphorus metabolism during vegetation succession in a semiarid region. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 147: 107814. |
| 54 | Sun Z C, Zhou Y R, Zhao Y N, et al. Responses of soil microbial mineralization to the anthropogenic introduced shrub encroachment and water gradients in the desert steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 1537-1550. |
| 孙忠超, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 等. 荒漠草原土壤微生物矿化对灌丛引入过程及水分的响应. 生态学报, 2021, 41(4): 1537-1550. | |
| 55 | Zhang Z J, Yu L, Wang H M. Characteristics of soil moisture threshold for the seedling establishment of two dominant plants in desert grassland-shrubland transition. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(19): 8061-8072. |
| 张振杰, 于露, 王红梅. 荒漠草原向灌丛转变过程两种优势植物定植土壤水分阈值特征. 生态学报, 2022, 42(19): 8061-8072. | |
| 56 | Chen H, Shao M, Li Y. Soil desiccation in the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma, 2008, 143(1/2): 91-100. |
| 57 | Zhu X, Li Y, Peng X, et al. Soils of the loess region in China. Geoderma, 1983, 29(3): 237-255. |
| 58 | Wang X C, Li J, Tahir M N, et al. Validation of the EPIC model and its utilization to research the sustainable recovery of soil desiccation after alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by grain crop rotation system in the semi-humid region of the Loess Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2012, 161: 152-160. |
| 59 | Jia X, Shao M, Zhang C, et al. Regional temporal persistence of dried soil layer along South-North transect of the Loess Plateau, China. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 528: 152-160. |
| 60 | Jia X, Zha T S, Gong J N, et al. Energy partitioning over a semi-arid shrubland in Northern China. Hydrological Processes, 2016, 30(6): 972-985. |
| 61 | Huang Z, Liu Y F, Cui Z, et al. Natural grasslands maintain soil water sustainability better than planted grasslands in arid areas. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2019, 286: 106683. |
| 62 | Fang X, Zhao W, Wang L, et al. Variations of deep soil moisture under different vegetation types and influencing factors in a watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2016, 20(8): 3309-3323. |
| 63 | Zhao C, Shao M, Jia X, et al. Factors affecting soil desiccation spatial variability in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2019, 83(2): 266-275. |
| 64 | Zhang X, Zhao W, Pereira P. Aggravated water deficit in the Loess Plateau of China as indicated by the soil available water content// EGU General Assembly 2020. Vienna:Copernicus Meetings, 2020: EGU2020-8619. |
| 65 | Li B, Zhang W, Li S, et al. Severe depletion of available deep soil water induced by revegetation on the arid and semiarid Loess Plateau. Forest Ecology and Management, 2021, 491: 119156. |
| 66 | Gao Y, Fan J, Peng X P, et al. Soil water depletion and infiltration under the typical vegetation in the waterwind erosion crisscross region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(23): 7038-7046. |
| 高宇, 樊军, 彭小平, 等. 水蚀风蚀交错区典型植被土壤水分消耗和补充深度对比研究. 生态学报, 2014, 34(23): 7038-7046. | |
| 67 | Gao X, Li H, Zhao X, et al. Identifying a suitable revegetation technique for soil restoration on water-limited and degraded land: considering both deep soil moisture deficit and soil organic carbon sequestration. Geoderma, 2018, 319: 61-69. |
| 68 | Pierret A, Maeght J L, Clément C, et al. Understanding deep roots and their functions in ecosystems: an advocacy for more unconventional research. Annals of Botany, 2016, 118(4): 621-635. |
| 69 | Niu X W, Ding Y C, Zhang Q, et al. Study on the characteristics of Caragana root development and some relevant physiology. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2003, 23(5): 860-865. |
| 牛西午, 丁玉川, 张强, 等. 柠条根系发育特征及有关生理特性研究. 西北植物学报, 2003, 23(5): 860-865. |
| [1] | 李俊瑶, 蒋星驰, 胡晋瑜, 魏栋光, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 生物有机肥施加对荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 34-45. |
| [2] | 鲍平安, 邱开阳, 黄业芸, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 骆欣怡, 杨云涛, 谢应忠. 荒漠草原植物在氮磷添加下叶功能性状特征及其可塑性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. |
| [3] | 赵敏, 赵坤, 王赟博, 殷国梅, 刘思博, 闫宝龙, 孟卫军, 吕世杰, 韩国栋. 长期放牧干扰降低了短花针茅荒漠草原植物多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 39-49. |
| [4] | 刘欣雷, 杜鹤强, 刘秀帆, 范亚伟. 内蒙古荒漠草原地表风沙活动对放牧强度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 1-11. |
| [5] | 陈彦硕, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽, 张振杰. 荒漠草原不同年限灌丛引入过程土壤细菌碳源利用特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 30-44. |
| [6] | 胡宇霞, 龚吉蕊, 朱趁趁, 矢佳昱, 张子荷, 宋靓苑, 张魏圆. 基于生态系统服务簇的内蒙古荒漠草原生态系统服务的空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 1-14. |
| [7] | 黄业芸, 邱开阳, 朱亚超, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 杨壹, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 鲍平安. 贺兰山不同海拔植被生物量与土壤分形特征和土壤水分的相关关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 24-35. |
| [8] | 李江文, 裴婧宏, 韩国栋, 何邦印, 李彩. 基于植物功能性状分析异常降水对不同载畜率下荒漠草原功能群多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 212-222. |
| [9] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波, 任小玢. 降水对荒漠草原地上生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 30-39. |
| [10] | 米扬, 郭蓉, 王媛, 王占军, 蒋齐, 俞鸿千, 马琨. 宁夏荒漠草原土壤细菌与真菌群落对降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 81-92. |
| [11] | 苏荣霞, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽. 荒漠草原不同间距灌丛引入对土壤细菌碳源利用和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 93-105. |
| [12] | 李惟婕, 王立, 马景永, 王自奎. 黄土旱塬区苹果园生草覆盖对深层土壤水分和根系分布特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 63-74. |
| [13] | 牛伟玲, 陈辉, 侯慧新, 郭晨睿, 马娇林, 武建双. 10年禁牧未改变藏西北高寒荒漠植物水氮利用效率[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [14] | 刘万龙, 许冬梅, 史佳梅, 许爱云. 不同群落生境蒙古冰草种群株丛结构和叶片功能性状的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. |
| [15] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||