

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 89-104.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023282
张俊豪( ), 柴雪茹, 马嵩科, 张冬霞, 张静, 乔唱唱, 李爽, 黄明, 王贺正(
), 柴雪茹, 马嵩科, 张冬霞, 张静, 乔唱唱, 李爽, 黄明, 王贺正( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-09
修回日期:2023-09-21
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
王贺正
作者简介:E-mail: wanghezh@163.com基金资助:
Jun-hao ZHANG( ), Xue-ru CHAI, Song-ke MA, Dong-xia ZHANG, Jing ZHANG, Chang-chang QIAO, Shuang LI, Ming HUANG, He-zheng WANG(
), Xue-ru CHAI, Song-ke MA, Dong-xia ZHANG, Jing ZHANG, Chang-chang QIAO, Shuang LI, Ming HUANG, He-zheng WANG( )
)
Received:2023-08-09
Revised:2023-09-21
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-03-20
Contact:
He-zheng WANG
摘要:
为明确秸秆还田配施磷肥对豫西旱地小麦碳同化物积累特性和产量的影响,2021-2022年度,以洛旱22为材料,采用裂区试验设计,主区为玉米秸秆还田处理,分别为秸秆不还田(S0)、秸秆全量还田(S1),副区为施磷量处理,分别为0 kg·hm-2 (P0)、75 kg·hm-2 (P1)、112.5 kg·hm-2 (P2)、150 kg·hm-2 (P3)、187.5 kg·hm-2 (P4),测定了不同处理下小麦干物质积累特性和产量及其构成因素,以及花后旗叶净光合速率、相对叶绿素含量(SPAD值),旗叶和籽粒的可溶性糖、蔗糖含量及蔗糖酶活性。结果表明,同一施磷水平下,与秸秆不还田相比,秸秆还田提高了小麦旗叶SPAD值和净光合速率,增加了旗叶和籽粒中的可溶性糖、蔗糖含量、蔗糖合成酶和磷酸蔗糖合成酶活性,最终使成熟期干物质积累量和籽粒产量分别显著增加9.25%~14.60%和2.17%~6.31%。同一秸秆处理下,随施磷量的增加,旗叶SPAD值、净光合速率,旗叶和籽粒中的可溶性糖、蔗糖含量、蔗糖合成酶和磷酸蔗糖合成酶及干物质积累量呈先上升后下降趋势。从互作效应看,S1P3处理下旗叶SPAD值和净光合速率,旗叶和籽粒中的可溶性糖和蔗糖含量,蔗糖合成酶和磷酸蔗糖合成酶活性等各指标均最高,从而获得最高产量,较S0P0处理增产35.70%。因此,秸秆还田配施磷150 kg·hm-2是本试验条件下的最适宜种植方式,可在豫西旱地小麦栽培上推广。
张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 马嵩科, 张冬霞, 张静, 乔唱唱, 李爽, 黄明, 王贺正. 秸秆还田配施磷肥对豫西旱地小麦碳同化物积累的影响及其生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 89-104.
Jun-hao ZHANG, Xue-ru CHAI, Song-ke MA, Dong-xia ZHANG, Jing ZHANG, Chang-chang QIAO, Shuang LI, Ming HUANG, He-zheng WANG. Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on carbon assimilate accumulation in dryland wheat and the associated physiological mechanisms[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 89-104.
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) | 穗数 Spikes (×104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains per spike | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | P0 | 5372.07±113.72f | 445.86±12.83e | 32.49±0.75g | 41.28±0.10c |
| P1 | 6146.39±63.71e | 487.52±13.92d | 33.78±0.20f | 45.06±0.43b | |
| P2 | 6589.81±174.07cd | 514.96±8.04bc | 36.00±0.17bc | 46.76±1.35ab | |
| P3 | 6975.86±148.71b | 524.20±10.10b | 35.78±0.50cd | 47.50±1.10ab | |
| P4 | 6847.51±341.78bc | 510.86±5.20bc | 35.30±0.36cde | 46.65±1.36ab | |
| S1 | P0 | 5638.46±117.42f | 462.52±12.50e | 34.70±0.36e | 42.24±0.99c |
| P1 | 6443.56±108.05d | 495.86±19.10cd | 35.52±0.54cde | 45.39±1.20b | |
| P2 | 7005.55±189.68b | 531.70±14.22b | 36.63±0.32b | 45.52±1.22a | |
| P3 | 7290.14±149.25a | 571.70±12.33a | 37.66±0.35a | 48.08±1.92a | |
| P4 | 6996.43±245.90b | 519.19±8.62b | 34.93±0.64de | 46.70±1.78ab | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 24.18** | 18.34** | 49.94** | 2.40 |
| P | 98.44** | 47.67** | 42.91** | 21.91** | |
| S×P | 0.54 | 2.48 | 7.63** | 0.39 |
表1 秸秆还田配施磷肥对小麦产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 1 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on wheat yield and components factors
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) | 穗数 Spikes (×104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains per spike | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | P0 | 5372.07±113.72f | 445.86±12.83e | 32.49±0.75g | 41.28±0.10c |
| P1 | 6146.39±63.71e | 487.52±13.92d | 33.78±0.20f | 45.06±0.43b | |
| P2 | 6589.81±174.07cd | 514.96±8.04bc | 36.00±0.17bc | 46.76±1.35ab | |
| P3 | 6975.86±148.71b | 524.20±10.10b | 35.78±0.50cd | 47.50±1.10ab | |
| P4 | 6847.51±341.78bc | 510.86±5.20bc | 35.30±0.36cde | 46.65±1.36ab | |
| S1 | P0 | 5638.46±117.42f | 462.52±12.50e | 34.70±0.36e | 42.24±0.99c |
| P1 | 6443.56±108.05d | 495.86±19.10cd | 35.52±0.54cde | 45.39±1.20b | |
| P2 | 7005.55±189.68b | 531.70±14.22b | 36.63±0.32b | 45.52±1.22a | |
| P3 | 7290.14±149.25a | 571.70±12.33a | 37.66±0.35a | 48.08±1.92a | |
| P4 | 6996.43±245.90b | 519.19±8.62b | 34.93±0.64de | 46.70±1.78ab | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 24.18** | 18.34** | 49.94** | 2.40 |
| P | 98.44** | 47.67** | 42.91** | 21.91** | |
| S×P | 0.54 | 2.48 | 7.63** | 0.39 |

图1 秸秆还田配施磷肥对小麦干物质积累的影响S0:秸秆不还田处理;S1:秸秆还田处理;P0~P4:施磷量分别为0 kg·hm-2 (P0)、75 kg·hm-2 (P1)、112.5 kg·hm-2 (P2)、150 kg·hm-2 (P3)、187.5 kg·hm-2 (P4)。图中不同小写字母表示不同处理在0.05水平差异显著。下同。 S0: Without straw return treatment; S1: Straw return treatment; P0 to P4: The phosphorus application levels were 0 kg·ha-1 (P0), 75 kg·ha-1 (P1), 112.5 kg·ha-1 (P2), 150 kg·ha-1 (P3), and 187.5 kg·ha-1 (P4), respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level among different treatments in the Figure. The same below.
Fig. 1 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on dry matter accumulation of wheat
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | TSSBA (kg·hm-2) | CRSSTBA (%) | TRSSBA (%) | MSDM (kg·hm-2) | ADMAA (kg·hm-2) | CRSSTAA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | P0 | 1860.09±38.78ef | 34.63±0.90a | 24.95±0.47a | 10967.10±67.06h | 3511.98±111.42g | 65.37±0.90e |
| P1 | 1954.56±30.84bcd | 31.80±0.80b | 23.44±1.04b | 12528.97±125.57f | 4191.83±91.72e | 68.20±0.80d | |
| P2 | 2060.27±15.14a | 31.26±0.37bc | 22.97±0.50bc | 13499.34±16.82e | 4529.54±53.04d | 68.74±0.37cd | |
| P3 | 2060.65±27.73a | 29.54±0.95cd | 20.50±0.44d | 14966.61±105.13c | 4915.21±169.94bc | 70.46±0.95bc | |
| P4 | 2028.09±67.36ab | 29.62±1.37cd | 22.11±0.98c | 13993.65±221.49d | 4819.43±184.15c | 70.38±1.37bc | |
| S1 | P0 | 1798.18±37.72f | 31.89±1.13b | 22.09±0.32c | 11981.54±226.26g | 3840.28±139.36f | 68.11±1.13d |
| P1 | 1915.48±48.73cde | 29.73±1.25cd | 20.29±0.42de | 13966.93±59.46d | 4528.08±156.06d | 70.27±1.25bc | |
| P2 | 1875.76±20.29def | 26.78±0.67e | 18.14±0.48f | 15470.65±214.06b | 5129.79±182.18ab | 73.22±0.67a | |
| P3 | 2067.00±15.41a | 28.35±0.69de | 18.28±0.44f | 16529.64±186.64a | 5223.14±155.74a | 71.65±0.69ab | |
| P4 | 1979.48±85.80abc | 28.29±1.49de | 19.13±1.07ef | 15362.66±204.86b | 5016.95±150.52abc | 71.71±1.49ab | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 15.02** | 38.44** | 167.13** | 652.10** | 48.48** | 38.44** |
| P | 21.33** | 19.59** | 31.89** | 642.91** | 99.09** | 19.59** | |
| S×P | 3.55* | 2.47 | 3.09** | 7.21** | 1.70 | 2.47 |
表2 秸秆还田配施磷肥对小麦干物质转运的影响
Table 2 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on dry matter transport of wheat
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | TSSBA (kg·hm-2) | CRSSTBA (%) | TRSSBA (%) | MSDM (kg·hm-2) | ADMAA (kg·hm-2) | CRSSTAA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | P0 | 1860.09±38.78ef | 34.63±0.90a | 24.95±0.47a | 10967.10±67.06h | 3511.98±111.42g | 65.37±0.90e |
| P1 | 1954.56±30.84bcd | 31.80±0.80b | 23.44±1.04b | 12528.97±125.57f | 4191.83±91.72e | 68.20±0.80d | |
| P2 | 2060.27±15.14a | 31.26±0.37bc | 22.97±0.50bc | 13499.34±16.82e | 4529.54±53.04d | 68.74±0.37cd | |
| P3 | 2060.65±27.73a | 29.54±0.95cd | 20.50±0.44d | 14966.61±105.13c | 4915.21±169.94bc | 70.46±0.95bc | |
| P4 | 2028.09±67.36ab | 29.62±1.37cd | 22.11±0.98c | 13993.65±221.49d | 4819.43±184.15c | 70.38±1.37bc | |
| S1 | P0 | 1798.18±37.72f | 31.89±1.13b | 22.09±0.32c | 11981.54±226.26g | 3840.28±139.36f | 68.11±1.13d |
| P1 | 1915.48±48.73cde | 29.73±1.25cd | 20.29±0.42de | 13966.93±59.46d | 4528.08±156.06d | 70.27±1.25bc | |
| P2 | 1875.76±20.29def | 26.78±0.67e | 18.14±0.48f | 15470.65±214.06b | 5129.79±182.18ab | 73.22±0.67a | |
| P3 | 2067.00±15.41a | 28.35±0.69de | 18.28±0.44f | 16529.64±186.64a | 5223.14±155.74a | 71.65±0.69ab | |
| P4 | 1979.48±85.80abc | 28.29±1.49de | 19.13±1.07ef | 15362.66±204.86b | 5016.95±150.52abc | 71.71±1.49ab | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 15.02** | 38.44** | 167.13** | 652.10** | 48.48** | 38.44** |
| P | 21.33** | 19.59** | 31.89** | 642.91** | 99.09** | 19.59** | |
| S×P | 3.55* | 2.47 | 3.09** | 7.21** | 1.70 | 2.47 |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 11.31±0.47e | 9.19±0.29e | 8.63±0.49e | 6.45±0.41f | 4.31±0.43e |
| P1 | 12.34±0.26e | 10.59±0.28d | 9.54±0.36d | 7.53±0.39e | 6.56±0.56d | |
| P2 | 14.68±0.40d | 11.55±0.45c | 10.64±0.25c | 8.71±0.24d | 7.27±0.01cd | |
| P3 | 17.58±0.37b | 13.99±0.14ab | 12.42±0.02a | 10.43±0.33b | 9.06±0.10ab | |
| P4 | 16.40±0.44c | 13.69±0.16b | 11.49±0.27b | 9.17±0.28cd | 8.64±0.04b | |
| S1 | P0 | 12.17±0.57e | 10.62±0.50d | 8.73±0.20e | 7.63±0.38e | 6.61±0.02d |
| P1 | 14.50±0.40d | 11.47±0.29cd | 10.53±0.36c | 8.69±0.39d | 7.60±0.58c | |
| P2 | 17.96±0.76b | 13.89±0.90ab | 11.69±0.03b | 10.87±0.43ab | 8.77±0.48b | |
| P3 | 20.15±0.87a | 14.76±0.60a | 12.61±0.22a | 11.13±0.50a | 9.60±0.43a | |
| P4 | 18.32±1.26b | 13.42±0.74b | 12.51±0.14a | 9.54±0.02c | 9.19±0.69ab | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 77.29** | 31.00** | 41.03** | 76.82** | 57.93** |
| P | 112.81** | 78.53** | 177.08** | 106.03** | 78.77** | |
| S×P | 2.63 | 5.43** | 4.21* | 5.67** | 4.45* | |
表3 秸秆还田配施磷肥对小麦花后净光合速率的影响
Table 3 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on net photosynthetic rate of wheat after flowering (μmol·m-2·s-1)
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 11.31±0.47e | 9.19±0.29e | 8.63±0.49e | 6.45±0.41f | 4.31±0.43e |
| P1 | 12.34±0.26e | 10.59±0.28d | 9.54±0.36d | 7.53±0.39e | 6.56±0.56d | |
| P2 | 14.68±0.40d | 11.55±0.45c | 10.64±0.25c | 8.71±0.24d | 7.27±0.01cd | |
| P3 | 17.58±0.37b | 13.99±0.14ab | 12.42±0.02a | 10.43±0.33b | 9.06±0.10ab | |
| P4 | 16.40±0.44c | 13.69±0.16b | 11.49±0.27b | 9.17±0.28cd | 8.64±0.04b | |
| S1 | P0 | 12.17±0.57e | 10.62±0.50d | 8.73±0.20e | 7.63±0.38e | 6.61±0.02d |
| P1 | 14.50±0.40d | 11.47±0.29cd | 10.53±0.36c | 8.69±0.39d | 7.60±0.58c | |
| P2 | 17.96±0.76b | 13.89±0.90ab | 11.69±0.03b | 10.87±0.43ab | 8.77±0.48b | |
| P3 | 20.15±0.87a | 14.76±0.60a | 12.61±0.22a | 11.13±0.50a | 9.60±0.43a | |
| P4 | 18.32±1.26b | 13.42±0.74b | 12.51±0.14a | 9.54±0.02c | 9.19±0.69ab | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 77.29** | 31.00** | 41.03** | 76.82** | 57.93** |
| P | 112.81** | 78.53** | 177.08** | 106.03** | 78.77** | |
| S×P | 2.63 | 5.43** | 4.21* | 5.67** | 4.45* | |
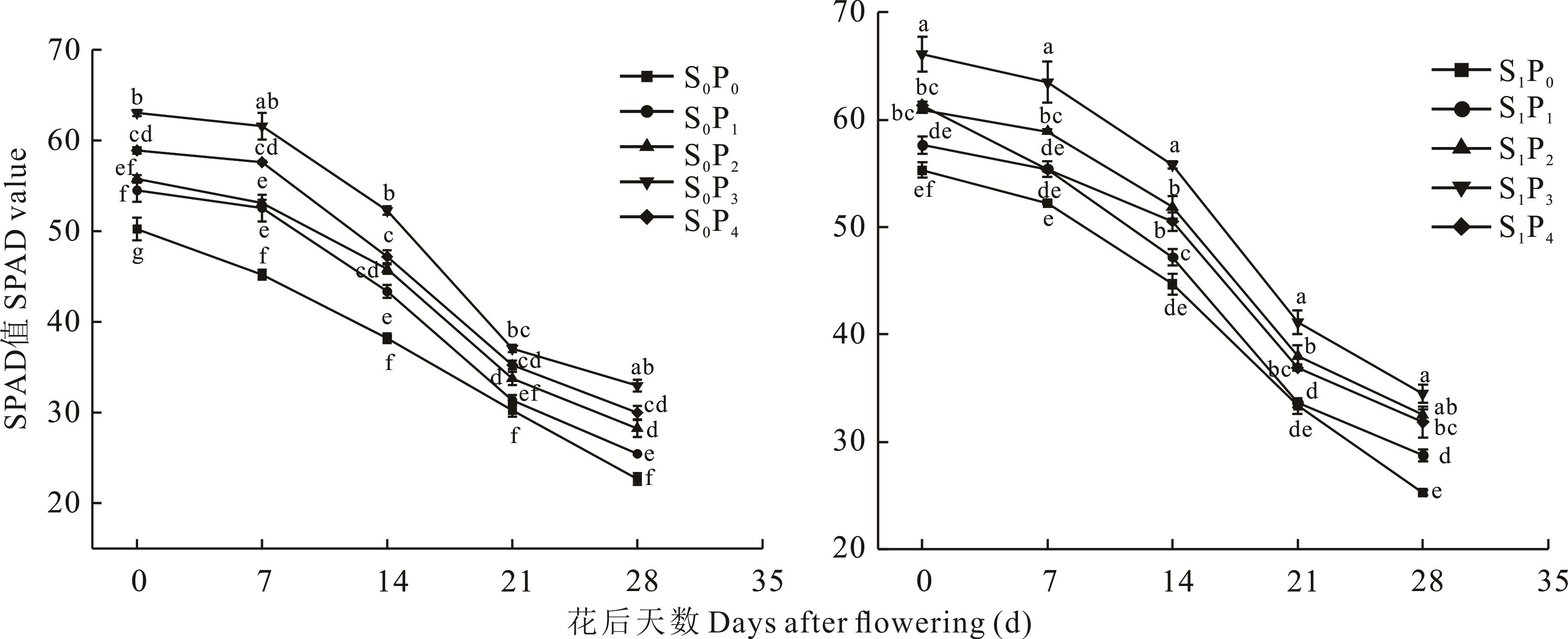
图2 秸秆还田配施磷对小麦旗叶SPAD值的影响不同小写字母表示花后同天不同处理下差异显著(P<0.05)。*: P<0.05;**: P<0.01。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level among different treatments in the same day after flowering. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01. The same below.
Fig. 2 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on SPAD value in flag leaves of wheat
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 2.98±0.07g | 3.22±0.01g | 7.07±0.19d | 5.11±0.09g | 3.71±0.16f | 2.03±0.02e |
| P1 | 3.27±0.08f | 3.43±0.14f | 7.13±0.16d | 5.39±0.06f | 3.74±0.18f | 2.63±0.11c | |
| P2 | 3.48±0.06de | 3.72±0.01de | 7.69±0.09c | 5.89±0.18de | 3.96±0.01de | 2.77±0.14c | |
| P3 | 3.90±0.10b | 4.15±0.04bc | 8.10±0.27b | 6.29±0.08b | 4.32±0.05b | 3.06±0.01ab | |
| P4 | 3.65±0.01c | 4.02±0.06c | 7.80±0.02bc | 6.02±0.15cd | 4.18±0.02bc | 2.93±0.01b | |
| S1 | P0 | 3.36±0.02ef | 3.56±0.03ef | 7.18±0.02d | 5.41±0.02f | 3.85±0.01ef | 2.40±0.04d |
| P1 | 3.59±0.01cd | 3.76±0.03d | 7.64±0.21c | 5.71±0.09e | 4.05±0.05cd | 2.75±0.04c | |
| P2 | 3.96±0.12b | 4.24±0.13b | 8.11±0.30b | 6.12±0.14bc | 4.20±0.08bc | 2.98±0.08b | |
| P3 | 4.27±0.05a | 4.61±0.08a | 8.72±0.18a | 6.69±0.03a | 4.57±0.02a | 3.16±0.04a | |
| P4 | 3.97±0.15b | 4.25±0.19b | 8.00±0.35bc | 6.17±0.18bc | 4.24±0.10b | 3.01±0.04b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 142.86** | 118.76** | 21.40** | 45.81** | 34.72** | 40.84** |
| P | 103.69** | 106.27** | 31.05** | 111.69** | 47.65** | 146.37** | |
| S×P | 0.97 | 2.18 | 1.36 | 1.27 | 1.53 | 4.91** | |
表4 秸秆还田配施磷对旗叶蔗糖合成酶活性的影响
Table 4 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on sucrose synthetase activity of flag leaves (mg·g-1·min-1)
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 2.98±0.07g | 3.22±0.01g | 7.07±0.19d | 5.11±0.09g | 3.71±0.16f | 2.03±0.02e |
| P1 | 3.27±0.08f | 3.43±0.14f | 7.13±0.16d | 5.39±0.06f | 3.74±0.18f | 2.63±0.11c | |
| P2 | 3.48±0.06de | 3.72±0.01de | 7.69±0.09c | 5.89±0.18de | 3.96±0.01de | 2.77±0.14c | |
| P3 | 3.90±0.10b | 4.15±0.04bc | 8.10±0.27b | 6.29±0.08b | 4.32±0.05b | 3.06±0.01ab | |
| P4 | 3.65±0.01c | 4.02±0.06c | 7.80±0.02bc | 6.02±0.15cd | 4.18±0.02bc | 2.93±0.01b | |
| S1 | P0 | 3.36±0.02ef | 3.56±0.03ef | 7.18±0.02d | 5.41±0.02f | 3.85±0.01ef | 2.40±0.04d |
| P1 | 3.59±0.01cd | 3.76±0.03d | 7.64±0.21c | 5.71±0.09e | 4.05±0.05cd | 2.75±0.04c | |
| P2 | 3.96±0.12b | 4.24±0.13b | 8.11±0.30b | 6.12±0.14bc | 4.20±0.08bc | 2.98±0.08b | |
| P3 | 4.27±0.05a | 4.61±0.08a | 8.72±0.18a | 6.69±0.03a | 4.57±0.02a | 3.16±0.04a | |
| P4 | 3.97±0.15b | 4.25±0.19b | 8.00±0.35bc | 6.17±0.18bc | 4.24±0.10b | 3.01±0.04b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 142.86** | 118.76** | 21.40** | 45.81** | 34.72** | 40.84** |
| P | 103.69** | 106.27** | 31.05** | 111.69** | 47.65** | 146.37** | |
| S×P | 0.97 | 2.18 | 1.36 | 1.27 | 1.53 | 4.91** | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 3.31±0.05g | 4.68±0.28f | 8.00±0.16g | 5.83±0.30g | 4.65±0.43g | 1.81±0.12f |
| P1 | 5.57±0.38f | 5.89±0.49e | 8.88±0.02f | 6.67±0.22f | 5.91±0.08f | 2.64±0.34de | |
| P2 | 6.64±0.03de | 6.33±0.33e | 9.50±0.47e | 7.60±0.22e | 6.72±0.09de | 3.66±0.25c | |
| P3 | 7.87±0.01b | 7.45±0.22d | 11.74±0.34b | 8.31±0.28cd | 7.58±0.09bc | 5.10±0.43b | |
| P4 | 7.13±0.42cd | 7.03±0.18d | 10.63±0.14c | 7.86±0.12de | 7.17±0.05cd | 4.79±0.19b | |
| S1 | P0 | 5.70±0.03f | 6.27±0.12e | 8.78±0.32f | 6.66±0.33f | 5.40±0.30f | 2.28±0.10ef |
| P1 | 6.48±0.46e | 6.97±0.05d | 9.39±0.19e | 7.36±0.28e | 6.50±0.40e | 2.96±0.30d | |
| P2 | 7.24±0.25c | 8.28±0.44c | 10.12±0.10d | 8.68±0.53c | 7.14±0.07cd | 3.97±0.22c | |
| P3 | 8.50±0.03a | 10.11±0.60a | 12.46±0.24a | 10.62±0.61a | 8.78±0.49a | 6.00±0.54a | |
| P4 | 7.86±0.56b | 9.19±0.54b | 11.58±0.36b | 9.72±0.64b | 8.08±0.44b | 5.22±0.31b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 88.75** | 206.45** | 49.23** | 105.15** | 45.30** | 18.56** |
| P | 130.68** | 79.92** | 172.23** | 77.94** | 92.01** | 136.20** | |
| S×P | 9.22** | 4.08* | 0.52 | 5.62** | 1.35 | 0.94 | |
表5 秸秆还田配施磷肥对旗叶磷酸蔗糖合成酶活性的影响
Table 5 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on sucrose phosphate synthetase activity of flag leaves (mg·g-1·min-1)
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 3.31±0.05g | 4.68±0.28f | 8.00±0.16g | 5.83±0.30g | 4.65±0.43g | 1.81±0.12f |
| P1 | 5.57±0.38f | 5.89±0.49e | 8.88±0.02f | 6.67±0.22f | 5.91±0.08f | 2.64±0.34de | |
| P2 | 6.64±0.03de | 6.33±0.33e | 9.50±0.47e | 7.60±0.22e | 6.72±0.09de | 3.66±0.25c | |
| P3 | 7.87±0.01b | 7.45±0.22d | 11.74±0.34b | 8.31±0.28cd | 7.58±0.09bc | 5.10±0.43b | |
| P4 | 7.13±0.42cd | 7.03±0.18d | 10.63±0.14c | 7.86±0.12de | 7.17±0.05cd | 4.79±0.19b | |
| S1 | P0 | 5.70±0.03f | 6.27±0.12e | 8.78±0.32f | 6.66±0.33f | 5.40±0.30f | 2.28±0.10ef |
| P1 | 6.48±0.46e | 6.97±0.05d | 9.39±0.19e | 7.36±0.28e | 6.50±0.40e | 2.96±0.30d | |
| P2 | 7.24±0.25c | 8.28±0.44c | 10.12±0.10d | 8.68±0.53c | 7.14±0.07cd | 3.97±0.22c | |
| P3 | 8.50±0.03a | 10.11±0.60a | 12.46±0.24a | 10.62±0.61a | 8.78±0.49a | 6.00±0.54a | |
| P4 | 7.86±0.56b | 9.19±0.54b | 11.58±0.36b | 9.72±0.64b | 8.08±0.44b | 5.22±0.31b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 88.75** | 206.45** | 49.23** | 105.15** | 45.30** | 18.56** |
| P | 130.68** | 79.92** | 172.23** | 77.94** | 92.01** | 136.20** | |
| S×P | 9.22** | 4.08* | 0.52 | 5.62** | 1.35 | 0.94 | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 5.68±0.20g | 7.95±0.21h | 9.13±0.23e | 4.51±0.35g | 2.36±0.08h | 1.17±0.12g |
| P1 | 6.28±0.40f | 8.79±0.38fg | 10.18±0.57de | 5.48±0.31f | 2.64±0.12g | 1.31±0.02fg | |
| P2 | 6.91±0.14e | 9.46±0.21e | 10.65±0.43cd | 5.89±0.17f | 3.31±0.07e | 1.41±0.04ef | |
| P3 | 8.28±0.50bc | 11.03±0.23b | 12.92±1.18b | 6.91±0.09cd | 4.04±0.11b | 1.67±0.12bc | |
| P4 | 7.38±0.30de | 10.12±0.43d | 11.67±0.42c | 6.37±0.20e | 3.54±0.11d | 1.52±0.02cde | |
| S1 | P0 | 6.35±0.27f | 8.53±0.19g | 10.95±0.13cd | 5.59±0.30f | 2.65±0.11g | 1.35±0.05ef |
| P1 | 7.11±0.17e | 9.32±0.05ef | 11.23±0.98cd | 6.51±0.35de | 2.84±0.08f | 1.46±0.07def | |
| P2 | 8.13±0.19cd | 10.28±0.43cd | 13.09±0.89ab | 7.08±0.11c | 3.77±0.10c | 1.59±0.11cd | |
| P3 | 9.47±0.42a | 11.98±0.52a | 14.21±0.07a | 8.52±0.46a | 4.64±0.08a | 2.10±0.06a | |
| P4 | 8.43±0.21b | 10.80±0.36bc | 13.66±0.08ab | 7.60±0.18b | 3.95±0.09b | 1.83±0.18b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 66.89** | 34.07** | 53.36** | 170.70** | 120.27** | 56.47** |
| P | 74.96** | 86.47** | 29.62** | 91.90** | 349.67** | 43.92** | |
| S×P | 0.98 | 0.39 | 1.12 | 1.15 | 3.72* | 2.55 | |
表6 秸秆还田配施磷肥对籽粒蔗糖合成酶活性的影响
Table 6 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on sucrose synthase activity of grain (mg·g-1·min-1)
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 5.68±0.20g | 7.95±0.21h | 9.13±0.23e | 4.51±0.35g | 2.36±0.08h | 1.17±0.12g |
| P1 | 6.28±0.40f | 8.79±0.38fg | 10.18±0.57de | 5.48±0.31f | 2.64±0.12g | 1.31±0.02fg | |
| P2 | 6.91±0.14e | 9.46±0.21e | 10.65±0.43cd | 5.89±0.17f | 3.31±0.07e | 1.41±0.04ef | |
| P3 | 8.28±0.50bc | 11.03±0.23b | 12.92±1.18b | 6.91±0.09cd | 4.04±0.11b | 1.67±0.12bc | |
| P4 | 7.38±0.30de | 10.12±0.43d | 11.67±0.42c | 6.37±0.20e | 3.54±0.11d | 1.52±0.02cde | |
| S1 | P0 | 6.35±0.27f | 8.53±0.19g | 10.95±0.13cd | 5.59±0.30f | 2.65±0.11g | 1.35±0.05ef |
| P1 | 7.11±0.17e | 9.32±0.05ef | 11.23±0.98cd | 6.51±0.35de | 2.84±0.08f | 1.46±0.07def | |
| P2 | 8.13±0.19cd | 10.28±0.43cd | 13.09±0.89ab | 7.08±0.11c | 3.77±0.10c | 1.59±0.11cd | |
| P3 | 9.47±0.42a | 11.98±0.52a | 14.21±0.07a | 8.52±0.46a | 4.64±0.08a | 2.10±0.06a | |
| P4 | 8.43±0.21b | 10.80±0.36bc | 13.66±0.08ab | 7.60±0.18b | 3.95±0.09b | 1.83±0.18b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 66.89** | 34.07** | 53.36** | 170.70** | 120.27** | 56.47** |
| P | 74.96** | 86.47** | 29.62** | 91.90** | 349.67** | 43.92** | |
| S×P | 0.98 | 0.39 | 1.12 | 1.15 | 3.72* | 2.55 | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 11.90±0.48h | 8.83±0.26h | 7.42±0.33h | 5.22±0.38g | 2.52±0.43g | 1.39±0.07g |
| P1 | 13.37±0.44g | 10.37±0.75g | 8.44±0.47g | 6.17±0.29ef | 3.37±0.40f | 1.74±0.11fg | |
| P2 | 14.55±0.31f | 11.37±0.76f | 9.46±0.45ef | 7.10±0.16d | 4.17±0.19e | 1.90±0.03ef | |
| P3 | 18.31±0.53c | 13.24±0.65cd | 10.90±0.66c | 8.08±0.06c | 5.53±0.13c | 2.35±0.16d | |
| P4 | 15.91±0.68e | 12.28±0.61e | 9.87±0.33de | 6.74±0.65de | 4.74±0.37d | 2.07±0.19def | |
| S1 | P0 | 13.03±0.15g | 10.45±0.41g | 8.38±0.44g | 5.98±0.35f | 3.07±0.14f | 1.89±0.08ef |
| P1 | 14.69±0.57f | 12.66±0.60de | 9.23±0.13f | 7.07±0.12d | 4.76±0.15d | 2.25±0.12de | |
| P2 | 17.41±0.92d | 13.82±0.60c | 10.33±0.41cd | 8.20±0.55c | 5.83±0.16bc | 3.05±0.13c | |
| P3 | 26.05±0.11a | 17.25±0.68a | 12.96±0.43a | 10.34±0.23a | 7.44±0.34a | 4.24±0.40a | |
| P4 | 20.13±0.17b | 15.03±0.12b | 11.59±0.11b | 9.13±0.30b | 6.20±0.17b | 3.62±0.40b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 366.35** | 351.15** | 108.69** | 121.19** | 187.31** | 201.67** |
| P | 351.46** | 184.31** | 132.08** | 82.72** | 152.11** | 56.01** | |
| S×P | 45.35** | 7.89** | 4.35* | 6.74** | 5.07** | 12.50** | |
表7 秸秆还田配施磷肥对籽粒磷酸蔗糖合成酶活性的影响
Table 7 Effects of straw return combined with phosphorus fertilizer on the activity of sucrose phosphate synthetase in grain (mg·g-1·min-1)
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 花后天数Days after flowering (d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||
| S0 | P0 | 11.90±0.48h | 8.83±0.26h | 7.42±0.33h | 5.22±0.38g | 2.52±0.43g | 1.39±0.07g |
| P1 | 13.37±0.44g | 10.37±0.75g | 8.44±0.47g | 6.17±0.29ef | 3.37±0.40f | 1.74±0.11fg | |
| P2 | 14.55±0.31f | 11.37±0.76f | 9.46±0.45ef | 7.10±0.16d | 4.17±0.19e | 1.90±0.03ef | |
| P3 | 18.31±0.53c | 13.24±0.65cd | 10.90±0.66c | 8.08±0.06c | 5.53±0.13c | 2.35±0.16d | |
| P4 | 15.91±0.68e | 12.28±0.61e | 9.87±0.33de | 6.74±0.65de | 4.74±0.37d | 2.07±0.19def | |
| S1 | P0 | 13.03±0.15g | 10.45±0.41g | 8.38±0.44g | 5.98±0.35f | 3.07±0.14f | 1.89±0.08ef |
| P1 | 14.69±0.57f | 12.66±0.60de | 9.23±0.13f | 7.07±0.12d | 4.76±0.15d | 2.25±0.12de | |
| P2 | 17.41±0.92d | 13.82±0.60c | 10.33±0.41cd | 8.20±0.55c | 5.83±0.16bc | 3.05±0.13c | |
| P3 | 26.05±0.11a | 17.25±0.68a | 12.96±0.43a | 10.34±0.23a | 7.44±0.34a | 4.24±0.40a | |
| P4 | 20.13±0.17b | 15.03±0.12b | 11.59±0.11b | 9.13±0.30b | 6.20±0.17b | 3.62±0.40b | |
| 方差分析和F值Variance analysis and F value | S | 366.35** | 351.15** | 108.69** | 121.19** | 187.31** | 201.67** |
| P | 351.46** | 184.31** | 132.08** | 82.72** | 152.11** | 56.01** | |
| S×P | 45.35** | 7.89** | 4.35* | 6.74** | 5.07** | 12.50** | |
| 1 | Lou M Y, Xue H L, Guo B B, et al. Relationship of phosphorus application rate, winter wheat yield and soil available phosphorus content. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(9): 1582-1593. |
| 娄梦玉, 薛华龙, 郭彬彬, 等. 施磷水平与冬小麦产量和土壤有效磷含量的关系. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(9): 1582-1593. | |
| 2 | Yang M D, Zhao P P, Yu Z Y, et al. Optimum phosphorus application rate for maintaining high yield and soil phosphorus fertility under winter wheat-summer maize rotation in Shanxi Province. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(3): 440-449. |
| 杨梦棣, 赵萍萍, 于志勇, 等. 晋南地区小麦-玉米轮作体系维持作物高产和土壤磷素水平的适宜施磷量研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(3): 440-449. | |
| 3 | Mao S S, Zhou J H, Meng F Y, et al. Effects of different amount of phosphorus on yield of wheat in the suburb of Beijing. Crop, 2014(4): 88-90. |
| 毛思帅, 周吉红, 孟范玉, 等. 磷肥不同用量对京郊小麦产量的影响. 作物杂志, 2014(4): 88-90. | |
| 4 | Yue J Q, Li X D, Shao Y H, et al. Effects of different phosphorus levels under same nitrogen-potassium ratios on photosynthetic, dry matter transportation and yield of winter wheat. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(4): 473-481. |
| 岳俊芹, 李向东, 邵运辉, 等. 氮钾固定配施下施磷量对小麦光合、干物质转运及产量形成的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(4): 473-481. | |
| 5 | Chen X X, Zhang W, Liang X Y, et al. Physiological and developmental traits associated with the grain yield of winter wheat as affected by phosphorus fertilizer management. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 16580. |
| 6 | Liu C, Jia Y H, Zhang J S, et al. Effects phosphorus application rates on dry matter translocation and nutrient uptake and utilization of winter wheat under different seeding patterns. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(5): 975-986. |
| 刘冲, 贾永红, 张金汕, 等. 施磷量对不同播种方式下冬小麦干物质转运及养分吸收利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(5): 975-986. | |
| 7 | Wang K K, Liao S P, Ren T, et al. Effect of continuous straw returning on soil phosphorus availability and crop phosphorus utilization efficiency of oilseed rape-rice rotation. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(1): 94-104. |
| 王昆昆, 廖世鹏, 任涛, 等. 连续秸秆还田对油菜水稻轮作土壤磷素有效性及作物磷素利用效率的影响. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(1): 94-104. | |
| 8 | Ma Y, Tian Y, Yu J, et al. Threshhold of soil available P and the response of wheat yield and grain N, P, and K concentrations to test-integrated fertilizer application in the northern wheat production region of China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(10): 1675-1691. |
| 马悦, 田怡, 于杰, 等. 北方麦区土壤有效磷阈值及小麦产量/籽粒氮磷钾含量对监控施肥的响应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(10): 1675-1691. | |
| 9 | Huang W, Wu J F, Pan X H, et al. Effects of long-term straw return on soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in a double cropped rice paddy in South China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(1): 236-247. |
| 10 | Pang L D, Meng T T, Zhang Y F, et al. Effects of maize straw returning with nitrogen fertilizer on soil enzyme activity, microbial biomass carbon content and respiration. Crops, 2017(1): 107-112. |
| 庞荔丹, 孟婷婷, 张宇飞, 等. 玉米秸秆配氮还田对土壤酶活性、微生物量碳含量及土壤呼吸量的影响. 作物杂志, 2017(1): 107-112. | |
| 11 | Cates M A, Ruark D M, Hedtcke L J, et al. Long-term tillage, rotation and perennialization effects on particulate and aggregate soil organic matter. Soil & Tillage Research, 2016, 155: 371-380. |
| 12 | Wang X R. The effect of increasing nitrogen on soil nutrient, biological index and yield under the condition of straw returning. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 王欣然. 旋耕秸秆还田条件下增氮对土壤养分、生物指标和玉米产量的影响. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2018. | |
| 13 | Chen J, Tang Y H, Yin Y P, et al. Effects of straw returning plus nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen utilization and grain yield in winter wheat. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2015, 41(1): 160-167. |
| 陈金, 唐玉海, 尹燕枰, 等. 秸秆还田条件下适量施氮对冬小麦氮素利用及产量的影响. 作物学报, 2015, 41(1): 160-167. | |
| 14 | Zhang L, Wang J, Pang H C, et al. Effect of granulated straw incorporation on soil nutrient and grain yield of winter wheat. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(12): 1770-1778. |
| 张莉, 王婧, 逄焕成, 等. 秸秆颗粒还田对土壤养分和冬小麦产量的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(12): 1770-1778. | |
| 15 | Li W, Zhang J B, Zhang C Z, et al. Effects of residue returning methods and fertilizer application on physiological characteristics and yield of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). Soils, 2013, 45(2): 214-219. |
| 李玮, 张佳宝, 张丛志, 等. 秸秆还田方式和施肥对冬小麦生理特性及产量的影响. 土壤, 2013, 45(2): 214-219. | |
| 16 | Li C S, Li M, Wu X L, et al. Effects of tillage and sowing practices on plant growth, soil nutrient uptake and utilization of wheat after rice. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(5): 1435-1442. |
| 李朝苏, 李明, 吴晓丽, 等. 耕作播种方式对稻茬小麦生长和养分吸收利用的影响. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(5): 1435-1442. | |
| 17 | Ma S, Yu Z, Li Z. et al. Soil water use, grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in a long-term study of tillage practices and supplemental irrigation on the north China plain. Agricultural Water Management, 2015, 150: 9-17. |
| 18 | Li H S. Principle and technology of plant physiological and biochemical experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 23. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 23. | |
| 19 | Anna B, Jennifer M, Szymon S, et al. Sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS), sucrose synthase (SUS) and their products in the leaves of Miscanthus×giganteus and Zea mays at low temperature. Planta, 2020, 252(2): 23. |
| 20 | Usman K, Khan E A, Yazdan F, et al. Short response of spring wheat to tillage, residue management and split nitrogen application in a rice-wheat system. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2014, 13(12): 2625-2633. |
| 21 | Wang J H, Li T L, Huang L, et al. Effects of straw returning instead of fertilizer on wheat yield and water and fertilizer utilization in loess dryland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(3): 236-243, 251. |
| 王嘉豪, 李廷亮, 黄璐, 等. 秸秆还田替代化肥对黄土旱塬小麦产量及水肥利用的影响. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(3): 236-243, 251. | |
| 22 | Zhang S M, Hao M D, Liu Y L. Effects of long-term application of P fertilizer on the yield of winter wheat and characteristic of N absorption and soil fertility in dry-land of loess plateau. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(7): 159-163. |
| 张少民, 郝明德, 柳燕兰. 黄土区长期施用磷肥对冬小麦产量、吸氮特性及土壤肥力的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(7): 159-163. | |
| 23 | Chen L, Kou X Y, Dang Y A, et al. Effects of phosphorus application rates in wheat season on wheat-maize rotation yield and available phosphorus in soil. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2024, 44(2): 185-194. |
| 陈丽, 寇心悦, 党亚爱, 等. 麦季施磷量对小麦-玉米轮作产量及土壤有效磷的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2024, 44(2): 185-194. | |
| 24 | Chen L W. Effects of straw return field and fertilizer application on winter wheat growth and soil physical and chemical properties. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 陈刘炜. 秸秆还田与化肥配施对冬小麦生长发育及土壤理化性质的影响. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018. | |
| 25 | Yan D C, Zhu Y, Wang S H, et al. A quantitative knowledge-based model for designing suitable growth dynamics in rice. Plant Production Science, 2006, 9(2): 93-105. |
| 26 | Huang Y F, Zhang H, Zhang L H, et al. Effects of phosphorus (P) fertilizer rates on wheat P uptake and soil P balance in high-P soil. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(2): 211-219. |
| 黄玉芳, 张辉, 张立花, 等. 施磷量对高磷土壤小麦磷素吸收和土壤磷平衡的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(2): 211-219. | |
| 27 | Xiang X L, Chen S H, Yang H K, et al. Effects of straw mulching and phosphorus application on wheat yield, phosphorus absorption and utilization in hilly dryland. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(24): 5194-5205. |
| 向晓玲, 陈松鹤, 杨洪坤, 等. 秸秆覆盖与施磷对丘陵旱地小麦产量和磷素吸收利用效应的影响. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(24): 5194-5205. | |
| 28 | Stagnari F, Galieni A, Speca S, et al. Effects of straw mulch on growth and yield of durum wheat during transition to conservation agriculture in Mediterranean environment. Field Crops Research, 2014, 167: 51-63. |
| 29 | Song W C. Research of phosphorus rates on wheat variety Qingmai 6. Qingdao: Qingdao Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 宋威辰. 旱地小麦新品种青麦6号适宜施磷量研究. 青岛: 青岛农业大学, 2011. | |
| 30 | Wang J N. Effects of tillage practices on wheat yield formation and carbon metabolism in rainfed areas of Longzhong. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 王嘉男. 陇中旱农区耕作措施对小麦产量形成及碳代谢特征的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2020. | |
| 31 | Huang J Z. Effects of nitrogen fertilization, sowing date and rate, straw returning on formation of grain yield and quality and the physiological mechanisms in wheat. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 黄金瓒. 氮肥和播期播量及秸秆还田对小麦籽粒产量和品质形成的影响及其生理机制. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2012. | |
| 32 | Tian Y L. Effects of phosphorus application rate on soil respiration and temperature sensitivity under straw returning. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 田艳领. 秸秆还田下施磷量对土壤呼吸及其温度敏感性的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022. | |
| 33 | Lu Y, Bao X L, Huo H N, et al. Effects of different amounts of stover mulching on improving photosynthetic characteristics and yield of maize in Mollisol of Northeast China under long-term no-tillage. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(5): 840-847. |
| 鲁悦, 鲍雪莲, 霍海南, 等. 免耕条件下不同量秸秆覆盖还田提高东北黑土区玉米光合性能和产量的效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(5): 840-847. | |
| 34 | Zheng C X, Zhang F C, Zhang Z L, et al. Effects of limited irrigation and phosphorus on leaf photosynthesis and WUE of winter wheat. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2009, 28(6): 78-80, 90. |
| 郑彩霞, 张富仓, 张志亮, 等. 限量灌溉和施磷对冬小麦光合性能及水分利用效率的影响. 灌溉排水学报, 2009, 28(6): 78-80, 90. | |
| 35 | Yang Q, Han J L, Li Y M, et al. Effects of phosphorus fertilization on flag leaves photosynthesis and yield components in wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2006, 12(6): 816-821. |
| 杨晴, 韩金玲, 李雁鸣, 等. 不同施磷量对小麦旗叶光合性能和产量性状的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2006, 12(6): 816-821. | |
| 36 | Qiu Y, Xu T, Wei B, et al. Effects of different phosphorus levels on chlorophyll and nucleic acid content in flag leaf and ear of wheat. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 40(1): 27-33. |
| 邱悦, 徐婷, 魏波, 等. 不同磷素水平对小麦旗叶和穗部叶绿素及核酸含量的影响. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40(1): 27-33. | |
| 37 | Liu Y G, Lin Q, Fang Q L, et al. Effects of dryland with straw return on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of wheat after flowering stage. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2013, 28(4): 110-114. |
| 刘义国, 林琪, 房清龙, 等. 旱地秸秆还田对小麦花后光合特性及产量的影响. 华北农学报, 2013, 28(4): 110-114. | |
| 38 | Li L N, Kong J Q. Gene organization, function and application of plant sucrose synthase. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2015(9): 904-913. |
| 李丽娜, 孔建强. 植物蔗糖合酶的结构、功能及应用. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2015(9): 904-913. | |
| 39 | Wang X D. Effect of phosphorus on kernel yield and quality and physiological basis in winter wheat. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2003. |
| 王旭东. 磷对小麦产量和品质的影响及其生理基础研究. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2003. | |
| 40 | Jiang Z Q, Feng C N, Huang L L, et al. Grain starch formation characteristics as affected by phosphorus application in weak-gluten wheat Yangmai 9. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2006, 26(6): 81-85. |
| 姜宗庆, 封超年, 黄联联, 等. 施磷量对弱筋小麦扬麦9号籽粒淀粉合成和积累特性的调控效应. 麦类作物学报, 2006, 26(6): 81-85. | |
| 41 | Yu Z C, Liu Y G, Lin Q. Effects of depth of straw return on sucrose content and yield of wheat. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(30): 11-14. |
| 于淙超, 刘义国, 林琪. 秸秆还田深度对小麦蔗糖转化及产量形成的影响. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(30): 11-14. |
| [1] | 苏尧, 叶苏梅, 鲁梦醒, 马跃, 王玉宝, 王珊珊, 柴如山, 叶新新, 张震, 马超. 整合分析秸秆还田对农田杂草多度和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 150-160. |
| [2] | 马嵩科, 霍克, 张冬霞, 张静, 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 王贺正. 玉米秸秆还田配施氮肥对豫西旱地小麦土壤酶活性和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 120-133. |
| [3] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| [4] | 吴科生, 车宗贤, 包兴国, 张久东, 卢秉林, 杨新强, 杨蕊菊. 河西绿洲灌区灌漠土长期秸秆还田土壤肥力和作物产量特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 59-70. |
| [5] | 王飞, 刘彩玲, 何春梅, 李清华, 刘玉洁, 黄毅斌. 适宜磷、钾肥配比及稻秆半量还田提高紫云英产量与养分截获[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 81-89. |
| [6] | 杨封科, 何宝林, 张国平, 张立功, 高应平. 膜下秸秆还田添加腐解剂对旱地土壤碳氮积累及土壤肥力性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 67-76. |
| [7] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 樊廷录, 王磊, 程万莉, 李尚中, 王淑英, 雷康宁, 张朝伟. 秸秆还田与氮肥减施对旱地春玉米产量及生理指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 156-165. |
| [8] | 骆凯, 张吉宇, 王彦荣. 种植密度和施磷肥对黄花草木樨种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 112-119. |
| [9] | 赵庆雷, 信彩云, 王瑜, 王佳, 刘奇华, 李景岭, 马加清. 稻麦轮作区连续秸秆还田和施肥条件下砂姜黑土无机磷分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 58-68. |
| [10] | 曾瑾汐, 文熙宸, MuhammadAliRaza, 陈国鹏, 陈诚, 彭霄, 马艳玮, 李丽, 官思成, 杨文钰, 王小春. 氮磷配施对玉米-大豆套作模式下种间作用、玉米产量及干物质积累与转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 166-176. |
| [11] | 李新乐, 侯向阳, 穆怀彬, 李西良, 郭丰辉. 连续6年施磷肥对土壤磷素积累、形态转化及有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 218-224. |
| [12] | 王静,胡靖,杜国祯. 施氮磷肥对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤线虫群落组成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(12): 20-28. |
| [13] | 陈益, 王正银, 唐静, 张晓玲, 杨东, 向华辉, 李戎. 磷肥用量对石灰性紫色土壤油麦菜产量、品质和养分形态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 183-193. |
| [14] | 张凡凡, 于磊, 马春晖, 张前兵, 鲁为华. 绿洲区滴灌条件下施磷对紫花苜蓿生产性能及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 175-182. |
| [15] | 徐国伟,李帅,赵永芳,陈明灿,李友军. 秸秆还田与施氮对水稻根系分泌物及氮素利用的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 140-146. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||