

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 155-165.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023238
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
申迪1,2,3( ), 曾子铭1,2,3, 庞凯悦1,2,3, 柴沙驼1,2,3,4, 聂洪辛1,2,3, 李毓敏1,2,3, 廖扬1,2,3, 王迅1,2,3, 黄伟华1, 刘书杰1,2,3,4, 杨英魁1,2,3,4(
), 曾子铭1,2,3, 庞凯悦1,2,3, 柴沙驼1,2,3,4, 聂洪辛1,2,3, 李毓敏1,2,3, 廖扬1,2,3, 王迅1,2,3, 黄伟华1, 刘书杰1,2,3,4, 杨英魁1,2,3,4( ), 王书祥1,2,3,4(
), 王书祥1,2,3,4( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-12
修回日期:2023-09-15
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
杨英魁,王书祥
作者简介:yykui@qhu.edu.cn基金资助:
Di SHEN1,2,3( ), Zi-ming ZENG1,2,3, Kai-yue PANG1,2,3, Sha-tuo CHAI1,2,3,4, Hong-xin NIE1,2,3, Yu-min LI1,2,3, Yang LIAO1,2,3, Xun WANG1,2,3, Wei-hua HUANG1, Shu-jie LIU1,2,3,4, Ying-kui YANG1,2,3,4(
), Zi-ming ZENG1,2,3, Kai-yue PANG1,2,3, Sha-tuo CHAI1,2,3,4, Hong-xin NIE1,2,3, Yu-min LI1,2,3, Yang LIAO1,2,3, Xun WANG1,2,3, Wei-hua HUANG1, Shu-jie LIU1,2,3,4, Ying-kui YANG1,2,3,4( ), Shu-xiang WANG1,2,3,4(
), Shu-xiang WANG1,2,3,4( )
)
Received:2023-07-12
Revised:2023-09-15
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Ying-kui YANG,Shu-xiang WANG
摘要:
本研究旨在探究低精料日粮和高精料日粮对牦牛瘤胃微生物菌群的影响。本试验选取3周岁,体重相近的12头牦牛,平均分为两组。分别用低精料[精粗比30∶70(C30组)]的日粮和高精料[精粗比70∶30(C70组)]的日粮,饲喂2个月。结果表明:1)C70组平均日增重极显著高于C30组(P<0.01)。2)C30组Chao1指数、Shannon指数和谱系多样性指数都极显著高于C70组(P<0.01)。3)在门水平上,髌骨细菌门、脱硫杆菌门、疣微菌门、蓝藻菌门相对丰富度C30组显著高于C70组(P<0.05)。厚壁菌门相对丰富度C30组极显著高于C70组(P<0.01)。拟杆菌门相对丰富度C70组极显著高于C30组(P<0.01),变形菌门C70组显著高于C30组(P<0.05)。在属水平上C30组牦牛的瘤胃微生物克里斯滕森菌科_R-7、未分类瘤胃细菌、NK4A214属、未培养菌(uncultured bacterium)和不确定的菌属(unidentified)的相对丰富度极显著高于C70组牦牛瘤胃微生物丰富度(P<0.01)。理研菌属丰富度C30组显著高于C70组(P<0.05)。普雷沃氏菌属、毛螺菌科-NK3A20、瘤胃球菌属C70组相对丰富度显著高于C30组(P<0.05)。4)在KEGG2水平上,所有的牦牛瘤胃样本中有31个基因家族。C70组运输和分解代谢(transport and catabolism)、辅因子和维生素代谢以及能量代谢显著高于C30组(P<0.05)。C70组的碳水化合物代谢(carbohydrate metabolism)极显著高于C30组(P<0.01)。C30组的免疫疾病(immune disease)极显著高于C70组,C70组的次级代谢产物的生物合成(biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites)极显著高于C30组(P<0.01)。综上所述,与低精料组相比饲喂高精料日粮降低了牦牛瘤胃微生物菌群的多样性,并减少了不利于瘤胃菌群健康的菌群丰富度,同时提高了优势菌群的丰富度。在代谢功能上,高精料日粮增加了碳水化合物代谢和其他营养因子代谢,降低了免疫疾病代谢。
申迪, 曾子铭, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 廖扬, 王迅, 黄伟华, 刘书杰, 杨英魁, 王书祥. 低精料日粮和高精料日粮对牦牛生长性能和瘤胃菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 155-165.
Di SHEN, Zi-ming ZENG, Kai-yue PANG, Sha-tuo CHAI, Hong-xin NIE, Yu-min LI, Yang LIAO, Xun WANG, Wei-hua HUANG, Shu-jie LIU, Ying-kui YANG, Shu-xiang WANG. Effects of low-concentrate and high-concentrate diets on yak growth performance and rumen microbiota structure[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 155-165.
项目 Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 原料Ingredients (%) | ||
| 燕麦干草Oats hay | 70.00 | 30.00 |
| 玉米Corn | 13.16 | 38.37 |
| 小麦Wheat | 3.72 | 0.00 |
| 麸皮Wheat bran | 3.78 | 12.23 |
| 食盐NaCl | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 菜籽粕Rapeseed meal | 3.75 | 12.64 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 1.31 | 0.00 |
| 菜籽油Rapeseed oil | 0.00 | 0.82 |
| 棕榈油脂肪粉Palm oil fat power1) | 1.28 | 0.94 |
| 磷酸氢钙CaHPO4 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 预混料Premix2) | 2.00 | 4.00 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 营养水平Nutrient levels3) | ||
| 干物质Dry matter (DM, %) | 89.20 | 88.29 |
| 代谢能Metabolic energy (ME, MJ·kg-1) | 9.79 | 12.61 |
| 粗蛋白质Crude protein (CP, %) | 11.53 | 12.79 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, %) | 45.47 | 29.38 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 29.41 | 15.84 |
| 钙Ca (%) | 0.43 | 0.22 |
| 磷P (%) | 0.41 | 0.56 |
表1 牦牛饲粮配比及营养水平(干物质基础)
Table 1 Proportion and nutritional level of yak diet (dry matter basis)
项目 Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 原料Ingredients (%) | ||
| 燕麦干草Oats hay | 70.00 | 30.00 |
| 玉米Corn | 13.16 | 38.37 |
| 小麦Wheat | 3.72 | 0.00 |
| 麸皮Wheat bran | 3.78 | 12.23 |
| 食盐NaCl | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 菜籽粕Rapeseed meal | 3.75 | 12.64 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 1.31 | 0.00 |
| 菜籽油Rapeseed oil | 0.00 | 0.82 |
| 棕榈油脂肪粉Palm oil fat power1) | 1.28 | 0.94 |
| 磷酸氢钙CaHPO4 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 预混料Premix2) | 2.00 | 4.00 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 营养水平Nutrient levels3) | ||
| 干物质Dry matter (DM, %) | 89.20 | 88.29 |
| 代谢能Metabolic energy (ME, MJ·kg-1) | 9.79 | 12.61 |
| 粗蛋白质Crude protein (CP, %) | 11.53 | 12.79 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, %) | 45.47 | 29.38 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 29.41 | 15.84 |
| 钙Ca (%) | 0.43 | 0.22 |
| 磷P (%) | 0.41 | 0.56 |
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 平均初重Average initial weight (kg) | 164.90±16.90a | 162.54±15.73a |
| 平均末重Average end weight (kg) | 186.04±13.72b | 211.73±15.86a |
| 平均增重Average weight gain (kg) | 21.14±4.87B | 49.19±6.51A |
| 平均日增重Average daily gain in weight (kg) | 0.35±0.06B | 0.78±0.12A |
| 干物质采食量Dry matter feed intake (DMI, kg·d-1) | 3.94b | 4.88a |
| 料重比Feed/gain (F/G) | 11.27A | 6.26B |
表2 饲喂不同精粗比日粮对牦牛生产性能的影响
Table 2 Effects of feeding different fine-to-rough diets on the production performance of the same yak
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 平均初重Average initial weight (kg) | 164.90±16.90a | 162.54±15.73a |
| 平均末重Average end weight (kg) | 186.04±13.72b | 211.73±15.86a |
| 平均增重Average weight gain (kg) | 21.14±4.87B | 49.19±6.51A |
| 平均日增重Average daily gain in weight (kg) | 0.35±0.06B | 0.78±0.12A |
| 干物质采食量Dry matter feed intake (DMI, kg·d-1) | 3.94b | 4.88a |
| 料重比Feed/gain (F/G) | 11.27A | 6.26B |
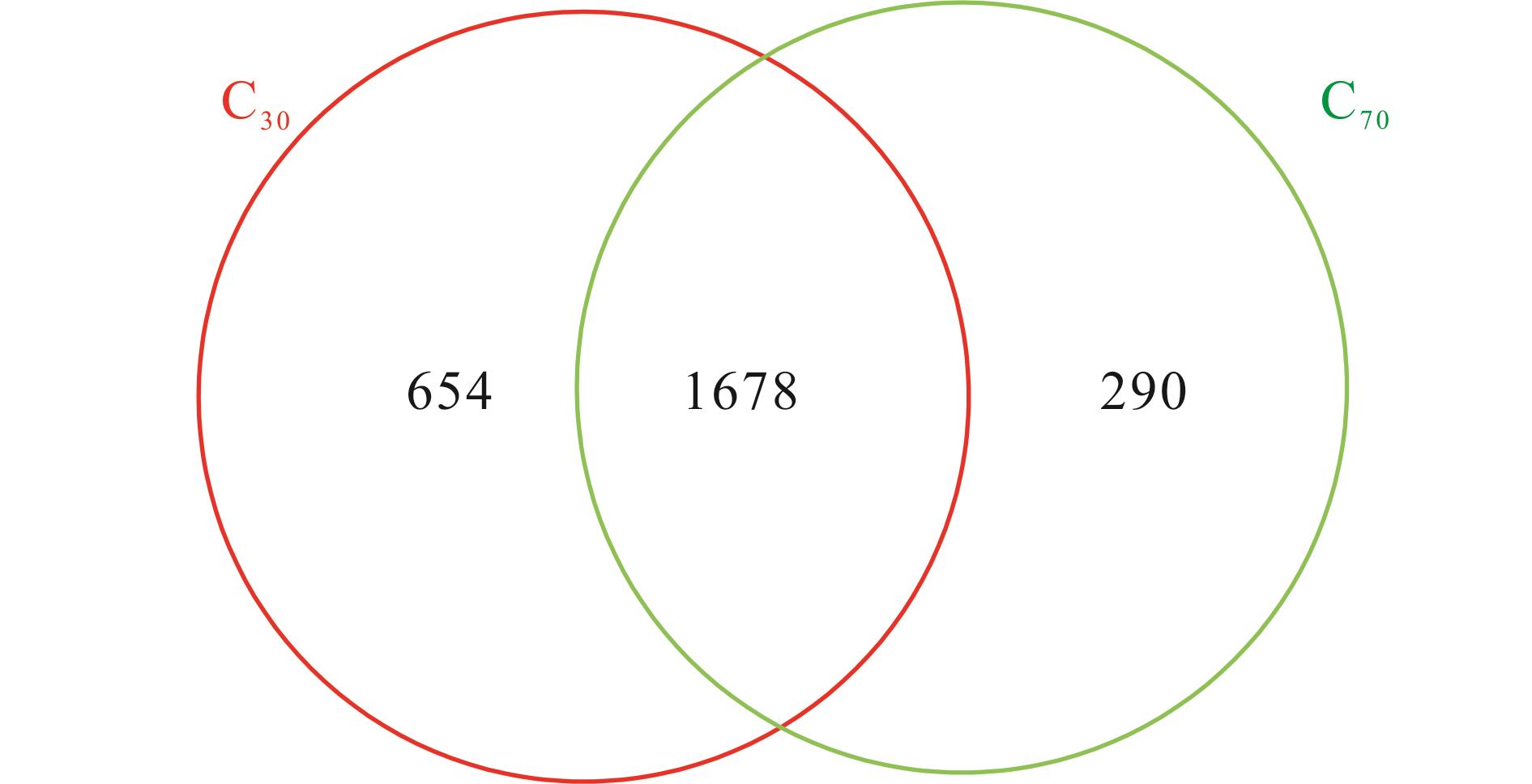
图1 韦恩图红色代表C30组的OTU,绿色代表C70组的OTU。The red circle represents the OTU of the C30 group, and the green circle represents the OTU of the C70 group.
Fig.1 Venn diagram
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| Chao1指数Chao1 index | 1569.71±60.55A | 1354.13±137.19B |
| Shannon指数Shannon index | 7.63±0.29A | 7.16±0.36B |
| 谱系多样性Phylogenetic diversity | 100.59±4.73A | 91.64±7.72B |
| 辛普森指数Simpson index | 0.98±0.00 | 0.97±0.02 |
表3 饲喂不同精粗比日粮的牦牛瘤胃菌群Alpha多样性指数
Table 3 Alpha diversity index of yak rumen microflora by changing the ratio of concentrate to roughness
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| Chao1指数Chao1 index | 1569.71±60.55A | 1354.13±137.19B |
| Shannon指数Shannon index | 7.63±0.29A | 7.16±0.36B |
| 谱系多样性Phylogenetic diversity | 100.59±4.73A | 91.64±7.72B |
| 辛普森指数Simpson index | 0.98±0.00 | 0.97±0.02 |
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 厚壁菌门Firmicutes | 68.98±7.19A | 64.19±5.92B |
| 拟杆菌门Bacteroidota | 20.86±2.65B | 30.04±5.12A |
| 放线菌门Actinobacteria | 6.54±4.77A | 2.78±1.98B |
| 髌骨细菌门Patescibacteria | 1.76±0.83a | 1.64±0.75b |
| 脱硫杆菌门Desulfobacterota | 0.36±0.16a | 0.24±0.07b |
| 变形菌门Proteobacteria | 0.24±0.15b | 0.35±0.22a |
| 疣微菌门Verrucomicrobia | 0.49±0.13A | 0.08±0.02B |
| 螺旋体门Spirochaetota | 0.16±0.10b | 0.29±0.12a |
| 蓝藻菌门Cyanobacteria | 0.24±0.19a | 0.08±0.05b |
| 绿弯菌门Chloroflexi | 0.10±0.06 | 0.08±0.04 |
表4 门水平上的菌群组成和相对丰富度
Table 4 Composition and relative abundance of flora at phylum level (%)
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 厚壁菌门Firmicutes | 68.98±7.19A | 64.19±5.92B |
| 拟杆菌门Bacteroidota | 20.86±2.65B | 30.04±5.12A |
| 放线菌门Actinobacteria | 6.54±4.77A | 2.78±1.98B |
| 髌骨细菌门Patescibacteria | 1.76±0.83a | 1.64±0.75b |
| 脱硫杆菌门Desulfobacterota | 0.36±0.16a | 0.24±0.07b |
| 变形菌门Proteobacteria | 0.24±0.15b | 0.35±0.22a |
| 疣微菌门Verrucomicrobia | 0.49±0.13A | 0.08±0.02B |
| 螺旋体门Spirochaetota | 0.16±0.10b | 0.29±0.12a |
| 蓝藻菌门Cyanobacteria | 0.24±0.19a | 0.08±0.05b |
| 绿弯菌门Chloroflexi | 0.10±0.06 | 0.08±0.04 |
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 克里斯滕森菌科_R-7 Christensenellaceae_R-7 | 10.91±1.91A | 7.91±2.51B |
| 普雷沃氏菌属Prevotella | 4.71±3.51b | 13.31±5.85a |
| 未分类瘤胃细菌Unclassified_rumen_bacterium | 9.61±3.37A | 6.98±2.10B |
| 毛螺菌科-NK3A20 Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group | 6.40±3.45b | 8.54±3.30a |
| NK4A214属NK4A214_group | 7.74±0.54A | 5.95±2.43B |
| 理研菌属Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group | 7.06±2.12a | 5.99±2.74b |
| 瘤胃球菌属Ruminococcus | 5.39±2.18b | 7.19±2.67a |
| 聚乙酸菌属Acetitomaculum | 4.62±2.30B | 7.02±3.67A |
| 未培养菌Uncultured_bacterium | 6.26±1.76A | 5.17±1.33B |
| 不确定的Unidentified | 5.72±1.95A | 4.25±1.42B |
表5 属水平上的菌群组成和相对丰富度
Table 5 Composition and relative abundance of flora at the genus level (%)
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 克里斯滕森菌科_R-7 Christensenellaceae_R-7 | 10.91±1.91A | 7.91±2.51B |
| 普雷沃氏菌属Prevotella | 4.71±3.51b | 13.31±5.85a |
| 未分类瘤胃细菌Unclassified_rumen_bacterium | 9.61±3.37A | 6.98±2.10B |
| 毛螺菌科-NK3A20 Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group | 6.40±3.45b | 8.54±3.30a |
| NK4A214属NK4A214_group | 7.74±0.54A | 5.95±2.43B |
| 理研菌属Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group | 7.06±2.12a | 5.99±2.74b |
| 瘤胃球菌属Ruminococcus | 5.39±2.18b | 7.19±2.67a |
| 聚乙酸菌属Acetitomaculum | 4.62±2.30B | 7.02±3.67A |
| 未培养菌Uncultured_bacterium | 6.26±1.76A | 5.17±1.33B |
| 不确定的Unidentified | 5.72±1.95A | 4.25±1.42B |
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 碳水化合物代谢Carbohydrate metabolism | 13.40±0.05B | 13.63±0.06A |
| 脂质代谢Lipid metabolism | 4.87±0.10 | 4.90±0.05 |
| 辅因子和维生素代谢Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | 12.76±0.33b | 12.93±0.10a |
| 能量代谢Energy metabolism | 5.60±0.06b | 5.69±0.05a |
| 核苷酸代谢Nucleotide metabolism | 2.06±0.02 | 2.10±0.02 |
| 氨基酸代谢Amino acid metabolism | 12.94±0.04 | 13.04±0.08 |
| 萜类化合物和聚酮类化合物的代谢Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | 10.23±0.25 | 10.20±0.13 |
| 次级代谢产物的生物合成Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 2.08±0.02B | 2.29±0.01A |
| 口服抗生素耐药性Drug resistance of antimicrobial | 0.15±0.02 | 0.15±0.01 |
| 外源性物质的生物降解和代谢Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | 2.70±0.26 | 2.69±0.20 |
| 其他氨基酸代谢Metabolism of other amino acids | 6.74±0.23 | 6.79±0.27 |
| 聚糖的生物合成和代谢Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism | 3.81±0.25 | 4.12±0.08 |
| 翻译Translation | 3.58±0.04 | 3.59±0.05 |
| 膜传输Membrane transport | 1.59±0.01 | 1.54±0.01 |
| 信号转导Signal transduction | 0.33±0.01 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 细胞运动Cell motility | 2.56±0.20 | 2.51±0.05 |
| 折叠分类和降解Folding, sorting and degradation | 3.28±0.06 | 3.25±0.03 |
| 转录Transcription | 1.17±0.02 | 1.21±0.02 |
| 复制和修复Replication and repair | 6.39±0.06 | 6.47±0.09 |
| 细胞生长与死亡Cell growth and death | 1.59±0.02 | 1.59±0.02 |
| 运输和分解代谢Transport and catabolism | 0.20±0.01b | 0.42±0.03a |
| 信号分子与相互作用Signaling molecules and interaction | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 内分泌系统Endocrine system | 0.09±0.00 | 0.09±0.00 |
| 免疫系统Immune system | 0.08±0.00 | 0.09±0.00 |
| 环境适应Environmental adaptation | 0.08±0.00 | 0.09±0.00 |
| 排泄系统Excretory system | 0.22±0.01 | 0.23±0.01 |
| 消化系统Digestive system | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 细菌传染病Infectious disease of bacterial | 0.04±0.01 | 0.06±0.00 |
| 细胞群落原核生物Cellular community-prokaryotes | 0.16±0.01 | 0.16±0.00 |
| 寄生虫传染病Infectious disease of parasitic | 0.18±0.01 | 0.19±0.01 |
| 免疫疾病Immune disease | 0.23±0.00A | 0.03±0.00B |
表6 KEGG2水平注释
Table 6 KEGG2 horizontal annotation
| 项目Items | C30组Group C30 | C70组Group C70 |
|---|---|---|
| 碳水化合物代谢Carbohydrate metabolism | 13.40±0.05B | 13.63±0.06A |
| 脂质代谢Lipid metabolism | 4.87±0.10 | 4.90±0.05 |
| 辅因子和维生素代谢Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | 12.76±0.33b | 12.93±0.10a |
| 能量代谢Energy metabolism | 5.60±0.06b | 5.69±0.05a |
| 核苷酸代谢Nucleotide metabolism | 2.06±0.02 | 2.10±0.02 |
| 氨基酸代谢Amino acid metabolism | 12.94±0.04 | 13.04±0.08 |
| 萜类化合物和聚酮类化合物的代谢Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | 10.23±0.25 | 10.20±0.13 |
| 次级代谢产物的生物合成Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 2.08±0.02B | 2.29±0.01A |
| 口服抗生素耐药性Drug resistance of antimicrobial | 0.15±0.02 | 0.15±0.01 |
| 外源性物质的生物降解和代谢Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | 2.70±0.26 | 2.69±0.20 |
| 其他氨基酸代谢Metabolism of other amino acids | 6.74±0.23 | 6.79±0.27 |
| 聚糖的生物合成和代谢Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism | 3.81±0.25 | 4.12±0.08 |
| 翻译Translation | 3.58±0.04 | 3.59±0.05 |
| 膜传输Membrane transport | 1.59±0.01 | 1.54±0.01 |
| 信号转导Signal transduction | 0.33±0.01 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 细胞运动Cell motility | 2.56±0.20 | 2.51±0.05 |
| 折叠分类和降解Folding, sorting and degradation | 3.28±0.06 | 3.25±0.03 |
| 转录Transcription | 1.17±0.02 | 1.21±0.02 |
| 复制和修复Replication and repair | 6.39±0.06 | 6.47±0.09 |
| 细胞生长与死亡Cell growth and death | 1.59±0.02 | 1.59±0.02 |
| 运输和分解代谢Transport and catabolism | 0.20±0.01b | 0.42±0.03a |
| 信号分子与相互作用Signaling molecules and interaction | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 内分泌系统Endocrine system | 0.09±0.00 | 0.09±0.00 |
| 免疫系统Immune system | 0.08±0.00 | 0.09±0.00 |
| 环境适应Environmental adaptation | 0.08±0.00 | 0.09±0.00 |
| 排泄系统Excretory system | 0.22±0.01 | 0.23±0.01 |
| 消化系统Digestive system | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 细菌传染病Infectious disease of bacterial | 0.04±0.01 | 0.06±0.00 |
| 细胞群落原核生物Cellular community-prokaryotes | 0.16±0.01 | 0.16±0.00 |
| 寄生虫传染病Infectious disease of parasitic | 0.18±0.01 | 0.19±0.01 |
| 免疫疾病Immune disease | 0.23±0.00A | 0.03±0.00B |
| 1 | Long R, Ding L, Shang Z. The yak grazing system on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau and its status. Rangeland Journal, 2008, 30(2): 241-246. |
| 2 | Ceconi I, Ruiz-Moreno M J, Dilorenzo N, et al. Effect of urea inclusion in diets containing corn dried distillers grains on feedlot cattle performance, carcass characteristics, ruminal fermentation, total tract digestibility, and purine derivatives-to-creatinine index. Journal of Animal Science, 2015, 93(1): 357-369. |
| 3 | Jiang S Z, Yang Z B, Yang W R, et al. Diets of differentially processed wheat alter ruminal fermentation parameters and microbial populations in beef cattle. Journal of Animal Science, 2015, 93(11): 5378-5385. |
| 4 | Wang Y Y. Effects of dietary nutrient levels on the bacterial flora, pH and VFA levels in rumen of Tan sheep. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2018. |
| 王尧悦. 日粮营养水平对滩羊瘤胃细菌区系及pH和VFA的影响. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. | |
| 5 | Liu J H, Bian G R, Zhu W Y, et al. Highgrain feeding causes strong shifts in ruminal epithelial bacterial community and expression of Tolllike receptor genes in goats. Fortiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6(9): 167. |
| 6 | Romeroperez G A, Ominski K H, Mcallister T A, et al. Effect of environmental factors and influence of rumen and hindgut biogeography on bacterial communities in steers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(1): 258-268. |
| 7 | Wang J Q, Yang H J, Mo F, et al. NY/T 815-2004. China feeding standard of beef cattle. Beijing: China Agricuture Press, 2004. |
| 王加启, 杨红建, 莫放, 等. NY/T 815-2004. 肉牛饲养标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004. | |
| 8 | Hu L H. Yak nutrition by collection research papers. Xining: Qinghai People’s Publishing House, 1997. |
| 胡令浩. 牦牛营养研究论文集. 西宁: 青海人民出版社, 1997. | |
| 9 | National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Nutrient requirements of beef cattle (Eighth revised edition). Washington D C: the National Academy Press, 2016. |
| 10 | Feng Y L, Lu Z N. Nutritional requirements and feed ingredients of dairy cows. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2007. |
| 冯仰廉, 陆治年. 奶牛营养需要和饲料成分. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. | |
| 11 | GB/T 6435-2014. Determination of moisture in feed stuffs. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014. |
| GB/T 6435-2014. 饲料中水分的测定. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. | |
| 12 | GB/T 6432-2018. Determination of crude protein in feeds-Kjeldahl method. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018. |
| GB/T 6432-2018. 饲料中粗蛋白的测定 凯氏定氮法. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 13 | GB/T 6436-2018. Determination of calcium in feed. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018. |
| GB/T 6436-2018. 饲料中钙的测定. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 14 | GB/T 6437-2018. Determination of phosphorus in feeds-Spectrophotometry. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018. |
| GB/T 6437-2018. 饲料中总磷的测定 分光光度法. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 15 | Lee C, Hristov A N. Short communication: evaluation of acid-insoluble ash and indigestible neutral detergent fiber as total-tract digestibility markers in dairy cows fed corn silage-based diets. Journal of Dairy Science, 2013, 96(8): 5295-5299. |
| 16 | Zhao J B, Song X M, Li Z C, et al. Determination of available energy and nutrient apparent total tract digestibility of different fiber ingredients in growing pigs. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(11): 6114-6122. |
| 赵金标, 宋孝明, 李忠超, 等. 不同纤维原料在生长猪的有效能和营养物质表观全肠道消化率的测定. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(11): 6114-6122. | |
| 17 | Zhang Z Y. Effects of different feeding strategies and dietary energy levels on yak production performance and rumen bacteria diversity. Lanzhou: Northwest Minzu University, 2021. |
| 张振宇. 饲养方式和日粮能量对牦牛生产性能及瘤胃细菌多样性的影响. 兰州: 西北民族大学, 2021. | |
| 18 | Li Y, Dai D W, Yang Y K, et al. Effects of diets with different concentrate to roughage ratios on growth performance, nutrient apparent digestibilities, serum biochemical indexes and rumen fermentation parameters of yaks in late stage of fattening. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(5): 3056-3065. |
| 李岩, 戴东文, 杨英魁, 等. 不同精粗比饲粮对育肥后期牦牛生长性能、营养物质表观消化率、血清生化指标及瘤胃发酵参数的影响. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(5): 3056-3065. | |
| 19 | Pang K Y, Dai D W, Yang Y K, et al. Effects of different feeding methods on rumen fermentation parameters and microbial flora of yaks. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(3): 1667-1682. |
| 庞凯悦, 戴东文, 杨英魁, 等. 不同饲养方式对牦牛瘤胃发酵参数及微生物菌群的影响. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(3): 1667-1682. | |
| 20 | Yang X, Fan W J, Tang Z P, et al. Effects of different mulching cultivation on bacterial diversity, enzyme activity and physicochemical properties of potato rhizosphere soil. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Science, 2021, 35(9): 2145-2153. |
| 杨鑫, 樊吴静, 唐洲萍, 等. 不同覆盖栽培对马铃薯根际土壤细菌多样性、酶活性及化学性状的影响. 核农学报, 2021, 35(9): 2145-2153. | |
| 21 | Huo J H, Fang S P, Wu P S, et al. Effects of diets with different concentration-roughage ratios on the microbial community structure of Nubian goat rumen. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(12): 2558-2566. |
| 霍俊宏, 方绍培, 吴平山, 等. 不同精粗比日粮对努比亚山羊瘤胃菌群结构的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(12): 2558-2566. | |
| 22 | Pang K Y, Chai S T, Wang X, et al. The effect of dietary concentrate to roughage ratio on the structure of rumen microbiota in yaks. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(10): 2201-2210. |
| 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 王迅, 等. 饲粮精粗比对牦牛瘤胃菌群结构的影响. 草业科学, 2022, 39(10): 2201-2210. | |
| 23 | Zhu X D, Li Y N, Xu X F. Research progress on rumen fiber-degrading microorganisms in ruminants. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici, 2021, 42(7): 8-13. |
| 朱相德, 李娅楠, 徐晓锋. 反刍动物瘤胃纤维降解微生物的研究进展. 家畜生态学报, 2021, 42(7): 8-13. | |
| 24 | Song F, Li Y, Su D Q Q G, et al. Comparison of the effects of Ceratoides arborescens and Medicago sativa pellets on the slaughter performance and meat quality of twin lambs. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 53(8): 32-36. |
| 宋峰, 李颖, 苏德其其格, 等. 比较驼绒藜和苜蓿颗粒料对双胞胎羔羊屠宰性能和肉品质的影响. 畜牧与兽医, 2021, 53(8): 32-36. | |
| 25 | Bi Y L, Zeng S Q, Zhang R, et al. Effects of dietary energy levels on rumen bacterial community composition in Holstein heifers under the same forage to concentrate ratio condition. BMC Microbiology, 2018, 18(3): 69. |
| 26 | Zhou Z M, Fang L, Meng Q X, et al. Assessment of ruminal bacterial and archaeal community structure in yak (Bos grunniens). Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8(7): 179. |
| 27 | Evans N J, Brown J M, Murray R D, et al. Characterization of novel bovine gastrointestinal tract Treponema isolates and comparison with bovine digital dermatitis treponemes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(1): 138-147. |
| 28 | Reigstad C S, Kashyap P C. Beyond phylotyping: understanding the impact of gut microbiota on host biology. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 2013, 25(5): 358-372. |
| 29 | Servin J A, Herbold C W, Skophammer R G, et al. Evidence excluding the root of the tree of life from the Actinobacteria. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2007, 25(1): 1-4. |
| 30 | Dai D W, Pang K Y, Wang X, et al. Effects of different concentrate supplement levels on rumen fermentation and microbial community structure of grazing yaks in the warm season. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 169-177. |
| 戴东文, 庞凯悦, 王迅, 等. 精料补饲水平对暖季放牧牦牛瘤胃发酵和菌群结构的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 169-177. | |
| 31 | Derrien M, Van Baarlen P, Hooiveld G, et al. Modulation of mucosal immune response, tolerance, and proliferation in mice colonized by the mucin-degrader Akkermansia muciniphila. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2011, 2(3): 166. |
| 32 | Li L S, Peng Z L, Chen S Y, et al. Effects of small peptides and yeast culture on rumen microbial diversity and fermentation parameters of yaks. China Feed, 2021(5): 16-23. |
| 黎凌铄, 彭忠利, 陈仕勇, 等. 小肽与酵母培养物对舍饲牦牛瘤胃微生物多样性和发酵参数的影响. 中国饲料, 2021(5): 16-23. | |
| 33 | Guo W, Guo X J, Zhou X, et al. The effect of corn straw fermented with compound bacterial agents on bacterial diversity in rumen fluid of sheep. Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 49(4): 736-745. |
| 郭威, 郭晓军, 周贤, 等. 复合菌剂发酵玉米秸秆对绵羊瘤胃液细菌多样性的影响. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018, 49(4): 736-745. | |
| 34 | Chittora D, Meena M, Barupal T, et al. Cyanobacteria as a source of biofertilizers for sustainable agriculture. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2020, 22: 100737. |
| 35 | Bjornsson L, Hugenholtz P, Tyson G W, et al. Filamentous chloro flexi (green nonsulfur bacteria) are abundant in wastewater treatment processes with biological nutrient removal. Microbiology, 2002, 148(8): 2309-2318. |
| 36 | Gao Z W, Liu F H, Jia M Q, et al. Illumina-based high-throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial community structure and diversity in Beidagang wetland sediment, Tianjin. Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 41(4): 45-52. |
| 高志伟, 刘凡惠, 贾美清, 等. 基于Illumina高通量测序的天津北大港湿地沉积物细菌群落特征和多样性分析. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 41(4): 45-52. | |
| 37 | Cai Z F. Characteristics of main seagrass beds microbial community in Wenchang and the effects of two kinds of land-based pollutants and vibrio on the bacterial community of Thalassia hemprichii. Haikou: Hainan University, 2021. |
| 蔡泽富. 文昌主要海草床微生物群落特征及两类陆源污染物与弧菌对泰来草细菌群落影响的研究. 海口: 海南大学, 2021. | |
| 38 | Zhang L. Effects of NFC/NDF ratios on performances of cows, rumen fermentation and bacterial microbiota in vitro. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 张林. 日粮NFC/NDF比例对奶牛生产性能、体外瘤胃发酵和细菌微生物区系的影响. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. | |
| 39 | He J, Hai L, Orgoldol K, et al. High-throughput sequencing reveals the gut microbiome of the bactrian camel in different ages. Current Microbiology, 2019, 76(7): 810-817. |
| 40 | Gao Y F. Effects of niacin on microorganism system in the rumen of cattle under high-concentrate diet. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 高雨飞. 高精料日粮条件下烟酸对牛瘤胃微生物区系的影响. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2017. | |
| 41 | Zhang L, Wang S D, Xie F, et al. Changes of intestinal flora and amino acid metabolism in rats with irritable bowel syndrome. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2018, 40(3): 240-244. |
| 张亮, 王世达, 谢方, 等. 肠易激综合征大鼠肠道菌群和氨基酸代谢的变化. 营养学报, 2018, 40(3): 240-244. | |
| 42 | Zhang H T. Effects of corn silage levels on rumen fluid microbiota and its metabolome in Holstein Heifers. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 张红涛. 不同玉米青贮水平对荷斯坦后备牛瘤胃液微生物组及其代谢组的影响. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. | |
| 43 | Zhang X J, Wang L Z. Effects of dietary neutral detergent fibre level on structure and composition of rumen bacteria in goats. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(4): 1377-1386. |
| 张雪娇, 王立志. 饲粮中性洗涤纤维水平对山羊瘤胃细菌结构及组成的影响. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(4): 1377-1386. | |
| 44 | Yang S, Wei Y R, Liang T, et al. Effect of grazing and supplementary feeding on the number of rumen microorganisms in Inner Mongolia cashmere goats. Feed Research, 2020, 43(9): 21-24. |
| 杨硕, 韦玥瑞, 梁天, 等. 放牧及补饲对内蒙古绒山羊瘤胃微生物数量的影响. 饲料研究, 2020, 43(9): 21-24. | |
| 45 | Lamendella R, Domingo J W, Ghosh S, et al. Comparative fecal metagenomics unveils unique functional capacity of the swine gut. BMC Microbiology, 2011, 11(6): 103. |
| 46 | Liu D Y, Fu D B, Qu M R, et al. The metabolism rule and requirements of energy of 11 to 12-month-old Xianan cattle. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2013, 35(4): 802-806. |
| 刘道杨, 付戴波, 瞿明仁, 等. 11~12月龄夏南牛能量代谢规律与需要量研究. 江西农业大学学报, 2013, 35(4): 802-806. | |
| 47 | Ley, Ruth E. Gut microbiota in 2015: Prevotella in the gut: choose carefully. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2016, 13(2): 69-70. |
| 48 | Lars C, Stine V, Roager H M, et al. Prevotella abundance predicts weight loss success in healthy, overweight adults consuming a whole-grain diet ad libitum: a post hoc analysis of a 6-wk randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Nutrition, 2019, 149(12): 2174-2181. |
| 49 | Pal D, Naskar M, Bera A, et al. Chemical synthesis of the pentasaccharide repeating unit of the O-specific polysaccharide from Ruminococcus gnavus. Carbohydrate Research, 2021, 507(8): 108384. |
| [1] | 张瑞, 安雪姣, 李建烨, 卢曾奎, 牛春娥, 徐振飞, 张金霞, 耿智广, 岳耀敬, 杨博辉. 湖羊及其不同杂交组合生长性能、产肉性能及肌肉品质比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 186-197. |
| [2] | 杨乾龙, 魏倩倩, 赵德辉, 郭肖兰, 张铁涛, 王晓旭, 鲍坤, 王凯英. 饲粮添加过瘤胃半胱氨酸对育成期梅花鹿生长性能、营养物质表观消化率和血清生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 148-159. |
| [3] | 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 申迪, 曾子铭, 廖扬, 王迅, 薛斌, 刘书杰, 王书祥, 杨英魁. 不同精粗比对牦牛粪便菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 189-197. |
| [4] | 王钊, 刘静, 于昊, 李鹏, 牛伟强, 万永杰, 张艳丽, 茆达干. 日粮添加蚕豆皮对湖羊生长性能、屠宰性能、器官发育和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 162-172. |
| [5] | 王循刚, 张晓玲, 徐田伟, 耿远月, 胡林勇, 赵娜, 刘宏金, 康生萍, 徐世晓. 饲粮蛋白质水平对藏系绵羊瘤胃真菌菌群结构及功能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 182-191. |
| [6] | 范阳, 齐伟彪, 朱崇淼, 殷雨洋, 毛胜勇. 日粮中添加发酵豆渣对湖羊生长性能、养分表观消化率、肉品质及血清生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 86-93. |
| [7] | 霍俊宏, 詹康, 黄秋生, 钟小军, 占今舜, 严学兵. 不同精粗比日粮对山羊生产性能、血清生化指标和瘤胃发酵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 151-161. |
| [8] | 蓝婧婷, 任瑞, 周瑞, 戴洪伟, 舒文秀, 朱凯, 王略宇, 徐红伟, 臧荣鑫. 花椰菜尾菜发酵饲料对保育猪生长性能、血清生化指标、小肠组织形态及经济效益的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 180-189. |
| [9] | 索效军, 张年, 杨前平, 陶虎, 熊琪, 李晓锋, 张凤, 陈明新. 日粮添加花生秧和苜蓿草粉对波麻杂交羊增重性能、内脏器官发育及血液指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 146-154. |
| [10] | 李蒋伟, 王志有, 侯生珍, 雷云, 贾建磊, 周力, 桂林生. 日粮精粗比对育肥藏羊瘤胃组织形态及微生物菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 100-109. |
| [11] | 张生伟, 王小平, 张展海, 马友记, 滚双宝, 杨巧丽, 高小莉, 张保军. 青贮杂交构树对杜湖杂交肉羊生长性能、血清生化指标和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. |
| [12] | 张磊, 韩雪林, 张娟, 李苏涛, 史文娇, 阳伏林. 岩藻多糖对肉兔生长性能、血清生化指标及养分表观消化率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 159-168. |
| [13] | 涂瑞, 苗建军, 彭忠利, 高彦华, 柏雪, 谢昕廷. 不同精粗比日粮中添加小肽对牦牛瘤胃体外发酵特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 78-88. |
| [14] | 钱志豪, 韩丙芳, 刘自婷, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲, 马红彬. 渗灌对宁夏引黄灌区苜蓿生长性状及水分利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 147-156. |
| [15] | 刘永嘉, 王聪, 刘强, 郭刚, 霍文婕, 张静, 裴彩霞, 张延利. 日粮补充异丁酸对犊牛生长性能、瘤胃发酵和纤维分解菌菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 151-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||