

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 161-171.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024065
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
余静菠( ), 张慧丽, 李进, 关皓, 周青平, 陈仕勇(
), 张慧丽, 李进, 关皓, 周青平, 陈仕勇( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-27
修回日期:2024-04-08
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
陈仕勇
作者简介:E-mail: chengshi8827@163.com基金资助:
Jing-bo YU( ), Hui-li ZHANG, Jin LI, Hao GUAN, Qing-ping ZHOU, Shi-yong CHEN(
), Hui-li ZHANG, Jin LI, Hao GUAN, Qing-ping ZHOU, Shi-yong CHEN( )
)
Received:2024-02-27
Revised:2024-04-08
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Shi-yong CHEN
摘要:
为探讨饲用燕麦在低磷环境下的变化及响应机制,筛选出磷高效饲用燕麦品种,以38份饲用燕麦品种为材料,采用水培法,在低磷(0.02 mmol·L-1 KH2PO4, LP)和正常磷(1 mmol·L-1 KH2PO4, NP)处理下,测定和分析供试燕麦品种苗期形态、根系等相关的15个指标。通过主成分分析、相关性分析、回归分析,结合隶属函数法和聚类分析,综合评价各燕麦品种的磷效率类型。结果表明,在低磷胁迫下,根冠比、总根长、根尖数、磷素利用效率均值显著升高(P<0.05);株高、地上部干重、地下部干重、生物量、根直径、磷含量和磷累积量显著下降(P<0.05)。低磷胁迫下,根尖数、根分叉数、根冠比等根系相关指标的变异系数较高,分别为49.24%、55.24%、46.11%。通过隶属函数法计算耐低磷综合评价值(D),将其与15个指标的耐低磷系数进行相关性分析,其中地上部干重、地下部干重、生物量、总根长、根表面积、根体积、根投影面积、根尖数、根分叉数、磷素利用效率的耐低磷系数与综合评价值D值之间呈显著相关关系。结合相关分析和多元回归分析,筛选了7个耐低磷鉴定指标,建立了耐低磷综合评价值D值回归方程。聚类结果将38份燕麦划分为磷高效型、磷中效型、磷低效型3类,其中优牧1号、科纳、甜燕1号饲用燕麦为磷高效型。
余静菠, 张慧丽, 李进, 关皓, 周青平, 陈仕勇. 38份饲用燕麦品种苗期磷利用效率综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 161-171.
Jing-bo YU, Hui-li ZHANG, Jin LI, Hao GUAN, Qing-ping ZHOU, Shi-yong CHEN. A multi-trait evaluation of phosphorus efficiency of 38 forage oat cultivars at the seedling stage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 161-171.
| 序号 No. | 品种Cultivar | 序号 No. | 品种Cultivar | 序号 No. | 品种Cultivar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 泰克Taike | 14 | 甜燕70 Sweet oat 70 | 27 | 梦龙Magnum |
| 2 | 青引2号Qingyin No. 2 | 15 | 多能 Duoneng | 28 | 燕王Forage plus |
| 3 | 青燕1号Qingyan No. 1 | 16 | 摄政王Prince regent | 29 | 领袖Souris |
| 4 | 哈维Haywire | 17 | 摩根Mogen | 30 | 骏马Cayuse |
| 5 | 猛士1号Mengshi No.1 | 18 | 莫妮卡Monica | 31 | 太阳神Titan |
| 6 | 青引1号Qingyin No. 1 | 19 | 蓝鸟1号Lanniao No. 1 | 32 | 科纳Kona |
| 7 | 青海甜燕麦Qinghai sweet oat | 20 | 甜燕60 Sweet oat 60 | 33 | 定燕2号Dingyan No. 2 |
| 8 | 甜燕75 Sweet oat 75 | 21 | 禾王King cereals | 34 | 甜燕2+ Sweet oat 2+ |
| 9 | 英迪米特Intimidator | 22 | 白燕7号Baiyan No. 7 | 35 | 甜燕1号Sweet oat No. 1 |
| 10 | 锋利Sharp | 23 | 陇燕5号Longyan No. 5 | 36 | 蒙燕1号Mengyan No. 1 |
| 11 | 青海444 Qinghai No. 444 | 24 | 旗帜 Flag | 37 | 魅力Charisma |
| 12 | 甜燕3号Sweet oat No. 3 | 25 | 优牧1号Youmu No. 1 | 38 | 白燕14 Baiyan No. 14 |
| 13 | 悍马Hanma | 26 | 边锋Blade |
表1 供试燕麦材料
Table 1 The oat cultivars in the study
| 序号 No. | 品种Cultivar | 序号 No. | 品种Cultivar | 序号 No. | 品种Cultivar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 泰克Taike | 14 | 甜燕70 Sweet oat 70 | 27 | 梦龙Magnum |
| 2 | 青引2号Qingyin No. 2 | 15 | 多能 Duoneng | 28 | 燕王Forage plus |
| 3 | 青燕1号Qingyan No. 1 | 16 | 摄政王Prince regent | 29 | 领袖Souris |
| 4 | 哈维Haywire | 17 | 摩根Mogen | 30 | 骏马Cayuse |
| 5 | 猛士1号Mengshi No.1 | 18 | 莫妮卡Monica | 31 | 太阳神Titan |
| 6 | 青引1号Qingyin No. 1 | 19 | 蓝鸟1号Lanniao No. 1 | 32 | 科纳Kona |
| 7 | 青海甜燕麦Qinghai sweet oat | 20 | 甜燕60 Sweet oat 60 | 33 | 定燕2号Dingyan No. 2 |
| 8 | 甜燕75 Sweet oat 75 | 21 | 禾王King cereals | 34 | 甜燕2+ Sweet oat 2+ |
| 9 | 英迪米特Intimidator | 22 | 白燕7号Baiyan No. 7 | 35 | 甜燕1号Sweet oat No. 1 |
| 10 | 锋利Sharp | 23 | 陇燕5号Longyan No. 5 | 36 | 蒙燕1号Mengyan No. 1 |
| 11 | 青海444 Qinghai No. 444 | 24 | 旗帜 Flag | 37 | 魅力Charisma |
| 12 | 甜燕3号Sweet oat No. 3 | 25 | 优牧1号Youmu No. 1 | 38 | 白燕14 Baiyan No. 14 |
| 13 | 悍马Hanma | 26 | 边锋Blade |
指标 Index | 正常处理Normal phosphorus | 低磷处理Low phosphorus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变异系数 CV (%) | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变异系数CV (%) | |
| 株高PH (cm) | 30.00 | 69.40 | 56.18±7.35a | 13.15 | 27.00 | 67.03 | 51.79±8.38b | 16.25 |
| 地上部干重SDW (g·plant-1) | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.24±0.08a | 35.02 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.16±0.06b | 34.51 |
| 地下部干重RDW (g·plant-1) | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.07±0.02a | 32.54 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.06±0.03a | 41.18 |
| 生物量TDW (g·plant-1) | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.30±0.10a | 32.74 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.23±0.07b | 30.48 |
| 根冠比RSR | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.30±0.08b | 27.02 | 0.04 | 1.08 | 0.42±0.19a | 46.11 |
| 总根长TRL (cm) | 149.23 | 1220.39 | 535.12±243.24b | 45.66 | 166.08 | 1558.65 | 701.68±266.35a | 38.13 |
| 根表面积RSA (cm2) | 15.44 | 111.54 | 54.66±22.53a | 41.41 | 17.40 | 133.94 | 61.74±20.87a | 33.96 |
| 根体积RV (cm3) | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.45±0.18a | 40.90 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0.44±0.14a | 32.87 |
| 根直径RD (mm) | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.33±0.04a | 12.97 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.29±0.03b | 10.98 |
| 根投影面积RPA (cm2) | 4.91 | 35.55 | 17.40±7.24a | 41.81 | 5.54 | 42.63 | 19.56±6.71a | 34.44 |
| 根尖数RT | 181.00 | 3697.00 | 1210.22±665.61b | 55.24 | 343.00 | 4336.00 | 1681.00±824.06a | 49.24 |
| 根分叉数RF | 78.00 | 3342.00 | 1335.88±740.45a | 55.67 | 168.00 | 5024.00 | 1476.56±812.01a | 55.24 |
表2 不同供磷水平下供试燕麦各性状变异分析
Table 2 Variation analysis of various traits of oat cultivars at different levels of phosphorus supply
指标 Index | 正常处理Normal phosphorus | 低磷处理Low phosphorus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变异系数 CV (%) | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变异系数CV (%) | |
| 株高PH (cm) | 30.00 | 69.40 | 56.18±7.35a | 13.15 | 27.00 | 67.03 | 51.79±8.38b | 16.25 |
| 地上部干重SDW (g·plant-1) | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.24±0.08a | 35.02 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.16±0.06b | 34.51 |
| 地下部干重RDW (g·plant-1) | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.07±0.02a | 32.54 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.06±0.03a | 41.18 |
| 生物量TDW (g·plant-1) | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.30±0.10a | 32.74 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.23±0.07b | 30.48 |
| 根冠比RSR | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.30±0.08b | 27.02 | 0.04 | 1.08 | 0.42±0.19a | 46.11 |
| 总根长TRL (cm) | 149.23 | 1220.39 | 535.12±243.24b | 45.66 | 166.08 | 1558.65 | 701.68±266.35a | 38.13 |
| 根表面积RSA (cm2) | 15.44 | 111.54 | 54.66±22.53a | 41.41 | 17.40 | 133.94 | 61.74±20.87a | 33.96 |
| 根体积RV (cm3) | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.45±0.18a | 40.90 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0.44±0.14a | 32.87 |
| 根直径RD (mm) | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.33±0.04a | 12.97 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.29±0.03b | 10.98 |
| 根投影面积RPA (cm2) | 4.91 | 35.55 | 17.40±7.24a | 41.81 | 5.54 | 42.63 | 19.56±6.71a | 34.44 |
| 根尖数RT | 181.00 | 3697.00 | 1210.22±665.61b | 55.24 | 343.00 | 4336.00 | 1681.00±824.06a | 49.24 |
| 根分叉数RF | 78.00 | 3342.00 | 1335.88±740.45a | 55.67 | 168.00 | 5024.00 | 1476.56±812.01a | 55.24 |

图1 不同磷处理下供试燕麦品种磷素相关指标的变化LP: 低磷处理Low phosphorus; NP: 正常磷处理Normal phosphorus. ***: P<0.001. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Changes in phosphorus-related indexes of different oat cultivars under different phosphorus concentration

图2 各指标耐低磷系数主成分分析A: 各指标耐低磷系数及品种主成分散点图Principal component dispersion points of low-phosphorus tolerance index; B: 不同磷处理下供试燕麦品种各综合指标累计贡献率Coefficient and contribution rate of comprehensive index under different phosphorus levels of oat at seedling stage. PC: 磷素含量Phosphorus content; PUE: 磷素利用效率Phosphorus use efficiency; PA: 磷素累积量Phosphorus accumulation. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Principal component analysis of low-phosphorus tolerance index of each indictor

图3 燕麦各性状耐低磷系数和磷效率能力综合评价值(D)之间相关性分析*: P<0.05. 下同The same below.
Fig.3 The correlation coefficient between the low phosphorus stress tolerance index and the comprehensive evaluation value (D) of low phosphorus tolerance in oat cultivars
多元回归方程 Multiple regression equation | F值 F value | 决定系数 R square (R2) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| D=-6.972+9.070TDW | 147.389 | 0.661 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.944+5.426TDW+1.965TRL | 245.733 | 0.765 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.816+4.360TDW+1.113TRL+2.856RSA | 576.854 | 0.885 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.776+4.326TDW+0.991TRL+2.346RSA+0.502RV | 606.393 | 0.890 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.723+4.246TDW+0.781TRL+2.146RSA+0.492RV+0.553RPA | 1128.741 | 0.933 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.824+4.222TDW+0.632TRL+1.957RSA+0.524RV+0.412RPA+0.556RF | 1709.509 | 0.981 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.955+3.931TDW+0.392TRL+1.553RSA+1.092RV+0.840RPA+0.611RF+0.146PUE | 2552.104 | 0.996 | <0.001 |
表3 燕麦品种耐低磷最优模型预测
Table 3 Prediction of optimal model for low phosphorus tolerance in oat cultivars
多元回归方程 Multiple regression equation | F值 F value | 决定系数 R square (R2) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| D=-6.972+9.070TDW | 147.389 | 0.661 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.944+5.426TDW+1.965TRL | 245.733 | 0.765 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.816+4.360TDW+1.113TRL+2.856RSA | 576.854 | 0.885 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.776+4.326TDW+0.991TRL+2.346RSA+0.502RV | 606.393 | 0.890 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.723+4.246TDW+0.781TRL+2.146RSA+0.492RV+0.553RPA | 1128.741 | 0.933 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.824+4.222TDW+0.632TRL+1.957RSA+0.524RV+0.412RPA+0.556RF | 1709.509 | 0.981 | <0.001 |
| D=-6.955+3.931TDW+0.392TRL+1.553RSA+1.092RV+0.840RPA+0.611RF+0.146PUE | 2552.104 | 0.996 | <0.001 |
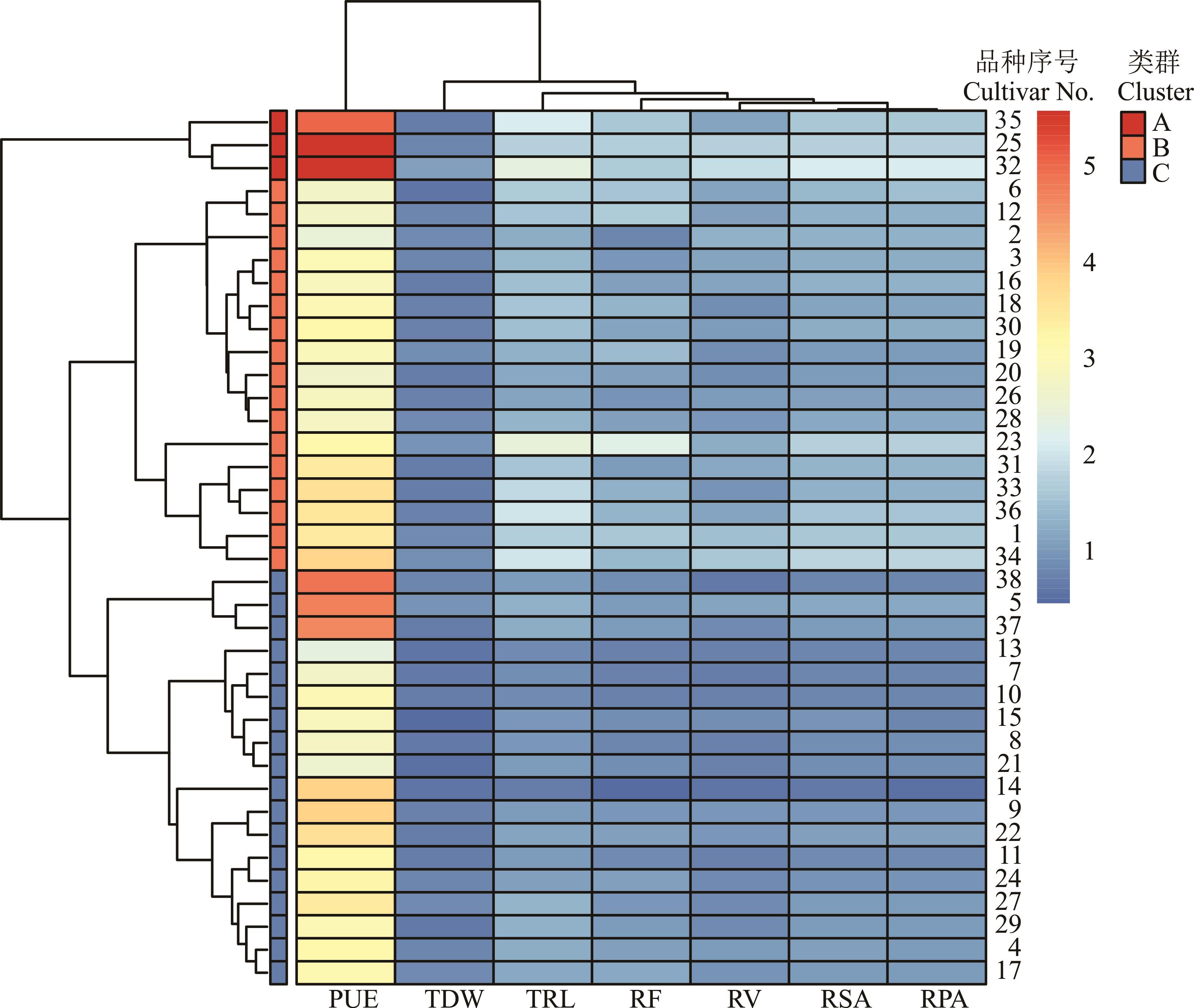
图4 不同燕麦品种磷效率聚类分析A: 磷高效型Phosphorus-high-efficient; B: 磷中效型Phosphorus-medium-efficient; C: 磷低效型Phosphorus-low-efficient. 下同The same below.
Fig.4 Cluster analysis of phosphorus efficiency in different oat cultivar

图5 3类磷效率燕麦品种间农艺性状的差异分析NS: P>0.05; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01.
Fig.5 Analysis of differences in agronomic traits among three clusters of phosphorus use efficiency oat cultivars
| 1 | Dissanayaka D, Ghahremani M, Siebers M, et al. Recent insights into the metabolic adaptations of phosphorus-deprived plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(2): 199-223. |
| 2 | Liu C, Chu H L, Wu L F, et al. Regulation mechanism of phosphate homeostasis in plants. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(2): 184-194. |
| 刘潮, 褚洪龙, 吴丽芳, 等. 植物磷稳态的调控机制. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(2): 184-194. | |
| 3 | Li Z S, Li Z Y, Zhang Q X, et al. Comparison of response mechanisms to low inorganic phosphate stress between alfalfa varieties Aohan abd Victoria. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(1): 50-59. |
| 李振松, 栗振义, 张绮芯, 等. 敖汉和维多利亚紫花苜蓿对低磷环境应激机制的比较. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 50-59. | |
| 4 | Hinsinger P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: A review. Plant and Soil, 2001, 237(2): 173-195. |
| 5 | Liu L L, Wang J C, Yao L R, et al. Evaluation of low phosphorus tolerance and germplasm screening of spring wheat. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(7): 999-1009. |
| 刘露露, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 等. 不同春小麦品种耐低磷性评价及种质筛选.中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(7): 999-1009. | |
| 6 | Cordell D, Drangert J, White S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19(2): 292-305. |
| 7 | Raghothama K G, Karthikeyan A S. Phosphate acquisition. Plant and Soil, 2005, 274(1): 37-49. |
| 8 | Chen H Y, Yu H Y, Chen G D, et al. Root morphological characteristics of barley genotype with high phosphorus efficiency under phosphorus stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(10): 3020-3026. |
| 陈海英, 余海英, 陈光登, 等. 低磷胁迫下磷高效基因型大麦的根系形态特征. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(10): 3020-3026. | |
| 9 | Zhu X Y, Zhang Q Q, Yu Y C, et al. Screening of low phosphorus tolerance genotypes and comprehensive evaluation of phosphorus efficiency in sweetpotato at seedling stage. Journal of Jiangsu Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 41(1): 27-31, 2. |
| 朱晓亚, 张强强, 于永超, 等. 甘薯苗期耐低磷基因型筛选及磷效率综合评价. 江苏师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(1): 27-31, 2. | |
| 10 | Xia J, Nan L L, Chen J, et al. Morphological and physiological responses of different root types of alfalfa under low phosphorus stress. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(10): 58-67. |
| 夏静, 南丽丽, 陈洁, 等. 低磷胁迫下不同根型苜蓿形态及生理响应. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(10): 58-67. | |
| 11 | Kayoumu M, Wumaierjiang X, Li X T, et al. Screening of low phosphorus tolerant germplasm in cotton at seedling stage and comprehensive evaluation of low phosphorus tolerance. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(21): 4150-4162. |
| 米热扎提江·喀由木, 西尔艾力·吾麦尔江, 李晓曈, 等. 棉花苗期耐低磷种质筛选及耐低磷综合评价. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(21): 4150-4162. | |
| 12 | Shi C Y. Selection of low phosphorus-tolerant rice varieties and research on the mechanism of low phosphorus-tolerant root morphology remodeling. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. |
| 史春阳. 耐低磷水稻品种筛选和根系形态重塑机制. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015. | |
| 13 | Chen Y L, Wang N, Shi L. Analysis of phosphorus efficiency and screening of P-efficient germplasm on natural population of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2023, 45(1): 56-62. |
| 陈燕玲, 王宁, 石磊. 甘蓝型油菜自然群体苗期磷效率分析及磷高效优异种质筛选. 中国油料作物学报, 2023, 45(1): 56-62. | |
| 14 | Li Z Y, Zhang Q X, Tong Z Y, et al. Analysis of morphological and physiological responses to low Pi stress in different alfalfas. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(20): 3898-3907. |
| 栗振义, 张绮芯, 仝宗永, 等. 不同紫花苜蓿品种对低磷环境的形态与生理响应分析. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(20): 3898-3907. | |
| 15 | Ye X L, Gan Z, Wan Y, et al. Advances and perspectives in forage oat breeding. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 等. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. | |
| 16 | Zhang B, Ren C Z. Advances in oat genomic research and molecular breeding. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 785-791. |
| 张波, 任长忠. 燕麦基因组学与分子育种研究进展. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 785-791. | |
| 17 | Ren C Z, Hu Y G. China oats. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2013: 11. |
| 任长忠, 胡跃高. 中国燕麦学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013: 11. | |
| 18 | Li J, Chen S Y, Zhao X, et al. Analysis of genetic structure and fingerprinting in oat varieties based on SCoT markers. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 72-81. |
| 李进, 陈仕勇, 赵旭, 等. 基于SCoT 标记的饲用燕麦品种遗传结构及指纹图谱分析. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 72-81. | |
| 19 | He X, Qi B J, Wang M, et al. Differences in biomass and phosphorus nutrition of oats with different phosphorus efficiency under low phosphorus stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 17(22): 7482-7487. |
| 贺鑫, 齐冰洁, 王敏, 等. 低磷胁迫下燕麦不同磷效率品种生物量及磷素营养的差异. 分子植物育种, 2020, 17(22): 7482-7487. | |
| 20 | Zhang H L, Ye L, Zhou Y, et al. Effects of different levels of phosphorus supply on the growth and development of forage oat seedlings. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2023(2): 27-31. |
| 张慧丽, 叶莉, 周洋, 等. 不同供磷水平对饲用燕麦幼苗生长发育的影响. 草学, 2023(2): 27-31. | |
| 21 | Liu Y X, Wen Y J, Huang J L, et al. Determination total phosphorus of maize plant samples by continuous flow analyzer in comparison with vanadium molybdate yellow colorimetric method. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2015, 32(6): 577-582. |
| 刘云霞, 温云杰, 黄金莉, 等. AA3型连续流动分析仪与钒钼黄比色法测定玉米植株全磷含量之比较. 农业资源与环境学报, 2015, 32(6): 577-582. | |
| 22 | Vance C P, Uhde-Stone C, Allan D L. Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytologist, 2003, 157(3): 423-447. |
| 23 | Qin C, Pei H B, Zhang Y Q, et al. Effects of phosphorus on the growth and development of adzuki bean at seedling stage. Crops, 2015(3): 122-129. |
| 秦成, 裴红宾, 张永清, 等. 磷素对小豆幼苗生长发育的影响. 作物杂志, 2015(3): 122-129. | |
| 24 | Wu A J. Mechanisms of root responses to low phosphorus stress in different crop species/genotypes with contrasting root systems. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. |
| 吴爱姣. 不同根系类型作物/品种的根系对低磷胁迫的响应机制. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2021. | |
| 25 | Yi K, Yang S, Kong W J, et al. Analysis of efficient phosphorus absorption characteristic based on root morphology and spatial distribution in sugarcane. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2022, 44(6): 1362-1372. |
| 易科, 杨曙, 孔吴俊, 等. 基于根系形态及空间分布的甘蔗磷高效吸收特征分析. 江西农业大学学报, 2022, 44(6): 1362-1372. | |
| 26 | Liu P, Wu A L, Wang J S, et al. Study on phosphorus use efficiency and phosphorus remobilization characteristics of four different sorghum genotypes. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(3): 344-349. |
| 刘鹏, 武爱莲, 王劲松, 等. 不同基因型高粱的磷效率和磷素转运特性研究. 山西农业科学, 2018, 46(3): 344-349. | |
| 27 | Wang H. Screening and seedling stage identification of phosphorus high-efficient soybean varieties. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 王辉. 磷高效大豆品种的筛选及苗期鉴定方法. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. | |
| 28 | Aluwihare Y C, Ishan M, Chamikara M D M, et al. Characterization and selection of phosphorus deficiency tolerant rice genotypes in Sri Lanka. Rice Science, 2016, 23(4): 184-195. |
| 29 | Luo Y, Li D M, Lei M M, et al. Evaluation of low-phosphorus tolerance of hulless barley at seedling stage. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(12): 1450-1458. |
| 罗园, 李东梅, 雷淼淼, 等. 青稞苗期耐低磷能力评价. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(12): 1450-1458. |
| [1] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [2] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [3] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [4] | 鲍根生, 李媛, 冯晓云, 张鹏, 孟思宇. 高寒区氮添加和间作种植互作对燕麦和豌豆根系构型影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 73-84. |
| [5] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [6] | 曾兵, 尚盼盼, 沈秉娜, 王胤晨, 屈明好, 袁扬, 毕磊, 杨兴云, 李文文, 周晓丽, 郑玉倩, 郭文强, 冯彦龙, 曾兵. 淹水胁迫下鸭茅根系基因差异表达及相关通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 93-111. |
| [7] | 刘芳, 王佩佩, 曹玉莹, 刘俊娥, 周正朝. 黄土高原典型草本植物根系分布特征及其对土壤理化性质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 1-13. |
| [8] | 李文龙, 李峰, 张仲鹃, 王殿清, 王欢, 靳慧卿, 特木热, 胡志玲, 陶雅. 鄂尔多斯高原北部一年两季燕麦种植模式生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 159-168. |
| [9] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [10] | 魏艳, 刘有斌, 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 颜哲豪, 都艺芝. 紫色土区拉巴豆和紫花苜蓿根-土复合体抗剪性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 82-90. |
| [11] | 杨瑞杰, 何淑勤, 周树峰, 杨晶月, 金钰宪, 郑子成. 杂交粱草生长期土壤抗冲性变化特征及其根系调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 149-159. |
| [12] | 廖小琴, 王长庭, 刘丹, 唐国, 毛军. 氮磷配施对高寒草甸植物根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 160-174. |
| [13] | 陈晓明, 韩东英, 宋桂龙. 砷(As)胁迫对海滨雀稗As吸收特征及根系形态影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 112-119. |
| [14] | 金媛媛, 陈振江, 王添, 李春杰. 内生真菌和田间管理措施对土壤真菌群落丰度和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 142-152. |
| [15] | 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 向达兵, 邬晓勇, 吴琪, 刘长英, 范昱, 邹亮. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||