

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 154-167.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024277
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
温小月1( ), 赵颖1,2,3(
), 赵颖1,2,3( ), 王宝强1,2,3, 王贤1,4, 朱晓林1,4, 王义真1,4, 魏小红1,2,3,4
), 王宝强1,2,3, 王贤1,4, 朱晓林1,4, 王义真1,4, 魏小红1,2,3,4
收稿日期:2024-07-16
修回日期:2024-09-05
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-04-03
通讯作者:
赵颖
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: 1137974332@qq.com基金资助:
Xiao-Yue WEN1( ), Ying ZHAO1,2,3(
), Ying ZHAO1,2,3( ), Bao-qiang WANG1,2,3, Xian WANG1,4, Xiao-lin ZHU1,4, Yi-zhen WANG1,4, Xiao-hong WEI1,2,3,4
), Bao-qiang WANG1,2,3, Xian WANG1,4, Xiao-lin ZHU1,4, Yi-zhen WANG1,4, Xiao-hong WEI1,2,3,4
Received:2024-07-16
Revised:2024-09-05
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-04-03
Contact:
Ying ZHAO
摘要:
紫花苜蓿是世界上种植最广泛的饲用豆科作物。APETALA2/ethylene-responsive factor(AP2/ERF)转录因子在植物抵御非生物胁迫中起着关键作用。一氧化氮(nitric oxide,NO)作为植物体内的一种信号分子,在植物抗旱中扮演重要角色。本研究利用生物信息学方法对紫花苜蓿MsAP2/ERF基因家族成员进行鉴定及其对NO和干旱的响应模式分析,并从MsAP2/ERF基因家族中筛选到强烈响应NO调控的MsERF07基因进行亚细胞定位。结果表明,该家族成员均含有AP2结构域,其蛋白质的氨基酸数目介于176~422;亚细胞定位预测大部分蛋白都定位在细胞核; MsERF01和MsERF11的亲缘关系较近,并且它们具有相似的结构域;61.54%的MsAP2/ERF基因只含有外显子,也具有高度相似的保守基序;蛋白互作显示MsERF01和MsERF11、MsERF05和MsERF07均处于蛋白互作图中的同一节点;13个MsAP2/ERF基因家族成员被不均匀分布在13条染色体上,MsAP2/ERF基因家族成员的启动子序列中有43个与光反应、组织特异性表达、胁迫以及植物激素相关的顺式调控元件。此外,紫花苜蓿的转录组测序数据分析表明大部分MsAP2/ERF基因家族成员在NO的调控下表达量增加,进一步qRT-RCR试验结果显示,外源NO促进了干旱胁迫下MsAP2/ERF基因的表达量。克隆MsERF07基因,亚细胞定位结果显示该蛋白定位在细胞核与细胞膜中,本研究为后续研究紫花苜蓿MsERF07基因响应干旱胁迫的分子机制提供了基础。
温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167.
Xiao-Yue WEN, Ying ZHAO, Bao-qiang WANG, Xian WANG, Xiao-lin ZHU, Yi-zhen WANG, Xiao-hong WEI. Expression analysis of AP2/ERFs genes in alfalfa regulated by exogenous NO under drought stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(6): 154-167.
登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 上游引物序列 Forward primer sequence | 下游引物序列 Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene057432.t1 | MsERF01 | AGATTACCAAACAGCCGCCA | TAGCACCACTGCCACGTAAG |
| MS.gene022984.t1 | MsERF02 | AACCGAAGAGTGAACAGCCT | TCCTGCAAGGGTTGGTTGAA |
| MS.gene31024.t1 | MsERF03 | TCGTAACCCTCCACCAGCTA | CCTTGCAGAAGGAATACCCGA |
| MS.gene011550.t1 | MsERF04 | ATGCGTCAATGGGGCAAATG | TTGAGGTAAGCCGAAGAGCC |
| MS.gene30848.t1 | MsERF05 | TGCCACTACTCAGGCAAAGG | GGCGGCTATAGTCGTGTCAA |
| MS.gene072828.t1 | MsERF06 | CTCTAACAGCCGCCTTGGAA | CAGTAGCCAGCAACACTCCA |
| MS.gene006341.t1 | MsERF07 | GCCGGAGAGTGTGTTTGAGA | ACTCCGGCACTGTATCCTCT |
| MS.gene58366.t1 | MsERF08 | CCACCGCCGCTTGATTTAAC | ACGTGCGAATGCGTCAAAAA |
| MS.gene022105.t1 | MsERF09 | ATGGGCAGCTGAAATACGTGA | TTGTGCCTTTGAATTTGAGTGC |
| MS.gene030784.t1 | MsERF10 | TACCGCGGAGTTAGACAACG | ATGGAAGCGCATGTGAGGAA |
| MS.gene025280.t1 | MsERF11 | CATCGGATGGGACGACAACA | TCTCCGGCACGTAGAAATCG |
| MS.gene067817.t1 | MsERF12 | CAGGAAGATGGCGTTGTTGC | AGCACGGGTCGAAATAGTGT |
| MS.gene016368.t1 | MsERF13 | AGGAATCAATGCCGTGACCA | AGGCGGGGTAGTTGTTGTTT |
表1 qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 qRT-PCR primers
登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 上游引物序列 Forward primer sequence | 下游引物序列 Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene057432.t1 | MsERF01 | AGATTACCAAACAGCCGCCA | TAGCACCACTGCCACGTAAG |
| MS.gene022984.t1 | MsERF02 | AACCGAAGAGTGAACAGCCT | TCCTGCAAGGGTTGGTTGAA |
| MS.gene31024.t1 | MsERF03 | TCGTAACCCTCCACCAGCTA | CCTTGCAGAAGGAATACCCGA |
| MS.gene011550.t1 | MsERF04 | ATGCGTCAATGGGGCAAATG | TTGAGGTAAGCCGAAGAGCC |
| MS.gene30848.t1 | MsERF05 | TGCCACTACTCAGGCAAAGG | GGCGGCTATAGTCGTGTCAA |
| MS.gene072828.t1 | MsERF06 | CTCTAACAGCCGCCTTGGAA | CAGTAGCCAGCAACACTCCA |
| MS.gene006341.t1 | MsERF07 | GCCGGAGAGTGTGTTTGAGA | ACTCCGGCACTGTATCCTCT |
| MS.gene58366.t1 | MsERF08 | CCACCGCCGCTTGATTTAAC | ACGTGCGAATGCGTCAAAAA |
| MS.gene022105.t1 | MsERF09 | ATGGGCAGCTGAAATACGTGA | TTGTGCCTTTGAATTTGAGTGC |
| MS.gene030784.t1 | MsERF10 | TACCGCGGAGTTAGACAACG | ATGGAAGCGCATGTGAGGAA |
| MS.gene025280.t1 | MsERF11 | CATCGGATGGGACGACAACA | TCTCCGGCACGTAGAAATCG |
| MS.gene067817.t1 | MsERF12 | CAGGAAGATGGCGTTGTTGC | AGCACGGGTCGAAATAGTGT |
| MS.gene016368.t1 | MsERF13 | AGGAATCAATGCCGTGACCA | AGGCGGGGTAGTTGTTGTTT |
基因 Gene name | 登录号 Gene ID | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性 GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsERF01 | MS.gene057432.t1 | 217 | 23830.29 | 4.58 | -0.535 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF02 | MS.gene022984.t1 | 233 | 26506.06 | 8.91 | -0.758 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsERF03 | MS.gene31024.t1 | 324 | 35332.93 | 9.76 | -0.572 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF04 | MS.gene011550.t1 | 199 | 21765.18 | 5.93 | -0.551 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF05 | MS.gene30848.t1 | 243 | 27717.37 | 6.55 | -0.676 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsERF06 | MS.gene072828.t1 | 231 | 25918.02 | 5.71 | -0.526 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF07 | MS.gene006341.t1 | 180 | 20443.92 | 5.76 | -0.687 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF08 | MS.gene58366.t1 | 210 | 22898.71 | 9.66 | -0.596 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsERF09 | MS.gene022105.t1 | 176 | 19699.82 | 7.89 | -0.823 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF10 | MS.gene030784.t1 | 288 | 32496.66 | 7.01 | -0.558 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF11 | MS.gene025280.t1 | 202 | 22322.82 | 4.58 | -0.446 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF12 | MS.gene067817.t1 | 259 | 28852.95 | 5.76 | -0.661 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF13 | MS.gene016368.t1 | 422 | 47454.26 | 5.54 | -0.928 | 细胞核Nucleus |
表2 13个MsAP2/ERFs基因的基本理化性质
Table 2 Basic physicochemical properties of 13 MsERFs genes
基因 Gene name | 登录号 Gene ID | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性 GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsERF01 | MS.gene057432.t1 | 217 | 23830.29 | 4.58 | -0.535 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF02 | MS.gene022984.t1 | 233 | 26506.06 | 8.91 | -0.758 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsERF03 | MS.gene31024.t1 | 324 | 35332.93 | 9.76 | -0.572 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF04 | MS.gene011550.t1 | 199 | 21765.18 | 5.93 | -0.551 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF05 | MS.gene30848.t1 | 243 | 27717.37 | 6.55 | -0.676 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsERF06 | MS.gene072828.t1 | 231 | 25918.02 | 5.71 | -0.526 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF07 | MS.gene006341.t1 | 180 | 20443.92 | 5.76 | -0.687 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF08 | MS.gene58366.t1 | 210 | 22898.71 | 9.66 | -0.596 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsERF09 | MS.gene022105.t1 | 176 | 19699.82 | 7.89 | -0.823 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF10 | MS.gene030784.t1 | 288 | 32496.66 | 7.01 | -0.558 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF11 | MS.gene025280.t1 | 202 | 22322.82 | 4.58 | -0.446 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF12 | MS.gene067817.t1 | 259 | 28852.95 | 5.76 | -0.661 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MsERF13 | MS.gene016368.t1 | 422 | 47454.26 | 5.54 | -0.928 | 细胞核Nucleus |
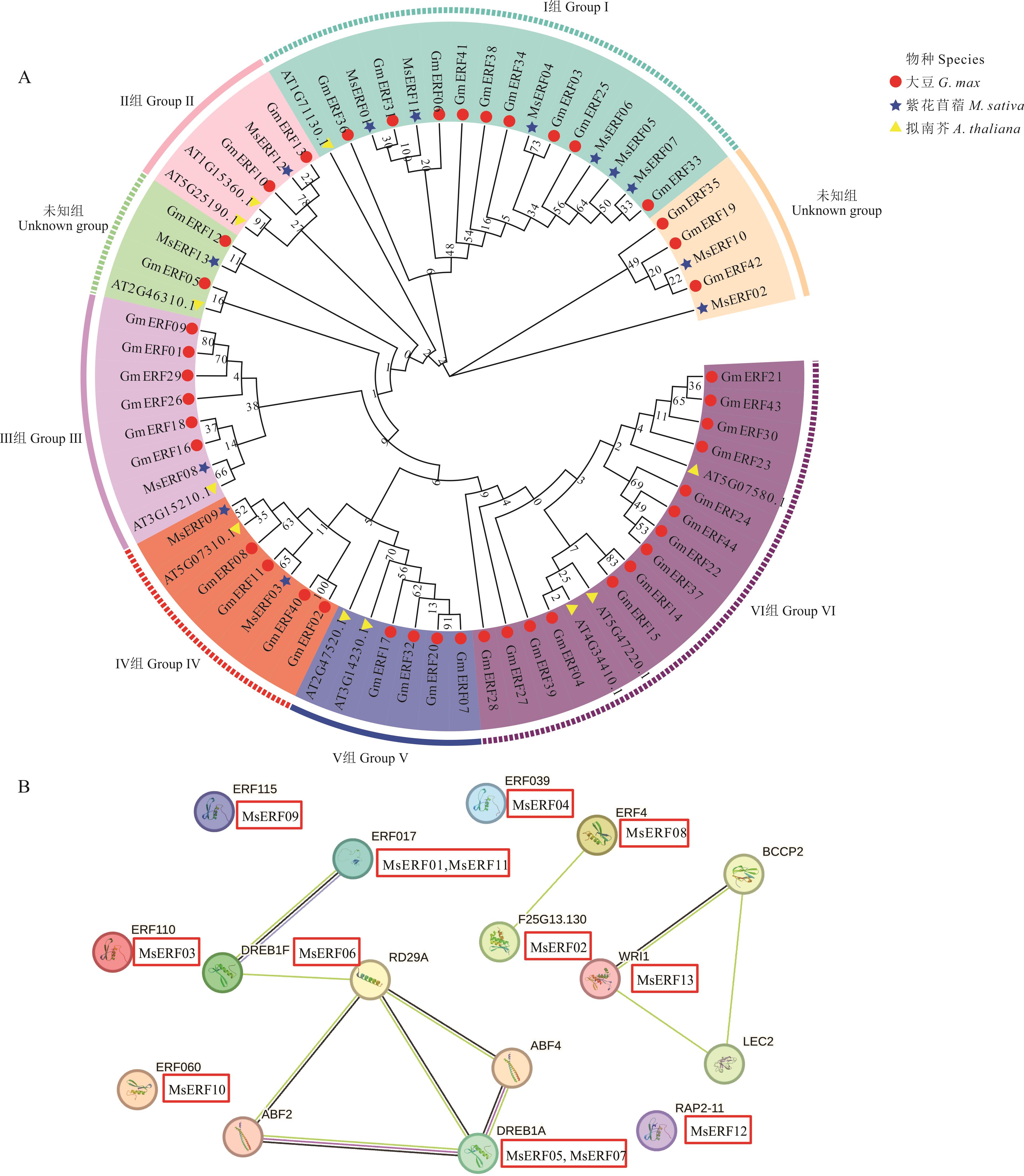
图1 基于紫花苜蓿、拟南芥和大豆AP2/ERF基因家族的氨基酸序列构建系统进化树(A)、蛋白互作网络图(B)
Fig. 1 Construction of phylogenetic tree (A) and protein interaction network (B) based on amino acid sequences of AP2/ERF gene family in alfalfa, Arabidopsis and soybean

图2 紫花苜蓿AP2/ERF的基因结构(A)与保守结构域中Motif分布(B)、Motif序列(C)
Fig.2 AP2/ERF gene structure (A) and Motif distribution (B), Motif sequence (C) in conserved domain of alfalfa

图6 通过qRT-PCR检测干旱(PEG)和干旱(PEG)+NO(SNP)胁迫下MsAP2/ERF的表达量10%PEG:干旱处理;0.1 mmol·L-1SNP+10%PEG:外源0.1 mmol·L-1SNP处理下的干旱胁迫。不同小写字母代表0.05水平上存在显著性差异。There was significant difference in the level of 0.05 for different lowercase letters. PEG: 聚乙二醇Polyethylene glycol. SNP: 硝普纳Sodium nitroprusside.
Fig.6 Expression levels of MsAP2/ERF gene family members in leaves of alfalfa seedlings under different treatments
| 1 | Gou J, Debnath S, Sun L, et al. From model to crop: functional characterization of SPL8 in M. truncatula led to genetic improvement of biomass yield and abiotic stress tolerance in alfalfa. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16(4): 951-962. |
| 2 | Xiao Y, Zhang J, Jia T T, et al. Effects of alternate furrow irrigation on the biomass and quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Agricultural Water Management, 2015, 161: 147-154. |
| 3 | Siddiqui M H, Al-Whaibi M H, Basalah M O. Role of nitric oxide in tolerance of plants to abiotic stress. Protoplasma, 2011, 248: 447-455. |
| 4 | Lian H, Qin C, Shen J, et al. Alleviation of adverse effects of drought stress on growth and nitrogen metabolism in mungbean (Vigna radiata) by sulphur and nitric oxide involves up-regulation of antioxidant and osmolyte metabolism and gene expression. Plants, 2023, 12(17): 3082. |
| 5 | Palmieri M C, Sell S, Huang X, et al. Nitric oxide-responsive genes and promoters in Arabidopsis thaliana: a bioinformatics approach. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(2): 177-186. |
| 6 | de Sousa L F, de Menezes-Silva P E, Lourenço L L, et al. Improving water use efficiency by changing hydraulic and stomatal characteristics in soybean exposed to drought: the involvement of nitric oxide. Physiologia Plantarum, 2020, 168(3): 576-589. |
| 7 | Abedi T, Pakniyat H. Antioxidant enzyme changes in response to drought stress in ten cultivars of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Czech Journal of Genetics and Plant Breeding, 2010, 46(1): 27-34. |
| 8 | Majeed S, Nawaz F, Naeem M, et al. Nitric oxide regulates water status and associated enzymatic pathways to inhibit nutrients imbalance in maize (Zea mays L.) under drought stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 155: 147-160. |
| 9 | Cai Z S. Effects of exogenous NO on seed germination and drought resistance of alfalfa under water stress. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 蔡卓山. 水分胁迫下外源NO对苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗抗旱生理的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. | |
| 10 | Zhao Y, Wei X, Long Y, et al. Transcriptional analysis reveals sodium nitroprusside affects alfalfa in response to PEG-induced osmotic stress at germination stage. Protoplasma, 2020, 257: 1345-1358. |
| 11 | Brouquisse R. Multifaceted roles of nitric oxide in plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(17): 4319-4322. |
| 12 | Shi K, Liu J, Liang H, et al. An alfalfa MYB-like transcriptional factor MsMYBH positively regulates alfalfa seedling drought resistance and undergoes MsWAV3-mediated degradation. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2024, 66(4): 683-699. |
| 13 | Feng K, Hou X L, Xing G M, et al. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2020, 40(6): 750-776. |
| 14 | Liu K, Yang Q, Yang T, et al. Transcriptome-based identification and expression profiling of AP2/ERF members in Caragana intermedia and functional analysis of CiDREB3. Molecular Biology Reports, 2021, 48(12): 7953-7965. |
| 15 | Jian W N, Zuo P, Zhang G Z, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of MsERF003 gene in drought stress from Medicago sativa. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(17): 5674-5681. |
| 坚伟宁, 左朋, 张国珍, 等. 紫花苜蓿MsERF003的基因克隆及其在干旱胁迫中的功能分析. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(17): 5674-5681. | |
| 16 | Jung S E, Bang S W, Kim S H, et al. Overexpression of OsERF83, a vascular tissue-specific transcription factor gene, confers drought tolerance in rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(14): 7656. |
| 17 | Chen K, Tang W, Zhou Y, et al. AP2/ERF transcription factor GmDREB1 confers drought tolerance in transgenic soybean by interacting with GmERFs. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 170: 287-295. |
| 18 | Wang Z, Zhao X, Ren Z, et al. ZmERF21 directly regulates hormone signaling and stress-responsive gene expression to influence drought tolerance in maize seedlings. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2022, 45(2): 312-328. |
| 19 | Zhu X, Wang B, Liu W, et al. Genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF gene and functional analysis of CqERF24 gene in drought stress in quinoa. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 253: 127582. |
| 20 | Li Y, Zhang H, Zhang Q, et al. An AP2/ERF gene, IbRAP2-12, from sweet potato is involved in salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 2019, 281: 19-30. |
| 21 | Wang Y Q, Xia D N, Wen Q L, et al. Overexpression of a tomato AP2/ERF transcription factor SlERF. B1 increases sensitivity to salt and drought stresses. Scientia Horticulturae, 2022, 304: 111332. |
| 22 | Jin X, Yin X, Ndayambaza B, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the ERF gene family in Medicago sativa L. under various abiotic stresses. DNA and Cell Biology, 2019, 38(10): 1056-1068. |
| 23 | Zhang H, Gao S, Lercher M J, et al. EvolView, an online tool for visualizing, annotating and managing phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(1): 569-572. |
| 24 | Bailey T L, Boden M, Buske F A, et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(S2): 202-208. |
| 25 | Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, et al. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(1): 296-303. |
| 26 | Gao T, Gao Y, Liu X, et al. Identification and functional analysis of the SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid protein. BMC Microbiology, 2021, 21(1): 58. |
| 27 | Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S, et al. STRING v9. 1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 41: 808-815. |
| 28 | Li X J, Yang J L, Hao B, et al. Comparative transcriptome and metabolome analyses provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying taproot thickening in Panax notoginseng. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 451. |
| 29 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 30 | Froger A, Hall J E. Transformation of plasmid DNA into E. coli using the heat shock method. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2007(6): e253. |
| 31 | Pawson T, Nash P. Assembly of cell regulatory systems through protein interaction domains. Science, 2003, 5618(300): 445-452. |
| 32 | Ke X W, Zhang J P, Liu G H, et al. Identification of adzuki bean AP2/ERF gene family and expression analysis in response to rust infection. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2020(4): 394-404. |
| 柯希望, 张金鹏, 刘国辉, 等. 小豆AP2/ERF基因家族鉴定及其应答锈菌侵染的表达分析. 植物病理学报, 2020(4): 394-404. | |
| 33 | Zhang Z, Li X. Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF superfamily genes and their expression during fruit ripening of Chinese jujube. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 15612. |
| 34 | Zhao Y Z. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in maize. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 赵御璋. 玉米AP2/ERF基因家族的分析与鉴定. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2022. | |
| 35 | Keller P A, Yvonne J K E. A primer of genome science. Briefings in Functional Genomics and Proteomics, 2002: 318-319, 10.1093/bfgp/1.3.318. |
| 36 | Liu M, Sun W, Ma Z, et al. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum tataricum). BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 84. |
| 37 | Ghorbani R, Zakipour Z, Alemzadeh A, et al. Genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors family in Brassica napus. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2020, 26(7): 1463-1476. |
| 38 | Guo B J, Wei Y F, Xu R B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of APETALA2/ethylene-responsive factor (AP2/ERF) gene family in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0161322. |
| 39 | Ma J, Zhang G Z, Ye Y C, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of HSF transcription factors in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under abiotic stress. Plants, 2022, 20(11): 2763. |
| 40 | Zhao Y, Xin X Q, Wei X H. Effects of nitric oxide on nitrogen metabolism of alfalfa under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. | |
| 41 | Barnard E, McFerran N V, Trudgett A, et al. Detection and localisation of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a split-GFP method. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2008, 45(5): 597-604. |
| [1] | 魏孔钦, 张盈盈, 回金峰, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷配施对紫花苜蓿根系非结构碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 40-50. |
| [2] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [3] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [4] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [5] | 董拓轩, 陈训锋, 梅大海, 郭永莎, 魏旭红, 宋秋艳. 纳米铁与铜对苜蓿壳二孢及其引致春季黑茎病的抑制与防治作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 201-211. |
| [6] | 王小风, 马步东, 黄海霞, 罗永忠, 齐建伟, 邓卓. 干旱胁迫及复水对裸果木幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 93-103. |
| [7] | 陈彩锦, 包明芳, 王文虎, 尚继红, 曾燕霞, 沙晓弟, 朱新忠, 王学敏, 刘文辉. 紫花苜蓿抗旱育种研究现状及展望[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 204-223. |
| [8] | 胡鹏飞, 叶雨浓, 王通锐, 王晶, 王星, 伏兵哲, 高雪芹. 紫花苜蓿半同胞家系农艺性状的遗传变异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 85-96. |
| [9] | 马超, 孙熙婧, 冯雅岚, 周爽, 琚吉浩, 吴毅, 王添宁, 郭彬彬, 张均. 紫花苜蓿GLK基因家族鉴定及渗透胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 174-190. |
| [10] | 蔡文祺, 李淑霞, 王晓彤, 宋文学, 麻旭霞, 马小梅, 李小红, 代昕瑶. 外源褪黑素与乙烯交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 80-93. |
| [11] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [12] | 卜祥琪, 李姗姗, 段莹娜, 王迎春, 郑琳琳. 一氧化氮对盐碱胁迫下盐地碱蓬抗逆性及饲用品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 60-69. |
| [13] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [14] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [15] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||