

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 80-93.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024093
蔡文祺1( ), 李淑霞1,2,3(
), 李淑霞1,2,3( ), 王晓彤1, 宋文学1, 麻旭霞1, 马小梅1, 李小红1, 代昕瑶1
), 王晓彤1, 宋文学1, 麻旭霞1, 马小梅1, 李小红1, 代昕瑶1
收稿日期:2024-03-25
修回日期:2024-04-26
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
李淑霞
作者简介:E-mail: lishuxia620@163.com基金资助:
Wen-qi CAI1( ), Shu-xia LI1,2,3(
), Shu-xia LI1,2,3( ), Xiao-tong WANG1, Wen-xue SONG1, Xu-xia MA1, Xiao-mei MA1, Xiao-hong LI1, Xin-yao DAI1
), Xiao-tong WANG1, Wen-xue SONG1, Xu-xia MA1, Xiao-mei MA1, Xiao-hong LI1, Xin-yao DAI1
Received:2024-03-25
Revised:2024-04-26
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Shu-xia LI
摘要:
为明确外源褪黑素和乙烯在调控植物耐盐性方面的交互作用,以‘中苜一号’紫花苜蓿为试验材料,通过叶面喷施褪黑素、乙烯利和褪黑素+乙烯利的方法,研究外源施加褪黑素和乙烯对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生长和生理特性的影响。结果表明:外源施加一系列浓度的褪黑素处理(0.01、0.02、0.05、0.10 mmol·L-1 MT)和乙烯利处理(0.05、0.15、0.25、0.50 mmol·L-1 ETH)均对盐胁迫下(250 mmol·L-1 NaCl)紫花苜蓿幼苗的生长损伤具有缓解作用,并以0.05 mmol·L-1 褪黑素处理和0.15 mmol·L-1乙烯利处理缓解效果最佳,其幼苗株高、叶面积、鲜重、叶绿素含量和类胡萝卜素含量显著增加,相对电导率显著降低。采用以上最佳处理浓度试验发现:与对照组相比,盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗的生长明显被抑制;与单独盐处理组相比,外源施加激素后紫花苜蓿幼苗长势明显较好,尤其是同时施加褪黑素和乙烯利时,紫花苜蓿幼苗的株高、叶面积和鲜重分别增加了54.1%、76.8%和32.1%,组织含水量和叶绿素含量分别增加了46.2%和47.8%,相对电导率和丙二醛含量分别降低了23.5%和39.7%,过氧化氢和超氧阴离子含量分别减少了42.7%和63.8%,超氧化物歧化酶SOD、过氧化物酶POD、过氧化氢酶CAT和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX活性分别增加了54.1%、54.1%、59.1%和62.0%,还原性谷胱甘肽GSH含量增加32.8%,脯氨酸和可溶性糖含量增加了42.2%和27.2%,钾钠离子比值增加了217.5%,植株内源褪黑素和乙烯含量分别增加了60.0%和10.6%。综合分析表明,外源施加褪黑素和乙烯能够显著降低紫花苜蓿膜脂过氧化水平和活性氧积累,增加抗氧化酶活性和渗透调节物质含量,调控植株体内离子平衡,增加幼苗内源激素含量,提高紫花苜蓿幼苗的耐盐性,从而促进盐胁迫下幼苗的生长。
蔡文祺, 李淑霞, 王晓彤, 宋文学, 麻旭霞, 马小梅, 李小红, 代昕瑶. 外源褪黑素与乙烯交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 80-93.
Wen-qi CAI, Shu-xia LI, Xiao-tong WANG, Wen-xue SONG, Xu-xia MA, Xiao-mei MA, Xiao-hong LI, Xin-yao DAI. Effects of interaction between exogenous melatonin and ethylene on the growth and physiological characteristics of Medicago sativa seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 80-93.
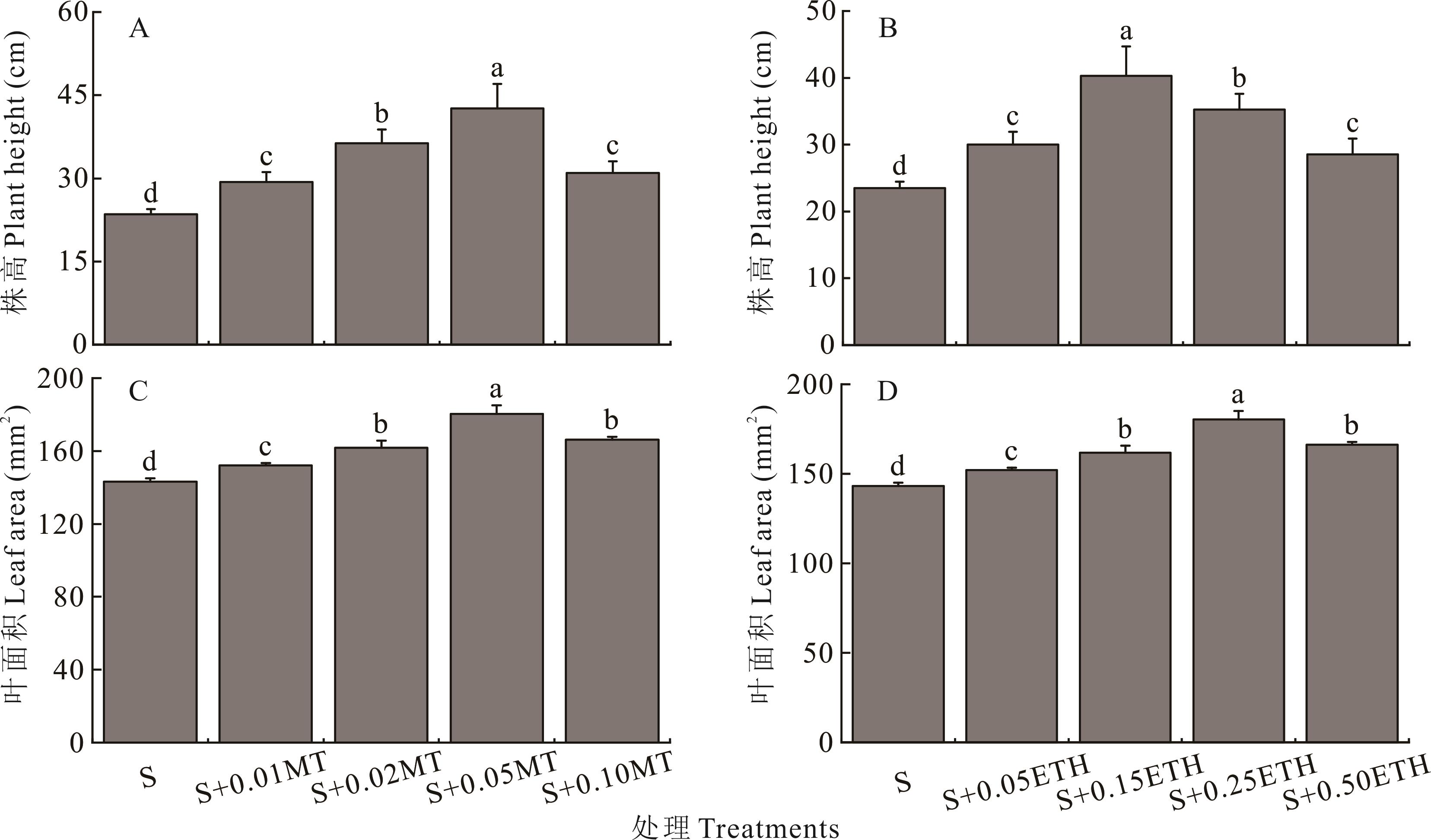
图1 不同浓度的褪黑素和乙烯利对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗株高和叶面积的影响不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significantly difference among treatments at the 0.05 level. S: 250 mmol·L-1盐NaCl; MT: 褪黑素Melatonin; ETH: 乙烯利Ethephon.下同The same below.
Fig.1 Influence of different concentrations of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) on plant height and leaf area of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
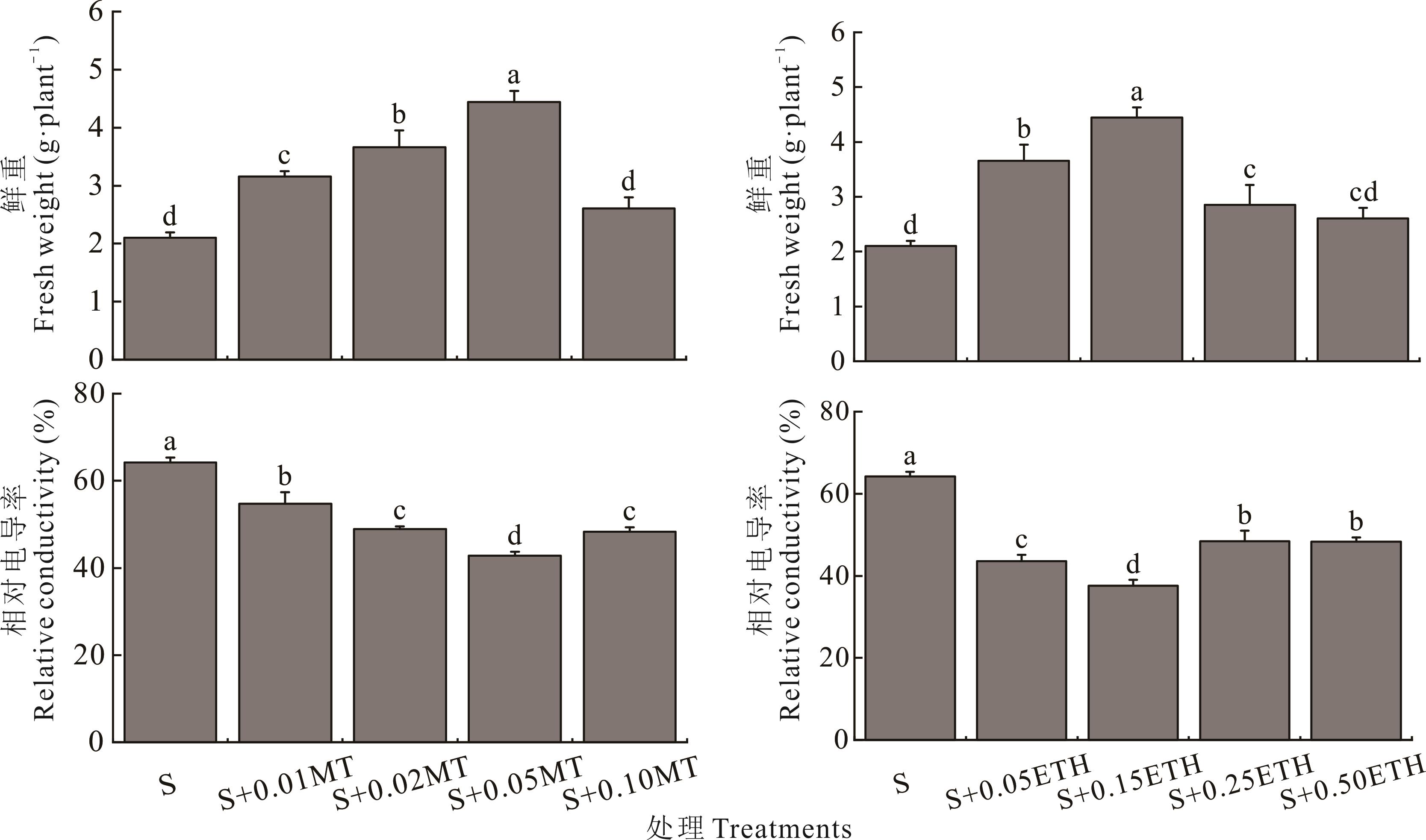
图2 不同浓度的褪黑素和乙烯利对紫花苜蓿幼苗在盐胁迫下的鲜重和相对电导率的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) on fresh weight and relative conductivity of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
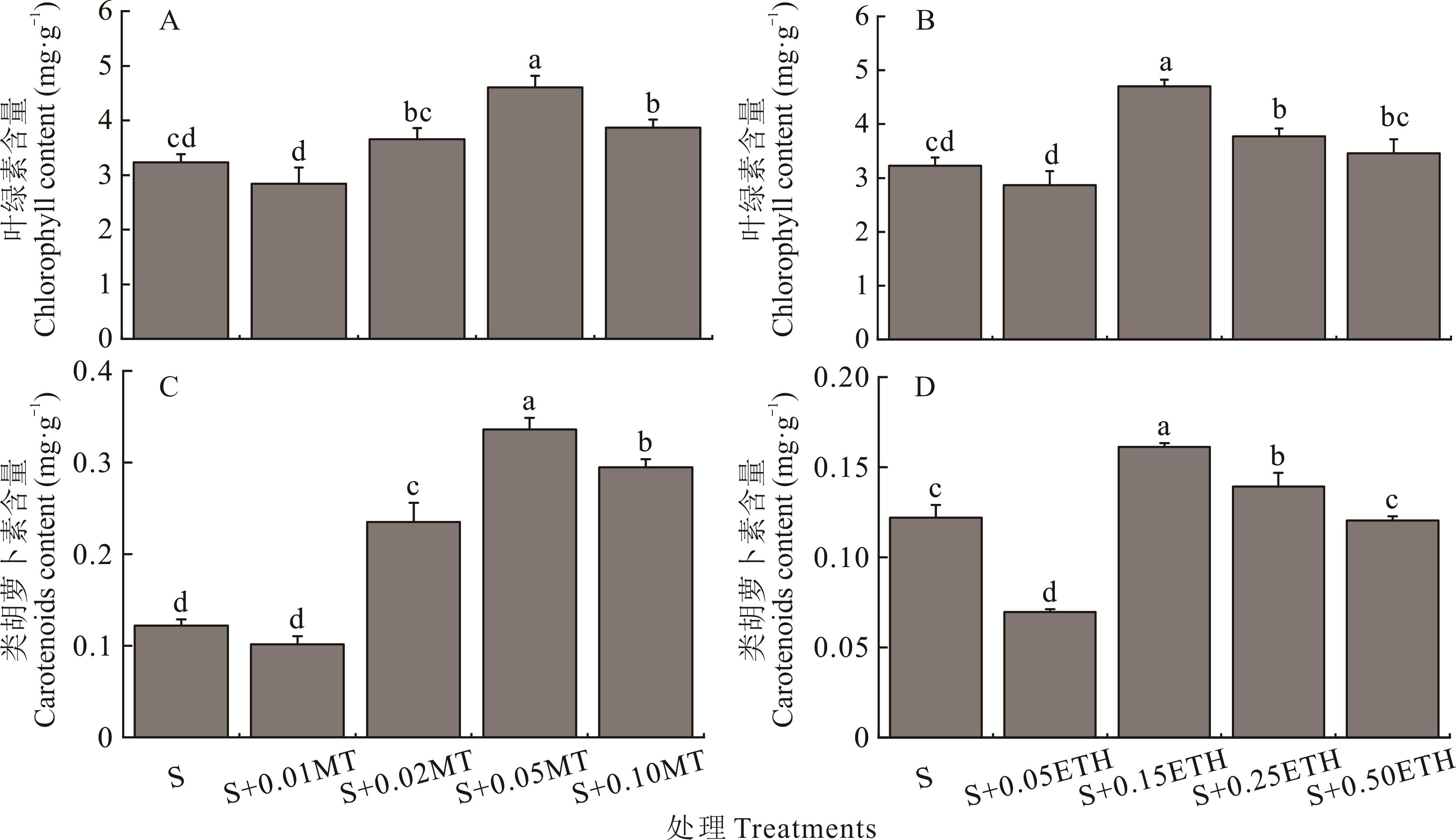
图3 不同浓度的褪黑素和乙烯利对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗光合色素含量的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) on the photosynthetic pigment content of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress

图4 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对紫花苜蓿幼苗在盐胁迫下表型、株高、叶面积和鲜重的影响CK: 对照Control; S: 250 mmol·L-1 NaCl; MT: 0.05 mmol·L-1褪黑素Melatonin; ETH: 0.15 mmol·L-1乙烯利Ethephon. 下同The same below.
Fig.4 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on phenotype, plant height, leaf area and fresh weight of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
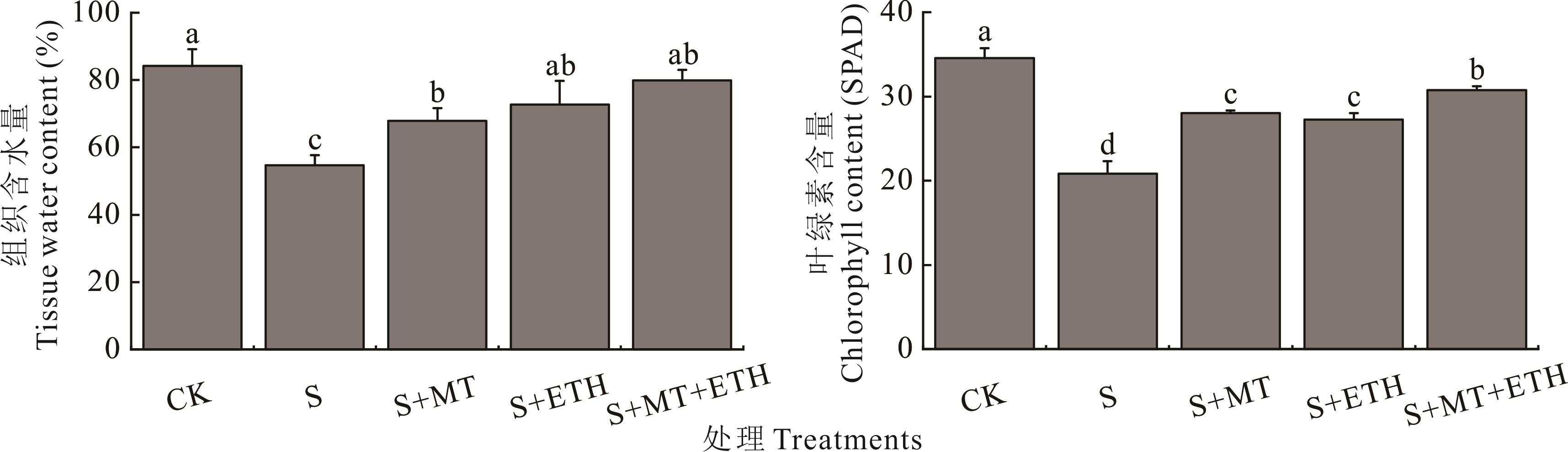
图5 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗组织含水量和叶绿素含量的影响
Fig.5 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on tissue water content and chlorophyll content of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
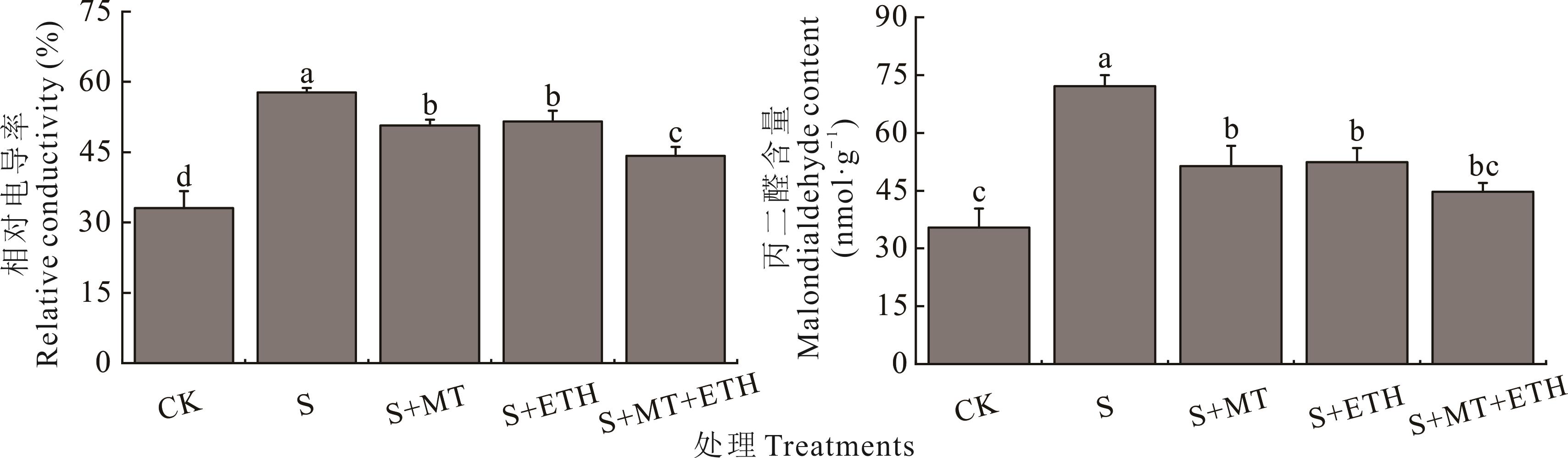
图6 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗相对电导率和丙二醛含量的影响
Fig.6 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on relative conductivity and malondialdehyde content in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
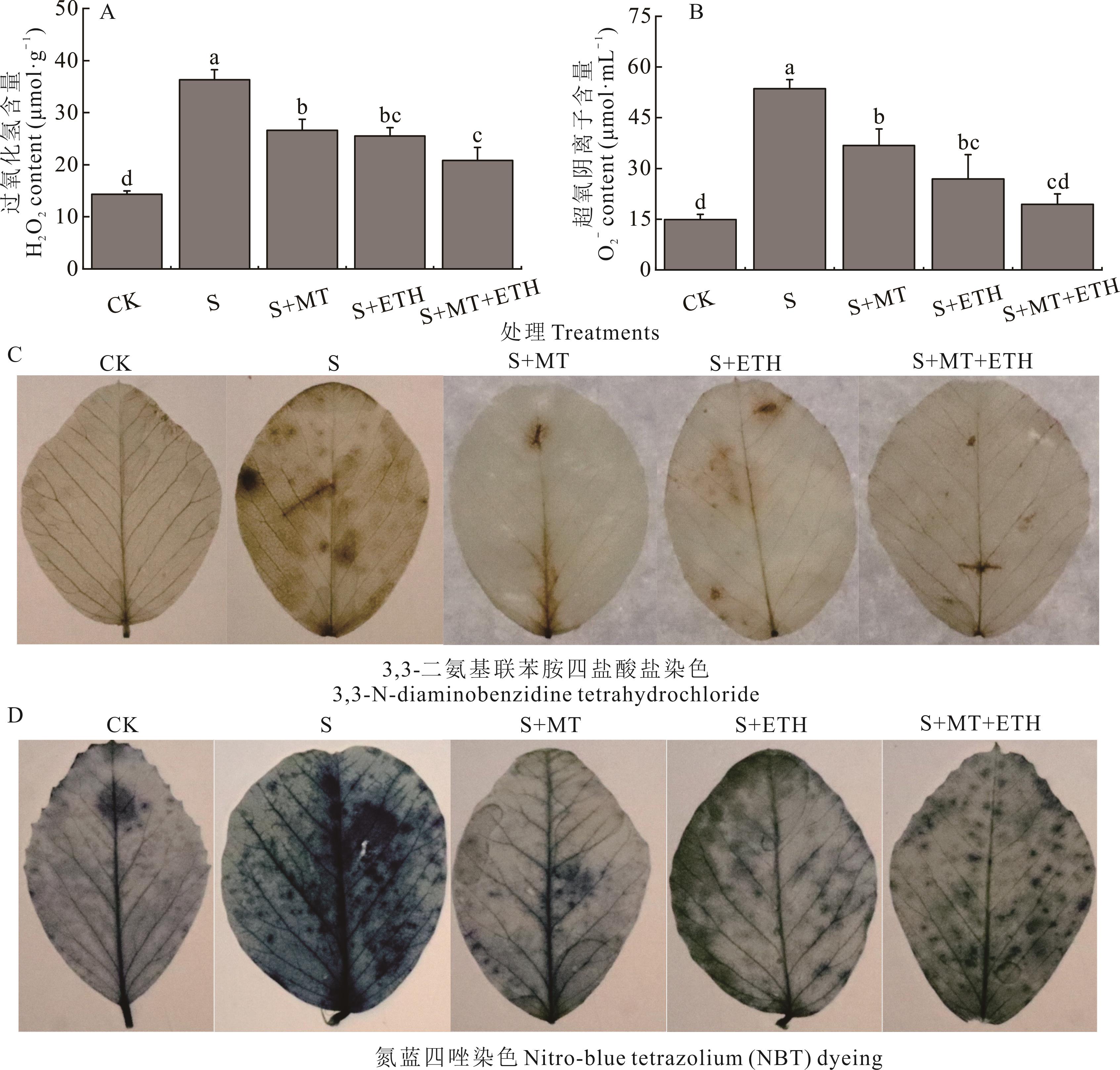
图7 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗活性氧含量的影响
Fig.7 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on reactive oxygen species content in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
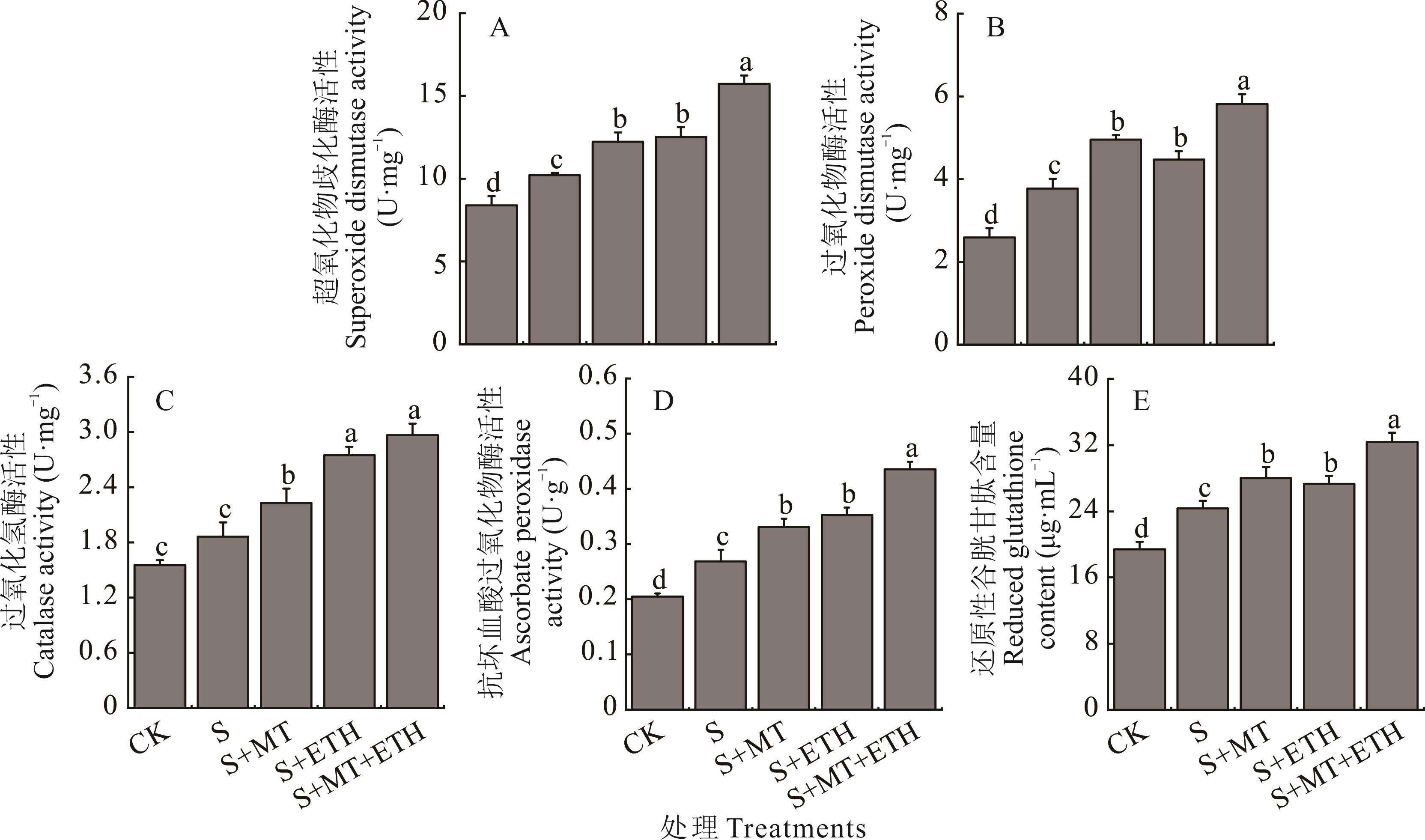
图8 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗抗氧化系统的影响
Fig.8 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on the antioxidant system of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
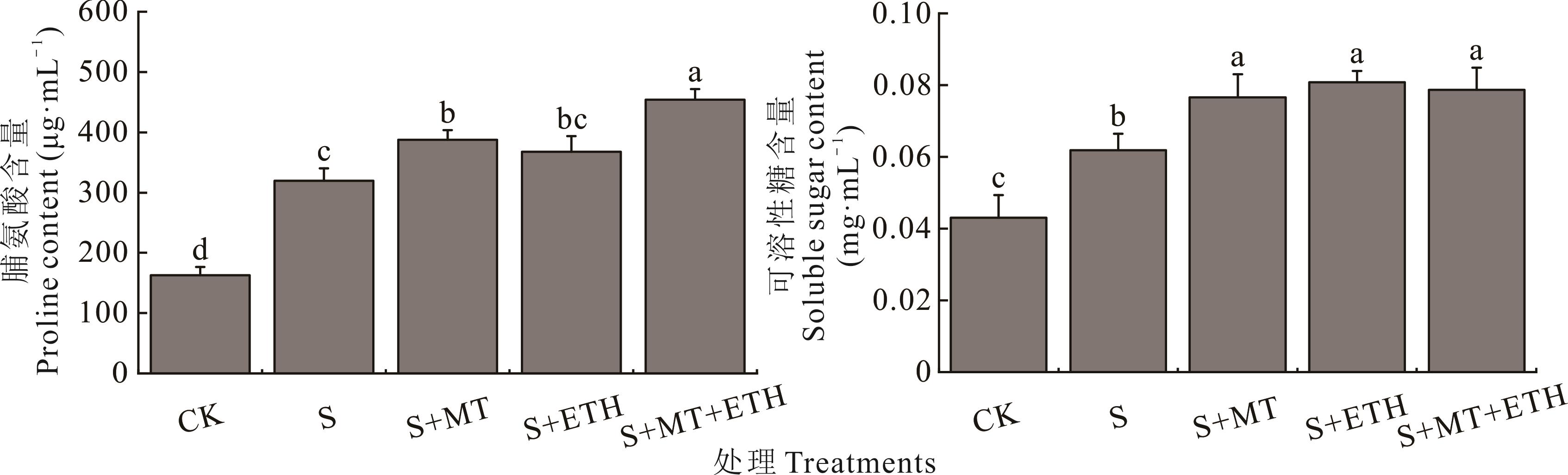
图9 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗渗透调节物质含量的影响
Fig.9 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on the content of osmotic regulatory substances in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
| 项目Item | CK | S | S+MT | S+ETH | S+MT+ETH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ (mg·g-1) | 19.01±0.58d | 76.32±2.76a | 52.01±0.40b | 49.60±1.75b | 34.48±1.09c |
| K+ (mg·g-1) | 42.03±0.96a | 29.22±1.24d | 32.64±1.25cd | 36.69±0.72bc | 39.99±0.29ab |
| K+/Na+ | 2.22±0.11a | 0.40±0.02c | 0.59±0.04c | 0.69±0.07bc | 1.27±0.28b |
表1 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗Na+和K+含量的影响
Table 1 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on Na+ and K+ content in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
| 项目Item | CK | S | S+MT | S+ETH | S+MT+ETH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ (mg·g-1) | 19.01±0.58d | 76.32±2.76a | 52.01±0.40b | 49.60±1.75b | 34.48±1.09c |
| K+ (mg·g-1) | 42.03±0.96a | 29.22±1.24d | 32.64±1.25cd | 36.69±0.72bc | 39.99±0.29ab |
| K+/Na+ | 2.22±0.11a | 0.40±0.02c | 0.59±0.04c | 0.69±0.07bc | 1.27±0.28b |
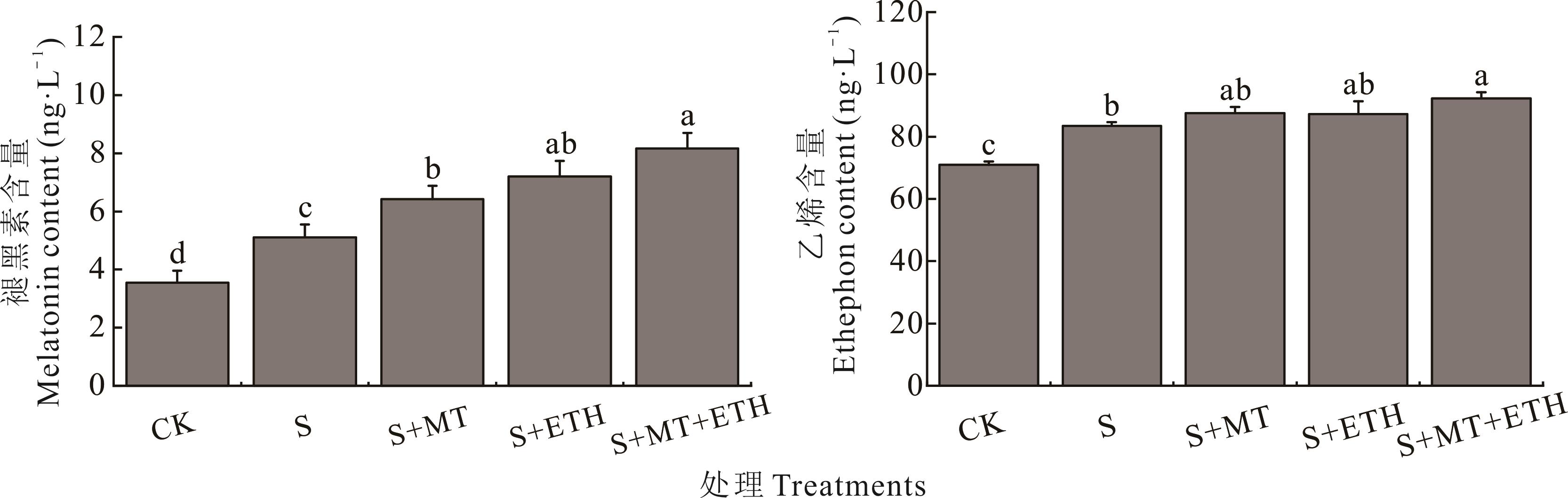
图10 褪黑素和乙烯利交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗MT和ETH含量的影响
Fig.10 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on MT and ETH content in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
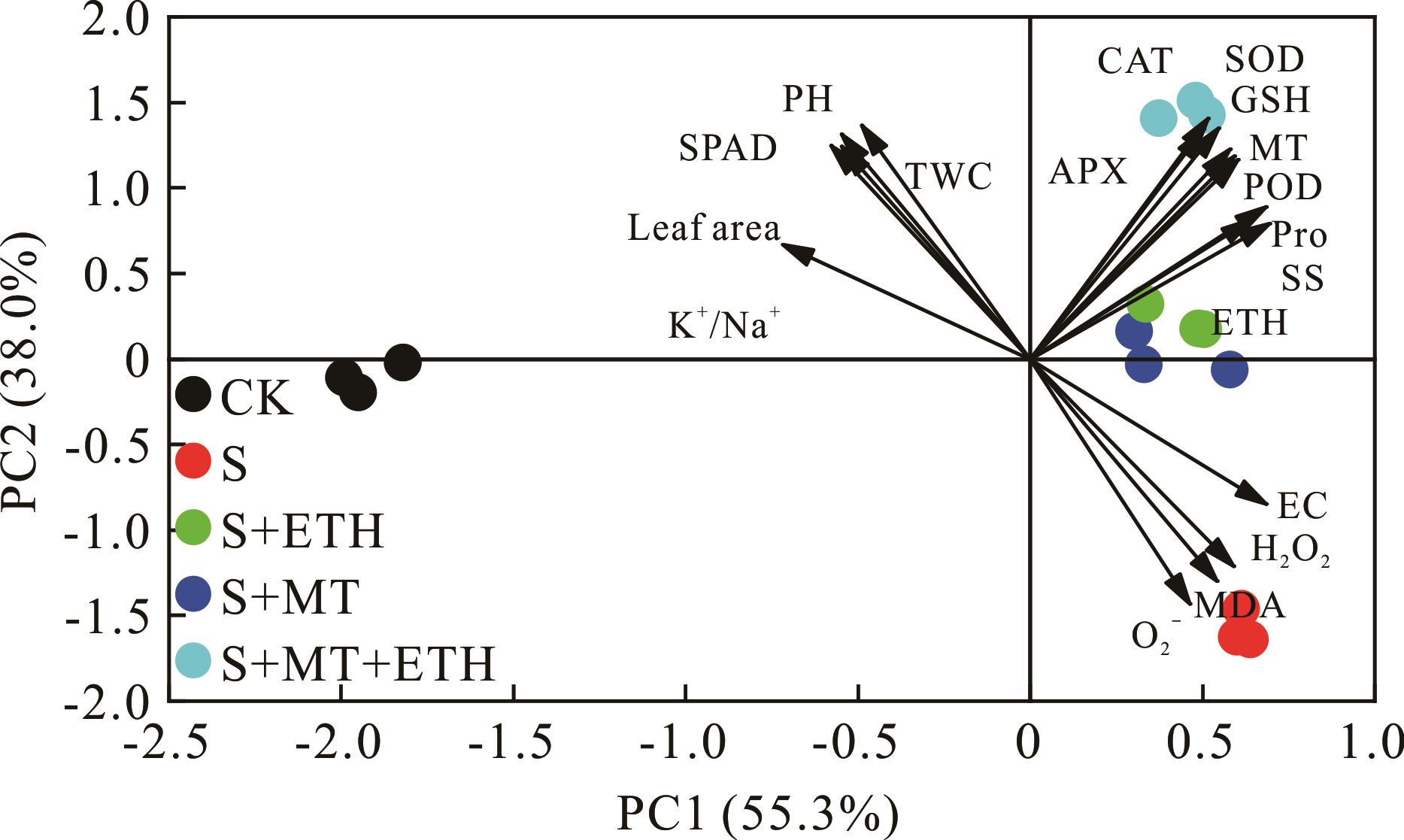
图11 各单项指标间的主成分分析PH: 株高Plant height; Leaf area: 叶面积; TWC: 组织含水量Tissue water content; SPAD: 叶绿素含量Chlorophyll content; EC: 相对电导率Relative conductivity; MDA: 丙二醛含量Malondialdehyde content; K+/Na+: 钾钠离子比值Potassium sodium ion ratio; H2O2: 过氧化氢含量Hydrogen peroxide content; O2-: 超氧阴离子含量Superoxide anion content; Pro: 脯氨酸含量Proline content; SS: 可溶性糖含量Soluble sugar content; SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶活性Superoxide dismutase activity; POD: 过氧化物酶活性Peroxidase activity; CAT: 过氧化氢酶活性Catalase activity; APX: 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶活性Ascorbate peroxidase activity; GSH: 还原性谷胱甘肽含量Reduced glutathione content; MT: 褪黑素含量Melatonin content; ETH: 乙烯利含量Ethephon content.
Fig.11 Principal component analysis among individual indicators
| 1 | Zhao L J, Ma D M, Wang W J, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin on antioxidant capacity and photosynthetic efficiency of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 1355-1363. |
| 赵丽娟, 麻冬梅, 王文静, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗抗氧化能力以及光合作用效率的影响. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(8): 1355-1363. | |
| 2 | Yu H R, Jia Y S, Jia P F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of growth, yield and quality of alfalfa in different saline-alkali soil. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(4): 143-149. |
| 于浩然, 贾玉山, 贾鹏飞, 等. 不同盐碱度对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(4): 143-149. | |
| 3 | Wang Y, Yu R N, Ma X S, et al. Effects of ethylene on seed germination and seedling growth under salt stress in Medicago sativa. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 52(1): 59-69. |
| 王月, 于若男, 马雪松, 等. 乙烯对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(1): 59-69. | |
| 4 | Zhang L S, Sun Y G, Ji J Q, et al. Flavonol synthase gene MsFLS13 regulates saline-alkali stress tolerance in alfalfa. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(4): 1218-1229. |
| 5 | Jin M Y, Li X H, Li F Z, et al. Effects of mixed saline-alkali stress on germination of rice. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(4): 566-574. |
| 金梦野, 李小华, 李昉泽, 等. 盐碱复合胁迫对水稻种子发芽的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(4): 566-574. | |
| 6 | Tan Y, Yin H. Effects of root application of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and melatonin on the growth, photosynthetic characteristics, and antioxidant system of Medicago sativa under salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. | |
| 7 | Feng L C, Li Q, Zhou D Q, et al. B. subtilis CNBG-PGPR-1 induces methionine to regulate ethylene pathway and ROS scavenging for improving salt tolerance of tomato. The Plant Journal, 2023, 117(1): 193-211. |
| 8 | Yang H B, Yang S P. Effects of ABA and ethephon on salt tolerance of buckwheat seedlings. Journal of Jilin Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 39(1): 13-15, 29. |
| 杨洪兵, 杨世平. ABA和乙烯利对荞麦幼苗耐盐性的效应. 吉林农业科学, 2014, 39(1): 13-15, 29. | |
| 9 | Yuan R M, Peng J, Wang J A, et al. Melatonin regulates salicylic acid and ethylene metabolism to maintain shaguo quality during storage. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(9): 1798-1805. |
| 袁瑞敏, 彭静, 王佳傲, 等. 褪黑素调控水杨酸和乙烯代谢维持沙果贮藏品质. 核农学报, 2023, 37(9): 1798-1805. | |
| 10 | Lin Y H. Study on the growth, accumulation and distribution of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients in Lanzhou edible lily. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(12): 8-18. |
| 林玉红. 兰州食用百合生长发育及氮磷钾素养分吸收累积与分配规律研究. 甘肃农业科技, 2019(12): 8-18. | |
| 11 | Zhao F M. The mechanism of RhELIP3 and RhHY5 improving leaf freezing tolerance in the evergreen azalea. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023. |
| 赵芳梦. 常绿杜鹃花RhELIP3和RhHY5提高叶片耐寒性的机制研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023. | |
| 12 | Zhou H P, Shi H F, Yang Y Q, et al. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2023, 51(1): 16-34. |
| 13 | Michard E, Simon A A. Melatonin’s antioxidant properties protect plants under salt stress. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(11): 2587-2590. |
| 14 | Waadt R, Seller C A, Hsu P, et al. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 23(10): 680-694. |
| 15 | Zhao D H. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid and melatonin on physiological characteristics of alfalfa under salt stress. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2023. |
| 赵东豪. 外源脱落酸和褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿生理特性的影响. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2023. | |
| 16 | Wang Y. Effects of ethylene on Madicago sativa L. seed germination and seedling growth under salt stress and investigation on the mechanism. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2019. |
| 王月. 乙烯对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响及其机制的研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2019. | |
| 17 | Xia J, Nan L L, Chen J, et al. Effects of low phosphorus stress on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of alfalfa with different root types. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2024, 42(1): 169-176. |
| 夏静, 南丽丽, 陈洁, 等. 低磷胁迫对不同根型苜蓿光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2024, 42(1): 169-176. | |
| 18 | Ma Y Y, Li G, He W, et al. Mitigating effects of exogenous melatonin on the physiological characteristics of strawberry seedlings under NaCl stress. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2486-2495. |
| 马媛媛, 李刚, 何旺, 等. 外源褪黑素对NaCl胁迫下草莓幼苗生理特性的缓解效应. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2486-2495. | |
| 19 | Sun H R, Sun M. Study on physiological response and salt tolerance of different parthenocissus plants. Journal of Zhongzhou University, 2019, 36(5): 114-118. |
| 孙浩冉, 孙淼. 盐胁迫下不同地锦属植物的生理响应及耐盐性研究. 中州大学学报, 2019, 36(5): 114-118. | |
| 20 | Li B F, Du H M. The effects of melation seed soak on growth of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018, 36(4): 30-34, 40. |
| 李本峰, 杜红梅. 褪黑素浸种对多年生黑麦草种子发芽和幼苗生长的初步研究. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 36(4): 30-34, 40. | |
| 21 | Li J C, Zhang Z W, Zhang J H, et al. The effect of spraying ethephon on low temperature stress in Zoysia japonica. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(12): 3000-3008. |
| 李进超, 张智韦, 张嘉航, 等. 乙烯利对结缕草响应低温胁迫的作用. 草业科学, 2023, 40(12): 3000-3008. | |
| 22 | Wang P T, Liu W C, Han C, et al. Reactive oxygen species: multidimensional regulators of plant adaptation to abiotic stress and development. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2023, 66(3): 330-367. |
| 23 | Wang J, Fu B Z, Li S X, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth and physiological characteristics of Agropyron mongolicum seedlings under drought stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(11): 2947-2957. |
| 王晶, 伏兵哲, 李淑霞, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下沙芦草幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(11): 2947-2957. | |
| 24 | Hou W J, Ma D M, Zhang L, et al. Modulation of salt tolerance in Echinochloa frumentacea by foliar spraying of epibrassinolide. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2024, 44(4): 517-528. |
| 侯汶君, 麻冬梅, 张玲, 等. 叶面喷施表油菜素内酯对湖南稷子耐盐性的调控作用. 西北植物学报, 2024, 44(4): 517-528. | |
| 25 | Gao L Y, Liu B, Zhang R, et al. Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Malus halliana Koehne under saline-alkali stress. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2020, 55(2): 90-97. |
| 高立杨, 刘兵, 张瑞, 等. 褪黑素对盐碱复合胁迫下垂丝海棠光合及生理特性的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(2): 90-97. | |
| 26 | Ma P T, Su S P, Li Y, et al. Effects of exogenous proline on osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzymes in the leaves of Nitraria tangutorum under natural drought. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2020, 55(4): 121-127, 136. |
| 马鹏图, 苏世平, 李毅, 等. 外源脯氨酸对自然干旱下白刺叶片渗透调节与抗氧化酶活性的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(4): 121-127, 136. | |
| 27 | Wang Y, Hou Y Y, Ma Y Q, et al. Effect of glycine betaine treatment on chilling injury and ascorbic acid-glutathione cycle metabolism in peach fruit. Food Science, 2021, 42(13): 158-165. |
| 王懿, 侯媛媛, 马钰晴, 等. 甘氨酸甜菜碱处理对桃果实冷害及抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环代谢的影响. 食品科学, 2021, 42(13): 158-165. | |
| 28 | Wang X. The physiological response of the antioxidant system in Leymus chinensis to different alkali-saline stress. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. |
| 王鑫. 羊草抗氧化系统对盐碱胁迫的响应特征. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015. | |
| 29 | Yan Z M, Sun J, Guo S R, et al. Effects of exogenous proline on the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in roots of Cucumis melo seedlings under salt stress. Plant Science Journal, 2014, 32(5): 502-508. |
| 颜志明, 孙锦, 郭世荣, 等. 外源脯氨酸对盐胁迫下甜瓜幼苗根系抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的影响. 植物科学学报, 2014, 32(5): 502-508. | |
| 30 | Li C Z Y. Effects of exogenous melatonin and ascorbic acid on physiological characteristics of apple rootstock M9T337 under NaCl stress. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 李晨智宇. 外源褪黑素和抗坏血酸对NaCl胁迫下苹果砧木M9T337生理特性的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2020. | |
| 31 | Wei H J, He W Y, Wang Y, et al. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and melatonin on the heat tolerance of perennial ryegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(12): 126-138. |
| 卫宏健, 贺文员, 王越, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌与褪黑素对多年生黑麦草耐热性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 126-138. | |
| 32 | Ma X Y, Song C, Meng Y J, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on germination, antioxidant enzyme activity, and osmotic adjustment substance content of cotton seed under cadmium stress. Cotton Science, 2023, 35(4): 313-324. |
| 马鑫颖, 宋晨, 孟妍君, 等. 外源褪黑素对镉胁迫下棉花种子萌发、抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响. 棉花学报, 2023, 35(4): 313-324. | |
| 33 | Gustavo C, Jessica M I, Alicia G, et al. Involvement of ethylene receptors in the salt tolerance response of Cucurbita pepo. Horticulture Research, 2021, 8(1): 73. |
| 34 | Wu C G, Zhang M, Liang Y F, et al. Salt stress responses in foxtail millet: Physiological and molecular regulation. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(4): 1011-1021. |
| 35 | Sun Z J, Li J Y, Guo D M, et al. Melatonin enhances KCl salinity tolerance by maintaining K+ homeostasis in Malus hupehensis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 21(11): 2273-2290. |
| 36 | Bian F E, Xiao Q H, Hao G M, et al. Effects of root-applied melatonin on endogenous melatonin and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in grapevine under NaCl stress. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(5): 952-963. |
| 卞凤娥, 肖秋红, 郝桂梅, 等. 根施褪黑素对NaCl胁迫下葡萄内源褪黑素及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(5): 952-963. | |
| 37 | Hu X. Study on the effect of ethylene on fruit abscission in Camellia oleifera. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2021. |
| 胡潇. 乙烯对油茶果实脱落的影响研究. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2021. |
| [1] | 马超, 孙熙婧, 冯雅岚, 周爽, 琚吉浩, 吴毅, 王添宁, 郭彬彬, 张均. 紫花苜蓿GLK基因家族鉴定及渗透胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 174-190. |
| [2] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [3] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [4] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [5] | 张震欢, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草AKR基因家族成员的鉴定及根系盐胁迫响应基因HgAKR42639的耐盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [6] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [7] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [8] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [9] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [10] | 王萌, 鲁雪莉, 王菊英, 张梦超, 宋奕汝, 孟晨, 张莉, 徐宗昌. 小黑麦种质萌发期苗期耐盐资源评价与筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 58-68. |
| [11] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [12] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [13] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [14] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [15] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||