

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 165-178.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024362
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
郭亮1( ), 胡雨彤1,2,3(
), 胡雨彤1,2,3( ), 廖雨1, 龚成毓1, 杨晓燕1, 管上淇1, 鞠成琦1
), 廖雨1, 龚成毓1, 杨晓燕1, 管上淇1, 鞠成琦1
收稿日期:2024-09-24
修回日期:2024-11-11
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-06-16
通讯作者:
胡雨彤
作者简介:E-mail: hyt_533@163.com基金资助:
Liang GUO1( ), Yu-tong HU1,2,3(
), Yu-tong HU1,2,3( ), Yu LIAO1, Cheng-yu GONG1, Xiao-yan YANG1, Shang-qi GUAN1, Cheng-qi JU1
), Yu LIAO1, Cheng-yu GONG1, Xiao-yan YANG1, Shang-qi GUAN1, Cheng-qi JU1
Received:2024-09-24
Revised:2024-11-11
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
Yu-tong HU
摘要:
本研究探讨了磷添加和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)侵染对羊草根系构型及养分吸收利用的影响。试验采用根袋盆栽方法,设置4个磷水平处理(P0: 0 mg·kg-1, P1: 11.32 mg·kg-1, P2: 22.63 mg·kg-1, P3: 33.95 mg·kg-1)和两种AMF处理(接种与未接种)交互作用共8个处理,每个处理重复5次。结果表明,磷和AMF处理显著影响羊草的根系生物量,接种AMF显著提高P1和P2处理下的根系生物量。AMF处理提高了总根长和总生物量,但对根平均直径、总根体积和分枝数有降低趋势。土壤理化性质分析表明,AMF处理提高了碱性磷酸酶活性和速效磷含量。养分分析表明AMF接种和磷处理显著影响植株P含量,降低了氮磷比,且AMF在高磷处理下提高了磷利用效率。此外,磷和AMF的交互作用对分形维数、分形丰度、根袋内pH、土壤速效磷和羊草地上部分磷含量均表现出显著影响。总体而言,P1施磷和AMF接种显著改善了羊草的根系生物量和构型,提高了养分吸收与利用效率。
郭亮, 胡雨彤, 廖雨, 龚成毓, 杨晓燕, 管上淇, 鞠成琦. 磷添加和丛枝菌根真菌对羊草根系构型以及植株养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 165-178.
Liang GUO, Yu-tong HU, Yu LIAO, Cheng-yu GONG, Xiao-yan YANG, Shang-qi GUAN, Cheng-qi JU. The impact of phosphorus addition and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on root architecture and nutrient utilization in Leymus chinensis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(8): 165-178.

图1 不同磷梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的地上、地下、总生物量及根冠比的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理之间在P<0.05水平差异显著。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at the P<0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of different phosphorus gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on aboveground biomass, belowground biomass, total biomass, and root to shoot ratio of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 生物量Biomass | 根冠比 Root/shoot | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
地上 Above ground | 地下 Below ground | 总计 Total | ||
| AMF | 6.383** | 7.930*** | 9.503*** | 3.151* |
| P | 3.709 | 15.810*** | 16.496*** | 7.266* |
| AMF×P | 1.500 | 0.377 | 0.254 | 1.115 |
表1 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草生物量和根冠比的双因素方差分析
Table1 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on the L. chinensis biomass and root to shoot ratio
因子 Factor | 生物量Biomass | 根冠比 Root/shoot | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
地上 Above ground | 地下 Below ground | 总计 Total | ||
| AMF | 6.383** | 7.930*** | 9.503*** | 3.151* |
| P | 3.709 | 15.810*** | 16.496*** | 7.266* |
| AMF×P | 1.500 | 0.377 | 0.254 | 1.115 |

图2 不同磷梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的总根长、总根表面积、根平均直径、总根体积、根尖数和分枝数的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different phosphorus gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on total root length,total surface area, average root diameter, total root volume, number of root tips, and number of branches of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 总根长 Total root length | 总根表面积 Total root surface area | 根平均直径 Root average diameter | 总根体积 Root volume | 根尖数 Number of root tips | 分枝数 Number of branches |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | 4.307* | 0.981 | 42.882*** | 12.547** | 0.078 | 2.472 |
| P | 7.596*** | 9.542*** | 1.081 | 8.692*** | 5.250** | 6.261** |
| AMF×P | 0.916 | 1.210 | 2.529 | 2.032 | 0.258 | 0.355 |
表2 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草根系平面几何构型参数的双因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on the root architectural parameters of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 总根长 Total root length | 总根表面积 Total root surface area | 根平均直径 Root average diameter | 总根体积 Root volume | 根尖数 Number of root tips | 分枝数 Number of branches |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | 4.307* | 0.981 | 42.882*** | 12.547** | 0.078 | 2.472 |
| P | 7.596*** | 9.542*** | 1.081 | 8.692*** | 5.250** | 6.261** |
| AMF×P | 0.916 | 1.210 | 2.529 | 2.032 | 0.258 | 0.355 |

图3 不同磷梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的比表面积、分枝密度、分形维数和分形丰度的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different phosphorus gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF)treatments on the specific root surface area, branching density, fractal dimension, and fractal abundance of L.chinensis
因子 Factor | 比表面积 Specific surface area | 分枝密度 Branching density | 分形维数 Fractal dimension | 分形丰度 Fractal abundance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | 10.029** | 36.231*** | 5.014* | 8.025** |
| P | 1.456 | 2.053 | 4.436* | 2.188 |
| AMF×P | 1.091 | 0.168 | 4.404* | 7.236*** |
表3 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草立体几何构型参数的双因素方差分析
Table 3 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on the spatial geometric parameters of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 比表面积 Specific surface area | 分枝密度 Branching density | 分形维数 Fractal dimension | 分形丰度 Fractal abundance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | 10.029** | 36.231*** | 5.014* | 8.025** |
| P | 1.456 | 2.053 | 4.436* | 2.188 |
| AMF×P | 1.091 | 0.168 | 4.404* | 7.236*** |
菌处理 Fungal treatment | 处理 Treatment | 侵染频率 MCF (%) | 侵染强度 MCI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| +AMF | P0 | 100a | 38.27±1.93a |
| P1 | 100a | 40.13±1.45a | |
| P2 | 100a | 34.50±3.56b | |
| P3 | 100a | 27.04±1.19c |
表4 不同施磷处理下菌根侵染频率和侵染强度
Table 4 Mycorrhizal colonization frequency (MCF) and mycorrhizal colonization intensity (MCI) under different phosphorus treatments (%)
菌处理 Fungal treatment | 处理 Treatment | 侵染频率 MCF (%) | 侵染强度 MCI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| +AMF | P0 | 100a | 38.27±1.93a |
| P1 | 100a | 40.13±1.45a | |
| P2 | 100a | 34.50±3.56b | |
| P3 | 100a | 27.04±1.19c |
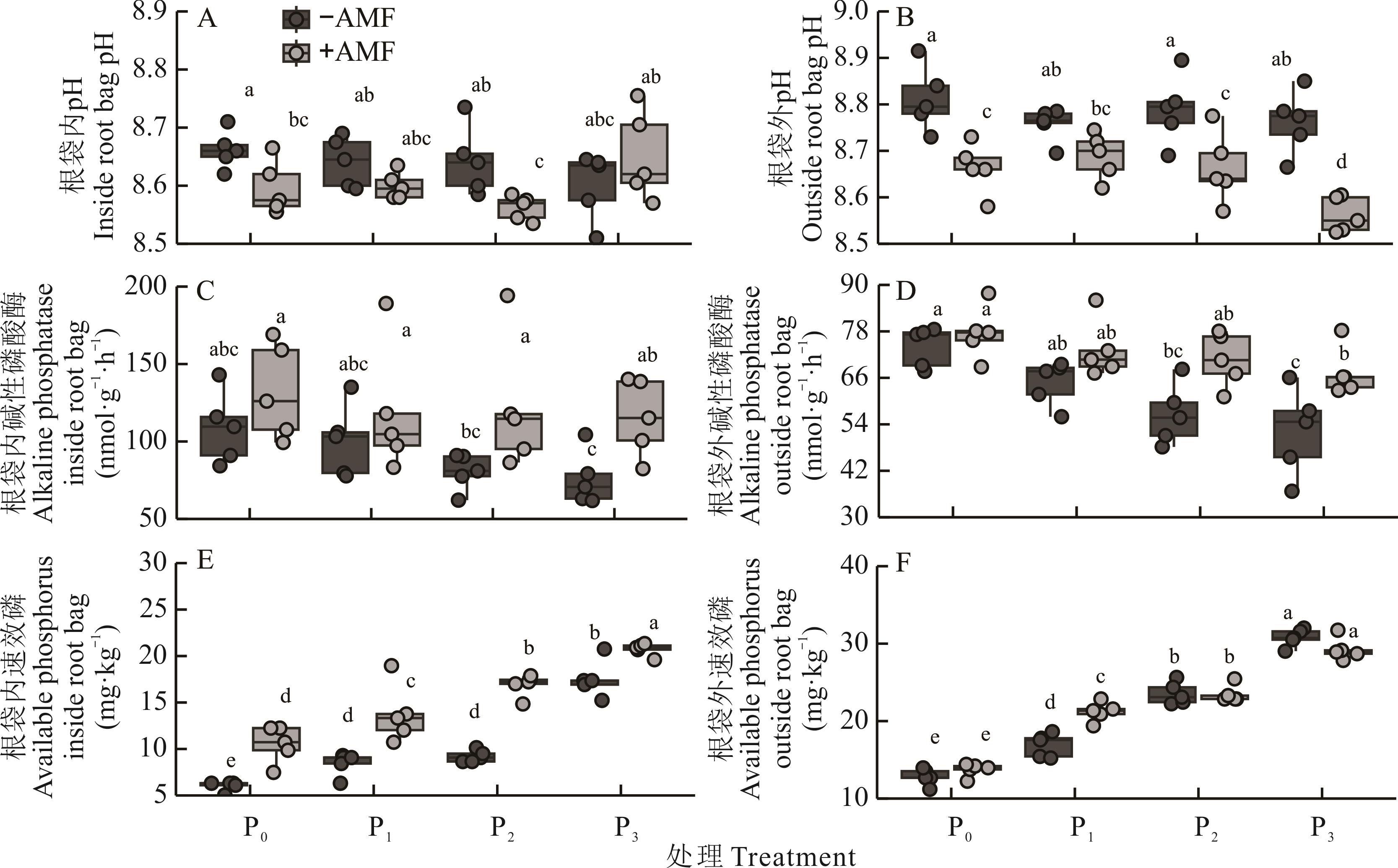
图4 不同磷梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的根袋内外pH、碱性磷酸酶和速效磷的影响
Fig.4 Effects of different phosphorus gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on the pH, alkaline phosphatase, and soil available phosphorus inside and outside the root bag of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | pH | 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase | 速效磷Soil available phosphorus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
根袋内 Inside root bag | 根袋外 Outside root bag | 根袋内 Inside root bag | 根袋外 Outside root bag | 根袋内 Inside root bag | 根袋外 Outside root bag | |
| AMF | 5.094* | 50.631*** | 11.273** | 19.580*** | 98.149*** | 5.166* |
| P | 0.603 | 3.175* | 1.390 | 8.869** | 77.561*** | 321.517*** |
| AMF×P | 3.687* | 2.058 | 0.407 | 1.284 | 3.230* | 9.735*** |
表5 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对土壤pH、碱性磷酸酶活性和土壤速效磷含量的双因素方差分析
Table 5 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on soil pH, alkaline phosphatase activity, and soil available phosphorus content
因子 Factor | pH | 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase | 速效磷Soil available phosphorus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
根袋内 Inside root bag | 根袋外 Outside root bag | 根袋内 Inside root bag | 根袋外 Outside root bag | 根袋内 Inside root bag | 根袋外 Outside root bag | |
| AMF | 5.094* | 50.631*** | 11.273** | 19.580*** | 98.149*** | 5.166* |
| P | 0.603 | 3.175* | 1.390 | 8.869** | 77.561*** | 321.517*** |
| AMF×P | 3.687* | 2.058 | 0.407 | 1.284 | 3.230* | 9.735*** |

图5 不同磷梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的地上地下部碳、磷、氮含量的影响
Fig.5 Effects of different phosphorus gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF)treatments on the carbon, phosphorus, and nitrogen contents of the aboveground and belowground parts of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 碳含量Carbon content | 磷含量Phosphorus content | 氮含量Nitrogen content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上Aboveground | 地下Belowground | 地上Aboveground | 地下Belowground | 地上Aboveground | 地下Belowground | |
| AMF | 0.466 | 27.113*** | 4.164* | 5.542** | 2.063 | 16.627*** |
| P | 2.516 | 1.125 | 106.267*** | 22.699*** | 19.191*** | 2.771 |
| AMF×P | 0.539 | 0.368 | 27.343*** | 1.490 | 0.298 | 0.465 |
表6 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的地上地下部碳、磷、氮含量双因素方差分析
Table 6 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on the carbon, phosphorus, and nitrogen contents of the aboveground and belowground parts of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 碳含量Carbon content | 磷含量Phosphorus content | 氮含量Nitrogen content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上Aboveground | 地下Belowground | 地上Aboveground | 地下Belowground | 地上Aboveground | 地下Belowground | |
| AMF | 0.466 | 27.113*** | 4.164* | 5.542** | 2.063 | 16.627*** |
| P | 2.516 | 1.125 | 106.267*** | 22.699*** | 19.191*** | 2.771 |
| AMF×P | 0.539 | 0.368 | 27.343*** | 1.490 | 0.298 | 0.465 |

图6 不同磷梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的氮磷比、磷吸收量、磷吸收效率和磷利用效率的影响
Fig.6 Effects of different phosphorus gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio, phosphorus uptake, phosphorus acquisition efficiency, and phosphorus utilization efficiency of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 氮磷比 N/P | 磷吸收量 Phosphorus uptake | 磷吸收效率 Phosphorus acquisition efficiency | 磷利用效率 Phosphorus utilization efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | 2.240 | 23.806*** | 2.910* | 29.650*** |
| P | 66.151*** | 11.322** | 0.038 | 1.504 |
| AMF×P | 1.547 | 2.009 | 0.226 | 5.288** |
表7 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对羊草的氮磷比、磷吸收量、磷吸收效率和磷利用效率的双因素方差分析
Table 7 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF)treatments on the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio, phosphorus uptake,phosphorus acquisition efficiency, and phosphorus utilization efficiency of L. chinensis
因子 Factor | 氮磷比 N/P | 磷吸收量 Phosphorus uptake | 磷吸收效率 Phosphorus acquisition efficiency | 磷利用效率 Phosphorus utilization efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF | 2.240 | 23.806*** | 2.910* | 29.650*** |
| P | 66.151*** | 11.322** | 0.038 | 1.504 |
| AMF×P | 1.547 | 2.009 | 0.226 | 5.288** |
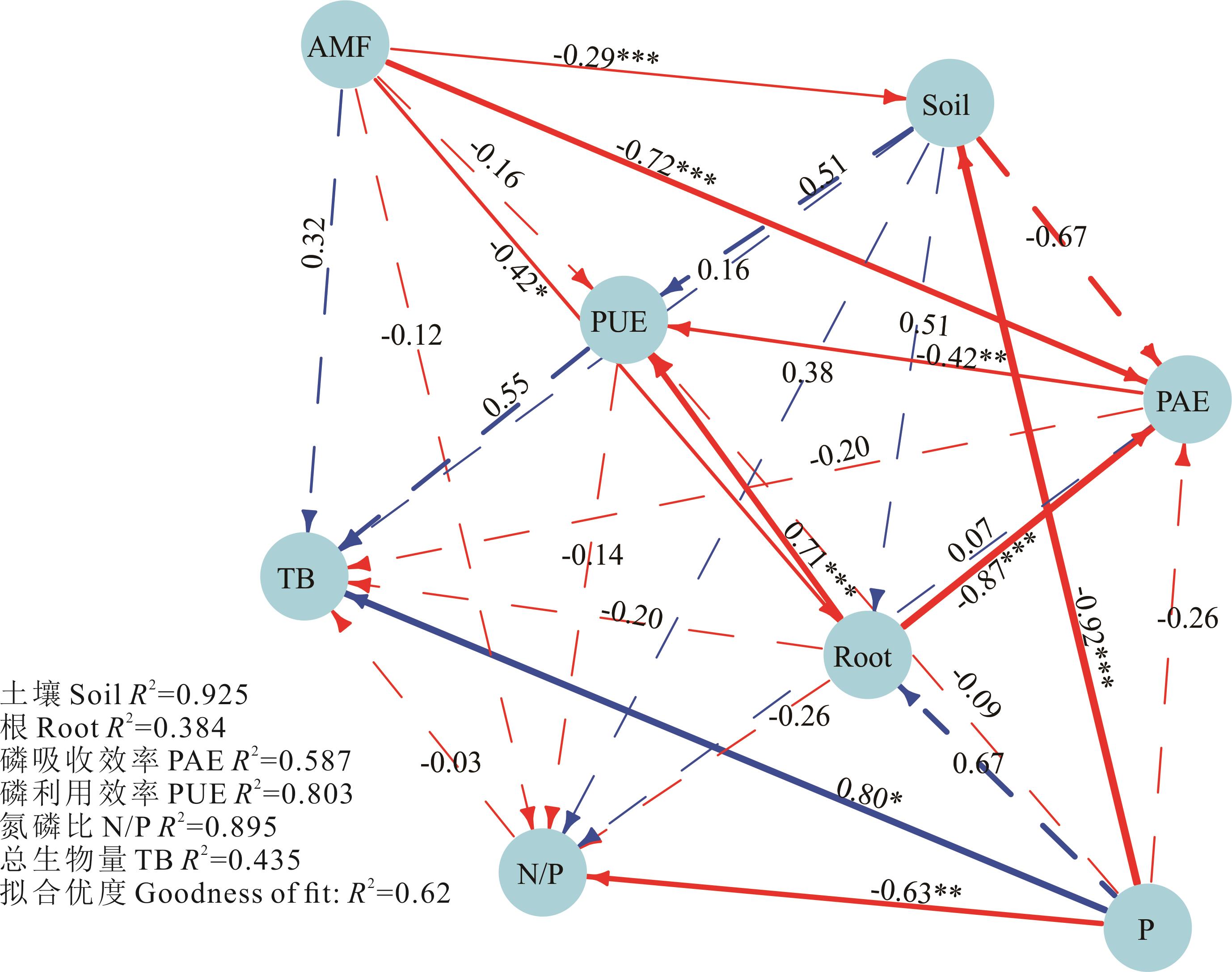
图7 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对土壤、根系构型、氮磷比、磷吸收效率、磷利用效率和总生物量影响的偏最小二乘法通径模型(PLS-PM)分析土壤包括速效磷与碱性磷酸酶;根系构型包括比表面积、平均直径、比根长、分枝密度。路径系数显示了各变量之间的直接影响程度及其显著性水平,虚线表示不存在显著性关系,实线表示存在显著关系,红色表示负影响,蓝色表示正影响,箭头粗细表示影响程度大小。*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; Soil includes available phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase; Root morphology (root) includes specific surface area, average diameter, specific root length, and branching density. Path coefficients indicate the direct effects between variables and their significance levels. Dashed lines represent non-significant relationships, while solid lines represent significant relationships. Red indicates a negative effect, blue indicates a positive effect, and the thickness of the arrows indicates the magnitude of the effect.
Fig.7 Partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM) analysis of the effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on soil, root configuration (Root), nitrogen to phosphorus ratio (N/P), phosphorus absorption efficiency (PAE), phosphorus use efficiency (PUE), and total biomass (TB)

图8 不同磷(P)梯度和丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)处理对土壤、根系构型、氮磷比、磷吸收效率、磷利用效率和总生物量影响的直接和间接效应
Fig.8 Direct and indirect effects of different phosphorus (P) gradients and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) treatments on soil, root morphology, nitrogen to phosphorus ratio, phosphorus uptake efficiency, phosphorus utilization efficiency, and total biomass
| 1 | Tilman D, Balzer C, Hill J, et al. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(50): 20260-20264. |
| 2 | Shen J, Yuan L, Zhang J, et al. Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 997-1005. |
| 3 | Wang L, Zhang L, George T S, et al. A core microbiome in the hyphosphere of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi has functional significance in organic phosphorus mineralization. New Phytologist, 2023, 238(2): 859-873. |
| 4 | Lynch J P. Root phenes for enhanced soil exploration and phosphorus acquisition: tools for future crops. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1041-1049. |
| 5 | Begum N, Qin C, Ahanger M A, et al. Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant growth regulation: implications in abiotic stress tolerance. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1068. |
| 6 | Qiu Q, Bender S F, Mgelwa A S, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mitigate soil nitrogen and phosphorus losses: a Meta-analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 807(1): 150857. |
| 7 | Chandrasekaran M. A Meta-analytical approach on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation efficiency on plant growth and nutrient uptake. Agriculture, 2020, 10(9): 370. |
| 8 | Qi S, Wang J, Wan L, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi contribute to phosphorous uptake and allocation strategies of Solidago canadensis in a phosphorous-deficient environment. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13(2): 831654. |
| 9 | Bruce A, Smith S E, Tester M. The development of mycorrhizal infection in cucumber: effects of P supply on root growth, formation of entry points and growth of infection units. New Phytologist, 1994, 127(3): 507-514. |
| 10 | Lekberg Y, Jansa J, McLeod M, et al. Carbon and phosphorus exchange rates in arbuscular mycorrhizas depend on environmental context and differ among co-occurring plants. New Phytologist, 2024, 242(4): 1576-1588. |
| 11 | Zhang D, Lyu Y, Li H, et al. Neighbouring plants modify maize root foraging for phosphorus: coupling nutrients and neighbours for improved nutrient-use efficiency. New Phytologist, 2020, 226(1): 244-253. |
| 12 | Smith S E, Read D J. Mycorrhizal symbiosis (the third edition). San Diego: Academic Press, 2008. |
| 13 | Plassard C, Dell B. Phosphorus nutrition of mycorrhizal trees. Tree Physiology, 2010, 30(9): 1129-1139. |
| 14 | Javot H, Penmetsa R V, Terzaghi N, et al. A Medicago truncatula phosphate transporter indispensable for the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(5): 1720-1725. |
| 15 | Smith F A, Jakobsen I, Grønlund M, et al. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant phosphorus nutrition: interactions between pathways of phosphorus uptake in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots have important implications for understanding and manipulating plant phosphorus acquisition. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1050-1057. |
| 16 | Xu H B, Xin X P, Baoyintaogetao, et al. Effects of grazing on biomass distribution in Leymus chinensis meadow steppe of Hulunbuir. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 768-774. |
| 许宏斌, 辛晓平, 宝音陶格涛, 等. 放牧对呼伦贝尔羊草草甸草原生物量分布的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 768-774. | |
| 17 | Li Y, Gong J R, Liu M, et al. Defense strategies of dominant plants under different grazing intensity in the typical temperate steppe of Nei Mongol, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(6): 642-653. |
| 李颖, 龚吉蕊, 刘敏, 等. 不同放牧强度下内蒙古温带典型草原优势种植物防御策略. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(6): 642-653. | |
| 18 | Qi Y C, Dong Y S, Geng Y B, et al. The progress in the carbon cycle researches in grassland ecosystem in China. Progress in Geography, 2003, 22(4): 342-352. |
| 齐玉春, 董云社, 耿元波, 等. 我国草地生态系统碳循环研究进展.地理科学进展, 2003, 22(4): 342-352. | |
| 19 | Balei. Competition and coexistence of Leymus chinensis and its main companion species in the Songnen grasslands. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2005. |
| 巴雷.松嫩草地羊草与其主要伴生种竞争与共存研究. 长春: 东北师范大学,2005. | |
| 20 | Zhen L N, Wang R M, Zhou F, et al. Influence of AM fungi on the growth of Leymus chinensis under phosphorus applying at different rate. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2015, 37(6): 56-61. |
| 甄莉娜, 王润梅, 周凤, 等. 不同施磷水平下AM真菌对羊草生长的影响.中国草地学报, 2015, 37(6): 56-61. | |
| 21 | Shan L W, Zhang Q, Zhu R F, et al. Effects of AMF on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Leymus chinensis and Medicago sativa with and without nitrogen and phosphorus application. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8):46-57. |
| 单立文, 张强, 朱瑞芬, 等. 氮、磷添加下AMF对羊草和苜蓿生长与光合生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. | |
| 22 | Shan L S. Studies on morphology and function of root of typical desert plant and its drought-resistant physiology characteristics on northwest China. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 单立山. 西北典型荒漠植物根系形态结构和功能及抗旱生理研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. | |
| 23 | Ketipearachchi K W, Tatsumi J. Local fractal dimensions and multifractal analysis of the root system of legumes. Plant Production Science, 2000, 3(3): 289-295. |
| 24 | Liu R J, Luo X S. A new method to quantify the inoculum potential of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytologist, 1994, 128(1): 89-92. |
| 25 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 26 | Lyu Y, Tang H L, Li H G, et al. Major crop species show differential balance between root morphological and physiological responses to variable phosphorus supply. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1939-1954. |
| 27 | Karlova R, Boer D, Hayes S, et al. Root plasticity under abiotic stress. Plant Physiology, 2021, 187(3): 1057-1070. |
| 28 | Razaq M, Zhang P, Shen H, et al. Influence of nitrogen and phosphorous on the growth and root morphology of Acer mono. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0171321. |
| 29 | Vain S, Tamm I, Tamm Ü, et al. Negative relationship between topsoil root production and grain yield in oat and barley. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2023, 349(2): 108467. |
| 30 | Sun J, Rong Z, Yang L, et al. Effects of AMF inoculation on the growth, photosynthesis and root physiological morphology of root-pruned Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings. Tree Physiology, 2024, 44(1): tpad130. |
| 31 | Zhang T, Zou X H, Li L X, et al. Research progress on the cost and benefit of root acquisition metabolism from plant resources. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2023, 38(4): 149-155. |
| 张婷, 邹显花, 李林鑫, 等. 根系获取资源过程中的代谢成本权衡策略研究进展. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(4): 149-155. | |
| 32 | Liu D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. |
| 33 | de Souza Kulmann M S, Aguilar M V M, Tassinari A, et al. Effects of increasing soil phosphorus and association with ectomycorrhizal fungi (Pisolithus microcarpus) on morphological, nutritional, biochemical, and physiological parameters of Pinus taeda L. Forest Ecology and Management, 2023, 544: 121207. |
| 34 | Gruber B D, Giehl R F H, Friedel S, et al. Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiology, 2013, 163(1): 161-179. |
| 35 | de Vries J, Evers J B, Kuyper T W, et al. Mycorrhizal associations change root functionality: a 3D modelling study on competitive interactions between plants for light and nutrients. New Phytologist, 2021, 231(3): 1171-1182. |
| 36 | Walk T C, Van Erp E, Lynch J P. Modelling applicability of fractal analysis to efficiency of soil exploration by roots. Annals of Botany, 2004, 94(1): 119-128. |
| 37 | Yang M Q, Wu R C, Wang X H, et al. Effects of slow-release fertilizer and mycorrhizal fungi on the root growth and architecture of Cyclobalanopsis gilva container seedlings. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2023, 29(9): 1761-1770. |
| 杨孟晴, 吴仁超, 王秀花, 等. 赤皮青冈容器苗根系生长和构型对缓释肥和菌根菌的响应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(9): 1761-1770. | |
| 38 | Vance C P, Uhde-Stone C, Allan D L. Phosphorus acquisition and use:critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytologist, 2003, 157(3): 423-447. |
| 39 | Qin M, Zhang Q, Pan J, et al. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil enzyme activity is coupled with increased plant biomass. European Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 71(1): 84-92. |
| 40 | Yu L, Zhang H, Zhang W, et al. Cooperation between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth-promoting bacteria and their effects on plant growth and soil quality. PeerJ, 2022, 10(1): e13080. |
| 41 | Delavaux C S, Smith-Ramesh L M, Kuebbing S E. Beyond nutrients: a Meta-analysis of the diverse effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plants and soils. Ecology, 2017, 98(8): 2111-2119. |
| 42 | Li Y L, Mao W, Zhao X Y, et al. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry in typical desert and desertified regions, North China. Environmental Science, 2010, 31(8): 1716-1725. |
| 李玉霖, 毛伟, 赵学勇, 等. 北方典型荒漠及荒漠化地区植物叶片氮磷化学计量特征研究. 环境科学, 2010, 31(8): 1716-1725. |
| [1] | 高守舆, 刘文静, 李钰莹, 向清源, 许佳俊, 舒蕾淇, 李肇中. 苗期白羊草对盐胁迫的生理生化响应及其耐盐阈值的界定[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 164-174. |
| [2] | 贾蕴欢, 胡雯颖, 邓健, 赵雪, 陈子玥, 王亚楠, 李江文, 张晓曦. 氮添加对黄土丘陵区草地土壤微生物养分限制特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 221-232. |
| [3] | 亓雯雯, 马红媛, 李亚晓, 杜艳, 孙梦丹, 武海涛. 优质牧草新品种选育方法研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 187-202. |
| [4] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [5] | 段海霞, 师茜, 康生萍, 苟海青, 罗崇亮, 熊友才. 丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌与植物共生研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 166-182. |
| [6] | 马路平, 石兆勇, 韦文敬, 杨爽. 基于Meta分析菌根菌对植物叶片生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 99-109. |
| [7] | 卢晓瑜, 刘雅洁, 白彩霞, 李进华, 王子贺, 杨春雪. 虎尾草伴生和丛枝菌根真菌对碱胁迫下羊草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 69-83. |
| [8] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷耦合下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量及磷素空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 104-115. |
| [9] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [10] | 杨斯琪, 鲍雅静, 叶佳琦, 吴帅, 张萌, 徐梦冉, 赵钰, 吕晓涛, 韩兴国. 氮添加和刈割条件下羊草光合-CO2响应过程及模型比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 160-172. |
| [11] | 亢燕, 王耀辉, 牛天慧, 滕哲, 祁智, 杨佳. 羊草LcZIP1的铁转运功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 173-180. |
| [12] | 于晓东, 余浩洋, 杨旭, 赵东旭, 张林刚. 内蒙古两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组序列差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 72-84. |
| [13] | 高守舆, 李钰莹, 杨志青, 董宽虎, 夏方山. 白羊草叶绿体基因组密码子使用偏好性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 85-95. |
| [14] | 安晓霞, 张盈盈, 马春晖, 李曼, 张前兵. 施磷与接种丛枝菌根真菌对苜蓿产量和磷素利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 71-84. |
| [15] | 丰吉, 刘志扩, 李海燕, 杨允菲, 郭健. 围栏封育和长期刈割对松嫩草地羊草和野古草种群营养繁殖特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 50-60. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||