

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 187-201.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024424
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
秦晓芳( ), 何芷睿, 贾彤, 杨玉娇, 付薇, 李航, 彭燕(
), 何芷睿, 贾彤, 杨玉娇, 付薇, 李航, 彭燕( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-28
修回日期:2024-12-16
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
彭燕
作者简介:E-mail: pengyanlee@163.com基金资助:
Xiao-fang QIN( ), Zhi-rui HE, Tong JIA, Yu-jiao YANG, Wei FU, Hang LI, Yan PENG(
), Zhi-rui HE, Tong JIA, Yu-jiao YANG, Wei FU, Hang LI, Yan PENG( )
)
Received:2024-10-28
Revised:2024-12-16
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Yan PENG
摘要:
几丁质酶是一种糖苷水解酶,在植物生长发育过程中发挥着重要作用。目前几丁质酶在白三叶应答各种生物和非生物胁迫的相关研究报道相对较少。本研究对白三叶的几丁质酶基因家族进行了全基因组鉴定,得到了44个几丁质酶基因,不均匀分布于白三叶16条染色体上,通过系统进化分析将这些几丁质酶分为GH18和GH19分支,5个不同的小组:I~V。其中29个基因属于GH18亚家族,15个基因属于GH19亚家族,且同一亚族基因具有相似的结构和功能,启动子分析发现,这44个几丁质酶基因的启动子区域包含与生长发育、激素及逆境胁迫相关的多种顺式作用元件,此外,qRT-PCR分析显示,盐胁迫和干旱胁迫处理显著诱导了几丁质酶基因的表达,进一步验证了其在植物胁迫响应中的作用。选择TrChit3基因深入研究几丁质酶基因的抗旱能力。在拟南芥中过表达TrChit3基因并进行干旱胁迫处理,测定相对电导率、丙二醛等生理指标,结果显示在干旱条件下过表达TrChit3基因能够显著提高拟南芥的耐旱能力。研究结果为植物中几丁质酶基因的探索奠定了基础。
秦晓芳, 何芷睿, 贾彤, 杨玉娇, 付薇, 李航, 彭燕. 白三叶几丁质酶基因家族鉴定及TrChit3功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 187-201.
Xiao-fang QIN, Zhi-rui HE, Tong JIA, Yu-jiao YANG, Wei FU, Hang LI, Yan PENG. Identification of the chitinase gene family and functional analysis of TrChit3 from white clover[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 187-201.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 上游引物Forward primer (5′-3′) | 下游引物Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| gene-P8452_04698 | CCGAACCCCTAAATTGAAC | CCACCGATAGAAAGCAACA |
| gene-P8452_70179 | TCAAATTATGTCAATCCAAAGG | GAGTTTCCGCCTAAGAAGTTAT |
| gene-P8452_47669 | AGCCCAAGAGTTAGGGTTTAC | ACAAGCAGGTTCTGATGATGT |
| gene-P8452_10179 | CATTGATCCTTTTGTTGGTCT | GTACCATCTCCTAAGTTTTGGC |
| gene-P8452_42935 | TTCTTGACGGCATTGATTT | GCATTTCCTATCCAAGCATC |
| gene-P8452_00576 | CATCGGAGGAGGTAATAGCA | AAGTCAACACCATCAAACCC |
| gene-P8452_23770 | CAGGGACAGATTGGTATGG | TTGAGAAAGAGCCCAGTTG |
| gene-P8452_72355 | TATTCTCTTTCATCGCCTCA | TGTTCATTTCGTTTGTGGTT |
| gene-P8452_10178 | AGTCCACAATCACAAAAGAAAA | TCCAAACATAATCAAATAAACCA |
| gene-P8452_10182 | TAGGTGATGCTGTTTTAGATGG | TTTGCTTTTGTGATTGTGAACT |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences
| 基因ID Gene ID | 上游引物Forward primer (5′-3′) | 下游引物Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| gene-P8452_04698 | CCGAACCCCTAAATTGAAC | CCACCGATAGAAAGCAACA |
| gene-P8452_70179 | TCAAATTATGTCAATCCAAAGG | GAGTTTCCGCCTAAGAAGTTAT |
| gene-P8452_47669 | AGCCCAAGAGTTAGGGTTTAC | ACAAGCAGGTTCTGATGATGT |
| gene-P8452_10179 | CATTGATCCTTTTGTTGGTCT | GTACCATCTCCTAAGTTTTGGC |
| gene-P8452_42935 | TTCTTGACGGCATTGATTT | GCATTTCCTATCCAAGCATC |
| gene-P8452_00576 | CATCGGAGGAGGTAATAGCA | AAGTCAACACCATCAAACCC |
| gene-P8452_23770 | CAGGGACAGATTGGTATGG | TTGAGAAAGAGCCCAGTTG |
| gene-P8452_72355 | TATTCTCTTTCATCGCCTCA | TGTTCATTTCGTTTGTGGTT |
| gene-P8452_10178 | AGTCCACAATCACAAAAGAAAA | TCCAAACATAATCAAATAAACCA |
| gene-P8452_10182 | TAGGTGATGCTGTTTTAGATGG | TTTGCTTTTGTGATTGTGAACT |
基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸长度Aminoacids length (aa) | 分子量Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点Isoelectric point (PI) | 不稳定指数 Instability index | 脂肪族氨基酸指数 Aliphatic index | 平均疏水性Grand average of hydrophobicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene-P8452_04693 | 298 | 32361.98 | 9.16 | 34.30 | 86.74 | 0.009 |
| gene-P8452_04697 | 362 | 39842.48 | 9.26 | 34.73 | 86.22 | -0.050 |
| gene-P8452_04698 | 291 | 32409.61 | 5.60 | 40.36 | 87.22 | -0.105 |
| gene-P8452_04688 | 275 | 29055.34 | 4.37 | 31.32 | 82.04 | -0.011 |
| gene-P8452_00576 | 383 | 43275.95 | 8.33 | 31.26 | 78.69 | -0.205 |
| gene-P8452_04690 | 278 | 29609.18 | 5.15 | 34.46 | 86.44 | 0.059 |
| gene-P8452_06296 | 383 | 43255.08 | 8.80 | 29.62 | 79.48 | -0.199 |
| gene-P8452_10187 | 297 | 32149.64 | 8.96 | 32.32 | 84.07 | 0.028 |
| gene-P8452_10182 | 275 | 28960.20 | 4.41 | 33.27 | 82.76 | -0.002 |
| gene-P8452_10188 | 292 | 32297.52 | 5.74 | 37.78 | 86.61 | -0.063 |
| gene-P8452_10178 | 297 | 31928.65 | 5.02 | 35.58 | 82.83 | -0.142 |
| gene-P8452_10179 | 206 | 22738.68 | 5.11 | 31.38 | 87.14 | -0.035 |
| gene-P8452_13386 | 207 | 22795.73 | 5.11 | 30.86 | 86.71 | -0.037 |
| gene-P8452_18384 | 303 | 33888.14 | 6.93 | 42.01 | 82.38 | -0.194 |
| gene-P8452_17128 | 621 | 68415.97 | 5.22 | 28.83 | 92.17 | 0.005 |
| gene-P8452_23770 | 365 | 39463.67 | 4.55 | 28.88 | 75.51 | -0.168 |
| gene-P8452_28219 | 132 | 14603.66 | 6.25 | 32.11 | 72.50 | -0.164 |
| gene-P8452_29322 | 362 | 39410.05 | 8.96 | 33.69 | 74.56 | -0.281 |
| gene-P8452_33777 | 331 | 35611.74 | 5.37 | 34.50 | 56.40 | -0.303 |
| gene-P8452_39032 | 256 | 27187.40 | 7.44 | 46.42 | 56.52 | -0.245 |
| gene-P8452_42935 | 294 | 31613.91 | 6.70 | 33.99 | 85.37 | -0.010 |
| gene-P8452_47669 | 294 | 31587.88 | 6.70 | 33.02 | 86.36 | 0.009 |
| gene-P8452_53931 | 212 | 22708.93 | 4.37 | 28.04 | 61.75 | -0.321 |
| gene-P8452_53932 | 211 | 22945.46 | 5.46 | 31.39 | 57.82 | -0.280 |
| gene-P8452_53933 | 186 | 20238.60 | 4.99 | 28.93 | 60.91 | -0.175 |
| gene-P8452_53934 | 283 | 30502.81 | 4.71 | 32.67 | 59.36 | -0.297 |
| gene-P8452_53930 | 275 | 29591.09 | 6.83 | 36.52 | 62.22 | -0.135 |
| gene-P8452_53929 | 278 | 29839.26 | 5.27 | 31.46 | 59.78 | -0.204 |
| gene-P8452_54091 | 411 | 45795.84 | 5.50 | 47.07 | 87.83 | -0.215 |
| gene-P8452_58401 | 391 | 43516.31 | 5.45 | 45.42 | 90.77 | -0.177 |
| gene-P8452_58243 | 284 | 30703.01 | 4.66 | 33.45 | 58.10 | -0.322 |
| gene-P8452_58237 | 235 | 25189.95 | 4.57 | 35.09 | 67.36 | -0.093 |
| gene-P8452_58242 | 178 | 19133.09 | 4.55 | 21.51 | 65.84 | -0.152 |
| gene-P8452_58236 | 241 | 25954.70 | 4.81 | 31.04 | 64.85 | -0.166 |
| gene-P8452_63358 | 328 | 36123.93 | 9.07 | 42.80 | 80.49 | -0.256 |
| gene-P8452_59011 | 322 | 35664.54 | 6.23 | 24.44 | 73.63 | -0.159 |
| gene-P8452_68078 | 303 | 33447.00 | 8.72 | 35.38 | 82.61 | -0.176 |
| gene-P8452_63938 | 322 | 35664.54 | 6.23 | 24.44 | 73.63 | -0.159 |
| gene-P8452_70179 | 298 | 32589.35 | 6.71 | 23.03 | 96.54 | 0.063 |
| gene-P8452_70182 | 297 | 31644.73 | 5.32 | 32.97 | 79.93 | -0.004 |
| gene-P8452_72355 | 378 | 41722.57 | 6.11 | 28.83 | 84.37 | 0.011 |
| gene-P8452_75297 | 296 | 32327.00 | 6.13 | 24.14 | 95.57 | 0.034 |
| gene-P8452_75301 | 270 | 28454.16 | 5.26 | 34.06 | 86.48 | 0.111 |
| gene-P8452_77241 | 388 | 42619.43 | 6.11 | 33.05 | 82.71 | -0.002 |
表2 白三叶几丁质酶基因家族蛋白理化性质
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of proteins in the chitinase gene family of white clover
基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸长度Aminoacids length (aa) | 分子量Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点Isoelectric point (PI) | 不稳定指数 Instability index | 脂肪族氨基酸指数 Aliphatic index | 平均疏水性Grand average of hydrophobicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene-P8452_04693 | 298 | 32361.98 | 9.16 | 34.30 | 86.74 | 0.009 |
| gene-P8452_04697 | 362 | 39842.48 | 9.26 | 34.73 | 86.22 | -0.050 |
| gene-P8452_04698 | 291 | 32409.61 | 5.60 | 40.36 | 87.22 | -0.105 |
| gene-P8452_04688 | 275 | 29055.34 | 4.37 | 31.32 | 82.04 | -0.011 |
| gene-P8452_00576 | 383 | 43275.95 | 8.33 | 31.26 | 78.69 | -0.205 |
| gene-P8452_04690 | 278 | 29609.18 | 5.15 | 34.46 | 86.44 | 0.059 |
| gene-P8452_06296 | 383 | 43255.08 | 8.80 | 29.62 | 79.48 | -0.199 |
| gene-P8452_10187 | 297 | 32149.64 | 8.96 | 32.32 | 84.07 | 0.028 |
| gene-P8452_10182 | 275 | 28960.20 | 4.41 | 33.27 | 82.76 | -0.002 |
| gene-P8452_10188 | 292 | 32297.52 | 5.74 | 37.78 | 86.61 | -0.063 |
| gene-P8452_10178 | 297 | 31928.65 | 5.02 | 35.58 | 82.83 | -0.142 |
| gene-P8452_10179 | 206 | 22738.68 | 5.11 | 31.38 | 87.14 | -0.035 |
| gene-P8452_13386 | 207 | 22795.73 | 5.11 | 30.86 | 86.71 | -0.037 |
| gene-P8452_18384 | 303 | 33888.14 | 6.93 | 42.01 | 82.38 | -0.194 |
| gene-P8452_17128 | 621 | 68415.97 | 5.22 | 28.83 | 92.17 | 0.005 |
| gene-P8452_23770 | 365 | 39463.67 | 4.55 | 28.88 | 75.51 | -0.168 |
| gene-P8452_28219 | 132 | 14603.66 | 6.25 | 32.11 | 72.50 | -0.164 |
| gene-P8452_29322 | 362 | 39410.05 | 8.96 | 33.69 | 74.56 | -0.281 |
| gene-P8452_33777 | 331 | 35611.74 | 5.37 | 34.50 | 56.40 | -0.303 |
| gene-P8452_39032 | 256 | 27187.40 | 7.44 | 46.42 | 56.52 | -0.245 |
| gene-P8452_42935 | 294 | 31613.91 | 6.70 | 33.99 | 85.37 | -0.010 |
| gene-P8452_47669 | 294 | 31587.88 | 6.70 | 33.02 | 86.36 | 0.009 |
| gene-P8452_53931 | 212 | 22708.93 | 4.37 | 28.04 | 61.75 | -0.321 |
| gene-P8452_53932 | 211 | 22945.46 | 5.46 | 31.39 | 57.82 | -0.280 |
| gene-P8452_53933 | 186 | 20238.60 | 4.99 | 28.93 | 60.91 | -0.175 |
| gene-P8452_53934 | 283 | 30502.81 | 4.71 | 32.67 | 59.36 | -0.297 |
| gene-P8452_53930 | 275 | 29591.09 | 6.83 | 36.52 | 62.22 | -0.135 |
| gene-P8452_53929 | 278 | 29839.26 | 5.27 | 31.46 | 59.78 | -0.204 |
| gene-P8452_54091 | 411 | 45795.84 | 5.50 | 47.07 | 87.83 | -0.215 |
| gene-P8452_58401 | 391 | 43516.31 | 5.45 | 45.42 | 90.77 | -0.177 |
| gene-P8452_58243 | 284 | 30703.01 | 4.66 | 33.45 | 58.10 | -0.322 |
| gene-P8452_58237 | 235 | 25189.95 | 4.57 | 35.09 | 67.36 | -0.093 |
| gene-P8452_58242 | 178 | 19133.09 | 4.55 | 21.51 | 65.84 | -0.152 |
| gene-P8452_58236 | 241 | 25954.70 | 4.81 | 31.04 | 64.85 | -0.166 |
| gene-P8452_63358 | 328 | 36123.93 | 9.07 | 42.80 | 80.49 | -0.256 |
| gene-P8452_59011 | 322 | 35664.54 | 6.23 | 24.44 | 73.63 | -0.159 |
| gene-P8452_68078 | 303 | 33447.00 | 8.72 | 35.38 | 82.61 | -0.176 |
| gene-P8452_63938 | 322 | 35664.54 | 6.23 | 24.44 | 73.63 | -0.159 |
| gene-P8452_70179 | 298 | 32589.35 | 6.71 | 23.03 | 96.54 | 0.063 |
| gene-P8452_70182 | 297 | 31644.73 | 5.32 | 32.97 | 79.93 | -0.004 |
| gene-P8452_72355 | 378 | 41722.57 | 6.11 | 28.83 | 84.37 | 0.011 |
| gene-P8452_75297 | 296 | 32327.00 | 6.13 | 24.14 | 95.57 | 0.034 |
| gene-P8452_75301 | 270 | 28454.16 | 5.26 | 34.06 | 86.48 | 0.111 |
| gene-P8452_77241 | 388 | 42619.43 | 6.11 | 33.05 | 82.71 | -0.002 |

图4 白三叶几丁质酶基因上游2000 bp启动子区域顺式作用元件预测结果
Fig. 4 Prediction results of cis-acting elements in the 2000 bp promoter region upstream of the chitinase gene of white clover
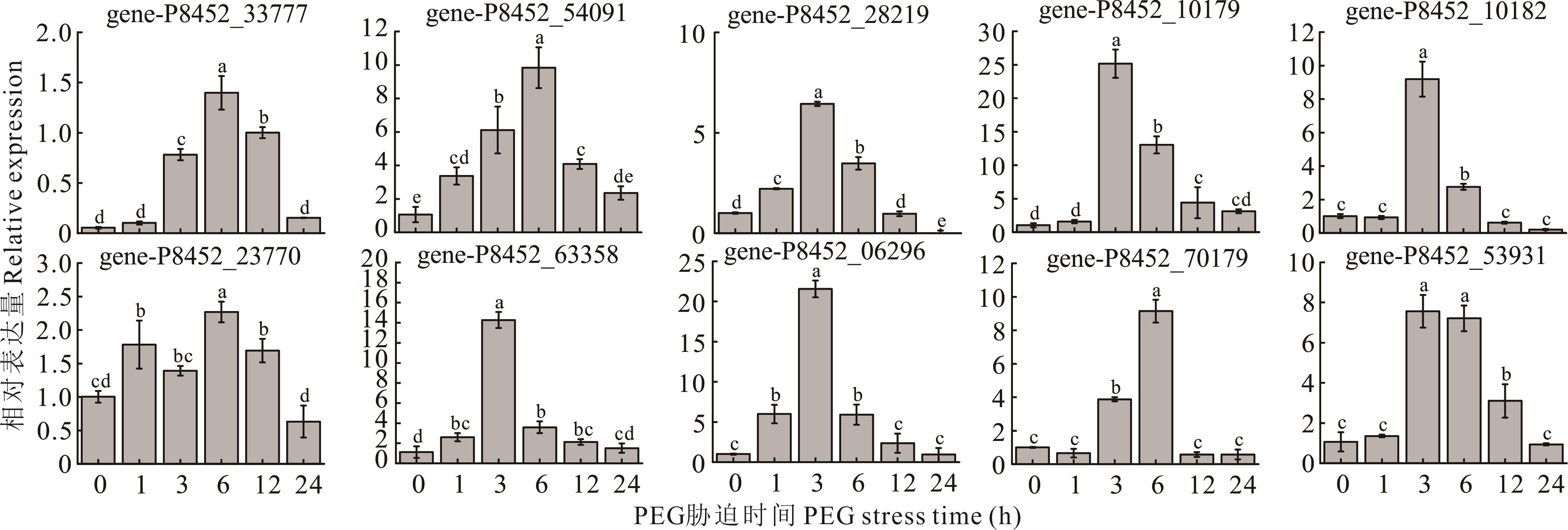
图5 干旱胁迫下白三叶几丁质酶基因qRT-PCR分析不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。下同。The different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.5 qRT-PCR analysis of the chitinase gene of white clover under drought stress
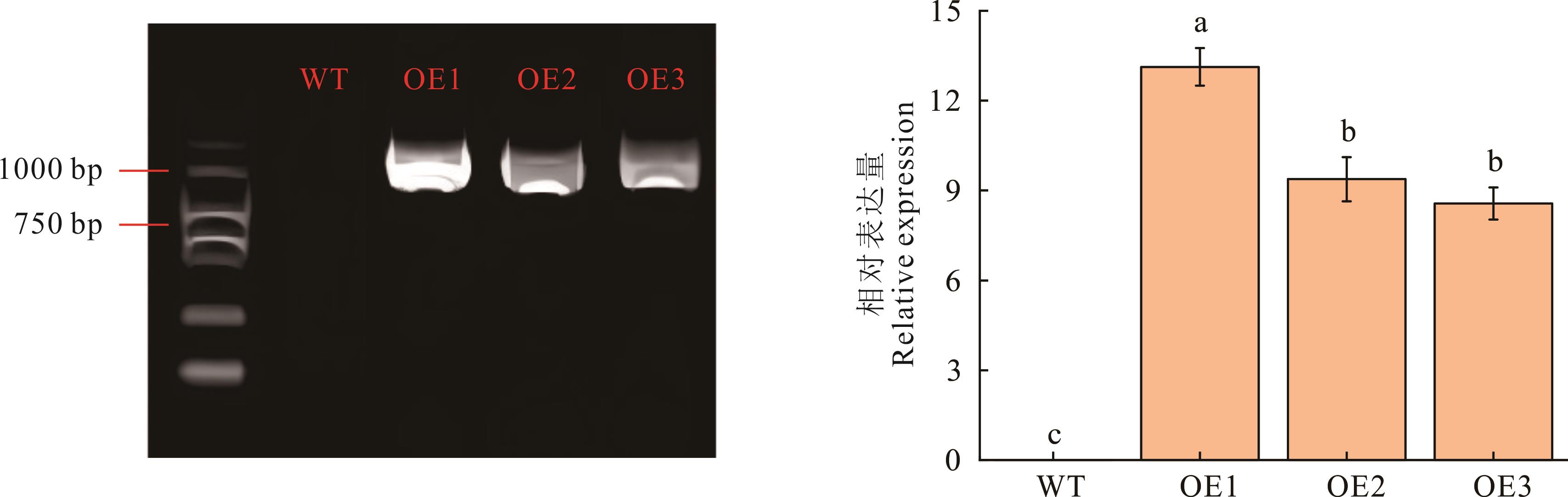
图7 过表达拟南芥植株鉴定及TrChit3基因表达量检测WT:野生型拟南芥。OE:过表达拟南芥。1、2、3是株系。WT: Wild type arabidopsis. OE: Overexpression arabidopsis. 1, 2, 3 is the strain.
Fig.7 Identification of over-expressed Arabidopsis plants and detection of TrChit3 gene expression
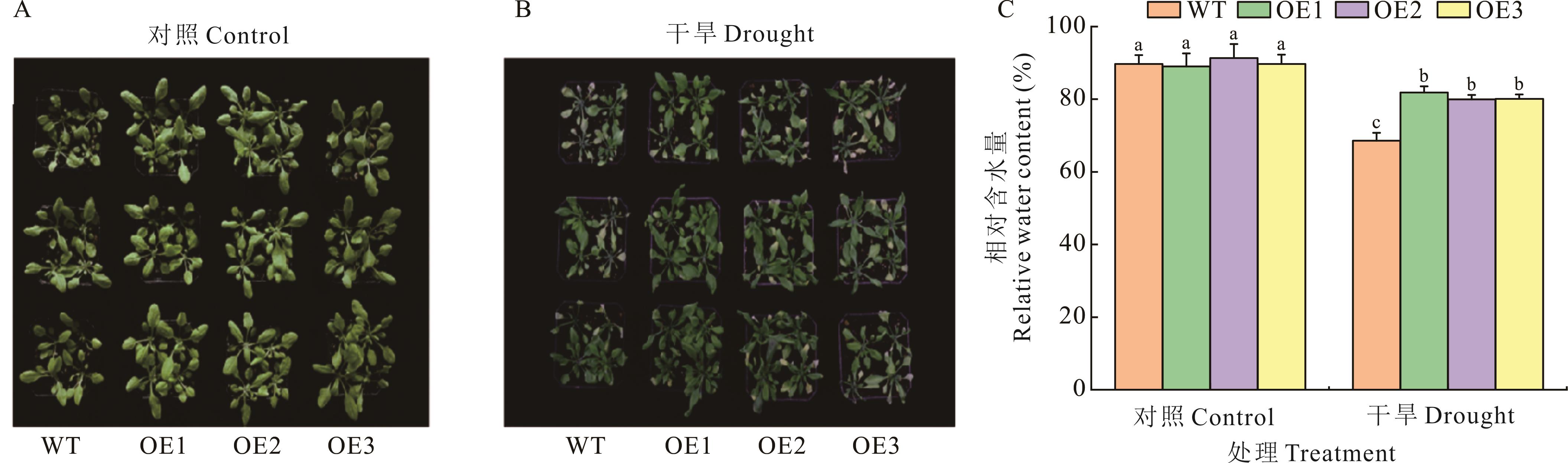
图8 过表达TrChit3拟南芥在12% PEG胁迫下的表型差异A:野生型(WT)及过表达拟南芥在对照条件下的表型;B:WT及过表达拟南芥在12% PEG胁迫下的表型;C: WT及过表达拟南芥在对照及12% PEG胁迫下的相对含水量。A: The phenotype of wild type (WT) and over-expressed A.thaliana under control conditions; B: Phenotypes of WT and over-expressing Arabidopsis under 12% PEG stress; C: The relative water content of WT and overexpression A. thaliana under control and 12% PEG stress.
Fig.8 Phenotypic differences of A. thaliana over-expressing TrChit3 under 12% PEG stress
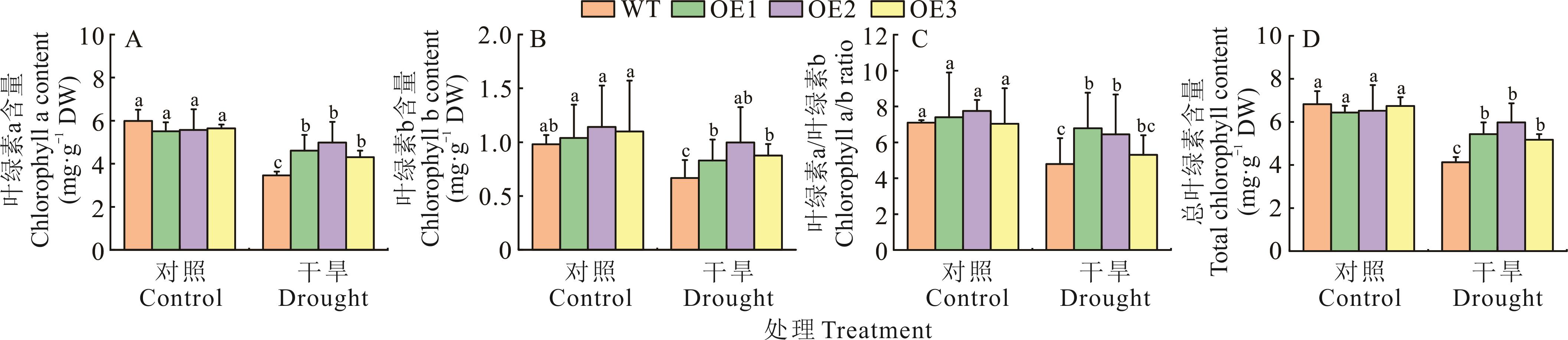
图9 干旱胁迫对过表达TrChit3拟南芥叶绿素含量的影响DW:干重Dry weight. 下同The same below.
Fig. 9 Effect of drought stress on chlorophyll content of A. thaliana over-expressing TrChit3

图11 干旱胁迫对过表达TrChit3和野生型拟南芥的丙二醛含量和相对电导率、总抗氧化能力、超氧阴离子O2 ·-产生速率和H2O2含量的影响FW:鲜重Fresh weight.
Fig.11 Effects of drought stress on malondialdehyde content, relative conductivity, total antioxidant capacity, superoxide anion O2·-production rate and H2O2 content in TrChit3-overexpressing and wild-type Arabidopsis
| [1] | Karasuda S, Tanaka S, Kajihara H, et al. Plant chitinase as a possible biocontrol agent for use instead of chemical fungicides. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2003, 67(1): 221-224. |
| [2] | Malik A. Purification and properties of plant chitinases: a review. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 2019, 43(3): e12762. |
| [3] | Dahiya N, Tewari R, Hoondal G S. Biotechnological aspects of chitinolytic enzymes: a review. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 71(6): 773-782. |
| [4] | Hamid R, Khan M A, Ahmad M, et al. Chitinases: an update. Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences, 2013, 5(1): 21-29. |
| [5] | Richa K, Tiwari I M, Devanna B, et al. Novel chitinase gene LOC_Os11g47510 from indica rice Tetep provides enhanced resistance against sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 596. |
| [6] | Passarinho P A, DE Vries S C. Arabidopsis chitinases: a genomic survey. Arabidopsis Book, 2002(1): e0023. |
| [7] | Tyler L, Bragg J N, Wu J, et al. Annotation and comparative analysis of the glycoside hydrolase genes in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics, 2010, 11(1): 600. |
| [8] | Su Y, Xu L, Wang S, et al. Identification, phylogeny and transcript of chitinase family genes in sugarcane. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 10708. |
| [9] | Sundheim L, Poplawsky A R, Ellingboe A H. Molecular cloning of two chitinase genes from Serratia marcescens and their expression in Pseudomonas species. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 1988, 33(3): 483-491. |
| [10] | Bai X, Zhan G, Tian S, et al. Transcription factor BZR2 activates chitinase Cht20.2 transcription to confer resistance to wheat stripe rust. Plant Physiology, 2021, 187(4): 2749-2762. |
| [11] | Datta K, Tu J, Oliva N, et al. Enhanced resistance to sheath blight by constitutive expression of infection-related rice chitinase in transgenic elite indica rice cultivars. Plant Science, 2001, 160(3): 405-414. |
| [12] | Wu C T, Bradford K J. Class I chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase are differentially regulated by wounding, methyl jasmonate, ethylene, and gibberellin in tomato seeds and leaves. Plant Physiology, 2003, 133(1): 263-273. |
| [13] | Kumar S A, Kumari P H, Jawahar G, et al. Beyond just being foot soldiers-osmotin like protein (OLP) and chitinase (Chi11) genes act as sentinels to confront salt, drought, and fungal stress tolerance in tomato. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 132(1): 53-65. |
| [14] | Wan K, Buitrago S, Cheng B, et al. Analysis of chitinase gene family in barley and function study of HvChi22 involved in drought tolerance. Molecular Biology Reports, 2024, 51(1): 731. |
| [15] | Pan X X, Hu M Y, Wang Z W, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the rice chitinases gene family and their expression profiles under different stress treatments. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 2022, 58(4): 746-756. |
| 潘晓雪, 胡明瑜, 王忠伟, 等. 水稻几丁质酶基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(4): 746-756. | |
| [16] | Zhang H, Li N, Xing X Z, et al. Chitinase gene identification and expression analysis of wild soybean and cultivated soybean. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2024, 25(9): 1573-1588. |
| 张华, 李娜, 邢馨竹, 等. 野生大豆与栽培大豆几丁质酶基因鉴定及其表达分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 2024, 25(9): 1573-1588. | |
| [17] | Yao C, Li X, Li Y, et al. Overexpression of a Malus baccata MYB transcription factor gene MbMYB4 increases cold and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(3): 1794. |
| [18] | Ma R, Liu W, Li S, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of the CIPK gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and the role of StCIPK10 in response to drought and osmotic stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(24): 13535. |
| [19] | Xu F, Liu S, Liu Y, et al. Effectiveness of lysozyme coatings and 1-MCP treatments on storage and preservation of kiwifruit. Food Chemistry, 2019, 288: 201-207. |
| [20] | Li T, Huang Y, Khadr A, et al. DcDREB1A, a DREB-binding transcription factor from Daucus carota, enhances drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana and modulates lignin levels by regulating lignin-biosynthesis-related genes. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2020, 169: 103896. |
| [21] | Liu D, He S, Zhai H, et al. Overexpression of IbP5CR enhances salt tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2014, 117: 1-16. |
| [22] | Li M, Zhang X, Zhang T, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY genes and their important roles during cold stress in white clover. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e15610. |
| [23] | Li M, Chen X, Huang W, et al. Comprehensive identification of the β-amylase (BAM) gene family in response to cold stress in white clover. Plants, 2024, 13(2): 154. |
| [24] | Zhang Y, Li Z, Peng Y, et al. Clones of FeSOD, MDHAR, DHAR genes from white clover and gene expression analysis of ROS-scavenging enzymes during abiotic stress and hormone treatments. Molecules, 2015, 20(11): 20939-20954. |
| [25] | Ma X F, Wright E, Ge Y, et al. Improving phosphorus acquisition of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) by transgenic expression of plant-derived phytase and acid phosphatase genes. Plant Science, 2009, 176(4): 479-488. |
| [26] | Mészáros P, Rybanský Ľ, Spieb N, et al. Plant chitinase responses to different metal-type stresses reveal specificity. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33: 1789-1799. |
| [27] | Shibuya N, Minami E. Oligosaccharide signalling for defence responses in plant. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 2001, 59(5): 223-233. |
| [28] | Wang J, Xu Z Q. Cloning and inducible expression of a class I chitinase gene FaChit1 from Festuca arundinacea. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(5): 869-875. |
| 王健, 徐子勤. 高羊茅FaChit1基因cDNA克隆及诱导表达. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(5): 869-875. | |
| [29] | Zhu C, Zhang S T, Chang X J, et al. Cloning and its expression analysis of chitinase under drought stress in Camellia sinensis. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2017, 38(5): 894-902. |
| 朱晨, 张舒婷, 常笑君, 等. 茶树几丁质酶基因的克隆及其在干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(5): 894-902. | |
| [30] | Kochieva E Z, Filyushin M A, Beletsky A V, et al. Identification and expression analysis of chitinase genes in parasitic plant Monotropa hypopitys. Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2017, 473(1): 111-113. |
| [31] | Yu L X, Djebrouni M, Chamberland H, et al. Chitinase: differential induction of gene expression and enzyme activity by drought stress in the wild (Lycopersicon chilense Dun.) and cultivated (L. esculentum Mill.) tomatoes. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1998, 153(5): 745-753. |
| [32] | Cao J, Tan X. Comprehensive analysis of the chitinase family genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Plants, 2019, 8(3): 52. |
| [33] | Hu Y P, Guo Y J, Ji Q H, et al. Structure, classification and evolutionary analysis of chitinase gene family in citrus. South China Fruit Tree, 2022, 51(6): 16-21. |
| 胡亚平, 郭雁君, 吉前华, 等. 柑桔几丁质酶基因家族的结构、分类与进化分析. 中国南方果树, 2022, 51(6): 16-21. | |
| [34] | Yao H. Analysis of grape chitinase and glucanase gene families. Qinghuangdao: Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology, 2024. |
| 姚姮. 葡萄几丁质酶和葡聚糖酶基因家族的分析. 秦皇岛: 河北科技师范学院, 2024. | |
| [35] | Xu W, Liu J F, Zhang G, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis under Fusarium graminearum stress of chitinase gene family in Triticum aestivum L. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(11): 7-17. |
| 徐武, 刘建丰, 张戈, 等. 小麦几丁质酶基因家族的全基因组鉴定及禾谷镰刀菌胁迫下的表达分析. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(11): 7-17. | |
| [36] | Bartholomew E S, Black K, Feng Z, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the chitinase gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): from gene identification and evolution to expression in response to Fusarium oxysporum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(21): 5309. |
| [37] | Haxim Y, Kahar G, Zhang X, et al. Genome-wide characterization of the chitinase gene family in wild apple (Malus sieversii) and domesticated apple (Malus domestica) reveals its role in resistance to Valsa mali. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1007936. |
| [38] | Jeffares D C, Penkett C J, Bähler J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends in Genetics, 2008, 24(8): 375-378. |
| [39] | Grover A. Plant chitinases: genetic diversity and physiological roles. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2012, 31(1): 57-73. |
| [40] | Gao Y, Zan X L, Wu X F, et al. Identification of fungus-responsive cis-acting element in the promoter of Brassica juncea chitinase gene, BjCHI1. Plant Science, 2014, 215: 190-198. |
| [41] | Taira T, Toma N, Ichi M, et al. Tissue distribution, synthesis stage, and ethylene induction of pineapple (Ananas comosus) chitinases. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2005, 69(4): 852-854. |
| [42] | Lyu P, Zhang C, Xie P, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of the chitinase gene family in response to white mold and drought stress in soybean (Glycine max). Life, 2022, 12(9): 1340. |
| [43] | Ali M, Gai W X, Khattak A M, et al. Knockdown of the chitin-binding protein family gene CaChiIV1 increased sensitivity to Phytophthora capsici and drought stress in pepper plants. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2019, 294: 1311-1326. |
| [44] | Amira M, Qados A. Effect of salt stress on plant growth and metabolism of bean plant Vicia faba (L.). Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 10(1): 7-15. |
| [45] | Manuka R, Saddhe A A, Kunar K. Expression of OsWNK9 in Arabidopsis conferred tolerance to salt and drought stress. Plant Science, 2018, 270: 58-71. |
| [46] | Flexas J, Medrano H. Drought-inhibition of photosynthesis in C3 plants: stomatal and non-stomatal limitations revisited. Annals of Botany, 2002, 89(2): 183-189. |
| [47] | Zlatev Z. Drought-induced changes in chlorophyll fluorescence of young wheat plants. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 2009, 23(1): 438-441. |
| [48] | Farmer E E, Mueller M J. ROS-mediated lipid peroxidation and RES-activated signaling. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2013, 64(1): 429-450. |
| [49] | Davey M, Stals E, Panis B, et al. High-throughput determination of malondialdehyde in plant tissues. Analytical Biochemistry, 2005, 347(2): 201-207. |
| [50] | Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, et al. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2010, 33(4): 453-467. |
| [1] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [2] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [3] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [4] | 汪欣瑶, 彭亚萍, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草HgS5基因的克隆与抗旱性鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 184-195. |
| [5] | 崔红丽, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族鉴定及低温逆境表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 111-125. |
| [6] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [7] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [8] | 吴毅, 冯雅岚, 王添宁, 琚吉浩, 肖慧淑, 马超, 张均. 小麦及其祖先物种Hsp70基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 53-67. |
| [9] | 张震欢, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草AKR基因家族成员的鉴定及根系盐胁迫响应基因HgAKR42639的耐盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [10] | 张许可, 夏红飞, 陈国立, 李德州, 张晓伟, 李克梅, 王丽丽. 白三叶草镰刀菌根腐病病原鉴定及其生物学特性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 175-187. |
| [11] | 黎泽斌, 邱永争, 刘延杰, 喻金秋, 王柏吉, 刘千宁, 王月, 崔国文. 紫花苜蓿BZR基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 106-122. |
| [12] | 史先飞, 高宇, 黄旭升, 周雅莉, 蔡桂萍, 李昕儒, 李润植, 薛金爱. 油莎豆CeWRKY转录因子响应非生物胁迫的功能表征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 186-201. |
| [13] | 冯华昊, 王涵, 周建祯, 张晗, 唐韬, 彭燕. 白三叶耐铝种质筛选及耐铝评价指标分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 100-111. |
| [14] | 李雯, 赵丽蓉, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 亚麻DMP基因家族的全基因组鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 91-106. |
| [15] | 姚佳明, 何悦, 郝欢欢, 黄心如, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草LpPIL5基因特征分析及转录调控[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 155-167. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||