

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 213-228.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024426
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
操鹏飞1,2( ), 汪水平1(
), 汪水平1( ), 黄桥深1, 周世龙3, 罗专4, 任莹3, 刘勇2, 李铁军2, 汤少勋2,5(
), 黄桥深1, 周世龙3, 罗专4, 任莹3, 刘勇2, 李铁军2, 汤少勋2,5( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-28
修回日期:2024-12-06
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
汪水平,汤少勋
作者简介:wangshuiping1979@sina.com基金资助:
Peng-fei CAO1,2( ), Shui-ping WANG1(
), Shui-ping WANG1( ), Qiao-shen HUANG1, Shi-long ZHOU3, Zhuan LUO4, Ying REN3, Yong LIU2, Tie-jun LI2, Shao-xun TANG2,5(
), Qiao-shen HUANG1, Shi-long ZHOU3, Zhuan LUO4, Ying REN3, Yong LIU2, Tie-jun LI2, Shao-xun TANG2,5( )
)
Received:2024-10-28
Revised:2024-12-06
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Shui-ping WANG,Shao-xun TANG
摘要:
本试验旨在探究两种青贮饲料桑替代豆粕比例对湘东黑山羊血液生化指标、抗氧化指标、瘤胃发酵指标以及瘤胃细菌区系的影响。试验选取45只5~6月龄健康、体重相近[(18.2±1.6) kg]的湘东黑山羊公羊,随机分为3组,分别为对照组(CK组)、50%替代组(S1组)和100%替代组(S2组),预试期7 d,正试期55 d,每日晨饲前称取昨日剩料,每两周进行一次称重,在正试期54 d晨饲前对每头羊进行颈静脉采血,正试期54 d晨饲3 h后和55 d晨饲前采集口腔瘤胃液,用于测定血液指标、瘤胃发酵指标和瘤胃微生物组成。结果显示:S1和S2组的终末重(FBW)、平均日增重(ADG)和干物质采食量(DMI)均显著高于CK组(P<0.05);S2组的血清低密度脂蛋白(LDL-C)显著低于CK和S1组(P<0.05),血清白蛋白(ALB)和胆碱酯酶(CHE)显著高于CK组(P<0.05)。另外S1和S2组的血清总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)均显著高于CK组(P<0.05),但S2组的血清丙二醛(MDA)也显著高于CK组(P<0.05)。随着青贮饲料桑替代比例的增加,乙酸和异戊酸的摩尔比显著降低(P<0.05),丙酸和戊酸摩尔比随替代比例增加而上升。使用青贮饲料桑替代豆粕不会显著影响瘤胃微生物的Alpha多样性(P>0.05),3组优势菌门均为拟杆菌门和芽孢杆菌门,随青贮饲料桑替代比例的增加,芽孢杆菌门的丰度显著上升(P<0.05),拟杆菌门的丰度显著降低(P<0.05)。3组的优势菌属为Xylanibacter、丁酸弧菌、Segatella、解琥珀酸菌属、纤维杆菌属和Olivibacter。S2组的丁酸弧菌显著高于CK和S1组(P<0.05),Olivibacter显著低于CK和S1组(P<0.05)。上述研究结果表明:使用青贮饲料桑替代豆粕可以改善动物机体的代谢,增强抗氧化能力,且不会影响瘤胃微生物的Alpha多样性,在反刍动物养殖中有很好的应用前景。
操鹏飞, 汪水平, 黄桥深, 周世龙, 罗专, 任莹, 刘勇, 李铁军, 汤少勋. 青贮饲料桑替代豆粕对肉羊血液指标、瘤胃发酵及瘤胃菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 213-228.
Peng-fei CAO, Shui-ping WANG, Qiao-shen HUANG, Shi-long ZHOU, Zhuan LUO, Ying REN, Yong LIU, Tie-jun LI, Shao-xun TANG. Effects of substituting mulberry silage for soybean meal on blood indexes, rumen fermentation, and rumen bacteria of goats[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 213-228.
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment (干物质基础 Dry matter basis) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |
| 日粮组成Diet composition | |||
| 玉米Corn (g·kg -1) | 258.6 | 244.8 | 194.8 |
| 麦麸Wheat bran (g·kg -1) | 44.0 | 128.9 | 251.9 |
| 青贮饲料桑Mulberry silage (g·kg -1) | 0.0 | 268.0 | 500.0 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal (g·kg -1) | 147.0 | 73.5 | 0.0 |
| 稻草Straw (g·kg -1) | 500.0 | 232.0 | 0.0 |
| 碳酸钙CaCO3 (g·kg -1) | 7.0 | 3.5 | 1.3 |
| 磷酸氢钙CaHPO3 (g·kg -1) | 18.5 | 24.2 | 26.9 |
| 食盐NaCl (g·kg -1) | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| 1)预混料Permix (g·kg -1) | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 |
| 总计 Total (g·kg -1) | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 |
| 营养水平Nutritional levels | |||
| 2)代谢能 Metabolizable energy (ME, MJ·kg -1) | 8.68 | 8.75 | 8.70 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (CP, g·kg -1) | 116.0 | 116.0 | 116.0 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fibre (NDF, g·kg -1) | 415.8 | 380.4 | 356.5 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fibre (ADF, g·kg -1) | 267.5 | 253.7 | 243.9 |
| 钙 Ca (g·kg -1) | 10.0 | 14.0 | 17.2 |
| 磷 P (g·kg -1) | 6.4 | 9.0 | 11.0 |
| 钙磷比 Ca∶P | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.56 |
表1 试验日粮组成及营养水平
Table 1 Experimental diet composition and nutrition level
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment (干物质基础 Dry matter basis) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |
| 日粮组成Diet composition | |||
| 玉米Corn (g·kg -1) | 258.6 | 244.8 | 194.8 |
| 麦麸Wheat bran (g·kg -1) | 44.0 | 128.9 | 251.9 |
| 青贮饲料桑Mulberry silage (g·kg -1) | 0.0 | 268.0 | 500.0 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal (g·kg -1) | 147.0 | 73.5 | 0.0 |
| 稻草Straw (g·kg -1) | 500.0 | 232.0 | 0.0 |
| 碳酸钙CaCO3 (g·kg -1) | 7.0 | 3.5 | 1.3 |
| 磷酸氢钙CaHPO3 (g·kg -1) | 18.5 | 24.2 | 26.9 |
| 食盐NaCl (g·kg -1) | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| 1)预混料Permix (g·kg -1) | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 |
| 总计 Total (g·kg -1) | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 |
| 营养水平Nutritional levels | |||
| 2)代谢能 Metabolizable energy (ME, MJ·kg -1) | 8.68 | 8.75 | 8.70 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (CP, g·kg -1) | 116.0 | 116.0 | 116.0 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fibre (NDF, g·kg -1) | 415.8 | 380.4 | 356.5 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fibre (ADF, g·kg -1) | 267.5 | 253.7 | 243.9 |
| 钙 Ca (g·kg -1) | 10.0 | 14.0 | 17.2 |
| 磷 P (g·kg -1) | 6.4 | 9.0 | 11.0 |
| 钙磷比 Ca∶P | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.56 |
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |||
| 初始重 Initial body weight (IBW, kg) | 18.3 | 18.0 | 18.5 | 0.43 | 0.643 |
| 终末重 Final body weight (FBW, kg) | 21.2b | 22.4ab | 22.5a | 0.28 | 0.002 |
| 平均日增重 Average daily gain (ADG, g·d-1) | 45.8b | 65.3a | 67.7a | 4.36 | 0.002 |
| 干物质采食量 Dry matter intake (DMI, g·d-1) | 607.0c | 788.0b | 893.0a | 137.41 | 0.002 |
| 料重比 Feed/gain (F/G) | 15.7a | 12.5b | 14.3a | 0.80 | 0.040 |
表2 青贮饲料桑替代不同比例豆粕对湘东黑山羊生长性能的影响
Table 2 Effects of silage mulberry replacing soybean meal with different proportions on growth performance of Xiangdong black goats
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |||
| 初始重 Initial body weight (IBW, kg) | 18.3 | 18.0 | 18.5 | 0.43 | 0.643 |
| 终末重 Final body weight (FBW, kg) | 21.2b | 22.4ab | 22.5a | 0.28 | 0.002 |
| 平均日增重 Average daily gain (ADG, g·d-1) | 45.8b | 65.3a | 67.7a | 4.36 | 0.002 |
| 干物质采食量 Dry matter intake (DMI, g·d-1) | 607.0c | 788.0b | 893.0a | 137.41 | 0.002 |
| 料重比 Feed/gain (F/G) | 15.7a | 12.5b | 14.3a | 0.80 | 0.040 |
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |||
| 葡萄糖 Glucose (GLU, mmol·L-1) | 3.71 | 3.89 | 4.31 | 0.186 | 0.081 |
| 胆固醇 Cholesterol (CHOL, mmol·L-1) | 2.35 | 2.34 | 2.12 | 0.121 | 0.297 |
| 甘油三酯 Triacylglycerol (TG, mmol·L-1) | 0.527 | 0.502 | 0.593 | 0.043 | 0.307 |
| 低密度脂蛋白 Low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C, μmol·L-1) | 0.827a | 0.825a | 0.552b | 0.060 | 0.002 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 High density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C, μmol·L-1) | 1.48 | 1.52 | 1.51 | 0.082 | 0.919 |
| 脂肪酶 Lipase (LIP, U·L-1) | 16.0 | 14.6 | 16.4 | 0.843 | 0.280 |
| 总蛋白 Total protein (TP, g·L-1) | 89.6 | 90.8 | 91.1 | 3.052 | 0.936 |
| 白蛋白 Albumin (ALB, g·L-1) | 38.6b | 41.8ab | 44.1a | 1.261 | 0.012 |
| 血尿素氮 Blood urine nitrogen (BUN, mmol·L-1) | 7.42 | 7.42 | 8.00 | 0.225 | 0.488 |
| 血氨 Blood ammonia (BA, μmol·L-1) | 144.0a | 116.0b | 104.0b | 4.813 | 0.007 |
| 胆碱酯酶 Cholinesterase (CHE, U·L-1) | 186.0b | 200.0ab | 217.0a | 4.335 | 0.017 |
| 谷草转氨酶Aspartate transaminase (AST, U·L-1) | 96.4 | 118.3 | 108.1 | 10.715 | 0.362 |
| 谷丙转氨酶Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, U·L-1) | 28.5 | 28.5 | 28.7 | 1.320 | 0.992 |
表3 青贮饲料桑替代不同比例豆粕对湘东黑山羊血清生化指标的影响
Table 3 Effects of silage mulberry replacing soybean meal with different proportions on serum biochemical indexes of Xiangdong black goats
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |||
| 葡萄糖 Glucose (GLU, mmol·L-1) | 3.71 | 3.89 | 4.31 | 0.186 | 0.081 |
| 胆固醇 Cholesterol (CHOL, mmol·L-1) | 2.35 | 2.34 | 2.12 | 0.121 | 0.297 |
| 甘油三酯 Triacylglycerol (TG, mmol·L-1) | 0.527 | 0.502 | 0.593 | 0.043 | 0.307 |
| 低密度脂蛋白 Low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C, μmol·L-1) | 0.827a | 0.825a | 0.552b | 0.060 | 0.002 |
| 高密度脂蛋白 High density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C, μmol·L-1) | 1.48 | 1.52 | 1.51 | 0.082 | 0.919 |
| 脂肪酶 Lipase (LIP, U·L-1) | 16.0 | 14.6 | 16.4 | 0.843 | 0.280 |
| 总蛋白 Total protein (TP, g·L-1) | 89.6 | 90.8 | 91.1 | 3.052 | 0.936 |
| 白蛋白 Albumin (ALB, g·L-1) | 38.6b | 41.8ab | 44.1a | 1.261 | 0.012 |
| 血尿素氮 Blood urine nitrogen (BUN, mmol·L-1) | 7.42 | 7.42 | 8.00 | 0.225 | 0.488 |
| 血氨 Blood ammonia (BA, μmol·L-1) | 144.0a | 116.0b | 104.0b | 4.813 | 0.007 |
| 胆碱酯酶 Cholinesterase (CHE, U·L-1) | 186.0b | 200.0ab | 217.0a | 4.335 | 0.017 |
| 谷草转氨酶Aspartate transaminase (AST, U·L-1) | 96.4 | 118.3 | 108.1 | 10.715 | 0.362 |
| 谷丙转氨酶Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, U·L-1) | 28.5 | 28.5 | 28.7 | 1.320 | 0.992 |
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |||
| 总抗氧化能力 Total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC, μmol·mL-1) | 17.54b | 28.03a | 28.05a | 1.08 | <0.01 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase (SOD, U·mL-1) | 28.00 | 41.18 | 35.46 | 2.31 | 0.07 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde (MDA, nmol·mL-1) | 1.22b | 1.94ab | 2.56a | 0.22 | 0.03 |
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px, μg·mL-1) | 150.43 | 134.59 | 148.62 | 3.77 | 1.86 |
表4 青贮饲料桑替代不同比例豆粕对湘东黑山羊血清抗氧化指标的影响
Table 4 Effects of silage mulberry replacing soybean meal with different proportions on serum antioxidant indexes of Xiangdong black goats
项目 Items | 日粮处理 Diet treatment | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S1 | S2 | |||
| 总抗氧化能力 Total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC, μmol·mL-1) | 17.54b | 28.03a | 28.05a | 1.08 | <0.01 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase (SOD, U·mL-1) | 28.00 | 41.18 | 35.46 | 2.31 | 0.07 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde (MDA, nmol·mL-1) | 1.22b | 1.94ab | 2.56a | 0.22 | 0.03 |
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px, μg·mL-1) | 150.43 | 134.59 | 148.62 | 3.77 | 1.86 |
日粮处理 Diet treatment | 采集时间 Acquisition time | pH | 总挥发性脂肪酸 Total volatile fatty acid (TVFA, mmol·L-1) | 挥发性脂肪酸摩尔百分比 Molar percentage of volatile fatty acids (%) | 乙丙比 Acetate acid∶propionate acid (A∶P) | 氨态氮 NH3-N (mmol·L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
乙酸 Acetate acid | 丙酸 Propionate acid | 异丁酸 Isobutyrate acid | 丁酸 Butyrate acid | 异戊酸 Isovalerate acid | 戊酸 Valerate acid | ||||||
| CK | 0H | 7.58 | 34.0 | 66.4 | 16.1 | 2.28 | 11.4 | 2.94 | 0.89 | 4.18 | 9.59 |
| 3H | 6.88 | 56.5 | 65.5 | 17.7 | 1.23 | 12.8 | 1.61 | 1.18 | 3.72 | 10.72 | |
| S1 | 0H | 7.53 | 32.9 | 66.7 | 15.7 | 2.18 | 12.8 | 2.62 | 0.99 | 4.31 | 8.63 |
| 3H | 7.06 | 60.7 | 61.8 | 21.6 | 1.25 | 12.8 | 1.37 | 1.46 | 2.93 | 9.94 | |
| S2 | 0H | 7.63 | 32.9 | 68.2 | 13.8 | 1.93 | 12.9 | 2.18 | 0.92 | 5.00 | 5.94 |
| 3H | 6.88 | 63.2 | 56.9 | 26.3 | 0.92 | 12.9 | 1.37 | 1.63 | 2.19 | 12.01 | |
| 分析Analyse | 标准误 SEM | 0.038 | 2.000 | 0.492 | 0.543 | 0.068 | 0.221 | 0.081 | 0.040 | 0.114 | 0.325 |
| 主效应 Main effects | |||||||||||
| 日粮处理 Diet treatment | |||||||||||
| CK | 7.23 | 45.1 | 65.8A | 17.0B | 1.76A | 12.2 | 2.28A | 1.03B | 3.92 | 10.16 | |
| S1 | 7.30 | 46.8 | 64.2B | 18.2B | 1.78A | 12.6 | 2.04B | 1.20A | 3.71 | 9.22 | |
| S2 | 7.25 | 50.0 | 62.3C | 20.3A | 1.40B | 13.0 | 1.76C | 1.29A | 3.61 | 8.95 | |
| 采集时间 Acquisition time | |||||||||||
| 0H | 7.58A | 33.0B | 67. 0A | 15.1B | 2.17A | 12.25 | 2.62A | 0.90B | 4.53A | 8.04B | |
| 3H | 6.94B | 61.5A | 61.3B | 21.8A | 1.14B | 12.86 | 1.45B | 1.43A | 2.97B | 10.86A | |
P值 P-value | 日粮处理Diet treatment | 0.205 | 0.269 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.349 | <0.010 | 0.010 | 0.085 | 0.236 |
| 采集时间Acquisition time | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.183 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | |
| 日粮处理×采集时间Diet treatment×acquisition time | <0.010 | 0.155 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.877 | 0.458 | 0.007 | 0.017 | <0.010 | <0.010 | |
表5 不同青贮饲料桑替代比例的湘东黑山羊瘤胃发酵指标
Table 5 Rumen fermentation indexes of Xiangdong black goats with different silage mulberry replacement ratios
日粮处理 Diet treatment | 采集时间 Acquisition time | pH | 总挥发性脂肪酸 Total volatile fatty acid (TVFA, mmol·L-1) | 挥发性脂肪酸摩尔百分比 Molar percentage of volatile fatty acids (%) | 乙丙比 Acetate acid∶propionate acid (A∶P) | 氨态氮 NH3-N (mmol·L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
乙酸 Acetate acid | 丙酸 Propionate acid | 异丁酸 Isobutyrate acid | 丁酸 Butyrate acid | 异戊酸 Isovalerate acid | 戊酸 Valerate acid | ||||||
| CK | 0H | 7.58 | 34.0 | 66.4 | 16.1 | 2.28 | 11.4 | 2.94 | 0.89 | 4.18 | 9.59 |
| 3H | 6.88 | 56.5 | 65.5 | 17.7 | 1.23 | 12.8 | 1.61 | 1.18 | 3.72 | 10.72 | |
| S1 | 0H | 7.53 | 32.9 | 66.7 | 15.7 | 2.18 | 12.8 | 2.62 | 0.99 | 4.31 | 8.63 |
| 3H | 7.06 | 60.7 | 61.8 | 21.6 | 1.25 | 12.8 | 1.37 | 1.46 | 2.93 | 9.94 | |
| S2 | 0H | 7.63 | 32.9 | 68.2 | 13.8 | 1.93 | 12.9 | 2.18 | 0.92 | 5.00 | 5.94 |
| 3H | 6.88 | 63.2 | 56.9 | 26.3 | 0.92 | 12.9 | 1.37 | 1.63 | 2.19 | 12.01 | |
| 分析Analyse | 标准误 SEM | 0.038 | 2.000 | 0.492 | 0.543 | 0.068 | 0.221 | 0.081 | 0.040 | 0.114 | 0.325 |
| 主效应 Main effects | |||||||||||
| 日粮处理 Diet treatment | |||||||||||
| CK | 7.23 | 45.1 | 65.8A | 17.0B | 1.76A | 12.2 | 2.28A | 1.03B | 3.92 | 10.16 | |
| S1 | 7.30 | 46.8 | 64.2B | 18.2B | 1.78A | 12.6 | 2.04B | 1.20A | 3.71 | 9.22 | |
| S2 | 7.25 | 50.0 | 62.3C | 20.3A | 1.40B | 13.0 | 1.76C | 1.29A | 3.61 | 8.95 | |
| 采集时间 Acquisition time | |||||||||||
| 0H | 7.58A | 33.0B | 67. 0A | 15.1B | 2.17A | 12.25 | 2.62A | 0.90B | 4.53A | 8.04B | |
| 3H | 6.94B | 61.5A | 61.3B | 21.8A | 1.14B | 12.86 | 1.45B | 1.43A | 2.97B | 10.86A | |
P值 P-value | 日粮处理Diet treatment | 0.205 | 0.269 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.349 | <0.010 | 0.010 | 0.085 | 0.236 |
| 采集时间Acquisition time | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.183 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010 | |
| 日粮处理×采集时间Diet treatment×acquisition time | <0.010 | 0.155 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.877 | 0.458 | 0.007 | 0.017 | <0.010 | <0.010 | |
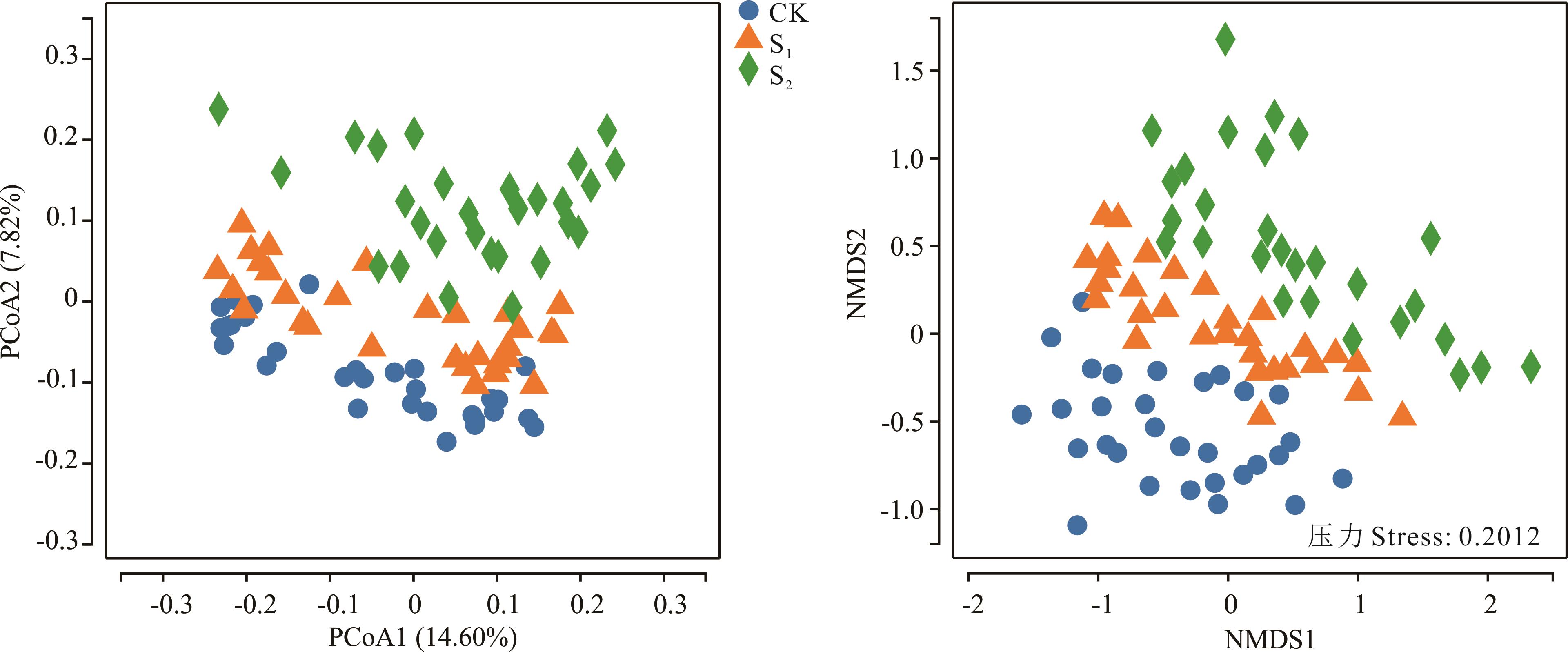
图2 瘤胃细菌菌群的主坐标分析(PCoA)和非度量多维排列(NMDS)分析
Fig.2 Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis of rumen bacterial flora
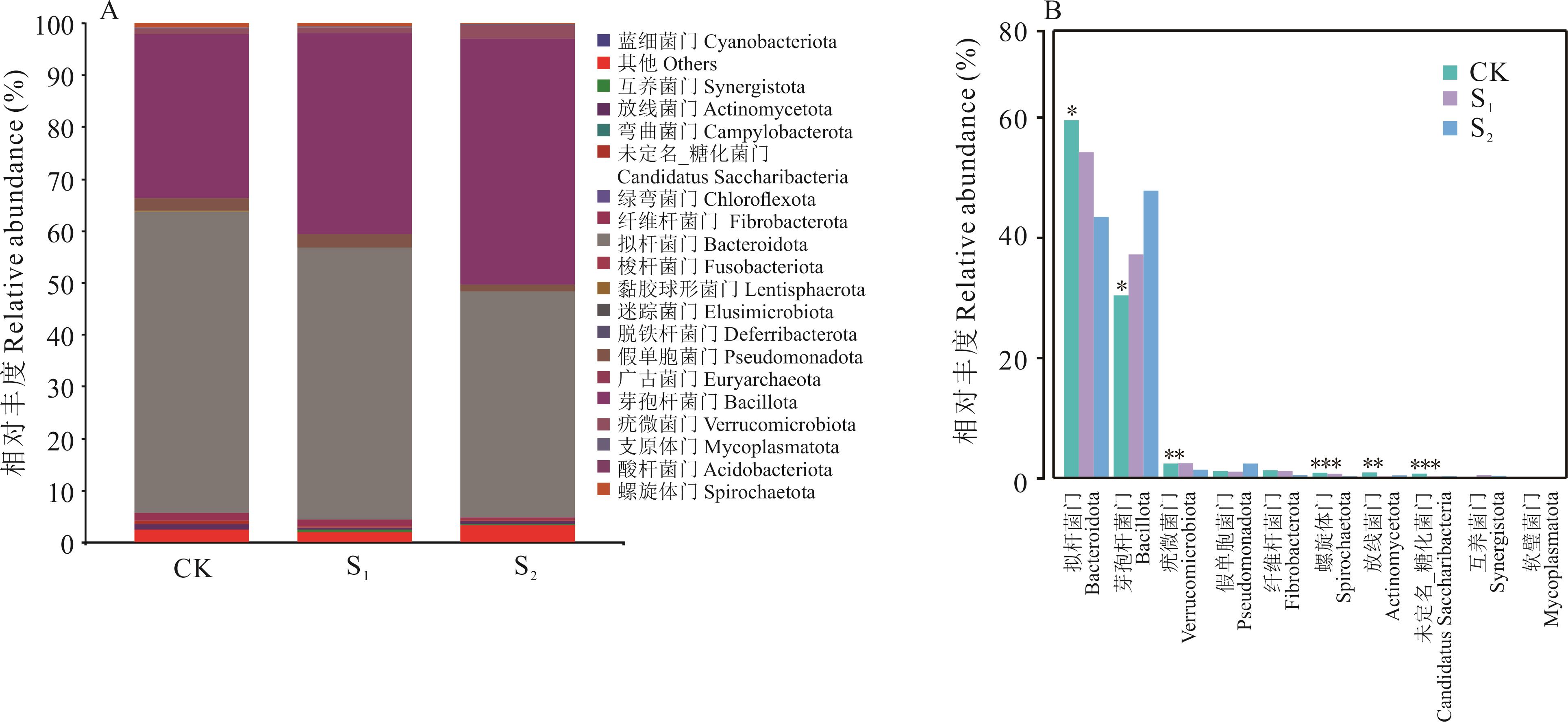
图4 门水平细菌组成及关键物种相对丰度差异图为丰度前10的物种,展示每组的平均相对丰度;***表示P≤0.001;**表示0.001<P≤0.01;*表示0.01<P≤0.05。下同。The figure shows the top ten species in abundance, showing the average relative abundance of each group; *** mean P≤0.001;** mean 0.001<P≤0.01;* mean 0.01<P≤0.05. The same below.
Fig.4 Phylum level bacterial composition and key species relative abundance difference

图6 瘤胃细菌KEGG功能注释A:KEGG通路1级;B:KEGG通路2级;C:KEGG通路3级。 A: KEGG pathway level 1; B: KEGG pathway level 2; C: KEGG pathway level 3.
Fig.6 KEGG function annotation of rumen bacteria
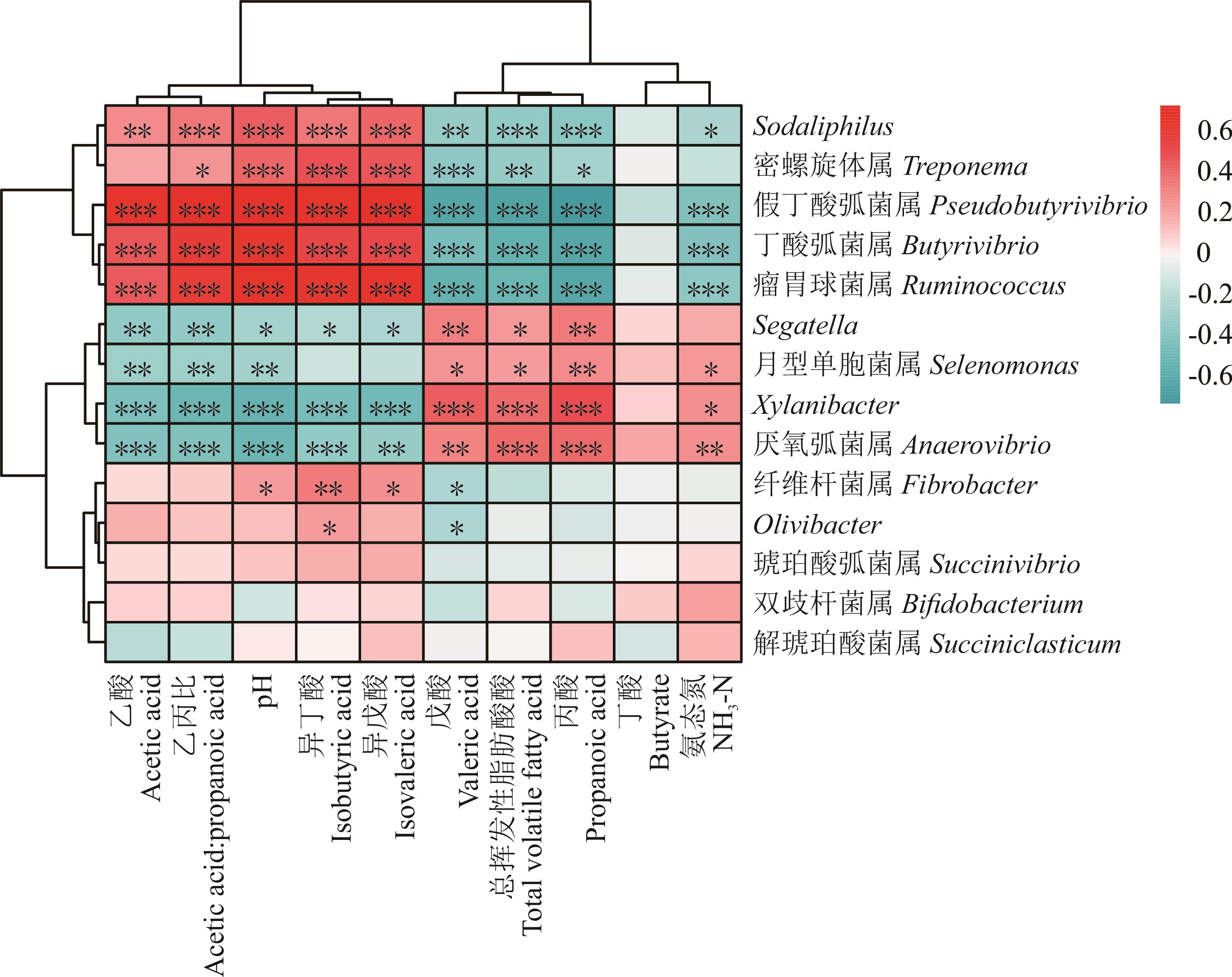
图7 瘤胃细菌与瘤胃发酵指标之间的相关性图中*表示具有显著相关性,其中**表示0.001<P≤0.01;*表示0.01<P≤0.05。In the figure, * represents a significant correlation, ** mean 0.001<P≤0.01;* mean 0.01<P≤0.05.
Fig.7 Correlation between rumen bacteria and rumen fermentation indexes
| [1] | National animal nutrition guidance committee. Work plan for reducing the use of corn and soybean meal in pig and chicken feed. http://www.moa.gov.cn/gk/nszd_1/2021/202104/t20210421_6366304.htm, 2021-04-21. |
| 全国动物营养指导委员会. 猪鸡饲料玉米豆粕减量替代工作方案. http://www.moa.gov.cn/gk/nszd_1/2021/202104/t20210421_6366304.htm, 2021-04-21. | |
| [2] | Wang Y C, Zhai S S, Li M M, et al. Analysis of nutritional components of mulberry twig leaves from different producing areas and the nutrient utilization efficiency in Sichuan while geese. China Feed, 2016(16): 18-22, 27. |
| 王永昌, 翟双双, 李孟孟, 等. 不同产地桑枝茎叶营养成分分析及四川白鹅对其养分利用率的测定. 中国饲料, 2016(16): 18-22, 27. | |
| [3] | Thaipitakwong T, Numhom S, Aramwit P. Mulberry leaves and their potential effects against cardiometabolic risks: a review of chemical compositions, biological properties and clinical efficacy. Pharmaceutical Biology, 2018, 56(1): 109-118. |
| [4] | Wang W Z. Nutritional characteristics and utilization status of forage mulberry. Feed China, 2017(12): 42-43. |
| 汪文忠. 饲料用桑的营养特性及其开发利用现状. 饲料广角, 2017(12): 42-43. | |
| [5] | Rodrigues E L, Marcelino G, Silva G T, et al. Nutraceutical and medicinal potential of the morus species in metabolic dysfunctions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(2): 301. |
| [6] | He X, Chen X, Ou X, et al. Evaluation of flavonoid and polyphenol constituents in mulberry leaves using HPLC fingerprint analysis. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2020, 55(2): 526-533. |
| [7] | Cui H, Lu T, Wang M, et al. Flavonoids from Morus alba L. leaves: Optimization of extraction by response surface methodology and comprehensive evaluation of their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and inhibition of α-amylase activities through analytical hierarchy process. Molecules, 2019, 24(13): 2398. |
| [8] | Wang H L, Zuo Y C, Zhou X K, et al.Influence of high planting density herbal cultivating on yield and quality of whole-plant mulberry (Morus alba). Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(5): 952-962. |
| 王红林, 左艳春, 周晓康, 等. 高密度草本化栽培对饲料桑全株产量及品质的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(5): 952-962. | |
| [9] | Li J M, Huang L, Zhu J N, et al. Preliminary study on mechanization mode of annual mulberry harvesting in Guangxi. Guangxi Agricultural Mechanization, 2018(6): 30-32. |
| 李建茂, 黄僚, 朱剑楠, 等. 广西全年条桑收获机械化模式初探. 广西农业机械化, 2018(6): 30-32. | |
| [10] | Xu Q B, Li Y P, Tang S W, et al. Preliminary report on research and development of 4QZ-2200S type feed mulberry harvesting machinery. North Sericulture, 2018, 39(4): 48-50. |
| 徐清波, 李一平, 唐守伟, 等. 4QZ-2200S型饲料桑收获机械研发初报. 北方蚕业, 2018, 39(4): 48-50. | |
| [11] | Huang J, Zhao N, Guo W Z, et al. Effects of feed mulberry on production performance, egg quality and intestinal tissue morphology of laying hens. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(2): 540-548. |
| 黄静, 赵娜, 郭万正, 等. 饲料桑对蛋鸡生产性能、蛋品质及肠道组织形态的影响. 中国畜牧兽医, 2024, 51(2): 540-548. | |
| [12] | Huang J P, Zhao W G, Yang Z J, et al. Effects of forage mulberry addition on performance, immune and antioxidant function and rumen microflora of perinatal holstein dairy cows. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(11): 7224-7234. |
| 黄军鹏, 赵卫国, 杨赵军, 等. 添加饲料桑对围产期奶牛生产性能、免疫和抗氧化功能及瘤胃微生物区系的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(11): 7224-7234. | |
| [13] | Fan Q W, Chen F, Du E C, et al. Effects of basal diet replaced by fermented feed mulberry with different proportions on rumen fermentation, rumen bacterial and fungal community structure of beef cattle. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2024, 36(4): 2475-2486. |
| 樊启文, 陈芳, 杜恩存, 等. 不同比例发酵饲料桑替代基础饲粮对肉牛瘤胃发酵、瘤胃细菌与真菌菌群结构的影响. 动物营养学报, 2024, 36(4): 2475-2486. | |
| [14] | Agricultural industry standards of the People’s Republic of China-feeding standard of meat-producing sheep and goats (NY/T816-2004). Hunan Feed, 2006(6): 9-15. |
| 中华人民共和国农业行业标准——肉羊饲养标准(NY/T816-2004). 湖南饲料, 2006(6): 9-15. | |
| [15] | Feng Z C, Gao M. Improvement of method for determination of ammonia nitrogen content in rumen fluid by colorimetric method. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2010, 31(Z1): 37. |
| 冯宗慈, 高民. 通过比色测定瘤胃液氨氮含量方法的改进. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2010, 31(Z1): 37. | |
| [16] | Hang Q. Effects of winter supplementary feeding of Leymus chinensis hay on fermentation performance and microbial diversity of rumen, liver metabolism for Hulunbuir ewes. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2023. |
| 黄棋. 冬季补饲羊草干草对呼伦贝尔母羊瘤胃发酵、微生物区系及肝脏代谢的影响. 重庆: 西南大学, 2023. | |
| [17] | Cai M. Study on evaluation of safety and feeding value of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves as animal feed. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 蔡明. 桑叶作为动物饲料的安全性及饲用价值评价研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| [18] | Dong Z, Wang S, Zhao J, et al. Effects of additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and aerobic stability of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves silage. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2019, 33(8): 1292-1300. |
| [19] | Ouyang Z L. Study on fattening test of mulberry leaf powder on binary hybrid pigs. Livestock and Poultry Industry, 2023, 34(10): 8-11. |
| 欧阳增理. 桑叶粉对二元杂交猪的育肥试验研究. 畜禽业, 2023, 34(10): 8-11. | |
| [20] | Li X, Ye T M, Liu G, et al. Effects of adding mulberry leaf powder into TMR granulated diets on growth performance, slaughter performance and economic benefits of Liuyang black goats. China Feed, 2023(11): 146-151. |
| 李霞, 叶添梅, 刘耕, 等. TMR颗粒饲粮中桑叶粉比例对浏阳黑山羊生长性能、屠宰性能及经济效益的影响. 中国饲料, 2023(11): 146-151. | |
| [21] | Kou Y F. Nutrition dynamics of mulberry and its effect on production performance of fattening Hu sheep. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 寇宇斐. 饲料桑的营养动态及其对育肥湖羊生产性能的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| [22] | Luo Y, Yi K L, He F, et al. Effects of different adding proportions of fermented mulberry leaves on growth performance, serum indexes, muscle amino acid and fatty acid contents of Xiangdong Black Goats. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(12): 7923-7934. |
| 罗阳, 易康乐, 何芳, 等. 不同添加比例发酵桑叶饲粮对湘东黑山羊生长性能、血清指标及肌肉氨基酸、脂肪酸含量的影响. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(12): 7923-7934. | |
| [23] | Luo Y. Associative effects of mulberry leaves with Leymus chinensis and affects on rumen fermentation, growth performance, fat deposition in sheep fed with the combined forage diet. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2019. |
| 罗阳. 桑树叶与羊草的组合效应及其对绵羊瘤胃发酵、生长性能、脂肪沉积和肉品质的影响. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2019. | |
| [24] | Ouyang J, Hou Q, Wang M, et al. Effects of dietary mulberry leaf powder on growth performance, blood metabolites, meat quality, and antioxidant enzyme-related gene expression of fattening Hu lambs. Canadian Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 100(3): 510-521. |
| [25] | Zhou G L, Tao Y, Ni L G, et al. Serum biochemistry and expression of carcass trait-related gene of Sujiang pigs as affected by dietary makeup at final growth stage. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(6): 668-677. |
| 周根来, 陶勇, 倪黎纲, 等. 日粮营养水平对育肥苏姜猪血清生化指标和肉质相关基因的影响. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(6): 668-677. | |
| [26] | Xu X D. Effect of mulberry leaf on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes and economic benefits of finishing pigs. Feed Research, 2023, 46(2): 46-50. |
| 许新迪. 蛋白桑对育肥猪生长性能、血清生化指标及养殖经济效益的影响. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(2): 46-50. | |
| [27] | Zhang S W, Wang X P, Zhang Z H, et al. Effects of Broussonetia papyrifera silage on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes and meat quality of Dorper×Hu crossbred sheep. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. |
| 张生伟, 王小平, 张展海, 等. 青贮杂交构树对杜湖杂交肉羊生长性能、血清生化指标和肉品质的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. | |
| [28] | Yin L. Effects of gallnut tannic acid on the growth performance, meat quality, blood biochemistry and rumen fermentation of Liuyang black goat. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 殷磊. 五倍子单宁酸对浏阳黑山羊生长性能、肉品质、血液生化及瘤胃发酵的影响. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2024. | |
| [29] | Yan J S, Huan H L, Zhou W R, et al. Effect of biologics on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters and endocrine hormone in late fattening pigs of microbial fermentation bed system. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2014, 41(12): 126-130. |
| 闫俊书, 宦海琳, 周维仁, 等. 日粮中添加生物制剂对发酵床育肥后期猪生长性能、血清生化指标及内分泌激素的影响. 中国畜牧兽医, 2014, 41(12): 126-130. | |
| [30] | Wan R, Liu M G, Liang Q B, et al. Effects of fermented mulberry leaves on growth performance and serum biochemical, antioxidant and immune indexes of Holstein calves. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(6): 3754-3760. |
| 万荣, 刘明革, 梁奇兵, 等. 发酵桑叶对荷斯坦犊牛生长性能及血清生化、抗氧化和免疫指标的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(6): 3754-3760. | |
| [31] | Lu D X, Xie C W. Modern ruminant nutrition research methods and techniques. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1991. |
| 卢德勋, 谢崇文. 现代反刍动物营养研究方法和技术. 北京: 农业出版社, 1991. | |
| [32] | Zhou Z, Zhou B, Ren L, et al. Effect of ensiled mulberry leaves and sun-dried mulberry fruit pomace on finishing steer growth performance, blood biochemical parameters, and carcass characteristics. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e85406. |
| [33] | Huang W Q, Lv X K, Wang S Q, et al. Effects of whole sugarcane on growth performance, nutrient apparent digestibility, serum indexes and rumen fermentation indexes of goats. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(12): 5182-5191. |
| 黄文琴, 吕小康, 王世琴, 等. 全株甘蔗对山羊生长性能、营养物质表观消化率、血清指标及瘤胃发酵参数的影响. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(12): 5182-5191. | |
| [34] | Aschenbach J R, Kristensen N B, Donkin S S, et al. Gluconeogenesis in dairy cows: The secret of making sweet milk from sour dough. Iubmb Life, 2010, 62(12): 869-877. |
| [35] | Mizrahi I, Wallace R J, Morais S. The rumen microbiome: balancing food security and environmental impacts. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 19(9): 553-566. |
| [36] | Deusch S, Camarinha-silva A, Conrad J, et al. A structural and functional elucidation of the rumen microbiome influenced by various diets and microenvironments. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8(1): 1605. |
| [37] | Liu C, Wu H, Liu S, et al. Dynamic alterations in yak rumen bacteria community and metabolome characteristics in response to feed type. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10(1): 1116. |
| [38] | Snelling T J, Wallace R J. The rumen microbial metaproteome as revealed by SDS-PAGE. BMC Microbiology, 2017, 17(1): 9. |
| [39] | Hart E H, Creevey C J, Hitch T, et al. Meta-proteomics of rumen microbiota indicates niche compartmentalisation and functional dominance in a limited number of metabolic pathways between abundant bacteria. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 10504. |
| [40] | Golder H M, Denman S E, Mcsweeney C, et al. Effects of partial mixed rations and supplement amounts on milk production and composition, ruminal fermentation, bacterial communities, and ruminal acidosis. Journal of Dairy Science, 2014, 97(9): 5763-5785. |
| [41] | Murovec U, Accetto T. Transcriptomic analysis of polysaccharide utilization loci reveals substrate preferences in ruminal generalists Segatella bryantii TF1-3 and Xylanibacter ruminicola KHP1. BMC Genomics, 2024, 25(1): 495. |
| [42] | Accetto T, Avgustin G. Non-oral prevotella stepping into the spotlight. Anaerobe, 2021, 68(1): 102321. |
| [43] | Niu W J. Effects of whole wheat on nutrient digestion, rumen fermentation and microflora of Holstein bulls. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 牛文静. 全株小麦对荷斯坦公牛养分消化、瘤胃发酵及微生物的影响. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. |
| [1] | 王红林, 文斌, 左艳春, 张凯, 吴子周, 严旭, 袁正才, 邓榆川, 肖蔹, 陈慧, 寇晶, 傅祥超, 杜周和. 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔肠道形态、血液生化指标、肌肉中氨基酸含量及经济效益的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 199-210. |
| [2] | 祁帅, 张艳丽, 万永杰, 牛伟强, 张积鑫, 高雪, 茆达干. 菌酶协同发酵豆秸对湖羊生长性能、血清指标和瘤胃微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 189-201. |
| [3] | 占今舜, 江浩筠, 王海波, 贾浩滨, 潘月, 钟小军, 霍俊宏. 羔羊断奶前后血清生化指标、抗氧化和免疫性能的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 202-211. |
| [4] | 韩航琪, 王梓凡, 丁赫, 陈玉荣, 王琦, 张晓庆. 燕麦干草与燕麦草块对绵羊瘤胃发酵及微生物组成影响的比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 212-222. |
| [5] | 杨攀平, 李惠侠, 胡亚美. 盐池滩羊肉品质特性及其潜在调控机理探讨[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 223-232. |
| [6] | 顾明明, 姜幸慧, 马志毅, 邱水玲, 刘浩宇, 张洺瑞, 卢佳宁, 丘宇俊, 王本治, 甘乾福. 甘薯和芋头在闽东山羊瘤胃中的降解特性及表面附着微生物群落变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 169-184. |
| [7] | 洪莉平, 李小冬, 于二汝, 裴成江, 尚以顺, 骆金红, 孙光, 周云昊, 李世歌, 杨航, 刘凤丹. 不同紫苏原料对贵州黑山羊血清抗氧化酶活性、瘤胃发酵参数、瘤胃微生物区系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 214-226. |
| [8] | 杨尚霖, 吴璇, 罗巧慧, 黄太华, 张正帆, 史海涛, 郭春华. 20~35 kg川中黑山羊蛋白质需要量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 119-129. |
| [9] | 申迪, 曾子铭, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 廖扬, 王迅, 黄伟华, 刘书杰, 杨英魁, 王书祥. 低精料日粮和高精料日粮对牦牛生长性能和瘤胃菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 155-165. |
| [10] | 赵洁, 陈恒光, 裴晓蒙, 于昊, 徐银莹, 茆达干. 围产期日粮添加白藜芦醇对山羊生产性能、血液指标及炎症因子基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 210-220. |
| [11] | 陈悦, 宋品, 侯曼曼, 杨笑然, 刘丽萍, 倪迎冬. 饲喂胆汁酸对亚急性瘤胃酸中毒山羊回肠黏膜形态、菌群组成和IFN-γ mRNA相对表达量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 188-200. |
| [12] | 覃娟清, 党浩千, 金华云, 郭宇康, 张富, 刘庆华. 不同添加剂处理笋壳对其发酵品质及湖羊瘤胃微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 155-167. |
| [13] | 周承福, 汪水平, 张佰忠, 张秀敏, 王荣, 马志远, 王敏. 水热处理对黄豆秸秆体外发酵、甲烷生成及微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 171-181. |
| [14] | 穆海婷, 王英哲, 苗一凡, 郁伟杰, 徐博. 重金属铜和铅胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 139-146. |
| [15] | 郭艳霞, 李孟伟, 唐振华, 彭丽娟, 彭开屏, 谢芳, 谢华德, 杨承剑. 添加亚油酸条件下不同剂量硝酸钠对水牛瘤胃体外发酵脂肪酸组成及相关微生物数量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 159-167. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||