

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 184-194.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024501
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
孙诗炫1( ), 王群森1, 杨志民1, 范宁丽1, 郝田1, 刘南清2, 于景金1(
), 王群森1, 杨志民1, 范宁丽1, 郝田1, 刘南清2, 于景金1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-23
修回日期:2025-03-10
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-10-09
通讯作者:
于景金
作者简介:E-mail: jingjin_yu@126.com基金资助:
Shi-xuan SUN1( ), Qun-sen WANG1, Zhi-min YANG1, Ning-li FAN1, Tian HAO1, Nan-qing LIU2, Jing-jin YU1(
), Qun-sen WANG1, Zhi-min YANG1, Ning-li FAN1, Tian HAO1, Nan-qing LIU2, Jing-jin YU1( )
)
Received:2024-12-23
Revised:2025-03-10
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-10-09
Contact:
Jing-jin YU
摘要:
选育能够耐受夏季高温高湿的苇状羊茅是气候过渡带地区延长牧草青绿期、满足草牧业可持续发展的重要途径之一。本研究以前期通过杂交育种自主培育的3份多分蘖牧草型苇状羊茅新品种“南牧1号”“南牧2号”“南牧3号”为试验材料,以生产上广泛使用的商业品种飞度(Fit)为对照,利用人工气候室开展环境因素控制试验模拟热胁迫,探究热胁迫(38 ℃/33 ℃,日/夜)及热后恢复条件下各份材料的生理、生长及营养成分的变化。结果表明,热胁迫使4份材料的电解质渗漏率(EL)上升,叶片相对含水量(RWC)、叶绿素含量(Chl)、净光合速率(Pn)下降,但3个新品种相比于对照品种均显著抑制了EL的上升及RWC、Chl和Pn的下降,说明新品种的耐热能力优于对照品种,且同时具有较好的热后恢复能力。在产量和品质方面,3个新品种的分蘖多、叶量丰富、茎叶比低、适口性好、粗蛋白含量高、品质佳,其中“南牧2号”品质最优。综上可知,3个新品种均是耐热、分蘖多、叶量丰富的高产优质牧草,能够在江苏等气候过渡带地区种植栽培。
孙诗炫, 王群森, 杨志民, 范宁丽, 郝田, 刘南清, 于景金. 自主选育苇状羊茅新品种耐热及热后恢复能力评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 184-194.
Shi-xuan SUN, Qun-sen WANG, Zhi-min YANG, Ning-li FAN, Tian HAO, Nan-qing LIU, Jing-jin YU. Evaluation of heat tolerance and post-heat recovery capacity of new varieties of tall fescue[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(11): 184-194.
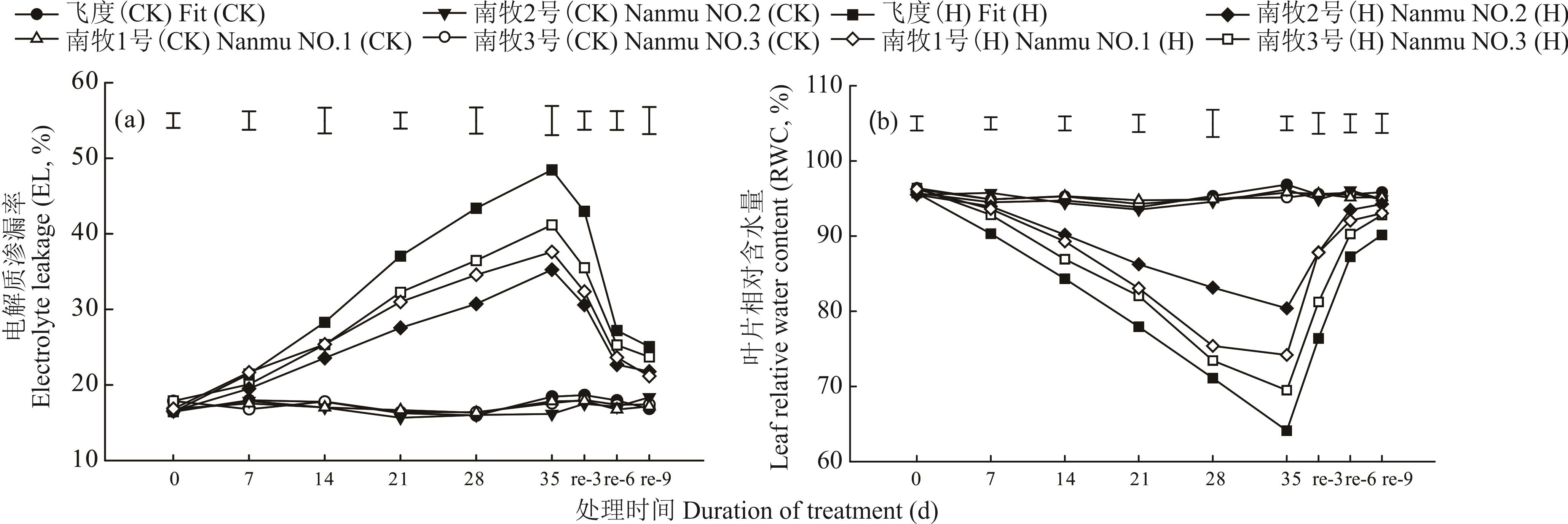
图1 热胁迫及热后恢复对苇状羊茅电解质渗漏率和相对含水量的影响飞度(CK)、南牧1号(CK)、南牧2号(CK)、南牧3号(CK)表示对照温度组(25 ℃/20 ℃),飞度(H)、南牧1号(H)、南牧2号(H)、南牧3号(H)表示热胁迫处理组(38 ℃/33 ℃),re-3、re-6、re-9表示热后恢复天数,竖线代表不同处理间的最小差异(P<0.05),下同。Fit (CK), Nanmu NO.1 (CK), Nanmu NO.2 (CK), and Nanmu NO.3 (CK) represent the control groups (25 ℃/20 ℃); Fit (H), Nanmu NO.1 (H), Nanmu NO.2 (H), and Nanmu NO.3 (H) represent the treated groups (38 ℃/33 ℃); re-3, re-6 and re-9 indicate 3, 6, and 9 days of post-heat recovery, respectively. Vertical bars means the least significant difference (LSD) among treatments (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of heat stress and post-heat recovery on electrolyte leakage and leaf relative water content in tall fescue
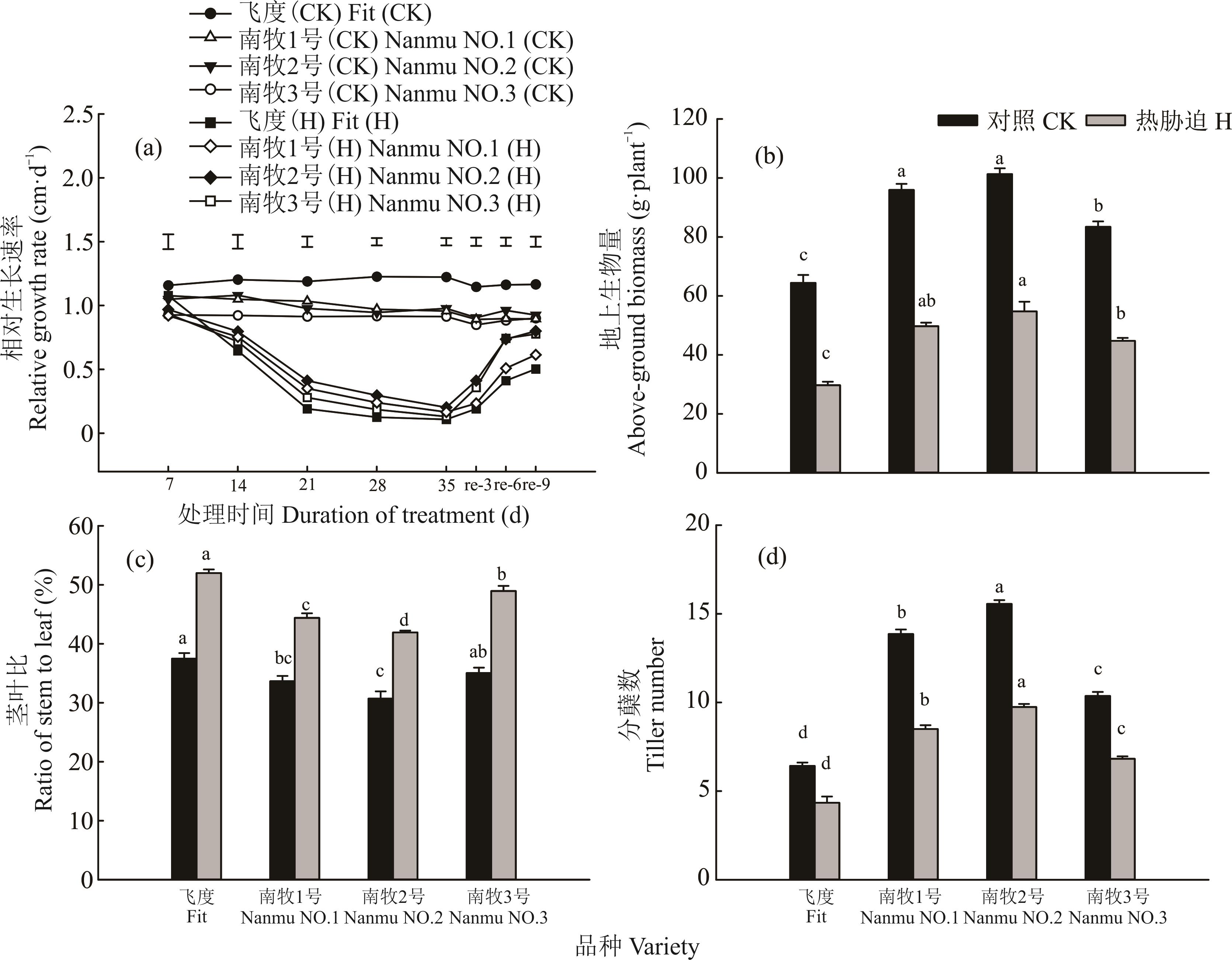
图3 热胁迫及热后恢复对苇状羊茅生长的影响不同小写字母代表不同品种间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different varieties (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.3 Effects of heat stress and post-heat recovery on plant growth in tall fescue
| [1] | Li S S, Lu J Y, Yan J P, et al. Spatiotemporal variability of temperature in northern and southern Qinling Mountains and its influence on climatic boundary. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(1): 13-24. |
| 李双双, 芦佳玉, 延军平, 等. 1970-2015年秦岭南北气温时空变化及其气候分界意义. 地理学报, 2018, 73(1): 13-24. | |
| [2] | Liu D L, Wang X P, Hu K Q, et al. Adaptability evaluation of cool-season turf grasses in Yangzhou. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(5): 967-971. |
| 刘大林, 王秀萍, 胡楷崎, 等. 15种冷季型草坪草在扬州地区的适应性评价. 草地学报, 2012, 20(5): 967-971. | |
| [3] | Ye Z W, Ji X, Liu Y X. Temporal change of air temperature in a typical north-south transitional climatic zone-a case study in Huaihe river basin. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2018, 39(3): 122-131. |
| 叶正伟, 纪旭, 刘育秀. 典型南北气候过渡带地区气温的时间变化特征—以淮河流域为例. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(3): 122-131. | |
| [4] | Young C A, Hume D E, Mcculley R L. Forages and pastures symposium: Fungal endophytes of tall fescue and perennial ryegrass: pasture friend or foe? Journal of Animal Science, 2013, 91(5): 2379-2394. |
| [5] | Xie X H, Ma Z J. Research on adaptability of the cool season turfgrasses in transitional climatic zone. Grassland of China, 2000(5): 56-59. |
| 谢晓鸿, 马子骏. 冷季型草坪草在过渡气候带的适应性研究. 中国草地, 2000(5): 56-59. | |
| [6] | Wang M T, Zhao Y H, Fang J P, et al. Evaluation of production performance and nutritional quality of two gramineae grasses in Linzhi City, Tibet. Feed Research, 2022, 45(1): 113-117. |
| 王明涛, 赵玉红, 方江平, 等. 西藏林芝2种禾草生产性能和营养品质评价. 饲料研究, 2022, 45(1): 113-117. | |
| [7] | Sun J X. Introduction test of nine American forage species in the eastern section of Gansu Hexi Corridor. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 1995, 30(4): 312-315. |
| 孙吉雄. 美国九种饲草在甘肃河西走廊东段的引种试验. 甘肃农业大学学报, 1995, 30(4): 312-315. | |
| [8] | Li Z H, Liu Y X, Wang H S. Study on the growth characteristics and quality of hybrid progeny between multiflora ryegrass×reedy fescue. Pratacultural Science, 1999, 16(4): 22-24. |
| 李志华, 刘亚雄, 王槐三. 多花黑麦草×苇状羊茅属间杂交后代生长特性及品质的研究. 草业科学, 1999, 16(4): 22-24. | |
| [9] | Wu J H, Mu Q, Tang C B, et al. Breeding of Qiancao 1, a new Festuca arundinacea variety. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 34(4): 75-79. |
| 吴佳海, 牟琼, 唐成斌, 等. 牧草新品种黔草1号高羊茅的选育. 贵州农业科学, 2006, 34(4): 75-79. | |
| [10] | Wang Y F, Li W, Han Y S, et al. Evaluation on nutritional value of six forages and straws. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2023, 103(12): 65-68. |
| 王艳菲, 李伟, 韩永胜, 等. 6种禾本科牧草及秸秆的营养品质评价. 现代畜牧科技, 2023, 103(12): 65-68. | |
| [11] | Cao Y H, Yang F, Chen S M, et al. Nutritional value analysis of seven common forage plants in southern China. China Feed, 2020(17): 117-121. |
| 曹艳红, 杨帆, 陈少梅, 等. 南方七种常见饲用植物营养价值分析. 中国饲料, 2020(17): 117-121. | |
| [12] | Yu J J, Du H M, Xu M, et al. Metabolic responses to heat stress under elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration in a cool-season grass species. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 2012, 137(4): 221-228. |
| [13] | Yu J J, Yang Z M, Jespersen D, et al. Photosynthesis and protein metabolism associated with elevated CO2 mitigation of heat stress damages in tall fescue. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2014, 99: 75-85. |
| [14] | Yu J J, Chen L H, Xu M, et al. Effects of elevated CO2 on physiological responses of tall fescue to elevated temperature, drought stress, and the combined stresses. Crop Science, 2012, 52(4): 1848-1858. |
| [15] | Yun X J, Yuan Q H, Su J K, et al. Code of practice for herbage variety registration: GB/T 30395-2013. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2014. |
| 贠旭疆, 袁庆华, 苏加楷, 等. 草品种审定技术规程: GB/T 30395-2013. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. | |
| [16] | Zhang L Y. Feed analysis and feed quality testing technology. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2007. |
| 张丽英. 饲料分析及饲料质量检测技术. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2007. | |
| [17] | Liang Y L, Xiang Q H, Zhang D H. The influence of illumination intensity and temperature on tillering of Festuca rubra L. Pennlawn. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 1999(2): 32-34. |
| 梁应林, 向清华, 张定红. 光照强度和温度对紫羊茅分蘖的影响. 四川草原, 1999(2): 32-34. | |
| [18] | Yang Y W, Liu D L, Wang L. Research progress on the effects of high temperature stress on Festuca arundinacea. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2022(1): 15-22. |
| 杨雨薇, 刘大林, 王琳. 高羊茅对高温胁迫应答机制的研究进展. 草学, 2022(1): 15-22. | |
| [19] | Ran M L, Song M, Song H, et al. Study on the identification technique system of heat tolerance for radish. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(11): 248-252. |
| 冉茂林, 宋明, 宋华, 等. 萝卜耐热性鉴定技术体系研究. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(11): 248-252. | |
| [20] | Wang Q, Wang K, Yu J J, et al. Effects of LBD on improving heat tolerance in creeping bentgrass. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(6): 1066-1073. |
| 王茜, 王恺, 于景金, 等. 绿比多对匍匐剪股颖耐热性的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(6): 1066-1073. | |
| [21] | Chu M, Zhuang Z Q, Wang X F, et al. Physiological responses of radish seedlings with different heat tolerance to high temperature stress. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University, 2014, 45(3): 334-339. |
| 初敏, 庄志群, 王秀峰, 等. 不同耐热性萝卜幼苗对高温胁迫的生理响应. 山东农业大学学报, 2014, 45(3): 334-339. | |
| [22] | Jia K Z, Chen G L. Tolerance of different eggplant varieties at seedling stage to high temperature stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(4): 398-401. |
| 贾开志, 陈贵林. 高温胁迫下不同茄子品种幼苗耐热性研究. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(4): 398-401. | |
| [23] | Liu Q, Sun H, He D W. Plant responses to the high temperature and moisture stress. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2005, 26(4): 364-368. |
| 刘琴, 孙辉, 何道文. 干旱和高温对植物胁迫效应的研究进展. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 26(4): 364-368. | |
| [24] | Ji P, Liu J W, Wang X T, et al. Response of leaf physiological characteristics of different rice varieties to heat stress at seedling stage. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 36-48. |
| 季平, 刘经威, 王欣婷, 等. 不同水稻品种苗期叶片生理特性对高温胁迫的响应. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(1): 36-48. | |
| [25] | Yan L, Li X T, Chao Y. Study advance on inheritance and breeding in tall fescue. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014(11): 275-276. |
| 颜兰, 李选统, 晁赢. 高羊茅遗传育种研究进展. 现代农业科技, 2014(11): 275-276. | |
| [26] | Gao G L, Feng Q, Zhang X Y, et al. An overview of stomatal and non-stomatal limitations to photosynthesis of plants. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(4): 929-937. |
| 高冠龙, 冯起, 张小由, 等. 植物叶片光合作用的气孔与非气孔限制研究综述. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(4): 929-937. | |
| [27] | Zhao Z J, Hu L X, Hu T, et al. Differential metabolic responses of two tall fescue genotypes to heat stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(3): 58-69. |
| 赵状军, 胡龙兴, 胡涛, 等. 不同品系高羊茅应答高温胁迫的初级代谢产物分析. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 58-69. | |
| [28] | Chen H Y, Ma S X, Guo P H. Research progress of high temperature stress on physiological characteristics of plants. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 27(5): 11-13. |
| 陈慧颖, 马石霞, 郭鹏辉. 热胁迫对植物生理影响的研究进展. 安徽农学通报, 2021, 27(5): 11-13. | |
| [29] | Lensch M, Herrmann R G, Sokolenko A. Identification and characterization of SppA, a novel light inducible chloroplast protease complex associated with thylakoid membranes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(36): 33645-33651. |
| [30] | Wang X T, Liu X N, Tang J W, et al. Comparison of yield and nutritional quality of 4 graminaceous forages on plateau under arid environment. Grassland and Turf, 2022, 42(1): 57-61, 68. |
| 王晓彤, 柳小妮, 唐俊伟, 等. 干旱环境下4种高原禾本科牧草产量及营养品质比较. 草原与草坪, 2022, 42(1): 57-61, 68. | |
| [31] | Chen Y, Wang Q, Chen X, et al. Effects of nitrogen deficiency stress on physiological characteristics of Festuca arundinacea at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(2): 9-15. |
| 陈莹, 王茜, 陈锡, 等. 低氮胁迫对高羊茅苗期生理特性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(2): 9-15. | |
| [32] | Sun X X, Peng J, Jiang Y F, et al. Nutritional value and molecular structure characteristics in different parts of Festuca sinensis from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(3): 1850-1862. |
| 孙晓旭, 彭婧, 江雨霏, 等. 青藏高原中华羊茅不同部位的营养价值及分子结构特性研究. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(3): 1850-1862. | |
| [33] | Li J Q, Wang L H, Zhan Q W, et al. The correlation study of SPAD value, chlorophyll content and crude protein content in two varieties of Lolium perenne. Pratacultural Science, 2010, 27(10): 39-42. |
| 李杰勤, 王丽华, 詹秋文, 等. 2个黑麦草品种SPAD值和叶绿素及粗蛋白含量的相关性研究. 草业科学, 2010, 27(10): 39-42. | |
| [34] | Wang H L, Zhang Y K, Zhao C C, et al. Effects of nitrogen levels on photosynthetic physiology and feeding quality of bermudagrass. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(3): 514-522. |
| 王宏力, 张寅坤, 赵春程, 等. 氮素水平对狗牙根光合生理及饲用品质的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(3): 514-522. | |
| [35] | Wang M T, Zhao Y H, Miao Y J, et al. Study on forage quality of mixed planting Medicago sativa L. and Festuca elata Keng ex E. Alexeev in Nyingchi Valley, Tibet. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(6): 1590-1596. |
| 王明涛, 赵玉红, 苗彦军, 等. 西藏林芝河谷地带紫花苜蓿和高羊茅混播牧草品质研究. 草地学报, 2022, 30(6): 1590-1596. | |
| [36] | Zhang X Q, Jin Y M, Tian J C, et al. Seasonal changes of nutrient content and in vitro digestibility of five grass species in Tibetan alpine grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(1): 71-77. |
| 张晓庆, 金艳梅, 田峻成, 等. 西藏高寒草原5种牧草养分含量及体外消化率季节变化. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(1): 71-77. |
| [1] | 邓清源, 付东青, 黄嵘峥, 张凡凡, 孙国君. 松针精油对构树青贮品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 85-94. |
| [2] | 张睿, 韩重阳, 蔡家邦, 汪阳, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 聂刚. 6个苇状羊茅(型)品种在成都平原区的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 138-148. |
| [3] | 李文龙, 李峰, 张仲鹃, 王殿清, 王欢, 靳慧卿, 特木热, 胡志玲, 陶雅. 鄂尔多斯高原北部一年两季燕麦种植模式生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 159-168. |
| [4] | 张适阳, 刘凤民, 崔均涛, 何磊, 冯月燕, 张伟丽. 三种外源物质对低温胁迫下柱花草生理与荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 85-99. |
| [5] | 纪童, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波. 7种禾本科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 144-156. |
| [6] | 游永亮, 赵海明, 李源, 武瑞鑫, 刘贵波, 周健东, 陈俊峰. 饲用麦类作物的生物量积累和营养品质动态变化规律[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 189-201. |
| [7] | 赵娟娟, 车大璐, 郭玮婷, 张伟涛, 刘连超, 赵俐辰, 高玉红, 孙新胜, 李雪梅, 王媛. 复方中药对热应激条件下杂交小尾寒羊生产性能、生理参数和血液理化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 178-189. |
| [8] | 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 刘敏洁. 老芒麦离区形态特征及生理特性差异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 81-92. |
| [9] | 王继卿, 沈继源, 刘秀, 李少斌, 罗玉柱, 赵孟丽, 郝志云, 柯娜, 宋宜泽, 乔莉蓉. 子午岭黑山羊与辽宁绒山羊产肉性能、肉品质、肌肉营养成分和脂肪酸含量比较[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 166-177. |
| [10] | 刘桃桃, 王思伟, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 王昆, 王丽娟, 沈宜钊, 孙雪丽, 张美琦, 闫金玲, 李建国, 高艳霞, 王美美. 利用尼龙袋法比较3个全株玉米品种青贮前后肉牛瘤胃降解特性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 159-169. |
| [11] | 别尔达吾列提·希哈依, 董乙强, 安沙舟, 魏鹏. 短期封育对白梭梭荒漠和盐生假木贼荒漠土壤营养成分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 56-62. |
| [12] | 张宇君, 尚以顺, 王普昶, 丁磊磊, 张文, 邹超. 干旱胁迫下保水剂对盘江白刺花幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 90-98. |
| [13] | 张强, 达娃央拉, 姬秋梅, 信金伟, 张成福, 朱勇, 洛桑顿珠, 次旦央吉, 孙光明, 姜辉. 西藏查吾拉地区不同性别牦牛产肉性能和肉营养成分的比较[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 193-198. |
| [14] | 杨宁, 马绍英, 马蕾, 张旭辉, 王娜, 李胜, 柴强. 重茬豌豆幼苗对接种复合根瘤菌的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 144-152. |
| [15] | 赵娜, 杨雪海, 魏金涛, 郭万正, 陈芳, 周广生, 傅廷栋. 饲用油菜的营养成分分析及其在山羊瘤胃降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 50-57. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||