

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 179-191.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025045
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
陈斌( ), 刘晏廷, 陈胜艳, 薛晴, 李梦雨, 王霁佳, 孙颖, 何淼(
), 刘晏廷, 陈胜艳, 薛晴, 李梦雨, 王霁佳, 孙颖, 何淼( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-18
修回日期:2025-04-07
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
何淼
作者简介:E-mail: hm2017148@126.com基金资助:
Bin CHEN( ), Yan-ting LIU, Sheng-yan CHEN, Qing XUE, Meng-yu LI, Ji-jia WANG, Ying SUN, Miao HE(
), Yan-ting LIU, Sheng-yan CHEN, Qing XUE, Meng-yu LI, Ji-jia WANG, Ying SUN, Miao HE( )
)
Received:2025-02-18
Revised:2025-04-07
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2025-11-13
Contact:
Miao HE
摘要:
干旱是影响菊花地理分布和生长发育的一个重要环境因子,MYB作为植物重要的转录因子家族广泛参与非生物胁迫的调控过程。本研究通过对课题组前期从神农香菊中克隆获得的CiMYB4基因以及启动子序列进行生物信息学分析,并测定干旱胁迫处理后过表达CiMYB4烟草和野菊株系的生理指标,初步解析CiMYB4在干旱胁迫中的功能。研究结果表明:CiMYB4开放阅读框全长846 bp,编码281个氨基酸,属于R2R3-MYB亚族,定位在细胞核中。CiMYB4启动子序列中存在7个与干旱胁迫相关的顺式作用元件,其中4个为脱落酸(ABA)响应元件,3个为STRE干旱胁迫响应元件。在干旱处理7和14 d时,过表达CiMYB4烟草和野菊株系的丙二醛(MDA)含量均显著低于野生型(P<0.05),而脯氨酸(Pro)含量以及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性均显著高于野生型(P<0.05)。综合上述结果可知,CiMYB4在干旱胁迫中具有正向调控功能,是培育抗旱性强的菊花新品种潜在的基因资源。
陈斌, 刘晏廷, 陈胜艳, 薛晴, 李梦雨, 王霁佳, 孙颖, 何淼. 神农香菊CiMYB4基因分析及其抗旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 179-191.
Bin CHEN, Yan-ting LIU, Sheng-yan CHEN, Qing XUE, Meng-yu LI, Ji-jia WANG, Ying SUN, Miao HE. Bioinformatics analysis of CiMYB4 in Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum and functional characterization of its role in drought resistance[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(1): 179-191.
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| CiMYB4-2001-F (P-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-1764 (P1-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-1299 (P2-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-954 (P3-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-417 (P4-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-2001-R (P-R) | ACCACCCGG |
表1 启动子克隆引物序列
Table 1 Promoter clone primers’ sequence
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| CiMYB4-2001-F (P-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-1764 (P1-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-1299 (P2-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-954 (P3-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-417 (P4-F) | GATTACGCC |
| CiMYB4-2001-R (P-R) | ACCACCCGG |
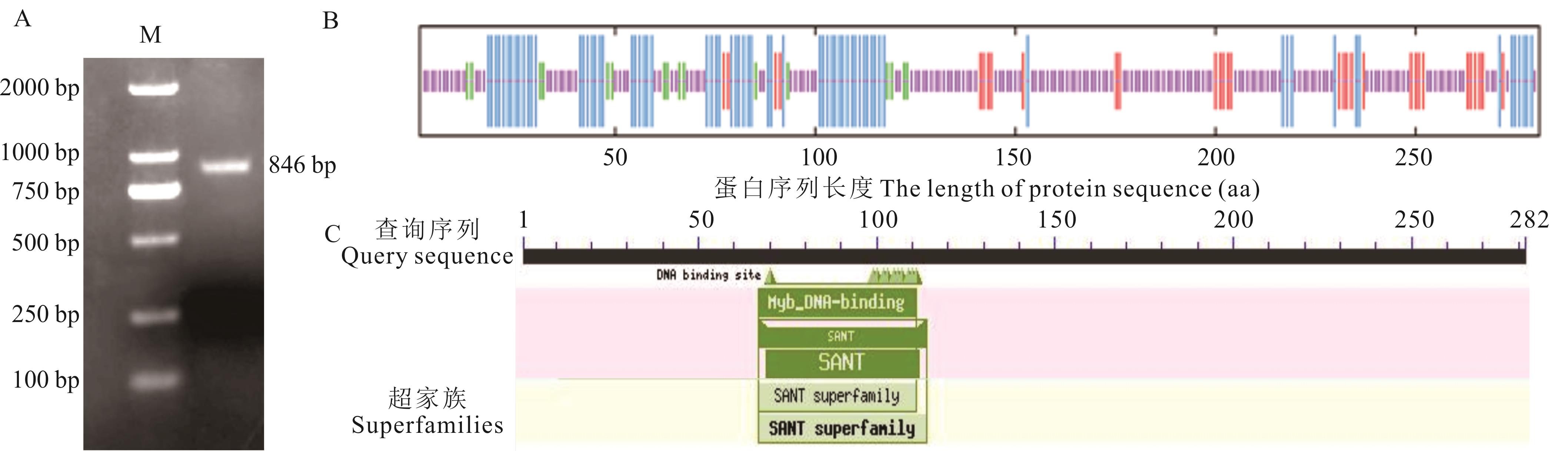
图2 CiMYB4的生物信息学分析A: CiMYB4的克隆Cloning of CiMYB4; B: CiMYB4蛋白的二级结构预测Prediction of CiMYB4 protein secondary structure. 紫色Purple: 无规则卷曲Random coil, 蓝色Blue: α螺旋α-helix, 绿色Green: β转角β-turn, 红色Red: 延伸链Extended strand; C: CiMYB4蛋白的保守结构域Conserved domain of CiMYB4.
Fig.2 Bioinformatics analysis of CiMYB4
类别 Category | 名称 Name | 核心序列 Core sequence | 功能 Function | 数量 Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构元件Structure elements | TATA-box | TATA | 核心启动子元件Core promoter element | 50 |
| CAAT-box | CAA(A)T | 启动子和增强子区域调控元件Regulatory element in promoter and enhancer regions | 35 | |
| 激素响应元件Phytohormone responsive elements | ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid responsive element | 3 |
| AAGAA-motif | GTAAAGAAA | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid responsive element | 1 | |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 生长素响应元件Auxin acid responsive element | 1 | |
| 胁迫响应元件Abiotic stress responsive elements | LTR | AAAGCC | 低温响应元件Low temperature responsive element | 1 |
| STRE | AGGGG | 干旱胁迫响应元件Drought stress responsive element | 3 | |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTTTCTT | 防卫和胁迫响应元件Defense and stress responsive element | 2 | |
| 光响应元件Light responsive elements | G-box | (T)CACGTG(T) | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 2 |
| GATA-motif | AAGGATAAGG | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 3 | |
| I-box | CCTTATCCT | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 2 | |
| chs-CMA1a | TTACTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| 生长发育调控元件Development-related elements | CAT-box | GCCACT | 分生组织表达元件Meristem expression element | 1 |
| 功能未知元件Function unknown elements | MYB CORE | TAACCA、CAACAG | MYB结合位点MYB binding site | 7 |
| MYC CORE | CATTTG、CAATTG | MYC结合位点MYC binding site | 3 | |
| A-box | CCGTCC | 未知功能元件Function unknown element | 2 | |
| AT~TATA-box | TATATA | 未知功能元件Function unknown element | 1 |
表2 CiMYB4启动子顺式作用元件
Table 2 Cis-acting elements of CiMYB4 promoter
类别 Category | 名称 Name | 核心序列 Core sequence | 功能 Function | 数量 Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构元件Structure elements | TATA-box | TATA | 核心启动子元件Core promoter element | 50 |
| CAAT-box | CAA(A)T | 启动子和增强子区域调控元件Regulatory element in promoter and enhancer regions | 35 | |
| 激素响应元件Phytohormone responsive elements | ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid responsive element | 3 |
| AAGAA-motif | GTAAAGAAA | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid responsive element | 1 | |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 生长素响应元件Auxin acid responsive element | 1 | |
| 胁迫响应元件Abiotic stress responsive elements | LTR | AAAGCC | 低温响应元件Low temperature responsive element | 1 |
| STRE | AGGGG | 干旱胁迫响应元件Drought stress responsive element | 3 | |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTTTCTT | 防卫和胁迫响应元件Defense and stress responsive element | 2 | |
| 光响应元件Light responsive elements | G-box | (T)CACGTG(T) | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 2 |
| GATA-motif | AAGGATAAGG | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 3 | |
| I-box | CCTTATCCT | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 2 | |
| chs-CMA1a | TTACTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | |
| 生长发育调控元件Development-related elements | CAT-box | GCCACT | 分生组织表达元件Meristem expression element | 1 |
| 功能未知元件Function unknown elements | MYB CORE | TAACCA、CAACAG | MYB结合位点MYB binding site | 7 |
| MYC CORE | CATTTG、CAATTG | MYC结合位点MYC binding site | 3 | |
| A-box | CCGTCC | 未知功能元件Function unknown element | 2 | |
| AT~TATA-box | TATATA | 未知功能元件Function unknown element | 1 |
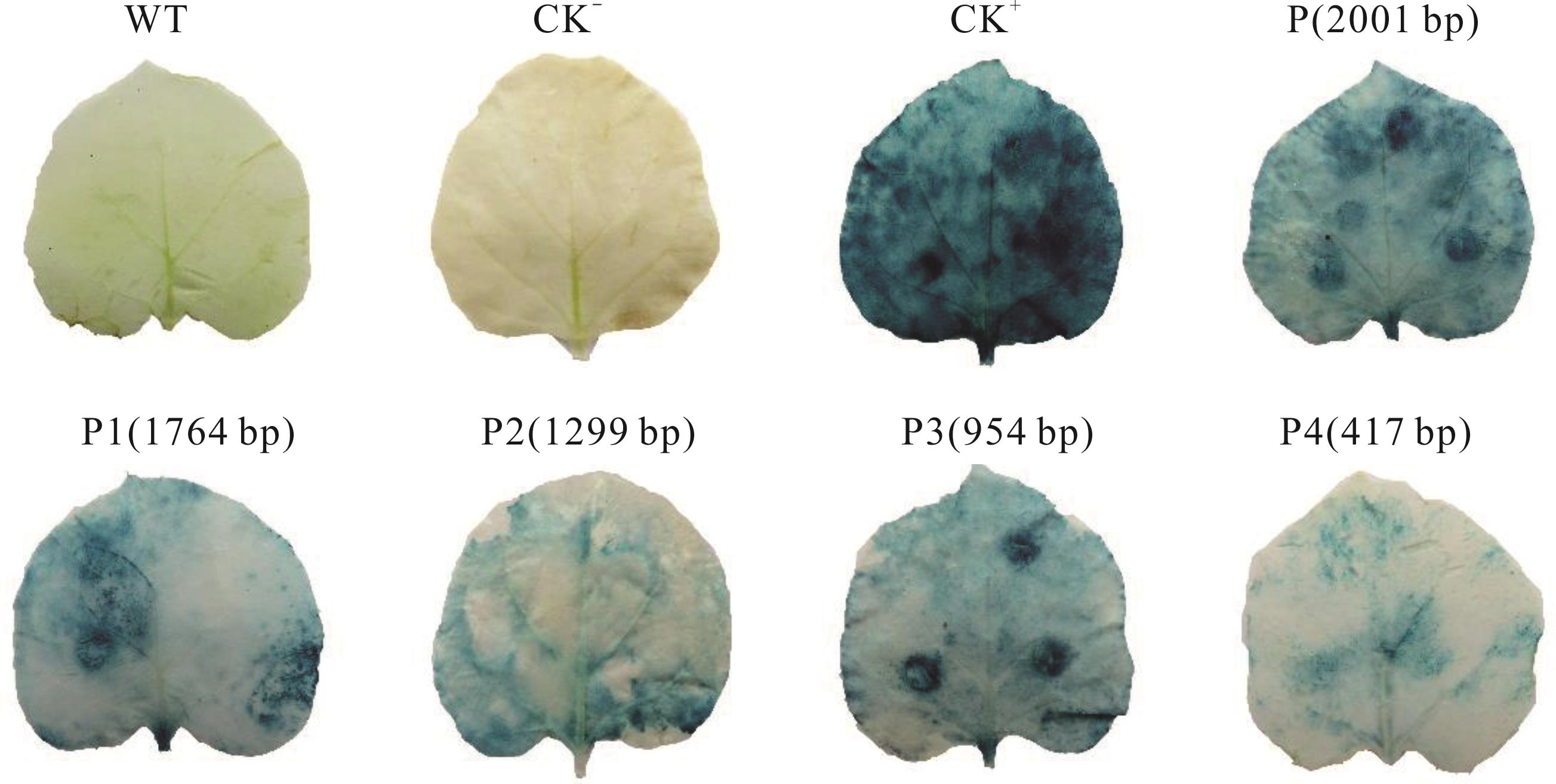
图5 CiMYB4启动子β-葡萄糖苷酸酶活性分析WT: 野生型Wild type; CK-: 阴性对照(仅注射缓冲液) Negative control (only buffer solution); CK+: 阳性对照(pBI121-GUS空载) Positive control (pBI121-GUS);P, P1, P2, P3, P4: 启动子5′端不同长度缺失片段Different length deletion fragments of promoter 5′ end.
Fig.5 Analysis of β-glucuronidase (GUS) activity of CiMYB4 promoter

图7 干旱胁迫对转基因烟草生理指标的影响不同小写字母表示不同株系不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。The different lowercase letters mean the significant differences among treatments of the different lines (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.7 Effects of drought stress on physiological index of CiMYB4 transgenic tobacco
| [1] | Gao S Z, Chen X H, Lin M H, et al. A birch ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 gene enhances UV-B and drought tolerance. Forestry Research, 2024, 4(1): e022. |
| [2] | Yu Z H, Chen X S, Chen Z W, et al. BcSRC2 interacts with BcAPX4 to increase ascorbic acid content for responding ABA signaling and drought stress in pak-choi. Horticulture Research, 2024, 11(8): uhae165. |
| [3] | Lynch J P. Rightsizing root phenotypes for drought resistance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(13): 3279-3292. |
| [4] | Li L L, Zhu H L, Ju Y Q, et al. Comparison of microstructure and physiological response of the leaves of six Rosa rugosa genotypes under drought stress. Ornamental Plant Research, 2024, 4(1): e016. |
| [5] | Li J Y, Ren J J, Lei X Y, et al. CsREV-CsTCP4-CsVND7 module shapes xylem patterns differentially between stem and leaf to enhance tea plant tolerance to drought. Cell Reports, 2024, 43(4): 113987. |
| [6] | He L Y, Tan M M, Che H T, et al. Cloning and analysis of drought tolerance function of the LpDREB9 in Lilium pumilum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 161-173. |
| 贺龙义, 谭萌萌, 车海涛, 等. 细叶百合LpDREB9基因克隆及耐旱性分析. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 161-173. | |
| [7] | Lim C, Kang K, Shim Y, et al. Inactivating transcription factor OsWRKY5 enhances drought tolerance through abscisic acid signaling pathways. Plant Physiology, 2022, 188(4): 1900-1916. |
| [8] | Zhao P P, Zhao M, Gao X Y, et al. GhWRKY1bD improves drought tolerance by co-regulation of ABA, ROS, and proline homeostasis in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Industrial Crops and Products, 2024, 220(1): 119179. |
| [9] | Ge M M, Tang Y, Guan Y J, et al. TaWRKY31, a novel WRKY transcription factor in wheat, participates in regulation of plant drought stress tolerance. BMC Plant Biology, 2024, 24(1): 27. |
| [10] | Liu J T, Wang Y Q, Ye X R, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in response to low-temperature and drought stresses in Cucurbita pepo L. Scientia Horticulture, 2024, 330(1): 113048. |
| [11] | Luo Y R, Xu X Y, Yang L F, et al. A R2R3-MYB transcription factor, FeR2R3-MYB, positively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis and drought tolerance in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 217(1): 109254. |
| [12] | Fan K, Wu Y C, Mao Z J, et al. A novel NAC transcription factor ZmNAC55 negatively regulates drought stress in Zea mays. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 214(1): 108938. |
| [13] | Yang X Z, Li X, Wang X, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of bZIP gene family explore the responses of PsebZIP44 and PsebZIP46 in Pseudoroegneria libanotica under drought stress. BMC Plant Biology, 2024, 24(1): 1-15. |
| [14] | Riechmann J L, Heard J, Martin G, et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science, 2000, 290(5499): 2105-2110. |
| [15] | Ren Z Z, Zhang P Y, Su H H, et al. Regulatory mechanisms used by ZmMYB39 to enhance drought tolerance in maize (Zea mays) seedlings. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 211(1): 108696. |
| [16] | Yang B C, Song Z H, Li C N, et al. RSM1, an Arabidopsis MYB protein, interacts with HY5/HYH to modulate seed germination and seedling development in response to abscisic acid and salinity. PLoS Genetics, 2018, 14(12): e1007839. |
| [17] | Li Q, Kang F, Xue Q, et al. Functional analysis of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor CiMYB4 of Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum in response to cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 128-142. |
| 李强, 康璠, 薛晴, 等. 神农香菊R2R3-MYB转录因子CiMYB4在镉胁迫中的功能分析. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 128-142. | |
| [18] | Zhou X, Lei D Y, Yao W T, et al. A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor PbMYB1L of Pyrus bretschneideri regulates cold tolerance and anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Cell Reports, 2024, 43(2): 34. |
| [19] | Zhu N, Duan B L, Zheng H L, et al. An R2R3-MYB gene GhMYB3 functions in drought stress by negatively regulating stomata movement and ROS accumulation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2023, 197(1): 107648. |
| [20] | Li B Z, Liu R N, Liu J, et al. ZmMYB56 regulates stomatal closure and drought tolerance in maize seedlings through the transcriptional regulation of ZmTOM7. New Crops, 2024, 1(1): 100012. |
| [21] | Song Q, Kong L F, Yang X R, et al. PtoMYB142, a poplar R2R3-MYB transcription factor, contributes to drought tolerance by regulating wax biosynthesis. Tree Physiology, 2022, 42(10): 2133-2147. |
| [22] | Zhang J P, Wang G R, Bie H, et al. Transcription factor ZmMYB153 enhances drought tolerance in maize seedlings by regulating stomatal movement through ABA signaling. Acta Agronomica Sinica, (2025-04-10)[2025-04-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1809.s.20250110.1231.002.html. |
| 张建鹏, 王国瑞, 别海, 等. 转录因子ZmMYB153通过ABA信号调节气孔运动增强玉米苗期抗旱性. 作物学报, (2025-04-10)[2025-04-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1809.s.20250110.1231.002.html. | |
| [23] | Wang J J. Cloning of CiMYB4 Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum and genetic transformation of Chrysanthemum indicum. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2019. |
| 王霁佳. 神农香菊CiMYB4基因的克隆及对野菊的遗传转化. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019. | |
| [24] | Xue Q. Functional analysis of CiMYB4 gene in response to cadmium stress and cloning, expression analyse of its promoter in Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2022. |
| 薛晴. 神农香菊CiMYB4响应镉胁迫的功能研究及其启动子克隆与表达分析. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022. | |
| [25] | Li M Y. Verification of drought tolerance function of CiMYB4 gene of Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum and construction of RNAi vector. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2020. |
| 李梦雨. 神农香菊CiMYB4基因抗旱性功能验证及RNAi载体构建. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020. | |
| [26] | Zhou L, Shi K, Cui X R, et al. Overexpression of MsNAC51 from alfalfa confers drought tolerance in tobacco. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2023, 205(1): 105143. |
| [27] | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Bejing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 中国高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| [28] | Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, et al. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(10): 573-581. |
| [29] | Ren M H, Zhang Y P, Xu T, et al. Identification and expression analyses of R2R3-MYB subfamily in alfalfa under drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 972-983. |
| 任明辉, 张雨蓬, 许涛, 等. 紫花苜蓿R2R3-MYB亚家族鉴定与干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 972-983. | |
| [30] | Jiang Y J, Yu Y P, Sun X Y, et al. Identification of R2R3-MYB gene family and analysis of its expression pattern in centipedegrass under drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(9): 2628-2641. |
| 蒋宇佳, 于元平, 孙向一, 等. 假俭草R2R3-MYB基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下的表达模式分析. 草地学报, 2023, 31(9): 2628-2641. | |
| [31] | Chen G Q, He W Z, Guo X X, et al. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the MYB transcription factor family in Petunia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(9): 4838. |
| [32] | Zhang T T, Cui Z, Li Y X, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor superfamily in Dendrobium catenatum. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021, 12(1): 714696. |
| [33] | Wei Q H, Chen R, Wei X, et al. Genome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB family in wheat and functional characteristics of the abiotic stress responsive gene TaMYB344. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 792. |
| [34] | Yang J H, Zhang B H, Gu G, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). BMC Genomics, 2022, 23(1): 432. |
| [35] | Feller A, Machemer K, Braun E L, et al. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. The Plant Journal, 2011, 66(1): 94-116. |
| [36] | Du H, Yang S S, Liang Z, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biology, 2012, 12(1): 106. |
| [37] | Chen Y H, Yang X Y, He K, et al. The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Molecular Biology, 2006, 60(1): 107-124. |
| [38] | Ding Q Q, Wang X T, Hu L Q, et al. MYB-like transcription factor SiMYB42 from foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) enhances Arabidopsis tolerance to low-nitrogen stress. Hereditas, 2018, 40(4): 327-338. |
| 丁庆倩, 王小婷, 胡利琴, 等. 谷子MYB类转录因子SiMYB42提高转基因拟南芥低氮胁迫耐性. 遗传, 2018, 40(4): 327-338. | |
| [39] | Yang S, Cai W W, Shen L, et al. A CaCDPK29-CaWRKY27b module promotes CaWRKY40 mediated thermotolerance and immunity to Ralstonia solanacearum in pepper. New Phytologist, 2022, 233(4): 1843-1863. |
| [40] | Liu W, Stewart J. Plant synthetic promoters and transcription factors. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 37(1): 36-44. |
| [41] | Chen B, Xue Q, Li Z W, et al. Effects of light intensities on physiological characteristics and ultrastructure of four Commelinaceae plants. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(2): 281-292. |
| 陈斌, 薛晴, 李子葳, 等. 光强对4种鸭跖草科植物叶片生理特性和超微结构的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(2): 281-292. | |
| [42] | Yang C W, An M Z, Ren W, et al. Contrasting cold tolerance and underlying physiological mechanisms in two rye varieties during seed germination and seedling stages. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(6): 1-9. |
| 杨朝伟, 安明珠, 任伟, 等. 两个黑麦品种种子萌发期和幼苗期耐寒性差异及其生理机制. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(6): 1-9. | |
| [43] | Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, et al. Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Sustainable Agriculture, 2009, 29(1): 185-212. |
| [44] | Bai A X, Lu X Y. Effects of calcium and calcium effectors on antioxidant system and osmotic adjustment substances content of sour jujube (Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa) seedlings under NaCl stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(9): 1910-1920. |
| 白爱兴, 鲁晓燕. 钙和钙效应剂对NaCl胁迫下酸枣幼苗抗氧化系统及渗透调节物质含量的影响. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(9): 1910-1920. |
| [1] | 未丽, 邓育轩, 赵静, 刘俊良, 马克华, 王锁民. 旱生植物霸王ZxCER6的基因克隆及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 154-169. |
| [2] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [3] | 赵媛媛, 蒲小剑, 徐成体, 王伟, 傅云洁. 蒺藜苜蓿MtBMI1基因克隆及抗旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 139-153. |
| [4] | 陈彩锦, 包明芳, 王文虎, 尚继红, 曾燕霞, 沙晓弟, 朱新忠, 王学敏, 刘文辉. 紫花苜蓿抗旱育种研究现状及展望[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 204-223. |
| [5] | 汪欣瑶, 彭亚萍, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草HgS5基因的克隆与抗旱性鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 184-195. |
| [6] | 霍晨敏, 袁敏, 张宝文, 王瑞菊. 野生稻CBF/DREB1转录因子的鉴定与生物信息学分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 126-144. |
| [7] | 李强, 康璠, 薛晴, 陈斌, 孙颖. 神农香菊R2R3-MYB转录因子CiMYB4在镉胁迫中的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 128-142. |
| [8] | 韩金秀, 陈斌, 刘晏廷, 孟儒, 金利妍, 何淼. 神农香菊CibHLH1的鉴定及对光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 89-101. |
| [9] | 王少鹏, 刘佳, 洪军, 林积圳, 张义, 史昆, 王赞. 紫花苜蓿MsPPR1基因的克隆及抗旱功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 49-60. |
| [10] | 王文娟, 师尚礼, 何龙, 武蓓, 刘旵旵. 干旱胁迫下多胺在植物体内的积累及其作用[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 186-202. |
| [11] | 纪童, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波. 7种禾本科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 144-156. |
| [12] | 畅志鹏, 孙莹莹, 李佳阳, 龚春梅. 柠条CkCAD基因的克隆转化及其抗旱功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 68-80. |
| [13] | 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 宫文龙. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| [14] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 贾瑜琀. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. |
| [15] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙晓梵, 孙宗玖. 新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 155-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||