

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 13-25.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025113
刘阳( ), 肖红(
), 肖红( ), 徐长林, 邓明月, 魏文强, 韩奥, 马凯, 王昀
), 徐长林, 邓明月, 魏文强, 韩奥, 马凯, 王昀
收稿日期:2025-04-01
修回日期:2025-06-25
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
肖红
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: xiaoh@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yang LIU( ), Hong XIAO(
), Hong XIAO( ), Chang-lin XU, Ming-yue DENG, Wen-qiang WEI, Ao HAN, Kai MA, Yun WANG
), Chang-lin XU, Ming-yue DENG, Wen-qiang WEI, Ao HAN, Kai MA, Yun WANG
Received:2025-04-01
Revised:2025-06-25
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Hong XIAO
摘要:
明晰东祁连山高寒草甸灌木扩张对草本植物群落特征的影响,对当地生态平衡和畜牧业发展具有重要意义。本研究在甘肃省天祝藏族自治县境内,以山生柳为优势灌木的高寒灌丛草甸为对象,运用空间演替代替时间演替的方法,在不同灌丛化程度(轻度、中度和重度)的灌丛斑块和草地斑块中,探究了不同功能群草本植物的高度、盖度和地上生物量以及群落物种多样性指数的变化规律。结果表明,随着灌丛化程度的增加,灌丛斑块和草地斑块中各功能群草本植物的高度均呈上升趋势,莎草科植物的盖度呈下降趋势,禾本科植物的生物量无显著变化;灌木扩张对杂类草的物种组成影响较大,在重度灌丛化处理下,灌丛斑块和草地斑块中均形成了以问荆为优势种的草本层。灌木扩张降低了灌丛斑块中草本群落的物种丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener指数、Simpson优势度指数和Pielou均匀度指数。相关性分析得出,灌丛斑块内山生柳灌木的高度和冠幅面积与草本植物物种多样性指数均呈显著负相关。综上,以山生柳为优势灌木的高寒灌丛草甸灌木扩张对草本群落既有竞争作用,又有一定的庇护作用,这种作用的大小因灌丛化程度和草本植物种类的不同而有所差异。
刘阳, 肖红, 徐长林, 邓明月, 魏文强, 韩奥, 马凯, 王昀. 东祁连山高寒草甸山生柳灌木扩张对草本植物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 13-25.
Yang LIU, Hong XIAO, Chang-lin XU, Ming-yue DENG, Wen-qiang WEI, Ao HAN, Kai MA, Yun WANG. Impact of Salix oritrepha shrub encroachment on characteristics of herbaceous plant communities in the alpine meadows of the Eastern Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 13-25.

图1 研究区地理位置、样地景观及灌丛斑块与草地斑块相对位置基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2024)0650号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。插图分别代表:(a)研究区位置、(b)灌丛斑块和草地斑块相对位置示意图、(c)轻度灌丛化草甸、(d)中度灌丛化草甸和(e)重度灌丛化草甸。Based on the standard map service website of the Ministry of Natural Resources with the drawing number: GS (2024) 0650, the boundary of the base map was not modified. Each illustration represents: (a) Location of the study area, (b) A schematic diagram of the relative positions of shrub patches and grass patches, (c) Lightly shrub-encroached meadow, (d) Moderately shrub-encroached meadow, and (e) Heavily shrub-encroached meadow.
Fig.1 Geographical location of the study area, sample plot landscape images, and relative positions of shrub patches and grass patches
| 灌丛特征Shrub characteristics | 灌丛化程度Degree of shrub encroachment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | |
| 高度Height (cm) | 45.67±1.20c | 71.67±1.20b | 127.67±1.45a |
| 冠幅面积Crown area (m2) | 0.19±0.05c | 0.48±0.10b | 1.44±0.41a |
| 地上生物量Aboveground biomass (g·clump-1) | 194.61±22.69c | 587.28±85.84b | 2395.89±101.44a |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 5.12±0.81c | 6.75±0.33b | 12.38±0.14a |
| 分蘖株数Tillering number (No.) | 24.00±1.15c | 45.00±2.31a | 29.67±0.67b |
表1 不同灌丛化程度下山生柳灌木的生长特征
Table 1 Growth characteristics of S. oritrepha shrub under varying degrees of shrub encroachment
| 灌丛特征Shrub characteristics | 灌丛化程度Degree of shrub encroachment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | |
| 高度Height (cm) | 45.67±1.20c | 71.67±1.20b | 127.67±1.45a |
| 冠幅面积Crown area (m2) | 0.19±0.05c | 0.48±0.10b | 1.44±0.41a |
| 地上生物量Aboveground biomass (g·clump-1) | 194.61±22.69c | 587.28±85.84b | 2395.89±101.44a |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 5.12±0.81c | 6.75±0.33b | 12.38±0.14a |
| 分蘖株数Tillering number (No.) | 24.00±1.15c | 45.00±2.31a | 29.67±0.67b |
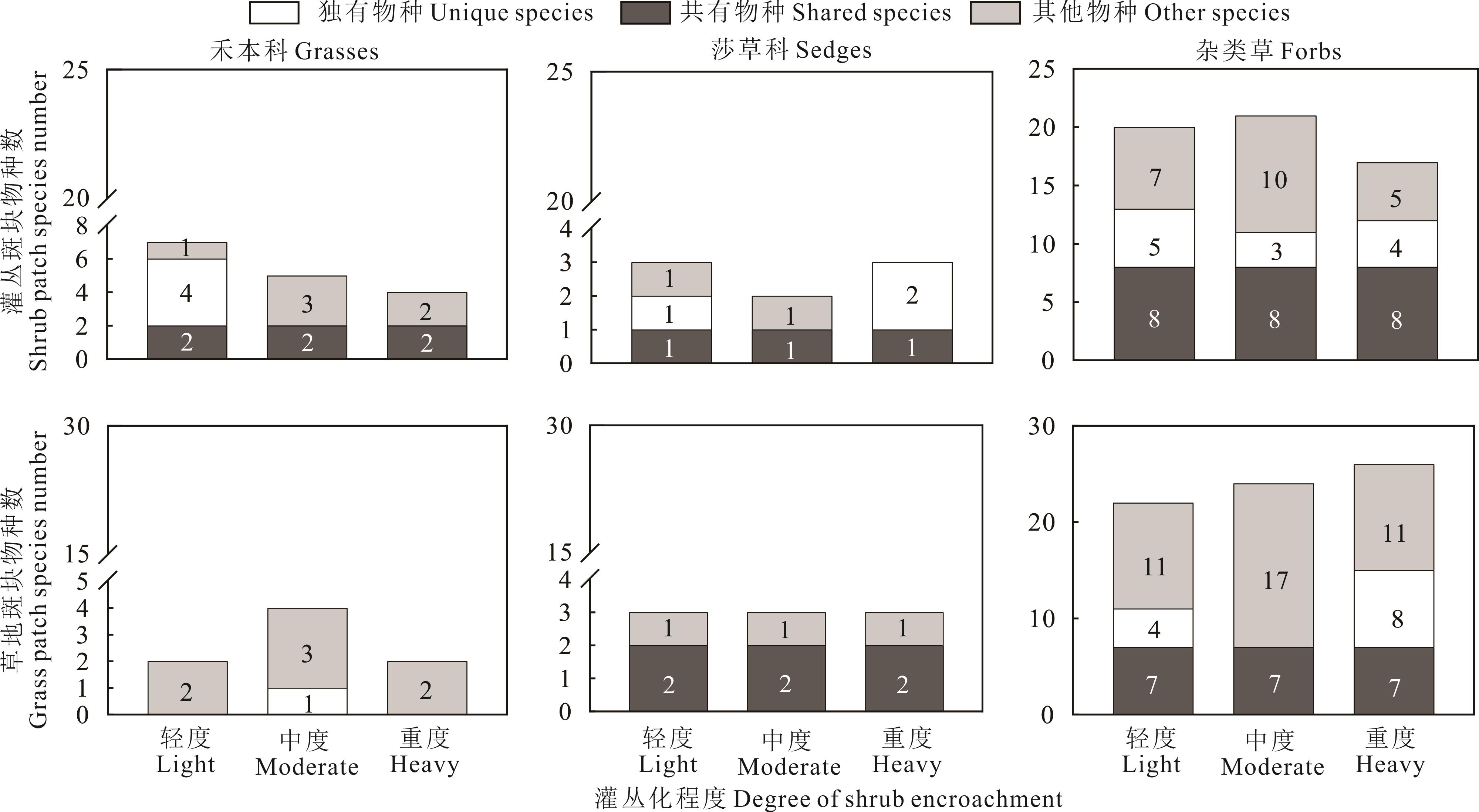
图2 不同灌丛化程度下灌丛斑块和草地斑块中各功能群物种数的变化独有物种、共有物种和其他物种分别指:相同斑块内某一灌丛化程度中独有的物种、3种灌丛化程度中共有的物种和斑块中除去独有和共有物种的剩余物种。Within a patch, “unique species” refer to species that are exclusive to a particular level of shrub encroachment. “Shared species” are those present across all levels of shrub encroachment. “Other species” are the remaining species in the patch after excluding both unique and shared species.
Fig.2 Changes in species richness of herbaceous plant functional groups in shrub and grass patches across different degrees of shrub encroachment
物种名 Species name | 科 Family | 灌丛斑块Shrub patch | 草地斑块Grass patch | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | ||
| 铃铃香青A. hancockii | 菊科Asteraceae | 4.00 | 1.67 | 1.33 | 15.67 | 9.67 | — |
| 钝苞雪莲Saussurea nigrescens | 菊科Asteraceae | — | 20.33 | 4.00 | — | — | — |
| 球花蒿A. smithii | 菊科Asteraceae | 1.00 | — | — | 12.00 | — | — |
| 黄帚橐吾Ligularia virgaurea | 菊科Asteraceae | — | — | — | — | — | 12.33 |
| 翻白草P. discolor | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 9.67 | 8.33 | — | 13.00 | 18.33 | 0.67 |
| 鹅绒委陵菜Potentilla anserina | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | — | — | — | — | 24.00 | 8.33 |
| 北方獐牙菜S. diluta | 龙胆科Gentianaceae | 4.00 | 0.67 | — | 6.33 | — | — |
| 珠芽蓼B. vivipara | 蓼科Polygonaceae | 18.00 | 7.00 | 11.67 | 46.33 | 51.33 | 17.67 |
| 银莲花Anemone cathayensis | 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 5.33 | 6.67 | 8.67 | 13.00 | 13.33 | 9.00 |
| 肉果草L. tibetica | 通泉草科Primulaceae | 1.33 | 3.33 | — | — | 0.33 | 1.67 |
| 问荆E. arvense | 木贼科Equisetaceae | — | 2.33 | 40.67 | — | 5.67 | 57.00 |
| 小米草Euphrasia pectinata | 玄参科Scrophulariaceae | — | — | — | 1.67 | 8.67 | 15.00 |
表2 不同灌丛化程度下灌丛斑块和草地斑块中主要杂类草的盖度
Table 2 Coverage of dominant forbs in shrub and grass patches across different intensities of shrub encroachment (%)
物种名 Species name | 科 Family | 灌丛斑块Shrub patch | 草地斑块Grass patch | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | 轻度Light | 中度Moderate | 重度Heavy | ||
| 铃铃香青A. hancockii | 菊科Asteraceae | 4.00 | 1.67 | 1.33 | 15.67 | 9.67 | — |
| 钝苞雪莲Saussurea nigrescens | 菊科Asteraceae | — | 20.33 | 4.00 | — | — | — |
| 球花蒿A. smithii | 菊科Asteraceae | 1.00 | — | — | 12.00 | — | — |
| 黄帚橐吾Ligularia virgaurea | 菊科Asteraceae | — | — | — | — | — | 12.33 |
| 翻白草P. discolor | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 9.67 | 8.33 | — | 13.00 | 18.33 | 0.67 |
| 鹅绒委陵菜Potentilla anserina | 蔷薇科Rosaceae | — | — | — | — | 24.00 | 8.33 |
| 北方獐牙菜S. diluta | 龙胆科Gentianaceae | 4.00 | 0.67 | — | 6.33 | — | — |
| 珠芽蓼B. vivipara | 蓼科Polygonaceae | 18.00 | 7.00 | 11.67 | 46.33 | 51.33 | 17.67 |
| 银莲花Anemone cathayensis | 毛茛科Ranunculaceae | 5.33 | 6.67 | 8.67 | 13.00 | 13.33 | 9.00 |
| 肉果草L. tibetica | 通泉草科Primulaceae | 1.33 | 3.33 | — | — | 0.33 | 1.67 |
| 问荆E. arvense | 木贼科Equisetaceae | — | 2.33 | 40.67 | — | 5.67 | 57.00 |
| 小米草Euphrasia pectinata | 玄参科Scrophulariaceae | — | — | — | 1.67 | 8.67 | 15.00 |
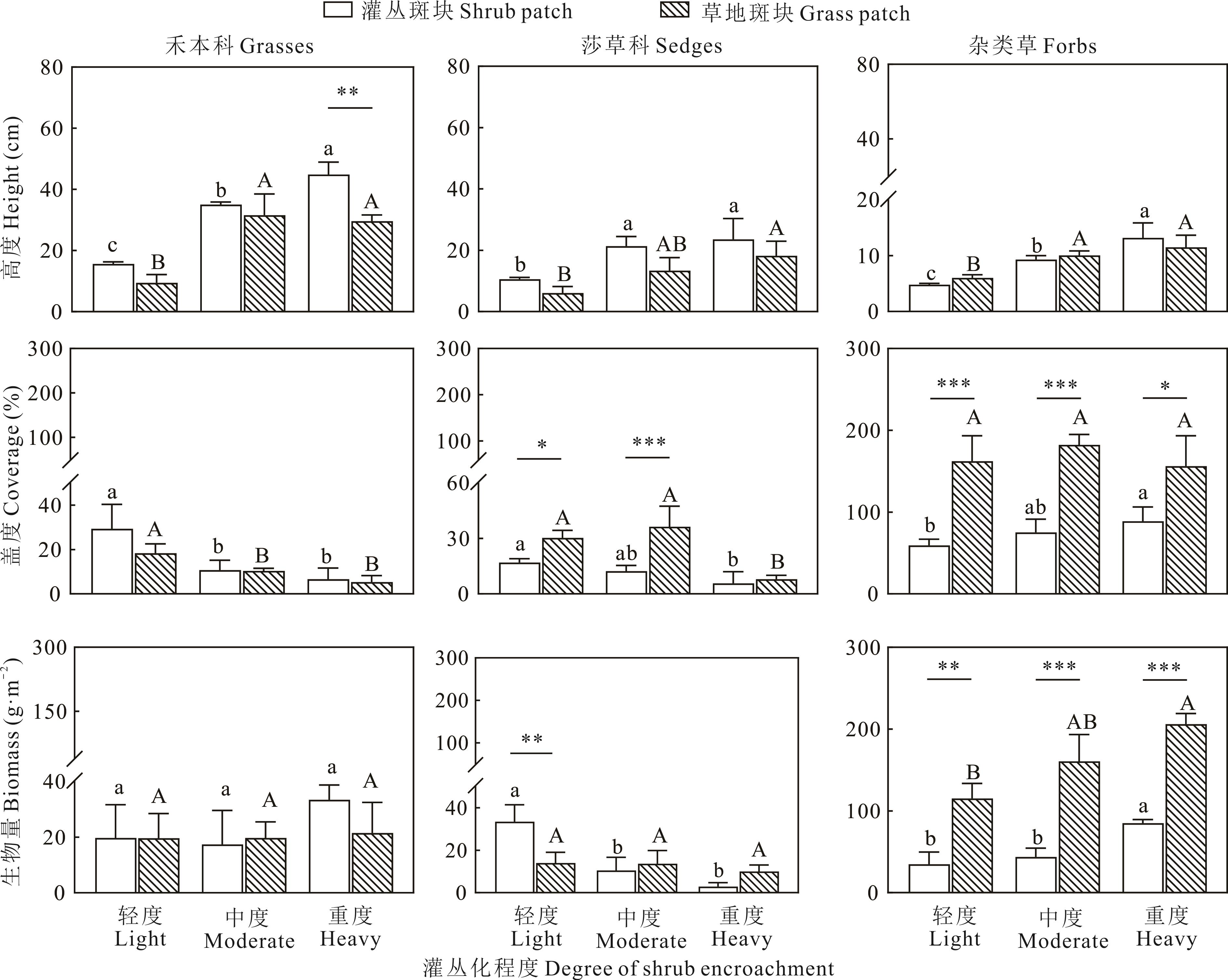
图3 不同灌丛化程度下灌丛斑块和草地斑块中草本植物不同功能群高度、盖度及生物量的变化不同小写字母代表灌丛斑块内不同灌丛化程度间存在显著差异(P<0.05),不同大写字母代表草地斑块内不同灌丛化程度间存在显著差异(P<0.05),星号代表同一灌丛化程度下灌丛斑块和草地斑块间存在显著差异,*P<0.05、**P<0.01、***P<0.001,下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the intensity of shrub encroachment within shrub patches (P<0.05). Different uppercase letters denote significant differences in the intensity of shrub encroachment within grass patches (P<0.05). Asterisks signify significant difference between shrub patches and grass patches at the same shrub encroachment level, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001, respectively. The same below.
Fig.3 Variations in height, coverage, and biomass of herbaceous plant functional groups in shrub patches and grass patches across different intensities of shrub encroachment
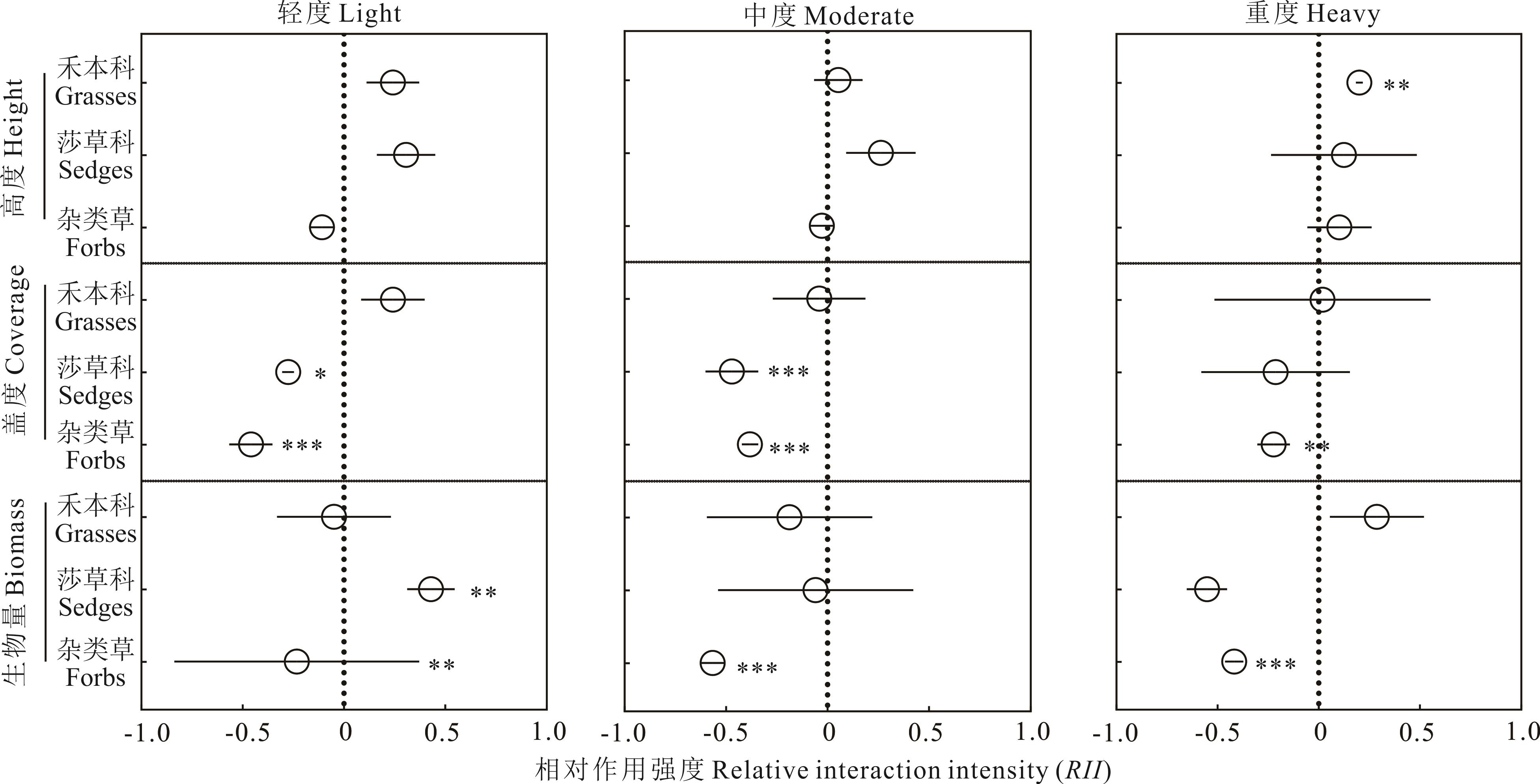
图4 草本植物不同功能群特征的相对作用强度(RII)虚线代表零线;RII正值(零线右侧)表示灌木扩张后变量值的增加,RII负值(零线左侧)表示变量值下降,下同。The dotted line represents the zero line. Positive RII values (right of the zero line) indicate an increase in trait value following shrub encroachment, while negative values (left) indicate a decrease. The same below.
Fig.4 Relative interaction intensity (RII) of different herbaceous plant functional groups in response to shrub encroachment

图5 不同灌丛化程度下灌丛斑块和草地斑块中草本植物群落物种多样性指数的变化
Fig.5 Changes in species diversity index of herbaceous communities in shrub patches and grass patches across different intensities of shrub encroachment
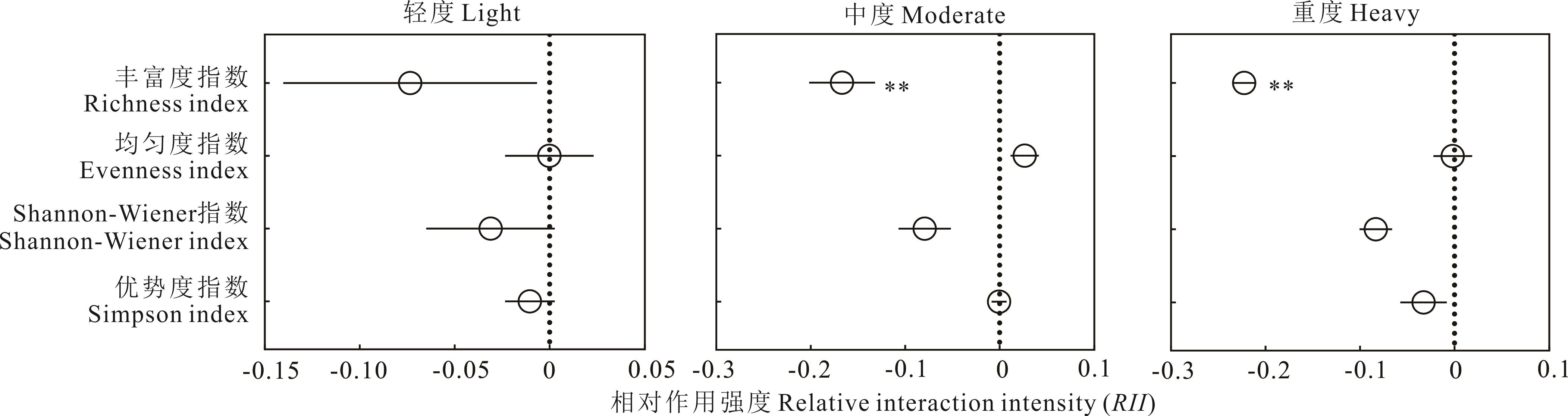
图6 不同灌丛化程度下草本植物群落物种多样性指数的相对作用强度(RII)
Fig.6 Relative interaction intensity (RII) of species diversity index of herbaceous communities across different intensities of shrub encroachment

图7 山生柳灌木生长特征与各功能群草本植物高度、盖度、地上生物量和群落物种多样性指数的相关分析
Fig.7 Relationship among the growth characteristics of S. oritrepha and the height, coverage, aboveground biomass, and community species diversity indexes of herbaceous plant functional groups

图8 山生柳灌丛盖度与灌丛斑块和草地斑块中不同功能群草本高度、盖度和生物量的线性关系
Fig.8 Linear relationships between coverage of S. oritrepha and the height, coverage, and biomass of herbaceous plant functional groups in shrub patches and grass patches
| [1] | Maestre F T, Bowker M A, Puche M D, et al. Shrub encroachment can reverse desertification in semi-arid Mediterranean grasslands. Ecology Letters, 2009, 12(9): 930-941. |
| [2] | Zhao L R, Li K X, Zhu N, et al. Shrub encroachment accelerates the processes of moisture redistribution in alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma, 2025, 454: 117196. |
| [3] | Maestre T F, Cortina J. Remnant shrubs in Mediterranean semi-arid steppes: effects of shrub size, abiotic factors and species identity on understorey richness and occurrence. Acta Oecologica, 2004, 27(3): 161-169. |
| [4] | Dang Y L, Zhang P, Jiang P X, et al. Temperature-dependent variations in under-canopy herbaceous foliar diseases following shrub encroachment in grasslands. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 1131. |
| [5] | Zhu Y K, Shen H H, Akinyemi D S, et al. Increased precipitation attenuates shrub encroachment by facilitating herbaceous growth in a Mongolian grassland. Functional Ecology, 2022, 36(9): 2356-2366. |
| [6] | Shi H J, Jiang S J, Bian J H, et al. Livestock exclusion enhances shrub encroachment in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 2023, 34(5): 1390-1402. |
| [7] | Zhou L H, Shen H H, Chen L Y, et al. Ecological consequences of shrub encroachment in the grasslands of Northern China. Landscape Ecology, 2019, 34(1): 119-130. |
| [8] | Chen L Y, Li H, Zhang P J, et al. Climate and native grassland vegetation as drivers of the community structures of shrub-encroached grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Landscape Ecology, 2015, 30(9): 1627-1641. |
| [9] | Howard S K, Eldridge J D, Soliveres S. Positive effects of shrubs on plant species diversity do not change along a gradient in grazing pressure in an arid shrubland. Basic and Applied Ecology, 2012, 13(2): 159-168. |
| [10] | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Li G Y, et al. Shrub encroachment with increasing anthropogenic disturbance in the semiarid Inner Mongolian grasslands of China. Catena, 2013, 109: 39-48. |
| [11] | Liu Y Y, Ding J Y. Research progress on shrub encroachment in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2025, 47(4): 127-141. |
| 刘奕吟, 丁婧祎. 中国草地灌丛化研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2025, 47(4): 127-141. | |
| [12] | Ding J Y, Eldridge D. The success of woody plant removal depends on encroachment stage and plant traits. Nature Plants, 2022, 9(1): 58-67. |
| [13] | Yang W, Qu G P, Kelly A R, et al. Positive effects of leguminous shrub encroachment on multiple ecosystem functions of alpine meadows and steppes greatly depended on increasing soil nutrient. Catena, 2024, 236: 107745. |
| [14] | Liu Y F, Zhang Z C, Liu Y, et al. Shrub encroachment enhances the infiltration capacity of alpine meadows by changing the community composition and soil conditions. Catena, 2022, 213: 106222. |
| [15] | Zhao Y D, Hu X, Pan P Y. Positive feedback relationship between shrub encroachment and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the Inner Mongolia grassland of northern China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 177: 104525. |
| [16] | Zhang J M, Zhu N, Cai Y R, et al. Effects of Caragana microphylla on herbaceous community characteristics. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(21): 8830-8839. |
| 张敬敏, 珠娜, 蔡育蓉, 等. 小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)灌丛对草本群落特征的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(21): 8830-8839. | |
| [17] | Ding J Y, Yin C C, Han Y, et al. Research progress and perspectives on the impact of shrub encroachment on ecosystem multifunctionality. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(20): 8257-8267. |
| 丁婧祎, 尹彩春, 韩逸, 等. 草原灌丛化对生态系统多功能性的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(20): 8257-8267. | |
| [18] | Li Y, Hu Z Z, Wang Z T. Studies on distribution pattern of Salix oritrepha population at alpine area in east Qilian mountain. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2002, 11(3): 48-54. |
| 李毅, 胡自治, 王志泰. 东祁连山高寒地区山生柳种群分布格局研究. 草业学报, 2002, 11(3): 48-54. | |
| [19] | Zhou C Y, Yang X Y, Shao X Q, et al. Relationship between plant species diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality in alpine meadow with different degradation degrees. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(12): 3410-3422. |
| 周宸宇, 杨晓渊, 邵新庆, 等. 不同退化程度高寒草甸植物物种多样性与生态系统多功能性关系. 草地学报, 2022, 30(12): 3410-3422. | |
| [20] | Li X Q. A brief overview of the main economic groups of grassland plants in Qinghai. Qinghai Prataculture, 2019, 28(1): 42-45. |
| 李旭谦. 青海草地植物主要经济类群简述. 青海草业, 2019, 28(1): 42-45. | |
| [21] | Peng S L. Studies on succession of plant community II. methods for dynamics research. Ecological Science, 1994(2): 117-119. |
| 彭少麟. 植物群落演替研究: II. 动态研究的方法. 生态科学, 1994(2): 117-119. | |
| [22] | Liu Y F, Fan H, Shi J J, et al. Climate change-induced shrub encroachment changes soil hydraulic properties and inhibits herbaceous growth in alpine meadows. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2023, 340: 109629. |
| [23] | Ma X X, Gao Y Z. Impact of shrub encroachment on soil hydrological processes in grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 212-222. |
| 马学喜, 高英志. 灌丛化对草地土壤水文过程影响的研究进展. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 212-222. | |
| [24] | Saixiyala, Ding Y, Zhang S D, et al. Facilitation by a spiny shrub on a rhizomatous clonal herbaceous in Thicketization-grassland in northern China: increased soil resources or shelter from herbivores. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 809. |
| [25] | Wang Y L, Wang X L, Ma Y S, et al. Effect of slope aspect on vegetation growth and soil nutrient characteristics of alpine grassland in the source region of Yangtze River. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(10): 2336-2346. |
| 王彦龙, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 等. 坡向对长江源区高寒草地植被生长和土壤养分特征的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(10): 2336-2346. | |
| [26] | Zhao H L, Su Y Z, Zhang H, et al. Multiple effects of shrub on soil properties and understory vegetation in Horqin sand land, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(3): 385-390. |
| 赵哈林, 苏永中, 张华, 等. 灌丛对流动沙地土壤特性和草本植物的影响. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(3): 385-390. | |
| [27] | Qu W L, Yang X P, Zhang C T, et al. Shrub-mediated “fertile island” effects in arid and semi arid grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4): 201-207. |
| 瞿王龙, 杨小鹏, 张存涛, 等. 干旱、半干旱地区天然草原灌木及其肥岛效应研究进展. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 201-207. | |
| [28] | Liu T, Ji M F, Deng Y, et al. Progress in asymmetric light competition research. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(1): 156-167. |
| 刘涛, 姬明飞, 邓燕, 等. 植物非对称性光竞争研究进展. 草业科学, 2020, 37(1): 156-167. | |
| [29] | Li Y F, Sun B, Nan Z B, et al. Classification system of inter-silva grasslands in northern China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(3): 175-188. |
| 李毅夫, 孙斌, 南志标, 等. 中国北方林间草地分类体系研究. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 175-188. | |
| [30] | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Tong S Y, et al. Effects of shrub encroachment on biomass and biodiversity in the typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(22): 7221-7229. |
| 彭海英, 李小雁, 童绍玉, 等. 内蒙古典型草原灌丛化对生物量和生物多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(22): 7221-7229. | |
| [31] | Guan J X, Li X Q, Zhang M W, et al. Effects of Caragana microphylla encroachment on mineral element concentrations in leaves and aboveground biomass accumulation of herbaceous plants along an aridity gradient. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(19): 8047-8056. |
| 关家欣, 李小琴, 张明伟, 等. 沿干旱梯度小叶锦鸡儿灌丛化对草本植物叶片矿质元素浓度及地上生物量累积的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(19): 8047-8056. | |
| [32] | Yu L, Wang H M, Guo T D, et al. Bistable-state of vegetation shift in the desert grassland-shrubland anthropogenic mosaic area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(24): 9773-9783. |
| 于露, 王红梅, 郭天斗, 等. 荒漠草原-灌丛镶嵌体的植被稳态转变特征. 生态学报, 2021, 41(24): 9773-9783. | |
| [33] | Chen J, Li F C, Jia B, et al. Regulation of soil nitrogen cycling by shrubs in grasslands. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2024, 191: 109327. |
| [34] | Ravolainen T V, Bråthen A K, Ims A R, et al. Shrub patch configuration at the landscape scale is related to diversity of adjacent herbaceous vegetation. Plant Ecology & Diversity, 2013, 6(2): 257-268. |
| [35] | Beck J J. Variation in plant-soil interactions among temperate forest herbs. Plant Ecology, 2021, 222(11): 1225-1238. |
| [36] | Jezequel A, Delaby L, Finn A J, et al. Sward species diversity impacts on pasture productivity and botanical composition under grazing systems. Grass and Forage Science, 2024, 79(4): 651-665. |
| [37] | Knapp K A, Briggs M J, Collins L S, et al. Shrub encroachment in North American grasslands: shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs. Global Change Biology, 2008, 14(3): 615-623. |
| [38] | Zhao J X, Yang W, Awei J S, et al. Shrub encroachment increases soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in alpine grassland ecosystems of the central Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma, 2023, 433: 116468. |
| [39] | Wu G L, Liu Y F, Wang D, et al. Divergent successions to shrubs- and forbs-dominated meadows decrease ecosystem multifunctionality of hillside alpine meadow. Catena, 2024, 236: 107718. |
| [1] | 周诗杰, 王义莲, 孙攀, 尚静, 杨文钰, 王学贵, 杨继芝. 四川省玉米大豆带状复合种植田杂草发生种类及群落特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 143-154. |
| [2] | 何佳奇, 吴林, 邱智敏, 高绪勇, 高伦伦, 付双彬, 杨燕萍, 王培龙, 徐婉, 周庄. 温州绕城高速公路边坡杂草物种多样性及群落特征[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 40-53. |
| [3] | 严双, 夏菲, 魏巍, 王敬龙, 吴皓阳, 冉林灵, 薛云尹, 石昊, 郑晒坤, 王军强, 贺俊东. 高寒草甸不同侵蚀样地植物多样性的差异及其关键影响因子[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 1-13. |
| [4] | 罗顺华, 刘新宇, 孟宝平, 陈璇黎, 胡仁杰, 于红妍, 王贤颖, 张勃, 秦彧. 祁连山国家公园高寒草地功能群多样性与生产力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 14-26. |
| [5] | 李雪萍, 许世洋, 李建军, 漆永红. 青稞根腐病根际土壤细菌多样性及群落结构变化规律[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 118-129. |
| [6] | 王守兴, 周华坤, 欧立鹏, 李成先, 王雁鹤, 宁晓春, 谷强, 魏代军, 杨明新. 三江源不同草地类型植被及土壤微生物多样性与土壤因子特征的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 16-26. |
| [7] | 马学喜, 高英志. 灌丛化对草地土壤水文过程影响的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 212-222. |
| [8] | 龚昕, 霍新茹, 李雯, 杨彦东, 刘超, 秦伟春, 沈艳, 王国会, 马红彬. 宁夏罗山山地草原植被群落特征及其空间分异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 1-15. |
| [9] | 吕娜, 高吉喜, 李政海, 尤春赫, 刘晓曼, 张彪, 莫宇, 朱萨宁, 彭阳, 杨雪. 植物生长中期施肥对草甸草原群落特征与物种多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 109-122. |
| [10] | 景煜都, 刘小伟, 梁可, 封俊豪, 于强, 郭梁. 灌丛化对黄土高原草地土壤有机碳组分与稳定性的影响及其微生物调控机制[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 1-15. |
| [11] | 吕烨昕, 叶茂, 钱娇蓉, 陈维龙, 车静, 李苗苗, 曾国燕. 新疆哈巴河林区草地物种多样性和系统发育多样性分析及影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 50-61. |
| [12] | 刘泽华, 陈林, 张雅琪, 龙进潇, 李学斌, 庞丹波. 灌丛化对荒漠草原猪毛蒿群落物种生态位和种间联结性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 1-15. |
| [13] | 刘倩, 丁彦芬, 宋杉杉, 许文婕, 杨威. 南京明城墙绿带草本层自生植物群落数量分类与排序分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 1-15. |
| [14] | 赵亚楠, 王红梅, 李志丽, 张振杰, 陈彦硕, 苏荣霞. 荒漠草原灌丛转变过程土壤水分亏缺空间特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. |
| [15] | 石昊, 杨彩红, 夏菲, 王军强, 魏巍, 王敬龙, 薛云尹, 郑晒坤, 吴皓阳, 冉林灵, 严双, 姜晓敏. 短期增温对修复过程中藏北高寒退化草地生产力的初期影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 30-45. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||