

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 65-74.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020224
彭磊1,2,3( ), 张力1,2,3, 周小龙1,2,3, 万彦博1,2,3, 师庆东1,2,3(
), 张力1,2,3, 周小龙1,2,3, 万彦博1,2,3, 师庆东1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2020-05-13
修回日期:2020-07-01
出版日期:2021-05-20
发布日期:2021-04-16
通讯作者:
师庆东
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail:shiqd@xju.edu.cn基金资助:
Lei PENG1,2,3( ), Li ZHANG1,2,3, Xiao-long ZHOU1,2,3, Yan-bo WAN1,2,3, Qing-dong SHI1,2,3(
), Li ZHANG1,2,3, Xiao-long ZHOU1,2,3, Yan-bo WAN1,2,3, Qing-dong SHI1,2,3( )
)
Received:2020-05-13
Revised:2020-07-01
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-04-16
Contact:
Qing-dong SHI
摘要:
水是制约干旱区植物生长的关键性限制因子。选取新疆准东干旱荒漠地区优势物种钠猪毛菜为研究对象,通过田间控制试验方法研究分析不同水分梯度对钠猪毛菜生长策略的影响,为新疆准东地区大规模露天矿区植被重建工作提供参考。结果表明:1)在不同生长时期,水分胁迫对钠猪毛菜的生物量分配具有显著影响,根冠比随胁迫程度增加而增加,地上生物量较地下生物量减少程度较快;2)应用模糊数学的隶属函数分析法,依此对钠猪毛菜生长状况进行评价,评价结果为幼苗期、生长期、繁殖期生长情况最优分别为5、10 d及对照组;3)钠猪毛菜各个生长阶段含水率差异显著,表现为幼苗期>生长期>繁殖期,且都随胁迫增加而降低;4)钠猪毛菜C、N含量在幼苗期、营养生长期、繁殖期差异显著,P含量差异不显著,N∶P在幼苗期、营养生长期均小于14,繁殖期大于16;5)钠猪毛菜在幼苗期和营养生长期偏向于地下权衡,在繁殖期的低胁迫下偏向于地上权衡,高胁迫下偏向于地下权衡。钠猪毛菜在幼苗期和生长期对水分胁迫具有相似的生存对策,繁殖期在低胁迫时生存对策与幼苗期、生长期相一致,而在高胁迫时恰好相反。
彭磊, 张力, 周小龙, 万彦博, 师庆东. 水分胁迫对新疆准东地区钠猪毛菜的生活史对策的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 65-74.
Lei PENG, Li ZHANG, Xiao-long ZHOU, Yan-bo WAN, Qing-dong SHI. Effects of water stress on life history strategy of Salsola nitraria in Zhundong, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 65-74.

图1 不同水分处理下不同生长时期根、枝叶、种子生物量分配占比
Fig.1 Proportion of biomass distribution of roots, branches and seeds in different growth stages under different water treatments
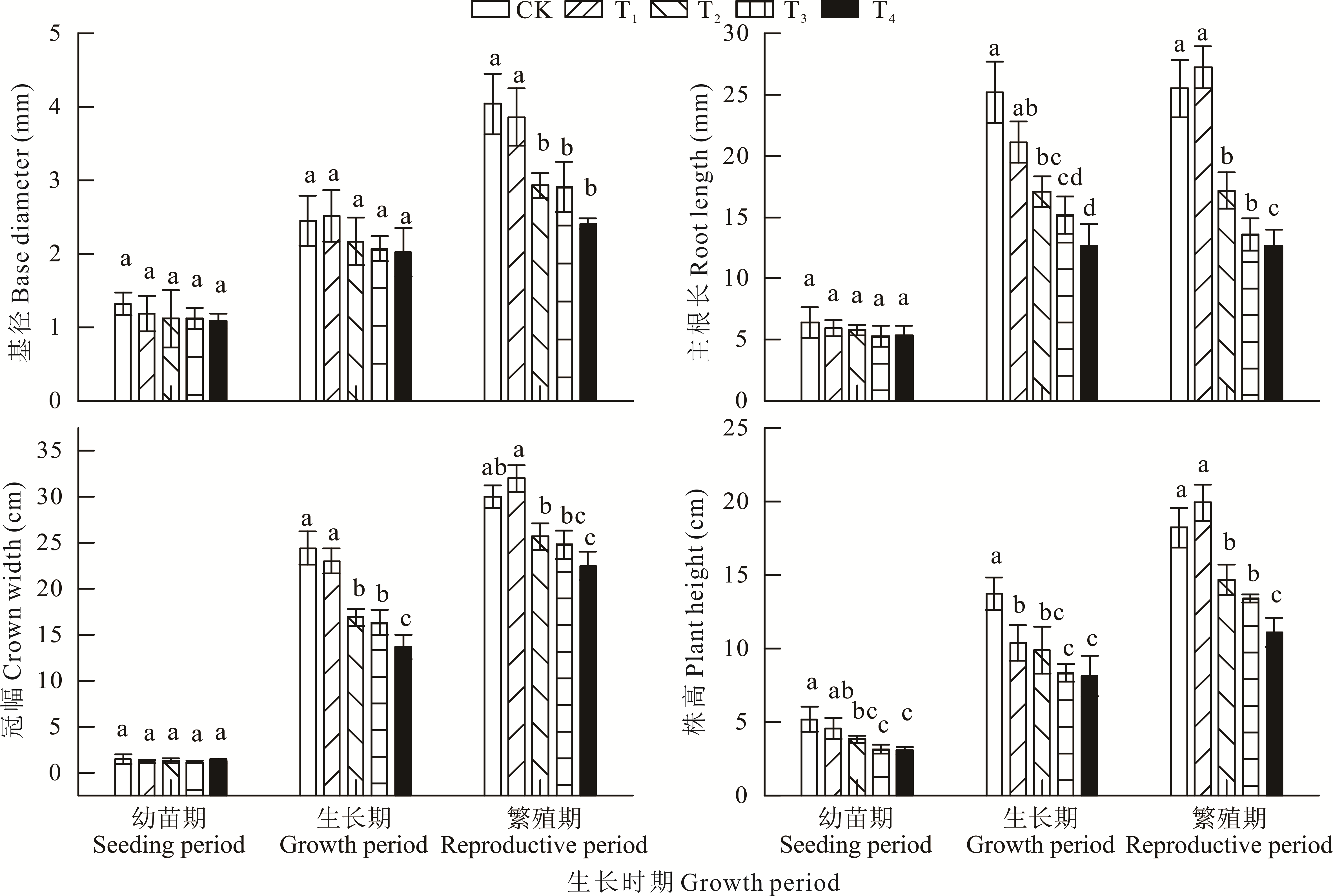
图2 水分胁迫对钠猪毛菜形态特征的影响不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different letters mean significant differences at the 0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.2 Effect of water stress on morphological characteristics of S. nitraria
生长时期 Growth period | 处理 Treatments | 根冠比 Root to crown ratio (%, mean±SD) | 根冠比胁迫指数 Root to crown ratio stress index |
|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling period | CK | 8.78±1.04a | 1.00 |
| T1 | 7.89±1.92a | 0.90 | |
| T2 | 8.38±1.95a | 0.95 | |
| T3 | 8.70±2.46a | 0.99 | |
| T4 | 8.98±0.60a | 1.02 | |
生长期 Growth period | CK | 15.24±0.63b | 1.00 |
| T1 | 10.11±1.13c | 0.66 | |
| T2 | 15.28±0.57b | 1.00 | |
| T3 | 17.73±0.77a | 1.16 | |
| T4 | 18.84±0.63a | 1.24 | |
繁殖期 Reproductive period | CK | 9.75±1.10c | 1.00 |
| T1 | 7.29±0.57d | 0.75 | |
| T2 | 11.71±0.80b | 1.20 | |
| T3 | 14.35±0.88a | 1.51 | |
| T4 | 15.82±1.03a | 1.62 |
表1 水分胁迫对钠猪毛菜根冠比及其胁迫指数的影响
Table 1 Effect of water stress on root-shoot ratio and stress index of S. nitraria
生长时期 Growth period | 处理 Treatments | 根冠比 Root to crown ratio (%, mean±SD) | 根冠比胁迫指数 Root to crown ratio stress index |
|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling period | CK | 8.78±1.04a | 1.00 |
| T1 | 7.89±1.92a | 0.90 | |
| T2 | 8.38±1.95a | 0.95 | |
| T3 | 8.70±2.46a | 0.99 | |
| T4 | 8.98±0.60a | 1.02 | |
生长期 Growth period | CK | 15.24±0.63b | 1.00 |
| T1 | 10.11±1.13c | 0.66 | |
| T2 | 15.28±0.57b | 1.00 | |
| T3 | 17.73±0.77a | 1.16 | |
| T4 | 18.84±0.63a | 1.24 | |
繁殖期 Reproductive period | CK | 9.75±1.10c | 1.00 |
| T1 | 7.29±0.57d | 0.75 | |
| T2 | 11.71±0.80b | 1.20 | |
| T3 | 14.35±0.88a | 1.51 | |
| T4 | 15.82±1.03a | 1.62 |
生长时期 Growth period | 处理 Treatments | 株高 Height (cm) | 基径 Base diameter (mm) | 冠幅 Crown (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g) | 地下生物量 Underground biomass (g) | 隶属函数值 Average membership function value | 评价 Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling period | CK | 0.503 | 0.243 | 0.440 | 0.517 | 0.450 | 0.600 | 0.459 | 2 |
| T1 | 0.576 | 0.602 | 0.555 | 0.633 | 0.429 | 0.600 | 0.566 | 5 | |
| T2 | 0.584 | 0.485 | 0.615 | 0.614 | 0.540 | 0.300 | 0.523 | 3 | |
| T3 | 0.605 | 0.454 | 0.412 | 0.434 | 0.500 | 0.300 | 0.451 | 1 | |
| T4 | 0.624 | 0.630 | 0.500 | 0.448 | 0.433 | 0.600 | 0.539 | 4 | |
生长期 Growth period | CK | 0.470 | 0.390 | 0.403 | 0.540 | 0.461 | 0.333 | 0.433 | 1 |
| T1 | 0.470 | 0.488 | 0.420 | 0.405 | 0.374 | 0.444 | 0.433 | 2 | |
| T2 | 0.490 | 0.581 | 0.629 | 0.589 | 0.565 | 0.467 | 0.553 | 5 | |
| T3 | 0.389 | 0.549 | 0.590 | 0.453 | 0.464 | 0.333 | 0.463 | 3 | |
| T4 | 0.370 | 0.467 | 0.600 | 0.506 | 0.478 | 0.600 | 0.504 | 4 | |
繁殖期 Reproductive period | CK | 0.494 | 0.617 | 0.508 | 0.511 | 0.662 | 0.532 | 0.554 | 5 |
| T1 | 0.493 | 0.532 | 0.569 | 0.510 | 0.573 | 0.632 | 0.552 | 4 | |
| T2 | 0.508 | 0.465 | 0.517 | 0.540 | 0.633 | 0.444 | 0.518 | 3 | |
| T3 | 0.250 | 0.537 | 0.553 | 0.526 | 0.387 | 0.580 | 0.472 | 1 | |
| T4 | 0.500 | 0.639 | 0.403 | 0.531 | 0.400 | 0.444 | 0.486 | 2 |
表2 不同水分处理下钠猪毛菜质量函数指标值及综合评价
Table 2 Quality function index value and comprehensive evaluation of S. nitraria under different water treatments
生长时期 Growth period | 处理 Treatments | 株高 Height (cm) | 基径 Base diameter (mm) | 冠幅 Crown (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g) | 地下生物量 Underground biomass (g) | 隶属函数值 Average membership function value | 评价 Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling period | CK | 0.503 | 0.243 | 0.440 | 0.517 | 0.450 | 0.600 | 0.459 | 2 |
| T1 | 0.576 | 0.602 | 0.555 | 0.633 | 0.429 | 0.600 | 0.566 | 5 | |
| T2 | 0.584 | 0.485 | 0.615 | 0.614 | 0.540 | 0.300 | 0.523 | 3 | |
| T3 | 0.605 | 0.454 | 0.412 | 0.434 | 0.500 | 0.300 | 0.451 | 1 | |
| T4 | 0.624 | 0.630 | 0.500 | 0.448 | 0.433 | 0.600 | 0.539 | 4 | |
生长期 Growth period | CK | 0.470 | 0.390 | 0.403 | 0.540 | 0.461 | 0.333 | 0.433 | 1 |
| T1 | 0.470 | 0.488 | 0.420 | 0.405 | 0.374 | 0.444 | 0.433 | 2 | |
| T2 | 0.490 | 0.581 | 0.629 | 0.589 | 0.565 | 0.467 | 0.553 | 5 | |
| T3 | 0.389 | 0.549 | 0.590 | 0.453 | 0.464 | 0.333 | 0.463 | 3 | |
| T4 | 0.370 | 0.467 | 0.600 | 0.506 | 0.478 | 0.600 | 0.504 | 4 | |
繁殖期 Reproductive period | CK | 0.494 | 0.617 | 0.508 | 0.511 | 0.662 | 0.532 | 0.554 | 5 |
| T1 | 0.493 | 0.532 | 0.569 | 0.510 | 0.573 | 0.632 | 0.552 | 4 | |
| T2 | 0.508 | 0.465 | 0.517 | 0.540 | 0.633 | 0.444 | 0.518 | 3 | |
| T3 | 0.250 | 0.537 | 0.553 | 0.526 | 0.387 | 0.580 | 0.472 | 1 | |
| T4 | 0.500 | 0.639 | 0.403 | 0.531 | 0.400 | 0.444 | 0.486 | 2 |
| 1 | Li Q Y, Lai L M, Zhou J H, et al. Water use characteristics of main species in different shrub encroachment stages on Ordos Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(1): 89-96. |
| 李巧燕, 来利明, 周继华, 等. 鄂尔多斯高原草地灌丛化不同阶段主要植物水分利用特征. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(1): 89-96. | |
| 2 | Yao X L, Zhou L, Feng M S, et al. Effects of drought stress on the growth and biomass of phoebe zhennan’ seedling in different substrates net container. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(1): 81-90. |
| 姚小兰, 周琳, 冯茂松, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同基质网袋桢楠幼苗生长及生物量的影响. 植物研究, 2018, 38(1): 81-90. | |
| 3 | Pigliucci M. Evolution of phenotypic plasticity: Where are we going now? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2005, 20(9): 481-486. |
| 4 | Sultan S E. Phenotypic plasticity for plant development, function and life history. Trends in Plant Science, 2000, 5(12): 537-542. |
| 5 | Gu Y B, Pan Y W, Chen F Y, et al. Effects of water level and nitrogen concentrationon growth and biomass allocation of Scirpus nipponicus seedlings. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(8): 2302-2309. |
| 古勇波, 潘艳文, 陈方圆, 等. 水位和氮浓度对三江藨草幼苗生长和生物量分配的影响. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(8): 2302-2309. | |
| 6 | Davidson R L. Effect of root/leaf temperature differentials on root/shoot ratios in some pasture grasses and clover. Annals of Botany, 1969, 33(131): 561-569. |
| 7 | Wang B S, Zhang R. Study of life-history strategy of farmland weeds in semi-arid areas. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(1): 257-260. |
| 王斌世, 张荣. 半干旱区农田杂草的生活史对策研究.草业学报, 2011, 20(1): 257-260. | |
| 8 | Zhang L, Lv G H, Jiang L M, et al. Relationship between primary productivity, carbon storage and functional traits of desert plants in arid regions. Journal of Xinjiang University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 37(1): 63-74. |
| 张磊, 吕光辉, 蒋腊梅, 等. 干旱区荒漠植物初级生产力及碳储量与功能性状之间的关系.新疆大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 37(1): 63-74. | |
| 9 | Zhang L Y, Hai Y. Plant communities excluded in the book of the vegetation and its utilization in XinJiang: I.The desert plant communities. Arid Land Geography , 2002(1): 84-89. |
| 张立运, 海鹰. 《新疆植被及其利用》专著中未曾记载的植物群落类型I.荒漠植物群落类型. 干旱区地理, 2002(1): 84-89. | |
| 10 | Zhang P, Zhang Q Q, Zhao X F, et al. Influence of nutrient and water additions on functional traits of Salsola nitraria in desert grassland. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(2): 134-146. |
| 张鹏, 张青青, 赵新风, 等. 养分与水分添加对荒漠草地植物钠猪毛菜功能性状的影响. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(2): 134-146. | |
| 11 | Eller F, Brix H. Different genotypes of Phragmites australis show distinct phenotypic plasticity in response to nutrient availability and temperature. Aquatic Botany, 2012, 103(Complete): 89-97. |
| 12 | Schlichting C D. The evolution of phenotypic plasticity in plants. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics, 1986, 17(1): 667-693. |
| 13 | Wang L L, Li Q H, Xu J, et al. Effects of drought stress to growth and morphological plasticity of different provenances of Artemisia ordosica seedings. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015, 43(10): 55-57,78. |
| 王林龙, 李清河, 徐军, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同种源油蒿幼苗的生长和形态可塑性的影响.东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(10): 55-57,78. | |
| 14 | Le Y. Study on seeding plasticity in Xanthoceras sorbifolium bunge under light stress. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University, 2015. |
| 乐也. 减光胁迫下文冠果幼苗可塑性研究. 北京:北京林业大学, 2015. | |
| 15 | Pang S L, Ou Z Y, Shen W H, et al. Effect of drought stress on phenotypic plasticity of Excentrodendron hsienmu seedlings. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2017, 37(5): 21-25. |
| 庞世龙, 欧芷阳, 申文辉, 等. 干旱胁迫对蚬木幼苗表型可塑性的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2017, 37(5): 21-25. | |
| 16 | Cao Y E, Zhang T T, Yang J J, et al. Grain sizes analysis and estimation on wind erosion amount in different land-use types of zhundong area.Journal of Xinjiang University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 34(2): 140-145. |
| 曹月娥, 张婷婷, 杨建军, 等. 准东地区不同土地利用类型土壤粒度特征分析及风蚀量估算.新疆大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 34(2): 140-145. | |
| 17 | Guenni O , Baruch Z , Douglas M. Responses to drought of five Brachiaria species. II. Water relations and leaf gas exchange. Plant & Soil, 2004, 258(1): 249-260. |
| 18 | Sun J, Ma B, Lu X. Grazing enhances soil nutrient effects: Trade‐offs between aboveground and belowground biomass in alpine grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 2018, 29(2): 337-348. |
| 19 | Sun J, Wang H. Soil nitrogen and carbon determine the trade-off of the above- and below-ground biomass across alpine grasslands, Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 60: 1070-1076. |
| 20 | Zhang S C, Yuan F, Guo J R, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on salt-tolerance of Sorghum bicolor seedlings by subordinate function values analysis. Plant Physiology Journal, 2015, 51(6): 893-902. |
| 张士超, 袁芳, 郭建荣, 等. 利用隶属函数值法对甜高粱苗期耐盐性的综合评价. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(6): 893-902. | |
| 21 | Gao X F, Wang J X, Zhan B, et al. Effects of drought stress on dry matter partitioning of young Robinia pseudoacacia at its different growth stages. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(6): 1103-1108. |
| 高小锋, 王进鑫, 张波, 等. 不同生长期干旱胁迫对刺槐幼树干物质分配的影响. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 1103-1108. | |
| 22 | Wang J, Ji L, Zhang Z H, et al. Effects of water stress on phenotypic plasticity of Quercus mongolica seedlings grown in two soil substrates. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(1): 51-59. |
| 王君, 及利, 张忠辉, 等. 不同土壤基质下水分胁迫对蒙古栎幼苗表型可塑性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(1): 51-59. | |
| 23 | Zhu T X, Gao Y, Gao K, et al. Organ biomass and resource allocation in response to drought stress in Jerusalem artichoke. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 39(21): 8021-8026. |
| 朱铁霞, 高阳, 高凯, 等. 干旱胁迫下菊芋各器官生物量及物质分配规律. 生态学报, 2019, 39(21): 8021-8026. | |
| 24 | Wei H D, Chen F, Zhang B, et al. Analysis of the canopy spectrum and water content of desert plants. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(3): 590-596. |
| 魏怀东, 陈芳, 张勃, 等. 民勤10种典型荒漠植物冠层光谱与含水率的特征分析. 草业科学, 2018, 35(3): 590-596. | |
| 25 | Wang W F, Duan Y X, Li S B, et al. Biomass allocation and soil water content characteristics of three typical shrubs in Mu Us sandy land. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2018, 47(3): 45-49. |
| 王伟峰, 段玉玺, 李少博, 等. 毛乌素沙地3种典型灌木生物量分配与土壤含水量特征. 西部林业科学, 2018, 47(3): 45-49. | |
| 26 | Fan H, Wu J, Liu W, et al. Linkages of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant & Soil, 2015, 392(12): 127-138. |
| 27 | Petter N. Effect of nitrogen on drought strain and nutrient uptake in Norway Spruce Picea abies (L.) Karst. trees. Plant & Soil, 1995, 172(1): 73-85. |
| 28 | Wang K, Shen C, Sun B, et al. Effects of drought stress on C, N and P stoichiometry of Ulmus pumila seedlings in Horqin sandy land, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(7): 2286-2294. |
| 王凯, 沈潮, 孙冰, 等. 干旱胁迫对科尔沁沙地榆树幼苗C、N、P化学计量特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(7): 2286-2294. | |
| 29 | Sabine G. N : P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. 2004, 164(2): 243-266. |
| 30 | Yang D M, Zhan F, Zhang H W. Trade-off between leaf size and number in current-year twigs of deciduous broad-leaved woody species at different altitudes on Qingliang Mountain, southeastern China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(4): 281-291. |
| 杨冬梅, 占峰, 张宏伟. 清凉峰不同海拔木本植物小枝内叶大小-数量权衡关系. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(4): 281-291. | |
| 31 | Ma X Y, Zhou G S. Effects of drought on the trade-off growth of leaf traits of summer maize in the seedling stage. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(5): 1758-1769. |
| 麻雪艳, 周广胜. 干旱对夏玉米苗期叶片权衡生长的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(5): 1758-1769. |
| [1] | 黄海霞, 杨琦琦, 崔鹏, 陆刚, 韩国君. 裸果木幼苗根系形态和生理特征对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 197-207. |
| [2] | 雷恩, 邵迪, 朱天彪, 舒星, 杨永兵, 王岳东, 唐启源. 饲用玉米器官含水率、力学强度与籽粒机收质量的关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 125-135. |
| [3] | 徐洪雨, 李向林. 控水处理对紫花苜蓿抗寒性影响的代谢组学分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 106-116. |
| [4] | 马蕾, 马绍英, 陈贵平, 柴强, 李胜. 豌豆与根瘤共生对水分胁迫的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 96-109. |
| [5] | 王梦茹, 魏岩. 古尔班通古特沙漠钠猪毛菜种子异型性及其萌发行为研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 85-92. |
| [6] | 李州, 彭燕, 尹淑霞, 韩烈保. 甘露糖对白三叶抗旱性、糖及糖醇类代谢物积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 85-93. |
| [7] | 范高华, 黄迎新, 赵学勇, 神祥金. 种群密度对沙米异速生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(3): 53-64. |
| [8] | 漆永红, 岳德成, 曹素芳, 李敏权. 全膜双垄沟播玉米土壤含水率和温度及杂草去除效应[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 176-184. |
| [9] | 李帅, 赵国靖, 徐伟洲, 高志娟, 吴爱姣, 徐炳成. 白羊草根系形态特征对土壤水分阶段变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 169-177. |
| [10] | 时振振, 李胜, 马绍英, 王雅梅, 苏李维, 唐斌, 赵生琴, 苏利荣. 不同品种小麦抗氧化系统对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 68-78. |
| [11] | 李州,彭燕. 亚精胺对水分胁迫下白三叶脯氨酸代谢、抗氧化酶活性及其基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 148-156. |
| [12] | 缪秀梅, 张丽静, 陈晓龙, 吴淑娟, 牛得草, 傅华. 水分胁迫下白沙蒿幼苗抗性与其膜脂构成关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 55-61. |
| [13] | 李州,王晓娟,彭丹丹,彭燕. Na+对水分胁迫下白三叶抗氧化防御和有机渗透调节物质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(5): 175-183. |
| [14] | 罗永忠,李广. 土壤水分胁迫对新疆大叶苜蓿的生长及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 213-219. |
| [15] | 何春雨,杜久元,刘广才,柴强,张礼军,申三宝,鲁清林,黄高宝. 全膜覆土穴播冬小麦农田土壤含水率与耗水量时空动态[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(1): 131-141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||