

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 75-85.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021439
周力1,2( ), 王志有1, 杨葆春1, 侯生珍1, 张峰硕1, 桂林生1(
), 王志有1, 杨葆春1, 侯生珍1, 张峰硕1, 桂林生1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-27
修回日期:2022-01-17
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-10-01
通讯作者:
桂林生
作者简介:E-mail: 3085968221@qq.com基金资助:
Li ZHOU1,2( ), Zhi-you WANG1, Bao-chun YANG1, Sheng-zhen HOU1, Feng-shuo ZHANG1, Lin-sheng GUI1(
), Zhi-you WANG1, Bao-chun YANG1, Sheng-zhen HOU1, Feng-shuo ZHANG1, Lin-sheng GUI1( )
)
Received:2021-11-27
Revised:2022-01-17
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-10-01
Contact:
Lin-sheng GUI
摘要:
为探讨不同中性洗涤纤维(NDF)饲粮对青海黑藏羊体尺指数、肌纤维类型组成及肉品质的影响。选取40只体况良好、体重相近[(10.28±0.43) kg]的2月龄黑藏羊,随机分为2组,每组20只,分别饲喂NDF为26.33%(L组)和46.14%(H组)的饲粮。通过酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)、ATP酶(ATPase)组织化学染色以及实时荧光定量PCR(real-time qPCR)对黑藏羊背最长肌的肌纤维特性、肌球蛋白重链(MyHCs)基因表达量及肉质特性进行了研究。结果显示:1)H组体躯指数显著小于L组(P<0.05)。2)H组Ⅱa型肌纤维数量比例显著大于L组(P<0.05),H组Ⅰ型和Ⅱa型肌纤维面积比例亦大于L组(P<0.05)。3)L组MyHC Ⅰ和MyHC Ⅱa基因的mRNA表达量显著小于H组(P<0.05),而MyHC Ⅱb和MyHC Ⅱx基因的mRNA表达量则相反(P<0.05)。4)相较于L组,H组超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)含量均提高,丙二醛(MDA)含量下降,其中二者总抗氧化能力差异显著(P<0.05)。5)L组剪切力显著大于H组(P<0.05),而红度(a*)则相反(P<0.05)。综上,与低水平NDF饲粮相比,高水平NDF饲粮条件下黑藏羊可有效减少酵解型肌纤维数量比例,并增强其抗氧化能力,在一定程度上能改善肉品质。
周力, 王志有, 杨葆春, 侯生珍, 张峰硕, 桂林生. 饲粮中性洗涤纤维水平对黑藏羊肌纤维类型组成比例与肉质特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 75-85.
Li ZHOU, Zhi-you WANG, Bao-chun YANG, Sheng-zhen HOU, Feng-shuo ZHANG, Lin-sheng GUI. Effects of dietary neutral detergent fiber on muscle fiber type composition and meat quality characteristics of black Tibetan sheep[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 75-85.
| 项目Items | H组Group H | L组 Group L |
|---|---|---|
| 原料 Ingredients | ||
| 燕麦青干草 Oat hay (%) | 35.00 | 15.00 |
| 燕麦青贮 Oat silage (%) | 35.00 | 15.00 |
| 玉米 Corn (%) | 16.14 | 40.05 |
| 菜籽粕 Rapeseed meal (%) | 2.28 | 14.13 |
| 棉籽粕 Cottonseed meal (%) | 2.22 | 6.39 |
| 豆粕 Soybean meal (%) | 2.16 | 2.23 |
| 食盐 NaCl (%) | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 石粉 Limestone (%) | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 小苏打 NaHCO3 (%) | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 磷酸氢钙 CaHPO4 (%) | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| 预混料 Premix1)(%) | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 合计 Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 营养水平Nutrient levels 2) | ||
| 消化能 Digestive energy (DE, MJ.kg-1) | 12.58 | 12.65 |
| 粗蛋白质 Crude protein (CP, %) | 13.78 | 13.86 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fibre (NDF, %) | 46.14 | 26.33 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 29.17 | 16.15 |
| 钙 Calcium (Ca, %) | 0.95 | 1.02 |
| 磷 Phosphorus (P, %) | 0.41 | 0.53 |
表1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平
Table 1 Basal diet composition and nutrient
| 项目Items | H组Group H | L组 Group L |
|---|---|---|
| 原料 Ingredients | ||
| 燕麦青干草 Oat hay (%) | 35.00 | 15.00 |
| 燕麦青贮 Oat silage (%) | 35.00 | 15.00 |
| 玉米 Corn (%) | 16.14 | 40.05 |
| 菜籽粕 Rapeseed meal (%) | 2.28 | 14.13 |
| 棉籽粕 Cottonseed meal (%) | 2.22 | 6.39 |
| 豆粕 Soybean meal (%) | 2.16 | 2.23 |
| 食盐 NaCl (%) | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 石粉 Limestone (%) | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 小苏打 NaHCO3 (%) | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 磷酸氢钙 CaHPO4 (%) | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| 预混料 Premix1)(%) | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 合计 Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 营养水平Nutrient levels 2) | ||
| 消化能 Digestive energy (DE, MJ.kg-1) | 12.58 | 12.65 |
| 粗蛋白质 Crude protein (CP, %) | 13.78 | 13.86 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fibre (NDF, %) | 46.14 | 26.33 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 29.17 | 16.15 |
| 钙 Calcium (Ca, %) | 0.95 | 1.02 |
| 磷 Phosphorus (P, %) | 0.41 | 0.53 |
Sequence of primer | GenBank 登录号 GenBank accession No. | 退火温度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyHC Ⅰ | XM-004010325.3 | |||
| MyHC Ⅱa | XM-012122422.2 | |||
| MyHC Ⅱb | XM-027974884.1 | |||
| MyHC Ⅱx | XM-004012706.4 | |||
| β-actin | F:GAGCGCAAGTACTCCGTGTG R:CATTTGCGGTGGACGATG | NM-001009784.1 |
表2 实时定量PCR引物
Table 2 Primer sequences used for real-time PCR
Sequence of primer | GenBank 登录号 GenBank accession No. | 退火温度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyHC Ⅰ | XM-004010325.3 | |||
| MyHC Ⅱa | XM-012122422.2 | |||
| MyHC Ⅱb | XM-027974884.1 | |||
| MyHC Ⅱx | XM-004012706.4 | |||
| β-actin | F:GAGCGCAAGTACTCCGTGTG R:CATTTGCGGTGGACGATG | NM-001009784.1 |
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| 体躯指数Tagma index | 115.48±3.06a | 101.03±6.78b | 0.039 |
| 体长指数 Body length index | 99.44±4.25 | 87.66±2.03 | 0.098 |
| 胸围指数 Heart girth index | 112.80±5.03 | 100.55±7.26 | 0.071 |
表3 不同NDF饲粮对黑藏羊体尺指数的影响
Table 3 Effects of different NDF diets on body size index of black Tibetan sheep (%)
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| 体躯指数Tagma index | 115.48±3.06a | 101.03±6.78b | 0.039 |
| 体长指数 Body length index | 99.44±4.25 | 87.66±2.03 | 0.098 |
| 胸围指数 Heart girth index | 112.80±5.03 | 100.55±7.26 | 0.071 |
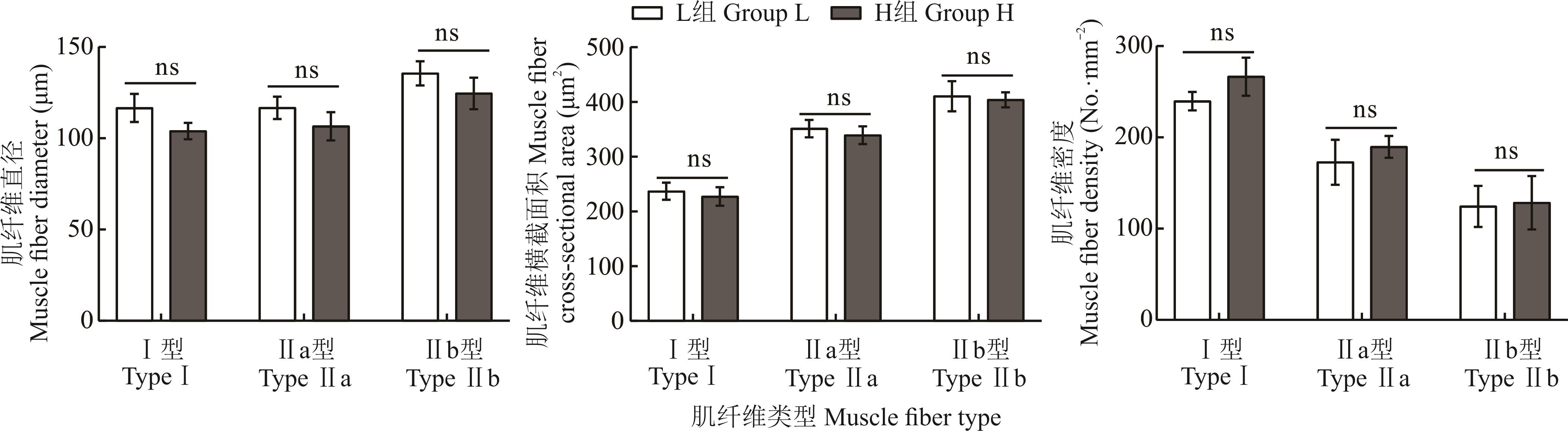
图2 不同NDF饲粮下黑藏羊肌纤维的直径、横截面积和密度*表示差异显著(P<0.05),ns表示差异不显著(P>0.05), 下同。* means significant differences (P<0.05), ns means no significant difference (P>0.05), the same below.
Fig.2 Muscle fiber diameter, cross-sectional area and density of black Tibetan sheep in different NDF diets
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| Ⅰ | 9.11±1.36 | 10.68±1.05 | 0.058 |
| Ⅱa | 23.71±4.62b | 30.57±5.11a | 0.017 |
| 67.18±7.02 | 58.75±6.84 | 0.061 | |
表4 不同NDF饲粮对黑藏羊肌纤维数量比例的影响
Table 4 Effects of different NDF diets on the proportion of muscle fiber in black Tibetan sheep (%)
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| Ⅰ | 9.11±1.36 | 10.68±1.05 | 0.058 |
| Ⅱa | 23.71±4.62b | 30.57±5.11a | 0.017 |
| 67.18±7.02 | 58.75±6.84 | 0.061 | |
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| Ⅰ | 2.95±0.43b | 3.87±0.51a | 0.036 |
| Ⅱa | 5.84±0.67b | 9.74±1.02a | 0.025 |
| 91.21±8.83 | 86.39±8.06 | 0.078 | |
表5 不同NDF饲粮对黑藏羊肌纤维面积比例的影响
Table 5 Effects of different NDF diets on the area of muscle fiber in black Tibetan sheep (%)
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| Ⅰ | 2.95±0.43b | 3.87±0.51a | 0.036 |
| Ⅱa | 5.84±0.67b | 9.74±1.02a | 0.025 |
| 91.21±8.83 | 86.39±8.06 | 0.078 | |
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
超氧化物歧化酶 SOD (ng·mL-1) | 15.37±0.86 | 15.83±0.94 | 0.466 |
过氧化氢酶 CAT (ng·mL-1) | 153.86±4.42 | 155.53±5.51 | 0.653 |
谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 GSH-Px (pg·mL-1) | 277.64±10.01 | 308.07±20.92 | 0.117 |
总抗氧化能力 T-AOC (U·mL-1) | 15.87±1.35b | 19.53±2.03a | 0.041 |
| 丙二醛 MDA (nmol·mL-1) | 6.43±0.80 | 6.22±0.25 | 0.256 |
表6 不同NDF饲粮对黑藏羊肌肉抗氧化能力的影响
Table 6 Effects of different NDF diets on muscle antioxidant capacity of black Tibetan sheep
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
超氧化物歧化酶 SOD (ng·mL-1) | 15.37±0.86 | 15.83±0.94 | 0.466 |
过氧化氢酶 CAT (ng·mL-1) | 153.86±4.42 | 155.53±5.51 | 0.653 |
谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 GSH-Px (pg·mL-1) | 277.64±10.01 | 308.07±20.92 | 0.117 |
总抗氧化能力 T-AOC (U·mL-1) | 15.87±1.35b | 19.53±2.03a | 0.041 |
| 丙二醛 MDA (nmol·mL-1) | 6.43±0.80 | 6.22±0.25 | 0.256 |
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| pH | 6.02±0.08 | 6.26±0.21 | 0.102 |
| 亮度Lightness (L*) | 27.42±2.65 | 24.67±1.68 | 0.089 |
| 红度Redness (a*) | 9.88±2.04b | 14.15±3.61a | 0.017 |
| 黄度Yellowness (b*) | 5.80±0.32 | 5.11±0.63 | 0.095 |
| 剪切力 Shear force (N) | 44.02±5.23a | 36.37±4.20b | 0.042 |
| 蒸煮损失 Cooking loss (%) | 38.87±7.12 | 36.28±3.69 | 0.059 |
表7 不同NDF饲粮对黑藏羊肌肉食用品质的影响
Table 7 Effects of different NDF diets on muscle dietary quality of black Tibetan sheep
P值 P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L组 Group L | H组 Group H | ||
| pH | 6.02±0.08 | 6.26±0.21 | 0.102 |
| 亮度Lightness (L*) | 27.42±2.65 | 24.67±1.68 | 0.089 |
| 红度Redness (a*) | 9.88±2.04b | 14.15±3.61a | 0.017 |
| 黄度Yellowness (b*) | 5.80±0.32 | 5.11±0.63 | 0.095 |
| 剪切力 Shear force (N) | 44.02±5.23a | 36.37±4.20b | 0.042 |
| 蒸煮损失 Cooking loss (%) | 38.87±7.12 | 36.28±3.69 | 0.059 |
| 1 | Şirin E, Aksoy Y, Ugurlu M, et al. The relationship between muscle fiber characteristics and some meat quality parameters in Turkish native sheep breeds. Small Ruminant Research, 2017, 150(10): 46-51. |
| 2 | Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiological Reviews, 2011, 91(4): 1447-1531. |
| 3 | Wang L. The effect of muscle fiber types and their differences in metabolic enzymes activity on postmortem tenderness of yak meat. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 王莉. 牦牛肉肌纤维类型组成及其代谢酶活力差异对宰后肉嫩度的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2016. | |
| 4 | Liang J, Zhang W J, Wang B. Research progress on influence factors of mutton quality. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 43(5): 1250-1254. |
| 梁静, 张文举, 王博. 影响羊肉品质因素的研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(5): 1250-1254. | |
| 5 | Zhou L, Zhang Y Y, Yang B C, et al. Effects of different NFC/NDF diets on nutritional components, amino acids and fatty acid contents of plateau type Tibetan sheep. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2021, 41(9): 1841-1847. |
| 周力, 张莹莹, 杨葆春, 等. 不同NFC/NDF饲粮对高原型藏羊肌肉营养成分、氨基酸及脂肪酸含量的影响. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41(9): 1841-1847. | |
| 6 | Zhou L, Gao Z H, Zhang C M, et al. Effects of different NFC/NDF diets on antioxidant function, myofiber type composition and related gene expression of Qinghai Tibetan ewes. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2021, 39(5): 639-645. |
| 周力, 高占红, 张春梅, 等. 不同NFC/NDF饲粮对青海藏羊育成母羊肌肉抗氧化功能、肌纤维类型组成及其相关基因表达的影响. 四川农业大学学报, 2021, 39(5): 639-645. | |
| 7 | Lang Y M, Wang Y F, Li J, et al. Study on muscle fiber types and meat quality traits of Chinese Simmental cattle. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 43(6): 1489-1493. |
| 郎玉苗, 王勇峰, 李敬, 等. 中国西门塔尔牛肌肉肌纤维类型和肉品质特性研究. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(6): 1489-1493. | |
| 8 | Zhao Y J, Yin L Q, Su L, et al. Effect of different feeding systems on muscle fiber types of longissimus doris from Sunit sheep. Food Science, 2017, 38(19): 30-34. |
| 赵雅娟, 尹丽卿, 苏琳, 等. 不同饲养方式对苏尼特羊背最长肌肌纤维类型组成的影响. 食品科学, 2017, 38(19): 30-34. | |
| 9 | Wang J Q, Lu D X, Yang H J, et al. Feeding standard of meat-producing sheep and goats, NY-T 816-2004. Beijing: Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2004. |
| 王加启, 卢德勋, 杨红建, 等. 肉羊饲养标准, NY-T 816-2004. 北京: 中华人民共和国农业部, 2004. | |
| 10 | Brooke M H, Kaiser K K. Three“myosin adenosine triphosphatase”systems:the nature of their pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry, 1970, 18(9): 670-672. |
| 11 | Wong M L, Medrano J. Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation.Biotechniques, 2005, 39(1): 75. |
| 12 | Yang L, Zhang W J, Zhang X Y, et al. Effect of different carbohydrate sources on growth performance, body size indexes and nutrients apparent digestibility of beef calves. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(6): 1726-1733. |
| 杨亮, 张文举, 张晓羊, 等. 不同糖源对肉用犊牛生长性能、体尺指数及营养物质表观消化率的影响. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44(6): 1726-1733. | |
| 13 | Xu T S, Wang D J, Liu X L, et al. A research on path analysis and optimum regression equation between body size and body weight of hainan black goat. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2005(1): 49-53. |
| 徐铁山, 王东劲, 刘小林, 等. 海南黑山羊体尺与体重的通径分析及最优回归模型的建立. 家畜生态学报, 2005(1): 49-53. | |
| 14 | Yang Z F, Li Z M, Li A H. Effect of adding fermented apple pomace on the growth performance of calf. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 37(1): 93-96. |
| 杨志峰, 李作明, 李爱华. 日粮中添加发酵苹果渣对犊牛生长性能的影响. 农业科学研究, 2016, 37(1): 93-96. | |
| 15 | Meng Y, Zan L S, Liang H W, et al. The measure of GH and INS and analysis of body measurement and weight of Qinchuan cattle. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2004, 20(5): 9-11. |
| 孟彦, 昝林森, 梁宏伟, 等. 秦川牛GH、INS的测定及体尺、体重分析. 中国农学通报, 2004, 20(5): 9-11. | |
| 16 | Cheng Y X, Tang Y G, Guo M, et al. Calculation and analysis on body measurement index most in use of Holstein cows in Mayishan cow farm. China Herbivores, 2005, 25(6): 28-30. |
| 程郁昕, 唐义国, 郭蜜, 等. 蚂蚁山奶牛场奶牛常用体尺指数的计算及分析. 中国草食动物, 2005, 25(6): 28-30. | |
| 17 | Lee S H, Choe J H, Choi Y M, et al. The influence of pork quality traits and muscle fiber characteristics on the eating quality of pork from various breeds. Meat Science, 2011, 90(2): 284-291. |
| 18 | Joo S T, Kim G D, Hwang Y H, et al. Control of fresh meat quality through manipulation of musclefiber characteristics. Meat Science, 2013, 95(4): 828-836. |
| 19 | Makin C A, Warkup C C, Mathews K R, et al. Pig muscle fibre characteristics as a source of variation in eating quality. Meat Science, 1997, 47(3/4): 237-248. |
| 20 | Choi Y M, Kio B C. Muscle fiber characteristics, myofibrillar protein isoforms, and meat quality. Livestock Science, 2009, 122(2/3): 105-118. |
| 21 | Offer G. Modelling of the formation of pale soft and exudative meat: Effect of chilling regime and rat and extent of glycolysis. Meat Science, 1991, 30(2): 157-184. |
| 22 | Renand G, Picard B, Touraille C, et al. Relationships between muscle characteristics and meat quality traits of young Charolais bulls. Meat Science, 2001, 59(1): 49-60. |
| 23 | Kim G D, Kim B W, Jeong J Y, et al. Relationship of carcass weight to muscle fiber characteristics and pork quality of crossbred(Korean Native Black Pig×Landrace) F2 pigs. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2013, 6(2): 522-529. |
| 24 | Zou Y, Wang Y J, Deng Y F, et al. Effects of feeding untreated, pasteurized and acidified waste milk and bunk tank milk on the performance, serum metabolic profiles, immunity, and intestinal development in Holstein calves. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2017, 8(4): 934-944. |
| 25 | Rossi R, Pastorelli G, Cannata S, et al. Effect of long term dietary supplementation with plant extract on carcass characteristics meat quality and oxidative stability in pork. Meat Science, 2013, 95(3): 542-548. |
| 26 | Huang J Y, Jiao J Z, Ran T, et al. Study on the developmental changes of meat and antioxidant capacity of grazing and house-feeding goats. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(14): 2827-2838. |
| 黄金玉, 焦金真, 冉涛, 等. 放牧与舍饲条件下山羊肌肉发育和抗氧化能力变化研究. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(14): 2827-2838. | |
| 27 | Sun Q, Jin E H, Zhou X J, et al. Effect of compound chinese herbal medicine on muscle antioxidant capacity of AA Broilers. Journal of Anhui Science and Technology University, 2017, 31(1): 19-24. |
| 孙启, 靳二辉, 周先建, 等. 复方中草药对AA肉鸡肌肉抗氧化能力的影响. 安徽科技学院学报, 2017, 31(1): 19-24. | |
| 28 | Tao X, Xu Z R, Wang Y Z. Effects of dietary fluoride levels on growth, serum indexes and antioxidant systems in growing pigs. Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Science, 2006, 30(1): 65-70. |
| 29 | Blaszczyk I, Grucka-Mamczar E, Kasperczyk S, et al. Influence of fluoride on rat kidney antioxidant system: Effects of methionine and vitamine. Biological Trace Element Research, 2008, 121(1): 51-59. |
| 30 | Nagaraga T G, Lechtenberg K F. Acidosis infeed lot cattle. Food Animal Practice, 2007, 23(2): 333-350. |
| 31 | Jiang N, Zhu Y B, Sun G M, et al. Effects of roughage to concentrate ratio on nutrient apparent digestibility, plasma biochemical parameters and antioxidant capacity of yak. China Herbivore Science, 2021, 41(3): 43-48. |
| 姜南, 朱彦宾, 孙光明, 等. 不同精粗比饲粮对牦牛养分表观消化率、血浆生化及抗氧化指标的影响. 中国草食动物科学, 2021, 41(3): 43-48. | |
| 32 | Shi L G, Zhao C P, Cao T, et al. Effects of different dietary concentration ratio on antioxidant performance of Hainan black goat. Chinese Herbivorous Science, 2015, 35(1): 29-31. |
| 施立光, 赵春萍, 曹婷, 等. 不同日粮精粗比对海南黑山羊抗氧化性能的影响. 中国草食动物科学, 2015, 35(1): 29-31. | |
| 33 | Wu G, Farouk M M, Clerens S, et al. Effect of beef ultimate pH and large structural protein changes with aging on meat tenderness. Meat Science, 2014, 98(4): 637-645. |
| 34 | De Araújo T L A C, Pereira E S, Mizubuti I Y, et al. Effects of quantitative feed restriction and sex on carcass traits, meat quality and meat lipid profile of Morada Nova lambs. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2017, 8(1): 993-1003. |
| 35 | Khliji S, Van De Ver R, Lamb T A, et al. Relationship between consumer ranking of lamb colour and objective measures of colour. Meat Science, 2010, 85(2): 224-229. |
| 36 | Mancini R A, Hunt M C. Current research in meat color. Meat Science, 2005, 71(1): 100-121. |
| 37 | Wang T, Hou M J, Shang Z H, et al. Characteristics of muscle fibers and relative meat quality of fattening sheep fed sweet sorghum silage and corn silage diets. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(11): 2722-2727. |
| 王婷, 侯明杰, 尚占环, 等. 甜高粱和玉米青贮对肉羊肌纤维组织及其相关肉质性状的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(11): 2722- 2727. | |
| 38 | Hou P X, Hou Y R, Bai Y P, et al. Effect of dietary linseed supplementation on muscle fiber characteristics and meat quality of Sunit sheep. Food Science, 2020, 41(11): 36-42. |
| 侯普馨, 侯艳茹, 白艳苹, 等. 日粮添加亚麻籽对苏尼特羊肌纤维特性及肉品质的影响. 食品科学, 2020, 41(11): 36-42. | |
| 39 | Guo P T, Mao F X, Luo H L, et al. The effect of concentrate supplement on production performance and meat quality of sheep and goats of Guizhou Province. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2015, 51(19): 33-37. |
| 郭娉婷, 毛凤显, 罗海玲, 等. 补饲精料对贵州地区绵山羊生产性能及肉品质的影响. 中国畜牧杂志, 2015, 51(19): 33-37. | |
| 40 | Shi A, Zhang J L, Li J C, et al. Effects of different concentrated protein levels on growing-fattening of Huangquqiao lamb. Feed Research, 2019(5): 1-4. |
| 施安, 张俊丽, 李聚才, 等. 不同蛋白营养水平精补料对黄渠桥羔羊生长育肥性能的影响. 饲料研究, 2019(5): 1-4. |
| [1] | 张耀, 黄小云, 陈鑫珠, 黄勤楼, 黄秀声, 韩海东. 海鲜菇菌糠发酵饲料对山羊屠宰性能及肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 195-205. |
| [2] | 范阳, 齐伟彪, 朱崇淼, 殷雨洋, 毛胜勇. 日粮中添加发酵豆渣对湖羊生长性能、养分表观消化率、肉品质及血清生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 86-93. |
| [3] | 孙旺斌, 付琪, 薛瑞林, 王伟萍, 张骞, 冯平. 不同枣粉添加水平对陕北白绒山羊屠宰性能和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 111-121. |
| [4] | 黄丽琴, 李松桥, 袁振中, 唐晶, 闫景彩, 唐启源. 全株水稻与平菇菌糠共发酵料对浏阳黑山羊屠宰性能、肉品质和器官指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [5] | 张生伟, 王小平, 张展海, 马友记, 滚双宝, 杨巧丽, 高小莉, 张保军. 青贮杂交构树对杜湖杂交肉羊生长性能、血清生化指标和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. |
| [6] | 王继卿, 沈继源, 刘秀, 李少斌, 罗玉柱, 赵孟丽, 郝志云, 柯娜, 宋宜泽, 乔莉蓉. 子午岭黑山羊与辽宁绒山羊产肉性能、肉品质、肌肉营养成分和脂肪酸含量比较[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 166-177. |
| [7] | 吴爽, 周玉香, 贾柔, 金亚东, 杨万宗. 纤维素酶处理荞麦秸秆对其纤维结构和滩羊肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 170-180. |
| [8] | 杨勤, 官久强, 柴志欣, 李华德, 曹诗晓, 张翔飞, 柏琴, 钟金城, 罗晓林. 低海拔舍饲对牦牛肌肉品质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 33-42. |
| [9] | 李柯, 周庄煜, 李四菊, 姚浩铮, 周莹, 缪雨静, 唐晓清, 王康才. 荆芥的生长、渗透调节和抗氧化能力对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 150-158. |
| [10] | 占今舜, 霍俊宏, 胡耀, 钟小军, 武艳平. 不同精粗比全混合日粮对努比亚山羊肉品质、血清指标和器官发育的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 139-148. |
| [11] | 都帅, 尤思涵, 包健, 格根图, 贾玉山. 补饲精料对乌珠穆沁羊生产性能、屠宰性能和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 196-203. |
| [12] | 苗建军, 彭忠利, 高彦华, 郭春华, 王鼎, 付洋洋. 青稞替代玉米对育肥牦牛生产性能和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 95-107. |
| [13] | 李欢欢, 史莹华, 张晓霞, 刘晓, 贾泽统, 王成章. 不同亚麻酸水平及饲料组成对育肥猪生长性能和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 98-107. |
| [14] | 葛莉, 姚园园, 康天兰, 李京耀, 何恒军, 杨德龙, 栗孟飞. 不同收获期贯叶连翘花中抗氧化能力、主要活性物质变化及挥发性组分分离鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 66-74. |
| [15] | 李江文, 李治国, 蒋立宏, 靳宇曦, 王舒新, 韩梦琪, 于丰源, 韩国栋. 呼伦贝尔短尾羊产前补饲精喂对家畜个体特征及生产效益的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 90-97. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||