

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 14-24.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020563
潘占东1,2( ), 马倩倩1,2, 陈晓龙1,2, 蔡立群1,2(
), 马倩倩1,2, 陈晓龙1,2, 蔡立群1,2( ), 蔡雪梅1,2, 董博1,3, 武均1,2, 张仁陟1,2
), 蔡雪梅1,2, 董博1,3, 武均1,2, 张仁陟1,2
收稿日期:2020-12-15
修回日期:2021-03-10
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2021-12-22
通讯作者:
蔡立群
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: cailq@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhan-dong PAN1,2( ), Qian-qian MA1,2, Xiao-long CHEN1,2, Li-qun CAI1,2(
), Qian-qian MA1,2, Xiao-long CHEN1,2, Li-qun CAI1,2( ), Xue-mei CAI1,2, Bo DONG1,3, Jun WU1,2, Ren-zhi ZHANG1,2
), Xue-mei CAI1,2, Bo DONG1,3, Jun WU1,2, Ren-zhi ZHANG1,2
Received:2020-12-15
Revised:2021-03-10
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2021-12-22
Contact:
Li-qun CAI
摘要:
黄土高原水土流失严重,导致部分土壤养分和质量明显下降。生物质炭在土壤改良方面被广泛应用,能提高作物产量和土壤生物活性水平。然而,生物质炭是否可以通过改善土壤养分、腐殖质组成及含量来提高黄绵土理化性质尚不清楚。以黄土高原黄绵土为研究对象,依托甘肃农业大学旱作农业试验站,设置6个生物质炭添加水平(0、10、20、30、40、50 t·hm-2)的4年定位试验,测定土壤养分、有机碳组分、结合态腐殖质构成及组分变化。结果表明:生物质炭添加量为20 t·hm-2及以上时能显著增加重组有机碳(HFOC)、轻组有机碳(LFOC)、有机质和全氮含量,对全磷、全钾含量无显著影响,而高添加量显著增加速效钾含量但降低速效磷含量,低添加量显著增加速效磷含量但降低速效钾含量;添加生物质炭20 t·hm-2及以上时土壤松结合态腐殖质(LCH)含量显著增加47.50%~65.83%;生物质炭添加量超过30 t·hm-2时,腐殖质组成成分富里酸(FA)的含量显著增加78.79%~133.33%;轻组有机碳、重组有机碳和松结合态腐殖质是促进土壤总有机碳(TOC)增加的直接作用因素,其中LFOC和HFOC对TOC的解释率分别为72.55%和89.74%。本研究为生物质炭在黄土高原旱作农业区土壤改良、肥力提升方面提供了理论参考。
潘占东, 马倩倩, 陈晓龙, 蔡立群, 蔡雪梅, 董博, 武均, 张仁陟. 添加生物质炭对黄土高原旱作农田土壤养分、腐殖质及其组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 14-24.
Zhan-dong PAN, Qian-qian MA, Xiao-long CHEN, Li-qun CAI, Xue-mei CAI, Bo DONG, Jun WU, Ren-zhi ZHANG. Effects of biochar addition on nutrient levels and humus and its components in dry farmland soils on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 14-24.

图1 添加生物质炭4年后对土壤养分的影响平均值±标准差Mean±standard deviation (n=3). 不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of adding biochar on soil nutrients after 4 years

图3 土壤轻、重组有机碳含量与土壤总有机碳含量的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between the content of soil light and heavy fraction organic carbon and the total soil organic carbon content
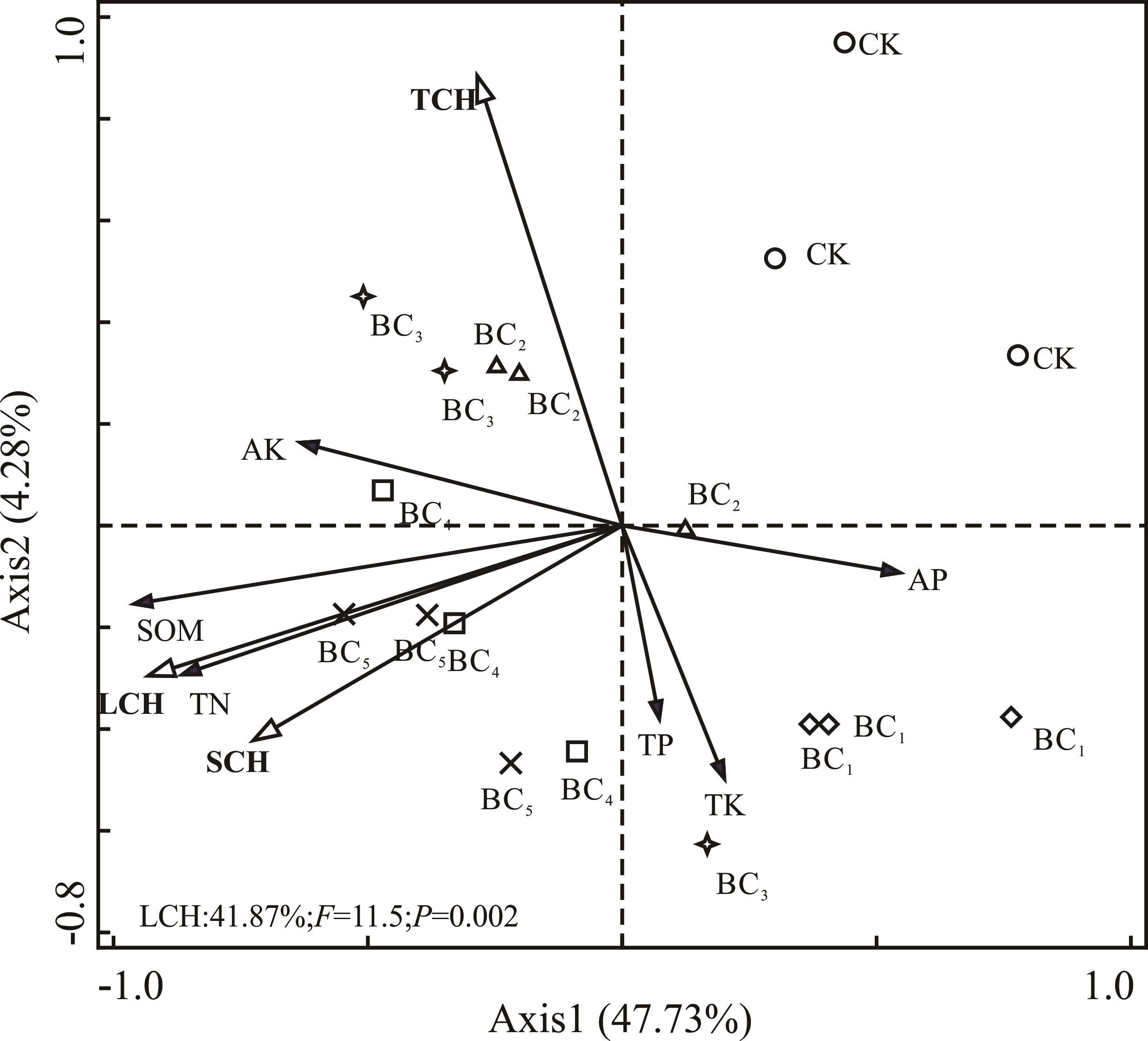
图5 结合态腐殖质与土壤养分的冗余分析TN:全氮 Total nitrogen. TK:全钾 Total potassium. TP:全磷 Total phosphorus. AK:速效钾 Available potassium. AP:速效磷 Available phosphorus. SOM:有机质 Soil organic matter. LCH:松结合态腐殖质 Loosely bound. TCH:紧结合态腐殖质 Tight combined humus. SCH:稳结合态腐殖质 Stable combined humus.
Fig.5 Redundancy analysis of combined humus and soil nutrients
因子 Factor | ryi | Pyi | 间接通径系数Indirect impact path coefficient | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| →x1 | →x2 | →x3 | →x4 | →x5 | →x6 | →x7 | →x8 | 合计Total | |||
| x1 | 0.8541** | 0.3950 | 0.2902 | 0.1837 | -0.0078 | 0.0448 | -0.0532 | 0.0037 | -0.0023 | 0.4591 | |
| x2 | 0.9472** | 0.4490 | 0.2553 | 0.2186 | 0.0147 | 0.0367 | -0.0513 | 0.0032 | 0.0211 | 0.4983 | |
| x3 | 0.9473** | 0.2390 | 0.3036 | 0.4106 | 0.0034 | 0.0404 | -0.0682 | 0.0036 | 0.0149 | 0.7083 | |
| x4 | 0.1735 | 0.0380 | -0.0810 | 0.1738 | 0.0213 | -0.0214 | 0.0151 | -0.0007 | 0.0287 | 0.1357 | |
| x5 | 0.7311** | 0.0590 | 0.2998 | 0.2793 | 0.1635 | -0.0138 | -0.0513 | 0.0039 | -0.0095 | 0.6720 | |
| x6 | -0.6698** | 0.0850 | -0.2471 | -0.2711 | -0.1917 | 0.0067 | -0.0356 | -0.0029 | -0.0130 | -0.7548 | |
| x7 | 0.7358** | 0.0050 | 0.2929 | 0.2881 | 0.1720 | -0.0052 | 0.0466 | -0.0495 | -0.0144 | 0.7305 | |
| x8 | 0.2874 | 0.0480 | -0.0188 | 0.1976 | 0.0744 | 0.0227 | -0.0116 | -0.0230 | -0.0015 | 0.2397 | |
表1 土壤有机碳组分及结合态腐殖质组分对土壤总有机碳的通径分析
Table 1 Path analysis of soil organic carbon components and combined humus components to soil total organic carbon
因子 Factor | ryi | Pyi | 间接通径系数Indirect impact path coefficient | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| →x1 | →x2 | →x3 | →x4 | →x5 | →x6 | →x7 | →x8 | 合计Total | |||
| x1 | 0.8541** | 0.3950 | 0.2902 | 0.1837 | -0.0078 | 0.0448 | -0.0532 | 0.0037 | -0.0023 | 0.4591 | |
| x2 | 0.9472** | 0.4490 | 0.2553 | 0.2186 | 0.0147 | 0.0367 | -0.0513 | 0.0032 | 0.0211 | 0.4983 | |
| x3 | 0.9473** | 0.2390 | 0.3036 | 0.4106 | 0.0034 | 0.0404 | -0.0682 | 0.0036 | 0.0149 | 0.7083 | |
| x4 | 0.1735 | 0.0380 | -0.0810 | 0.1738 | 0.0213 | -0.0214 | 0.0151 | -0.0007 | 0.0287 | 0.1357 | |
| x5 | 0.7311** | 0.0590 | 0.2998 | 0.2793 | 0.1635 | -0.0138 | -0.0513 | 0.0039 | -0.0095 | 0.6720 | |
| x6 | -0.6698** | 0.0850 | -0.2471 | -0.2711 | -0.1917 | 0.0067 | -0.0356 | -0.0029 | -0.0130 | -0.7548 | |
| x7 | 0.7358** | 0.0050 | 0.2929 | 0.2881 | 0.1720 | -0.0052 | 0.0466 | -0.0495 | -0.0144 | 0.7305 | |
| x8 | 0.2874 | 0.0480 | -0.0188 | 0.1976 | 0.0744 | 0.0227 | -0.0116 | -0.0230 | -0.0015 | 0.2397 | |
| 1 | Lian G, Guo X D, Wang J, et al. Soil quality and sustainable land management (SLM). Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005(2): 163-169. |
| 连纲, 郭旭东, 王静, 等. 土壤质量与可持续土地利用管理. 生态学杂志, 2005(2): 163-169. | |
| 2 | Allaire S E, Baril B, Vanasse A, et al. Carbon dynamics in a biochar-amended loamy soil under switchgrass. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 95(1): 1-13. |
| 3 | Mierzwa-Hersztek M, Klimkowicz-Pawlas A, Gondek K. Influence of poultry litter and poultry litter biochar on soil microbial spiration and nitrifying bacteria activity. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2018, 9(3): 379-389. |
| 4 | Kwapinski W, Byrne C M P, Kryachko E, et al. Biochar from biomass and waste. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2010, 1(2): 177-189. |
| 5 | Dou S, Zhou G Y, Yang X Y, et al. Biochar and its relationship to humus carbon in soil: A short review. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(4): 796-802. |
| 窦森, 周桂玉, 杨翔宇, 等. 生物质炭及其与土壤腐殖质碳的关系. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(4): 796-802. | |
| 6 | Meng F R, Dou S, Yin X B, et al. Effects of corn straw biochar on humus composition and humic acid structure of black soil. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(1): 122-128. |
| 孟凡荣, 窦森, 尹显宝, 等. 施用玉米秸秆生物质炭对黑土腐殖质组成和胡敏酸结构特征的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(1): 122-128. | |
| 7 | Zeng A, Liao Y C, Zhang J L, et al. Effects of biochar on soil moisture, organic carbon and available nutrients contents in manural loessial soils. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(5): 1009-1015. |
| 曾爱, 廖允成, 张俊丽, 等. 生物炭对塿土土壤含水量、有机碳及速效养分含量的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(5): 1009-1015. | |
| 8 | Ma L, Lv N, Ye J, et al. Effects of biochar on organic carbon content and fractions of gray desert soil. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(8): 976-981. |
| 马莉, 吕宁, 冶军, 等. 生物碳对灰漠土有机碳及其组分的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(8): 976-981. | |
| 9 | Shang J, Geng Z C, Chen X X, et al. Effects of biochar on soil organic carbon and nitrogen and their fractions in a rainfed farmland. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(3): 509-517. |
| 尚杰, 耿增超, 陈心想, 等. 施用生物炭对旱作农田土壤有机碳、氮及其组分的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(3): 509-517. | |
| 10 | Kathrin W, Peter Q. Properties of biochar. Fuel, 2018, 217: 240-261. |
| 11 | Cui T T, Li Z H, Wang S J. Effects of in-situ straw decomposition on composition of humus and structure of humic acid at different soil depths. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2017, 17(10): 2391-2399. |
| 12 | Cai H G, Wang L C, Zhang J J, et al. First characterization of humic-like substances isolated from maize straw biochar. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2015, 24(5A): 1815-1821. |
| 13 | Zhang J J, Wei Y X, Liu J Z, et al. Effects of maize straw and its biochar application on organic and humic carbon in water-stable aggregates of a mollisol in northeast China: A five-year field experiment. Soil & Tillage Research, 2019, 190: 1-9. |
| 14 | Agegnehu G, Bass A M, Nelson P N, et al. Benefits of biochar, compost and biochar-compost for soil quality, maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions in a tropical agricultural soil. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 543: 295-306. |
| 15 | Huang Z Q, Zhou Q, Hu L C, et al. Effects of biochar input on soil humus composition. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(24): 285-288. |
| 黄兆琴, 周强, 胡林潮, 等. 生物炭添加对土壤腐殖物质组成的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(24): 285-288. | |
| 16 | Sui Y H, Gao J P, Liu C H, et al. Interactive effects of straw-derived biochar and N fertilization on soil C storage and rice productivity in rice paddies of northeast China. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 544: 203-210. |
| 17 | Cheng C H, Lehmann J, Thies J E, et al. Oxidation of black carbon by biotic and abiotic processes. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(11): 1477-1488. |
| 18 | Fungo B, Lehmann J, Kalbitz K, et al. Emissions intensity and carbon stocks of a tropical ultisol after amendment with tithonia green manure, urea and biochar. Field Crops Research, 2017, 209: 179-188. |
| 19 | Yang X, Meng J, Lan Y, et al. Effects of maize stover and its biochar on soil CO2 emissions and labile organic carbon fractions in northeast China. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 240: 24-31. |
| 20 | Chan K Y, Van Z L, Meszaros I, et al. Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment.Australian Journal of Soil Research, 2007, 45: 629-634. |
| 21 | Novak J M, Busscher W J, Laird D L, et al. Impact of biochar amendment on fertility of a Southeastern Coastal Plain soil. Soil Science, 2009, 174: 105-112. |
| 22 | Shi L, Zhang R, Ma L, et al. Quantitative response of wheat yield and soil properties to biochar amendment in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(7): 1273-1283. |
| 史雷, 张然, 马龙, 等. 小麦产量及土壤性状对施用生物质炭的量化响应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(7): 1273-1283. | |
| 23 | Liu Y S, Liu F, Chen Z Y, et al. Regulation effects of biochar on the biological characteristics and nutrient availability of dryland soils. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(3): 166-171, 178. |
| 刘元生, 刘方, 陈祖拥, 等. 生物质炭对旱作土壤生物性状及养分有效性的调控效应. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(3): 166-171, 178. | |
| 24 | Wan Z M, Song C C, Yang G S, et al. The active soil organic carbon fraction and its relationship with soil enzyme activity in different types of marshes in the Sanjiang Plain. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(2): 406-412. |
| 万忠梅, 宋长春, 杨桂生, 等. 三江平原湿地土壤活性有机碳组分特征及其与土壤酶活性的关系. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(2): 406-412. | |
| 25 | Jie X H, Yang L J, Zhou C J, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on the contents of combined formation of humus in the protected cultivation. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2009, 40(4): 805-808. |
| 接晓辉, 杨丽娟, 周崇峻, 等. 长期施肥对保护地土壤腐殖质总量及各形态之间比值的影响. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(4): 805-808. | |
| 26 | Liu S Q, Du M Y, Zhou J X, et al. Study on the relationship between organic-inorganic complex degree and humus combination form and soil fertility in different fertility soils. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1989(6): 267-270. |
| 刘树庆, 杜孟庸, 周健学, 等. 不同肥力土壤有机无机复合度及腐殖质结合形态及其与肥力关系研究. 土壤通报, 1989(6): 267-270. | |
| 27 | Zhou G Y, Dou S, Liu S J. The structural characteristics of biochar and its effects on soil available nutrients and humus composition. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(10): 2075-2080. |
| 周桂玉, 窦森, 刘世杰. 生物质炭结构性质及其对土壤有效养分和腐殖质组成的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(10): 2075-2080. | |
| 28 | Zhang G, Dou S, Xie Z B, et al. Effects of biochar application on composition of soil humus and structural characteristics of humic acid. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 614-620. |
| 张葛, 窦森, 谢祖彬, 等. 施用生物质炭对土壤腐殖质组成和胡敏酸结构特征影响. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 614-620. | |
| 29 | Orlova N, Abakumov E, Orlova E, et al. Soil organic matter alteration under biochar amendment: Study in the incubation experiment on the podzol soils of the leningrad region (Russia). Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19(6): 2708-2716. |
| 30 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis (Third Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 31 | E S Z, Shi X J, Che Z X, et al. Effects of organic materials on soil organic carbon combination form and composition of humus in the desert soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(6): 1436-1448. |
| 俄胜哲, 时小娟, 车宗贤, 等. 有机物料对灌漠土结合态腐殖质及其组分的影响. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(6): 1436-1448. | |
| 32 | Agricultural industry standard of the Peoples Republic of China. Determination of humus composition in soil: Extraction of potassium dichromate by sodium pyrophosphate sodium hydroxide oxidation volumetric method, NY/T1867-2010. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010. |
| 中华人民共和国农业行业标准. 土壤腐殖质组成的测定焦磷酸钠-氢氧化钠提取重铬酸钾氧化容量法, NY/T1867-2010. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010. | |
| 33 | Wang Q A, Guo Y X. Analysis on nutrient change of cultivated land and fertilization countermeasures in Huojia County. Agriculture of Henan, 2009(20): 55-56. |
| 王庆安, 郭永祥. 获嘉县耕地养分变化分析及施肥对策. 河南农业, 2009(20): 55-56. | |
| 34 | Rossel R A V, Lee J, Behrens T, et al. Continental-scale soil carbon composition and vulnerability modulated by regional environmental controls. Nature Geoscience, 2019, 12(7): 547-552. |
| 35 | Laird D A, Fleming P, Davis D D, et al. Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma, 2010, 158(3): 443-449. |
| 36 | Hou Y H, Wang L, Fu X H, et al. Response of straw and straw biochar returning to soil carbon budget and its mechanism. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(7): 2655-2661. |
| 侯亚红, 王磊, 付小花, 等. 土壤碳收支对秸秆与秸秆生物炭还田的响应及其机制. 环境科学, 2015, 36(7): 2655-2661. | |
| 37 | Meng Y T, Zhao C S, Li X Q, et al. Effects of biochar on organic carbon pools in phaeozem. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2018, 40(6): 1340-1347. |
| 孟雨田, 赵承森, 李晓庆, 等. 生物质炭对黑土有机碳组分的影响. 江西农业大学学报, 2018, 40(6): 1340-1347. | |
| 38 | Xu G P, Wang X F, Wei M M, et al. Influence of bagasse biochar on the soil properties in sugarcane fields soil. Sugarcane and Canesugar, 2016(4): 16-22. |
| 许桂苹, 王晓飞, 魏萌萌, 等. 蔗渣生物质炭对蔗田土壤理化性质的影响. 甘蔗糖业, 2016(4): 16-22. | |
| 39 | Zhao S X, Yu X L, Li Z H, et al. Effects of biochar pyrolyzed at varying temperatures on soil organic carbon and its components: Influence on the soil active organic carbon. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(1): 333-342. |
| 赵世翔, 于小玲, 李忠徽, 等. 不同温度制备的生物质炭对土壤有机碳及其组分的影响: 对土壤活性有机碳的影响. 环境科学, 2017, 38(1): 333-342. | |
| 40 | Reverchon F, Flicker R C, Yang H, et al. Changes in delta n-15 in a soil-plant system under different biochar feedstocks and application rates. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2014, 50(2): 275-283. |
| 41 | Li Y, Yu Y L, Zhang X, et al. Effects of continuous application of biochar-based fertilizer and biochar on organic nitrogen fractions in brown soil. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(10): 2903-2909. |
| 李玥, 余亚琳, 张欣, 等. 连续施用炭基肥及生物炭对棕壤有机氮组分的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(10): 2903-2909. | |
| 42 | Ge S F, Peng L, Ren Y H, et al. Effects of straw and biochar on soil bulk density, cation exchange capacity and nitrogen absorption in apple orchard soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(2): 366-373. |
| 葛顺峰, 彭玲, 任饴华, 等. 秸秆和生物质炭对苹果园土壤容重、阳离子交换量和氮素利用的影响. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(2): 366-373. | |
| 43 | Guan T Y. Effects of straw manurning on soil organic carbon fractions. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 管天玉. 秸秆还田方式对土壤有机碳组分的影响. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. | |
| 44 | Han W, Shen S H, Xie Z B, et al. Effects of biochar and straw on both the organic carbon in different density fractions and the microbial biomass in paddy soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(18): 5838-5846. |
| 韩玮, 申双和, 谢祖彬, 等. 生物炭及秸秆对水稻土各密度组分有机碳及微生物的影响. 生态学报, 2016, 36(18): 5838-5846. | |
| 45 | Li X M. Effects of straw biochar on carbon pool in mollisol. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 李晓梅. 秸秆生物炭对黑土碳库的影响. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2015. | |
| 46 | Gao S, Deluca T H. Wood biochar impacts soil phosphorus dynamics and microbial communities in organically-managed croplands.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 126: 144-150. |
| 47 | DeLuca T H, MacKenzie M D, Gundale M J. Biochar effects on soil nutrient transformations. London: Earthscan Publications Ltd., 2009: 251-270. |
| 48 | Liu Z Q, Yu L, Yang T X, et al. Effects of biochar application pattern on soil fertility and enzyme activity under limited fertilization conditions. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(4): 544-551. |
| 刘遵奇, 宇兰, 杨铁鑫, 等. 减肥条件下生物炭施用方式对土壤肥力及酶活性的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(4): 544-551. | |
| 49 | Dilly O, Pfeiffer E, Lehmann J. Biochar effects on soil biota-A review. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2011, 43(9): 1812-1836. |
| 50 | Wang G L, Duan J N. The way of mobilization and utilization of mineral potassium in soils. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004(6): 802-805. |
| 王改兰, 段建南. 土壤矿物钾活化途径. 土壤通报, 2004(6): 802-805. | |
| 51 | Xiong Y. Organic inorganic compound and soil fertility. Soils, 1982(5): 161-167. |
| 熊毅. 有机无机复合与土壤肥力. 土壤, 1982(5): 161-167. | |
| 52 | Li J M, Wu J G, Wang L H. Effects of different organic materials on the combined states of humus in black soil. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(8): 1608-1615. |
| 李建明, 吴景贵, 王利辉. 不同有机物料对黑土腐殖质结合形态影响差异性的研究. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(8): 1608-1615. | |
| 53 | Zhao X Y, Wu J G, Li J M, et al. Effects of maize straw and its related wastes on the combined states of humus in black soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(5): 193-198. |
| 赵欣宇, 吴景贵, 李建明, 等. 玉米秸秆及相关废弃物对黑土腐殖质结合形态的影响. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(5): 193-198. | |
| 54 | Shi Y, Chen X, Shen S M.Stable mechanisms of soil aggregate and effects of human activities.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002(11): 1491-1494. |
| 史奕, 陈欣, 沈善敏. 土壤团聚体的稳定机制及人类活动的影响. 应用生态学报, 2002(11): 1491-1494. | |
| 55 | Zhao S X, Yu X L, Li Z H, et al. Effects of biochar pyrolyzed at varying temperatures on soil organic carbon and its components: Influence on the composition and properties of humic substances. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(2): 769-782. |
| 赵世翔, 于小玲, 李忠徽, 等. 不同温度制备的生物质炭对土壤有机碳及其组分的影响: 对土壤腐殖物质组成及性质的影响. 环境科学, 2017, 38(2): 769-782. | |
| 56 | Dou S, Zhang J J, Lichtfouse E, et al. Study on dynamic changes of soil organic matter during corn stalk decomposition by δ13C method. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2003(3): 328-334. |
| 窦森, 张晋京, Lichtfouse E, 等. 用δ13C方法研究玉米秸秆分解期间土壤有机质数量动态变化. 土壤学报, 2003(3): 328-334. |
| [1] | 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| [2] | 侯金伟, 陈焘, 南志标. 不同埋藏方式及杀菌剂处理对黄土高原3种植物种子存活的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 129-136. |
| [3] | 李文, 魏廷虎, 永措巴占, 才仁塔次, 周玉海, 张雁平, 李文浩, 郭卫兴. 混播比例对三江源人工草地植被和土壤养分特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 39-48. |
| [4] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [5] | 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 赵艳丽, 张裕年, 肖斌, 付贵全, 杜娟. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [6] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 王宏生. 围封和防除狼毒对狼毒斑块土壤理化性质和微生物量影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 63-72. |
| [7] | 黄玙璠, 舒英格, 肖盛杨, 陈梦军. 喀斯特山区不同草地土壤养分与酶活性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 93-104. |
| [8] | 魏鹏, 安沙舟, 董乙强, 孙宗玖, 别尔达吾列提·希哈依, 李超. 基于高通量测序的准噶尔盆地荒漠土壤细菌多样性及群落结构特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. |
| [9] | 王婷, 张永超, 赵之重. 青藏高原退化高寒湿地植被群落结构和土壤养分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 9-18. |
| [10] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [11] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [12] | 柳书俊, 姚新转, 赵德刚, 吕立堂. 湄潭茶园土壤养分特征及肥力质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 33-45. |
| [13] | 施颖, 胡廷花, 高红娟, 罗巧玉, 于应文. 两种放牧模式下高寒草甸群落植被构成及稳定性特征[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 1-10. |
| [14] | 帅林林, 周青平, 陈有军, 苟小林, 周蓉. 高寒半湿润沙地草本修复期土壤微生物变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 11-22. |
| [15] | 王丽娜, 罗久富, 杨梅香, 张利, 刘学敏, 邓东周, 周金星. 氮添加对退化高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 38-48. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||