

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 213-220.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020539
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
白婕1( ), 臧真凤1, 刘丛1, 昝看卓1, 龙明秀1, 王可珍2, 屈洋2, 何树斌1(
), 臧真凤1, 刘丛1, 昝看卓1, 龙明秀1, 王可珍2, 屈洋2, 何树斌1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-12
修回日期:2021-07-07
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2021-12-22
通讯作者:
何树斌
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: heshubin@nwafu.edu.cn基金资助:
Jie BAI1( ), Zhen-feng ZANG1, Cong LIU1, Kan-zhuo ZAN1, Ming-xiu LONG1, Ke-zhen WANG2, Yang QU2, Shu-bin HE1(
), Zhen-feng ZANG1, Cong LIU1, Kan-zhuo ZAN1, Ming-xiu LONG1, Ke-zhen WANG2, Yang QU2, Shu-bin HE1( )
)
Received:2021-05-12
Revised:2021-07-07
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2021-12-22
Contact:
Shu-bin HE
摘要:
为研究紫花苜蓿叶片和根系对水分和外源氮(N)添加的响应规律,在温室条件下设置水分胁迫处理(WS)(35%±5%)田间持水量(field water capacity,FWC)和充分灌溉且未渍水(WW)(70%±5%)FWC两个水分梯度,每个水分梯度下设置0、5和10 mmol·L-1 3个N添加水平(Nn、Nm和Nh),研究了紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化的程度及C、N特征对不同水分条件和外源N添加的响应规律。结果表明:WS和外源N提高了紫花苜蓿叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量,但对根系没有显著影响。WS和N添加未影响紫花苜蓿叶片C含量,但N添加提高了根系C含量。WS未改变紫花苜蓿叶片N含量,但提高了根系N含量。外源N添加不但提高了叶片N含量,还增加了根系N含量,但叶片N含量在WW处理下对外源N添加较为敏感,而根系N含量在WS处理下对外源N的添加较为敏感,这说明紫花苜蓿叶片和根系C、N状态对N添加的响应受土壤水分条件的调控。紫花苜蓿根系C/N较叶片更高,且对水分和外源N添加的响应更为敏感。WS处理显著提高了根系δ13C,对叶片δ13C无显著影响。外源N添加降低了叶片和根系δ15N,且在WS处理下根系δ15N显著降低,叶片中δ15N在WW处理下显著降低。总之,相比叶片,紫花苜蓿根系生理参数及C、N特征对水分和外源N添加采取了更为积极的策略,在生长中发挥着更重要的作用。该研究结果有助于全面掌握紫花苜蓿各器官对水分和外源N添加的响应策略,为我国旱作农业区紫花苜蓿制定精准的水肥管理制度提供了理论依据。
白婕, 臧真凤, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 王可珍, 屈洋, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化及C、N特征对水分和N添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 213-220.
Jie BAI, Zhen-feng ZANG, Cong LIU, Kan-zhuo ZAN, Ming-xiu LONG, Ke-zhen WANG, Yang QU, Shu-bin HE. Lipid peroxidation and carbon and nitrogen characteristics in leaves and roots of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) in response to water and nitrogen addition[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 213-220.
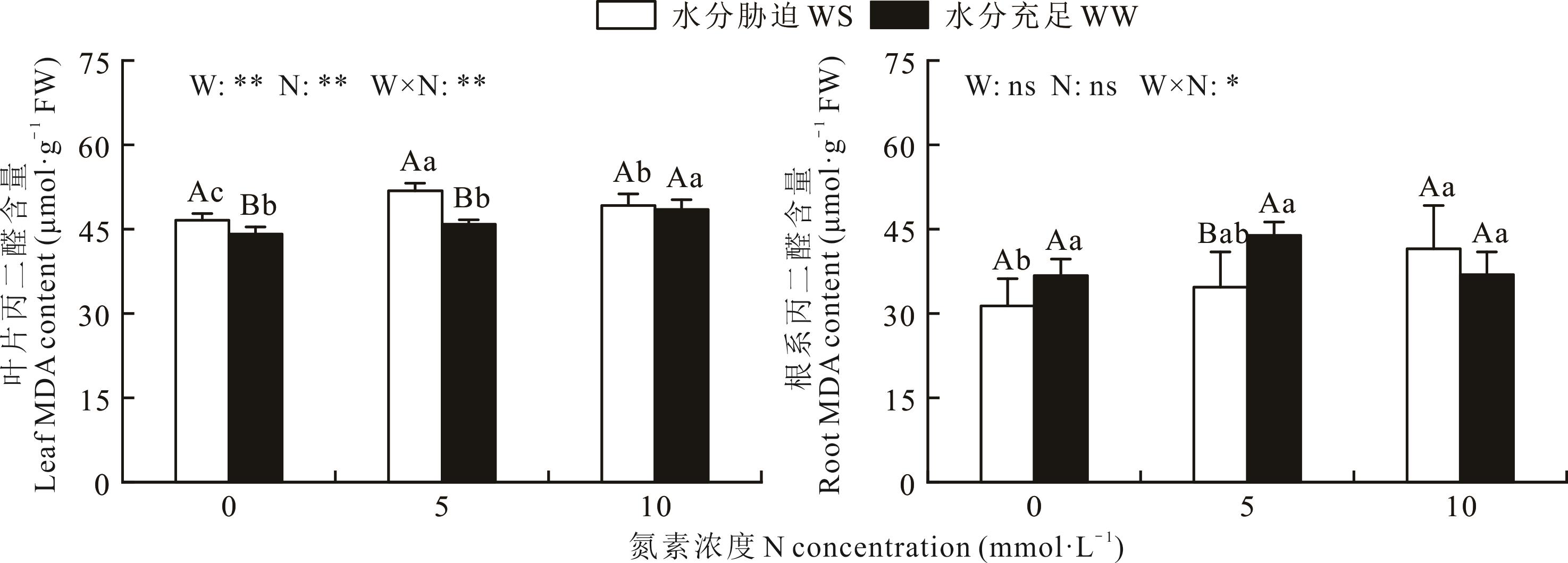
图1 水分和外源N添加对叶片和根系中MDA含量的影响W:水分处理;N:外源N处理;W×N:水分处理和外源N处理的交互作用;不同小写字母表示同一水分水平不同氮浓度之间差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示同一氮水平不同水分条件下差异显著(P<0.05);ns表示差异不显著; *和**分别表示在0.05, 0.01水平差异显著。下同。WS: Water stress. WW: Well-watered. W: Water stress; N: Exogenous N addition; W×N: Interaction of water stress and exogenous N addition; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different N concentrations at the same water condition (P<0.05); Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different water condition at the same N concentration (P<0.05); ns: Not significant; * and ** indicate significant differences at the 0.05, and 0.01 level, respectively. The same below.
Fig.1 MDA content in leaves and roots subjected to water and exogenous nitrogen addition
| 1 | Hong F Z. Alfalfa science. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2009. |
| 洪绂曾. 苜蓿科学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2009. | |
| 2 | Gao L M, Su J, Tian Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen accumulation and root nitrogenase activity in Medicago sativa at different soil water contents. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. |
| 高丽敏, 苏晶, 田倩, 等. 施氮对不同水分条件下紫花苜蓿氮素吸收及根系固氮酶活性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. | |
| 3 | Zhang C, Shi S, Liu Z, et al. Drought tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) varieties is associated with enhanced antioxidative protection and declined lipid peroxidation. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2019, 232: 226-240. |
| 4 | Fan L X, Liu G B, Xue J, et al. Synergistic effects of doubled CO2 concentration and drought stress on the photosynthetic characteristics of Medicago sativa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2014, 22(1): 85-93. |
| 樊良新, 刘国彬, 薛萐, 等. CO2浓度倍增及干旱胁迫对紫花苜蓿光合生理特性的协同影响. 草地学报, 2014, 22(1): 85-93. | |
| 5 | Gao L M, Su J, Tian Q, et al. Contrasting strategies of nitrogen absorption and utilization in alfalfa plants under different water stress. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2020, 20(3): 1515-1523. |
| 6 | Soba D, Zhou B W, Arrese-Igor C, et al. Physiological, hormonal and metabolic responses of two alfalfa cultivars with contrasting responses to drought. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(20): 5099. |
| 7 | Aranjuelo I, Tcherkez G, Molero G, et al. Concerted changes in N and C primary metabolism in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under water restriction. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(4): 1-17. |
| 8 | Erice G, Louahlia S, Irigoyen J J, et al. Biomass partitioning, morphology and water status of four alfalfa genotypes submitted to progressive drought and subsequent recovery. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2010, 167(2): 114-120. |
| 9 | Garcia A L, Marcelis L, Garcia-Sanchez F, et al. Moderate water stress affects tomato leaf water relations in dependence on the nitrogen supply. Biologia Plantarum, 2007, 51(4): 707-712. |
| 10 | Helalia A M, Altahir O A, Alnabulsi Y A. The influence of irrigation water salinity and fertilizer management on the yield of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Agricultural Water Management, 1996, 31: 105-114. |
| 11 | Esechie H A, Al-Barhi B, Al-Gheity S, et al. Root and shoot growth in salinity-stressed alfalfa in response to nitrogen source. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2002, 25(11): 2559-2569. |
| 12 | Guinet M, Nicolardot B, Revellin C, et al. Comparative effect of inorganic N on plant growth and N2 fixation of ten legume crops: Towards a better understanding of the differential response among species. Plant and Soil, 2018, 432(1): 207-227. |
| 13 | Volenec J J, Ourry A, Joern B C. A role for nitrogen reserves in forage regrowth and stress tolerance. Physiologia Plantarum, 1996, 97(1): 185-193. |
| 14 | Araujo W L, Tohge T, Ishizaki K, et al. Protein degradation-an alternative respiratory substrate for stressed plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2011, 16(9): 489-498. |
| 15 | Wang W B, Kim Y H, Lee H S, et al. Analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity during germination of alfalfa under salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(7): 570-577. |
| 16 | Chen Y T, Luo Y Z, Shen H N, et al. Response of biomass and antioxidant enzyme activity of Medicago sativa cv. Xinjiang daye to soil water stress. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2020, 55(4): 128-136. |
| 陈雅婷, 罗永忠, 申海宁, 等. 新疆大叶苜蓿生物量及抗氧化酶类对土壤水分胁迫的响应. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(4): 128-136. | |
| 17 | Meuriot F, Avice J C, Decau M L, et al. Accumulation of N reserves and vegetative storage protein (VSP) in taproots of non-nodulated alfalfa ( Medicago sativa L.) are affected by mineral N availability. Plant Science, 2003, 165(4): 709-718. |
| 18 | Li H S. Experimental principle and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002. | |
| 19 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis (The 3th Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 268-270. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 268-270. | |
| 20 | Bei M R, Luo X H, Yang H Z. Simultaneous determination of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in rubber leaf samples by AA3 continuous flow analyzer (CFA). Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2011, 32(7): 1258-1264. |
| 贝美容, 罗雪华, 杨红竹. AA3型连续流动分析仪(CFA)同时测定橡胶叶全氮、全磷、全钾的方法研究. 热带作物学报, 2011, 32(7): 1258-1264. | |
| 21 | Che Y L, Cheng R F, Zhang Y T, et al. Effects of distillers’ grains biogas residue substrate on tomato growth and quality. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 52(4): 98-105. |
| 车艳丽, 程瑞锋, 张雅婷, 等. 酒糟沼渣基质对番茄生长及其品质的影响. 山东农业科学, 2020, 52(4): 98-105. | |
| 22 | Liu Z J, Zhang X L, Bai J G, et al. Exogenous paraquat changes antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in drought-stressed cucumber leaves. Scientia Horticulturae, 2009, 121(2): 138-143. |
| 23 | Boldaji S A H, Khavari-Nejad R A, Sajedi R H, et al. Water availability effects on antioxidant enzyme activities, lipid peroxidation, and reducing sugar contents of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2012, 34(3): 1177-1186. |
| 24 | Avice J C, Dily F L, Goulas E, et al. Vegetative storage proteins in overwintering storage organs of forage legumes: Roles and regulation. Canadian Journal of Botany, 2003, 81(12): 1198-1212. |
| 25 | Voisin A S, Salon C, Munier-Jolain N G, et al. Effect of mineral nitrogen on nitrogen nutrition and biomass partitioning between the shoot and roots of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant and Soil, 2002, 242(2): 251-262. |
| 26 | Gupta A, Rico-Medina A, Cano-Delgado A I. The physiology of plant responses to drought. Science, 2020, 368(6488): 266-269. |
| 27 | Crozat Y, Aveline A, Coste F, et al. Yield performance and seed production pattern of field-grown pea and soybean in relation to N nutrition. European Journal of Agronomy, 1994, 3(2): 135-144. |
| 28 | Barber L D, Joern B C, Volenec J J, et al. Supplemental nitrogen effects on alfalfa regrowth and nitrogen mobilization from roots. Crop Science, 1996, 36(5): 1217-1223. |
| 29 | Antolín M C, Muro I, Sánchez-Díaz M. Application of sewage sludge improves growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant activities of nodulated alfalfa plants under drought conditions. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2010, 68(1): 75-82. |
| 30 | Saura-Mas S, Lloret F. Foliar stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in woody Mediterranean species with different life form and post-fire regeneration. Plant Biology, 2010, 12(1): 125-133. |
| 31 | Hu M J, Penuelas J, Sardans J, et al. Stoichiometry patterns of plant organ N and P in coastal herbaceous wetlands along the East China Sea: Implications for biogeochemical niche. Plant and Soil, 2018, 431(1/2): 273-288. |
| 32 | Ronquim C C, Prado C H B D, De Paula N F. Growth and photosynthetic capacity in two woody species of cerrado vegetation under different radiation availability. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 2003, 46(2): 243-252. |
| 33 | Bertholdi A A D S, Costa V E, Rodrigues A L, et al. Water deficit modifies the carbon isotopic composition of lipids, soluble sugars and leaves of Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. (Fabaceae). Acta Botanica Brasilica, 2018, 32(1): 80-87. |
| 34 | Kou L, Chen W, Jiang L, et al. Simulated nitrogen deposition affects stoichiometry of multiple elements in resource-acquiring plant organs in a seasonally dry subtropical forest. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 624(53): 611-620. |
| 35 | Román M, Rendal S, Fernández E, et al. Seasonal variability of the carbon and nitrogen isotopic signature in a Zostera noltei meadow at the NW Iberian Peninsula. Wetlands, 2018, 38(4): 739-753. |
| 36 | Lu J Y, He S B, Wang Z N, et al. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry in differently aged lucerne stands during flowering. Legume Research, 2016, 39(4): 595-600. |
| 37 | Lopes M S, Araus J L. Nitrogen source and water regime effects on durum wheat photosynthesis and stable carbon and nitrogen isotope composition. Physiologia Plantarum, 2006, 126(3): 435-445. |
| 38 | Gottlicher S, Knohl A, Wanek W, et al. Short-term changes in carbon isotope composition of soluble carbohydrates and starch: from canopy leaves to the root system. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2006, 20(4): 653-660. |
| 39 | Roberts P, Blumenthal S A, Dittus W, et al. Stable carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen, isotope analysis of plants from a South Asian tropical forest: Implications for primatology. American Journal of Primatology, 2017, 79(6): e22656. |
| 40 | Peri P L, Ladd B, Pepper D A, et al. Carbon (δ13C) and nitrogen (δ15N) stable isotope composition in plant and soil in Southern Patagonia’s native forests. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18(1): 311-321. |
| 41 | Liu J, Wang C, Peng B, et al. Effect of nitrogen addition on the variations in the natural abundance of nitrogen isotopes of plant and soil components. Plant and Soil, 2017, 412(1/2): 453-464. |
| 42 | Chen C J, Jia Y F, Chen Y Z, et al. Nitrogen isotopic composition of plants and soil in an arid mountainous terrain: South slope versus north slope. Biogeosciences, 2018, 15(1): 369-377. |
| [1] | 张岳阳, 李芳, 梁维维, 李彦忠. 新疆昌吉32个紫花苜蓿品种的田间抗病性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 133-146. |
| [2] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| [3] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [4] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [5] | 徐睿智, 吴晓娟, 杨惠敏. 刈割后追肥对建植当年紫花苜蓿生长和生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 195-204. |
| [6] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [7] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| [8] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| [9] | 周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52. |
| [10] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [11] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [12] | 王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟. 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [13] | 彭磊, 张力, 周小龙, 万彦博, 师庆东. 水分胁迫对新疆准东地区钠猪毛菜的生活史对策的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 65-74. |
| [14] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [15] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||