

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 183-194.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021464
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
马士龙1,2( ), 李小伟4, 李响1,2, 谢书琼2,3, 刘益丽1,2, 唐娇2,3, 江明锋1,2(
), 李小伟4, 李响1,2, 谢书琼2,3, 刘益丽1,2, 唐娇2,3, 江明锋1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-13
修回日期:2022-03-14
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
江明锋
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: mingfengjiang@vip.sina.com基金资助:
Shi-long MA1,2( ), Xiao-wei LI4, Xiang LI1,2, Shu-qiong XIE2,3, Yi-li LIU1,2, Jiao TANG2,3, Ming-feng JIANG1,2(
), Xiao-wei LI4, Xiang LI1,2, Shu-qiong XIE2,3, Yi-li LIU1,2, Jiao TANG2,3, Ming-feng JIANG1,2( )
)
Received:2021-12-13
Revised:2022-03-14
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Ming-feng JIANG
摘要:
麦洼牦牛是青藏高原地区优良的乳肉兼用型牦牛品种,本研究旨在探究四川省龙日种畜场麦洼牦牛保种群的遗传多样性和遗传结构,评价3个不同保种群的保种效果并挖掘重要种质特性基因。对麦洼牦牛3个保种群粉嘴群(n=140)、全黑群(n=211)、弗洛群(n=55)进行GBS简化基因组测序,基于检测到的126122个单核苷酸多态性(SNPs)标记计算遗传统计量,结果表明,整个牦牛群的平均观测杂合度(Ho)和平均期望杂合度(He)为0.3038和0.3036,麦洼牦牛的遗传多样性较丰富。全黑群、粉嘴群、弗洛群的观测杂合度Ho分别为0.3029、0.3042、0.3044,近交系数Fis分别为0.0144、0.0152、0.0209,弗洛群和粉嘴群受人工选择的强度大于全黑群,较低的近交水平说明3个群的保种效果较好。Structure分析中全黑、弗洛群部分个体血缘较纯正,而其他个体血缘关系非常混杂;粉嘴群和全黑群的遗传分化系数(Fst)和遗传距离(DR)最大为0.03513、0.0358,结合系统进化树表明两者亲缘关系最远,有遗传分化趋势。利用Fst和π法对3个保种群进行选择信号分析,发现有104个受选择基因广泛参与生殖机能、免疫系统、胚胎发育、脂质代谢等条目以及生殖激素、内/外分泌、信号传递等通路,其中部分基因提示麦洼牦牛的繁殖、肉质、毛色性状以及应激反应得到了人工选择,如PPP3CC、KCNMA1、ROCK2、GNAQ、MEF2C、KIT等。现有的麦洼牦牛保种策略是可行的,研究结果为未来麦洼牦牛的保种选育和遗传改良提供了参考依据。
马士龙, 李小伟, 李响, 谢书琼, 刘益丽, 唐娇, 江明锋. 基于GBS简化基因组测序评估3个麦洼牦牛保种群的遗传结构研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 183-194.
Shi-long MA, Xiao-wei LI, Xiang LI, Shu-qiong XIE, Yi-li LIU, Jiao TANG, Ming-feng JIANG. Assessment of genetic structure of 3 Maiwa yak preserved populations based on genotyping-by-sequencing technology[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 183-194.
群体 Population | 年龄 Age (year) | 样本量 Sample number | 公牛数 Bulls | 母牛数 Cows | 地理来源 Geographic origin | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全黑群QH | 1~12 | 211 | 51 | 160 | 红原Hongyuan | 3566 | 32°33′ | 102°16′ |
| 弗洛群FL | 1~12 | 55 | 12 | 43 | 红原Hongyuan | 3572 | 32°35′ | 102°17′ |
| 粉嘴群FZ | 1~12 | 140 | 31 | 109 | 红原Hongyuan | 3598 | 32°37′ | 102°15′ |
| 共计Total | - | 406 | 94 | 312 | - | - | - | - |
表1 3个保种群的采集信息
Table 1 The sample information of 3 breeding populations
群体 Population | 年龄 Age (year) | 样本量 Sample number | 公牛数 Bulls | 母牛数 Cows | 地理来源 Geographic origin | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全黑群QH | 1~12 | 211 | 51 | 160 | 红原Hongyuan | 3566 | 32°33′ | 102°16′ |
| 弗洛群FL | 1~12 | 55 | 12 | 43 | 红原Hongyuan | 3572 | 32°35′ | 102°17′ |
| 粉嘴群FZ | 1~12 | 140 | 31 | 109 | 红原Hongyuan | 3598 | 32°37′ | 102°15′ |
| 共计Total | - | 406 | 94 | 312 | - | - | - | - |
图1 部分样本血液基因组DNA电泳图M: BM5000 DNA指示剂BM5000 DNA marker; 1~15: 不同样本DNA DNA samples from different samples.
Fig.1 Genome DNA electrophoresis of some blood samples
类型 Type | 原始碱基数 Raw bases (Mb) | 有效碱基数 Clean bases (Mb) | 有效率 Effective rate (%) | 碱基检测错误率 Error rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麦洼牦牛Maiwa yak | 279.211~2456.350 | 279.210~2456.340 | 99.990~100.000 | 0.040~0.060 |
| 共计Toal | 327.517 | 327.512 | - | - |
| 平均Mean | 806.690 | 806.680 | 99.990 | 0.044 |
表2 麦洼牦牛测序数据统计
Table 2 Summary of sequencing data of Maiwa yak
类型 Type | 原始碱基数 Raw bases (Mb) | 有效碱基数 Clean bases (Mb) | 有效率 Effective rate (%) | 碱基检测错误率 Error rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麦洼牦牛Maiwa yak | 279.211~2456.350 | 279.210~2456.340 | 99.990~100.000 | 0.040~0.060 |
| 共计Toal | 327.517 | 327.512 | - | - |
| 平均Mean | 806.690 | 806.680 | 99.990 | 0.044 |
类型 Type | Q20 (%) | GC (%) | 有效读长数Clean reads (Mb) | 有效读长数比对率Mapping rate (%) | 测序深度Average depth (×) | 覆盖度 Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麦洼牦牛Maiwa yak | 93.83~97.58 | 36.56~40.28 | 1.94~17.08 | 92.60~99.68 | 5.65~31.64 | 2.03~6.13 |
| 平均Mean | 95.73 | 38.88 | 5.60 | 98.75 | 14.33 | 3.46 |
表3 测序数据质量评估
Table 3 Quality assessment of sequencing
类型 Type | Q20 (%) | GC (%) | 有效读长数Clean reads (Mb) | 有效读长数比对率Mapping rate (%) | 测序深度Average depth (×) | 覆盖度 Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麦洼牦牛Maiwa yak | 93.83~97.58 | 36.56~40.28 | 1.94~17.08 | 92.60~99.68 | 5.65~31.64 | 2.03~6.13 |
| 平均Mean | 95.73 | 38.88 | 5.60 | 98.75 | 14.33 | 3.46 |
群体 Population | 观测杂合度Ho | 期望杂合度He | 核苷酸多样度π | 近交系数Fis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全黑群QH | 0.3029 | 0.3030 | 0.3030 | 0.0144 |
| 粉嘴群FZ | 0.3042 | 0.3025 | 0.3020 | 0.0152 |
| 弗洛群FL | 0.3044 | 0.3052 | 0.3009 | 0.0209 |
| 平均Mean | 0.3038 | 0.3036 | 0.3020 | 0.0168 |
表4 麦洼牦牛3个育种群遗传多样性参数
Table 4 Genetic diversity parameters of three preserved populations of Maiwa yak
群体 Population | 观测杂合度Ho | 期望杂合度He | 核苷酸多样度π | 近交系数Fis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全黑群QH | 0.3029 | 0.3030 | 0.3030 | 0.0144 |
| 粉嘴群FZ | 0.3042 | 0.3025 | 0.3020 | 0.0152 |
| 弗洛群FL | 0.3044 | 0.3052 | 0.3009 | 0.0209 |
| 平均Mean | 0.3038 | 0.3036 | 0.3020 | 0.0168 |
| 群体Population | 粉嘴群FZ | 弗洛群FL | 全黑群QH |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粉嘴群FZ | - | 0.02760 | 0.03580 |
| 弗洛群FL | 0.02726 | - | 0.02540 |
| 全黑群QH | 0.03513 | 0.02504 | - |
表5 群体间的遗传分化系数(Fst)(对角线下)和遗传距离(DR)(对角线上)
Table 5 Genetic differentiation index (below diagonal) and genetic distance (above diagonal) among three populations of Maiwa yak
| 群体Population | 粉嘴群FZ | 弗洛群FL | 全黑群QH |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粉嘴群FZ | - | 0.02760 | 0.03580 |
| 弗洛群FL | 0.02726 | - | 0.02540 |
| 全黑群QH | 0.03513 | 0.02504 | - |

图5 麦洼牦牛structure群体遗传结构A:3个群体不同K值下的群体结构,每个颜色代表1个分组;B:不同K值下群体结构的CV值曲线。A: The population structure of three groups with different K values, each color represents a group; B: The CV curve of the population structure with different K values.
Fig.5 Genetic structure of Maiwa yak structure populations
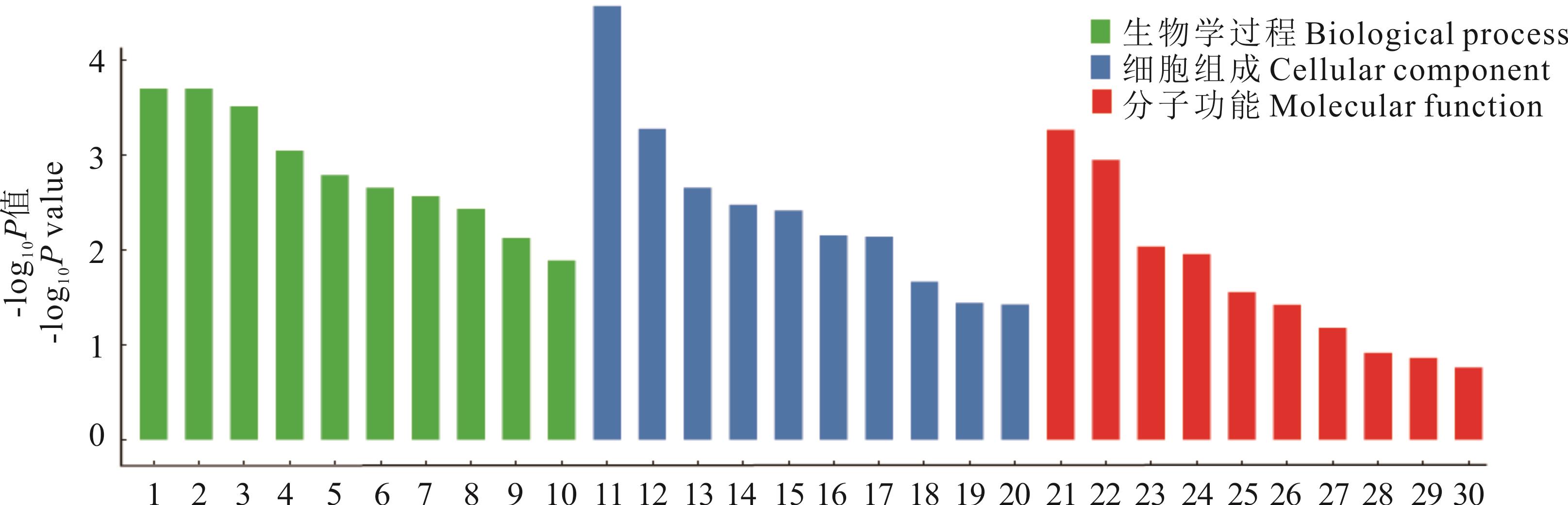
图7 受选择基因的GO富集条目1.有丝分裂细胞周期G1/S转换;2.氯离子跨膜运输;3.节律过程;4.细胞DNA损伤的刺激反应;5.细胞信号转导;6.神经元凋亡过程的负调控;7.细胞黏着;8.趋化性;9.细胞分裂;10.细胞表面受体信号通路;11.氯离子通道复合体;12.细胞间连接;13.膜的锚固组分;14.树突;15.细胞连接;16.线粒体;17.质膜的整体组分;18.突触后膜;19.蛋白质复合体;20.胞质;21.氯离子通道活性;22.酶结合;23.蛋白质二聚化活性;24.锌离子结合;25.镁离子结合;26.细胞因子活性;27.蛋白质同源二聚体化活性;28.蛋白质异源二聚体化活性;29.RNA结合;30.金属离子结合。1. G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; 2. Chloride transmembrane transport; 3. Rhythmic process; 4. Cellular response to DNA damage stimulus; 5. Cell-cell signaling; 6. Negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process; 7. Cell adhesion; 8. Chemotaxis; 9. Cell division; 10. Cell surface receptor signaling pathway; 11. Chloride channel complex; 12. Cell-cell junction; 13. Anchored component of membrane; 14. Dendrite; 15. Cell junction; 16. Mitochondrion; 17. Integral component of plasma membrane; 18. Postsynaptic membrane; 19. Protein complex; 20. Cytosol; 21. Chloride channel activity; 22. Enzyme binding; 23. Protein dimerization activity; 24. Zinc ion binding; 25. Magnesium ion binding; 26. Cytokine activity; 27. Protein homodimerization activity; 28. Protein heterodimerization activity; 29. RNA binding; 30. Metal ion binding.
Fig.7 GO enrichment items of selected gene
| KEGG通路KEGG pathway | 分类号ID | 基因名Gene name |
|---|---|---|
| 催产素信号通路Oxytocin signaling pathway | bom04921 | GNAQ; MAP2K5; PPP3CC; MEF2C; KCNJ3; ROCK2; ITPR2; CACNB4 |
| 缝隙连接Gap junction | bom04540 | GNAQ; MAP2K5; PRKG1; PDGFRB; ITPR2 |
| 雌激素信号通路Estrogen signaling pathway | bom04915 | ITPR1; GNAQ; OPRM1; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 钙信号通路Calcium signaling pathway | bom04020 | GNAQ; ADORA2B; GNA14; PTAFR; PPP3CC; PDGFRB; ITPR2 |
| cGMP-PKG信号通路cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | bom04022 | GNAQ; PRKG1; KCNMA1; MEF2C; ROCK2; ITPR2 |
| 血管平滑肌收缩Vascular smooth muscle contraction | bom04270 | GNAQ; ADORA2B; PRKG1; KCNMA1; ROCK2; ITPR2 |
| 逆行神经的信号Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | bom04723 | ITPR1; GNAQ; GABRA1; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 果糖和甘露糖代谢Fructose and mannose metabolism | bom00051 | ENOSF1; SORD; MPI |
| 肾素分泌Renin secretion | bom04924 | GNAQ; KCNMA1; PPP3CC; ITPR2 |
| 内分泌等因素调节钙的重吸收Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption | bom04961 | GNAQ; CLTC; CALB1 |
| 唾液分泌Salivary secretion | bom04970 | GNAQ; PRKG1; KCNMA1; ITPR2 |
| 胰腺分泌Pancreatic secretion | bom04972 | GNAQ; SLC4A4; KCNMA1; ITPR2 |
| Rap1信号通路Rap1 signaling pathway | bom04015 | ADORA2B; KIT; VEGFC; NGF; PDGFRB |
| 谷氨酸突触Glutamatergic synapse | bom04724 | GNAQ; PPP3CC; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 卵母细胞减数分裂Oocyte meiosis | bom04114 | ANAPC10; YWHAQ; PPP3CC; ITPR2 |
| 甲状腺激素的合成Thyroid hormone synthesis | bom04918 | GNAQ; PAX8; ITPR2 |
| MAPK信号通路MAPK signaling pathway | bom04010 | NGF; PPP3CC; MEF2C; PDGFRB; CACNB4 |
| 血小板激活Platelet activation | bom04611 | GNAQ; PRKG1; ROCK2; ITPR2 |
| 多巴胺能神经突触Dopaminergic synapse | bom04728 | GNAQ; PPP3CC; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 胆汁分泌Bile secretion | bom04976 | NCEH1; SLC5A1 |
| 促性腺激素信号通路GnRH signaling pathway | bom04912 | GNAQ; ITPR2 |
| 节律导引Circadian entrainment | bom04713 | GNAQ; PRKG1; KCNJ3 |
| 炎症介质调节TRP通道Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | bom04750 | GNAQ; NGF; ITPR2 |
| Ras信号通路Ras signaling pathway | bom04014 | KIT; VEGFC; NGF; PDGFRB |
| 磷脂酰肌醇信号系统Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | bom04070 | PI4KA; ITPK1; ITPR2 |
表6 受选择基因的KEGG通路
Table 6 KEGG pathway of differential expression genes
| KEGG通路KEGG pathway | 分类号ID | 基因名Gene name |
|---|---|---|
| 催产素信号通路Oxytocin signaling pathway | bom04921 | GNAQ; MAP2K5; PPP3CC; MEF2C; KCNJ3; ROCK2; ITPR2; CACNB4 |
| 缝隙连接Gap junction | bom04540 | GNAQ; MAP2K5; PRKG1; PDGFRB; ITPR2 |
| 雌激素信号通路Estrogen signaling pathway | bom04915 | ITPR1; GNAQ; OPRM1; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 钙信号通路Calcium signaling pathway | bom04020 | GNAQ; ADORA2B; GNA14; PTAFR; PPP3CC; PDGFRB; ITPR2 |
| cGMP-PKG信号通路cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | bom04022 | GNAQ; PRKG1; KCNMA1; MEF2C; ROCK2; ITPR2 |
| 血管平滑肌收缩Vascular smooth muscle contraction | bom04270 | GNAQ; ADORA2B; PRKG1; KCNMA1; ROCK2; ITPR2 |
| 逆行神经的信号Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | bom04723 | ITPR1; GNAQ; GABRA1; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 果糖和甘露糖代谢Fructose and mannose metabolism | bom00051 | ENOSF1; SORD; MPI |
| 肾素分泌Renin secretion | bom04924 | GNAQ; KCNMA1; PPP3CC; ITPR2 |
| 内分泌等因素调节钙的重吸收Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption | bom04961 | GNAQ; CLTC; CALB1 |
| 唾液分泌Salivary secretion | bom04970 | GNAQ; PRKG1; KCNMA1; ITPR2 |
| 胰腺分泌Pancreatic secretion | bom04972 | GNAQ; SLC4A4; KCNMA1; ITPR2 |
| Rap1信号通路Rap1 signaling pathway | bom04015 | ADORA2B; KIT; VEGFC; NGF; PDGFRB |
| 谷氨酸突触Glutamatergic synapse | bom04724 | GNAQ; PPP3CC; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 卵母细胞减数分裂Oocyte meiosis | bom04114 | ANAPC10; YWHAQ; PPP3CC; ITPR2 |
| 甲状腺激素的合成Thyroid hormone synthesis | bom04918 | GNAQ; PAX8; ITPR2 |
| MAPK信号通路MAPK signaling pathway | bom04010 | NGF; PPP3CC; MEF2C; PDGFRB; CACNB4 |
| 血小板激活Platelet activation | bom04611 | GNAQ; PRKG1; ROCK2; ITPR2 |
| 多巴胺能神经突触Dopaminergic synapse | bom04728 | GNAQ; PPP3CC; KCNJ3; ITPR2 |
| 胆汁分泌Bile secretion | bom04976 | NCEH1; SLC5A1 |
| 促性腺激素信号通路GnRH signaling pathway | bom04912 | GNAQ; ITPR2 |
| 节律导引Circadian entrainment | bom04713 | GNAQ; PRKG1; KCNJ3 |
| 炎症介质调节TRP通道Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | bom04750 | GNAQ; NGF; ITPR2 |
| Ras信号通路Ras signaling pathway | bom04014 | KIT; VEGFC; NGF; PDGFRB |
| 磷脂酰肌醇信号系统Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | bom04070 | PI4KA; ITPK1; ITPR2 |
| 1 | Zhang Y J, Wang F. Investigation and analysis report on yak market and industry in China. Agricultural Products Market, 2021(23): 54-55. |
| 张越杰, 王芳. 我国牦牛市场与产业调查分析报告. 农产品市场, 2021(23): 54-55. | |
| 2 | Cai B L. Maiwa yak. China Yak, 1981(1): 33-36. |
| 蔡伯凌. 麦洼牦牛. 中国牦牛, 1981(1): 33-36. | |
| 3 | Zhou F L, Liu X X, He X Q, et al. Preliminary study on breeding of Maiwa yak. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2021(4): 73-75, 79. |
| 周凡莉, 刘晓霞, 何小强, 等. 麦洼牦牛选育初探. 草学, 2021(4): 73-75, 79. | |
| 4 | Yin Z. Strengthening the functions of livestock farms, promoting the development of yak industry. Prataculture & Animal Husbandry, 2011(12): 61-62. |
| 银忠. 强化种畜场职能, 促进牦牛业发展. 草业与畜牧, 2011(12): 61-62. | |
| 5 | Li S L, Luo G R, Xiao M, et al. Comparing the production performance between Maiwa yaks with different coat colors. Prataculture & Animal Husbandry, 2014(3): 30-32. |
| 李世林, 罗光荣, 肖敏, 等. 不同特征麦洼牦牛生产性能分析. 草业与畜牧, 2014(3): 30-32. | |
| 6 | Li Z, He S M, Wu J B, et al. Correlation analysis between body sizes and meat production performance of yak under standardized production condition. Contemporary Animal Husbandry, 2020, 2: 13-17. |
| 李铸, 何世明, 吴锦波, 等. 标准化生产牦牛体尺与产肉性能相关性分析. 当代畜牧, 2020, 2: 13-17. | |
| 7 | Luo H, Zhao F F, Sun L, et al. Screening the polymorphic tri-nucleotide repeat microsatellites from the genome of Maiwa yak and their genetic diversity analysis. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(5): 1438-1445. |
| 罗辉, 赵芳芳, 孙磊, 等. 麦洼牦牛基因组三碱基重复微卫星的挖掘及其遗传多态性分析. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44(5): 1438-1445. | |
| 8 | Zhu Y B, Pingcuo Z D, Luosang D Z, et al. Population genetic diversity assessment of local yak and semi-wild yak in Gaize county based on MHC genetic markers. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(21): 209-211. |
| 朱彦宾, 平措占堆, 洛桑顿珠, 等. 基于MHC遗传标记的改则县本地牦牛与半野血牦牛群体遗传多样性评估. 现代农业科技, 2019(21): 209-211. | |
| 9 | Mao Y J, Chang H, Yang Z P, et al. Population genetic analysis of yak blood protein locus in Qinghai Plateau. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2008(5): 8-10. |
| 毛永江, 常洪, 杨章平, 等. 青海高原牦牛血液蛋白基因座群体遗传学分析. 中国畜牧杂志, 2008(5): 8-10. | |
| 10 | Ji Q M, Tang Y T, Zhang C F, et al. Genetic diversity and evolution relationship of Tibet yaks inferred from mtDNA cytb. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2012, 43(11): 1723-1732. |
| 姬秋梅, 唐懿挺, 张成福, 等. 西藏牦牛mtDNA cytb基因的序列多态性及其系统进化分析. 畜牧兽医学报, 2012, 43(11): 1723-1732. | |
| 11 | Shi F, Chai Z X, Luo X L, et al. Polymorphic frequency of genetic variation in Maiwa yak by RAPD. Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 47(2): 5-10. |
| 师方, 柴志欣, 罗晓林, 等. 麦洼牦牛的随机扩增多态性DNA遗传多样性分析. 畜牧与兽医, 2015, 47(2): 5-10. | |
| 12 | Wang X D, Guo X, Wu X Y, et al. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic analysis of mtDNA Cytb gene and D-loop region in yak of Qinghai Plateau. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2021, 40(1): 9-17. |
| 王兴东, 郭宪, 吴晓云, 等. 青海高原牦牛mtDNA Cytb基因和D-loop区遗传多样性及系统进化分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2021, 40(1): 9-17. | |
| 13 | Ji H, Guan J Q, Wang H, et al. Genetic structure and diversity of Yading yak and Larima yak populations. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 134-145. |
| 纪会, 官久强, 王会, 等. 亚丁牦牛和拉日马牦牛遗传多样性及遗传结构分析. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 134-145. | |
| 14 | Zhu F, Cui Q Q, Hou Z C. SNP discovery and genotyping using genotyping-by-sequencing in Pekin ducks. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-5. |
| 15 | Xue X J, Du X Y, Gai Y, et al. Application progress of SNPs in plants based on GBS sequencing. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(13): 62-68. |
| 薛晓杰, 杜晓云, 盖艺, 等. 基于GBS测序开发SNP在植物上的应用进展. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(13): 62-68. | |
| 16 | Zhu F. Construction of GBS platform for Peking ducks and genome wide association analysis of some economic traits. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 朱峰. 北京鸭GBS平台构建及部分经济性状全基因组关联分析. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. | |
| 17 | Gao X G, Bao X B, Gao M L. Analysis of genetic diversity of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with genotyping-by-sequencing technology. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(36): 80-82. |
| 高祥刚, 鲍相渤, 高美玲. 基于GBS技术的中华绒螯蟹的遗传特征分析. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(36): 80-82. | |
| 18 | Dong S W, Wang T J, Liu H M, et al. Analysis of genomic SNP characteristics of sika deer, deer and their hybrid progenies based on GBS technology. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2019, 50(12): 2422-2430. |
| 董世武, 王天骄, 刘华淼, 等. 基于GBS技术对梅花鹿、马鹿及其杂交后代基因组SNP特征的分析. 畜牧兽医学报, 2019, 50(12): 2422-2430. | |
| 19 | Zhang D, Zhang X, Li F, et al. Whole-genome resequencing identified candidate genes associated with the number of ribs in Hu sheep. Genomics, 2021, 113(4): 2077-2084. |
| 20 | Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(16): 2078-2079. |
| 21 | Liu Y, Yi F, Yang G, et al. Geographic population genetic structure and diversity of Sophora moorcroftiana based on genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS). PeerJ, 2020, 8: e9609. |
| 22 | Ren Y, Macphillamy C, To T H, et al. Adaptive selection signatures in river buffalo with emphasis on immune and major histocompatibility complex genes. Genomics, 2021, 113(6): 3599-3609. |
| 23 | Zhang C, Dong S S, Xu J Y, et al. PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(10): 1786-1788. |
| 24 | Deniskova T, Dotsev A, Petrov S, et al. Genomic assessment and phenotypic characteristics of F2 resource sheep population. Agricultural Science Euro-North-East, 2019, 20(5): 498-507. |
| 25 | Zhao F F. Mining and screening verifying the microsatellites from the genome of yak. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2015. |
| 赵芳芳. 牦牛基因组微卫星挖掘与筛选验证. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2015. | |
| 26 | Hou M D, Wang H, Chai Z X, et al. The polymorphisms of yak RETN gene and its associations with growth traits. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2020, 39(10): 4432-4440. |
| 侯孟典, 王会, 柴志欣, 等. 牦牛RETN基因遗传多态性与生长性状相关性分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2020, 39(10): 4432-4440. | |
| 27 | Chai Z X, Wang Y, Zhong J C, et al. Association of MC4R gene polymorphism with growth traits in Maiwa yak. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2013, 22(9): 1-6. |
| 柴志欣, 王永, 钟金城, 等. 麦洼牦牛MC4R基因多态性及与生长性状的相关分析. 西北农业学报, 2013, 22(9): 1-6. | |
| 28 | Li R, Li C, Chen H, et al. Genome-wide scan of selection signatures in Dehong humped cattle for heat tolerance and disease resistance. Animal Genetics, 2020, 51(2): 292-299. |
| 29 | Porto N L R, Sonstegard T S, Liu G E, et al. Genomic divergence of zebu and taurine cattle identified through high-density SNP genotyping. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14(1): 1-12. |
| 30 | Li J, Liu J, Campanile G, et al. Novel insights into the genetic basis of buffalo reproductive performance. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1): 1-11. |
| 31 | Yi K L, Zhou X, Shi D S. Effects of nerve growth factor on the development of parthenogenetic and in vitro fertilized bovine early embryo. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2008(5): 588-591. |
| 易康乐, 周虚, 石德顺. NGF对牛体外受精和孤雌激活早期胚胎发育的影响. 中国兽医学报, 2008(5): 588-591. | |
| 32 | Li Z. Study on the biological function of Gnaq and Gnas genes in sheep. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 李振. 绵羊Gnaq和Gnas基因生物学功能研究. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2017. | |
| 33 | Zielak-Steciwko A E, Browne J A, Mcgettigan P A, et al. Expression of microRNAs and their target genes and pathways associated with ovarian follicle development in cattle. Physiological Genomics, 2014, 46(19): 735-745. |
| 34 | Zhan Z Y. Genetic variation and analysis of their effects and tissue expression regular pattern of MEF2C gene in yellow cattle. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2014. |
| 展召阳. 黄牛MEF2C基因遗传变异及其效应分析和组织表达规律研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. | |
| 35 | Pelosi M, Marampon F, Zani B M, et al. ROCK2 and its alternatively spliced isoform ROCK2m positively control the maturation of the myogenic program. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2007, 27(17): 6163-6176. |
| 36 | Yee M, Cohen E D, Domm W, et al. Neonatal hyperoxia depletes pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes in adult mice via mitochondrial oxidation. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 2018, 314(5): 846-859. |
| 37 | Cheruiyot E K, Haile M M, Cocks B G, et al. New loci and neuronal pathways for resilience to heat stress in cattle. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 1-16. |
| 38 | Jiang E Z, Zhang Y F, Guo Y Y, et al. Progress in the research of the effect of the KIT gene on the formation of white coat in mammals. Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 51(11): 147-150. |
| 姜恩泽, 张宇飞, 郭跃跃, 等. KIT基因影响哺乳动物白色被毛形成的研究进展. 畜牧与兽医, 2019, 51(11): 147-150. |
| [1] | 任雪锋, 邓亚博, 臧国长, 郑轶琦. 基于SSR标记的河南省狗牙根遗传多样性及群体遗传结构分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 60-70. |
| [2] | 尹晓凡, 魏娜, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿反转录转座子IRAP分子标记开发及应用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 131-144. |
| [3] | 李进, 陈仕勇, 赵旭, 田浩琦, 陈智华, 周青平. 基于SCoT标记的饲用燕麦品种遗传结构及指纹图谱分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 72-81. |
| [4] | 纪会, 官久强, 王会, 周建旭, 阿农呷, 何宗伟, 樊珍详, 邱龙康, 曹诗晓, 安添午, 柏琴, 钟金城, 罗晓林. 亚丁牦牛和拉日马牦牛遗传多样性及遗传结构分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 134-145. |
| [5] | 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 张茂, 董瑞. 利用数字图像分析132份胡枝子种子表型性状遗传多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 87-97. |
| [6] | 雷雄, 游明鸿, 白史且, 陈丽丽, 邓培华, 熊毅, 熊艳丽, 余青青, 马啸, 杨建, 张昌兵. 川西北高原50份燕麦种质农艺性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 131-142. |
| [7] | 丁永福, 王纪良, 陈奋奇, 庄泽龙, 白明兴, 陆晏天, 金兵兵, 彭云玲. 玉米自交系SSR多样性与穗部性状的关联分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 143-153. |
| [8] | 王建丽, 马利超, 申忠宝, 刘杰淋, 朱瑞芬, 韩微波, 钟鹏, 邸桂俐, 韩贵清, 郭长虹. 基于遗传多样性评估燕麦品种的农艺性状[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 133-141. |
| [9] | 张彦军, 苟作旺, 王兴荣, 李玥, 祁旭升. 西北地区和尚头小麦遗传多样性及农艺性状的关联分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 142-155. |
| [10] | 宫文龙, 王赞, 赵桂琴, 马琳, 韦宝, 龚攀, 刘希强. 沙打旺EST-SSR分子标记开发及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 147-158. |
| [11] | 朱永群, 彭丹丹, 林超文, 聂刚, 许文志, 黄琳凯, 罗付香, 彭建华, 张新全. 苏丹草转录组SSR分子标记开发及遗传多样性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 178-189. |
| [12] | 杨艳婷, 侯向阳, 魏臻武, 乔志宏, 常春, 任卫波, 武自念. 羊草叶绿体非编码区多态性标记筛选及群体遗传多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 147-157. |
| [13] | 刘丽, 王贵珍, 周延山, 楚彬, 马素洁, 姬程鹏, 田永亮, 花立民. 基于小尺度高原鼢鼠种群遗传结构研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 123-130. |
| [14] | 涂明月, 李杰, 何亚丽, 李醒, 李俊, 袁晓君. 利用RAPD标记鉴定草地早熟禾种质资源的遗传多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 71-81. |
| [15] | 陈辉, 杨晖, 强维亚. 十个歪头菜居群遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 96-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||