

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 160-170.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023104
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
李庭伦1( ), 李一亨1, 余慧1, 江再莉2, 唐立涛1, 王长庭1, 胡雷1(
), 李一亨1, 余慧1, 江再莉2, 唐立涛1, 王长庭1, 胡雷1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-04
修回日期:2023-05-08
出版日期:2023-12-20
发布日期:2023-10-18
通讯作者:
胡雷
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: hl007873@163.com基金资助:
Ting-lun LI1( ), Yi-heng LI1, Hui YU1, Zai-li JIANG2, Li-tao TANG1, Chang-ting WANG1, Lei HU1(
), Yi-heng LI1, Hui YU1, Zai-li JIANG2, Li-tao TANG1, Chang-ting WANG1, Lei HU1( )
)
Received:2023-04-04
Revised:2023-05-08
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2023-10-18
Contact:
Lei HU
摘要:
本研究通过模拟铅卤钙钛矿泄漏导致的不同铅(Pb)胁迫梯度(0, 36, 72, 130, 170和260 mg·kg-1),监测高寒草甸优质牧草垂穗披碱草幼苗生长情况,重点分析Pb胁迫对垂穗披碱草幼苗Pb富集能力和耐受能力的影响。结果表明:1)垂穗披碱草的出苗率并未受到Pb胁迫梯度的显著影响,但出苗速率和出苗持续时间随Pb胁迫增加而显著降低;2)Pb胁迫显著抑制垂穗披碱草幼苗高度,但单株幼苗生物量则表现为浓度效应,小于72 mg·kg-1 Pb浓度作用不显著,大于72 mg·kg-1时表现为抑制作用,在260 mg·kg-1时无法萌发;3)垂穗披碱草幼苗的Pb富集能力显著降低,Pb耐受范围为68.42~205.94 mg·kg-1;4)结构方程模型表明,铅卤钙钛矿泄漏导致的Pb胁迫通过降低土壤pH和增加硝态氮含量改变垂穗披碱草幼苗生长情况,进而影响其Pb富集能力和耐受范围。土壤pH值和硝态氮含量是影响垂穗披碱草幼苗生长的重要因子,在铅卤钙钛矿泄漏情境下可以通过提高土壤pH增加其Pb耐受能力。
李庭伦, 李一亨, 余慧, 江再莉, 唐立涛, 王长庭, 胡雷. 铅卤钙钛矿泄漏对垂穗披碱草幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 160-170.
Ting-lun LI, Yi-heng LI, Hui YU, Zai-li JIANG, Li-tao TANG, Chang-ting WANG, Lei HU. Effects of the lead halide perovskite on the seedling growth of Elymus nutans[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(12): 160-170.
铅浓度 Pb concentration (mg·kg-1) | 出苗率 Emergence ratio (%) | 出苗时滞 Emergence delay (d) | 出苗速率 Emergence rate (No.·d-1) | 出苗持续时间 Emergence duration (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16.0±3.16a | 3.6±0.49b | 0.321±0.068a | 10.8±3.87a |
| 36 | 16.4±1.72a | 4.0±0.00ab | 0.319±0.041a | 7.0±2.53b |
| 72 | 19.2±3.44a | 3.4±0.49b | 0.292±0.053ab | 8.2±1.33ab |
| 130 | 14.4±2.40a | 4.2±0.75ab | 0.188±0.033ab | 8.2±1.60ab |
| 170 | 13.2±1.20a | 4.6±0.49a | 0.159±0.010b | 6.4±0.49b |
表1 不同铅浓度对垂穗披碱草出苗情况的影响
Table 1 The effects of Pb gradients on the seedlings emergence of E.nutans
铅浓度 Pb concentration (mg·kg-1) | 出苗率 Emergence ratio (%) | 出苗时滞 Emergence delay (d) | 出苗速率 Emergence rate (No.·d-1) | 出苗持续时间 Emergence duration (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16.0±3.16a | 3.6±0.49b | 0.321±0.068a | 10.8±3.87a |
| 36 | 16.4±1.72a | 4.0±0.00ab | 0.319±0.041a | 7.0±2.53b |
| 72 | 19.2±3.44a | 3.4±0.49b | 0.292±0.053ab | 8.2±1.33ab |
| 130 | 14.4±2.40a | 4.2±0.75ab | 0.188±0.033ab | 8.2±1.60ab |
| 170 | 13.2±1.20a | 4.6±0.49a | 0.159±0.010b | 6.4±0.49b |

图1 不同铅浓度梯度处理下垂穗披碱草幼苗高度和生物量的变化不同小写字母表示不同铅浓度处理之间差异显著 (P<0.05),下同。Different lowercases indicate the significant differences among the different Pb concentration (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Changes in height and biomass of E. nutans seedling with Pb concentration gradients
铅浓度 Pb concentration (mg·kg-1) | 土壤pH Soil pH | NH4+-N含量 NH4+-N content (mg·kg-1) | NO3--N含量 NO3--N content (mg·kg-1) | 全碳含量 Total carbon content (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8.48±0.06a | 0.97±0.23a | 3.97±1.27b | 11.93±0.49ab |
| 36 | 8.40±0.03ab | 0.73±0.03a | 5.97±0.66ab | 11.97±0.01ab |
| 72 | 8.43±0.01ab | 1.07±0.20a | 5.80±0.17ab | 11.27±0.02b |
| 130 | 8.39±0.03ab | 1.41±0.83a | 6.71±0.41ab | 11.50±0.06ab |
| 170 | 8.31±0.01b | 0.57±0.05a | 7.62±1.67a | 12.37±0.01a |
表2 不同铅浓度梯度土壤理化性质
Table 2 Soil physicochemical properties with different Pb concentration gradients
铅浓度 Pb concentration (mg·kg-1) | 土壤pH Soil pH | NH4+-N含量 NH4+-N content (mg·kg-1) | NO3--N含量 NO3--N content (mg·kg-1) | 全碳含量 Total carbon content (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8.48±0.06a | 0.97±0.23a | 3.97±1.27b | 11.93±0.49ab |
| 36 | 8.40±0.03ab | 0.73±0.03a | 5.97±0.66ab | 11.97±0.01ab |
| 72 | 8.43±0.01ab | 1.07±0.20a | 5.80±0.17ab | 11.27±0.02b |
| 130 | 8.39±0.03ab | 1.41±0.83a | 6.71±0.41ab | 11.50±0.06ab |
| 170 | 8.31±0.01b | 0.57±0.05a | 7.62±1.67a | 12.37±0.01a |
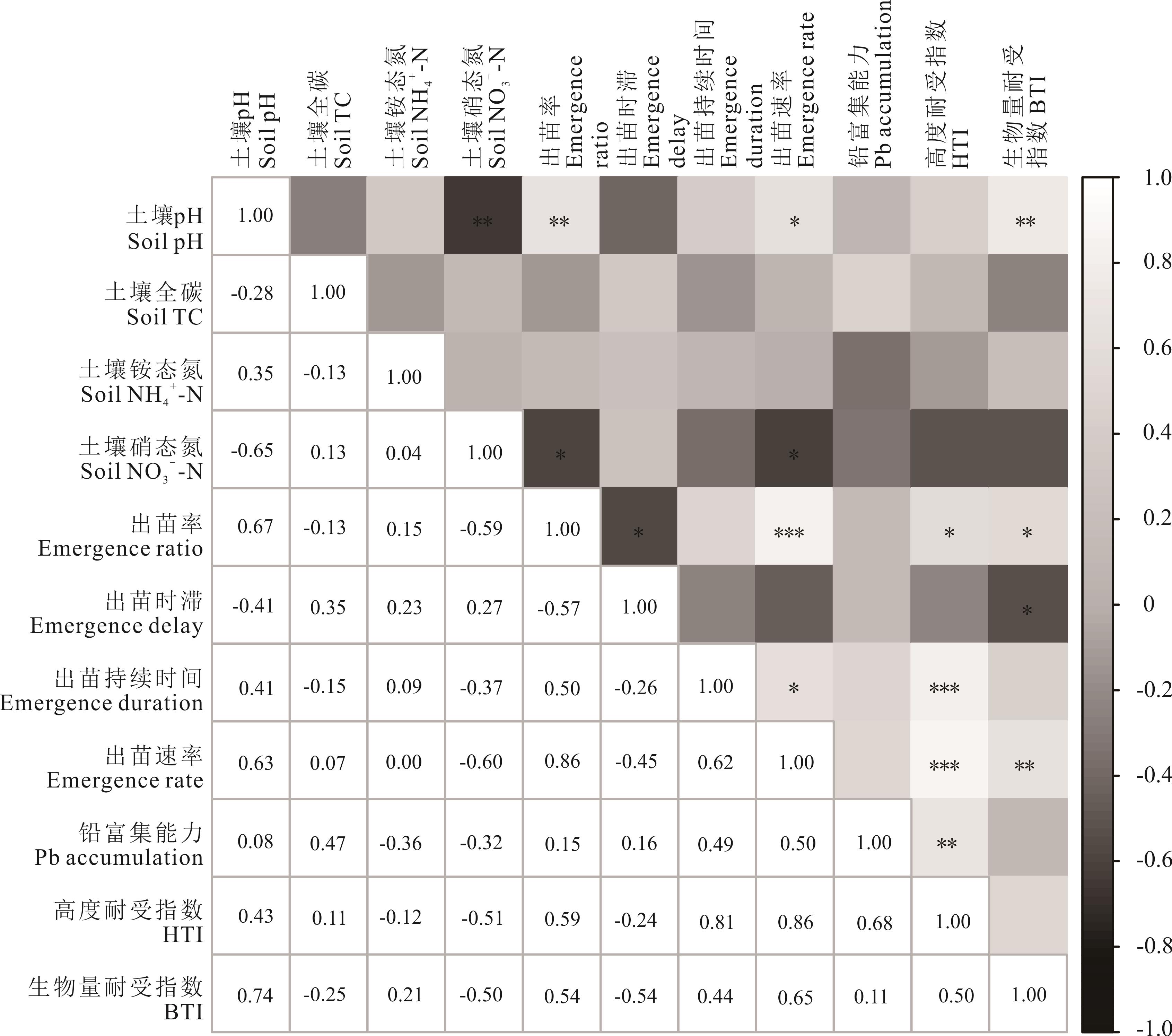
图 4 土壤理化性质和垂穗披碱草幼苗性状的Pearson相关性分析*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001.
Fig.4 The Pearson correlation analysis among soil physicochemical properties and seedling characteristics of E. nutans
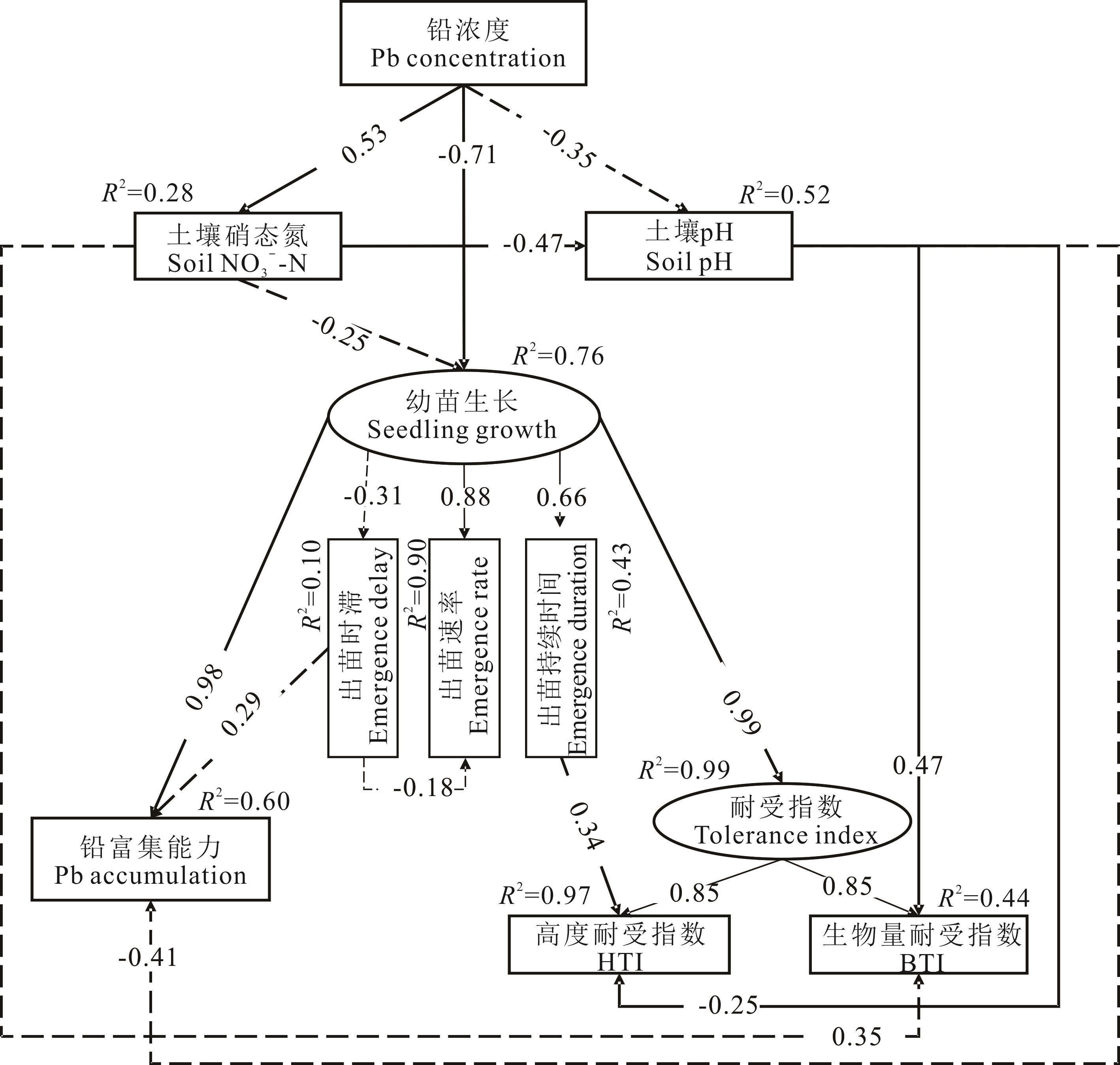
图5 铅浓度对垂穗披碱草幼苗生长情况的SEM分析比较拟合指数/自由度Compare the fit index/free degree (CFI/DF)=0.343, 拟合优度指标Goodness of fit index (GFI)=0.930, 渐进误差均方根Root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA)<0.001, P=0.993.实线表示路径显著(P<0.05),虚线表示路径不显著(P>0.05) The solid lines indicated the significant effects (P<0.05), and the dotted lines indicated the insignificant effects (P>0.05).
Fig.5 The SEM analysis for the seedling growth of E. nutans affected by Pb concentration gradients
变量 Variables | 铅胁迫Pb concentration | 硝态氮 NO3--N | 土壤pH Soil pH | 幼苗生长 Seedling growth | 铅耐受能力Pb tolerance index | 出苗时滞 Emergence delay | 出苗持续时间 Emergence duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硝态氮NO3--N | 0.529 | ||||||
| 土壤pH Soil pH | -0.601 | -0.467 | |||||
| 幼苗生长Seedling growth | -0.847 | -0.255 | |||||
| 铅耐受能力Pb tolerance index | -0.847 | -0.255 | 0.999 | ||||
| 出苗时滞Emergence delay | 0.262 | 0.079 | -0.309 | ||||
| 出苗持续时间Emergence duration | -0.558 | -0.168 | 0.659 | ||||
| 出苗速率Emergence rate | -0.793 | -0.238 | 0.936 | -0.177 | |||
| 生物量耐受指数BTI | -0.821 | -0.090 | 0.472 | 0.851 | 0.851 | ||
| 高度耐受指数HTI | -0.765 | -0.160 | -0.245 | 1.000 | 0.853 | 0.341 | |
| 铅富集能力Pb accumulation | -0.510 | -0.037 | -0.405 | 0.889 | 0.294 |
表3 不同变量的综合影响系数
Table 3 The standardized total effects of the variables
变量 Variables | 铅胁迫Pb concentration | 硝态氮 NO3--N | 土壤pH Soil pH | 幼苗生长 Seedling growth | 铅耐受能力Pb tolerance index | 出苗时滞 Emergence delay | 出苗持续时间 Emergence duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硝态氮NO3--N | 0.529 | ||||||
| 土壤pH Soil pH | -0.601 | -0.467 | |||||
| 幼苗生长Seedling growth | -0.847 | -0.255 | |||||
| 铅耐受能力Pb tolerance index | -0.847 | -0.255 | 0.999 | ||||
| 出苗时滞Emergence delay | 0.262 | 0.079 | -0.309 | ||||
| 出苗持续时间Emergence duration | -0.558 | -0.168 | 0.659 | ||||
| 出苗速率Emergence rate | -0.793 | -0.238 | 0.936 | -0.177 | |||
| 生物量耐受指数BTI | -0.821 | -0.090 | 0.472 | 0.851 | 0.851 | ||
| 高度耐受指数HTI | -0.765 | -0.160 | -0.245 | 1.000 | 0.853 | 0.341 | |
| 铅富集能力Pb accumulation | -0.510 | -0.037 | -0.405 | 0.889 | 0.294 |
| 1 | Ma C Q, Felix T E, Lee S H, et al. Unveiling facet-dependent degradation and facet engineering for stable perovskite solar cells. Science, 2023, 379: 173-178. |
| 2 | Zhao X M, Liu T R, Quinn C B, et al. Accelerated aging of all-inorganic, interface-stabilized perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 377: 307-310. |
| 3 | Babayigit A, Duy Thanh D, Ethirajan A, et al. Assessing the toxicity of Pb- and Sn-based perovskite solar cells in model organism Danio rerio. Scientific Reports, 2016(6): 18721. |
| 4 | Bekele H, Hailegnaw S, Rran E, et al. Rain on methylammonium lead iodide-based perovskites: possible environmental effects of perovskite solar cells. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2015, 6(9): 1543-1547. |
| 5 | Aristidou N, Sanchez M I, Thana C, et al. The role of oxygen in the degradation of methylammonium lead trihalide perovskite photoactive layers. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 127(28): 8326-8330. |
| 6 | Tsai S M, Mesina M, Goshia T, et al. Perovskite nanoparticles toxicity study on airway epithelial cells. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2019, 14(14): 1-8. |
| 7 | Zhai Y J, Zhuang W, Wang G Y, et al. The fate and toxicity of Pb-based perovskite nanoparticles on soil bacterial community: impacts of pH, humic acid, and divalent cations. Chemosphere, 2020, 249: 126564. |
| 8 | Danae P, Cristina D R, Ana I C, et al. Exposure to Pb-halide perovskite nanoparticles can deliver bioavailable Pb but does not alter endogenous gut microbiota in zebrafish. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 715(5): 136941. |
| 9 | Li J, Cao H L, Jiao W B, et al. Biological impact of lead from halide perovskites reveals the risk of introducing a safe threshold. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 310. |
| 10 | Li J X, Li H Y, Liu L E, et al. Tolerance mechanisms of plants under lead stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023(3): 1-11. |
| 李嘉欣, 李鸿燕, 刘丽娥, 等. 植物在铅胁迫下的耐受机制. 分子植物育种, 2023(3): 1-11. | |
| 11 | Duan D C, Yu M G, Shi J Y. Research advances in uptake, translocation, accumulation and detoxification of Pb in plants. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(1): 287-296. |
| 段德超, 于明革, 施积炎. 植物对铅的吸收、转运、累积和解毒机制研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(1): 287-296. | |
| 12 | Liu L. Translocation, migration, and control of heavy metals and health risk assessment in soil-vegetable system. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2018. |
| 刘丽. 重金属在土壤-蔬菜系统中的迁移转运与调控及其健康风险评估. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2018. | |
| 13 | Williams S T, McNeilly T, Wellington E M H. The decomposition of vegetation growing on metal mine wastes.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1977, 9: 271-275. |
| 14 | Barry S, Clark S C. Problems of interpreting the relationship between the amounts of lead and zinc in plants and soil on metalliferous wastes. New Phytologist, 1978, 81: 773-783. |
| 15 | Hu N, Li B C, Yao L R, et al. Effects of different heavy metals on the seed germination and establishment of Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(6): 66-81. |
| 胡娜, 李葆春, 姚立蓉, 等. 不同重金属胁迫对盐生草种子萌发特性的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 66-81. | |
| 16 | Begonia G B, Davis C D, Begonia M F, et al. Growth responses of Indian mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern] and its phytoextraction of lead from a contaminated soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1998, 61(1): 38-43. |
| 17 | Miller J E, Hassett J J, Keoppe D E. The effect of soil properties and extract able lead levels on lead uptake by soybeans. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1975, 6: 339-347. |
| 18 | Wu J, Meng X X, Li K. Phytoremediation of soils contaminated by lead. Soils, 2005, 37(3): 258-264. |
| 伍钧, 孟晓霞, 李昆. 铅污染土壤的植物修复研究进展. 土壤, 2005, 37(3): 258-264. | |
| 19 | Bai Y Z, Xie Y H, Chen C C, et al. Effects of 14 native herbaceous plants on Pb speciation characteristic and content in polluted soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(1): 136-140. |
| 白彦真, 谢英荷, 陈灿灿, 等. 14种本土草本植物对污染土壤铅形态特征与含量的影响. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(1): 136-140. | |
| 20 | Zhu Q, Li R, Liu Y J. Effects of lead stress on growth and physiological characteristics of 5 species of Cruciferae. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(4): 88-90. |
| 朱强, 李瑞, 刘玉娟. 铅胁迫对十字花科5种植物生长及生理特性的影响. 农业科技通讯, 2013(4): 88-90. | |
| 21 | Wang C Q, Miao Y J, Wang J L, et al. Studies on drought resistance of wild Elymus nutans in Tibet under drought stress at seedlings stage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(4): 116-120. |
| 王传旗, 苗彦军, 王建林, 等. 西藏野生垂穗披碱草苗期抗旱性研究. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(4): 116-120. | |
| 22 | Wang P, Chen J H, Wang P, et al. Status of research into the abiotic stress tolerance of Elymus species. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(5): 151-162. |
| 王沛, 陈玖红, 王平, 等. 披碱草属植物抗逆性研究现状和存在的问题. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 151-162. | |
| 23 | Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Soil environment quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agriculture land, GB15618-2018. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group, 2018. |
| 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行), GB15618-2018. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2018. | |
| 24 | Wang R K. Determination of soil pH by potentiometry. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2018, 3: 64-65. |
| 王瑞琨. 用电位法测定土壤pH值. 山西化工, 2018, 3: 64-65. | |
| 25 | Lu R K. Analysis method of agricultural chemistry in soil. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 26 | Bi X Y, Ren L M, Gong M, et al. Transfer of cadmium and lead from soil to mangoes in an uncontaminated area, Hainan Island, China. Geoderma, 2010, 155(1): 115-120. |
| 27 | Yan L Y, Fan C W, Zhao Z Y, et al. Heavy metal absorption and enrichment characteristics of dominant weed species naturally growing on farmland in Northern Guizhou. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(10): 237-244. |
| 严莲英, 范成五, 赵振宇, 等. 黔北轻污染耕地12种优势杂草重金属含量及富集特征. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 237-244. | |
| 28 | Liu X M, Nie J H, Wang Q R. Research on lead uptake and tolerance in six plants. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2002, 26(5): 533-537. |
| 刘秀梅, 聂俊华, 王庆仁. 6种植物对Pb的吸收与耐性研究. 植物生态学报, 2002, 26(5): 533-537. | |
| 29 | Wang B Q, Zhang X P, Chen J, et al. Adsorbability and tolerance capacity of sludges heavy metals by Carallia brachiata and Pinus elliottii. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2021, 209(2): 11-15. |
| 王冰清, 张学平, 陈杰, 等. 竹节树、湿地松对污泥重金属的吸附与耐受能力研究. 防护林科技, 2021, 209(2): 11-15. | |
| 30 | Yang E H. Effects of lead and cadmium stress on germination and seeding morphology of wheat and identification of the tolerance (resistance) for American wheat germplasm. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2017. |
| 杨二航. 铅、镉胁迫对小麦种子萌发和幼苗形态的影响及美国小麦种质耐(抗)性鉴定. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2017. | |
| 31 | Li H S. Modern plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002: 421-429. |
| 李合生.现代植物生理学. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002: 421-429. | |
| 32 | Zhang J Q, Chen J L, Li F, et al. Responses of seed germination and seedling growth of Poa pratensis to lead stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(1): 130-140. |
| 张金青, 陈金龙, 李凡, 等. 草地早熟禾种子萌发和幼苗生长对铅胁迫的适应性. 草地学报, 2020, 28(1): 130-140. | |
| 33 | Wang M, Wang J X, Wang Y X, et al. Effects of lead stress on seed and seedling of Bothriochloa ischaemum under different soil moisture. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(4): 841-848. |
| 王敏, 王进鑫, 王榆鑫, 等. 不同土壤水分条件下铅胁迫对白羊草种子和幼苗的影响. 草地学报, 2016, 24(4): 841-848. | |
| 34 | Liu H Q, Han J C, Liu H P, et al. Influence of lead gradient stress on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(6): 57-63. |
| 刘慧芹, 韩巨才, 刘慧平, 等. 铅梯度胁迫对多年生黑麦草幼苗生理生化特性影响. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 57-63. | |
| 35 | Chen J W. Study on response and potential phytoremediation of Bidens pilosa L.in cadmium and lead stress. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2013. |
| 谌金吾. 三叶鬼针草(Bidens pilosa L.)对重金属Cd、Pb胁迫的响应与修复潜能研究. 重庆: 西南大学, 2013. | |
| 36 | Li H F, Wang Y, Yuan Q H, et al. The impacts of lead stress on the growth of forage grasses and their enzyme activities. Seed, 2014, 33(8): 1-7. |
| 李慧芳, 王瑜, 袁庆华, 等. 铅胁迫对禾本科牧草的生长及体内酶活性的影响. 种子, 2014, 33(8): 1-7. | |
| 37 | Cheng J M, Pan G X, Zheng G W, et al. Several paddy soils buffering capacity to heavy metals in Tai Lake area. Agricultural Environmental Protection, 2000, 19(1): 21-24. |
| 成杰民, 潘根兴, 郑根伟, 等. 太湖地区几种水稻土对重金属的缓冲能力初探. 农业环境保护, 2000, 19(1): 21-24. | |
| 38 | Han Z P, Wang C Y. Accumulation and distribution of cadmium, lead, mercury, and copper in Arundo donax of different ecotype. Ecology and Environment, 2007(4): 1092-1097. |
| 韩志萍, 王趁义. 不同生态型芦竹对Cd、Hg、Pb、Cu的富集与分布. 生态环境, 2007(4): 1092-1097. | |
| 39 | Xu Y M, Wang C Q, Wu J X, et al. Effects of Mn2+ and Pb2+ on seed germination and seedling growth of Elymus nutans. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(3): 194-200. |
| 徐雅梅, 王传旗, 武俊喜, 等. Mn2+、Pb2+对野生垂穗披碱草种子萌发与幼苗生长的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 194-200. | |
| 40 | Liu X Q, Peng K J, Wang A G, et al. Cadmium accumulation and distribution in populations of Phytolacca americana L. and the role of transpiration. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(9): 1136-1141. |
| 41 | Kovalchuk I, Titov V, Hohn B, et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals similarities and differences in plant responses to cadmium and lead. Mutation Research, 2005, 570(2): 149-161. |
| 42 | Chen M Y. Study on tolerance and enrichment characteristics of cadmium, lead in Malva sinensis Cavan. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 陈明英. 锦葵对镉、铅的耐性和富集特征研究. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2011. | |
| 43 | Dong Y T, Cui Y S, Wang Q R. Uptake of Cd, Zn and Pb by two susceptible plants under mono- and multiple-contamination conditions. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003(5): 1018-1024. |
| 董艺婷, 崔岩山, 王庆仁. 单一与复合污染条件下两种敏感性植物对Cd、Zn、Pb的吸收效应. 生态学报, 2003(5): 1018-1024. | |
| 44 | Punamiya P, Datta R, Sarkar D, et al. Symbiotic role of Glomus mosseae in phytoextraction of lead in vetiver grass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1): 465-474. |
| 45 | Vega F A, Andrade M L, Covelo E F. Influence of soil properties on the sorption and retention of cadmium, copper and lead, separately and together, by 20 soil horizons: comparison of linear regression and tree regression analyses. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1): 522-533. |
| [1] | 马绍英, 陈桂平, 王娜, 马蕾, 连荣芳, 李胜, 张绪成. 豌豆土壤中潜在自毒物质的鉴定及自毒效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. |
| [2] | 何伟鹏, 胡夏嵩, 刘昌义, 李璇, 李希来, 付江涛, 卢海静, 杨馥铖, 李国荣. 黄河源区不同禁牧年限对垂穗披碱草单根及其根-土复合体力学强度特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 106-117. |
| [3] | 陆姣云, 田宏, 张鹤山, 熊军波, 刘洋, 王振南. H2O2浸种对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 141-152. |
| [4] | 许浩宇, 赵颖, 阮倩, 朱晓林, 王宝强, 魏小红. 不同混合盐碱下藜麦幼苗的抗性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 122-130. |
| [5] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| [6] | 穆海婷, 王英哲, 苗一凡, 郁伟杰, 徐博. 重金属铜和铅胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 139-146. |
| [7] | 张鹏, 任茜, 孟思宇, 魏小星, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对盐胁迫下紫花针茅种子萌发和幼苗生长的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 110-121. |
| [8] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生垂穗披碱草成苗期间的耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 76-85. |
| [9] | 闫慧芳, 孙娟. 含水量和劣变时间对高丹草种子活力及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 152-160. |
| [10] | 高玉莲, 常静, 王贻卉, 李锋, 李海平, 马崇勇. 瑞香狼毒根提取物对3种作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 83-91. |
| [11] | 李凤兰, 武佳文, 姚树宽, 赵梓颐, 赵潇璨, 贺付蒙, 朱元芳, 石奇海, 周磊, 徐永清. 假苍耳不同部位水浸提液对5种土著植物化感作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 169-178. |
| [12] | 崔雪莲, 夏超. 外源脱落酸对醉马草内生真菌共生体幼苗建植过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 70-80. |
| [13] | 梁军, 全小龙, 张杰雪, 史惠兰, 段中华, 乔有明. 3种禾草水提取液对其种子发芽和幼苗生长的潜在化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 81-89. |
| [14] | 李柯, 施宠, 何飞焱, 李昊宇. Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. |
| [15] | 黄勇, 郭猛, 张红瑞, 周艳, 李贺敏, 高致明, 王盼盼. 盐胁迫对石竹种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 105-111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||