

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 135-148.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023477
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-12-13
修回日期:2024-01-31
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
吴佳文
作者简介:E-mail: wujiawende@126.com基金资助:
Xiao-xiao LI( ), Pan ZHANG, Yuan LU, Ting LI, Na ZHAO, Jia-wen WU(
), Pan ZHANG, Yuan LU, Ting LI, Na ZHAO, Jia-wen WU( )
)
Received:2023-12-13
Revised:2024-01-31
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Jia-wen WU
摘要:
我国耕地镉污染问题非常严峻,阐明非生物逆境锻炼对玉米镉胁迫的生理响应,一方面可利用降低镉积累的非生物逆境锻炼保障玉米的品质,另一方面还可利用促进镉积累的非生物逆境锻炼提高玉米修复镉污染土壤的效率。本研究选取干旱、盐胁迫、缺铁和低浓度镉预处理分别作为交叉和同种非生物逆境短期锻炼玉米幼苗,然后施加或不施加镉胁迫处理,测定不同非生物逆境锻炼后玉米在镉胁迫下的生物量、根系形态、耐受系数、镉浓度及积累量、镉的亚细胞分布,以及抗氧化防御系统能力的变化。结果表明:缺铁、盐胁迫和干旱锻炼降低了玉米根、茎和叶干重,但这些非生物逆境锻炼显著提高了玉米对镉的耐受系数。干旱锻炼降低了玉米根、茎和叶镉浓度及积累量,而且干旱锻炼促使更多的镉分布在液泡。相比之下,低浓度镉锻炼增加了玉米根和叶镉浓度及叶片镉积累量,但没有改变亚细胞镉的分布比例。非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米叶片和根超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性无显著性的影响,表明非生物逆境锻炼没有刺激抗氧化酶响应玉米的镉胁迫。通过相关性分析发现玉米总根长与非生物逆境锻炼下镉积累密切相关,叶片细胞壁镉浓度与玉米镉积累呈正相关,根液泡镉浓度与玉米镉积累呈负相关。非生物逆境锻炼能显著提高玉米耐镉性,其中干旱锻炼可应用于降低玉米积累镉。
李霄霄, 张盼, 卢园, 李婷, 赵娜, 吴佳文. 非生物逆境锻炼对玉米镉胁迫的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 135-148.
Xiao-xiao LI, Pan ZHANG, Yuan LU, Ting LI, Na ZHAO, Jia-wen WU. Abiotic stress priming affects the responses of maize (Zea mays) plants to cadmium stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 135-148.

图1 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫玉米根、茎和叶干重的影响小写字母表示不加镉(CK)时各处理之间在Duncan多重比较P<0.05水平差异显著,大写字母表示加镉时各处理之间差异显著。***、**、*和ns分别表示不加镉和加镉处理之间在student t检验P<0.001、0.001<P<0.01、0.01<P<0.05水平有差异和没有显著性差异。下同。Lowercase letters represent significant differences among treatments without Cd addition (CK) at the level of 0.05 based on Duncan’ multiple range comparisons, while uppercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments with Cd addition. “***”, “**”, “*” and “ns” respectively represent significant differences between -Cd and +Cd based on student t-test at the level of 0.001, 0.01, 0.05 and no significant difference. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of abiotic stress priming on dry weight of roots, stems and leaves in maize under Cd stress
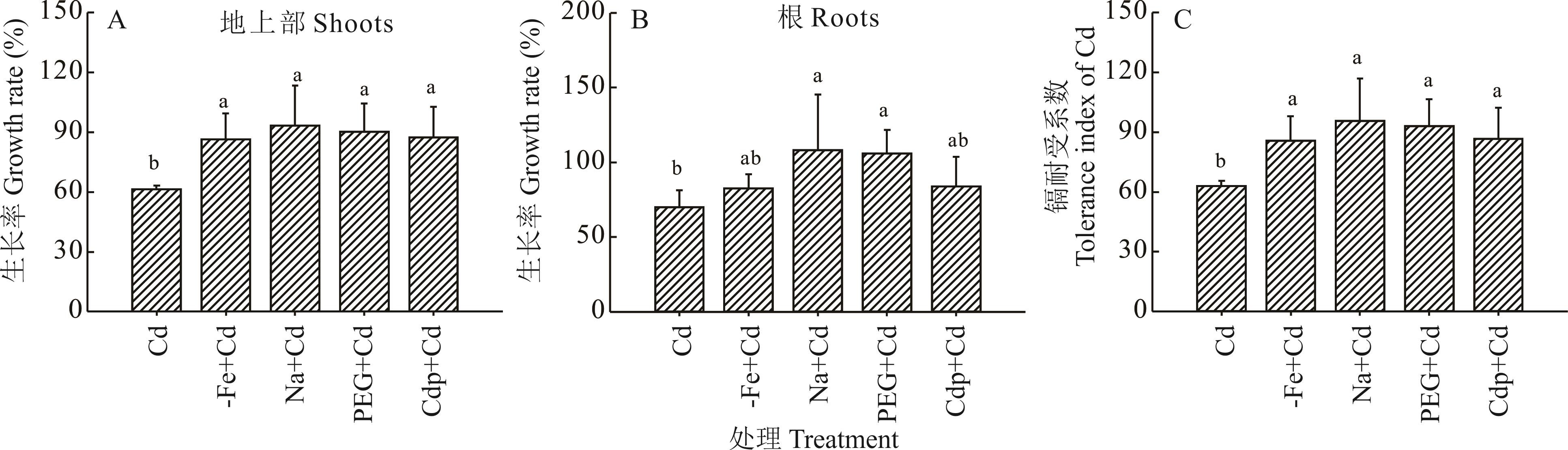
图2 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫玉米地上部和根生长率及镉耐受系数的影响不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著,下同。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences among different treatments at P<0.05, the same below.
Fig.2 Effects of abiotic stress priming on growth rates of shoots, roots and tolerance index of Cd in maize under Cd stress
处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Number of root tips | 根直径 Root diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -Cd | |||||
| CK | 1819±404a | 880±141a | 244±88a | 1674±230a | 1.5±0.4ab |
| -Fe | 1168±372b | 573±194b | 155±61b | 1110±397bc | 1.0±0.4b |
| Na | 1093±307b | 595±42b | 171±45ab | 1109±279bc | 1.1±0.2b |
| PEG | 1082±258b | 704±128ab | 223±45ab | 984±129c | 1.7±0.5a |
| Cdp | 1525±243ab | 660±128b | 155±49b | 1465±220ab | 1.0±0.3b |
| +Cd | |||||
| CK | 945±141c | 559±57a | 169±54a | 803±122c | 1.3±0.3a |
| -Fe | 1093±51bc | 536±15a | 131±12ab | 1050±148bc | 1.0±0.0ab |
| Na | 1363±426ab | 648±104a | 149±48a | 1220±386ab | 1.1±0.4ab |
| PEG | 849±120c | 415±130b | 85±39b | 860±135c | 0.8±0.4b |
| Cdp | 1536±224a | 646±20a | 132±10ab | 1434±252a | 0.9±0.1ab |
| -Cd v.s. +Cd (P值P value) | |||||
| CK | 0.002** | 0.005** | 0.151ns | 0.000*** | 0.466ns |
| -Fe | 0.674ns | 0.695ns | 0.432ns | 0.766ns | 0.804ns |
| Na | 0.287ns | 0.337ns | 0.491ns | 0.618ns | 0.936ns |
| PEG | 0.119ns | 0.007** | 0.001*** | 0.176ns | 0.010** |
| Cdp | 0.947ns | 0.815ns | 0.371ns | 0.838ns | 0.317ns |
表1 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米根系形态的影响
Table 1 Effects of abiotic stress priming on root morphology of maize under Cd stress
处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Number of root tips | 根直径 Root diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -Cd | |||||
| CK | 1819±404a | 880±141a | 244±88a | 1674±230a | 1.5±0.4ab |
| -Fe | 1168±372b | 573±194b | 155±61b | 1110±397bc | 1.0±0.4b |
| Na | 1093±307b | 595±42b | 171±45ab | 1109±279bc | 1.1±0.2b |
| PEG | 1082±258b | 704±128ab | 223±45ab | 984±129c | 1.7±0.5a |
| Cdp | 1525±243ab | 660±128b | 155±49b | 1465±220ab | 1.0±0.3b |
| +Cd | |||||
| CK | 945±141c | 559±57a | 169±54a | 803±122c | 1.3±0.3a |
| -Fe | 1093±51bc | 536±15a | 131±12ab | 1050±148bc | 1.0±0.0ab |
| Na | 1363±426ab | 648±104a | 149±48a | 1220±386ab | 1.1±0.4ab |
| PEG | 849±120c | 415±130b | 85±39b | 860±135c | 0.8±0.4b |
| Cdp | 1536±224a | 646±20a | 132±10ab | 1434±252a | 0.9±0.1ab |
| -Cd v.s. +Cd (P值P value) | |||||
| CK | 0.002** | 0.005** | 0.151ns | 0.000*** | 0.466ns |
| -Fe | 0.674ns | 0.695ns | 0.432ns | 0.766ns | 0.804ns |
| Na | 0.287ns | 0.337ns | 0.491ns | 0.618ns | 0.936ns |
| PEG | 0.119ns | 0.007** | 0.001*** | 0.176ns | 0.010** |
| Cdp | 0.947ns | 0.815ns | 0.371ns | 0.838ns | 0.317ns |

图3 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米根、茎和叶镉浓度以及镉积累量的影响
Fig.3 Effects of abiotic stress priming on Cd concentrations and Cd accumulation in roots, stems and leaves of maize under Cd stress
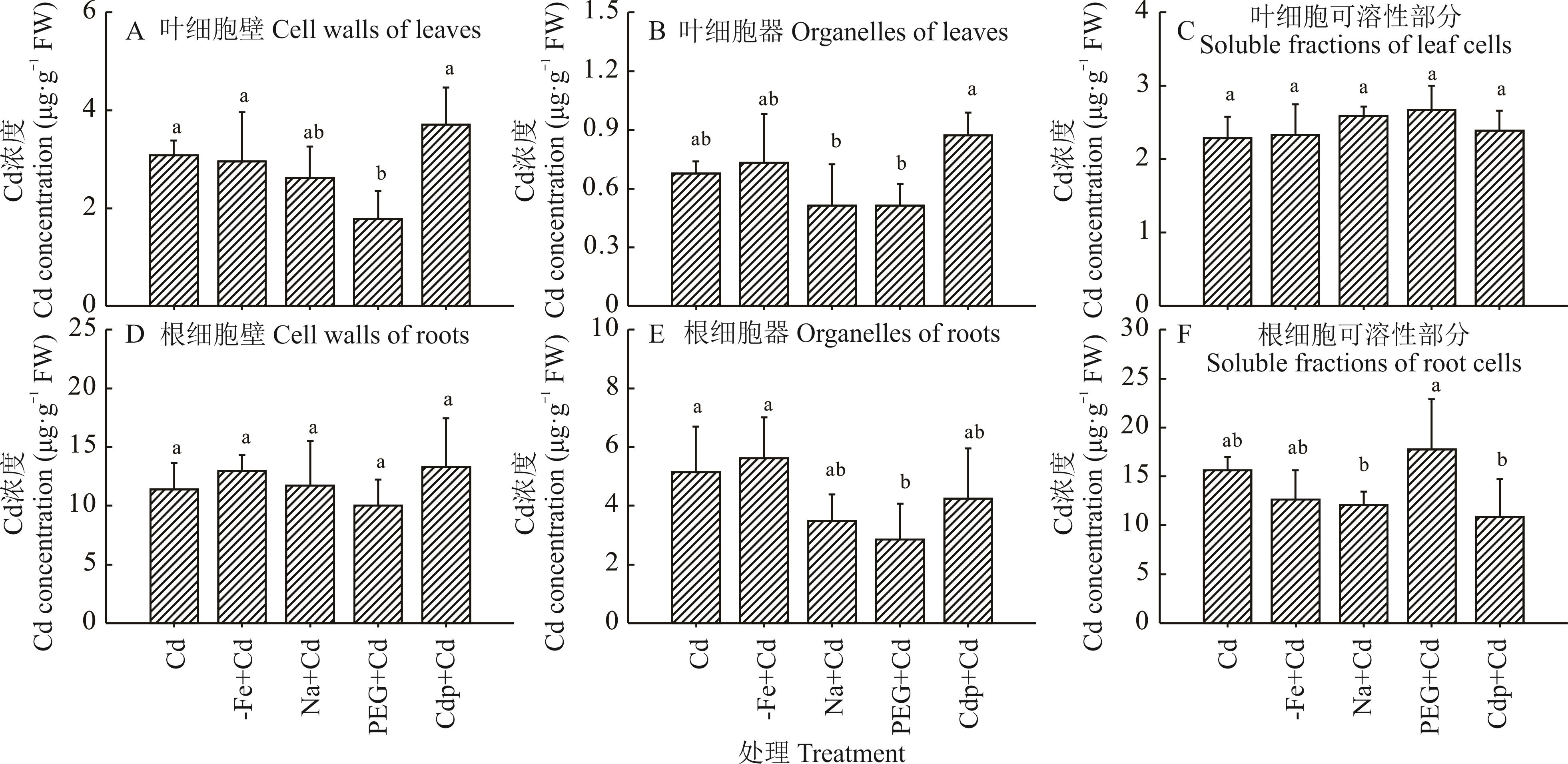
图4 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米叶和根镉亚细胞分布浓度的影响
Fig.4 Effects of abiotic stress priming on subcellular distribution of Cd concentrations in leaves and roots of maize under Cd stress
组织 Organ | 处理 Treatment | 细胞壁 Cell wall | 细胞器 Organelle | 细胞可溶性部分 Cell soluble fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶 Leaves | Cd | 50.97±4.22a | 11.23±0.98a | 37.80±4.21bc |
| -Fe+Cd | 48.04±10.70a | 12.34±4.66a | 39.62±10.10bc | |
| Na+Cd | 45.35±5.37ab | 8.98±3.81a | 45.68±3.89ab | |
| PEG+Cd | 35.45±8.07b | 10.50±2.75a | 54.04±6.48a | |
| Cdp+Cd | 52.85±8.17a | 12.60±2.27a | 34.56±6.26c | |
| 根 Roots | Cd | 35.21±4.70ab | 16.12±4.88a | 48.67±0.92ab |
| -Fe+Cd | 41.93±4.29ab | 17.97±3.83a | 40.10±5.60b | |
| Na+Cd | 42.11±8.60ab | 12.65±1.32ab | 45.23±9.39ab | |
| PEG+Cd | 33.19±5.26b | 9.03±1.48b | 57.77±5.50a | |
| Cdp+Cd | 46.59±12.50a | 14.67±4.93ab | 38.74±14.20b |
表2 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米叶和根镉亚细胞分布比例的影响
Table 2 Effects of abiotic stress priming on subcellular distribution proportions of Cd in leaves and roots of maize under Cd stress (%)
组织 Organ | 处理 Treatment | 细胞壁 Cell wall | 细胞器 Organelle | 细胞可溶性部分 Cell soluble fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶 Leaves | Cd | 50.97±4.22a | 11.23±0.98a | 37.80±4.21bc |
| -Fe+Cd | 48.04±10.70a | 12.34±4.66a | 39.62±10.10bc | |
| Na+Cd | 45.35±5.37ab | 8.98±3.81a | 45.68±3.89ab | |
| PEG+Cd | 35.45±8.07b | 10.50±2.75a | 54.04±6.48a | |
| Cdp+Cd | 52.85±8.17a | 12.60±2.27a | 34.56±6.26c | |
| 根 Roots | Cd | 35.21±4.70ab | 16.12±4.88a | 48.67±0.92ab |
| -Fe+Cd | 41.93±4.29ab | 17.97±3.83a | 40.10±5.60b | |
| Na+Cd | 42.11±8.60ab | 12.65±1.32ab | 45.23±9.39ab | |
| PEG+Cd | 33.19±5.26b | 9.03±1.48b | 57.77±5.50a | |
| Cdp+Cd | 46.59±12.50a | 14.67±4.93ab | 38.74±14.20b |

图5 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米叶片过氧化氢含量、超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性的影响
Fig.5 Effects of abiotic stress priming on H2O2 contents, superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT) activities in leaves of maize under Cd stress

图6 非生物逆境锻炼对镉胁迫下玉米根过氧化氢含量、超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性的影响
Fig.6 Effects of abiotic stress priming on H2O2 contents, superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT) activities in roots of maize under Cd stress
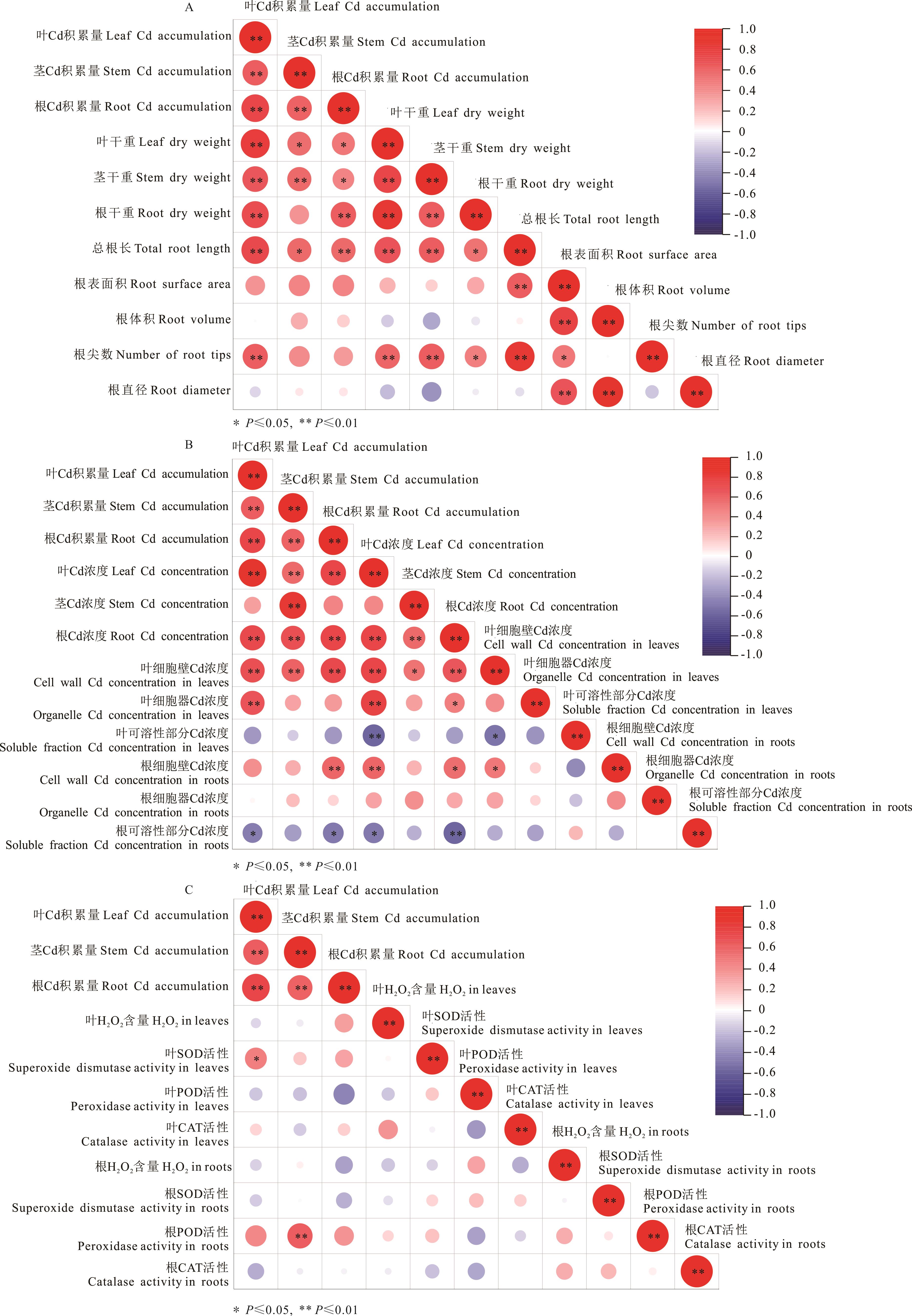
图7 非生物逆境锻炼下玉米镉积累量与生长(A)、镉分布(B)及抗氧化防御体系(C)的相关性
Fig.7 Correlation relationship of Cd accumulation with plant growth (A),Cd distribution (B) and antioxidant defense system (C) in maize under abiotic stress priming
| 1 | Wu J W, Li R J, Lu Y, et al. Sustainable management of cadmium-contaminated soils as affected by exogenous application of nutrients: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 295: 113081. |
| 2 | Chen Y L, Weng L P, Ma J, et al. Review on the last ten years of research on source identification of heavy metal pollution in soils. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(10): 2219-2238. |
| 陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 等. 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(10): 2219-2238. | |
| 3 | Wu J W, Geilfus C M, Pitann B, et al. Silicon-enhanced oxalate exudation contributes to alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 131: 10-18. |
| 4 | Zhou X Y. Development and future development trend of corn feed industry in China. Feed Research, 2023, 46(9): 178-181. |
| 周新莹. 我国玉米饲粮产业发展情况及未来发展趋势. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(9): 178-181. | |
| 5 | Zhang Q Y, Wang L, Xiao Y X, et al. Migration and transformation of Cd in four crop rotation systems and their potential for remediation of Cd-contaminated farmland in southern China. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 885: 163893. |
| 6 | Hechmi N, Aissa N B, Abdennaceur H, et al. Phytoremediation potential of maize (Zea mays L.) in co-contaminated soils with pentachlorophenol and cadmium. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2013, 15(7): 703-713. |
| 7 | Wang X, Cai J, Zhou Q, et al. Physiological mechanisms of abiotic stress priming induced the crops stress tolerance: A review. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(11): 2287-2301. |
| 王笑, 蔡剑, 周琴, 等. 非生物逆境锻炼提高作物耐逆性的生理机制研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(11): 2287-2301. | |
| 8 | Li H J, Ming L L, Zhang W S. Uptake, translocation and tolerance mechanism of cadmium in plants: A review. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(2): 86-95. |
| 李慧君, 明荔莉, 张文生. 植物对镉吸收、转运及耐性调控机制研究进展. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(2): 86-95. | |
| 9 | Clemens S, Aarts M G M, Thomine S, et al. Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends in Plant Science, 2013, 18(2): 92-99. |
| 10 | Bai X J, Liu L J, Zhang C H, et al. Effect of H2O2 pretreatment on Cd tolerance of different rice cultivars. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(4): 391-397. |
| 白晓娟, 刘丽娟, 张春华, 等. H2O2预处理对不同水稻品种Cd耐性的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(4): 391-397. | |
| 11 | Zhang S, Tan X, Zhou Y H, et al. Effects of a heavy metal (cadmium) on the responses of subtropical coastal tree species to drought stress. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(5): 12682-12694. |
| 12 | Bashir W, Anwar S, Zhao Q, et al. Interactive effect of drought and cadmium stress on soybean root morphology and gene expression. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 175: 90-101. |
| 13 | Liu X R, Chen L H, Zhang J, et al. Effects of drought and cadmium pollution on the physiology and cadmium enrichment of Pennisetum sinese. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(2): 277-284. |
| 刘选茹, 陈良华, 张健, 等. 干旱及镉污染对巨菌草生理和镉富集特征的影响. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(2): 277-284. | |
| 14 | Shi G R, Xia S L, Ye J, et al. PEG-simulated drought stress decreases cadmium accumulation in castor bean by altering root morphology. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015, 111: 127-134. |
| 15 | Wang S Q, Dai H P, Cui S, et al. The effects of salinity and pH variation on hyperaccumulator Bidens pilosa L. accumulating cadmium with dynamic and real-time uptake of Cd2+ influx around its root apexes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(14): 41435-41444. |
| 16 | Zou R, Wang L, Li Y C, et al. Cadmium absorption and translocation of amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L.) affected by iron deficiency. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 256: 113410. |
| 17 | Afzal M, Yu M J, Tang C X, et al. The negative impact of cadmium on nitrogen transformation processes in a paddy soil is greater under non-flooding than flooding conditions. Environment International, 2019, 129: 451-460. |
| 18 | Xiao A W, Chen D T, Li W C, et al. Root morphology and anatomy affect cadmium translocation and accumulation in rice. Rice Science, 2021, 28(6): 594-604. |
| 19 | Yi Z R, Zhuge Y P, Lou Y H, et al. Effects of spermidine on growth and physiological characteristics of Salix integra under cadmium stress. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(10): 2306-2312. |
| 20 | Zacchini M, Pietrini F, Scarascia M G, et al. Metal tolerance, accumulation and translocation in poplar and willow clones treated with cadmium in hydroponics. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2009, 197: 23-34. |
| 21 | Weigel H J, Jäger H J. Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cadmium in bean plants. Plant Physiology, 1980, 65(3): 480-482. |
| 22 | Bai Z Q, Li D, Zhu L, et al. Nitrate increases cadmium accumulation in sweet sorghum for improving phytoextraction efficiency rather than ammonium. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 643116. |
| 23 | Wu J W, Guo J, Hu Y H, et al. Distinct physiological responses of tomato and cucumber plants in silicon-mediated alleviation of cadmium stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 453. |
| 24 | Karimi F, Hamidian Y, Behrouzifar F, et al. An applicable method for extraction of whole seeds protein and its determination through Bradford’s method. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2022, 164: DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113053. |
| 25 | Liu S P, Pang X L, Cao J Y, et al. Measurement of SOD in fresh jujube fruit and analysis of its content. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2012(15): 36-38. |
| 刘世鹏, 庞小亮, 曹娟云, 等. 鲜枣果实中超氧化物歧化酶的测定及含量的分析. 湖南农业科学, 2012(15): 36-38. | |
| 26 | Huang Z, Dai S H, Ma L K, et al. Changes of peroxidase activity in the seed germination of watermelon. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2010(9): 43-45. |
| 黄智, 戴思慧, 马凌珂, 等. 西瓜种子萌发过氧化物酶活性变化的研究. 湖南农业科学, 2010(9): 43-45. | |
| 27 | Yang X, Li J C, Zheng Y Z, et al. Salinity elevates Cd bioaccumulation of sea rice cultured under co-exposure of cadmium and salt. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 126: 602-611. |
| 28 | Xia S L, Wang X M, Su G Q, et al. Effects of drought on cadmium accumulation in peanuts grown in a contaminated calcareous soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22: 18707-18717. |
| 29 | Yang J S, Dai Y, Liu Y, et al. Reduced cadmium accumulation in tobacco by sodium chloride priming. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(30): 37410-37418. |
| 30 | Yi L P, Wang Z W. Effects of three salts to oilseed rape (Brassica napus) accumulating cadmium in Cd-contaminated soil. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(4): 798-802. |
| 弋良朋, 王祖伟. 土壤中三种盐对油菜富集镉的影响. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(4): 798-802. | |
| 31 | Chen C, Cao Q Q, Jiang Q, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals gene network regulating cadmium uptake and translocation in peanut roots under iron deficiency. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 1-14. |
| 32 | Liu D Q, Chen X, Ge Y. Adsorption of iron and cadmium in rhizosphere and their uptake and translocation in rice pretreated with iron deficiency. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(2): 224-230. |
| 刘丹青, 陈雪, 葛滢. 缺Fe预处理对Fe、Cd根际吸附与水稻吸收和转运的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(2): 224-230. | |
| 33 | Ji Y J, Wan Y N, Wang Q, et al. Effects of root characteristics and transpiration on cadmium uptake by cucumber seedlings under varied iron levels. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(5): 1939-1946. |
| 季玉洁, 万亚男, 王琪, 等. 不同铁营养状况下根系特征及蒸腾对黄瓜幼苗吸收镉的影响. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(5): 1939-1946. | |
| 34 | Li S Z, Song Z Z, Liu X Q, et al. Mediation of zinc and iron accumulation in maize by ZmIRT2, a novel iron-regulated transporter. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2022, 63(4): 521-534. |
| 35 | Chen Y M, Huang J N, Wei J Q, et al. Low-level cadmium exposure influences rice resistance to herbivores by priming jasmonate signaling. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 194: 104741. |
| 36 | Chakrabarti M, Mukherjee A. Investigating the underlying mechanism of cadmium-induced plant adaptive response to genotoxic stress. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 209: 111817. |
| 37 | Wu J W, Shi Y, Zhu Y X, et al. Mechanisms of enhanced heavy metal tolerance in plants by silicon: a review. Pedosphere, 2013, 23(6): 815-825. |
| 38 | Wu J W, Mock H P, Giehl R F H, et al. Silicon decreases cadmium concentrations by modulating root endodermal suberin development in wheat plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 364: 581-590. |
| 39 | Shi X D, Fang Y, Jiao F, et al. Research on the dynamics of leaf cytoderm expansin accumulation under drought stress in flue-cured tobacco. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2010, 16(1): 41-44. |
| 时向东, 方圆, 焦枫, 等. 干旱胁迫下烤烟叶片细胞壁expansin积累动态研究. 中国烟草学报, 2010, 16(1): 41-44. | |
| 40 | Xian J P, Wang Y, Zhang J Y. Effects of PEG pretreatment on physiological metabolism of Lolium perenne under salt and cadmium stress. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(3): 358-364. |
| 鲜靖苹, 王勇, 张家洋. PEG预处理对盐及镉胁迫下黑麦草生理代谢的影响. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(3): 358-364. | |
| 41 | Zhang S W, Mei Y X, Wei W, et al. Influence of PEG pretreatment on antioxdant enzyme activties of rice seedling to subsequent Cd stress. Journal of Shenyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 33(3): 437-441. |
| 张诗婉, 梅映学, 魏玮, 等. PEG对Cd胁迫下水稻幼苗抗氧化酶活性的影响. 沈阳师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 33(3): 437-441. | |
| 42 | McInturf S A, Khan M A, Gokul A, et al. Cadmium interference with iron sensing reveals transcriptional programs sensitive and insensitive to reactive oxygen species. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2022, 73(1): 324-338. |
| 43 | Zhang B L, Shang S H, Zhang H T, et al. Sodium chloride enhances cadmium tolerance through reducing cadmium accumulation and increasing anti-oxidative enzyme activity in tobacco. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2013, 32(6): 1420-1425. |
| 44 | Mohammad A H, Soumen B, Saed-Moucheshi A, et al. Hydrogen peroxide priming modulates abiotic oxidative stress tolerance: insights from ROS detoxification and scavenging. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 420. |
| 45 | Wu J W, Sagervanshi A, Mühling K H. Sulfate facilitates cadmium accumulation in leaves of Vicia faba L. at flowering stage. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 156: 375-382. |
| [1] | 郭荣, 景海飞, 杨仪, 辛国省, 杨婷. 纳米硒对滩羊生长性能、血液生化及代谢组的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 199-213. |
| [2] | 洪莉平, 李小冬, 于二汝, 裴成江, 尚以顺, 骆金红, 孙光, 周云昊, 李世歌, 杨航, 刘凤丹. 不同紫苏原料对贵州黑山羊血清抗氧化酶活性、瘤胃发酵参数、瘤胃微生物区系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 214-226. |
| [3] | 米春娇, 洪流, 马馼, 毛培胜. 谷胱甘肽引发对老化燕麦种胚线粒体抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 51-59. |
| [4] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [5] | 何邦印, 裴婧宏, 野起瑞, 胡佳佳, 郑彩雪, 李江文. 不同人工经济林凋落叶浸提液对豆禾草种的化感效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 199-208. |
| [6] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [7] | 祁兆奔, 任晓艳, 李怡彤, 马金云, 刘权. 红三叶多糖的酶提取方法及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 105-115. |
| [8] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [9] | 岳海旺, 魏建伟, 王广才, 刘朋程, 陈淑萍, 卜俊周. 基于环境型鉴定技术划分生态区综合评价黄淮海青贮玉米品种[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 120-138. |
| [10] | 孟超楠, 赵玉洁, 陈佳欣, 张旖璐, 王彦佳, 冯丽荣, 孙玉刚, 郭长虹. 2株青贮玉米根际固氮菌的筛选鉴定及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 174-185. |
| [11] | 黄丽娟, 孙镕基, 高文婧, 张志飞, 陈桂华. 全株水稻表面优势乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 117-125. |
| [12] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [13] | 蒋丛泽, 受娜, 高玮, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区不同青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 216-228. |
| [14] | 李超男, 王磊, 周继强, 赵长兴, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣. 微塑料对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [15] | 刘爱瑜, 王超, 吴占军, 赵寿培, 赵俐辰, 李晓宇, 张伟涛, 王乐天, 高玉红. 热应激对断奶绵羔羊生长性能、抗氧化性能和瘤胃菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 173-182. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 124
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 145
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||