

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 216-228.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022350
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
蒋丛泽1,2,3( ), 受娜1,2,3, 高玮1,2,3, 马仁诗1,2,3, 沈禹颖1,2,3, 杨宪龙1,2,3(
), 受娜1,2,3, 高玮1,2,3, 马仁诗1,2,3, 沈禹颖1,2,3, 杨宪龙1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-30
修回日期:2022-11-28
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-05-26
通讯作者:
杨宪龙
作者简介:E-mail: yangxianl@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Cong-ze JIANG1,2,3( ), Na SHOU1,2,3, Wei GAO1,2,3, Ren-shi MA1,2,3, Yu-ying SHEN1,2,3, Xian-long YANG1,2,3(
), Na SHOU1,2,3, Wei GAO1,2,3, Ren-shi MA1,2,3, Yu-ying SHEN1,2,3, Xian-long YANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2022-08-30
Revised:2022-11-28
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-05-26
Contact:
Xian-long YANG
摘要:
为筛选出适宜在陇东旱塬地区栽培的青贮玉米品种,本试验以8份青贮玉米品种为研究对象,通过田间试验比较了不同青贮玉米品种在该地区的农艺表现、营养成分含量及水氮资源利用状况,并采用灰色关联分析法对各品种的综合表现进行了量化评价。结果表明:品种对主要农艺性状有显著影响(P<0.05)。株高最高的品种是豫青贮23,为299.6 cm;茎粗最大的品种是东单60号,为29.5 mm;叶长、叶宽分别以豫青贮23和京科青贮516最大,为83.3 cm和9.6 cm;单株鲜重最大的品种是中科甜928,为1147.1 g·株-1,单株干重最大的品种是京科青贮516,为341.1 g·株-1。产量性状方面,鲜草产量超过80 t·hm-2的品种有豫青贮23、东单60号和中科甜928,干草产量和粗蛋白产量最大的品种是东科301,分别为29.0 t·hm-2和1.85 t·hm-2。营养品质方面,全株粗蛋白含量最高的品种是文玉3号,为7.42%;粗灰分含量以中科甜928最高,为4.58%;中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维含量以京科301最低,分别为28.87%和12.63%。水氮资源利用方面,干物质水分利用效率和氮肥偏生产力最高的品种是东科301,分别为77.0 kg·hm-2·mm-1和161.2 kg·kg-1。灰色关联分析结果显示,等权关联度和加权关联度综合评价结果较为一致,二者均表明豫青贮23、文玉3号和东科301兼顾丰产、优质和水氮资源高效利用优点,适宜在陇东旱塬区推广种植。
蒋丛泽, 受娜, 高玮, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区不同青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 216-228.
Cong-ze JIANG, Na SHOU, Wei GAO, Ren-shi MA, Yu-ying SHEN, Xian-long YANG. A multivariate evaluation of production performance and nutritional quality of different varieties of silage maize in the dry plateau area of Longdong[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 216-228.

图1 试验地2021年月降水量和月均气温及多年(2001-2021)平均月降水量和气温
Fig.1 Monthly precipitation and average monthly temperature in 2021 and monthly average precipitation and average temperature in multi-years (2001-2021) at the experiment field
品种 Variety | 发芽率 Germination percentage | 发芽势 Germination energy | 来源 Sources of varieties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 94.0b | 91.0ab | 北京佰青源畜牧业科技发展有限公司 Beijing Baiqingyuan Animal Husbandry Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 东单60号Dongdan No.60 | 96.0ab | 88.0b | 辽宁东亚种业有限公司Liaoning Dongya Seed Co., Ltd. |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 99.0a | 94.0ab | 辽宁东亚种业有限公司 Liaoning Dongya Seed Co., Ltd. |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 98.0ab | 95.0ab | 北京屯玉种业有限责任公司Beijing Tunyu Co., Ltd. |
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 100.0a | 95.0ab | 北京大京九农业开发有限公司Beijing Dajingjiu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 99.0a | 98.0a | 北京中农绿桥科技有限公司Beijing Zhongnong Green Bridge Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 100.0a | 96.0ab | 河南秋丰农业科技有限公司Henan Qiufeng Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 99.0a | 93.0ab | 北京顺鑫农科种业科技有限公司Beijing Shunxin Nongke Seed Technology Co., Ltd. |
表1 供试品种发芽率、发芽势及种子来源
Table 1 Germination percentage, germination energy and seed sources of the 8 silage maize varieties used in this study (%)
品种 Variety | 发芽率 Germination percentage | 发芽势 Germination energy | 来源 Sources of varieties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 94.0b | 91.0ab | 北京佰青源畜牧业科技发展有限公司 Beijing Baiqingyuan Animal Husbandry Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 东单60号Dongdan No.60 | 96.0ab | 88.0b | 辽宁东亚种业有限公司Liaoning Dongya Seed Co., Ltd. |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 99.0a | 94.0ab | 辽宁东亚种业有限公司 Liaoning Dongya Seed Co., Ltd. |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 98.0ab | 95.0ab | 北京屯玉种业有限责任公司Beijing Tunyu Co., Ltd. |
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 100.0a | 95.0ab | 北京大京九农业开发有限公司Beijing Dajingjiu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 99.0a | 98.0a | 北京中农绿桥科技有限公司Beijing Zhongnong Green Bridge Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 100.0a | 96.0ab | 河南秋丰农业科技有限公司Henan Qiufeng Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 99.0a | 93.0ab | 北京顺鑫农科种业科技有限公司Beijing Shunxin Nongke Seed Technology Co., Ltd. |
品种 Variety | 生育时期 Growth stages | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
播种期 Sowing stage (月-日 Month-day) | 出苗期 Emergence stage (月-日Month-day) | 拔节期 Elongation stage (月-日Month-day) | 抽穗期 Heading stage (月-日Month-day) | 开花期 Flowering stage (月-日Month-day) | 乳熟期 Milk stage (月-日Month-day) | 收获期 Harvesting date (月-日Month-day) | 生长天数 Growth days (d) | |
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-22 | 07-19 | 07-23 | 08-18 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 东单60号Dongdan No.60 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-15 | 07-23 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-16 | 07-20 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-16 | 07-20 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-18 | 07-23 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-09 | 07-15 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-09 | 07-15 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-22 | 07-09 | 07-18 | 08-18 | 09-01 | 136 |
表2 不同青贮玉米品种生育时期
Table 2 The growth stage of different silage maize varieties
品种 Variety | 生育时期 Growth stages | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
播种期 Sowing stage (月-日 Month-day) | 出苗期 Emergence stage (月-日Month-day) | 拔节期 Elongation stage (月-日Month-day) | 抽穗期 Heading stage (月-日Month-day) | 开花期 Flowering stage (月-日Month-day) | 乳熟期 Milk stage (月-日Month-day) | 收获期 Harvesting date (月-日Month-day) | 生长天数 Growth days (d) | |
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-22 | 07-19 | 07-23 | 08-18 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 东单60号Dongdan No.60 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-15 | 07-23 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-16 | 07-20 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-16 | 07-20 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-18 | 07-23 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-09 | 07-15 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-20 | 07-09 | 07-15 | 08-14 | 09-01 | 136 |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 04-17 | 05-06 | 05-22 | 07-09 | 07-18 | 08-18 | 09-01 | 136 |
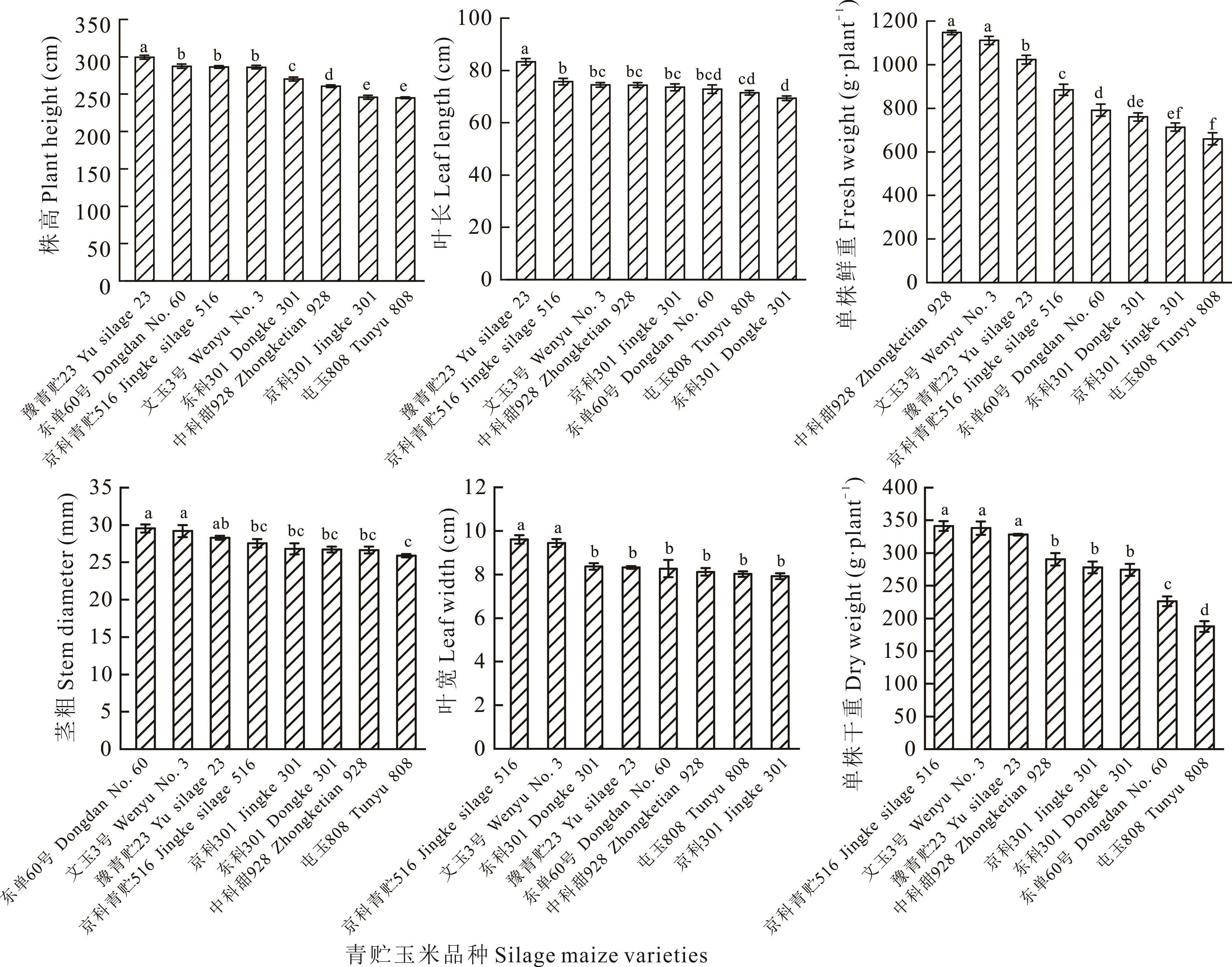
图2 不同青贮玉米品种农艺性状不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。The different lowercase letters mean significant differences (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.2 Agronomic traits of different silage maize varieties
品种 Variety | 鲜草产量 Fresh grass yield (t·hm-2) | 干草产量 Hay grass yield (t·hm-2) | 粗蛋白产量 Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 干鲜比 Dry/fresh | 茎比重 Stem proportion (%) | 叶比重 Leaf proportion (%) | 穗比重 Ear proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 81.8±1.9a | 24.8±0.6bc | 1.67ab | 0.30c | 43.2±10.5a | 9.4±0.8ab | 47.5±10.9bc |
| 东单60号Dongdan No.60 | 80.2±1.6a | 21.1±0.4d | 1.36c | 0.26e | 37.7±1.4ab | 10.3±0.5a | 52.0±1.5abc |
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 78.9±2.5ab | 23.2±0.7cd | 1.75a | 0.29d | 42.7±9.1a | 8.4±0.5ab | 48.8±9.1bc |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 78.1±2.1ab | 23.3±0.6bcd | 1.67ab | 0.30c | 32.3±1.8ab | 8.8±0.3ab | 58.9±1.8abc |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 80.7±1.7a | 21.3±0.5d | 1.47bc | 0.26e | 45.6±3.3a | 9.1±1.1ab | 45.3±4.2c |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 73.0±1.7bc | 29.0±0.7a | 1.85a | 0.40a | 27.5±3.2ab | 7.1±0.9b | 65.4±2.9ab |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 65.3±2.0d | 12.8±0.4e | 0.76d | 0.20f | 31.8±4.3ab | 9.3±1.3ab | 58.9±5.7abc |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 68.2±2.8cd | 25.3±1.0b | 1.38c | 0.37b | 23.9±1.6b | 6.8±0.8b | 69.3±0.8a |
表3 不同青贮玉米品种生产性能
Table 3 Production performance of different silage maize varieties
品种 Variety | 鲜草产量 Fresh grass yield (t·hm-2) | 干草产量 Hay grass yield (t·hm-2) | 粗蛋白产量 Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 干鲜比 Dry/fresh | 茎比重 Stem proportion (%) | 叶比重 Leaf proportion (%) | 穗比重 Ear proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 81.8±1.9a | 24.8±0.6bc | 1.67ab | 0.30c | 43.2±10.5a | 9.4±0.8ab | 47.5±10.9bc |
| 东单60号Dongdan No.60 | 80.2±1.6a | 21.1±0.4d | 1.36c | 0.26e | 37.7±1.4ab | 10.3±0.5a | 52.0±1.5abc |
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 78.9±2.5ab | 23.2±0.7cd | 1.75a | 0.29d | 42.7±9.1a | 8.4±0.5ab | 48.8±9.1bc |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 78.1±2.1ab | 23.3±0.6bcd | 1.67ab | 0.30c | 32.3±1.8ab | 8.8±0.3ab | 58.9±1.8abc |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 80.7±1.7a | 21.3±0.5d | 1.47bc | 0.26e | 45.6±3.3a | 9.1±1.1ab | 45.3±4.2c |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 73.0±1.7bc | 29.0±0.7a | 1.85a | 0.40a | 27.5±3.2ab | 7.1±0.9b | 65.4±2.9ab |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 65.3±2.0d | 12.8±0.4e | 0.76d | 0.20f | 31.8±4.3ab | 9.3±1.3ab | 58.9±5.7abc |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 68.2±2.8cd | 25.3±1.0b | 1.38c | 0.37b | 23.9±1.6b | 6.8±0.8b | 69.3±0.8a |
品种 Variety | 耗水量 Evapotranspiration (mm) | 干物质水分利用效率 Dry matter water use efficiency (kg·hm-2·mm-1) | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial productivity (kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 378.8a | 65.5bc | 137.8bc |
| 东单60号 Dongdan No.60 | 389.6a | 54.2d | 117.4d |
| 文玉3号 Wenyu No.3 | 386.5a | 59.9c | 128.7cd |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 370.6ab | 62.8bc | 129.3bcd |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 347.6b | 61.2bc | 118.2d |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 377.1a | 77.0a | 161.2a |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 363.6ab | 35.3e | 71.3e |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 382.3a | 66.2b | 140.6b |
表4 不同青贮玉米品种耗水量、水分利用效率和氮肥偏生产力
Table 4 Evapotranspiration, water use efficiency and nitrogen partial productivity of different silage maize varieties
品种 Variety | 耗水量 Evapotranspiration (mm) | 干物质水分利用效率 Dry matter water use efficiency (kg·hm-2·mm-1) | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial productivity (kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 378.8a | 65.5bc | 137.8bc |
| 东单60号 Dongdan No.60 | 389.6a | 54.2d | 117.4d |
| 文玉3号 Wenyu No.3 | 386.5a | 59.9c | 128.7cd |
| 京科青贮516 Jingke silage 516 | 370.6ab | 62.8bc | 129.3bcd |
| 中科甜928 Zhongketian 928 | 347.6b | 61.2bc | 118.2d |
| 东科301 Dongke 301 | 377.1a | 77.0a | 161.2a |
| 屯玉808 Tunyu 808 | 363.6ab | 35.3e | 71.3e |
| 京科301 Jingke 301 | 382.3a | 66.2b | 140.6b |
| 1 | Wang Y H, Zhao J, Shen Q Y, et al. Studies on accumulation of organism yield and nutrition of silage maize. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2005, 13(4): 81-85. |
| 王永宏, 赵健, 沈强云, 等. 青贮玉米生物产量及营养积累规律研究. 玉米科学, 2005, 13(4): 81-85. | |
| 2 | Li C X, Ye R R, Du Y G, et al. Research on production performance of silage maize in alpine meadow region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(6): 1214-1217. |
| 李春喜, 叶润蓉, 杜岩功, 等. 高寒牧区青贮玉米生产性能初步研究. 草地学报, 2013, 21(6): 1214-1217. | |
| 3 | Yan H Y, Li C X, Tang S H, et al. Production performance and quality evaluation of three silage maize varieties in dryland of Qinghai. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(9): 1915-1921. |
| 闫慧颖, 李春喜, 唐生华, 等. 青海旱地3个青贮玉米品种的生产性能及品质评价. 草业科学, 2017, 34(9): 1915-1921. | |
| 4 | Lu X S. 2020 analysis of forage commodity production situation in China and outlook for 2021. Animal Agriculture, 2021(3): 31-36. |
| 卢欣石. 2020我国饲草商品生产形势分析与2021年展望. 畜牧产业, 2021(3): 31-36. | |
| 5 | Qingyang Agricultural and Rural Bureau. Adhering to the development of the whole industry chain and creating livestock industry clusters——Qingyang City has achieved obvious results in the high-quality development of modern livestock industry. [2022-04-24] (2022-08-14). https://nync.zgqingyang.gov.cn |
| 庆阳农业农村局. 坚持全产业链开发打造畜牧产业集群——庆阳市现代畜牧业高质量发展取得明显成效. [2022-04-24] (2022-08-14). https://nync.zgqingyang.gov.cn | |
| 6 | Zhang S L, Lovdahl L, Grip H, et al. Effects of mulching and catch cropping on soil temperature, soil moisture and wheat yield on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2009, 102(1): 78-86. |
| 7 | Li X, Zhang Y M, Zhu L L, et al. Evaluation of silage performance and nutritional quality of different corn cultivars in Qinghai Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(6): 1194-1208. |
| 李想, 张业猛, 朱丽丽, 等. 青海高原地区不同玉米品种青贮性能及营养品质评价. 草业科学, 2021, 38(6): 1194-1208. | |
| 8 | Liu J N, Shi Y H, Wu X M, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and analysis of the performance and nutritional value of 15 silage maize varieties in Jinzhong basin. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 1043-1049. |
| 刘建宁, 石永红, 吴欣明, 等. 晋中盆地15个青贮玉米品种生产性能及营养价值评价. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 1043-1049. | |
| 9 | Wang W X. Study on production characteristics and nutritional quality of different silage maize in Guanzhong region. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2018. |
| 王薇星. 关中地区不同品种青贮玉米生产性能与营养品质的评价. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. | |
| 10 | Wang Y R, Yu L, Hu X W, et al. Rules of seed testing for forage, turfgrass and other herbaceous plant-The germination test, GB/T 2930.4-2017. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2017. |
| 王彦荣, 余玲, 胡小文, 等. 草种子检验规程—发芽试验, GB/T 2930.4-2017. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. | |
| 11 | Su M F, Wei X H, Xin X Q, et al. Exogenous cGMP regulates seed germination of ryegrass under salt stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(17): 6171-6179. |
| 宿梅飞, 魏小红, 辛夏青, 等. 外源 cGMP 调控盐胁迫下黑麦草种子萌发机制. 生态学报, 2018, 38(17): 6171-6179. | |
| 12 | Liu B H, Zhao H M, You Y L, et al. The production performance and adaptability of silage corn varieties introduced in Haihe plain. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(3): 632-641. |
| 柳斌辉, 赵海明, 游永亮, 等. 海河平原区引进青贮玉米品种的生产性能及适应性评价. 草地学报, 2016, 24(3): 632-641. | |
| 13 | Gao P. The effect of slow-controlled release fertilizers on yield and agronomic traits of summer maize. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2019. |
| 高鹏. 缓控释肥对夏玉米产量及其农艺性状的效应. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. | |
| 14 | Wu R X, Yang L, He Y F, et al. Determination of crude ash content in feed, GB/T 6438-2007. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2007. |
| 武润仙, 杨林, 何一帆, 等. 饲料中粗灰分的测定, GB/T 6438-2007. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. | |
| 15 | Xiao Z M, Fan X, Ma D X, et al. Determination of crude protein in feed, GB/T 6432-2018. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018. |
| 肖志明, 樊霞, 马东霞, 等. 饲料中粗蛋白的测定, GB/T 6432-2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 16 | Wang J Q, Yu J G, Wu K Q, et al. Determination of neutral detergent fiber in feed, GB/T 20806-2006. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2006. |
| 王加启, 于建国, 吴克谦, 等. 饲料中中性洗涤纤维的测定, GB/T 20806-2006. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. | |
| 17 | Li H L, Zhao C H, Jia Q, et al. Determination of acid detergent fiber in feed, NY/T 1459-2007. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2007. |
| 李会玲, 赵彩会, 贾青, 等. 饲料中酸性洗涤纤维的测定, NY/T 1459-2007. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. | |
| 18 | Zhang X L, Hu Z Q, Chu S L. Methods for measuring soil water content: A review. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2005, 36(1): 118-123. |
| 张学礼, 胡振琪, 初士立. 土壤含水量测定方法研究进展. 土壤通报, 2005, 36(1): 118-123. | |
| 19 | Wu Y, Jia Z K, Ren X L, et al. Effects of ridge and furrow rainwater harvesting system combined with irrigation on improving water use efficiency of maize (Zea mays L.) in semi-humid area of China. Agricultural Water Management, 2015, 158: 1-9. |
| 20 | Oweis T Y, Farahani H J, Hachum A Y. Evapotranspiration and water use of full and deficit irrigated cotton in the Mediterranean environment in northern Syria. Agricultural Water Management, 2011, 98(8): 1239-1248. |
| 21 | Huang Y L, Chen L D, Fu B J, et al. The wheat yields and water-use efficiency in the Loess Plateau: straw mulch and irrigation effects. Agricultural Water Management, 2004, 72(3): 209-222. |
| 22 | Jiang C Q, Wang H Y, Lu D J, et al. Single fertilization of urea in root zone improving crop yield, nutrient uptake and use efficiency in summer maize. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(12): 146-153. |
| 姜超强, 王火焰, 卢殿君, 等. 一次性根区穴施尿素提高夏玉米产量和养分吸收利用效率. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(12): 146-153. | |
| 23 | Zhang H S, Zhang D G, Liu X J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of turf quality under different treatments by grey correlation analysis. Pratacultural Science, 2007, 24(11): 73-76. |
| 张鹤山, 张德罡, 刘晓静, 等. 灰色关联度分析法对不同处理下草坪质量的综合评判. 草业科学, 2007, 24(11): 73-76. | |
| 24 | Ren L J, Chen Y K, Shan L Y, et al. Analysis of comprehensive quality of whole plant corn silage based on principal component and grey correlation degree. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48(4): 1211-1221. |
| 任丽娟, 陈雅坤, 单丽燕, 等. 基于主成分和灰色关联度对全株玉米青贮综合品质的分析. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48(4): 1211-1221. | |
| 25 | Sun Z Q, Xu F, Zhang Y Q, et al. Comparison and correlation of agronomic characteristics and fermentation quality of different types of hybrid corn. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(1): 250-256. |
| 孙志强, 徐芳, 张元庆, 等. 不同品种玉米农艺性状及青贮发酵品质的比较及相关性研究. 草地学报, 2019, 27(1): 250-256. | |
| 26 | Han X Q, Deng H S, Pu T L, et al. The study on agronomic characters of silage maize varieties in dry-hot valley region of Jinsha river. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(6): 1327-1335. |
| 韩学琴, 邓红山, 普天磊, 等. 金沙江干热河谷区青贮玉米品种农艺性状分析. 草地学报, 2021, 29(6): 1327-1335. | |
| 27 | Wang Y C, Lu G X, Deng H, et al. Evaluation and screening of agricultural characters of silage maize varieties based on principal component analysis. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1725-1732. |
| 王英成, 芦光新, 邓晖, 等. 基于主成分分析的青贮玉米品种农艺性状评价及筛选研究. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1725-1732. | |
| 28 | Wu X M, Fang Z H, Chi H W, et al. Comparison of 30 maize (Zea mays) varieties for food and feed in the Yanmenguan area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| 吴欣明, 方志红, 池惠武, 等. 30个青贮玉米在雁门关地区品种评比试验. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. | |
| 29 | Ren L J, Zhao L S, Chen Y K, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of silage quality of whole corn silage for different verieties in Northeast China based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(8): 3856-3868. |
| 任丽娟, 赵连生, 陈雅坤, 等. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析方法综合评价东北地区不同品种全株玉米青贮饲料的青贮品质. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(8): 3856-3868. | |
| 30 | Zhang J K, Liu Y, Yuan X F, et al. Effects of different planting densities on the quality of silage maize. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(15): 5176-5183. |
| 张佳阔, 刘瑶, 袁晓峰, 等. 不同种植密度对青贮玉米品质的影响. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(15): 5176-5183. | |
| 31 | Sun J Y, Gao J L, Wang Z G, et al. Effect of planting density on forage yield and nutritive value of different maize varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1733-1742. |
| 孙继颖, 高聚林, 王志刚, 等. 不同类型青贮玉米饲用产量及营养价值对密度调控的响应. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1733-1742. | |
| 32 | Cao L J, Zhang S X, Yao Y N, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the production performance and nutritional value of 14 silage maize varieties in rainfed areas of Ningxia. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(5): 977-987. |
| 曹立娟, 张顺香, 姚亚妮, 等. 14个青贮玉米品种在宁夏雨养区的生产性能和营养价值综合评价. 草业科学, 2022, 39(5): 977-987. | |
| 33 | Cheng G L, Qiu J, Wang X G, et al. Changes of agronomic traits, biomass yield and quality of national silage maize combinations (varieties). Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. |
| 成广雷, 邱军, 王晓光, 等. 我国青贮玉米组合(品种)的农艺性状、生物产量和品质变化. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. | |
| 34 | Yu M, Li C F, Yu Z, et al. Quality grading for silage maize, GB/T25 882-2010. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2011. |
| 余鸣, 李存福, 玉柱, 等. 青贮玉米品质分级, GB/T25 882-2010. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. | |
| 35 | Zhao Y W, Ma X, Zhang R, et al. Selection of high-yield and good-quality oat varieties in the eastern agricultural area of Qinghai Province. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(3): 532-541. |
| 赵祎伟, 马祥, 张然, 等. 青海东部农区高产优质燕麦品种筛选. 草业科学, 2020, 37(3): 532-541. | |
| 36 | Chen Y H, Li J C, Li R D, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of field traits for 24 new varieties (lines) of mung bean based on grey correlation analysis in southern Guangxi. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2020, 51(11): 2644-2652. |
| 陈燕华, 李经成, 李荣丹, 等. 基于灰色关联度分析法综合评价24个绿豆新品种(系)在桂南地区的田间性状表现. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(11): 2644-2652. | |
| 37 | Liu Z, Shao H F, Wen W, et al. Evaluation of agronomic traits and nutritional quality of 34 silage maize varieties in southern Ningxia. Feed Research, 2021, 44(11): 98-104. |
| 刘卓, 邵怀峰, 温万, 等. 宁南地区34个青贮玉米品种农艺性状及营养品质评价研究. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(11): 98-104. | |
| 38 | Zhang S X, Wang X, Ma L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of performance and forage quality of silage maize in farming-pastoral ecotone. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(6): 1517-1524. |
| 张书兴, 王筱, 马琳, 等. 农牧交错带青贮玉米生产性能和饲草品质综合评价. 草地学报, 2022, 30(6): 1517-1524. |
| [1] | 严翊丹, 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 高兴发, 饶彦章, 饶雄, 张洪志, 赵查书, 竺艳萍, 朱玉波. 西南山区冬闲田功能型燕麦品种潜力挖掘评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 42-53. |
| [2] | 朱丽丽, 张业猛, 李万才, 赵亚利, 李想, 陈志国. 39个我国不同生态区培育的青贮玉米品种在青海高原适应性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 68-78. |
| [3] | 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 李满有, 倪旺, 冯琴, 妥昀昀, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| [4] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [5] | 李影正, 程榆林, 徐璐璐, 李万松, 严旭, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 周阳, 郑军军, 汪星宇, 张德龙, 程明军, 夏运红, 何建美, 唐祈林. 不同玉米品种(系)的全株、果穗与秸秆青贮特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [6] | 蒋紫薇, 刘桂宇, 安昊云, 石薇, 常生华, 张程, 贾倩民, 侯扶江. 种植密度与施氮对玉米/秣食豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. |
| [7] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| [8] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [9] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [10] | 刘丽英, 贾玉山, 范文强, 尹强, 成启明, 王志军. 影响苜蓿自然干燥的主要环境因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 121-132. |
| [11] | 韩重阳, 王栓, 左粟田, 闫三博, 汪阳, 蔡家邦, 马骢毓, 张新全, 聂刚. 10个白三叶品种在成都平原的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 105-117. |
| [12] | 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 柴继宽. 海拔和品种对燕麦营养品质及表面附着微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 147-157. |
| [13] | 吴欣明, 方志红, 池惠武, 贾会丽, 刘建宁, 石永红, 王学敏. 30个青贮玉米在雁门关地区品种评比试验[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| [14] | 徐强, 田新会, 杜文华. 高寒牧区黑麦和箭筈豌豆混播对草产量和营养品质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 49-59. |
| [15] | 祁鹤兴, 芦光新, 李宗仁, 徐成体, 德科加, 周孝娟, 王英成, 马桂花. 青海省青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌鉴定及其致病力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 94-105. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 464
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 265
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||