

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 111-125.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023393
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
崔红丽1( ), 孙明哲1, 贾博为1,2(
), 孙明哲1, 贾博为1,2( ), 孙晓丽1(
), 孙晓丽1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-19
修回日期:2023-11-29
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-06-20
通讯作者:
贾博为,孙晓丽
作者简介:csmbl2016@126.com基金资助:
Hong-li CUI1( ), Ming-zhe SUN1, Bo-wei JIA1,2(
), Ming-zhe SUN1, Bo-wei JIA1,2( ), Xiao-li SUN1(
), Xiao-li SUN1( )
)
Received:2023-10-19
Revised:2023-11-29
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-06-20
Contact:
Bo-wei JIA,Xiao-li SUN
摘要:
高渗门控钙渗透通道(hyperosmolality-gated calcium-permeable channel,OSCA)是一类高渗胁迫感受器。本研究通过全基因组鉴定,从蒺藜苜蓿中筛选鉴定出13个MtOSCAs基因,并根据其与拟南芥OSCA基因家族成员的同源性命名为MtOSCA1.1~4.1。染色体定位分析表明MtOSCAs基因不均匀地分布在8条染色体上。MtOSCA家族按系统进化关系可分为4个亚家族,且同一亚家族内的成员具有相似的内含子-外显子模式。功能结构域和保守基序分析表明该家族在进化中高度保守,进一步共线性分析发现MtOSCAs和大豆OSCAs亲缘关系近,而与拟南芥OSCAs亲缘关系远。基因表达模式分析发现,不同亚家族的MtOSCAs基因表现出组织特异性。非生物胁迫转录组数据分析及qRT-PCR分析表明MtOSCA2.5/2.6/3.1显著受低温胁迫诱导表达。顺式作用元件分析证实MtOSCAs启动子区包含多种光、激素和逆境响应的顺式作用元件。上述结果为今后MtOSCAs基因调控蒺藜苜蓿抗逆性的功能研究奠定了坚实的理论基础。
崔红丽, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族鉴定及低温逆境表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 111-125.
Hong-li CUI, Ming-zhe SUN, Bo-wei JIA, Xiao-li SUN. Genome-wide analysis and expression of the OSCA family genes from Medicago truncatula in response to low temperature stresses[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 111-125.
| 基因名Gene name | 正向引物Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| MtOSCA1.1 | GCTGGGTCAGCATTTCAACA | CTTCAGCAGCTATACCAGACCA |
| MtOSCA2.2 | CAATATGTGAGGCGGGTGGT | CTTCCTTCCACTGCGGGAAA |
| MtOSCA2.5 | CTCCGGCACCTAAGGATGTT | GTTGGTAAGCCCCTGAACGA |
| MtOSCA2.6 | CAGAGGCTTCATTGGCAGGA | GAGGTTCTGGAGCCAACTCA |
| MtOSCA3.1 | GCCTTGAGCTGTCCCGATTA | AGCGGGGATTCTTGTTGCAT |
| MtActin | CCCACTGGATGTCTGTAGGTT | AGAATTAAGTAGCAGCGCAAA |
表 1 qRT-PCR验证引物
Table 1 qRT-PCR validation primers
| 基因名Gene name | 正向引物Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| MtOSCA1.1 | GCTGGGTCAGCATTTCAACA | CTTCAGCAGCTATACCAGACCA |
| MtOSCA2.2 | CAATATGTGAGGCGGGTGGT | CTTCCTTCCACTGCGGGAAA |
| MtOSCA2.5 | CTCCGGCACCTAAGGATGTT | GTTGGTAAGCCCCTGAACGA |
| MtOSCA2.6 | CAGAGGCTTCATTGGCAGGA | GAGGTTCTGGAGCCAACTCA |
| MtOSCA3.1 | GCCTTGAGCTGTCCCGATTA | AGCGGGGATTCTTGTTGCAT |
| MtActin | CCCACTGGATGTCTGTAGGTT | AGAATTAAGTAGCAGCGCAAA |
序号 Number | 基因名 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | DNA (bp) | mRNA (bp) | cDNA (bp) | 蛋白Protein (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (KD) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (pI) | 跨膜结构域数量Numbers of transmembrane domains | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MtOSCA1.1 | Medtr4g132570 | 5714 | 2325 | 2325 | 774 | 88.26 | 9.22 | 10 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 2 | MtOSCA1.2 | Medtr5g086610 | 6495 | 2919 | 2301 | 766 | 87.40 | 8.83 | 8 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 3 | MtOSCA1.3 | Medtr7g094570 | 5471 | 2295 | 2295 | 764 | 87.18 | 8.29 | 8 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 4 | MtOSCA1.4 | Medtr5g027510 | 6020 | 2899 | 2400 | 799 | 92.16 | 9.35 | 7 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 5 | MtOSCA2.1 | Medtr3g103560 | 9504 | 2211 | 2211 | 736 | 83.45 | 8.90 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 6 | MtOSCA2.2 | Medtr1g017170 | 9579 | 2961 | 2307 | 768 | 86.60 | 8.93 | 10 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 7 | MtOSCA2.3 | Medtr6g012870 | 6782 | 2697 | 2139 | 712 | 81.25 | 8.72 | 10 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 8 | MtOSCA2.4 | Medtr7g011610 | 5670 | 2373 | 2373 | 790 | 89.60 | 8.09 | 11 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 9 | MtOSCA2.5 | Medtr4g082340 | 4734 | 2911 | 2169 | 722 | 82.28 | 9.01 | 8 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 10 | MtOSCA2.6 | Medtr5g042560 | 6634 | 2593 | 2136 | 711 | 80.74 | 9.12 | 11 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 11 | MtOSCA2.7 | Medtr3g019070 | 5019 | 2136 | 2136 | 711 | 81.10 | 8.80 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 12 | MtOSCA3.1 | Medtr2g018780 | 5377 | 2916 | 2169 | 722 | 81.61 | 9.25 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 13 | MtOSCA4.1 | Medtr8g074970 | 3216 | 3216 | 2406 | 801 | 90.09 | 6.81 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
表2 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族成员信息
Table 2 Information of OSCA gene family in M. truncatula
序号 Number | 基因名 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | DNA (bp) | mRNA (bp) | cDNA (bp) | 蛋白Protein (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (KD) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (pI) | 跨膜结构域数量Numbers of transmembrane domains | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MtOSCA1.1 | Medtr4g132570 | 5714 | 2325 | 2325 | 774 | 88.26 | 9.22 | 10 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 2 | MtOSCA1.2 | Medtr5g086610 | 6495 | 2919 | 2301 | 766 | 87.40 | 8.83 | 8 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 3 | MtOSCA1.3 | Medtr7g094570 | 5471 | 2295 | 2295 | 764 | 87.18 | 8.29 | 8 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 4 | MtOSCA1.4 | Medtr5g027510 | 6020 | 2899 | 2400 | 799 | 92.16 | 9.35 | 7 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 5 | MtOSCA2.1 | Medtr3g103560 | 9504 | 2211 | 2211 | 736 | 83.45 | 8.90 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 6 | MtOSCA2.2 | Medtr1g017170 | 9579 | 2961 | 2307 | 768 | 86.60 | 8.93 | 10 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 7 | MtOSCA2.3 | Medtr6g012870 | 6782 | 2697 | 2139 | 712 | 81.25 | 8.72 | 10 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 8 | MtOSCA2.4 | Medtr7g011610 | 5670 | 2373 | 2373 | 790 | 89.60 | 8.09 | 11 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 9 | MtOSCA2.5 | Medtr4g082340 | 4734 | 2911 | 2169 | 722 | 82.28 | 9.01 | 8 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 10 | MtOSCA2.6 | Medtr5g042560 | 6634 | 2593 | 2136 | 711 | 80.74 | 9.12 | 11 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 11 | MtOSCA2.7 | Medtr3g019070 | 5019 | 2136 | 2136 | 711 | 81.10 | 8.80 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 12 | MtOSCA3.1 | Medtr2g018780 | 5377 | 2916 | 2169 | 722 | 81.61 | 9.25 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| 13 | MtOSCA4.1 | Medtr8g074970 | 3216 | 3216 | 2406 | 801 | 90.09 | 6.81 | 9 | 质膜Plasma membrane |
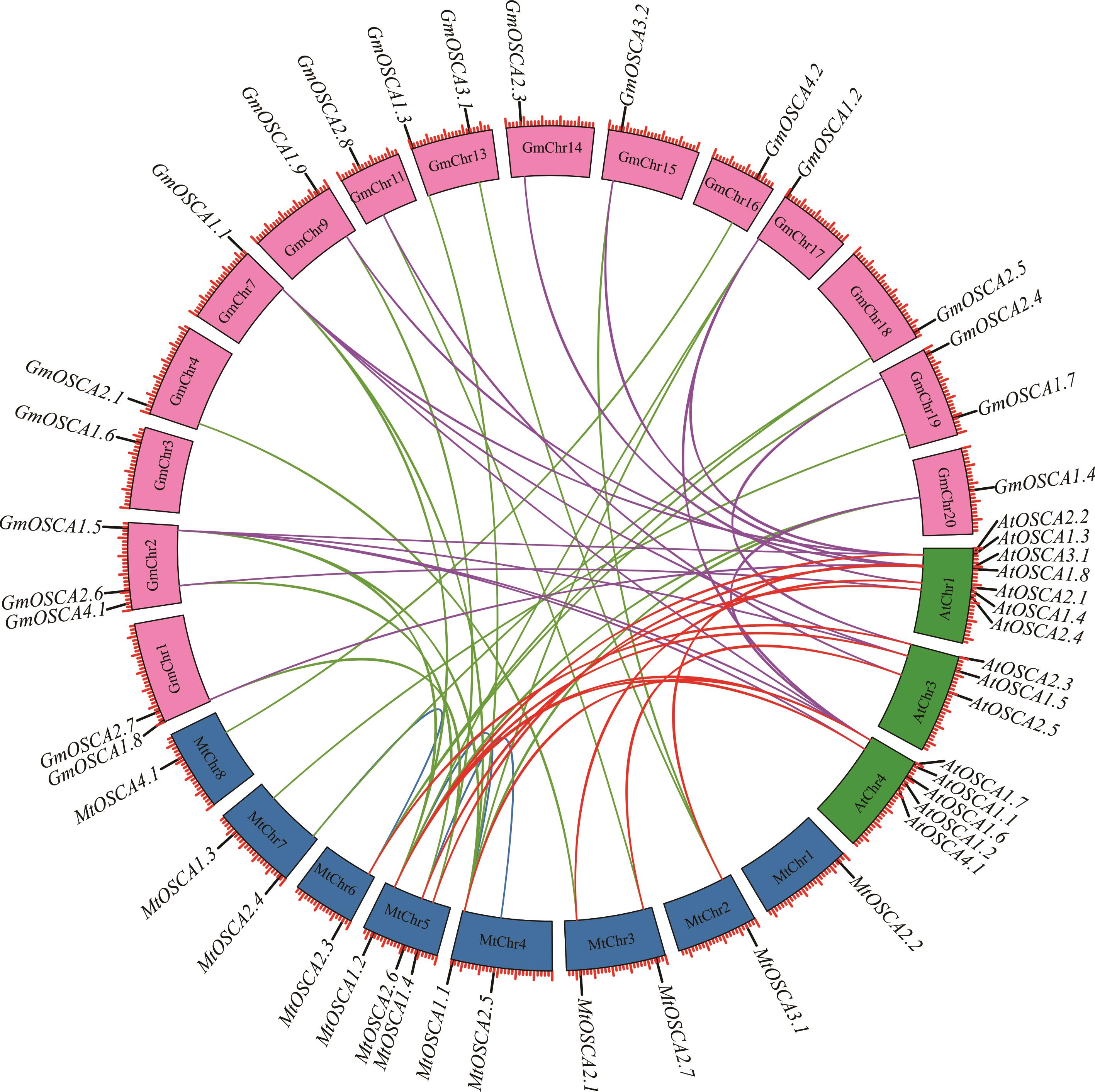
图3 蒺藜苜蓿、拟南芥和大豆OSCA基因共线性关系蓝色实线表示蒺藜苜蓿旁系同源基因,红色实线表示蒺藜苜蓿与拟南芥直系同源基因,绿色实线表示蒺藜苜蓿与大豆直系同源基因,紫色实线表示大豆与拟南芥直系同源基因。Blue lines indicate alfalfa paralogous genes, red lines indicate orthologous genes between alfalfa and A. thaliana, green lines indicate orthologous genes between alfalfa and soybean, purple lines indicate orthologous genes between soybean and A. thaliana.
Fig.3 Syntenic relationship of OSCA genes among M. truncatula, A. thaliana and G. max

图5 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族的保守结构域和基序分析a: 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族保守功能结构域The conserved domains of the OSCA gene family from M. truncatula; b: 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族保守基序The conserved motifs of the OSCA gene family from M. truncatula.
Fig.5 Conserved domains and motifs analysis of OSCA family from M. truncatula
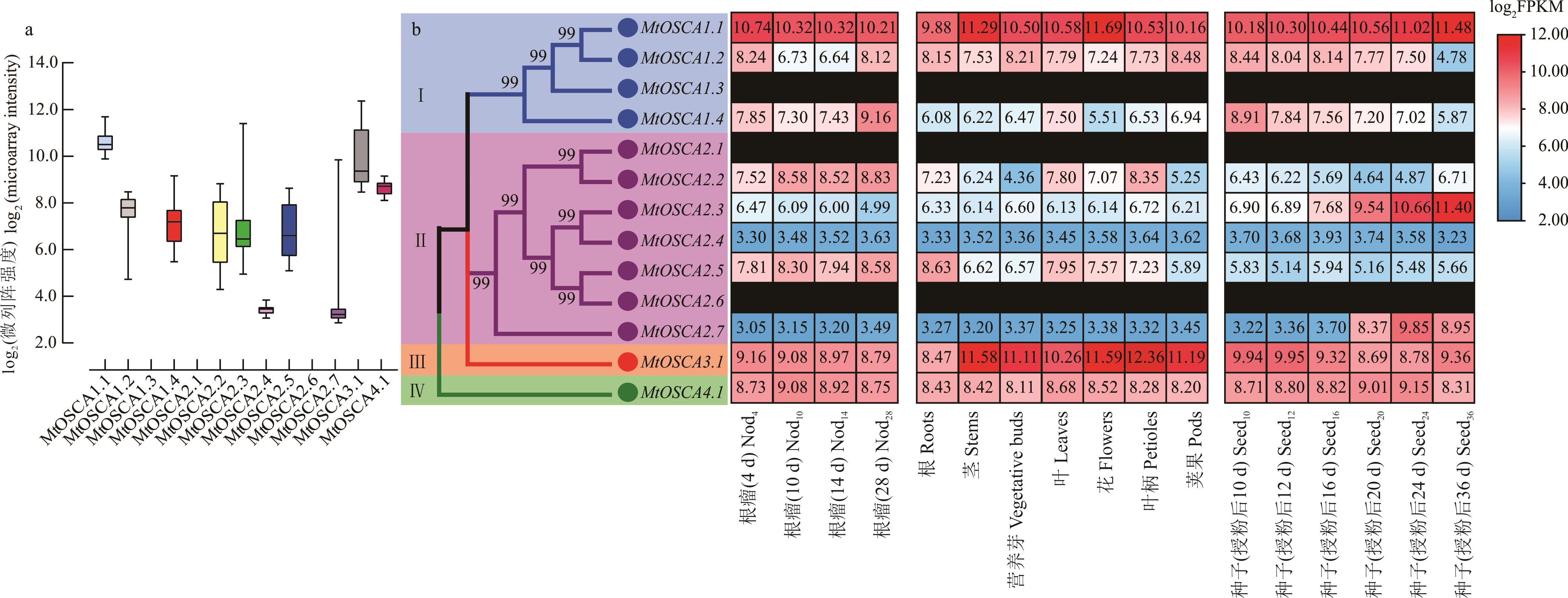
图6 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族组织表达特性分析a: 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族在整个发育过程中的相对表达变化Variation of relative expression of OSCA family gene in M. truncatula throughout a developmental time course; b: 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族在不同组织中的表达分析Expression analysis of OSCA family gene of M. truncatula in different tissues. 黑色代表未检测到基因表达量Black stands for no expression was detected.
Fig.6 Expression feature analysis of OSCA genes family of M. truncatula in different tissues
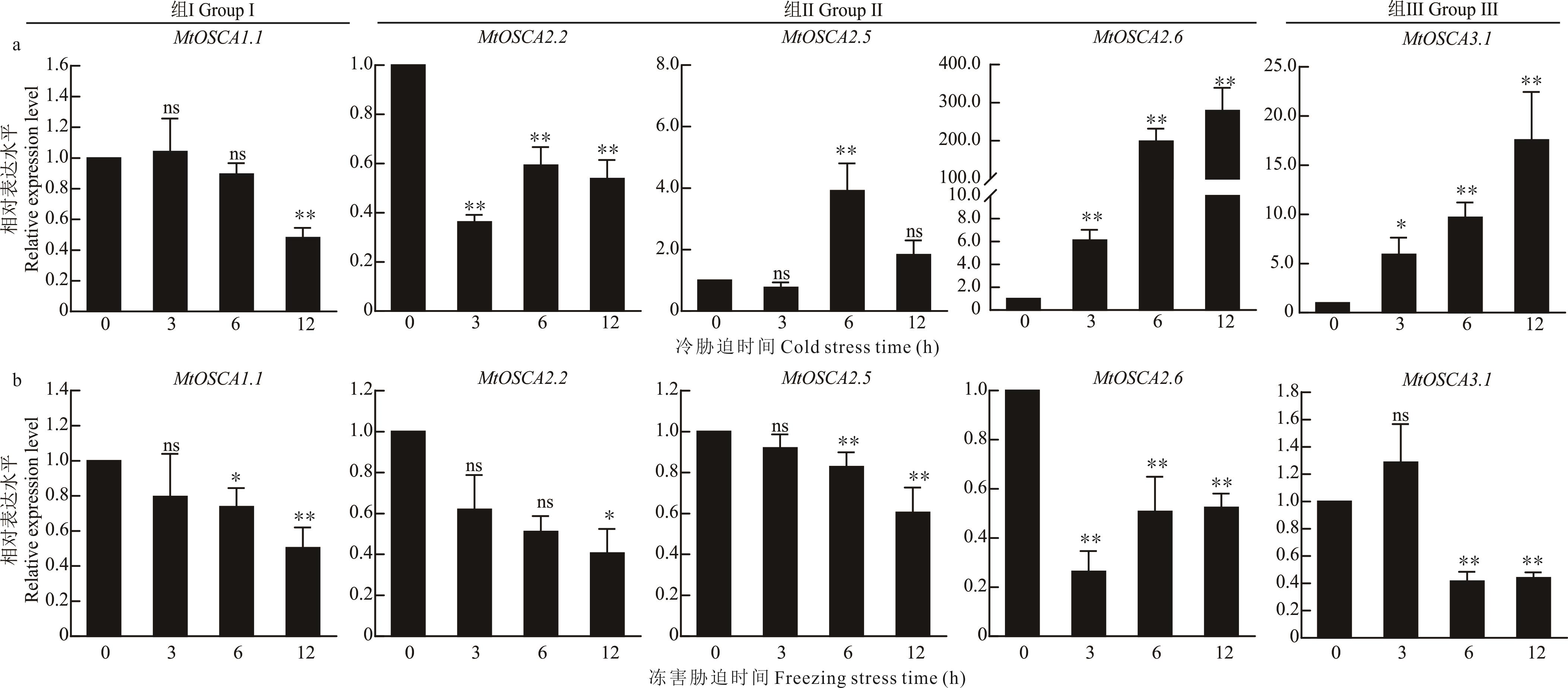
图8 低温胁迫应答中MtOSCA基因的qRT-PCR验证a: 蒺藜苜蓿MtOSCA基因冷胁迫表达模式验证The expression validation of MtOSCA gene of M. truncatula under cold stress; b: 蒺藜苜蓿MtOSCA基因冻害胁迫表达模式验证The expression validation of MtOSCA gene of M. truncatula under freezing stress. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ns: P>0.05.
Fig.8 qRT-PCR validation of MtOSCA genes in the response to low temperature stresses
| 1 | Ahanger M A, Alyemeni M N, Wijaya L, et al. Potential of exogenously sourced kinetin in protecting Solanum lycopersicum from NaCl-induced oxidative stress through up-regulation of the antioxidant system, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. PLoS One, 2018, 13(9): e0202175. |
| 2 | Scheres B, van der Putten W H. The plant perceptron connects environment to development. Nature, 2017, 543: 337-345. |
| 3 | Hubbard K E, Siegel R S, Valerio G, et al. Abscisic acid and CO2 signalling via calcium sensitivity priming in guard cells, new CDPK mutant phenotypes and a method for improved resolution of stomatal stimulus-response analyses. Annals of Botany, 2012, 109(1): 5-17. |
| 4 | Steinhorst L, Jörg K. Calcium-A central regulator of pollen germination and tube growth. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2013, 1833(7): 1573-1581. |
| 5 | Yuan F, Yang H, Xue Y, et al. OSCA1 mediates osmotic-stress-evoked Ca2+ increases vital for osmosensing in Arabidopsis. Nature, 2014, 514(7522): 367-371. |
| 6 | Chai L F. Origin and evolution of OSCA family in plants. Taiyuan: Shanxi Normal University, 2019. |
| 柴利芳. 植物OSCA家族的起源与进化. 太原: 山西师范大学, 2019. | |
| 7 | Hou C C, Tian W, Kleist T, et al. DUF221 proteins are a family of osmosensitive calcium-permeable cation channels conserved across eukaryotes. Cell Research, 2014, 24(5): 632-635. |
| 8 | Li J W, Yang J K, Jia B W, et al. Evolution and expression analysis of OSCA gene family in soybean. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2017, 39(5): 589-599. |
| 李建伟, 杨珺凯, 贾博为, 等. 大豆基因组中OSCA基因家族的进化和表达分析. 中国油料作物学报, 2017, 39(5): 589-599. | |
| 9 | Ding S C, Feng X, Du H W, et al. Genome-wide analysis of maize OSCA family members and their involvement in drought stress. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e6765. |
| 10 | Zhang H J, Zhu D H, Du L Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the OSCA gene family in wheat. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(12): 25-33. |
| 张红娟, 朱德鹤, 杜琳颖, 等. 小麦OSCA基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(12): 25-33. | |
| 11 | Li Y S, Yuan F, Wen Z H, et al. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the OSCA gene family in rice. BMC Plant Biology, 2015, 15: 261. |
| 12 | Li J Q, Luo S L, Zhang S L, et al. Genome-wide identification of pepper OSCA gene family and expression analysis under different stress conditions. Plant Science Journal, 2022, 40(2): 187-196. |
| 李嘉琪, 罗石磊, 张帅磊, 等. 辣椒OSCA 基因家族的全基因组鉴定及不同胁迫条件下表达分析. 植物科学学报, 2022, 40(2): 187-196. | |
| 13 | Li S S, Li H, Yang W G, et al. Physiology and molecular mechanism of drought resistance in alfalfa. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(2): 331-340. |
| 李莎莎, 李红, 杨伟光, 等. 苜蓿抗旱生理与分子机制. 草业科学, 2018, 35(2): 331-340. | |
| 14 | Blondon F, Marie D, Brown S, et al. Genome size and base composition in Medicago sativa and M. truncatula species. Genome, 1994, 37(2): 264-270. |
| 15 | Tian J Y, Wang Q X, Zheng S W, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of the CPP gene family in Medicago truncatula. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 等. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. | |
| 16 | Huang S Y, Hu T M, Yang P Z. Identification and function analysis of the PYL gene family in Medicago truncatula. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(2): 422-433. |
| 黄思源, 呼天明, 杨培志. 蒺藜苜蓿PYL基因家族的全基因组鉴定、表达和功能分析. 草业科学, 2019, 36(2): 422-433. | |
| 17 | He H L, Piao J P, Sun J N, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CIPK gene family in Medicago truncatula. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(9): 1-13. |
| 贺红利, 朴京培, 孙嘉囡, 等. 蒺藜苜蓿CIPK基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(9): 1-13. | |
| 18 | Wang C N, Wang H, Zhu H, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase family genes in Medicago truncatula. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2021, 256: 153308. |
| 19 | Letunic I, Bork P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(D1): D493-D496. |
| 20 | El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, et al. The pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): D427-D432. |
| 21 | Marchler-Bauer A, Bryant S H. CD-Search: protein domain annotations on the fly. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(Web Server issue2): W327-W331. |
| 22 | Xu L, Dong Z B, Fang L, et al. OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(W1): W52-W58. |
| 23 | Bailey T L, Boden M, Buske F A, et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(Web Server issue2): W202-W208. |
| 24 | Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194-1202. |
| 25 | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, 30(1): 325-327. |
| 26 | Sebastien C, Jerome V, Pascal G. MtExpress, a comprehensive and curated RNAseq-based gene expression atlas for the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2021, 62(9): 1494-1500. |
| 27 | Shu Y J, Liu Y, Zhang J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily genes and their responses to abiotic stress in Medicago truncatula. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 1247. |
| 28 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 29 | Hartmann F P, Tinturier E, Julien J L, et al. Between stress and response: function and localization of mechanosensitive Ca2+ channels in herbaceous and perennial plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(20): 11043. |
| 30 | Zhang M, Wang D, Kang Y, et al. Structure of the mechanosensitive OSCA channels. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2018, 25(9): 850-858. |
| 31 | Priest H D, Filichkin S A, Mockler T C. Cis-regulatory elements in plant cell signaling. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2009, 12(5): 643-649. |
| 32 | Biłas R, Szafran K, Hnatuszko-Konka K, et al. Cis-regulatory elements used to control gene expression in plants. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2016, 127: 269-287. |
| 33 | Wu T, Liu Y M, Jin J, et al. Identification and expression characteristics of a cation/H+ exchanger gene family in Medicago truncatula. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 181-194. |
| 吴彤, 刘云苗, 金军, 等. 蒺藜苜蓿cation/H+ exchanger基因家族鉴定及表达特征分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 181-194. | |
| 34 | Li F, He X H, Zhang X M, et al. Identification, evolution and characteristic analysis of 14-3-3 gene family in Medicago. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2017, 36(12): 5238-5243. |
| 李菲, 何小红, 张习敏, 等. 苜蓿14-3-3基因家族的鉴定与进化和特征分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2017, 36(12): 5238-5243. | |
| 35 | Yang C L, Duan R J, Wu X X, et al. Genome-wide identification, sequence variation and expression analysis of GPAT gene family in Medicago truncatula L. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(10): 1966-1974. |
| 杨成兰, 段瑞君, 武雄雄, 等. 蒺藜苜蓿GPAT基因家族的全基因组鉴定、序列变异和表达分析. 草业科学, 2021, 38(10): 1966-1974. | |
| 36 | Zhang X Z, Huang H J, Sun Y W, et al. Genome identification and expression analysis of CBL gene family in Medicago truncatula L. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(7): 1-11. |
| 张兴政, 黄浩捷, 孙一闻, 等. 蒺藜苜蓿CBL基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(7): 1-11. | |
| 37 | Murthy S E, Dubin A E, Whitwam T, et al. OSCA/TMEM63 are an evolutionarily conserved family of mechanically activated ion channels. eLife, 2018, 7: e41844. |
| 38 | Zhai Y J, Wen Z H, Han Y, et al. Heterogeneous expression of plasma-membrane-localised OsOSCA1.4 complements osmotic sensing based on hyperosmolality and salt stress in Arabidopsis osca1 mutant. Cell Calcium, 2020, 91: 102261. |
| 39 | Cao L, Zhang P, Lu X, et al. Systematic analysis of the maize OSCA genes revealing ZmOSCA family members involved in osmotic stress and ZmOSCA2.4 confers enhanced drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(1): 351. |
| 40 | Zeng C T, Qiu X W, Li D, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of the OSCA gene family in Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. Molecular Plant Breeding. (2023-02-16)[2023-10-10]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail//46.1068.S.20230216.0841.002.html. |
| 曾春涛, 仇学文, 李丹, 等. 豇豆OSCA基因家族生物信息学分析. 分子植物育种. (2023-02-16)[2023-10-10]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail//46.1068.S.20230216.0841.002.html. | |
| 41 | Lackey J A. Chromosome numbers in the Phaseoleae (Fabaceae: Faboideae) and their relation to taxonomy. American Journal of Botany, 1980, 67(4): 595-602. |
| 42 | Jojoa-Cruz S, Saotome K, Murthy S E, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the mechanically activated ion channel OSCA1.2. eLife, 2018, 7: e41845. |
| 43 | Liu X, Wang J W, Sun L F. Structure of the hyperosmolality-gated calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.2. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 5060. |
| 44 | Maity K, Heumann J M, McGrath A P, et al. Cryo-EM structure of OSCA1.2 from Oryza sativa elucidates the mechanical basis of potential membrane hyperosmolality gating. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(28): 14309-14318. |
| 45 | Schroeder B C, Cheng T, Jan Y N, et al. Expression cloning of TMEM16A as a calcium-activated chloride channel subunit. Cell, 2008, 134(6): 1019-1029. |
| 46 | Yang S T, Zhu C X, Chen J J, et al. Identification and expression profile analysis of the OSCA gene family related to abiotic and biotic stress response in cucumber. Biology, 2022, 11(8): 1134. |
| 47 | Li Y Y, Zhang Y B, Li B, et al. Preliminary expression analysis of the OSCA gene family in maize and their involvement in temperature stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(21): 13658. |
| 48 | Han Y, Wang Y X, Zhai Y J, et al. OsOSCA1.1 mediates hyperosmolality and salt stress sensing in Oryza sativa. Biology, 2022, 11(5): 678. |
| 49 | She K J, Pan W Q, Yan Y, et al. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expressional analysis of OSCA gene family in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(21): 13027. |
| 50 | Shuang M, Li F S, Han Y, et al. Identification of OSCA gene family in Solanum habrochaites and its function analysis under stress. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23(1): 547. |
| 51 | Zhang Y, Wu C J, Su W Z, et al. Genome-wide identification and stress response analysis of OSCA gene family in watermelon. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2021, 52(12): 3330-3339. |
| 张瑜, 吴才君, 苏文桢, 等. 西瓜OSCA基因家族全基因组鉴定及胁迫响应分析. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(12): 3330-3339. | |
| 52 | Sanyal S K, Rao S, Mishra L K, et al. Plant stress responses mediated by CBL-CIPK phosphorylation network. The Enzymes, 2016, 40: 31-64. |
| 53 | Sangwan V, Orvar B L, Beyerly J, et al. Opposite changes in membrane fluidity mimic cold and heat stress activation of distinct plant MAP kinase pathways. Plant Journal, 2002, 31(5): 629-638. |
| [1] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [2] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [3] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [4] | 李雯, 赵丽蓉, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 亚麻DMP基因家族的全基因组鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 91-106. |
| [5] | 姚佳明, 何悦, 郝欢欢, 黄心如, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草LpPIL5基因特征分析及转录调控[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 155-167. |
| [6] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [7] | 刘亚男, 于人杰, 高燕丽, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 武志海, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2基因的表达模式及盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 124-134. |
| [8] | 高莉娟, 张正社, 文裕, 宗西方, 闫启, 卢丽燕, 易显凤, 张吉宇. 象草全基因组bHLH转录因子家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 47-59. |
| [9] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [10] | 吴彤, 刘云苗, 金军, 董伟峰, 才晓溪, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿cation/H+ exchanger基因家族鉴定及表达特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 181-194. |
| [11] | 罗维, 舒健虹, 刘晓霞, 王子苑, 牟琼, 王小利, 吴佳海. 高羊茅FaRVE8基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 60-69. |
| [12] | 刘文文, 崔会婷, 尉春雪, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿叶绿素酸酯a加氧酶(MtCAO)基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 171-181. |
| [13] | 杨婷, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 胡麻异质型ACCase亚基基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 111-120. |
| [14] | 夏曾润, 王文颖, 刘亚琪, 王锁民. 罗布麻K+通道编码基因AvAKT1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 180-189. |
| [15] | 张智琦, 王珍, 张铁军, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 蒺藜苜蓿MtNSN1的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 200-208. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||