

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 81-93.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023373
王晓彤1( ), 李小红1, 麻旭霞1, 蔡文祺1, 冯学丽1, 李淑霞1,2,3(
), 李小红1, 麻旭霞1, 蔡文祺1, 冯学丽1, 李淑霞1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-09
修回日期:2023-12-27
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-06-20
通讯作者:
李淑霞
作者简介:E-mail: lishuxia620@163.com基金资助:
Xiao-tong WANG1( ), Xiao-hong LI1, Xu-xia MA1, Wen-qi CAI1, Xue-li FENG1, Shu-xia LI1,2,3(
), Xiao-hong LI1, Xu-xia MA1, Wen-qi CAI1, Xue-li FENG1, Shu-xia LI1,2,3( )
)
Received:2023-10-09
Revised:2023-12-27
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-06-20
Contact:
Shu-xia LI
摘要:
果糖-1,6-二磷酸醛缩酶(FBA)是糖酵解、糖异生和卡尔文循环中的关键酶,在调控植物生长发育和非生物胁迫中发挥重要作用。本研究利用生物信息学方法在全基因组水平对紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族进行了鉴定,并对其理化性质、系统进化关系、染色体定位、基因结构特征、启动子顺式作用元件和基因表达模式进行了分析。研究结果表明,紫花苜蓿中有11个MsFBA基因,分布于1、4、5、7、8号染色体和contig633end上。理化性质分析结果表明,MsFBAs编码111~437个氨基酸,预测都为亲水性蛋白。系统进化关系分析表明,MsFBA家族蛋白被分为2个亚家族,MsFBA蛋白在不同物种间保守性较高。紫花苜蓿与拟南芥和蒺藜苜蓿FBAs之间的共线性分析结果显示,紫花苜蓿与蒺藜苜蓿之间的同源性更高。启动子顺式作用元件预测结果表明, MsFBAs启动子区域存在很多植物激素响应元件和非生物胁迫响应元件。对MsFBA基因在不同组织和非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析表明,MsFBAs在地上组织中的表达量明显高于地下组织,具有组织表达特异性;MsFBA基因的表达受低温、脱落酸、干旱、盐胁迫的诱导,说明MsFBAs在调控非生物胁迫方面具有重要作用。本研究可为进一步研究紫花苜蓿FBA基因的功能提供理论支撑。
王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93.
Xiao-tong WANG, Xiao-hong LI, Xu-xia MA, Wen-qi CAI, Xue-li FENG, Shu-xia LI. Identification and analysis of members of the FBA gene family in alfalfa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 81-93.
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 染色体号 Chromosome number | 氨基酸 长度 Amino acid length (aa) | 分子质量 Molecular weight (MW, Da) | 等电点 pI | 总平均亲水性 GRAVY | 不稳定系数 Instability index (Ⅱ) | 跨膜结构域数目 Number of transmembrane helices | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsG0180003404.01.T01 | MsFBA1 | Chr1 | 333 | 35812.29 | 8.35 | -0.083 | 33.89 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0180005906.01.T01 | MsFBA2 | Chr1 | 387 | 42396.99 | 7.68 | -0.315 | 41.72 | 0 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsG0480021327.01.T01 | MsFBA3 | Chr4 | 400 | 43179.18 | 6.86 | -0.131 | 36.27 | 0 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsG0480021331.01.T01 | MsFBA4 | Chr4 | 398 | 43036.90 | 6.39 | -0.139 | 36.93 | 0 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsG0580028117.01.T01 | MsFBA5 | Chr5 | 437 | 46728.29 | 5.54 | -0.115 | 28.23 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0580028118.01.T01 | MsFBA6 | Chr5 | 364 | 39003.51 | 6.05 | -0.071 | 29.82 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0780041081.01.T01 | MsFBA7 | Chr7 | 358 | 38635.98 | 6.56 | -0.236 | 31.16 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0780041082.01.T01 | MsFBA8 | Chr7 | 358 | 38560.96 | 6.63 | -0.221 | 32.19 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0880047090.01.T01 | MsFBA9 | Chr8 | 111 | 11971.70 | 9.52 | -0.132 | 48.21 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0880047091.01.T01 | MsFBA10 | Chr8 | 211 | 23009.69 | 8.60 | -0.006 | 32.72 | 1 | 胞外Extracellular |
| MsG0080049045.01.T01 | MsFBA11 | contig633end | 358 | 38332.81 | 7.00 | -0.153 | 32.62 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
表1 MsFBA基因家族的基本信息分析
Table 1 Analysis of basic information about the MsFBA gene family
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 染色体号 Chromosome number | 氨基酸 长度 Amino acid length (aa) | 分子质量 Molecular weight (MW, Da) | 等电点 pI | 总平均亲水性 GRAVY | 不稳定系数 Instability index (Ⅱ) | 跨膜结构域数目 Number of transmembrane helices | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsG0180003404.01.T01 | MsFBA1 | Chr1 | 333 | 35812.29 | 8.35 | -0.083 | 33.89 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0180005906.01.T01 | MsFBA2 | Chr1 | 387 | 42396.99 | 7.68 | -0.315 | 41.72 | 0 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsG0480021327.01.T01 | MsFBA3 | Chr4 | 400 | 43179.18 | 6.86 | -0.131 | 36.27 | 0 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsG0480021331.01.T01 | MsFBA4 | Chr4 | 398 | 43036.90 | 6.39 | -0.139 | 36.93 | 0 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MsG0580028117.01.T01 | MsFBA5 | Chr5 | 437 | 46728.29 | 5.54 | -0.115 | 28.23 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0580028118.01.T01 | MsFBA6 | Chr5 | 364 | 39003.51 | 6.05 | -0.071 | 29.82 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0780041081.01.T01 | MsFBA7 | Chr7 | 358 | 38635.98 | 6.56 | -0.236 | 31.16 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0780041082.01.T01 | MsFBA8 | Chr7 | 358 | 38560.96 | 6.63 | -0.221 | 32.19 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0880047090.01.T01 | MsFBA9 | Chr8 | 111 | 11971.70 | 9.52 | -0.132 | 48.21 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MsG0880047091.01.T01 | MsFBA10 | Chr8 | 211 | 23009.69 | 8.60 | -0.006 | 32.72 | 1 | 胞外Extracellular |
| MsG0080049045.01.T01 | MsFBA11 | contig633end | 358 | 38332.81 | 7.00 | -0.153 | 32.62 | 0 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 蛋白质 Protein | α-螺旋 Alpha helix | β-转角 Beta turn | 延伸链 Extended strand | 无规则卷曲 Random coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsG0180003404.01.T01 | MsFBA1 | MsFBA1 | 52.25 | 6.61 | 13.51 | 27.63 |
| MsG0180005906.01.T01 | MsFBA2 | MsFBA2 | 50.13 | 6.98 | 12.40 | 30.49 |
| MsG0480021327.01.T01 | MsFBA3 | MsFBA3 | 47.50 | 6.75 | 13.00 | 32.75 |
| MsG0480021331.01.T01 | MsFBA4 | MsFBA4 | 50.25 | 5.53 | 12.56 | 31.66 |
| MsG0580028117.01.T01 | MsFBA5 | MsFBA5 | 49.89 | 6.18 | 14.65 | 29.29 |
| MsG0580028118.01.T01 | MsFBA6 | MsFBA6 | 51.92 | 6.59 | 12.64 | 28.85 |
| MsG0780041081.01.T01 | MsFBA7 | MsFBA7 | 50.84 | 7.54 | 14.80 | 26.82 |
| MsG0780041082.01.T01 | MsFBA8 | MsFBA8 | 47.77 | 8.66 | 14.11 | 29.47 |
| MsG0880047090.01.T01 | MsFBA9 | MsFBA9 | 56.76 | 1.80 | 10.81 | 30.63 |
| MsG0880047091.01.T01 | MsFBA10 | MsFBA10 | 52.61 | 7.58 | 13.74 | 26.07 |
| MsG0080049045.01.T01 | MsFBA11 | MsFBA11 | 51.68 | 6.70 | 13.69 | 27.93 |
表2 MsFBA蛋白质二级结构
Table 2 The secondary structure of MsFBA protein in alfalfa (%)
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 蛋白质 Protein | α-螺旋 Alpha helix | β-转角 Beta turn | 延伸链 Extended strand | 无规则卷曲 Random coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsG0180003404.01.T01 | MsFBA1 | MsFBA1 | 52.25 | 6.61 | 13.51 | 27.63 |
| MsG0180005906.01.T01 | MsFBA2 | MsFBA2 | 50.13 | 6.98 | 12.40 | 30.49 |
| MsG0480021327.01.T01 | MsFBA3 | MsFBA3 | 47.50 | 6.75 | 13.00 | 32.75 |
| MsG0480021331.01.T01 | MsFBA4 | MsFBA4 | 50.25 | 5.53 | 12.56 | 31.66 |
| MsG0580028117.01.T01 | MsFBA5 | MsFBA5 | 49.89 | 6.18 | 14.65 | 29.29 |
| MsG0580028118.01.T01 | MsFBA6 | MsFBA6 | 51.92 | 6.59 | 12.64 | 28.85 |
| MsG0780041081.01.T01 | MsFBA7 | MsFBA7 | 50.84 | 7.54 | 14.80 | 26.82 |
| MsG0780041082.01.T01 | MsFBA8 | MsFBA8 | 47.77 | 8.66 | 14.11 | 29.47 |
| MsG0880047090.01.T01 | MsFBA9 | MsFBA9 | 56.76 | 1.80 | 10.81 | 30.63 |
| MsG0880047091.01.T01 | MsFBA10 | MsFBA10 | 52.61 | 7.58 | 13.74 | 26.07 |
| MsG0080049045.01.T01 | MsFBA11 | MsFBA11 | 51.68 | 6.70 | 13.69 | 27.93 |

图2 MsFBAs与其他物种的FBAs系统进化树Ms: 紫花苜蓿M. sativa; At: 拟南芥A. thaliana; Sl: 番茄S. lycopersicum; Nt: 烟草N. tabacum.
Fig.2 Phylogenetic tree of FBAs in alfalfa and other species
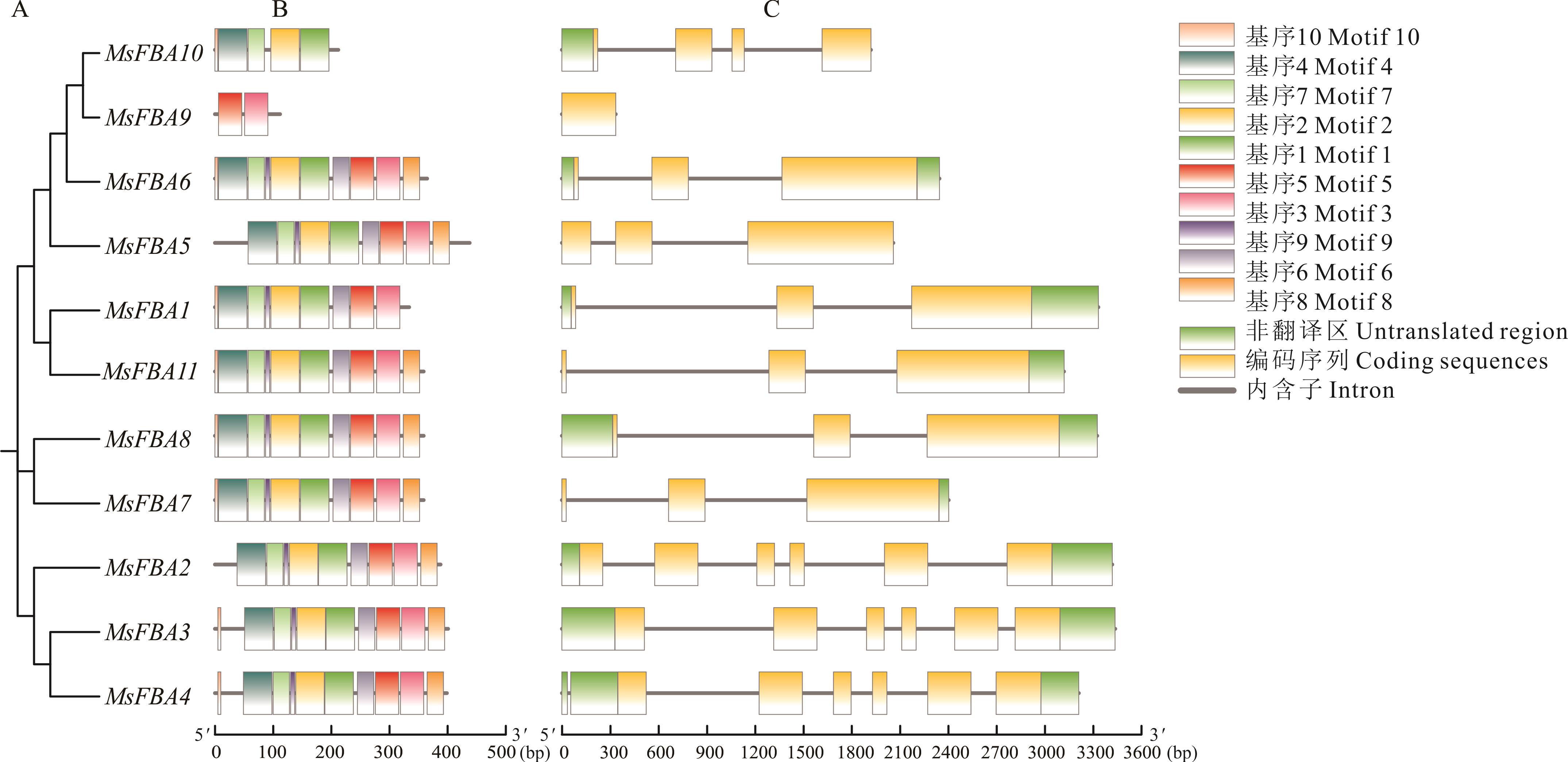
图3 MsFBA基因家族系统进化关系(A)、保守基序(B)及基因结构(C)分析
Fig.3 Phylogenetic relationships (A), conserved motif analyses (B) and gene structure(C) of the MsFBA gene family
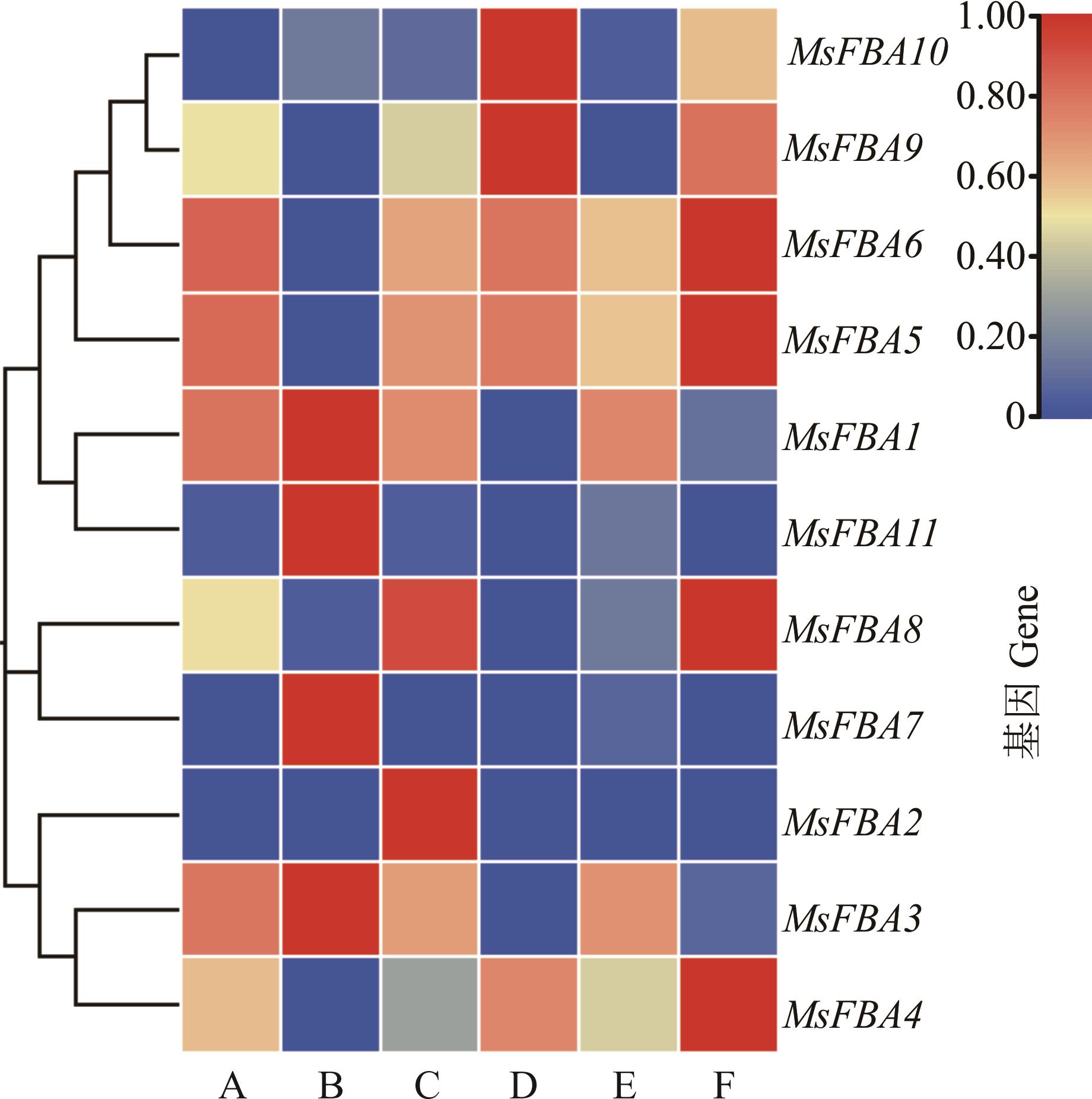
图7 MsFBA基因家族在紫花苜蓿各组织中的表达模式A:伸长茎Elongating stem;B:叶Leaf;C:花Flower;D:根瘤Nodule;E:后伸长茎Postelongating stem;F:根Root. 图例中的数字为基因相对表达量。The numbers in the legend are relative gene expression. 下同The same below.
Fig.7 Expression patterns of the MsFBA gene family in alfalfa tissues
| 1 | Zhao W, Liu H F, Zhang L, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of FBA gene family in polyploid crop Brassica napus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(22): 5749. |
| 2 | Nakahara K, Yamamoto H, Miyake C, et al. Purification and characterization of class-Ⅰ and class-Ⅱ fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2003, 44(3): 326-333. |
| 3 | Carrera D Á, George G M, Fischer-Stettler M, et al. Distinct plastid fructose bisphosphate aldolases function in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic metabolism in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(10): 3739-3755. |
| 4 | Lu W, Tang X L, Huo Y Q, et al. Identification and characterization of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase genes in Arabidopsis reveal a gene family with diverse responses to abiotic stresses. Gene, 2012, 503(1): 65-74. |
| 5 | Song J B, Wang Y X, Li H B, et al. The F-box family genes as key elements in response to salt, heavy mental, and drought stresses in Medicago truncatula. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2015, 15(4): 495-507. |
| 6 | Zhao Y, Jiao F C, Tang H, et al. Genome-wide characterization, evolution, and expression profiling of FBA gene family in response to light treatments and abiotic stress in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2021, 16(10): 1938442. |
| 7 | Cai B B, Li Q, Xu Y C, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) gene family and functional characterization of FBA7 in tomato. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 108(7): 251-265. |
| 8 | Qiu Z M, Bai M Y, Kuang H Q, et al. Cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases modulate primary metabolism and phytohormone homeostasis in soybean. Agronomy, 2023, 13(5): 1383. |
| 9 | Gao L T, Jia S Z, Cao L, et al. An F-box protein from wheat, TaFBA-2A, negatively regulates JA biosynthesis and confers improved salt tolerance and increased JA responsiveness to transgenic rice plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 182(4): 227-239. |
| 10 | Feng C H, Niu M X, Liu X, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the FBA subfamily of the poplar F-box gene family and its role under drought stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(5): 4823. |
| 11 | Long R C, Yang Q C, Kang J M, et al. Cloning and characterization of a fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase gene in Medicago sativa L. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1075-1082. |
| 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 等. 紫花苜蓿果糖-1,6-二磷酸醛缩酶基因全长克隆及分析. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(6): 1075-1082. | |
| 12 | Li Y Q, Jiao S Y, Zhang J N, et al. Effect of alfalfa on improving soil in constructed reclamation land. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(3): 78-83. |
| 李永强, 焦树英, 张佳楠, 等. 紫花苜蓿对建筑复垦土壤的改良效果. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(3): 78-83. | |
| 13 | Yuan Y Y, Yu J Q, Kong L Z L, et al. Genome-wide investigation of the PLD gene family in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): identification, analysis and expression. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23(1): 243. |
| 14 | Zhao M R, Shen Y H, Li Y C, et al. Research progress in the genetic engineering of alfalfa stress resistance. Acta Agrestia Sinaca, 2014, 22(2): 243-248. |
| 赵美荣, 申玉华, 李永春, 等. 紫花苜蓿抗逆基因工程研究进展. 草地学报, 2014, 22(2): 243-248. | |
| 15 | Shen C, Du H L, Chen Z, et al. The chromosome-level genome sequence of the autotetraploid alfalfa and resequencing of core germplasms provide genomic resources for alfalfa research. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(9): 1250-1261. |
| 16 | Blum M, Chang H Y, Chuguransky S, et al. The interPro protein families and domains database: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D344-D354. |
| 17 | Artimo P, Jonnalagedda M, Arnold K, et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(W1): W597-W603. |
| 18 | Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, et al. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2001, 305(3): 567-580. |
| 19 | Geourjon C, Deléage G. SOPMA: significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Bioinformatics, 1995, 11(6): 681-684. |
| 20 | Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, et al. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(W1): W296-W303. |
| 21 | Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers. Bioinformatics, 1994, 10(2): 189-191. |
| 22 | Yuan J, Amend A, Borkowski J, et al. MULTICLUSTAL: a systematic method for surveying Clustal W alignment parameters. Bioinformatics, 1999, 15(10): 862-863. |
| 23 | Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1987, 4(4): 406-425. |
| 24 | Bailey T L, Boden M, Buske F A, et al. MEME Suite: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(suppl_2): W202-W208. |
| 25 | Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194-1202. |
| 26 | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, 30(1): 325-327. |
| 27 | Zhou Q, Luo D, Chai X T, et al. Multiple regulatory networks are activated during cold stress in Medicago sativa L. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(10): 3169. |
| 28 | Luo D, Wu Y G, Liu J, et al. Comparative transcriptomic and physiological analyses of Medicago sativa L. indicates that multiple regulatory networks are activated during continuous ABA treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(1): 47. |
| 29 | Luo D, Zhou Q, Wu Y G, et al. Full-length transcript sequencing and comparative transcriptomic analysis to evaluate the contribution of osmotic and ionic stress components towards salinity tolerance in the roots of cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 32. |
| 30 | O’Rourke J A, Fu F L, Bucciarelli B, et al. The Medicago sativa gene index 1.2: a web-accessible gene expression atlas for investigating expression differences between Medicago sativa subspecies. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 502. |
| 31 | Lu W. Genome-wide analysis of the fructose bisphosphate aldolases in Arabidopsis. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 路玮. 拟南芥果糖1, 6-二磷酸醛缩酶家族分析. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2011. | |
| 32 | Kopecká R, Kameniarová M, Černý M, et al. Abiotic stress in crop production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(7): 6603. |
| 33 | Wood N T. Synthetic promoters illuminate roles of cis-acting elements in plant defence. Trends in Plant Science, 2002, 7(7): 288. |
| 34 | Mu J Q, Fu Y J, Liu B C, et al. SiFBA5, a cold-responsive factor from Saussurea involucrata promotes cold resilience and biomass increase in transgenic tomato plants under cold stress. BMC Plant Biology, 2021, 21(1): 75. |
| 35 | Shehzad M, Ditta A, Cai X Y, et al. Genome wide characterization, evolution and expression analysis of FBA gene family under salt stress in Gossypium species. Biologia, 2019, 74(11): 1539-1552. |
| [1] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [2] | 李伟, 王涵, 王常清, 潘玉鑫, 侯建荣, 康文娟, 尚素琴, 师尚礼. 苜蓿生卡螨种群参数对温度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 181-189. |
| [3] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [4] | 吴毅, 冯雅岚, 王添宁, 琚吉浩, 肖慧淑, 马超, 张均. 小麦及其祖先物种Hsp70基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 53-67. |
| [5] | 张震欢, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草AKR基因家族成员的鉴定及根系盐胁迫响应基因HgAKR42639的耐盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [6] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [7] | 伍国强, 于祖隆, 魏明. PGPR调控植物响应逆境胁迫的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 203-218. |
| [8] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [9] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [10] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [11] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [12] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [13] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [14] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [15] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||