

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 145-156.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025028
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
胡泽龙1,2( ), 梁国玲1,2(
), 梁国玲1,2( ), 刘文辉1,2, 王文虎1,2
), 刘文辉1,2, 王文虎1,2
收稿日期:2025-01-21
修回日期:2025-03-27
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-10-20
通讯作者:
梁国玲
作者简介:E-mail: qhliangguoling@163.com基金资助:
Ze-long HU1,2( ), Guo-ling LIANG1,2(
), Guo-ling LIANG1,2( ), Wen-hui LIU1,2, Wen-hu WANG1,2
), Wen-hui LIU1,2, Wen-hu WANG1,2
Received:2025-01-21
Revised:2025-03-27
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-10-20
Contact:
Guo-ling LIANG
摘要:
为明确两种粒色燕麦光合特性与色素含量变化在籽粒发育过程中的差异,本研究对黑色和黄色籽粒燕麦抽穗至成熟阶段的光合特性、光合色素、花色苷、黑色素及花色苷合成相关酶的动态变化进行研究和分析。结果表明,两种粒色燕麦稃片颜色显著分化,抽穗后20 d起,黄色籽粒燕麦稃片逐渐转为黄色,而黑色籽粒燕麦稃片则转为黑色,其表型变化与花色苷和黑色素积累规律高度吻合;黄色籽粒燕麦在发育中期(抽穗后20~30 d),光合色素含量及净光合速率(Pn)、气孔导度(Gs)、蒸腾速率(Tr)均极显著高于黑色籽粒(P<0.01),但开花期和乳熟期Pn日变化呈双峰型,存在明显“光合午休”现象;而黑色籽粒燕麦自抽穗后15 d起花色苷与黑色素含量持续积累,至成熟期分别较黄色籽粒燕麦高83.96%和39.8倍,且其Pn日变化呈单峰型,无光抑制现象。结构方程模型显示,籽粒颜色对净光合速率综合影响最大,光合色素正向影响光合速率,花色苷和黑色素负向影响光合速率。本研究可为培育适应性强、光合效率高的燕麦新品种提供科学依据。
胡泽龙, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 王文虎. 两种粒色燕麦籽粒色素与光合特性动态变化[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 145-156.
Ze-long HU, Guo-ling LIANG, Wen-hui LIU, Wen-hu WANG. Dynamic changes in pigment contents and photosynthetic characteristics of grains of black-grained and yellow-grained oat (Avena sativa)[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(12): 145-156.

图1 不同粒色燕麦籽粒发育过程中稃片的颜色动态变化图中依次为4个品种从抽穗期到完熟期籽粒颜色动态变化,每隔5 d取样拍摄The Figure shows the dynamic changes in grain color of four varieties from the heading stage to the fully ripe stage, with samples taken and photographed every five days.
Fig.1 Dynamic changes in lemma color during the development of different colored oat kernels
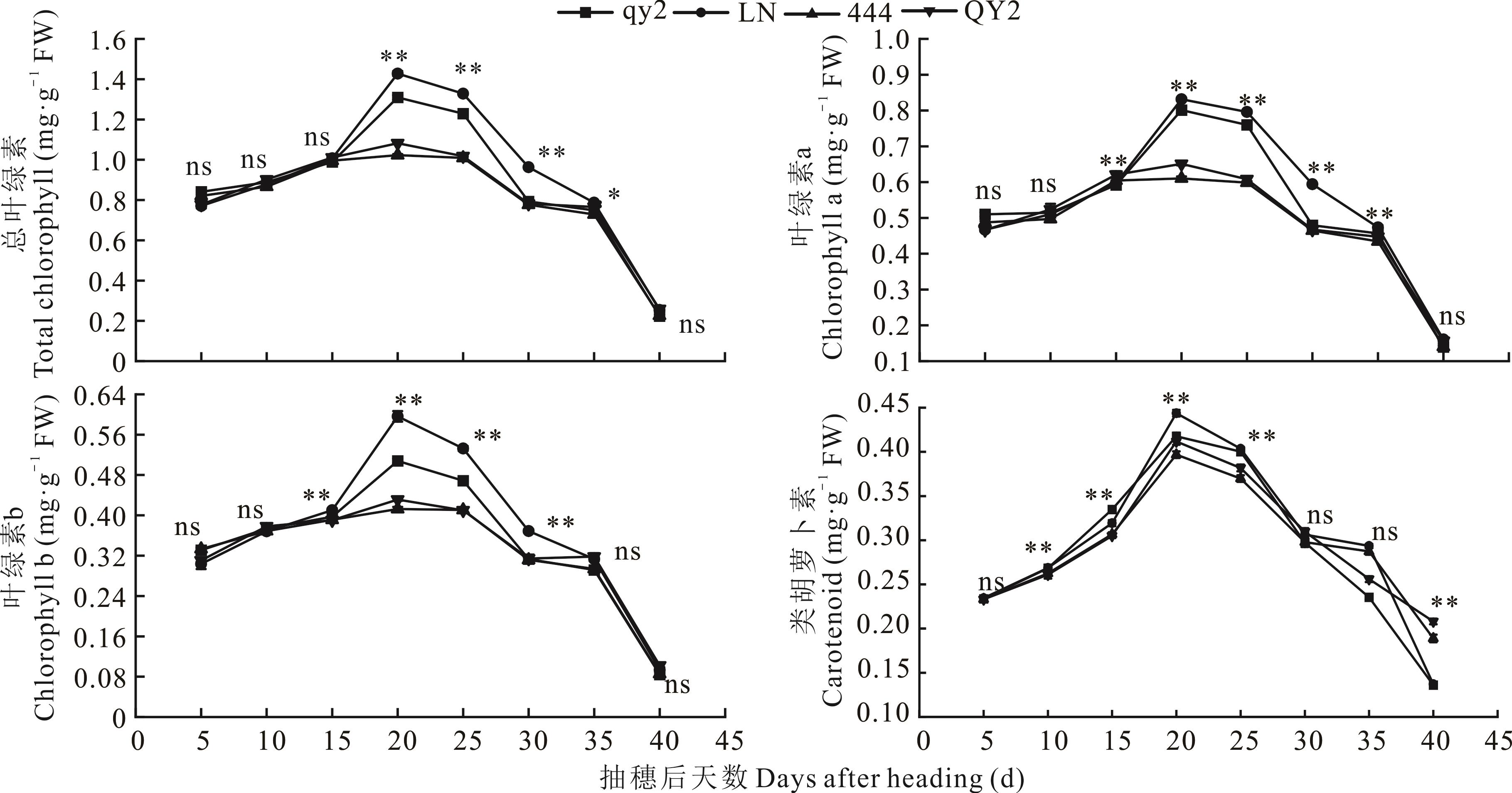
图2 不同粒色燕麦籽粒发育过程中稃片光合色素变化ns: 两种粒色间不存在显著差异(P>0.05)No significant difference between the two grain colors (P>0.05); *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Photosynthetic pigment changes in lemma during the development of different colored oat kernels
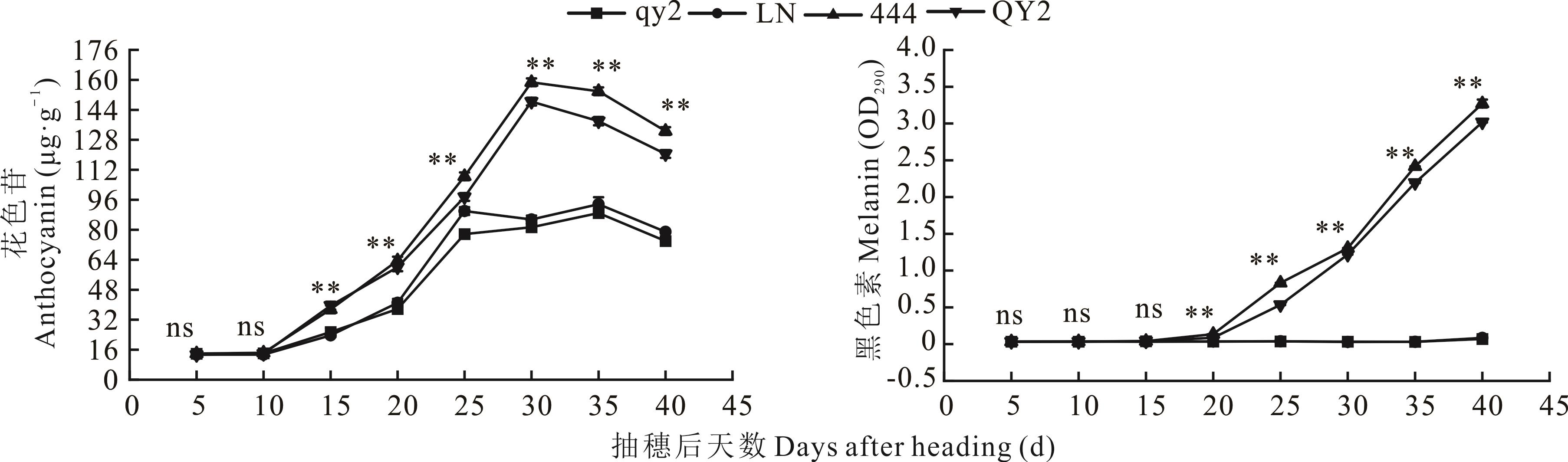
图3 不同粒色燕麦籽粒发育过程中稃片花色苷和黑色素含量变化
Fig.3 Change in the content of anthocyanin and melanin in the lemma during the development of different colored oat kernels
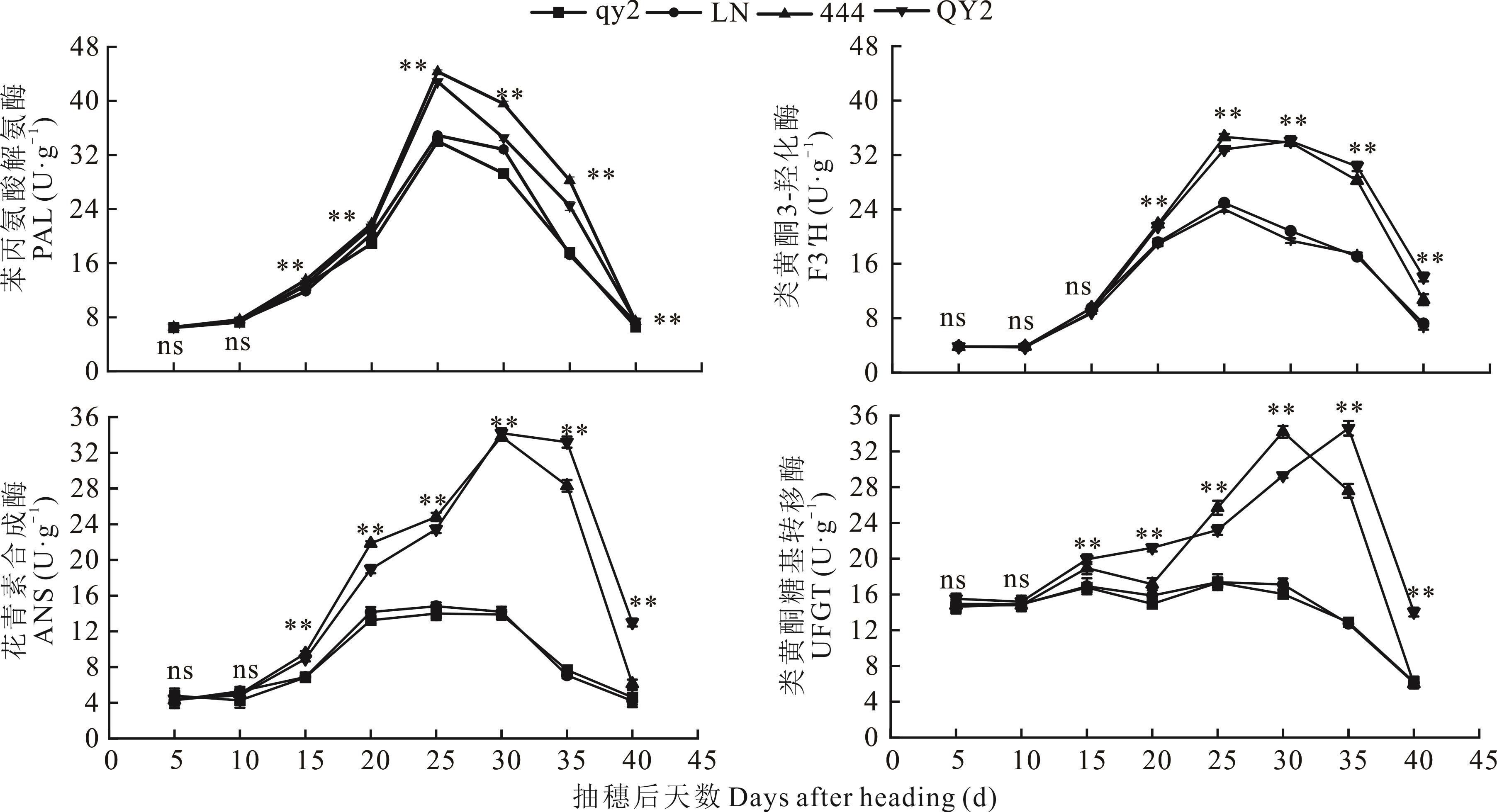
图4 不同粒色燕麦籽粒发育过程中稃片花色苷合成相关酶活性变化
Fig.4 Changes in the activity of enzymes related to the synthesis of anthocyanin in the lemma during the development of different colored oat kernels
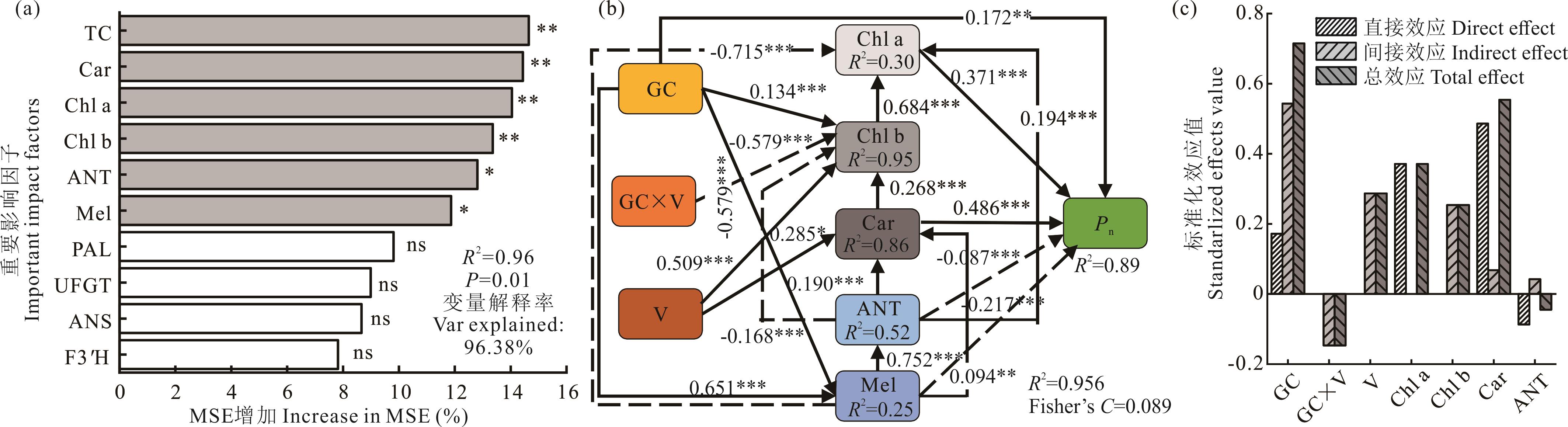
图9 燕麦稃片净光合速率影响因素分析a: 燕麦稃片净光合速率主要影响因素排序The sequence of main factors affecting the net photosynthetic rate of oat glume; b: 分段式结构模型分析燕麦稃片色素对净光合速率的影响过程及其路径The process and path the segmented structure model analysis of the effect of oat glume pigment on the net photosynthetic rate; c: 各影响因子的标准化效应值The standardized effect value of each influencing; TC: 总叶绿素Total chlorophyll; Car: 类胡萝卜素Carotenoid; Chl a: 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a; Chl b: 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b; ANT: 花色苷Anthocyanins; Mel: 黑色素Melanin; PAL: 苯丙氨酸解氨酶Phenylalanine ammonia lyase; F3′H: 类黄酮3-羟化酶Flavonoid 3-hydroxylase; ANS: 花青素合成酶Anthocidin synthase; UFGT: 类黄酮糖基转移酶Flavonoid UDP-glucosyltransferase; GC: 籽粒颜色Grain color; V: 品种Variety; GC×V: 籽粒颜色与品种交互作用The interaction between grain color and variety.
Fig.9 Analysis of factors affecting net photosynthetic rate in oat lemma
| [1] | Baum B R. Typification of Linnaean species of oats, Avena. Taxon, 1974, 23(4): 579-583. |
| [2] | Aschan G, Hardy P. Non-foliar photosynthesis-a strategy of additional carbon acquisition. Flora-Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants, 2003, 198(2): 81-97. |
| [3] | Yun Q W, Wen X X, Zhi M W, et al. Contribution of ear photosynthesis to grain yield under rainfed and irrigation conditions for winter wheat cultivars released in the past 30 years in north China plain. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(10): 2247-2256. |
| [4] | Simkin A J, Faralli M, Ramamoorthy S, et al. Photosynthesis in non-foliar tissues: implications for yield. The Plant Journal, 2020, 101(4): 1001-1015. |
| [5] | Li X J, Zhi M X, Shi X H, et al. Effect of spike photosynthesis on the grains and glumes in different floret position in wheat. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2006, 26(5): 146-148. |
| 李秀菊, 职明星, 石晓华, 等. 小麦穗光合对不同花位籽粒及颖壳的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2006, 26(5): 146-148. | |
| [6] | Zeng H G, Yi K, Yang S F, et al. Photosynthetic performance of glumes of oat spikelets is more stable for grain-filling stage under drought stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 214(1): 108890. |
| [7] | Tian H Q, Zhou Q P, Liu W H, et al. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics of oat flag leaf and spike to drought stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 917528. |
| [8] | Wojtacki M, Żuk-gołaszewska K, Gołaszewski J. Modeling the effects of agronomic factors and physiological and climatic parameters on the grain yield of hulled and hulless oat. European Journal of Agronomy, 2025, 162: 127425. |
| [9] | Alemu A, Feyissa T, Tuberosa R, et al. Genome-wide association mapping for grain shape and color traits in Ethiopian durum wheat(Triticum turgidum). The Crop Journal, 2020, 8(5): 757-768. |
| [10] | Barros J, Dixon R A. Plant phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyases. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 25(1): 66-79. |
| [11] | Wang F Y, Liang G L, Liu W H. Genetic diversity analysis of nutritional organs phenotype in 590 oat germplasms. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(1): 158-167. |
| 王凤宇, 梁国玲, 刘文辉. 590份燕麦种质资源营养器官表型性状遗传多样性分析. 草地学报, 2024, 32(1): 158-167. | |
| [12] | Młodzińska E. Survey of plant pigments: molecular and environmental determinants of plant colors. Acta Biologica Cracovienca Series Botanica, 2009, 51(1): 7-16. |
| [13] | Li M, Wang Z, Chen L Q, et al. The relationship between the photosynthetic pigments, carotenoids and yield of broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum; Poaceae). Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2021, 19(1): 191-203. |
| [14] | Zhang Y C, Liang G L, Qin Y, et al. Characteristics of chlorophyll and photosynthesis in leaves and their response to nutrients during aging of Elymus sibiricus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 等. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. | |
| [15] | Mushtaq M A, Pan Q, Chen D, et al. Comparative leaves transcriptome analysis emphasizing on accumulation of anthocyanins in brassica: molecular regulation and potential interaction with photosynthesis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 311. |
| [16] | Liu B, Zhang D, Sun M, et al. Psii activity was inhibited at flowering stage with developing black bracts of oat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(10): 5258. |
| [17] | Zhuang H, Wang H L, Zhang T, et al. NONSTOP GLUMES1 encodes a C2H2 zinc finger protein that regulates spikelet development in rice. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(2): 392-413. |
| [18] | Ren D, Hu J, Xu Q K, et al. FZP determines grain size and sterile lemma fate in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(20): 4853-4866. |
| [19] | Tong C C, Liu X J, Lin F, et al. Yield effect of optimisation of photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfa through balanced fertilization. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 等. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. | |
| [20] | Varga M, Berkesi O, Darula Z, et al. Structural characterization of allomelanin from black oat. Phytochemistry, 2016, 130: 313-320. |
| [21] | Rodríguez-mega E, Piñeyro-nelson A, Gutierrez C, et al. Role of transcriptional regulation in the evolution of plant phenotype: a dynamic systems approach. Developmental Dynamics, 2015, 244(9): 1074-1095. |
| [22] | Matus-cádiz M A, Hucl P, Perron C E, et al. Genotype× environment interaction for grain color in hard white spring wheat. Crop Science, 2003, 43(1): 219-226. |
| [23] | Yang W P, Wang C H, Wang Y S. Comparison of chlorophyll content and senescence physiology of flag leaves between two gluten-type winter wheat varieties. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 38(24): 9-11. |
| 杨文平, 王春虎, 王玉帅. 两种筋型冬小麦品种旗叶叶绿素含量和衰老生理性状比较. 广东农业科学, 2011, 38(24): 9-11. | |
| [24] | Li G H, Guo X, Sun Y B, et al. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms underlying the role of anthocyanin in acquired tolerance to salt stress in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1368260. |
| [25] | Sharma H, Sharma P, Kumar A, et al. Multifaceted regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants: a comprehensive review. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2024, 43(9): 3048-3062. |
| [26] | Dong N, Lin H. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(1): 180-209. |
| [27] | Hong M J, Ko C S, Kim D Y. Genome-wide association study to identify marker-trait associations for seed color in colored wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(7): 3600. |
| [28] | Liu X M, Meng Y, Gu W R, et al. Plant growth regulators application improves spring maize yield by improving net photosynthesis and grain filling rate. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2019, 22(5): 1223-1230. |
| [29] | Wu L Y, Zhang J G, Chang W Q, et al. Diurnal change in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in three desert plants. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 203-213. |
| 吴路遥, 张建国, 常闻谦, 等. 三种荒漠植物叶绿素荧光参数日变化特征. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 203-213. | |
| [30] | Zhao S S, Blum J A, Ma F F, et al. Anthocyanin accumulation provides protection against high light stress while reducing photosynthesis in apple leaves. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(20): 12616. |
| [31] | Zheng G S, Wang T. Nonstomatic limitations in midday depression of photosynthesis in winter wheat leaves. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001, 12(5): 799-800. |
| 郑国生, 王焘. 田间冬小麦叶片光合午休过程中的非气孔限制. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(5): 799-800. | |
| [32] | Nie R X, Wei X L, Jin N Q, et al. Response of photosynthetic pigments, gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters to light quality in Phoebe bournei seedlings. Plant Growth Regulation, 2024, 103(3): 675-687. |
| [33] | Dabravolski S A, Isayenkov S V. The role of anthocyanins in plant tolerance to drought and salt stresses. Plants, 2023, 12(13): 2558. |
| [34] | Yu Z C, Zheng X T, Lin W, et al. Different photoprotection strategies for mid-and late-successional dominant tree species in a high-light environment in summer. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2020, 171: 103927. |
| [35] | Ferguson H, Cooper C S, Brown J H, et al. Effect of leaf color, chlorohyll concentration, and temperature on photosynthetic rates of isogenic barley lines. Agronomy Journal, 1972, 64(5): 671-673. |
| [36] | Mu Q, Dong M Q, Xu J T, et al. Photosynthesis of winter wheat effectively reflected multiple physiological responses under short-term drought-rewatering conditions. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2022, 102(6): 2472-2483. |
| [37] | Song Q F, Van R J, Den B B, et al. Diurnal and seasonal variations of photosynthetic energy conversion efficiency of field grown wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 817654. |
| [38] | Maai E, Nishimura K, Takisawa R, et al. Light stress-induced chloroplast movement and midday depression of photosynthesis in sorghum leaves. Plant Production Science, 2020, 23(2): 172-181. |
| [39] | Chen L, Wen D Q, Shi G L, et al. Different photoprotective strategies for white leaves between two co-occurring Actinidia species. Physiologia Plantarum, 2023, 175(2): e13880. |
| [40] | Ulloa-inostroza E M, Córdova C, Campos M, et al. Methyl jasmonate improves antioxidants, protecting photosynthetic apparatus in blueberry plants under water deficit. Horticulturae, 2024, 10(3): 259. |
| [41] | Rashidi S, Yousefi A R, Pouryousef M, et al. Total phenol, anthocyanin, and terpenoid content, photosynthetic rate, and nutrient uptake of Solanum nigrum L. and Digitaria sanguinalis L. as affected by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation. Weed Biology and Management, 2020, 20(3): 95-108. |
| [42] | Glagoleva A Y, Shoeva O Y, Khlestkina E K. Melanin pigment in plants: current knowledge and future perspectives. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 770. |
| [43] | Sun Y L, Wei K Q, Liu X S, et al. Diurnal changes in photosynthesis and photosynthetic product partitioning in alfalfa in response to phosphorus application. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 85-94. |
| 孙延亮, 魏孔钦, 刘选帅, 等. 紫花苜蓿光合日进程及光合产物分配对施磷的响应. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 85-94. |
| [1] | 张志鹏, 蒋庆雪, 周昕越, 苗童, 唐俊, 仪登霞, 王学敏, 马琳. 转录组和蛋白组联合筛选饲用燕麦株高性状候选基因[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 147-161. |
| [2] | 韩航琪, 王梓凡, 丁赫, 陈玉荣, 王琦, 张晓庆. 燕麦干草与燕麦草块对绵羊瘤胃发酵及微生物组成影响的比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 212-222. |
| [3] | 鲍根生, 李媛, 冯晓云, 赵倩. 施氮量和混播方式对燕麦/饲用豌豆间作系统氮素吸收和干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 161-173. |
| [4] | 侯文璐, 康文娟, 陆保福, 韩宜霖, 关键, 王晶晶. 不同共生效应根瘤菌株对紫花苜蓿光合特性和呼吸代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 66-80. |
| [5] | 马文艳, 李杰东, 周镇磊, 曹东, 刘宝龙, 张怀刚, 王东霞. 肥料、保水剂和播种量互作对燕麦综合生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 107-119. |
| [6] | 郭璟, 王越, 祁存英, 李静. 内生真菌浸种对燕麦生长和根部内生真菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 151-160. |
| [7] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [8] | 关皓, 许多, 李海萍, 贾志锋, 马祥, 刘文辉, 陈有军, 李欣洋, 黄艳玲, 周青平, 陈仕勇. 高寒地区17个燕麦品种营养品质及瘤胃降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 185-198. |
| [9] | 米春娇, 洪流, 马馼, 毛培胜. 谷胱甘肽引发对老化燕麦种胚线粒体抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 51-59. |
| [10] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [11] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [12] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [13] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [14] | 张昭, 伏莹莹, 孙浩文, 孙逢雪, 闫慧芳. 不同品种燕麦种子活力鉴定与耐贮藏性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 165-174. |
| [15] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||